States of matter
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the 3 states of matter?
Solids
Liquids
Gases
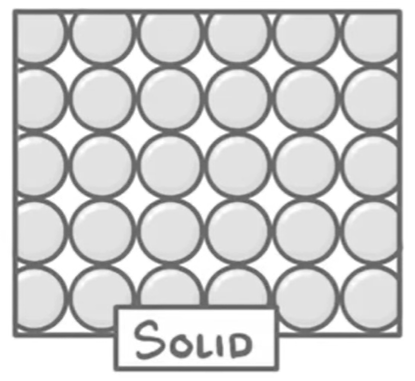
What are the properties of solids?
Arrangement: Particles are close together & regularly arranged
Movement: Particles vibrate around a fixed position
Energy: Lowest KE
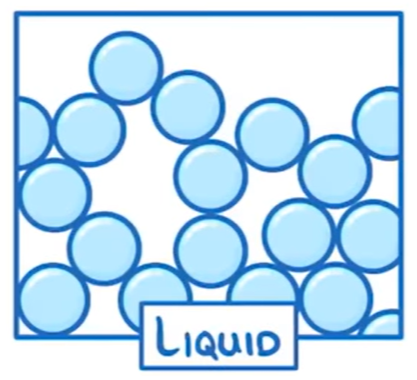
What are the properties of liquids?
Arrangement: Particles are close together & irregularly arranged
Movement: Particles move freely
Energy: KE greater than solids but lower than gases
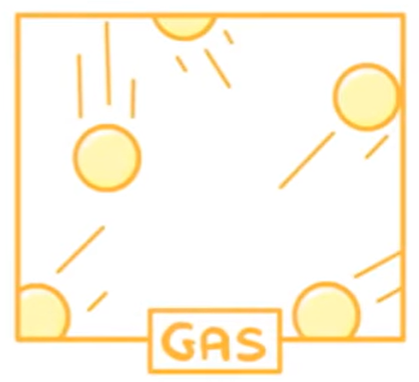
What are the properties of gases?
Arrangement: Particles are far apart & irregularly arranged
Movement: Particles move freely & randomly
Energy: Greatest KE
Solid → liquid
Melting
Liquid → solid
Freezing
Liquid → gas
Boiling / evaporation
Gas → liquid
Condensation
Solid → gas
Sublimation
Gas → solid
Deposition
Why does heating a liquid cause it to evaporate faster?
Because when a liquid is heated it gains more KE
This means that the particles in the liquid can overcome the forces of attraction holding them together, making it easier for them to evaporate into a gas
What term is used to describe the energy change between gases & liquids?
Exothermic
This is because heat energy is released
A solvent is…
a substance in which a solute can dissolve in
A solute is…
a substance that can be dissolved to form a solution

A solution is…
a mixture formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent
Dilution is…
When more solvent is added to a solution, causing the particles to spread further apart
What is a saturated solution?
A solution that contains the maximum concentration of solute so that no more of it can be dissolved into the solution
What is solubility?
The maximum mass of a solute that can be dissolved in 100g of solvent
(grams of solute per 100 grams of solvent)
The solubility of solids increases when…
The temperature increases
The solubility of gases increases when…
The pressure increases
What is a solubility curve?
A graph showing the solubility of a substance against temperature
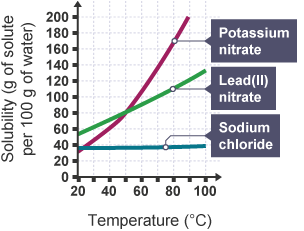
Any mass below the line for a solute at a specific temperature means that…
The solution is unsaturated
Any mass above the line for a solute at a specific temperature means that…
The solution is saturated & unstable
Why does diffusion not occur in solids?
Because diffusion requires particles that are free to move & the particles in solids are not free to move as they only vibrate in fixed positions
Explain a method to investigate the solubility of a solid in water at a specific temperature
1 At a specific temperature (e.g. 40⁰C) a saturated solution (e.g. KNO3) is created
2 Some of this solution is poured off & weighed & then heated using a Bunsen burner
3 Water from the solution evaporates, leaving behind a residue of solute which is then weighed
4 Mass of evaporated water = mass of saturated solution - mass of solute
5 Solubility = mass of solute ÷ mass of solvent × 100
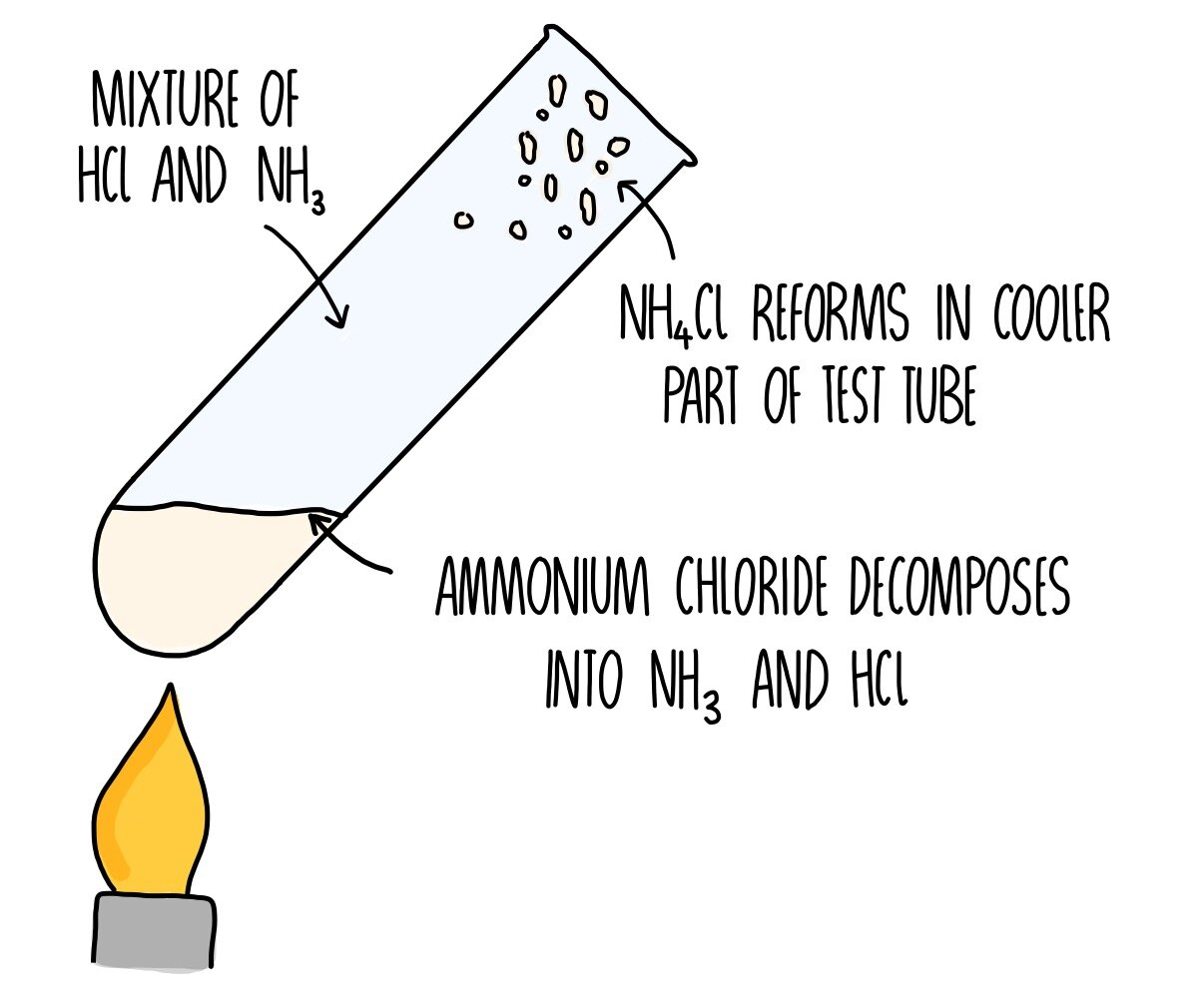
What happens when ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is heated in a test tube?
- A mixture of 2 gases form (NH3 & HCl)
- A white solid forms (NH4Cl)
- Decomposition & neutralisation occur