Lecture 14-15 Ethylene Glycol + Ethanol Mini Topic
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
What is the most common source of ethylene glycol?
antifreeze (94.6%)
What are less common sources of ethylene glycol?
radiator fluid, paints, lotions, heat exchange fluids, ice rink freezing equipment, snow globes (some up to 10%)
True or False? Ethylene glycol has a sweet odor and is blue-green in color.
False. EG is colorless and odorless, but antifreeze may be sweet tasting and blue-green
Antifreeze, wiper fluids, boat anti-freeze may have other active ingredients other than EG like ___, ____, and ___.
propylene glycol, methanol, diethylene glycol
It is important to ask client for the ____ regarding antifreeze toxicity!
NAME

When you see CNS lethargy think of the ____.
little ol’s: ethylene glycol, methanol, ethanol, propylene glycol, isopropanol, xylitol, pentobarbital
___, ____, and ____ are RARE!
diethylene glycol, dipropylene glycol, glycol ethers
What species are susceptible to EG?
all species, particularly dogs and cat
What amount is required to cause EG toxicity in a dog and cat?
SMALL amounts
e.g. 40lb dog ~3-6 tbsp, 10lb cat 1.5 tsp
True or False? EG toxicity primarily occurs in the winter/cold seasons.
False. EG toxicity happens all year round because in addition to accidental exposures, malicious exposures.
Mortality rates with EG toxicity can be ____ because of what?
very high, due to difficulty in dx and narrow time frame to work in
In a study in dogs, within ___ hours of ingestion, save ___. In ___ hours of ingetion, save ___.
6 hrs, 100%
8 hrs, 75%
Ideally want to treat dogs within ___ hrs and in cats ___ hrs.
6-8 hrs
3 hrs
Why is it important to understand the pharmacodynamics of EG toxicity?
Determines criteria (clinical signs, pathological signs) you will use to establish a dx and guides treatment
With metabolism of EG the ___ and ___ will change over time.
clinical signs, clinical pathologic data
Absorption of EG in the GI is ___. Peak blood levels in ___ hrs makes ___ difficult, and has half-life of ___ hrs. By ___ hrs, all EG is metabolized or excreted.
rapid
1-4hrs
2-10hrs
16-24hrs
Metabolism of EG occurs in the ___ via a series of ___ reactions.
liver, oxidation
Describe the EG chart starting from ethylene glycol to glyoxylic acid
ethylene glycol — alcohol dehydrogenase —> glycoaldehyde —> glyoxal OR aldehyde dehydrogenase —> glycolic acid —lactate dehydrogenase—> glyoxylic acid
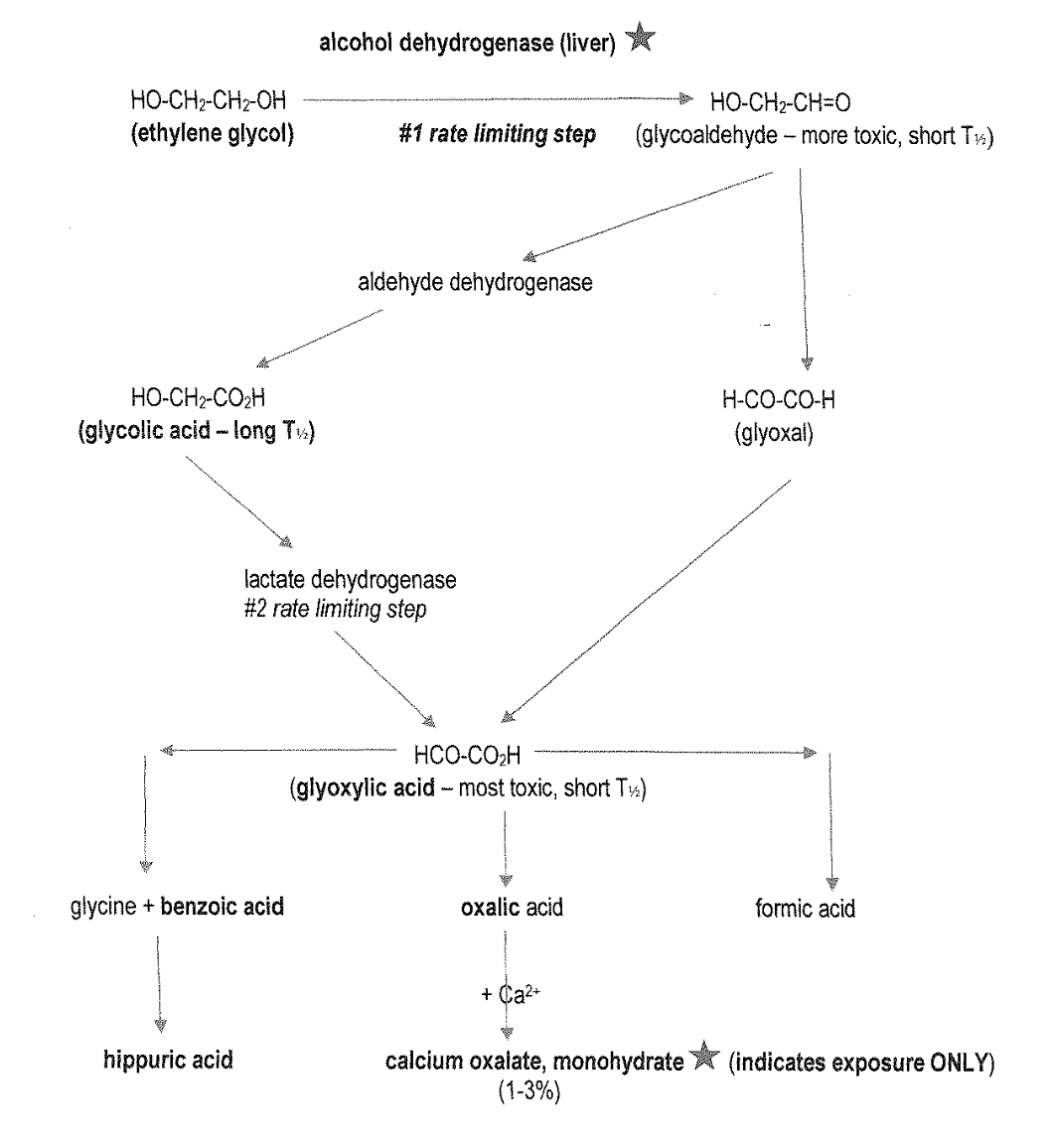
From glyoxylic acid, name its metabolites
glyoxylic acid breaks down to
glycine+benzoic acid → hippuric acid
oxalic acid → with calcium → calcium oxalate, monohydrate
formic acid
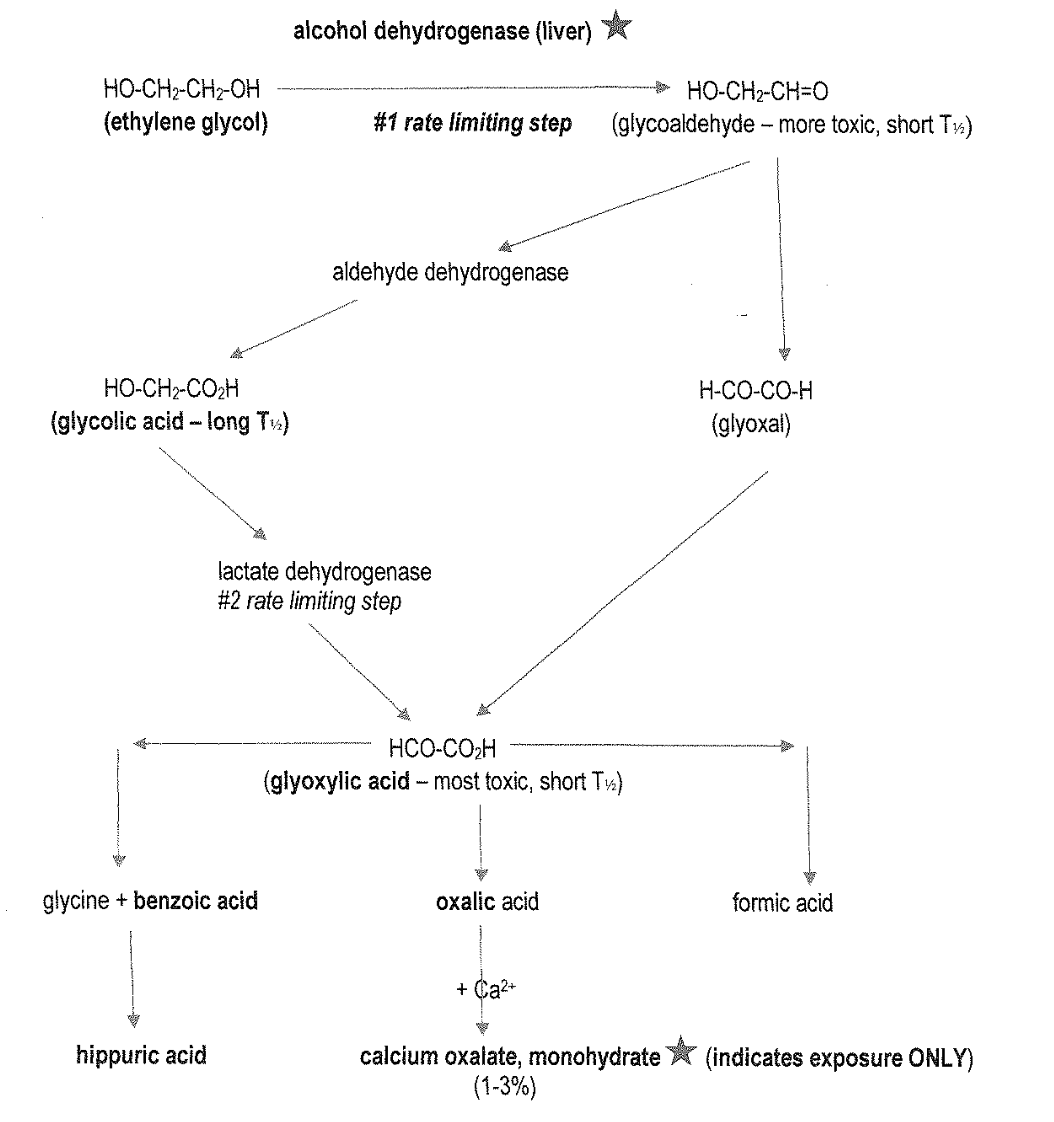
What is the #1 rate limiting step of EG metabolism?
alcohol dehydrogenase (liver)
What is the #2 rate limiting step of EG metabolism?
lactate dehydrogenase
Glycoaldehyde is more/less toxic than EG, and has a short/long half life.
Glycolic acid has a short/long half life.
Glycoaldehyde: more toxic, short half life
Glycolic acid: long half life
What metabolites of EG metabolism causes CNS depression which may lead to coma/death if dose high enough?
ethylene glycol, glycoaldehyde, glycolic acid
Metabolites of EG, particularly glycolic acid, induces what?
severe metabolic acidosis and electrolyte abnormalities
Metabolites of EG in addition to metabolic acidosis can cause ___.
cytotoxicity to renal tubular cells
___ crystals from EG metabolism can cause what?
calcium oxalate monohydrate,
mechanical obstruction and cytotoxicity or acute oxalate nephrosis
True or False? Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals in the urine indicate renal damage.
False. Crystals in urine indicate EXPOSURE to EG, not necessarily renal damage yet.
Clinical signs of EG toxicity will vary depending on what?
dose, time of presentation → where they are at in metabolism cycle!
What is the time frame of the stages of EG toxicity?
Stage 1: 1-3-12 hours, may overlap
Stage 2: 6-8-12 hours
Stage 3: 6-12 hours, up to 12-24 hours+
What are the clinical signs seen in Stage 1 of EG toxicity?
Within 1-3-12 hours: CNS depression, lethargy, vomiting, ataxia, PU/PD, death if severe CNS depression
Why do you see PU/PD in Stage 1 of EG toxicity?
PU - osmotic diuretic, PD - rise in serum osmolality stimulates thirst
What are the clinical signs seen in Stage 2 of EG toxicity?
Within 6-8-12 hours: metabolic acidosis, tachypnea, PU/PU, worsening or recovering slightly from CNS depression as EG and glycoaldehyde metabolized
What are the clinical signs seen in Stage 3 of EG toxicity?
Within 6-12 hours, to 12-24 hours: oliguric, anuric renal disease, renal failure, lethargy, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, anorexia, seizures (uncommon) retinal lesions
Abnormalities caused by EG in clinical pathology is ____ dependent. It is not ___, but ___ for ethylene glycol. Look for a ____ of ____.
time
specific, consistent
preponderance of evidenceA
Almost all clinical pathology for EG occurs in the first ____.
6-8 hours
What are the early clinical lab abnormalities with EG toxicity?
hyperosmolality/elevated osmolal gap, elevated anion gap, metabolic acidosis, calcium oxalate monohydrate crystalluria, hypocalcemia (in 50% of cases)
How do you calculate the anion gap?
(Na + K) - (HCO3 + Cl)
Elevated osmol gap of >__ is concern, >__ is significant.
10, 20
Elevated anion gap of >___ is signifcant.
25 mEq/L
Metabolic acidosis is relevant when pH <____
7.3
Acidosis will kill ___, but ___ can get extremely acidotic and can still survive.
cats, dogs
True or False? If the urine is negative for calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals, you can rule out EG exposure.
False. If negative, do not rule out as can be too early or too late when in stage 3!
True or False? Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystalluria indicates renal disease.
False. Crystalluria does not ALWAYS equate renal disease but is evidence of exposure.
What might you see on labwork if it has been >6-12 hours from EG exposure?
oliguric/anuric renal disease-failure in Stage 3, azotemia, hyperphosphatemia (from rust preservatives), hyperkalemia, hyperglycemia, isosthenuria, glucosuria, proteinuria, casts
___ can be present in all stages of EG.
isosthenuria
What is the acronym for the ddx of hypocalcemia?
PEACE PAIN
PEACE PAIN, ddx for hypocalcemia
Phosphate enema
Eclampsia
Albumin is low
Chronic renal disease
Ethylene glycol toxicity
Parathyroid deficiency
Acute pancreatitis
Intestinal malabsorption
Nutritional (deficiency in vitamin D)
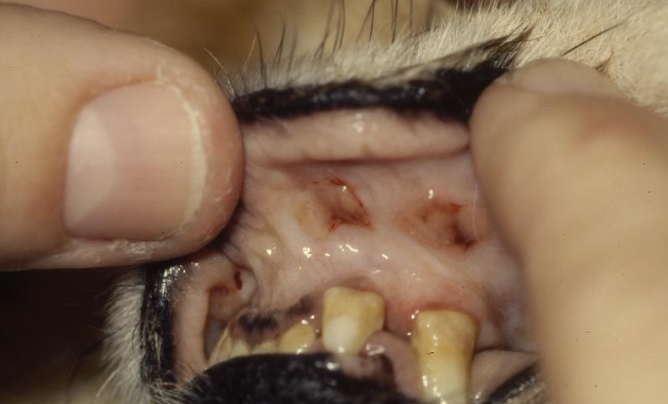
Describe the gross lesions seen in EG toxicity
nonspecific - may see mouth ulcers from urea to ammonia
Describe the microscopic lesions seen with EG toxicity
proximal tubule degeneration and necrosis, birefringent calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals within renal tubules (brain, GIT vasculature)
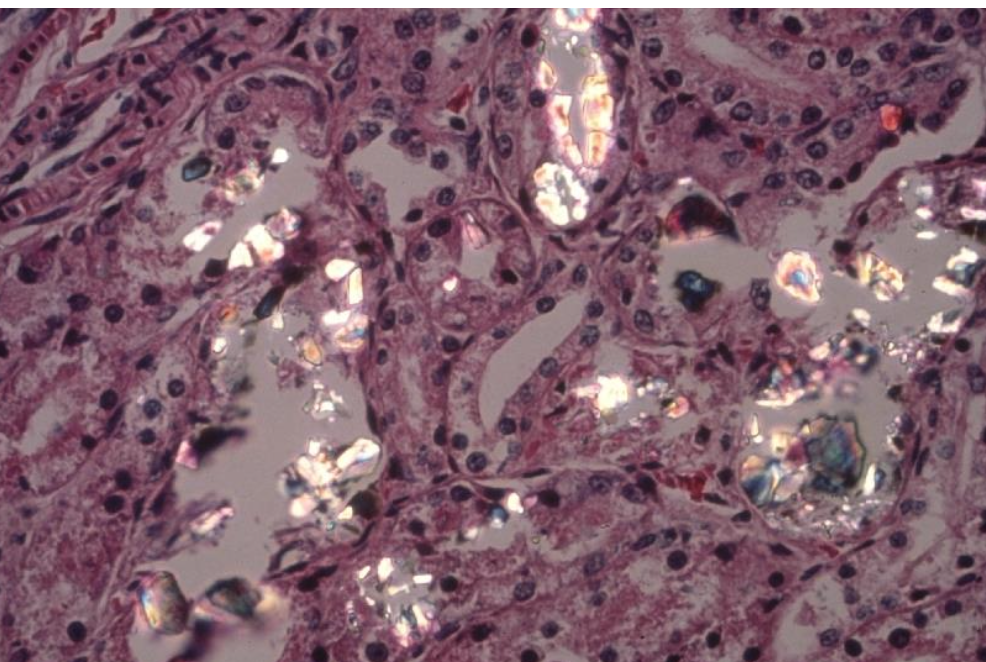
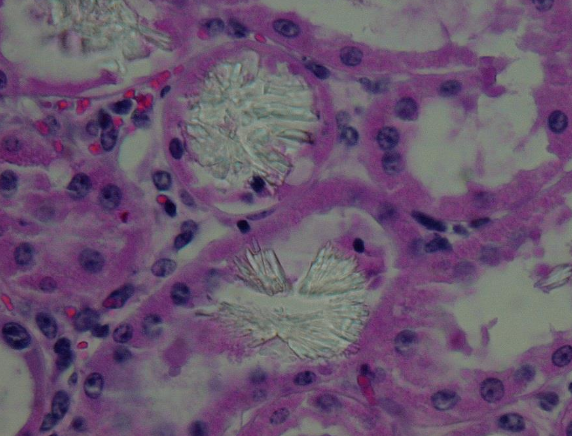
True or False? EG is the only cause of renal oxalates.
False. Think EG first, then think soluble oxalate containing plants - Halogeton, e.g. Bovine kidney exposed to Cenchrus ciliaris
List the key diagnostic criteria for EG toxicity
exposure history (within 6-8 hours in dogs, 1-3 in cats)
clinical signs
clinicopathological changes - comprehensive testing via CBC, Chen, UA, acid-base and interpret based on stage
chemical analysis kits best used first 12 hours as screening, but can have false ±, screen blood/urine/serum/plasma for EG
wood’s light, postmortem
A cheap test to see if there’s antifreeze is a suspect material:
see if it will freeze in the freezer
If a patient looks drugged, anesthetized, CNS depressed, think ___.
-ols = ethlyene glycol, ethanol, propylene glycol, methanol, xylitol, pentobarbital (and ivermectin, amitraz, mushrooms, marijuana, tranquilizers)
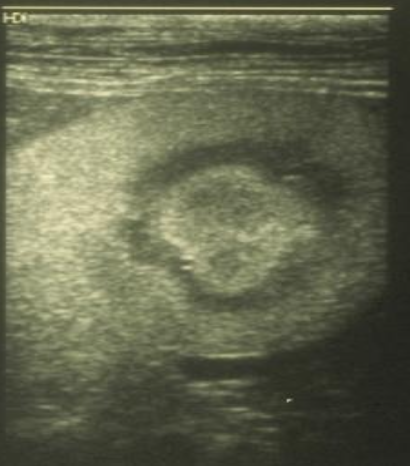
What is a halo sign?
seen in stage 3, increase renal cortical and medullary echogenicity
Treatment of EG toxicity depends on ___ and ___.
clinical presentation, stage
What treatments should be considered if in Stage 1 or Stage 2 of EG toxicity?
fluid therapy to treat dehrydation. maintenance, promote excretion, support kidneys
monitoring bw, calcium, acid-base, urine output continuously
ethanol or fomepizole to stop metabolism of EG
____ is not commonly used because EG is rapidly absorbed.
decontamination (emesis, AC, cathartics, gastric lavage)
What is the monitoring protocol/timeline for EG toxicity?
Monitor bw, calcium, acid-base, urine output q3h x9h; for first 12h and 24h then daily for 3d; Ca checked q4-6h x24h
Why do you want to give ethanol to a EG patient?
competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase, cheap and effective, few side effects e.g. ethanol stupor
Why do you want to give 4-methylpyrazole aka fomepizole to a EG patient?
direct inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase, fewer side effects and more effective than ethanol BUT more expesnive
What is the purpose of ethanol or fomepizole in treatment of EG?
preventing toxic metabolites, and allows EG to be excreted in urine unchanged
True or False? It is recommended to use ethanol and fomepizole in treating EG toxicity.
False. Don’t use if in stage 3 or when EG no longer around, and is not recommended to combine treatments
What are the core goals of EG treatment?
correct acidosis
correct hypocalcemia
get them to eat
Treat EG toxicity until what?
until normal renal values and normal acid-base data for 24 hours
What is the prognosis for each stage of EG toxicity?
1 and 2 - guarded
3 - poor, $$$, QOL, cannot predict full recovery
What are ddx for acute renal disease?
lily (cat), Vitis-tamarinds-cream of tartar, NSAIDs, aminoglycoside antibiotics, vitamin D, mushrooms, leptospirosis, ethylene glycol, paraquat
Which antifreeze products cause toxicities but without renal involvement?
propylene glycol, methanol
Which antifreeze products cause toxicities with a renal component but no crystalluria?
diethylene glycol, dipropylene glycol
Rank the #1-4 antifreeze sources.
ethylene glycol
propylene glycol
methanol
diethylene glycol
Do pets like ethanol?
YES
How much is too much ethanol?
clinical signs seen at 1 mL/kg of 95% ethanol
When is the onset of clinical signs of ethanol?
within minutes to 1-2 hours, rapid absorption
What is a common source of ethanol toxicity?
fermented raw bread dough (yeast)

True or False? Baker’s yeast, brewer’s yeast, nutritional yeast, baking soda and powder are all sources of ethanol and CO2 problems in pets.
False. Only baker’s yeast (cake yeast, active dry yeast, instant dry yeast, rapid rise yeast, quick rise yeast) converts carbs to ethanol and CO2
Ingesting yeast is generally NOT a problem unless what?
dose is high and there is a source of carbs in stomach
What are signs of fermented raw bread dough ingestion?
ethanol depression, ataxia, urinary incontinence, vomiting, bloat from CO2
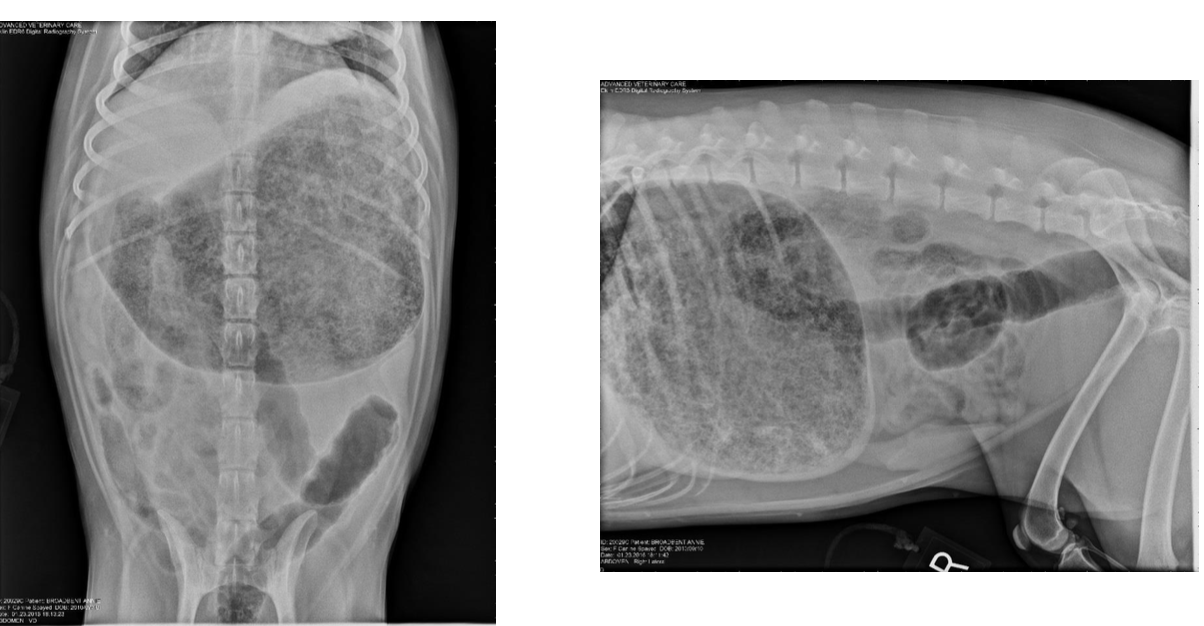
What are treatment options for ethanol toxicity?
decontamination use with caution, emesis within 1 hour, NO AC
manage hypothermia, CV function, respiratory depression, maintain airway
monitor for hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis
IV fluids to offset ethanol diuresis from affecting ADH
Ice chips if alert and can swallow or cold water lavage with stomach tube
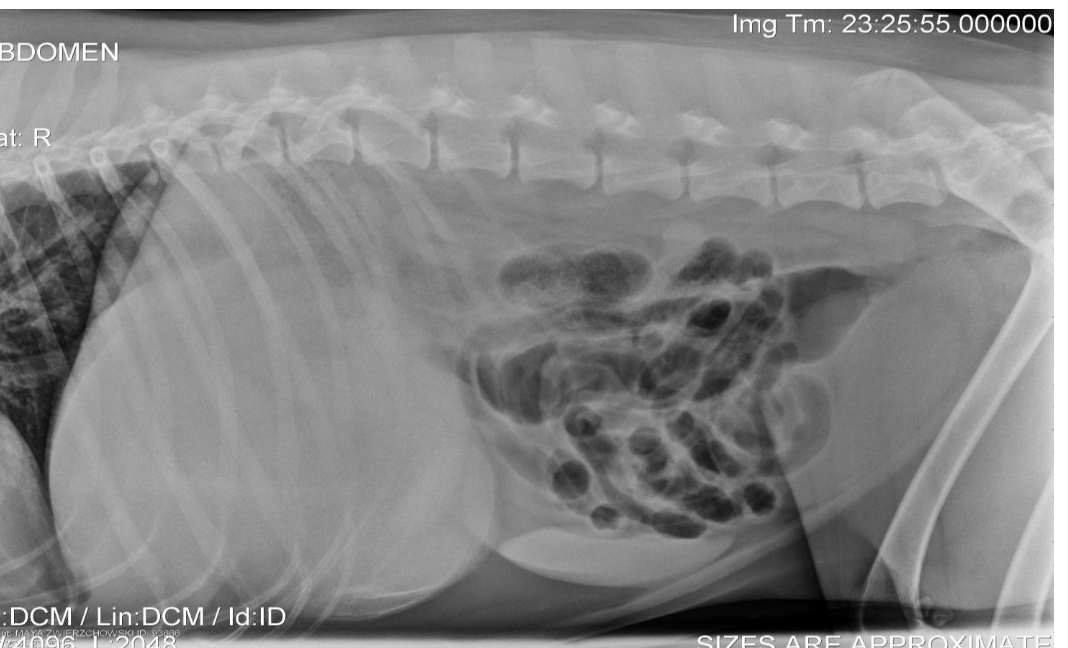
True or False? Surgical removal of bread dough blob is a common method of treatment to decompress the stomach.
False. It is rare to need surgery to remove the surgery if unsuccessful in decompression.
Drunken gummies and jello shots can be source of ___ and ___ poisoning in dogs!
ethanol, xylitol
