Diagnostic Imaging: Exam 2
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Patients should be positioned with the area of interest:
as close as possible to the x-ray table
What do you do when there are significant differences in measurement of the cranial and caudal abdomen of a patient?
Take two separate images of each region
When the area of interest is a long bone what other areas are included in the final image?
the joint above and below the bone
Decubitus
refers to a lateral projection that is exposed using a horizontal beam technique
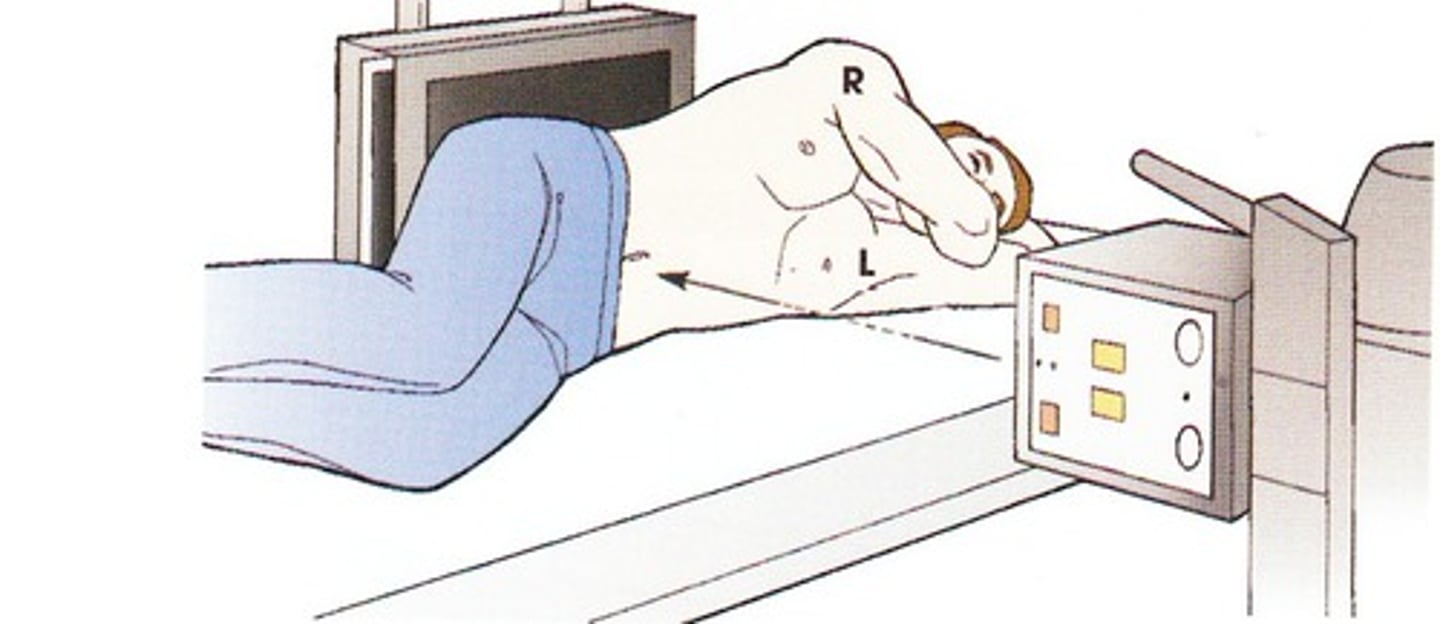
In most cases, two x-ray exposures are made at _____________ angles to each other
right
V-troughs
Positions patients into dorsal recumbency. When obtaining a caliper measurement you should include the depth of the trough
Split plate
Cassette that uses a lead blocker to block half of the film while the other half is exposed. Split plates can take two views on a single cassette & are used for distal limb views and small animals
Caudal (Cd)
Structures or areas situated toward the tail
Caudocranial (CdCr)
From the back of the limb to the front of the limb. Primarily used for views proximal to the carpus/tarsus joint
Dorsopalmar (DPa)
Enters dorsal surface of forelimb (from carpus distally) and exits palmar surface
Dorsoplantar (DPI)
Enters dorsal surface of forelimb (from carpus distally) and exits plantar surface
Oblique (O)
The x-ray beam enters at an angle (other than 90 degrees) to a structure. Commonly used for dental images
Palmar (Pa)
Situated on the caudal aspect of the front limb, distal to the carpus
Palmarodorsal (PaD)
direction from the palmar surface of the forelimb toward the dorsal surface of the body
Patients must be __________ and _________ before radiographs are exposed
clean & dry
What organization determines the directional terminology used in veterinary radiology?
American College of Veterinary Radiology (ACVR)
For most imaging studies (excluding dental and oblique images) the patient is placed with the area of interest _________________ to the x-ray tube to minimize image distortion
Perpendicular
Abdominal images should be taken during the ___________________ _______________
Respiratory pause
Lateral decubitus
Lying down on the side (with x-ray beam horizontally positioned). Used when free fluid/gas is suspected or when a regular VD would compromise the pt
Modified Lateral Abdominal View
Used when evaluation of the entire length of the urinary tract is needed & limbs would've obscured the final image in standard lateral

Which bones make up the thoracic girdle?
scapula and clavicles
Dorsoventral (DV) positioning is primarily used in thoracic views when imaging the:
Heart
Ventrodorsal (VD) positioning provides better visualization of the _____________
Lungs
Thoracic images are exposed at peak _______________ unless pneumothorax is suspected
inspiration. Pneumothorax images should be taken during the expiratory pause
How can you tell a VD/DV thoracic view is properly positioned?
The sternum will be superimposed over the thoracic vertebrae
What organization provides services for dogs to certify they don't have hip dysplasia or elbow dysplasia
Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA)
Which technique is used to evaluate the quality of the hip joint and the degree of laxity?
the PennHIP technique
How are hindlimb images taken for cats and dogs?
With the x-ray cassette on the tabletop
Techniques for imaging the thorax are similar to techniques for imaging the _______________
abdomen
When should the measurement be done when setting up for radiographs?
When the patient is in position
Where should the central beam be positioned when taking abdominal images?
Below the last rib
How can you tell the patient is in proper position for a lateral abdominal view?
The rib heads will be superimposed over the coxofemoral joints and the intervertebral foramina will be the same size in the final image
The ventral border of collimation on an abdominal view should be the:
sternum
For thoracic views the central beam is centered:
at the caudal border of the scapula
Thoracic views usually measure at the:
caudal border of the scapula/5th intercostal space
The cranial border for thoracic films is the:
thoracic inlet
How are forelimbs positioned in VD thoracic films?
Forelimbs are extended cranially
Where should markers be placed on lateral thoracic films?
Near the axilla (armpit area)
How are stifles positioned in VD hip films for OFA evaluation?
stifles are rotated medially so they are parallel to each other and the patella has to be centered over the trochlear groove
How do you know you've positioned a patient correctly for a lateral pelvic film?
The beam should be centered on the greatest trochanter of the femur. In the final image either the hip joints and legs are superimposed over each other or the limbs are in a scissor position
Where is the thickest part of the pelvis?
Over the hip joints at the level of the trochanter
What are the collimation borders for a lateral humerus image?
Above the shoulder and below the elbow
Where is the affected limb positioned during a craniocaudal image of the humerus?
extended cranially
During a mediolateral projection of the elbow the center beam should be directed towards:
the distal condyles of the humerus
When positioning for a flexed mediolateral image of the elbow, the elbow is flexed:
dorsally
The collimation borders for a radius/ulna projection are
above the elbow and below the carpus
Positioning technique for DV skull views
Place a strip of tape across the cervical region to maintain the position. Center the beam between the canthi of the eyes
VD cervical spine views are collimated
from the base of the skull to the shoulder joint
What should you do if there is a significant difference in the measurement between the cranial and caudal areas of the cervical spine?
Take two views: measure and center on the C2-C3 space for the cranial view and measure and center on the C5-C6 space for the caudal view
What collimation window is used when taking a lateral lumbar spinal radiograph?
from the last rib to the acetabulum (hip joint)
For a lateral coccygeal spine projection the measurement is taken:
at the thickest part of the tail
Due to the divergence of the X-ray beam, intervertebral disc spaces will appear _____________ towards the center of the film and ________________ towards the end of the film
wider, narrower
What are the components of a x-ray cassette in order from front to back?
Front, padding, intensifying screen, film, intensifying screen, padding, back
Precise positioning is important in skull radiographs to obtain images that represent
the symmetry of the skull
When placing craniocaudal radiographs of the stifle joint on a viewer to evaluate, how should you orient the film?
The lateral side of the right limb should be on the viewers left & the lateral side of the left limb should be on the viewers right
Standard Lateral Projection
Also used when the presence of air or fluid within the thorax is suspected or when the animal would be compromised using the standard positioning. Mitchell marker should be used to show direction of gravity
Where should you measure for a ventrodorsal cervical spine projection?
at the C4-C5 intervertebral space
A boxing glove shape of air on the abdominal film of a dog is indicative of:
Gastric dilation and volvus
Where should labeling be placed for an abdominal film?
Markers should be within the collimated area in the lower caudal border
If an animal is in respiratory distress, many times will the veterinarian request they be positioned lying on their belly for chest films. What position is this called?
Dorsoventral
If lung sounds aren't present during auscultation you should place the patient onto the table with the _________________ side down
unaffected
What landmark is used as the cranial border for thoracic films?
the thoracic inlet
Where should you center the x-ray beam when taking abdominal films?
slightly caudal to the last rib
Where do you measure when taking a mediolateral image of the carpus?
Directly over the carpal joint
For an oblique view which markers are required?
Mark both sides
If the dog being submitted for OFA hip film evaluation is an AKC registered dog, where is this information recorded?
On the film
When taking radiographs of horse hooves and distal limbs using a portable machine you need to:
Use a positioning block to elevate the hoof. The portable x-ray machine does not allow the primary beam to be centered less than 10cm from the ground
Teleradiology
the activity of sending and receiving radiographs between veterinarians and radiologists
The dorsal border in abdominal films is the:
spinous processes of the vertebral column
Where is the primary beam centered in thoracic films?
At the caudal aspect of the last rib
Which of the following radiograph exposure factors controls the speed at which the electrons are accelerated between the cathode and the anode?
Kilovoltage peak
Where should you place markers in abdominal films?
along the caudal border of the abdomen (aka inguinal area)
Changing the focal film distance has a similar effect to altering the ________ value
mAs
The liver is in the ________________ portion of the abdomen
Cranial
A patient presenting with an orbital fracture should be measured:
at the widest point of the cranium
To increase contrast in abdominal films you should increase the ________ value
kVp
Patients are positioned into _________________ recumbency for caudocranial projections of the fibula and fibula
ventral
What should you include when imaging the tarsus?
Include the distal part of the tibia and the proximal 1/3 of the metatarsals
For mediolateral views of hind limbs the marker is placed ____________ to the area of interest
cranial
What is the thickest part of the pelvis?
usually at the level of the greatest trochanter
Where should you center the primary beam on a lateral projection of the pelvis?
At the greater trochanter on the femur
In properly positioned pelvic views the ______________ is aligned with the spine
tail
Lateral radiographs should be viewed
spine facing upwards with the cranial part of the pt to your left
Dorsoventral/Ventrodorsal radiographs should be viewed
with the cranial part of the animal facing up and the patient's left on your right (like you're shaking hands)
Lateromedial, mediolateral, or oblique radiographs of limbs should be viewed
with the proximal part of the limb pointing upwards, and the cranial or dorsal aspect of the limb to your left
Craniocaudal/caudocranial radiographs of limbs should be viewed
with the lateral side of the right limb to the viewers left and the lateral side of the left limb to the viewers right
the ventral border of collimation on an abdominal view should be the
sternum
The cranial collimation for a VD abdominal film should be positioned halfway between the caudal border of the ____________ and the ____________
scapula, xiphoid
Why are patients anesthetized for OFA extended hip VD views?
To allow for proper positioning of the hip joints and patellas
Where is the primary beam centered on OFA films?
midline at the ischial tuberosities
When setting up for a temporomandibular joint projection the collimation window is
just cranial & caudal to the joint
Ventrodorsal cervical spine projection is collimated from which landmarks?
the base of the skull to the shoulder joint
Extremely small and some exotic animals are often placed on a pedestal to elevate them above the x-ray table. What does this do to the final image?
The area of interest is magnified on the final image
The cranial border for thoracic views is the _____________ _______________, the caudal border is the 1st lumbar vertebrae
thoracic inlet
When performing a standing lateral thoracic projection with a horizontal beam, a ________________ marker should be used to indicate the direction of gravity
Mitchell