Module 7 Resonance and Filtering
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
sound waves produced by the vocal folds will be altered by a process called _____ and _____ to produce various vowels
resonance
filtering
the principle of resonance
when a periodic force is applied to an elastic system, the system is forced to vibrate at the frequency of the applied force, not at fnat of the elastic system
the closer the frequency of the applied force to the natural frequency of the system, the greater the amplitude of vibration
natural frequency of middle ear
2000 Hz
greatest amplitude happens at ____ of the elastic system
fnat
the more remote from the natural frequency….
the more amplitude decreases
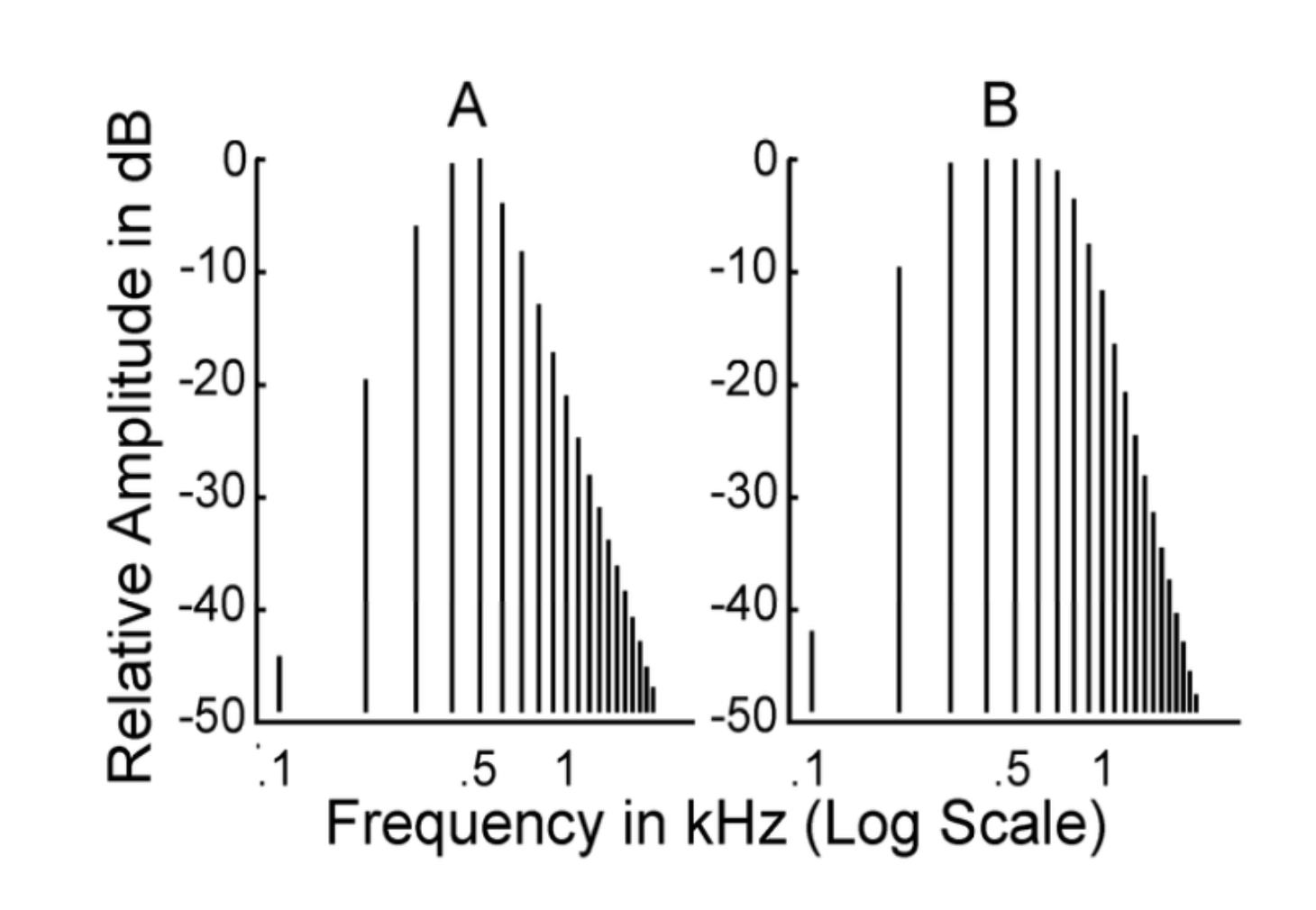
what does 0 dB mean on this graph?
500 Hz
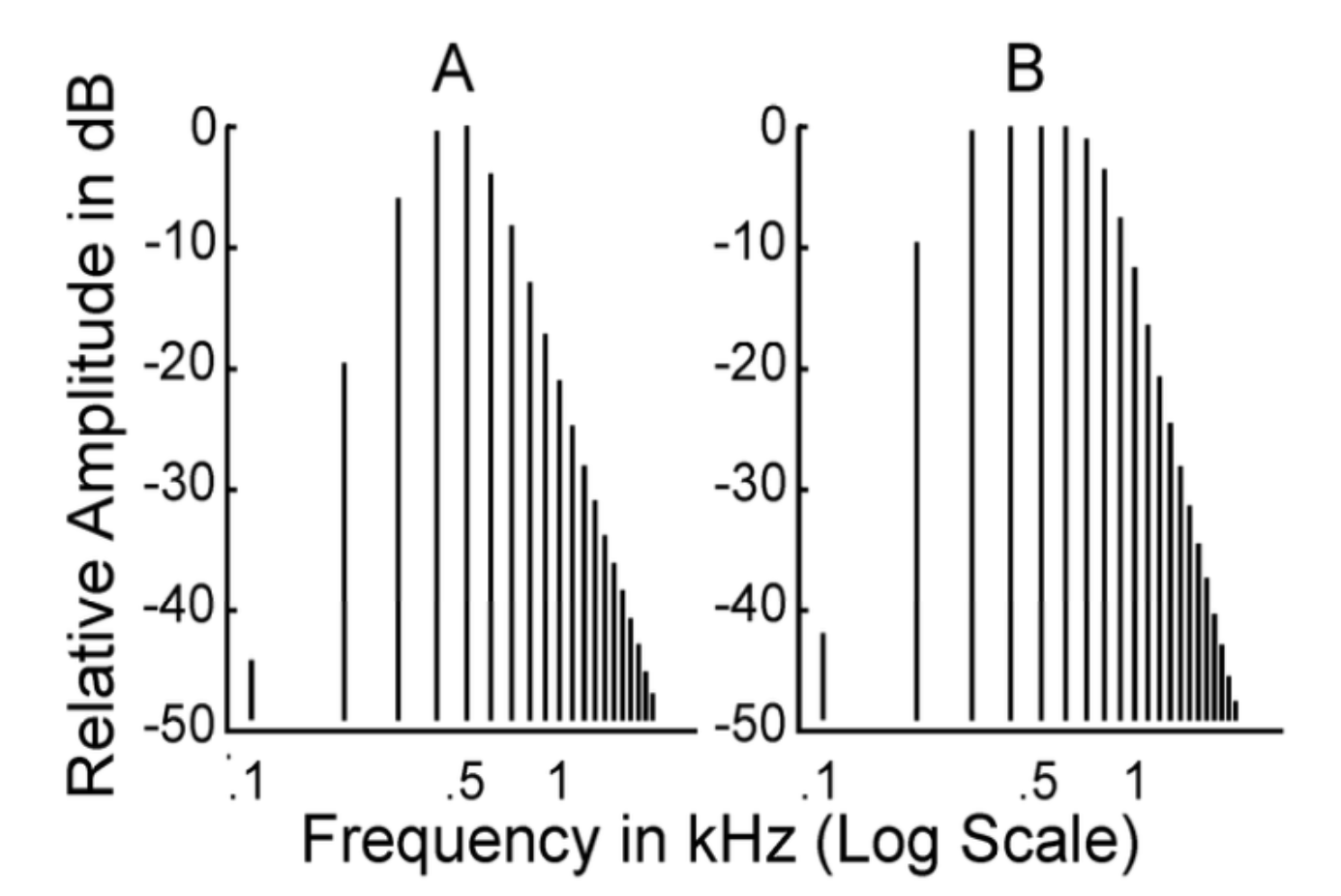
what does 0 dB mean on this graph?
level of harmonics with greatest amplitude
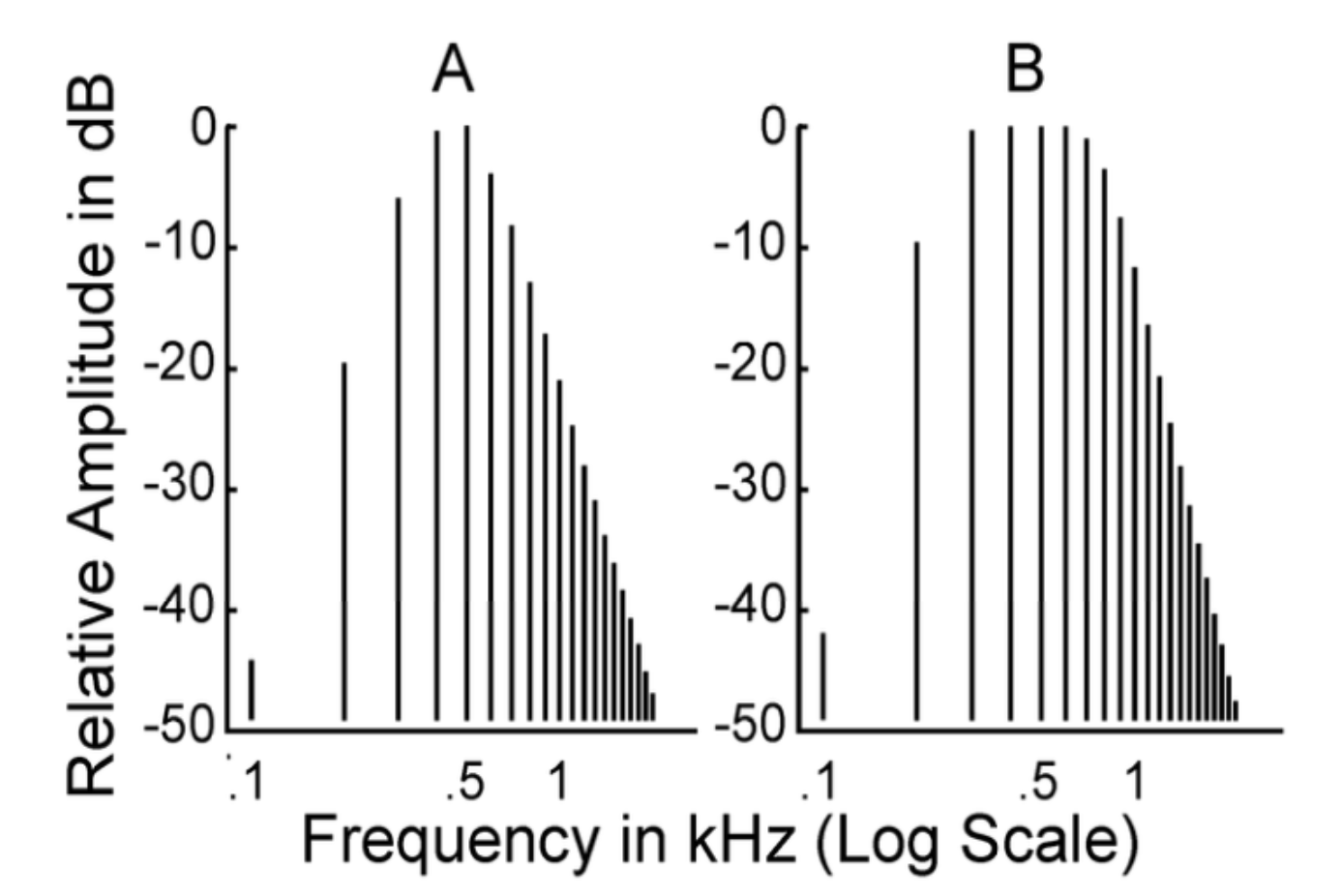
does A or B represent a complex tone?
B
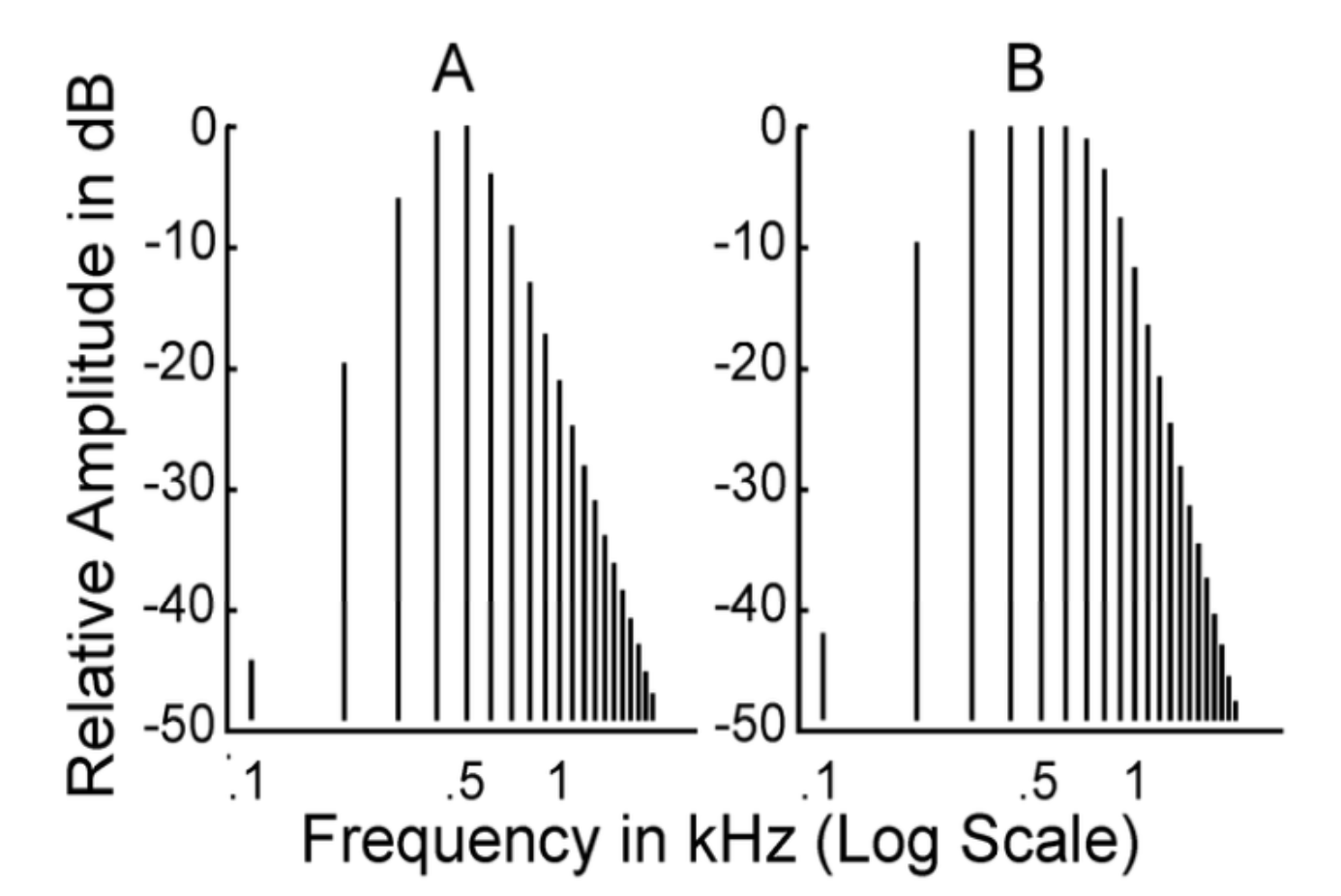
at the input, amplitudes are _____, but in the output, amplitudes _____ with _______
do these graphs show the input or the output?
constant
vary, frequency
output
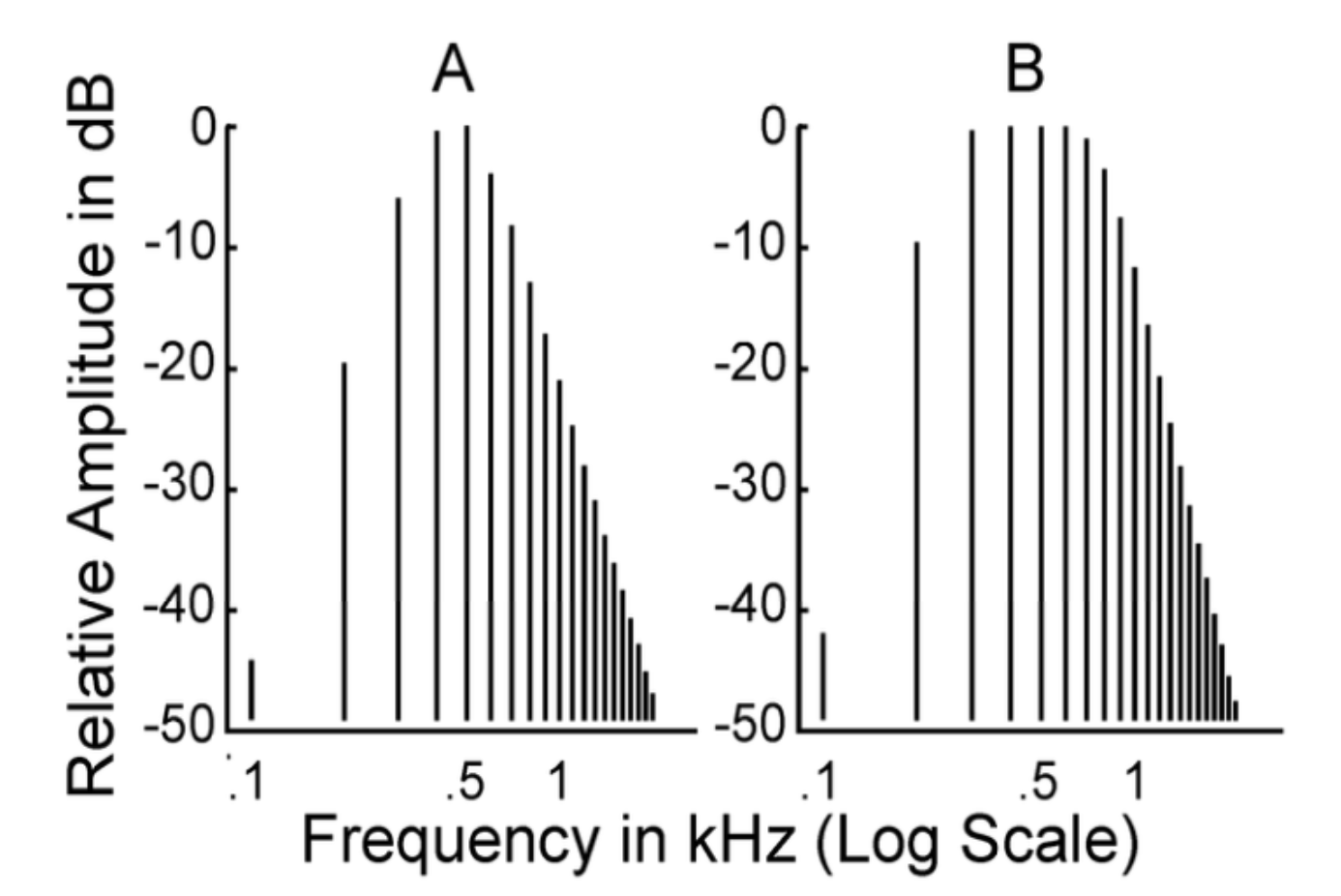
list a characteristic of these graphs make them different
B shows a complex tone
A shows a pure tone
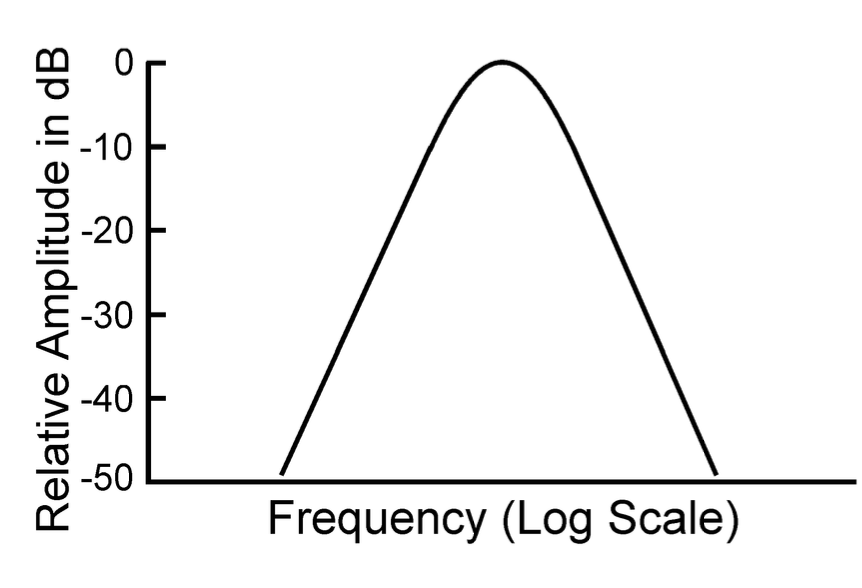
this is NOT a _____ but a ______
sound wave
frequency-selective system
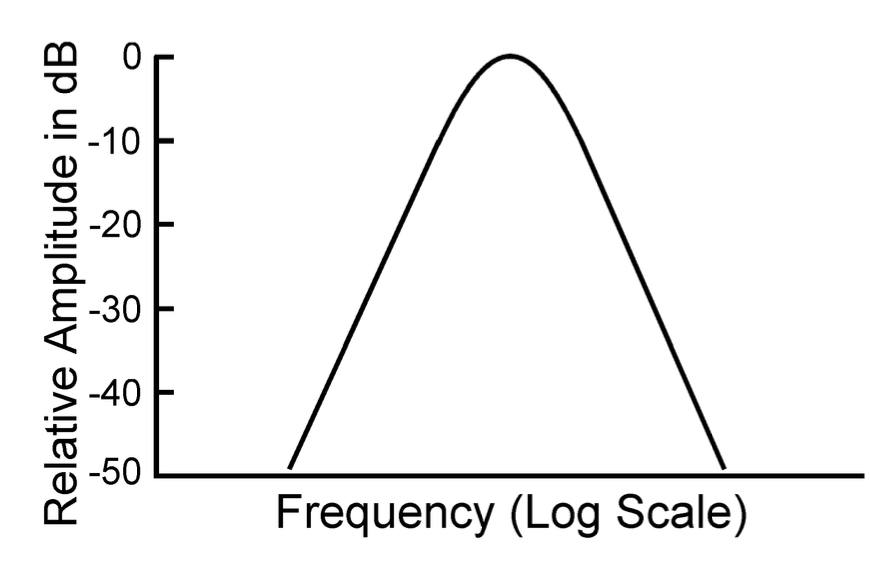
what does this graph show?
it shows the relative amplitude of forced vibrations as a function of frequency that would be realized if driving forces of variable frequency, but constant amplitude, were applied
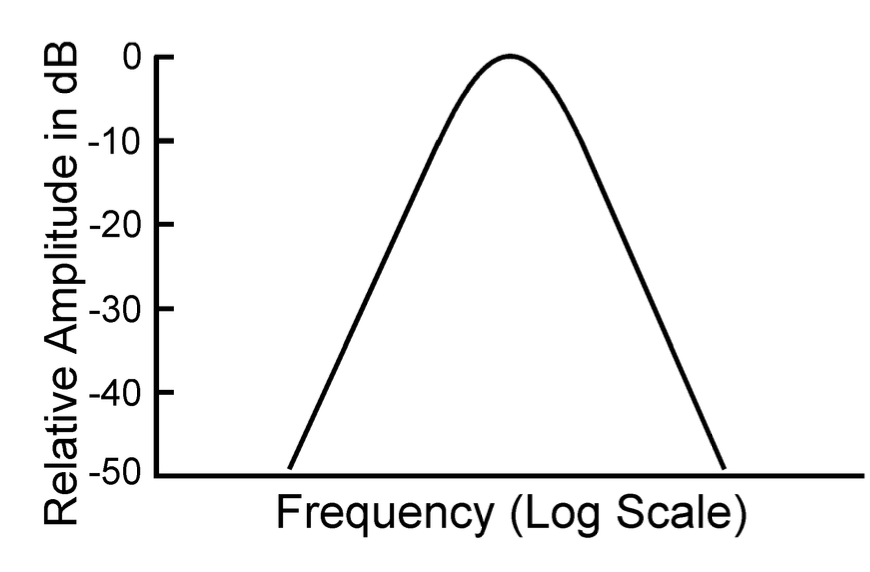
what are the names of this curve?
resonance curve
filter curve
system transfer function
amplitude response
frequency response
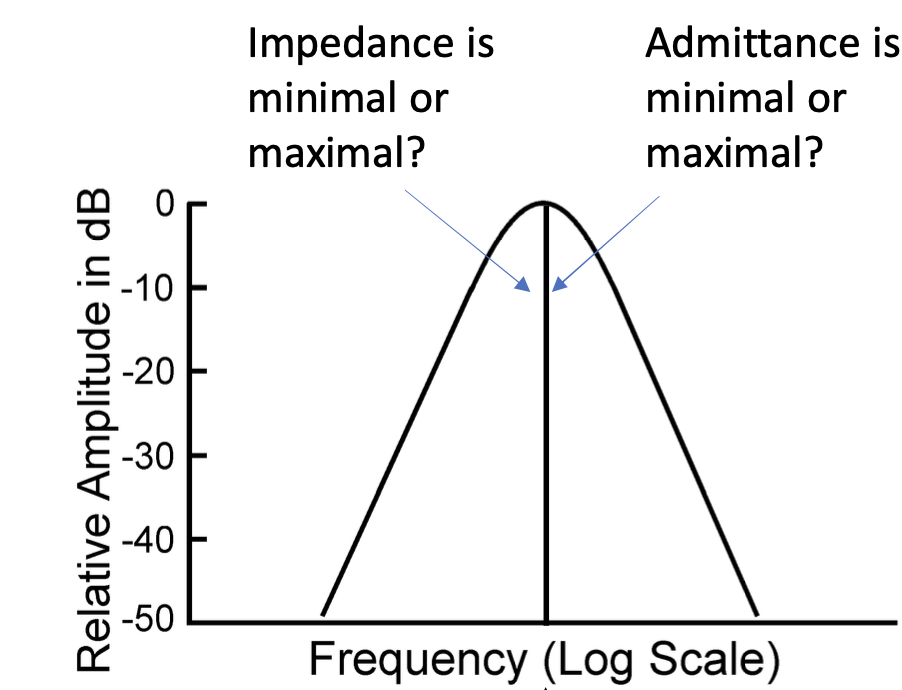
Answer the questions on the graph.
Impedance is minimal
Admittance is maximal
_____ and _______ of the elastic system determines its natural, or resonant frequency
mass
stiffness
elastic system is forced to vibrate at…
frequency of the applied force
amplitude of vibration of elastic system is greatest when the _____ _______ equals the ______ ________ of the system
driving frequency
natural frequency
stiff and light objects
vibrate rapidly and produce high-frequency sound waves
heavy objects
vibrate slowly and produce low-frequency sounds
if there is less resistance to the vibration of motion
then it may continue vibrating for some time before the energy is dissipated
if there is more resistance to the vibration of motion
then the oscillation will be brief, and the energy will dissipate quickly
harmonics above and below the center are attenuated because _______ increases
impedance
parameters of a filter
center frequency (Fc)
upper cutoff frequency (FL)
lower cutoff frequency (FU)
bandwidth (BW or ΔF)
attenuation rate
center frequency
maximum amplitude of vibration, the natural frequency
upper cutoff frequency
that frequency above fc for which amplitude of response is 3 dB less than response at Fc
the 3 dB down point, or the half power point
lower cutoff frequency
that frequency below Fc for which amplitude of response is 3 dB less than response at Fc
the 3 dB down point, or half-power point
why is it called the half-power point
10log(1/2) = -3 dB
bandwidth
the width of the passband of the system, the range of frequencies passed by the filter
ΔF = FU - FL
quantifies how narrowly or broadly tuned the filter is
attenuation rate
the rate at which energy for frequency above or below the center frequency are rejected
reported in dB/octave
slope of the filter curve
also known as the roll-off or rejection rate
change in filter curve should be…
slow
attenuation rate quantifies the _____ of a filter
selectivity or energy concentration
when we specify parameters of a real filter, we describe it as if it were an ____ filter
idealized
specification of attenuation rate reveals how much _____ filter departs from the _____ one
realized
idealized
the idealized filter is in the shape of a…
rectangle
types of filter
low-pass
high-pass
band-pass
stop-band
low-pass filter
allows low frequencies through and attenuates high frequencies
above cutoff frequency, frequency components are attenuated
high-pass filter
allows high-frequencies through and attenuates low-frequencies
below cutoff frequency, frequency components are attenuated
band-pass filter
allows limited range of frequencies to pass through
has a low cutoff and high cutoff, bandwidth, and center frequency
stop band filter
opposite of bandpass filter
attenuates range of frequencies
filter skirts
determines the attenuation of frequency components outside the pass band, usually reported in dB per octave
there is/is not a perfect filter
there is not a perfect filter
what are the two values of attenuation are commonly used
3 dB and 10 dB
Q of a filter
center frequency/BW
high Q filter
sharply tuned filter
low Q filter
broad tuning filter
Equivalent Rectangular Bandwidth Filter
approximation of bandwidths of the filter in human hearing
bandwidth of a rectangular filter with the same peak output and same area as that filter
impulse/click/transient signals _____ and ______ response can be altered when they are passed through a _______ filter
temporal, frequency
band-pass
wide bandwidth of filter, broader spectrum, _____ impulse response
briefer
narrower bandwidth, steeper filter skirts, ____ duration of impulse response
greater
the longer you present a sound, the _____ the response
better