3- Spinal Nerves, Dermatomes, and Myotomes
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
dorsal root
sensory branch of each spinal nerve
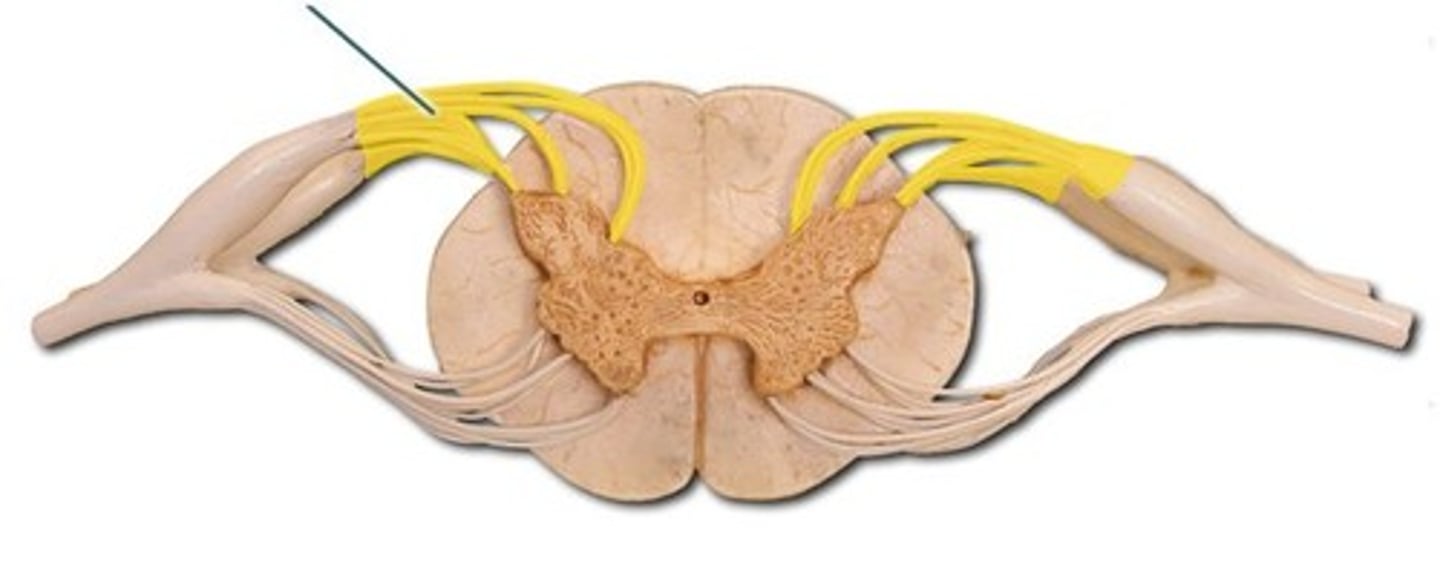
ventral root
motion (efferent info)
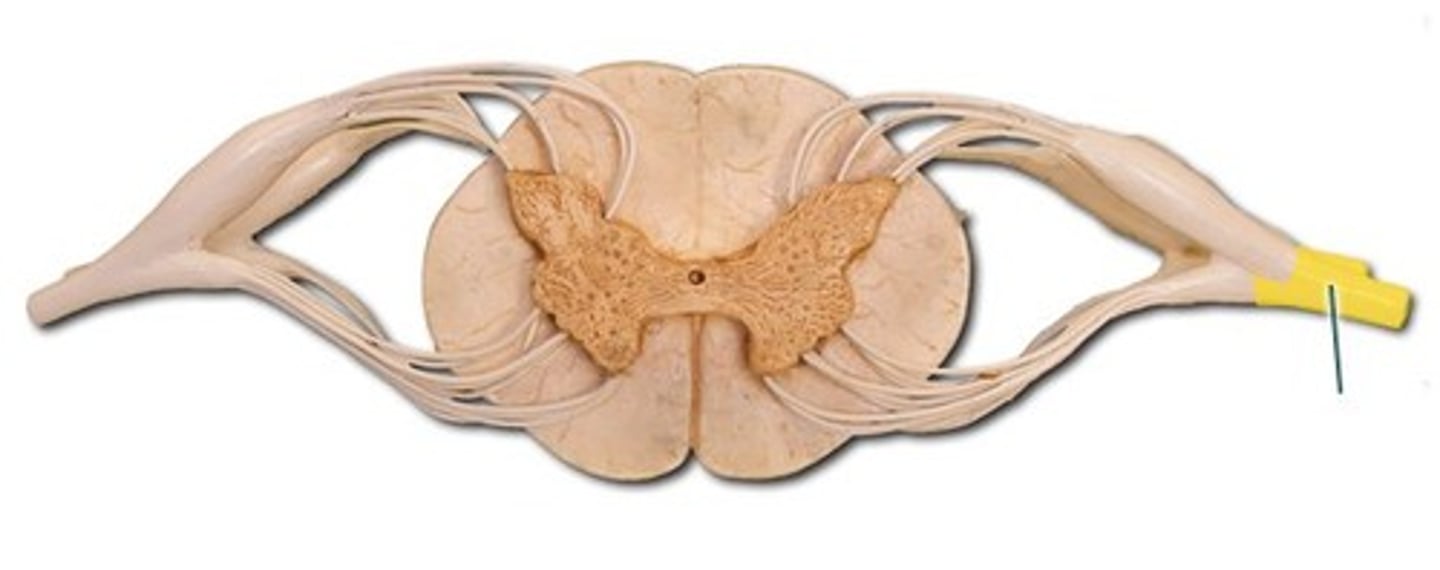
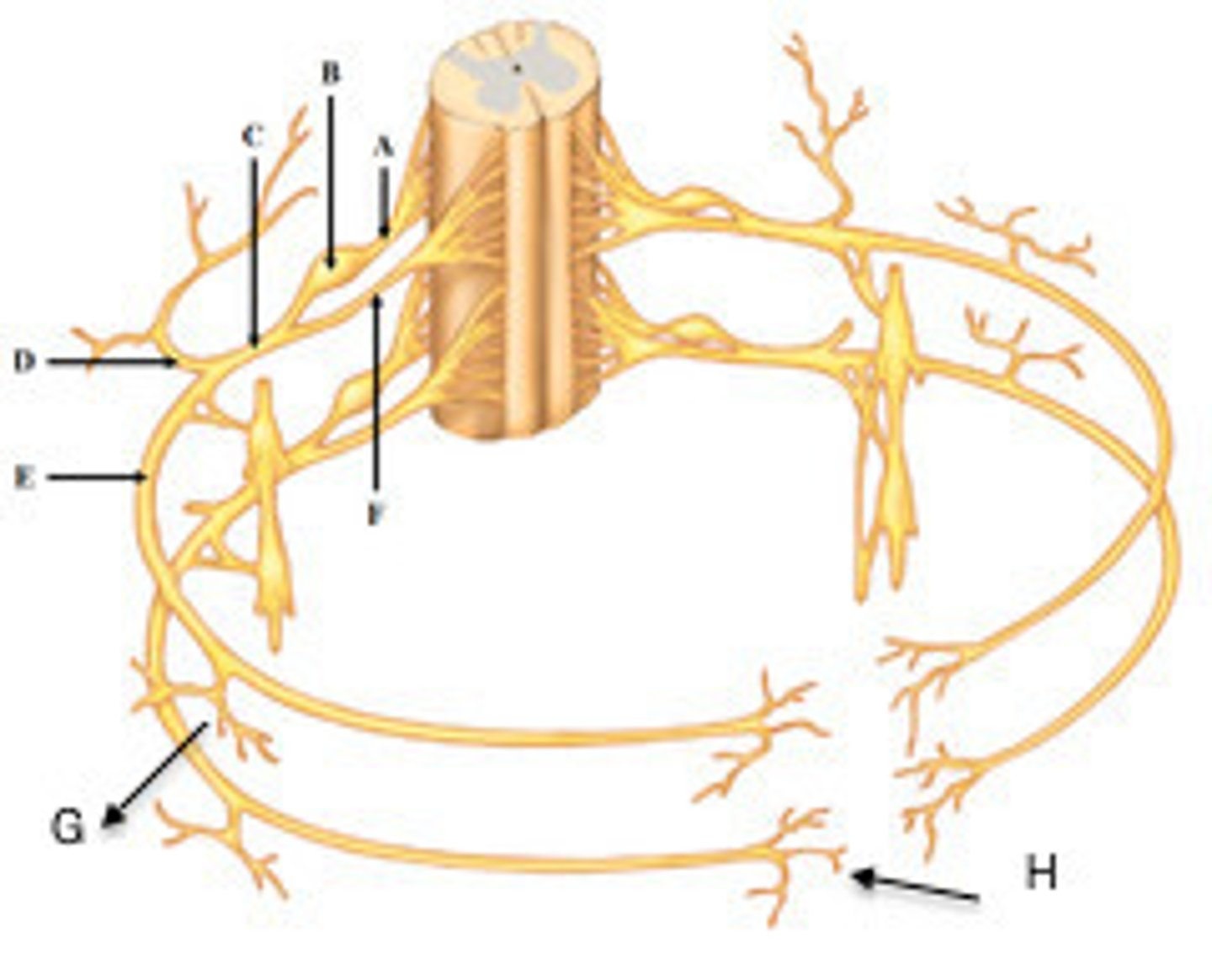
spinal nerve
a nerve that emerges from the spinal cord; _____ once they leave vertebrae; both motor/sensory
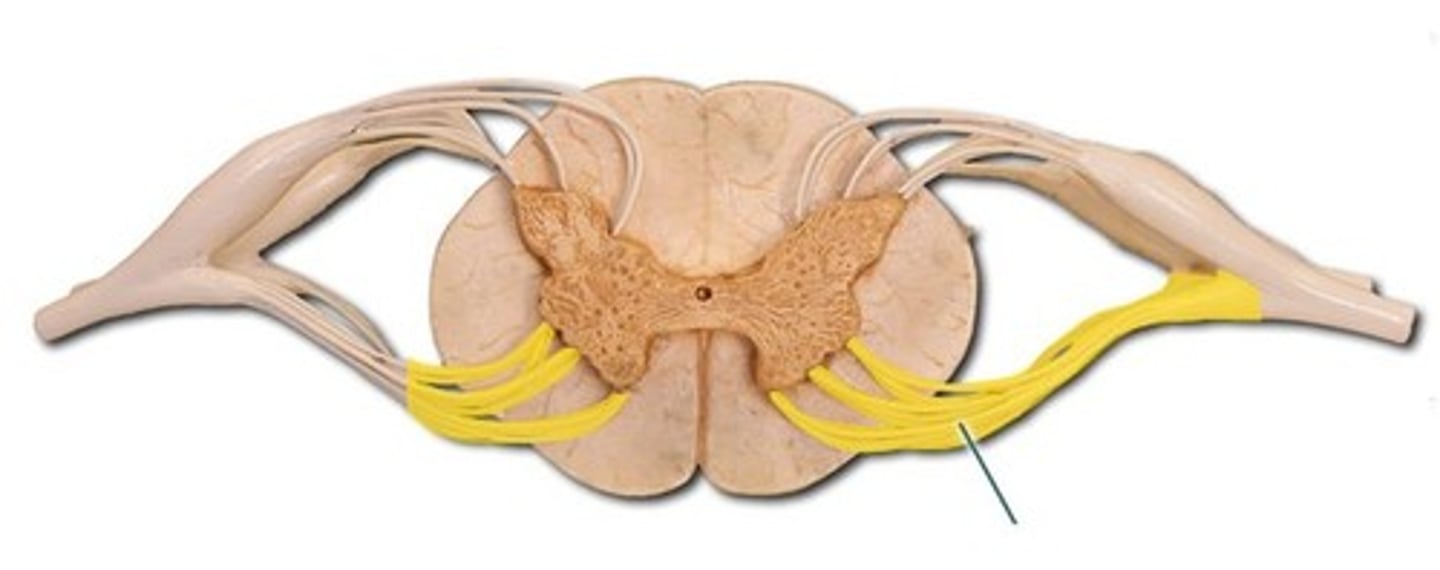
dorsal primary ramus (DPR)
innervates deep muscles of the back, skin (posterior) of head, neck, and back
ventral primary ramus (VPR)
innervates anterior trunk and makes up plexuses to the extremities; legs, anterior trunk, and limbs
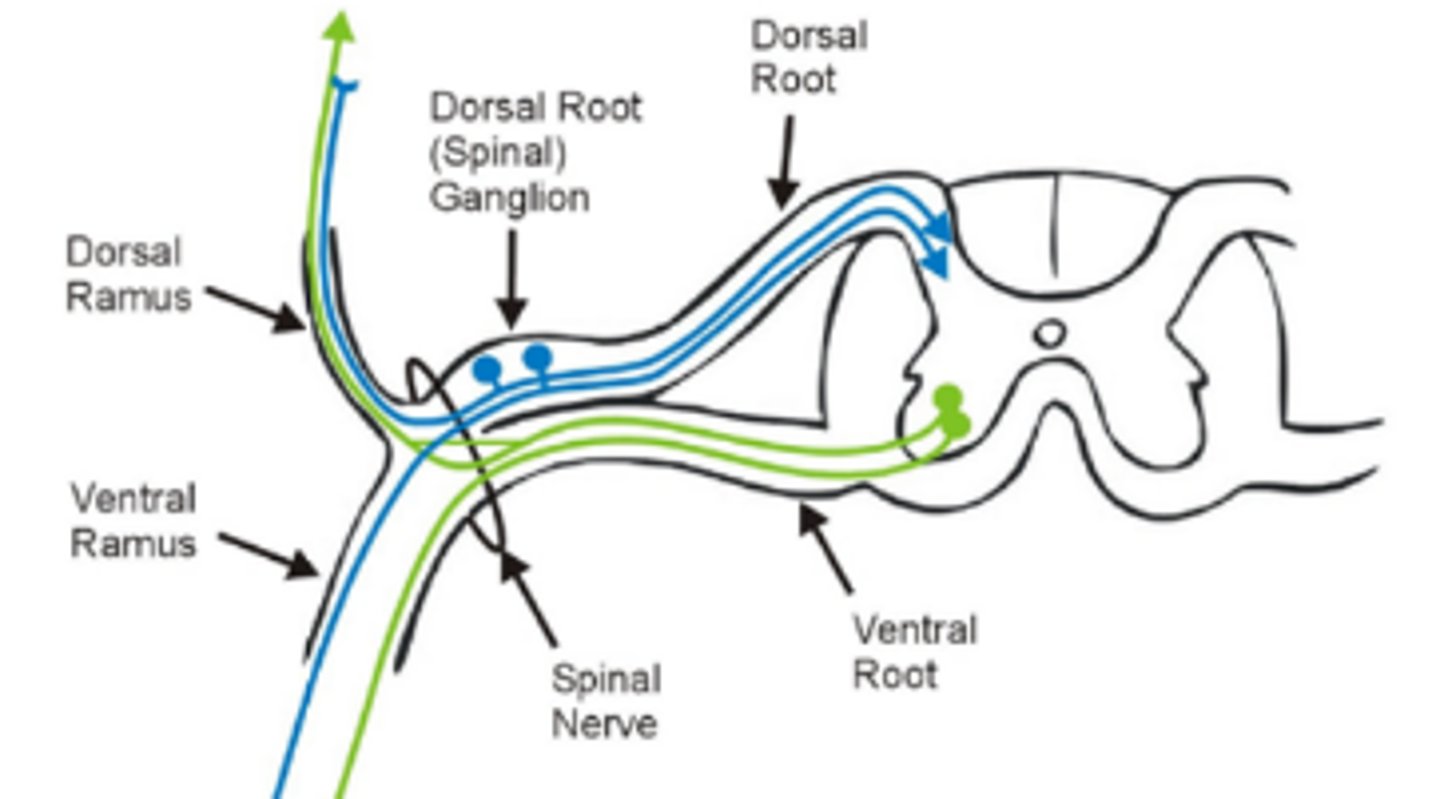
dorsal root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
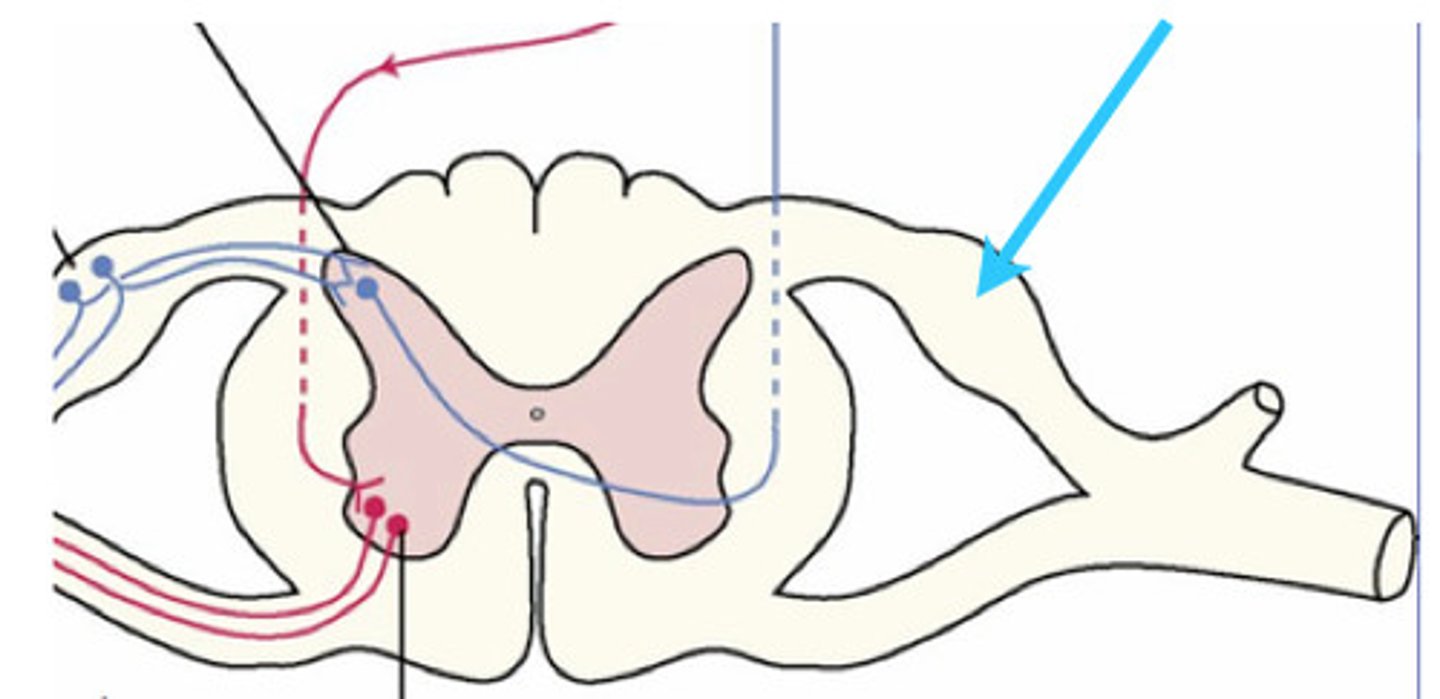
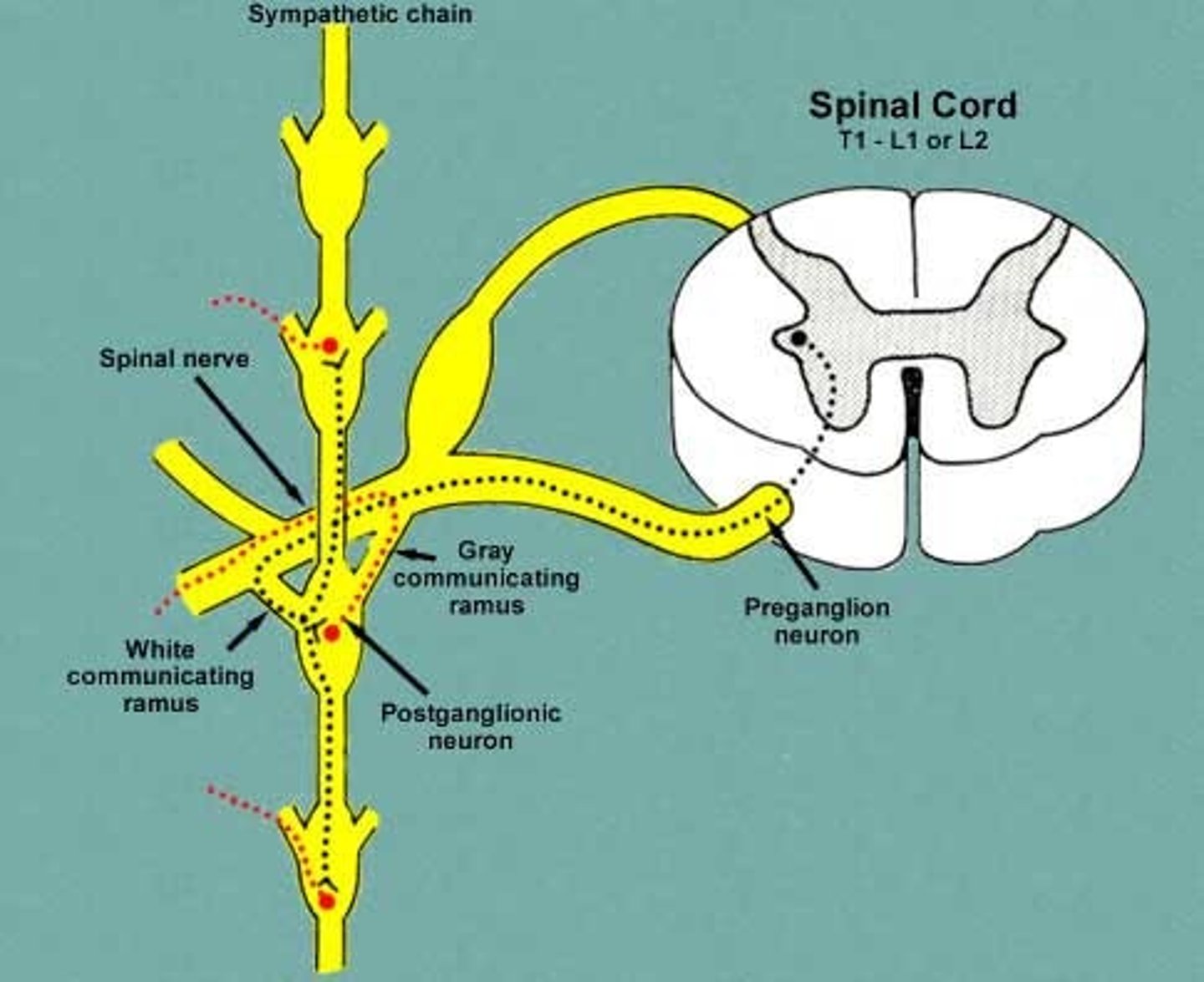
sympathetic chain ganglion
What ganglion receives preganglionic sympathetic fibers from T1 to L1-2 and innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, head, thoracic viscera, and blood vessels of the body wall and limbs?
general somatic efferent (GSE)
carry motor impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles
general somatic afferent (GSA)
mediates sensory innervation from somatic muscles, skin, ligaments, and joints; sensory info from the body (hot/cold)
general visceral efferent, general visceral afferent
Types of autonomic information carried by nerves
general visceral efferent
innervates smooth (non-voluntary) muscle, glands, organs; movement in digestive
general visceral afferent
what is sensory information that is conscious and unconscious?
true
t/f All spinal nerves carry some form of motor and sensory information
yes, except cranial nerves
Do typical spinal nerves innervate nearly all the body wall, extremities, and most of the muscles?
muscles
Where do motor commands go?
CNS
Where does sensory information go?
dermatomes
-A band or region of skin supplied (innervated) by a single sensory nerve
-Can be described in 2 ways: with reference to a dorsal nerve root and with reference to a given cutaneous nerve
What are the ways dermatomes can be described?
With reference to a dorsal nerve root and with reference to a given cutaneous nerve
cutaneous nerve
-nerve that innervates the skin
-body sensation is attributed to/described by the _____________ that innervates a given area
-more localized
opthalmic nerve
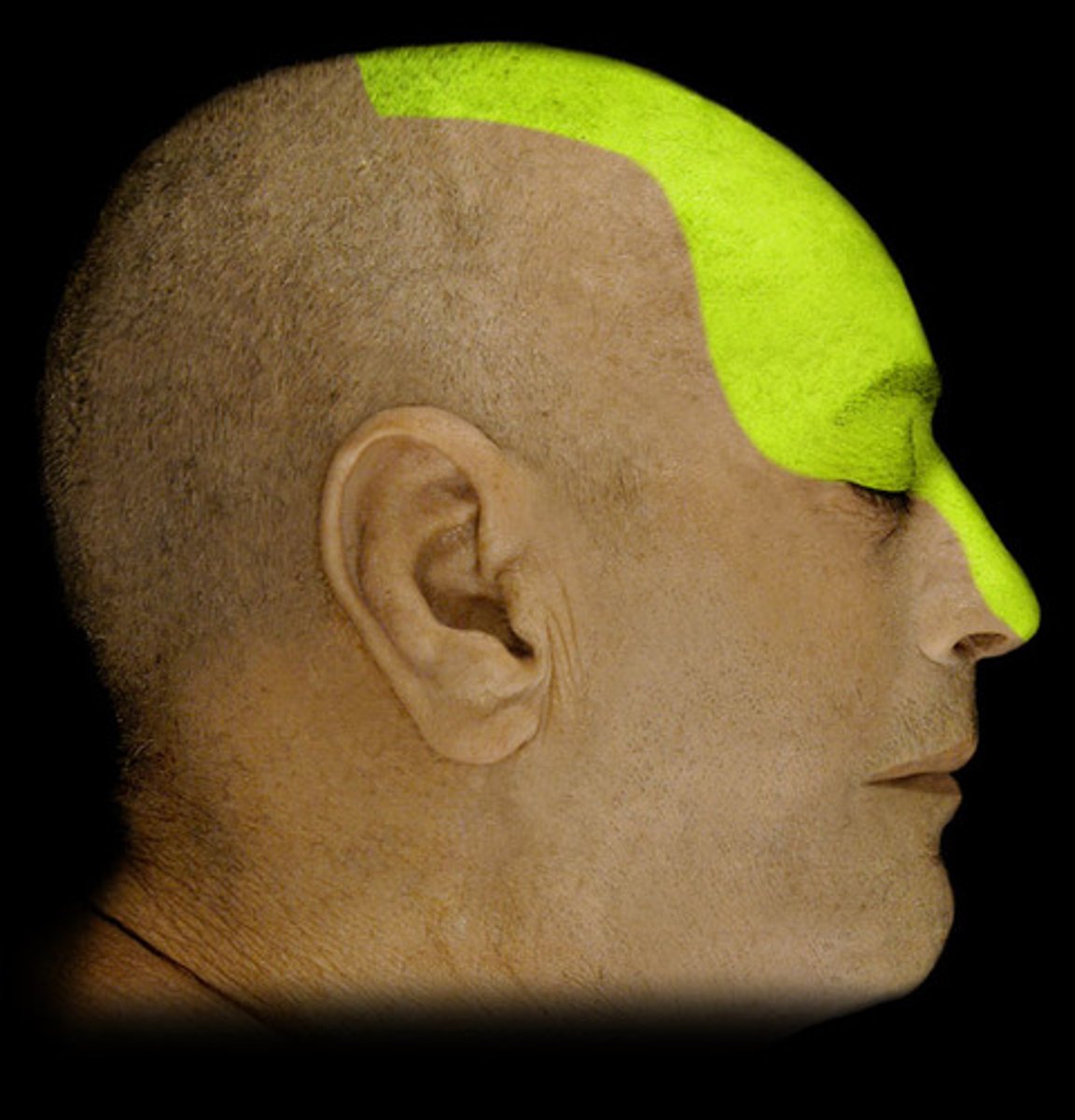
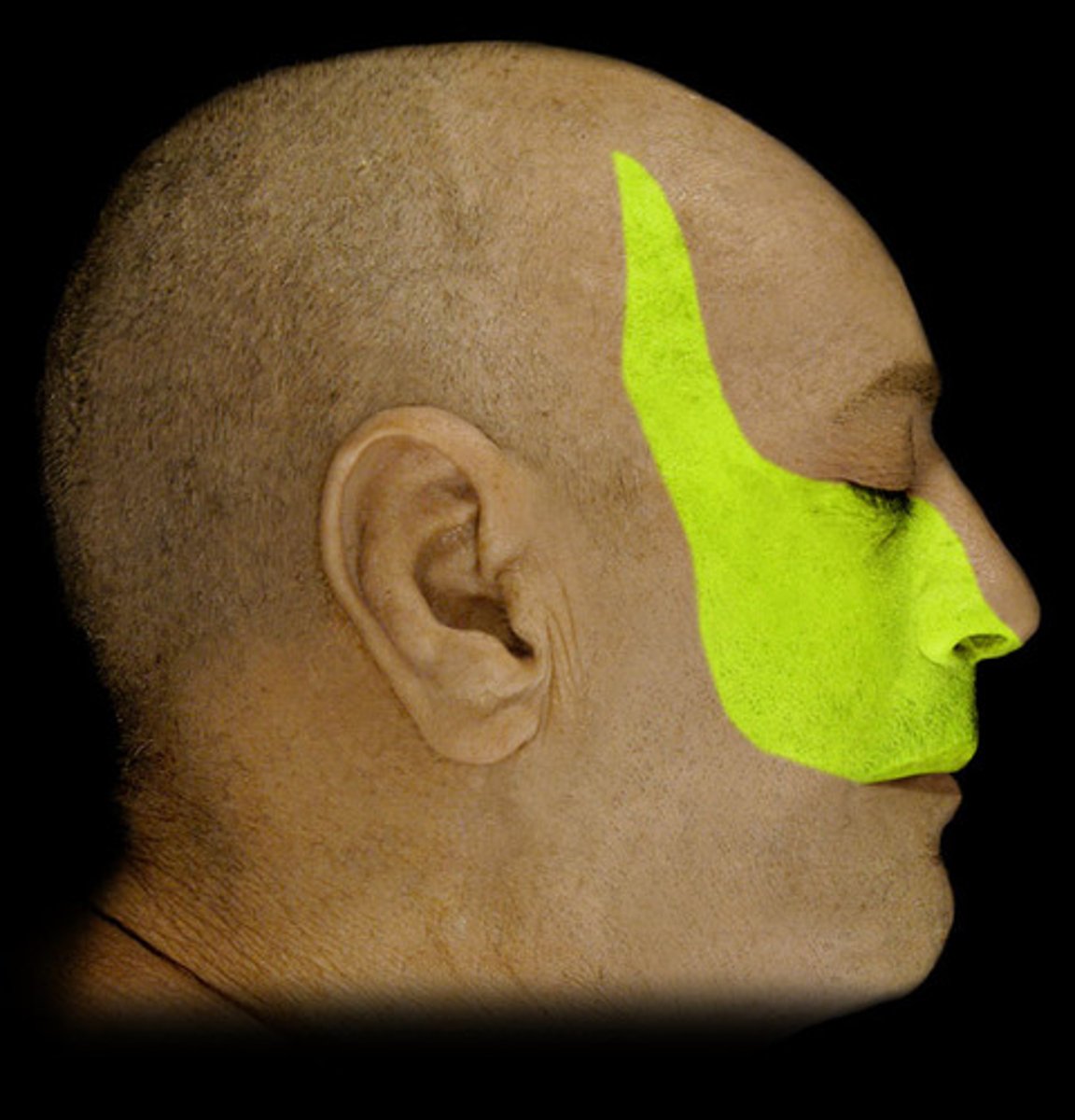
maxillary nerve
mandibular nerve

trigeminal nerve
opthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve, mandibular nerve
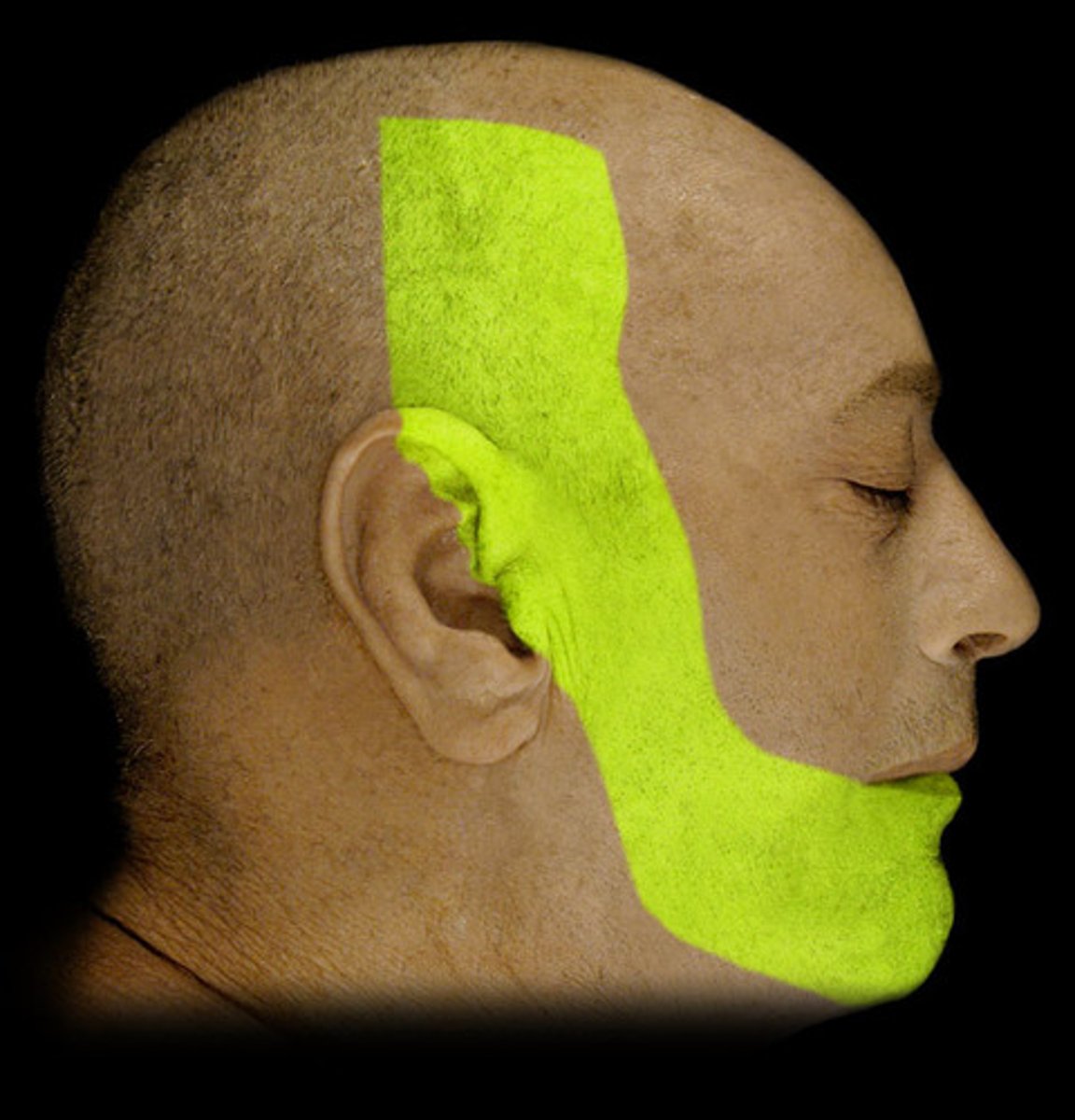
great auricular nerve, innervates the skin of the neck and posterior ear

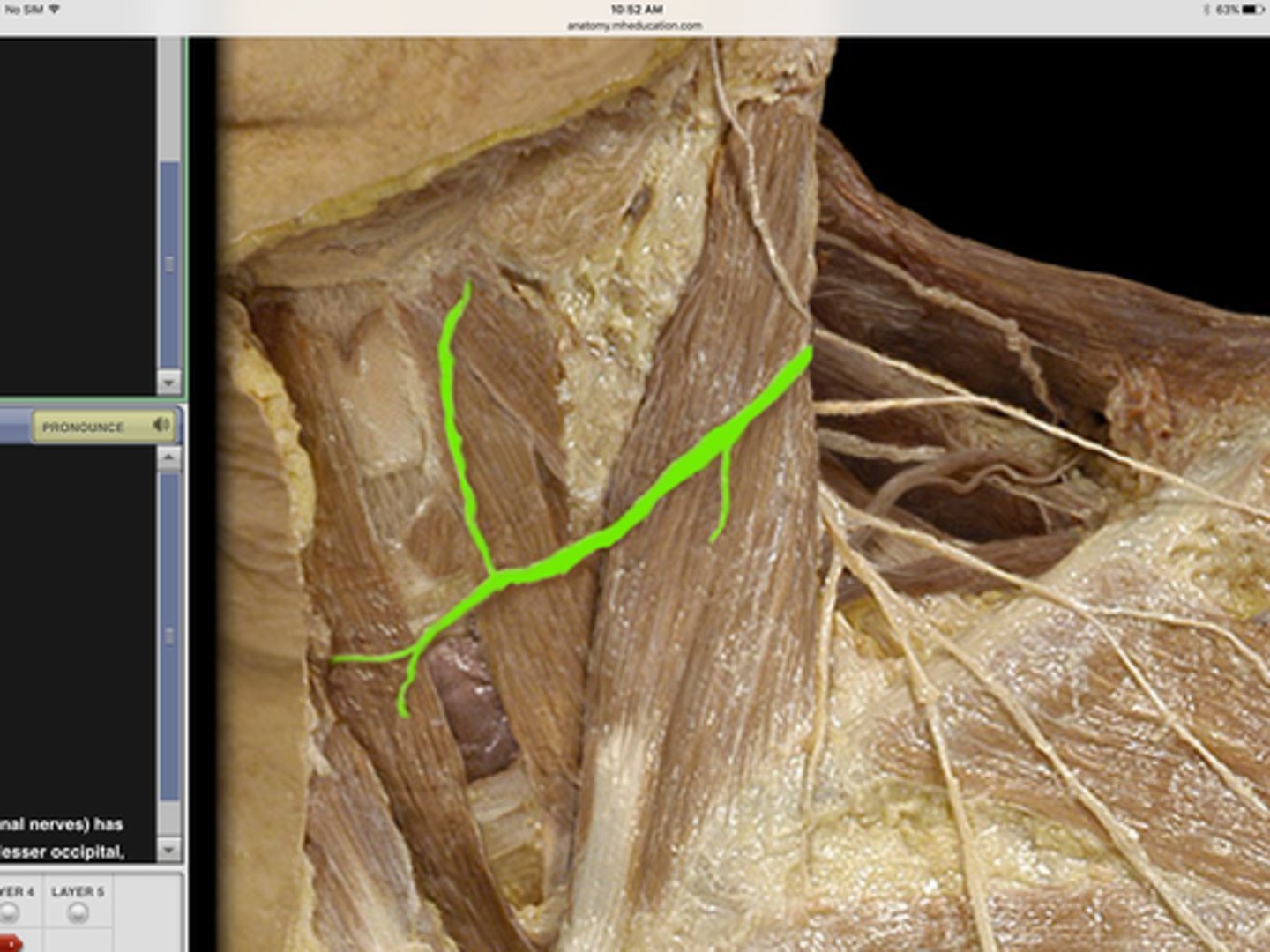
transverse cervical nerve
supraclavicular nerves
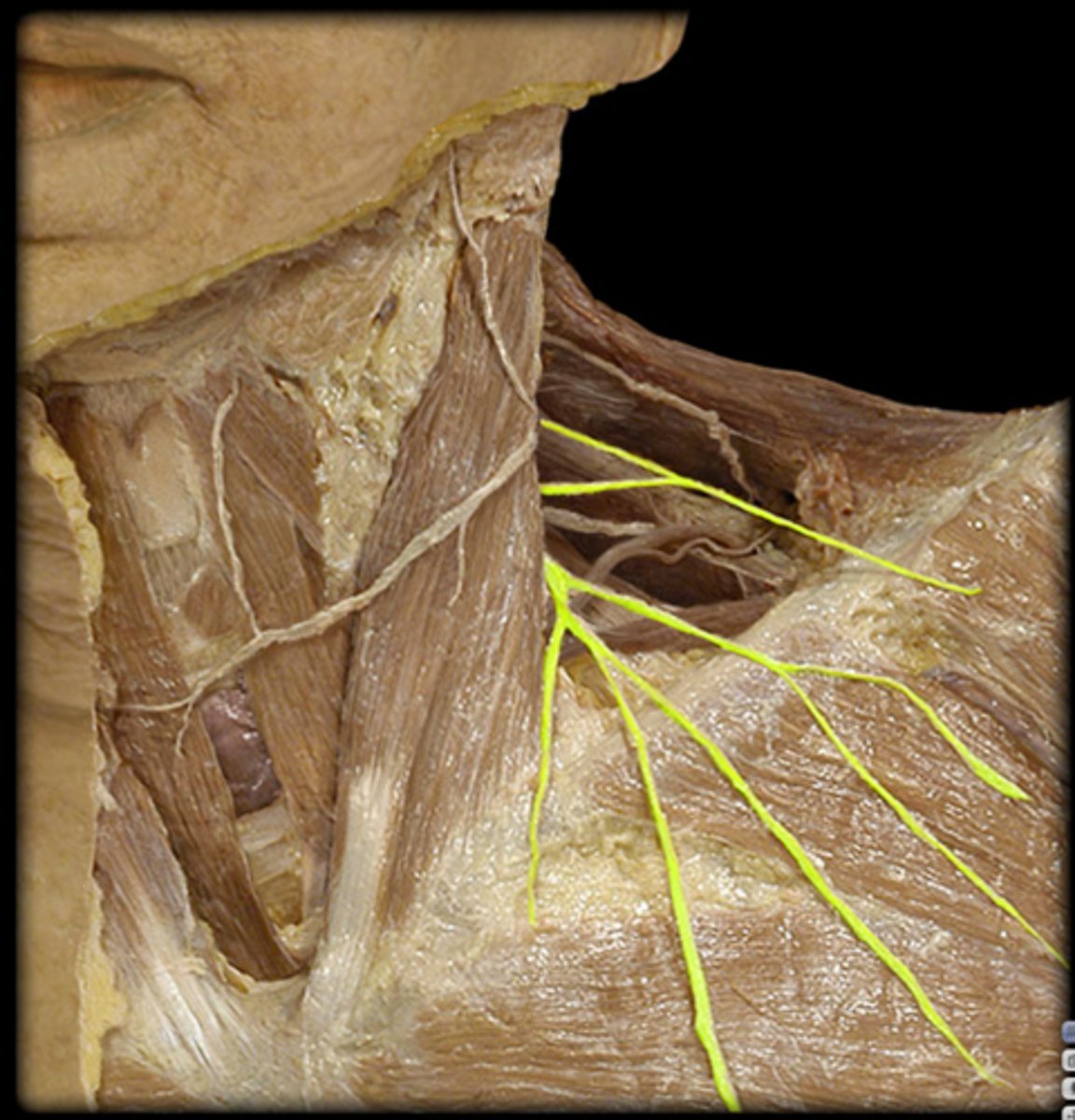
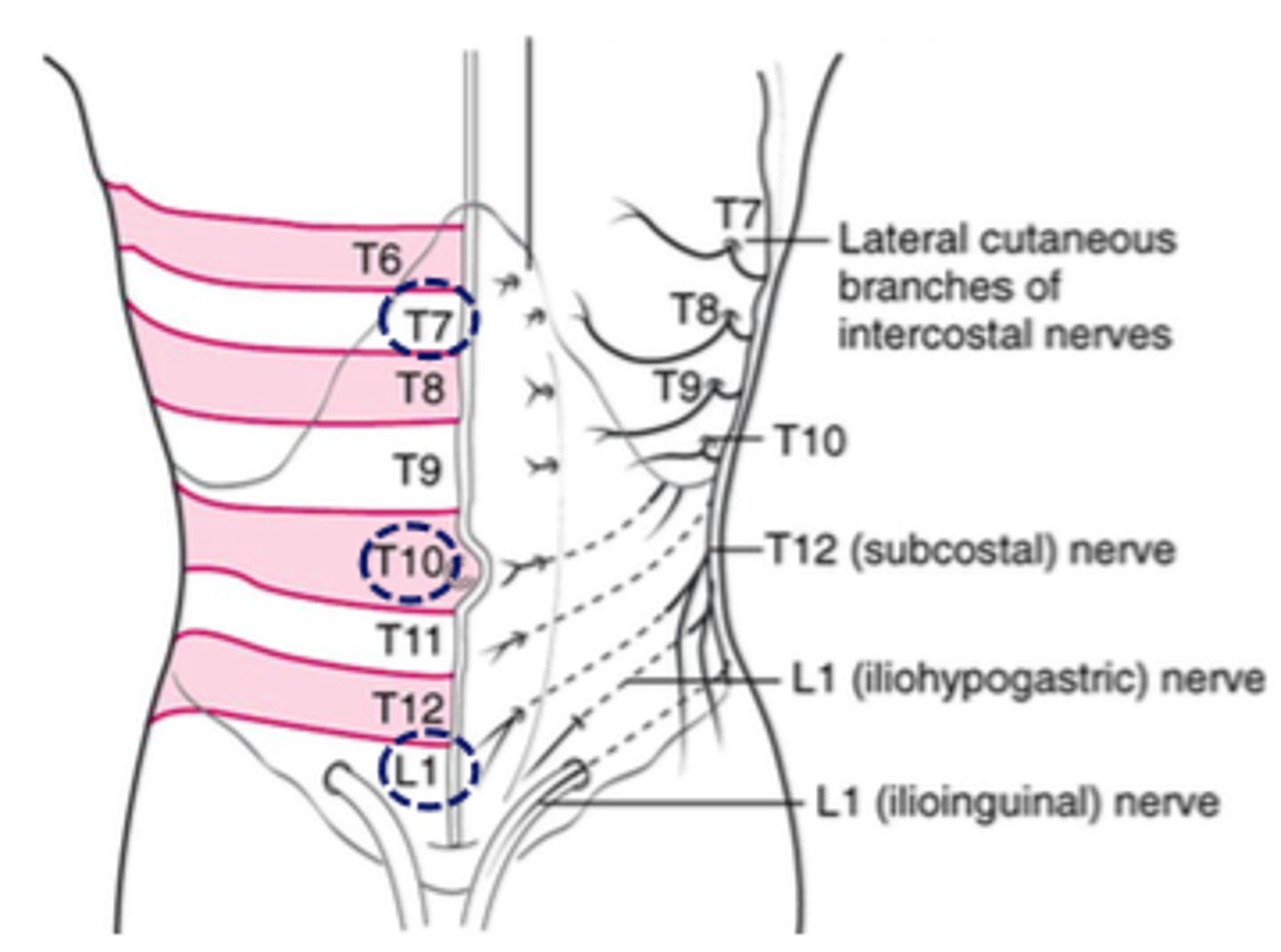
intercostal nerves
anterior cutaneous rami, lateral cutaneous rami
anterior cutaneous rami
lateral cutaneous rami
axillary nerve
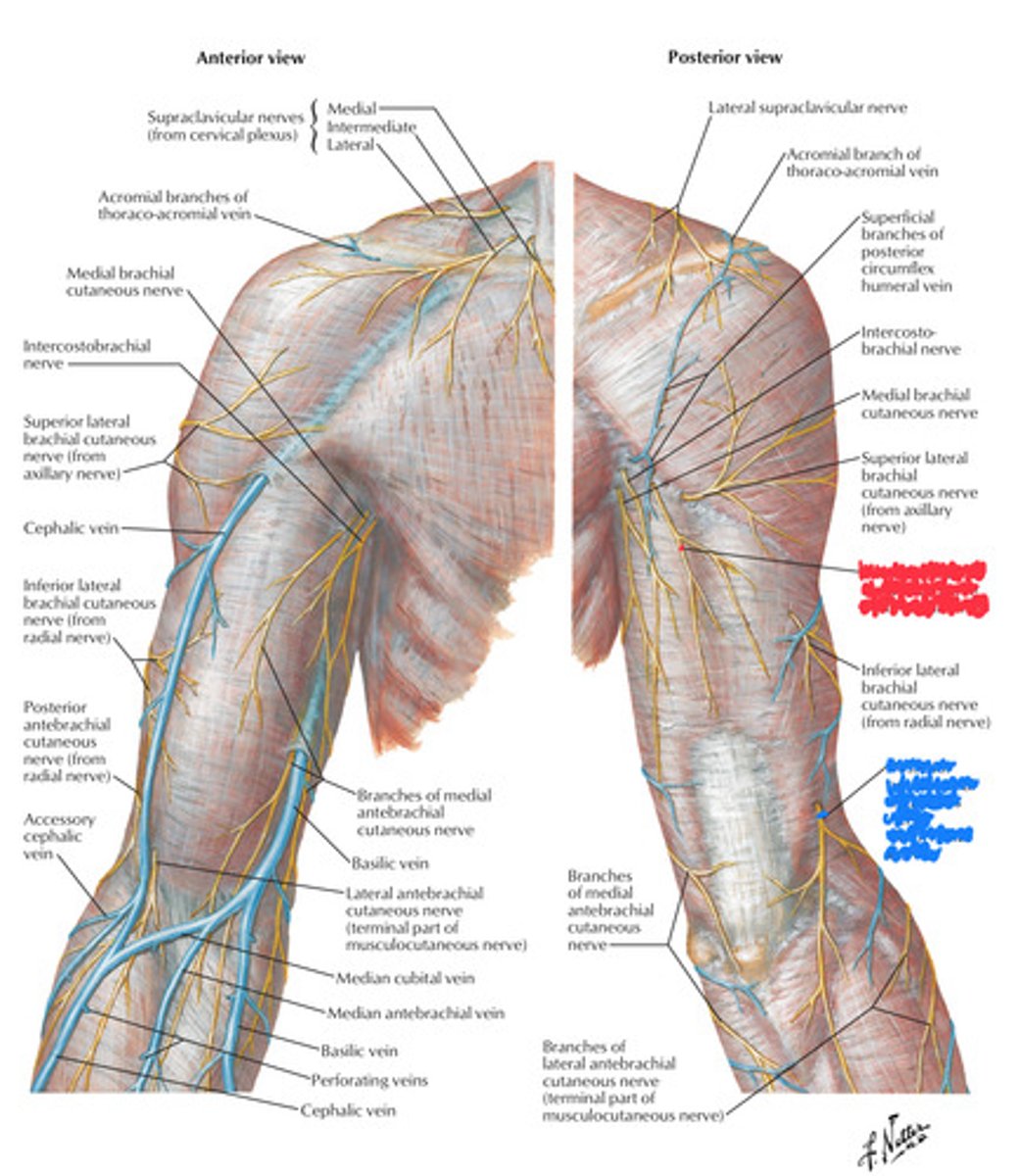
medial brachial cutaneous nerve
intercostobrachial nerves
innervation of the skin on medial surface of the arm are called what?
inferior lateral brachial cutaneous nerve
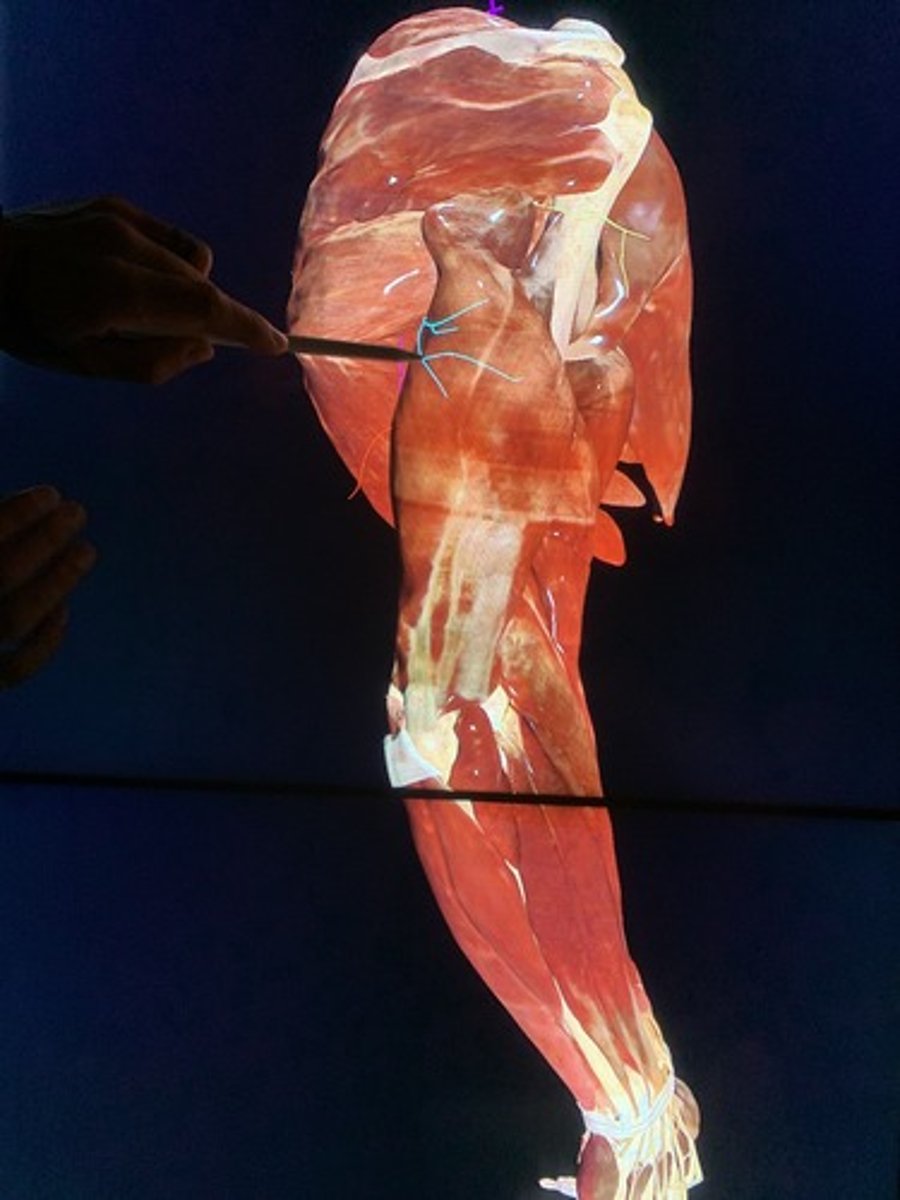
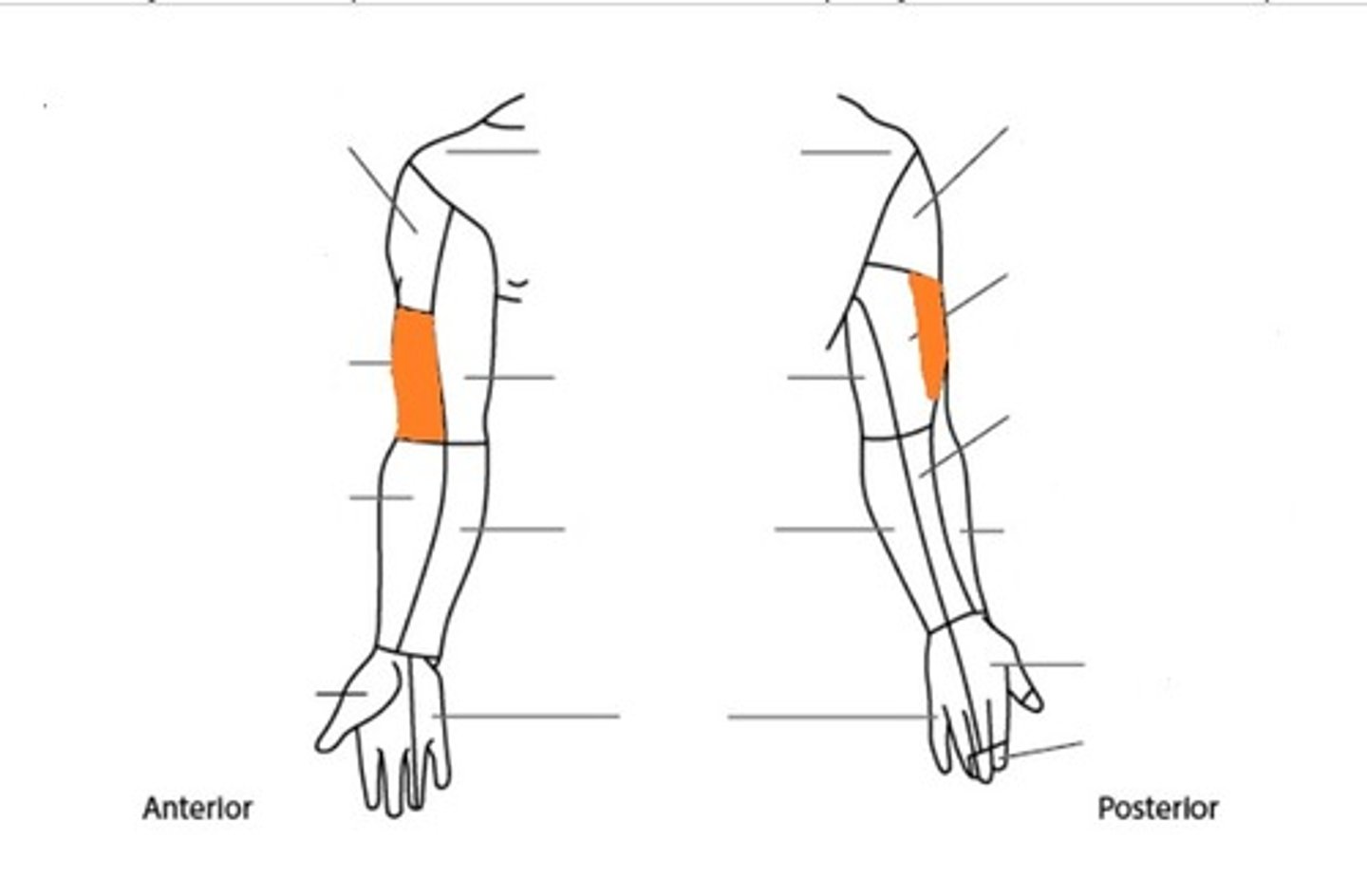
medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
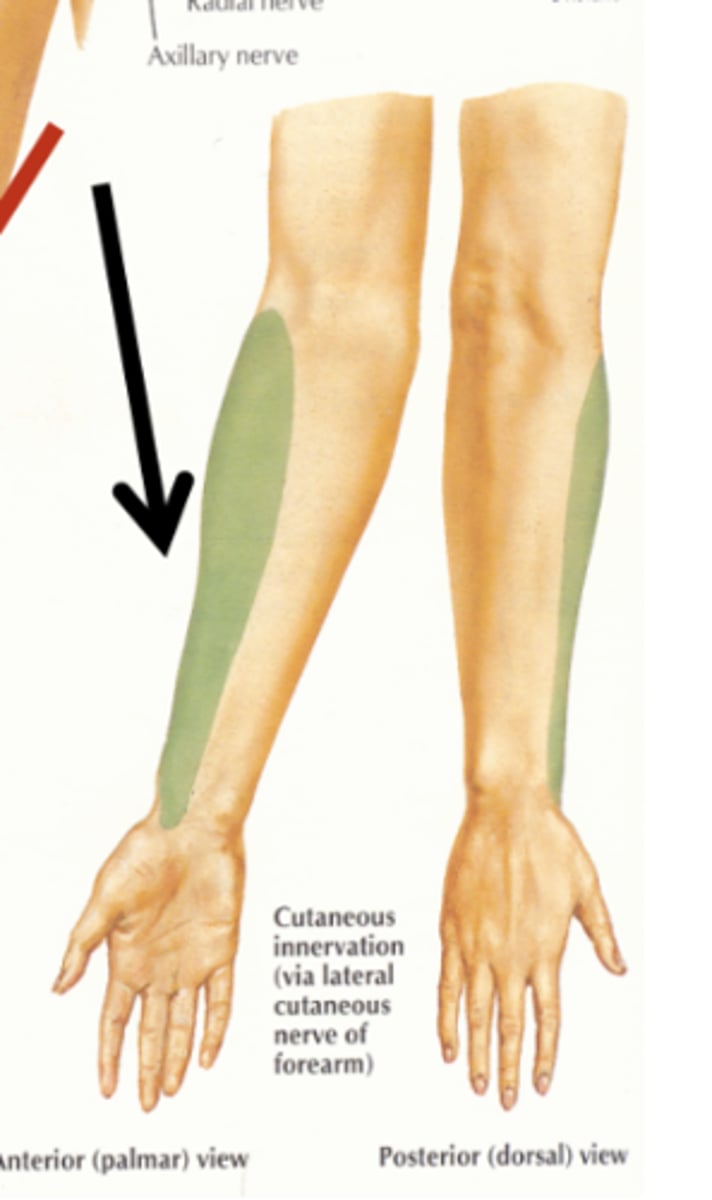
lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve
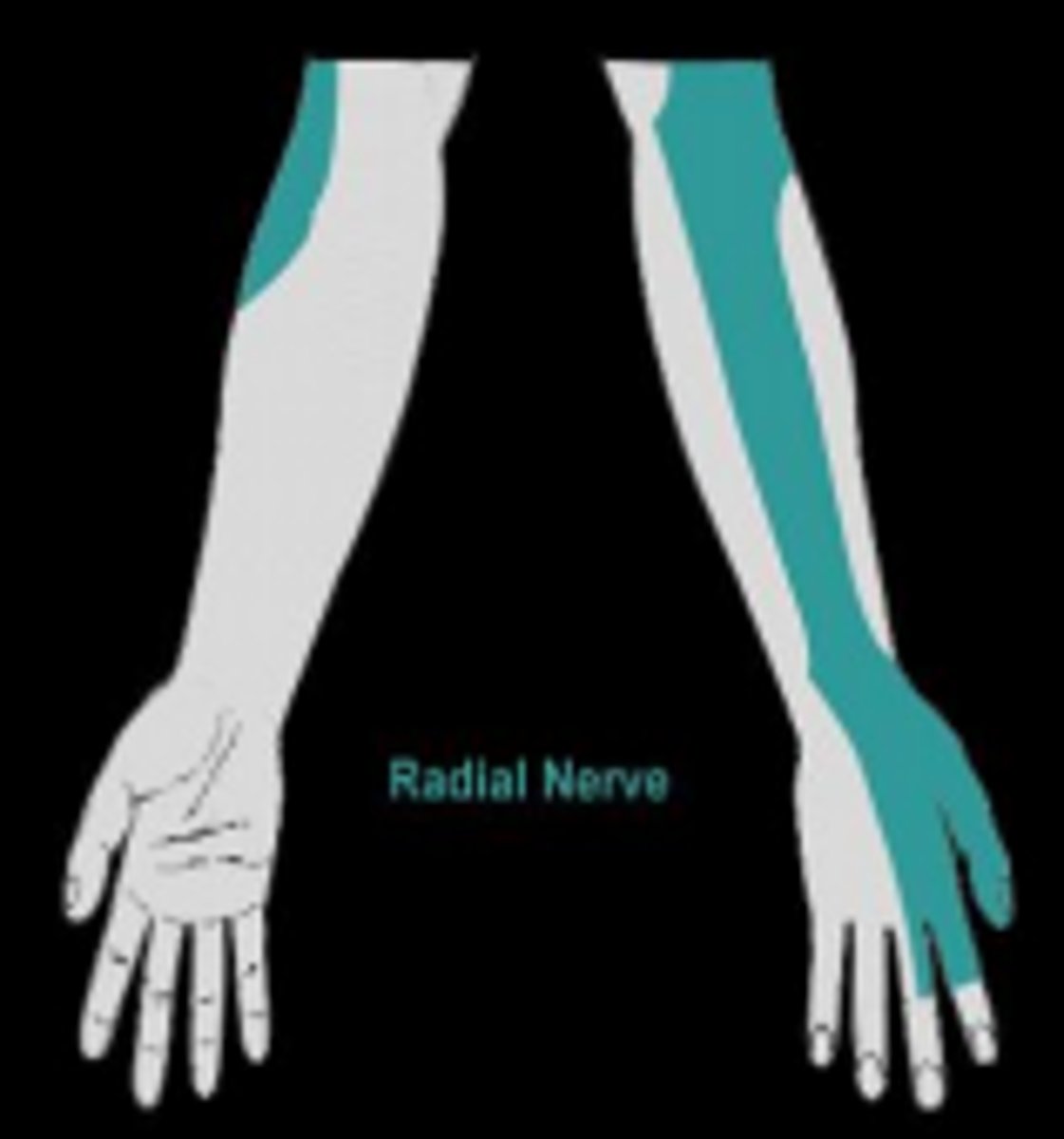
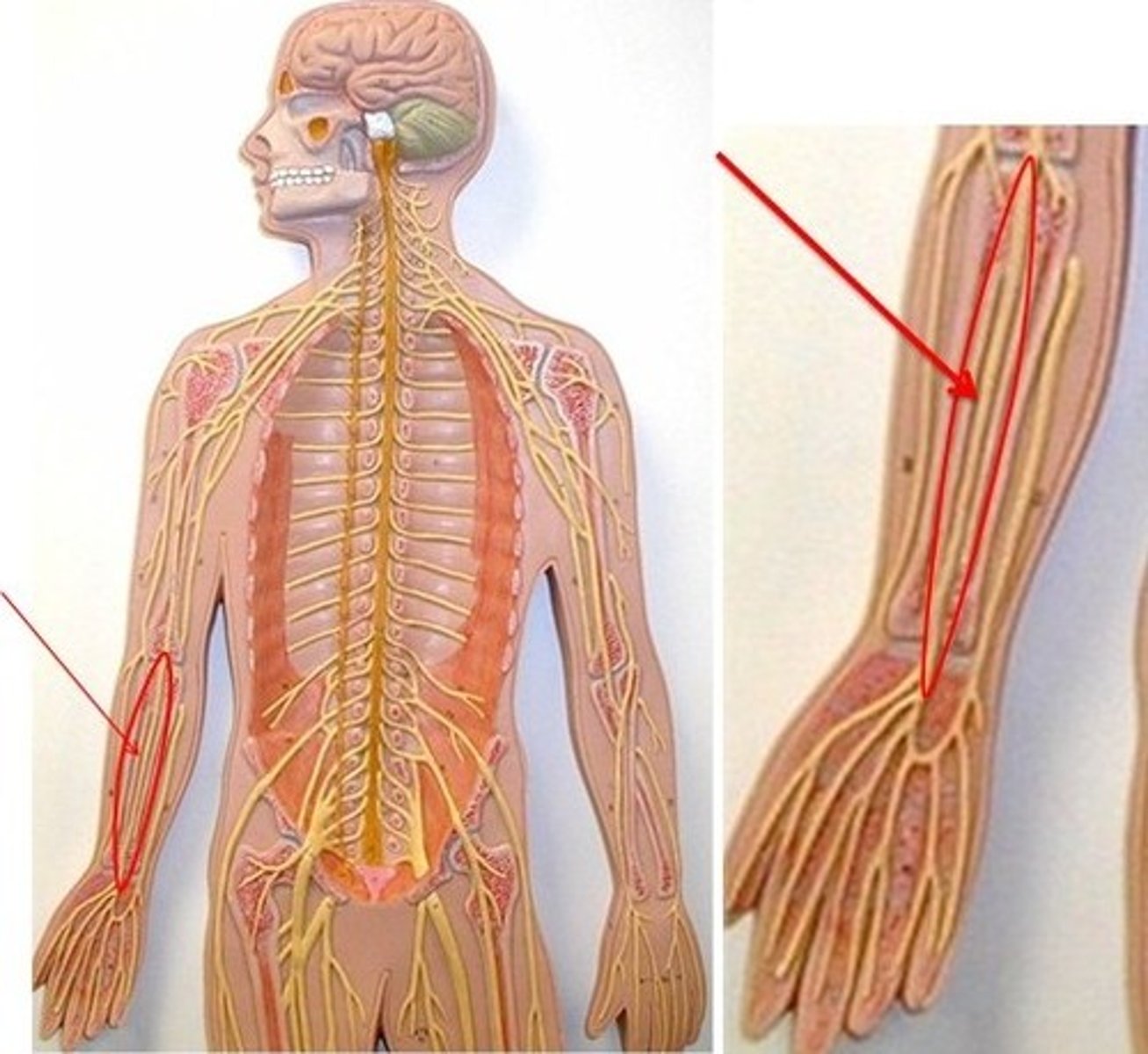
radial nerve
ulnar nerve
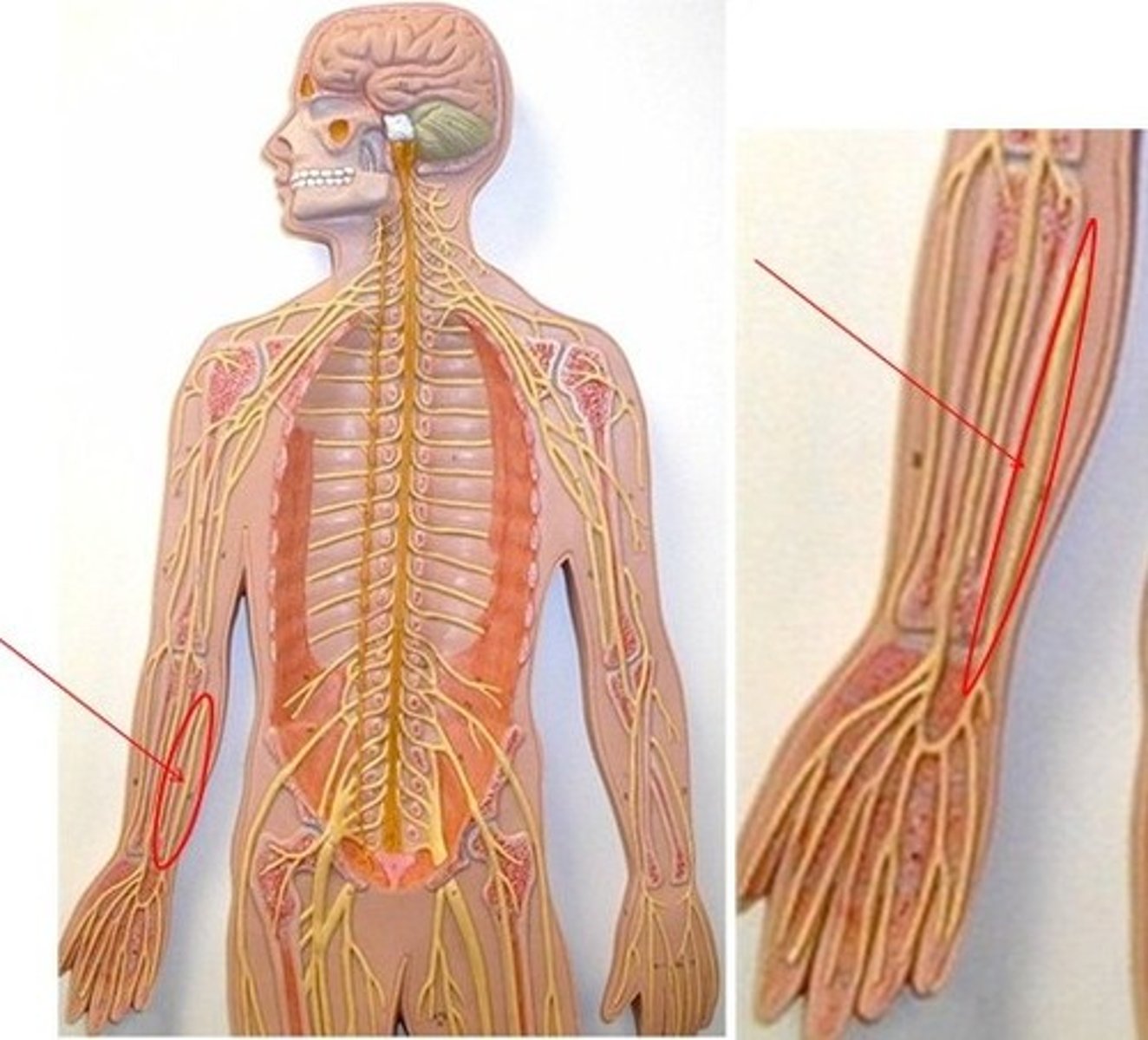
median nerve
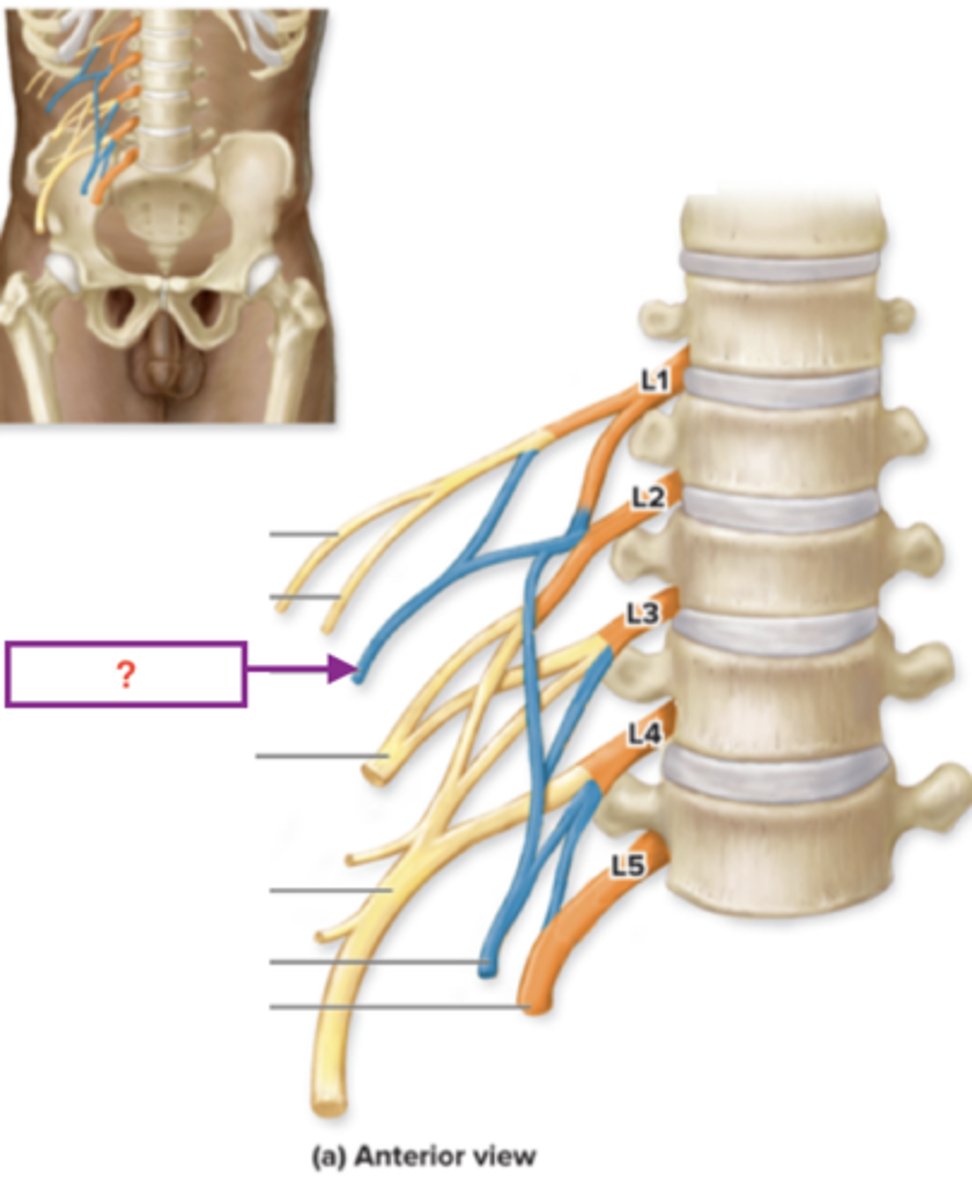
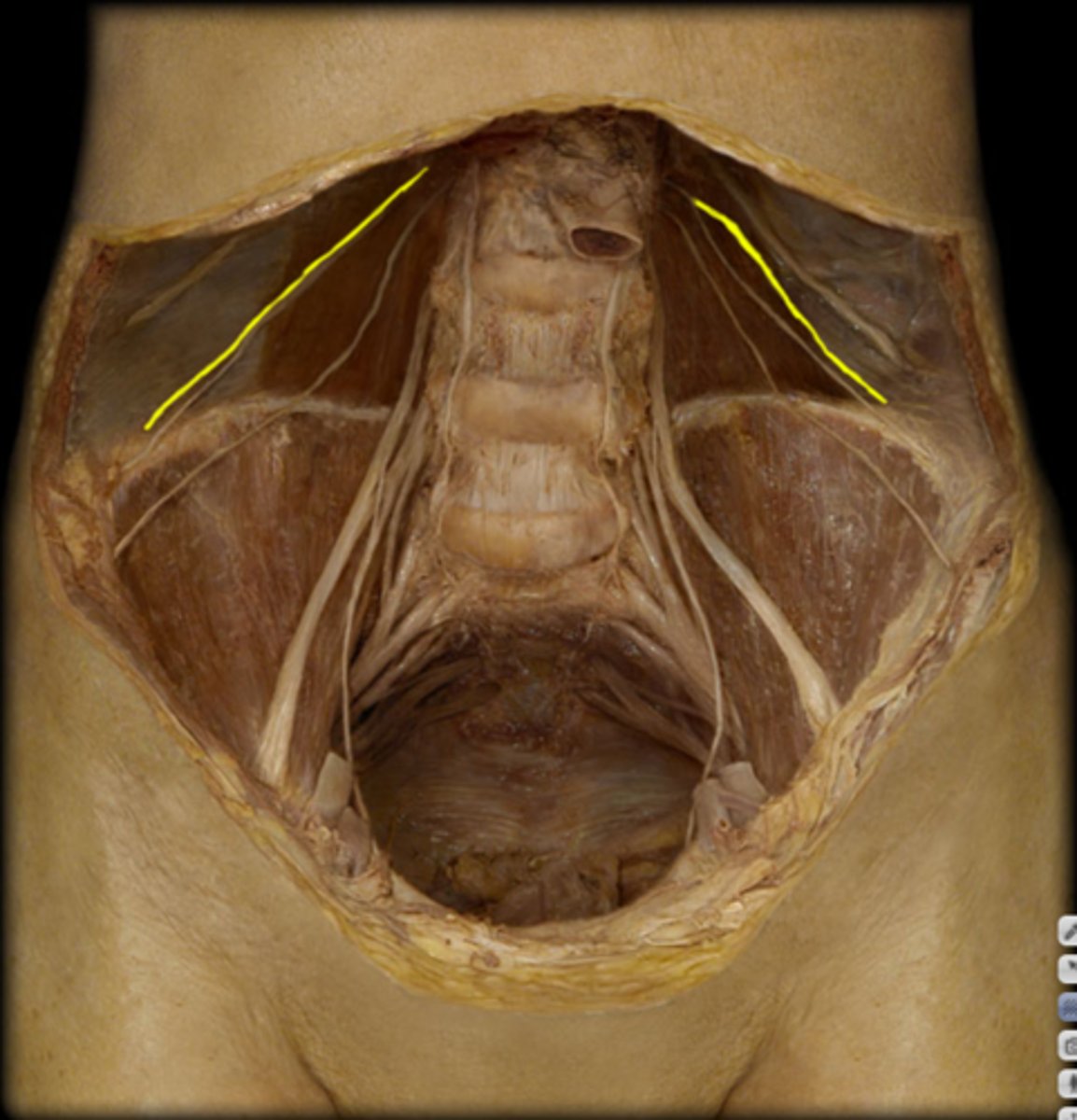
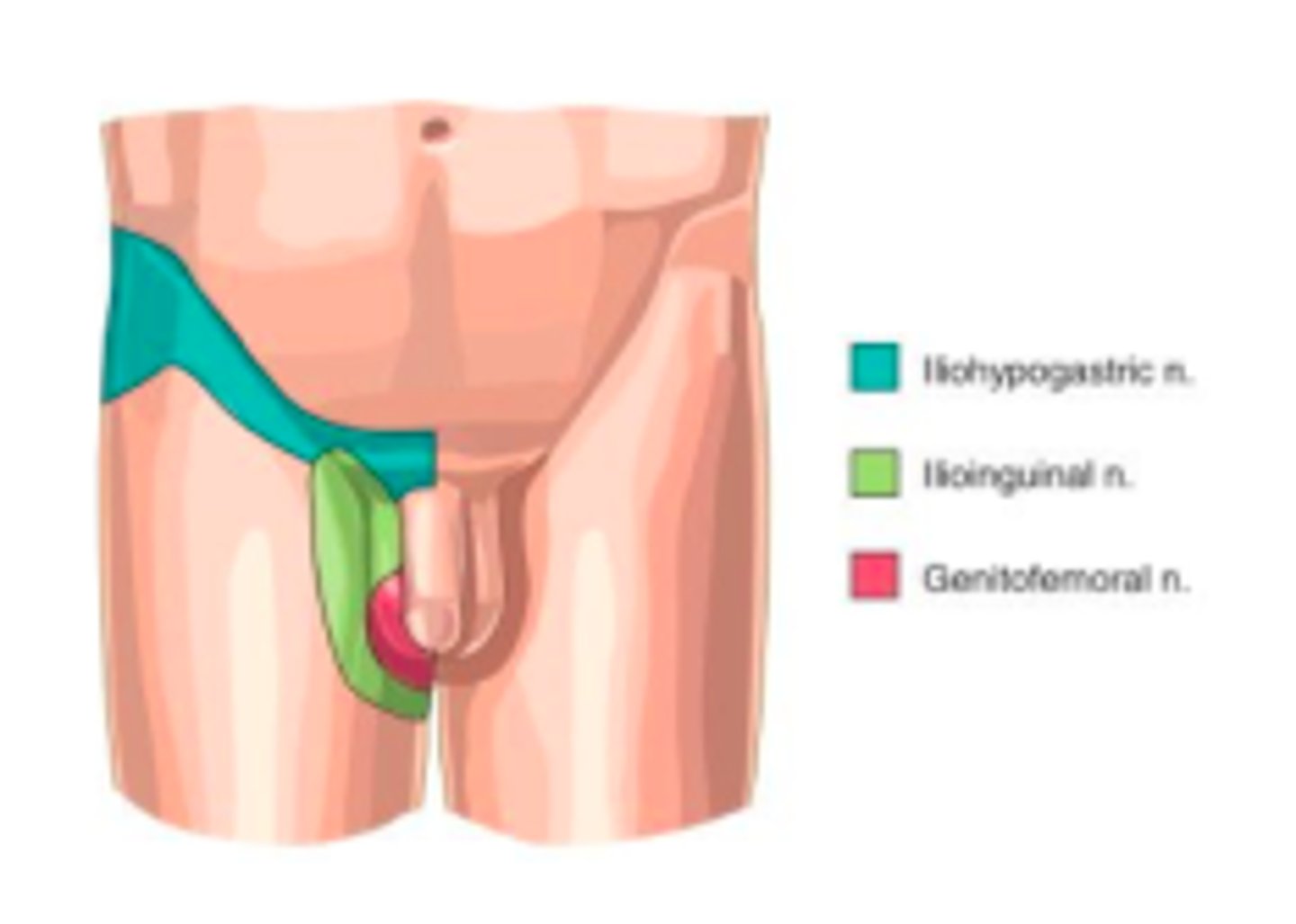
ilioinguinal nerve
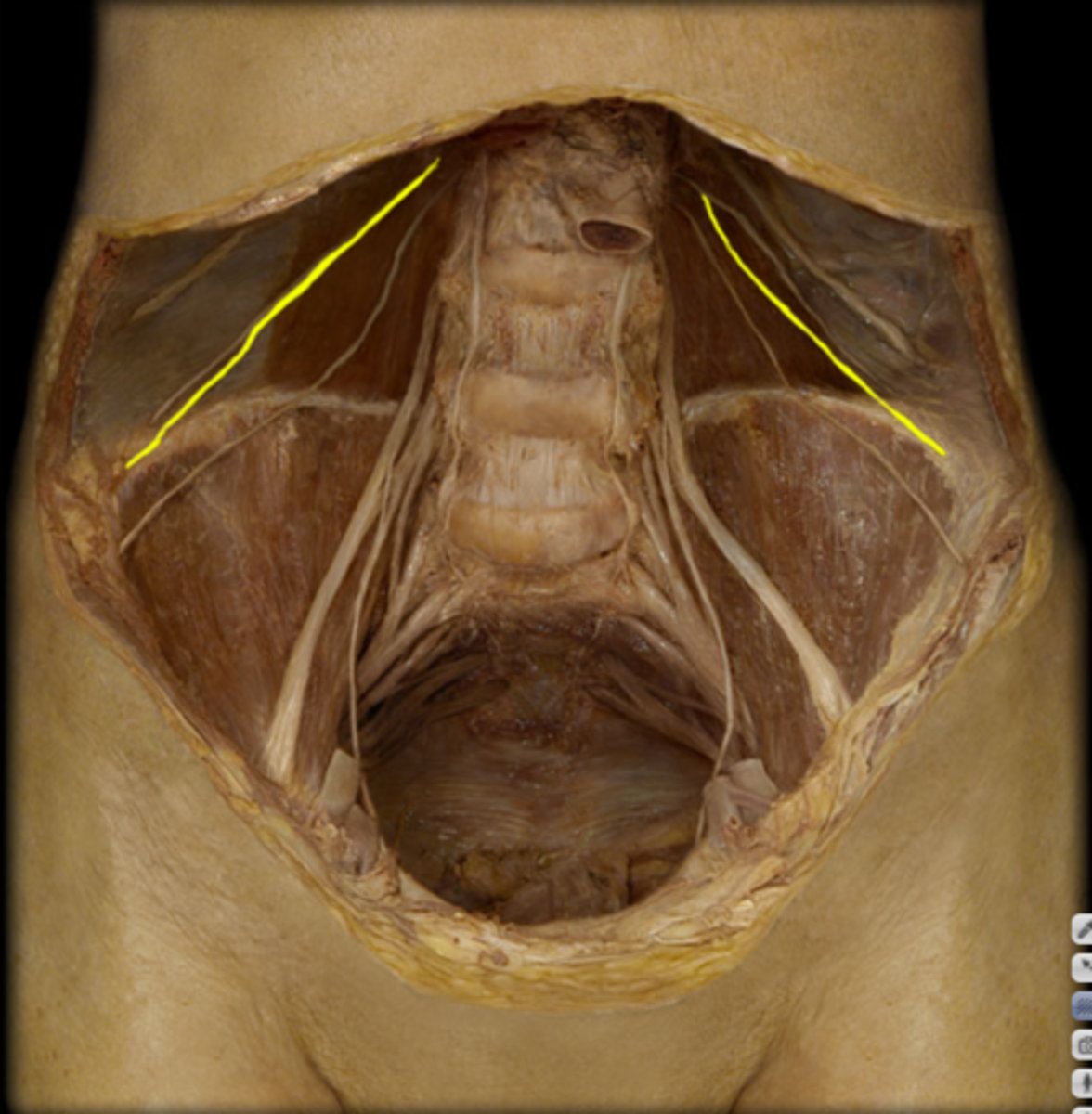
iliohypogastric nerve
arises from L1, gives motor functino to the naterolateral abdominal wall msucles and innervates sensory fro skin in the pubic region. Injury to the anterior branch can occur during appendectomy causing decreased sensation at the suprapubic region.
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
a cutaneous nerve that innervates the skin on the lateral part of the thigh.
L3
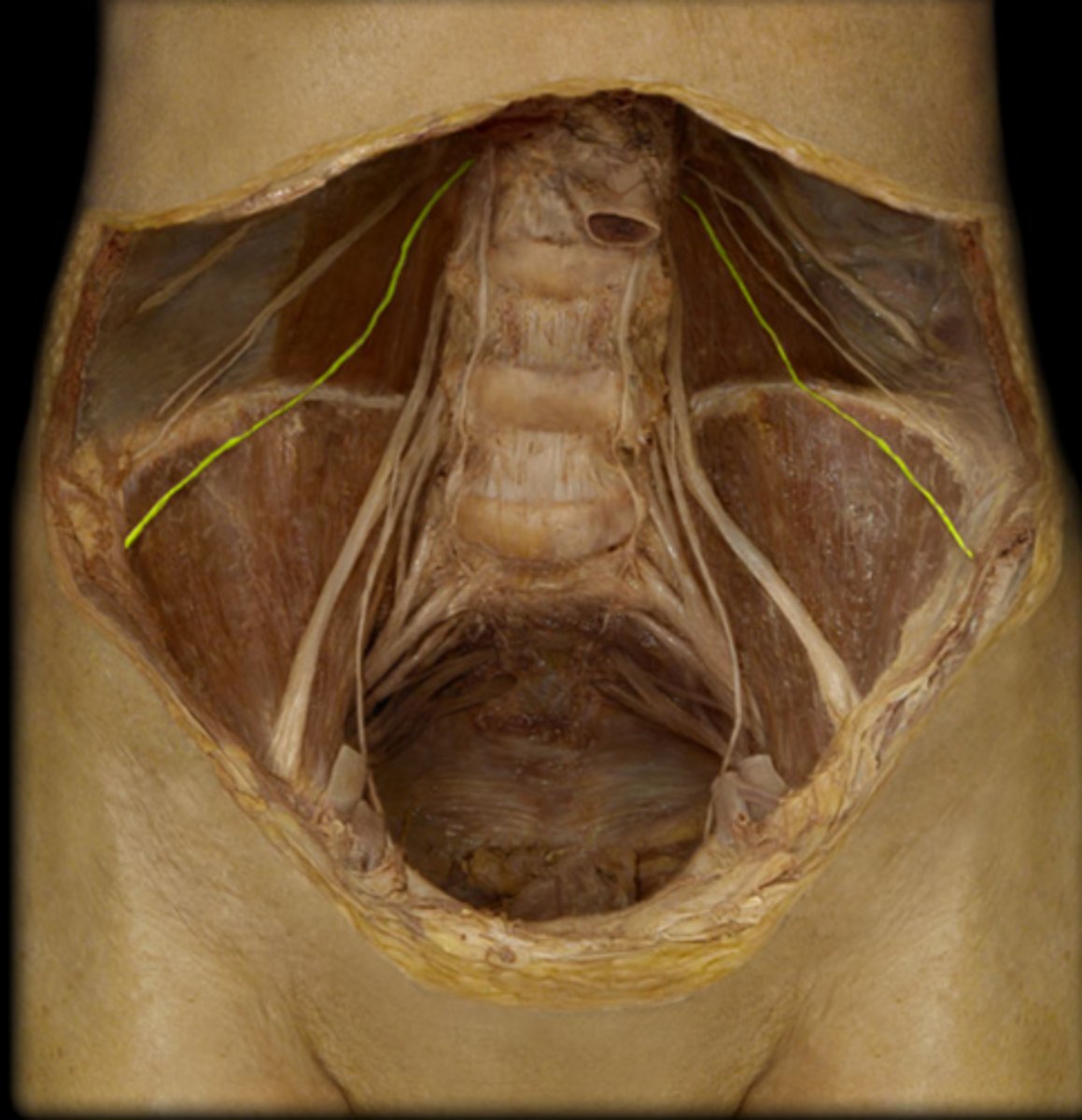
obturator nerve
passes through obturator foramen to innervate adductor muscles
anterior femoral cutaneous nerve
branches of femoral nerve to serve anterior and medial surfaces of thigh
may be subdivided into intermediate and medial branches
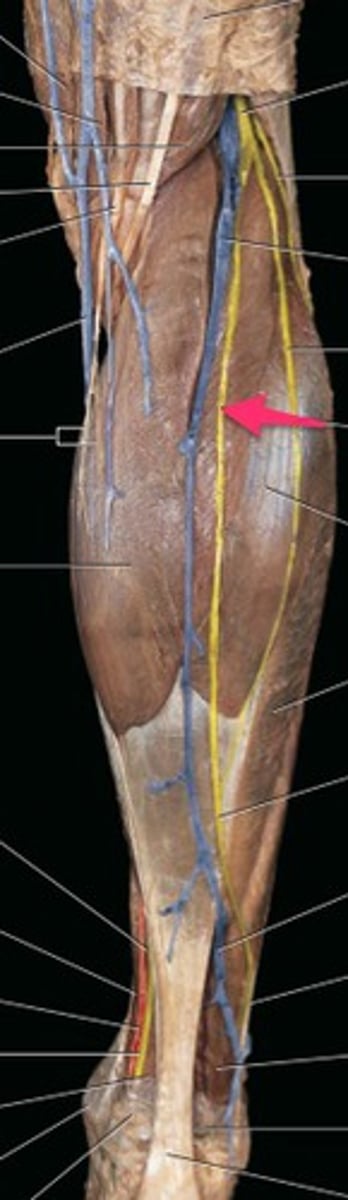
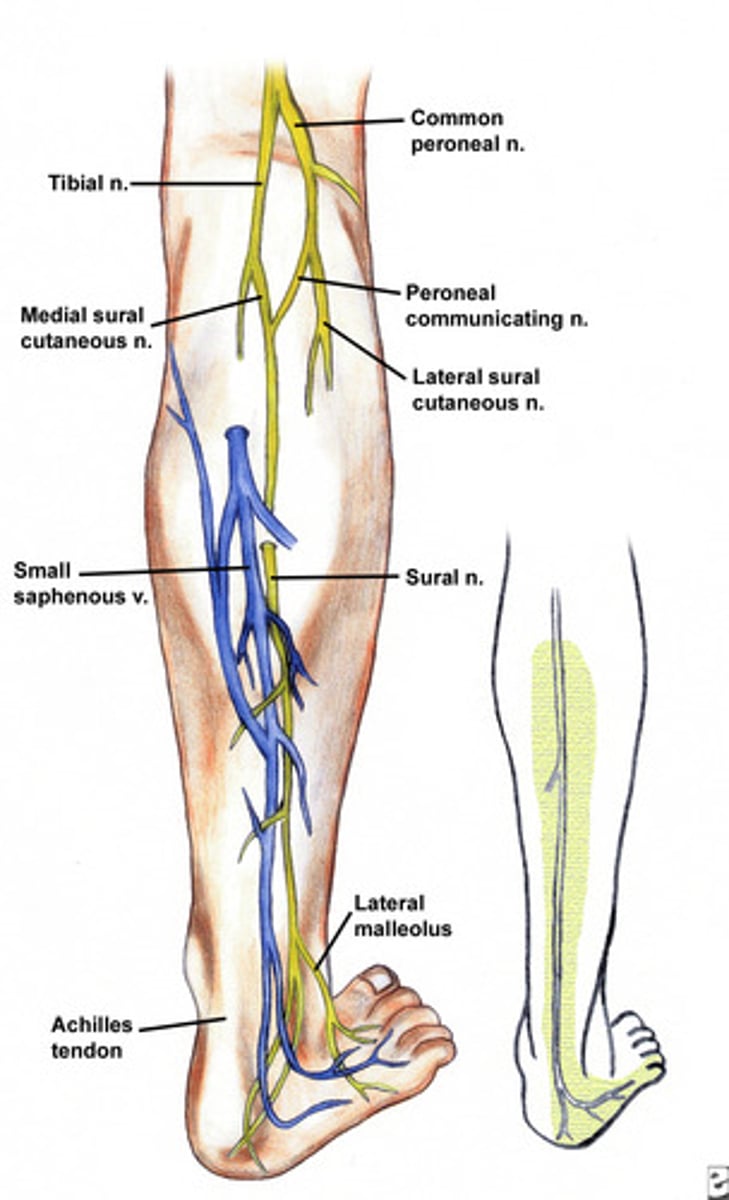
lateral sural cutaneous nerve
from dorsal divisions of ventral rami L-5, S-1 & S-2; arises in the popliteal fossa and passes into the superficial fascia over the lateral calf region to supply the superior part of the lateral aspect of the leg
saphenous nerve
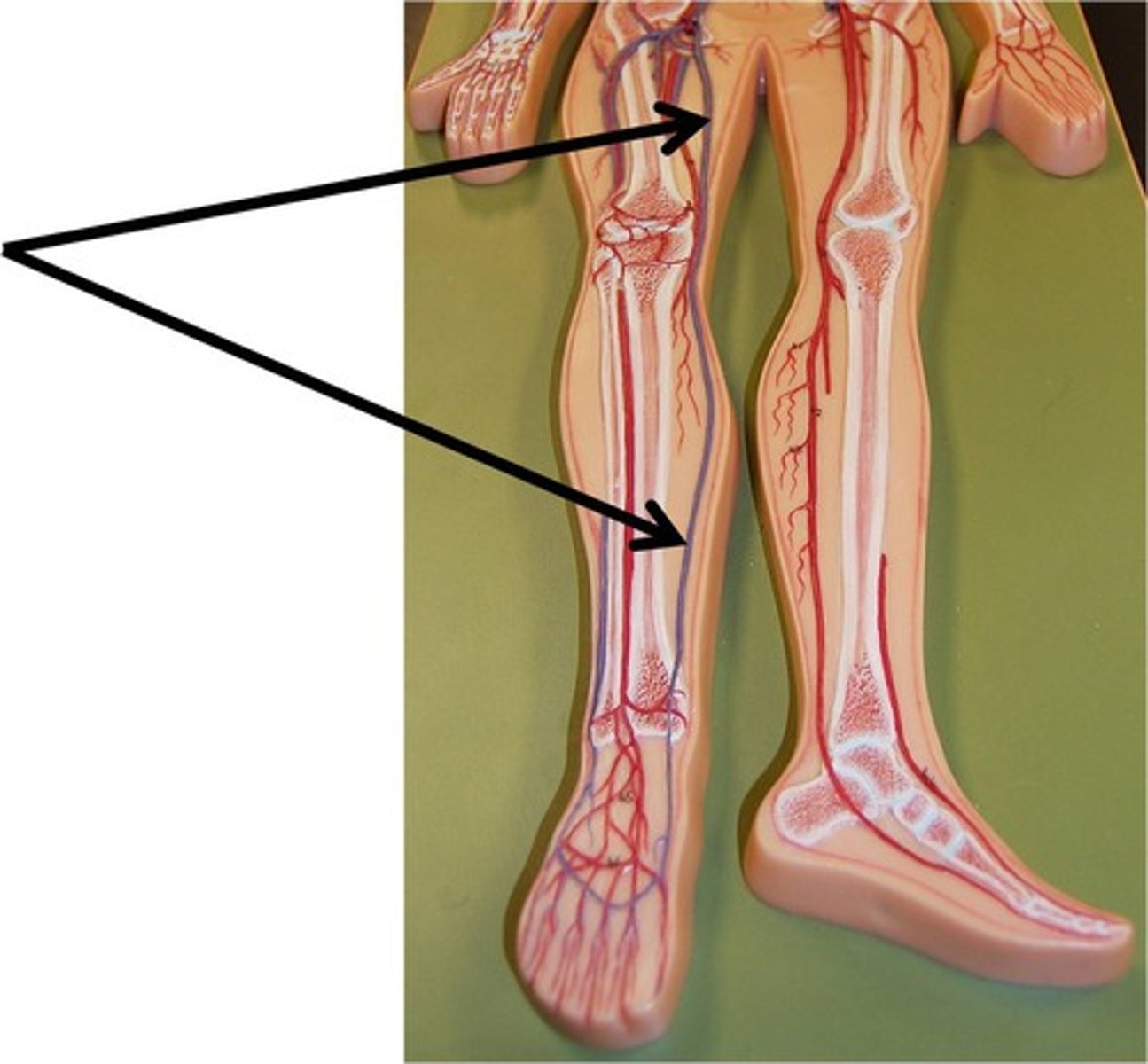
superficial peroneal nerve
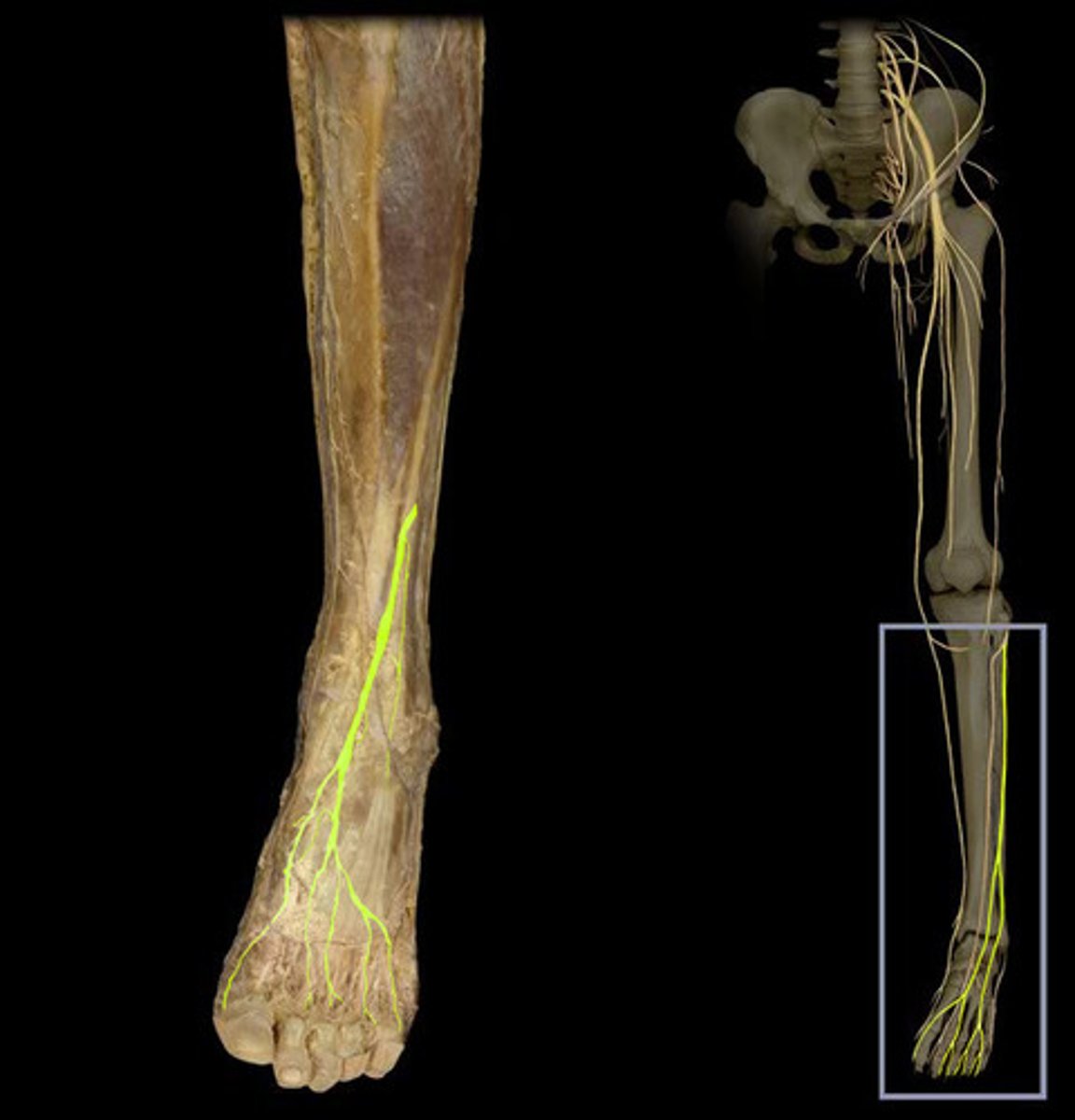
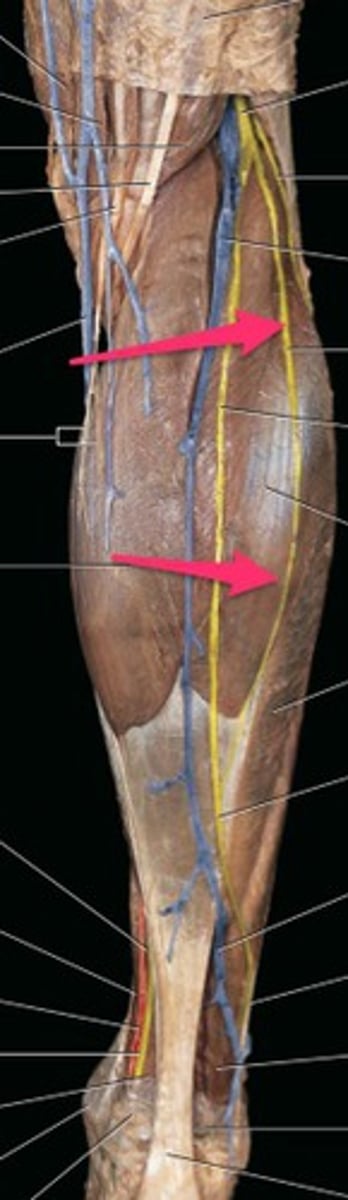
sural nerve
deep peroneal nerve
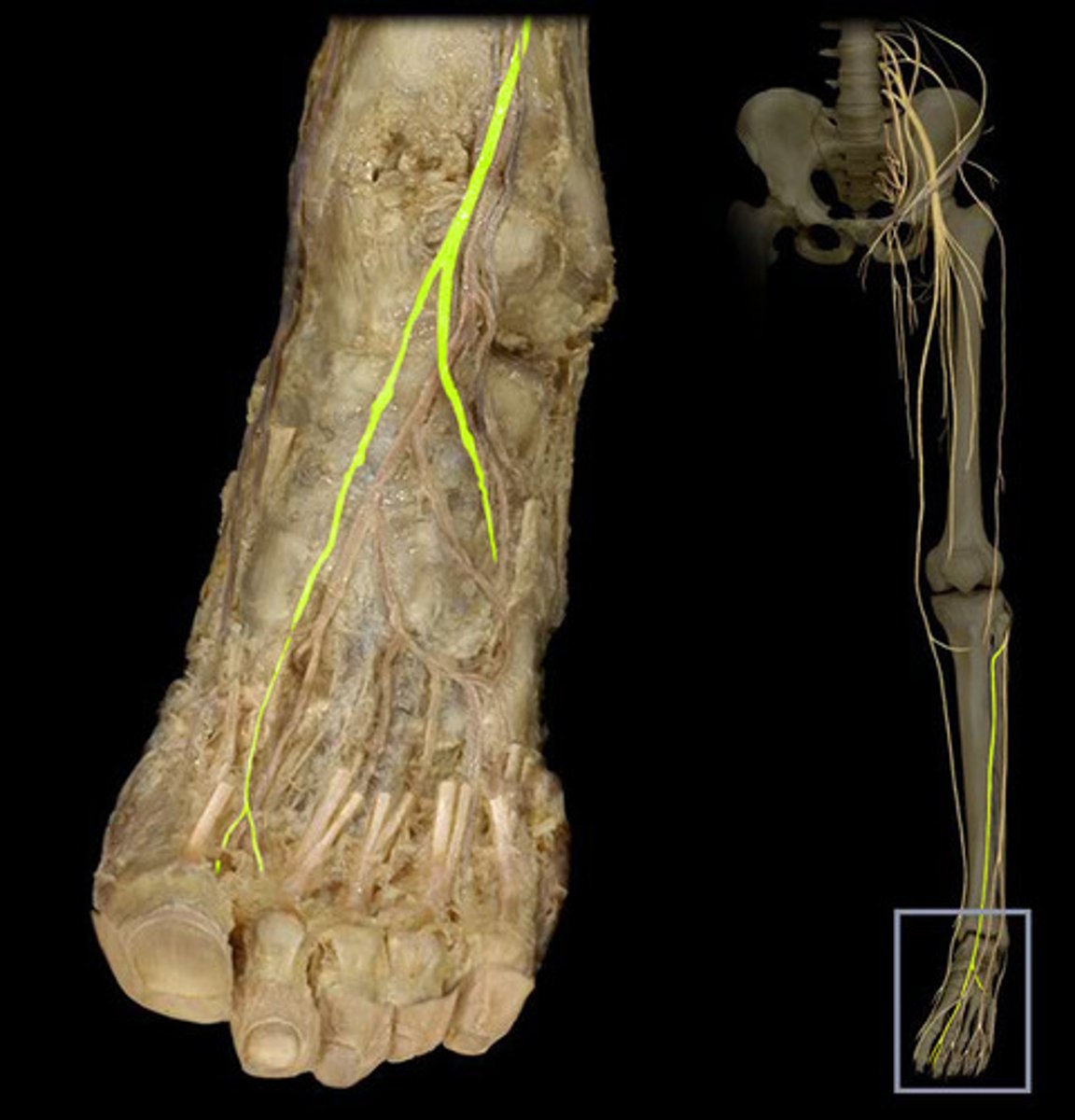
fibular nerve
-Also known as anterior tibial nerve; it extends down the front of the leg, behind the muscles. It supplies impulses to these muscles and also to the muscles and skin on the top of the foot and adjacent sides of the first and second toes.
-superficial peroneal nerve, sural nerve, deep peroneal nerve
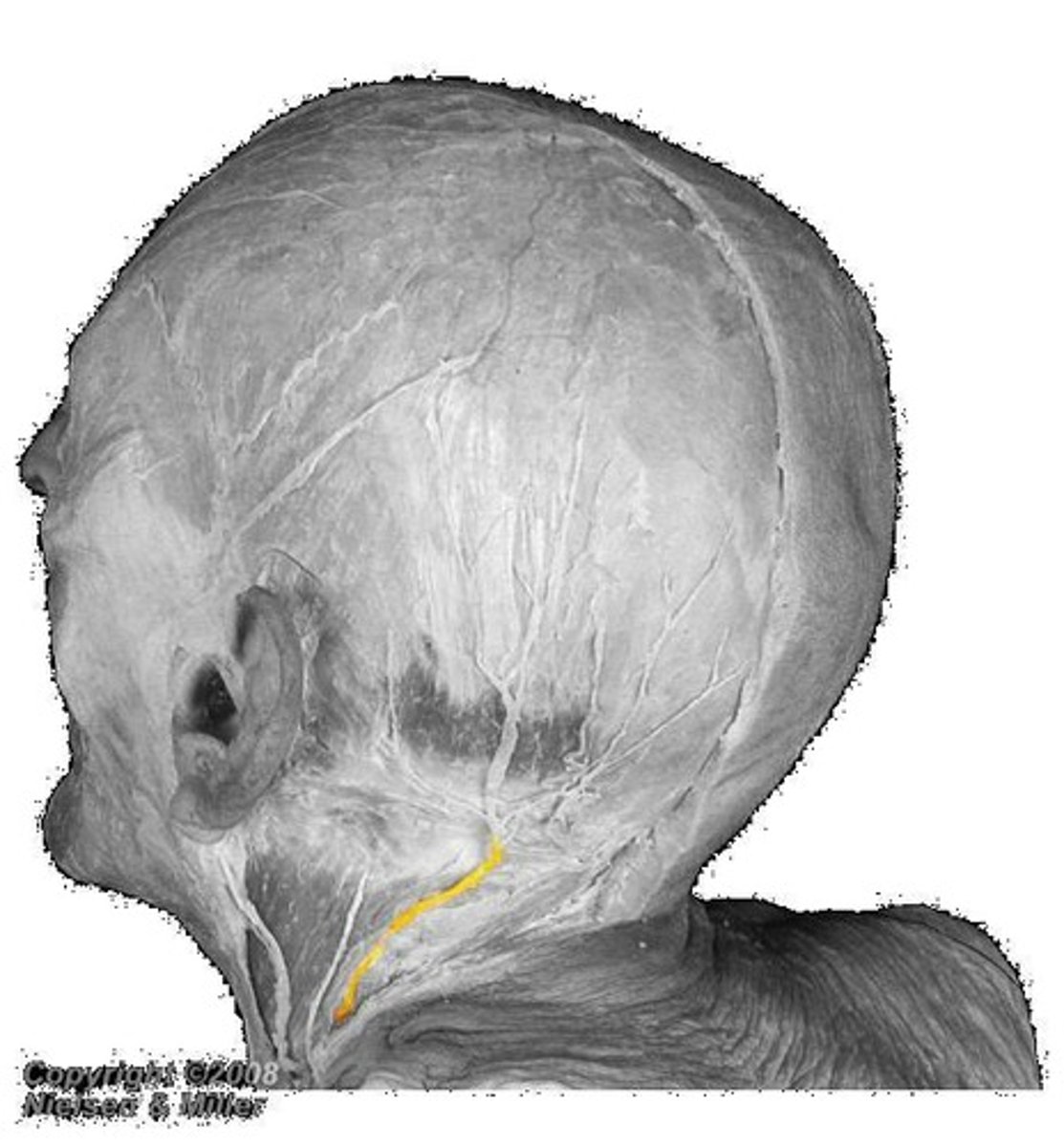
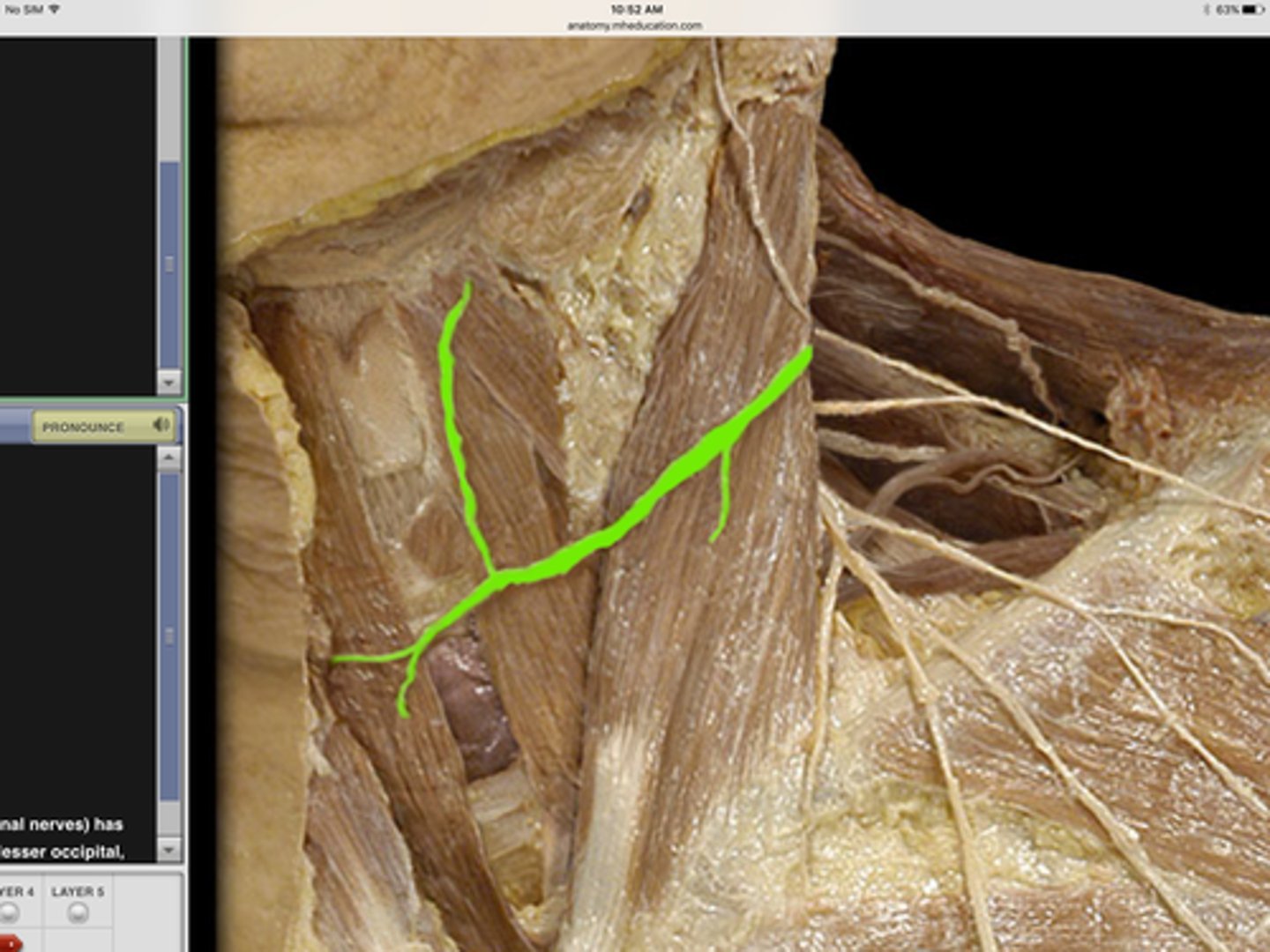
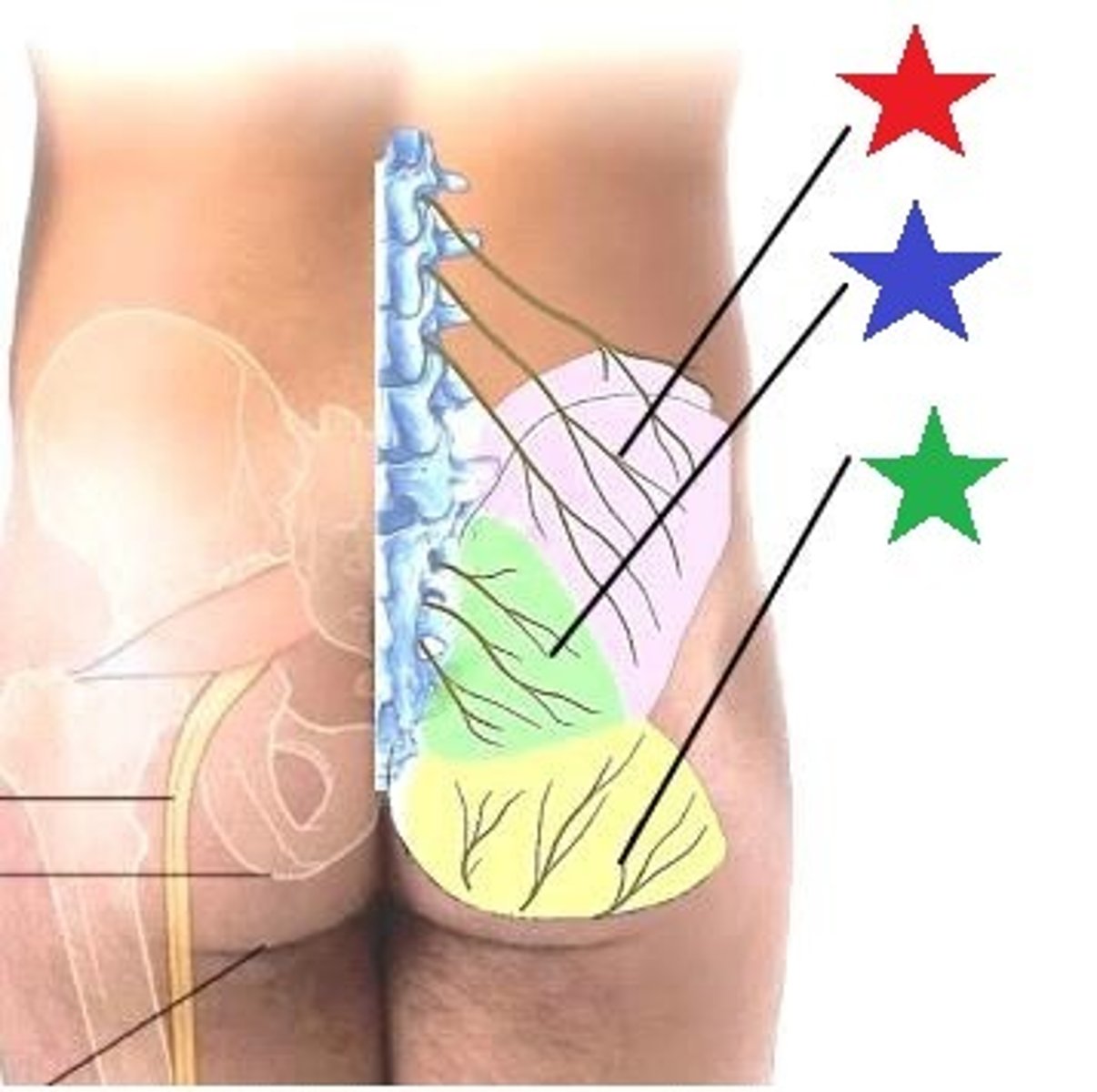
greater occipital nerve
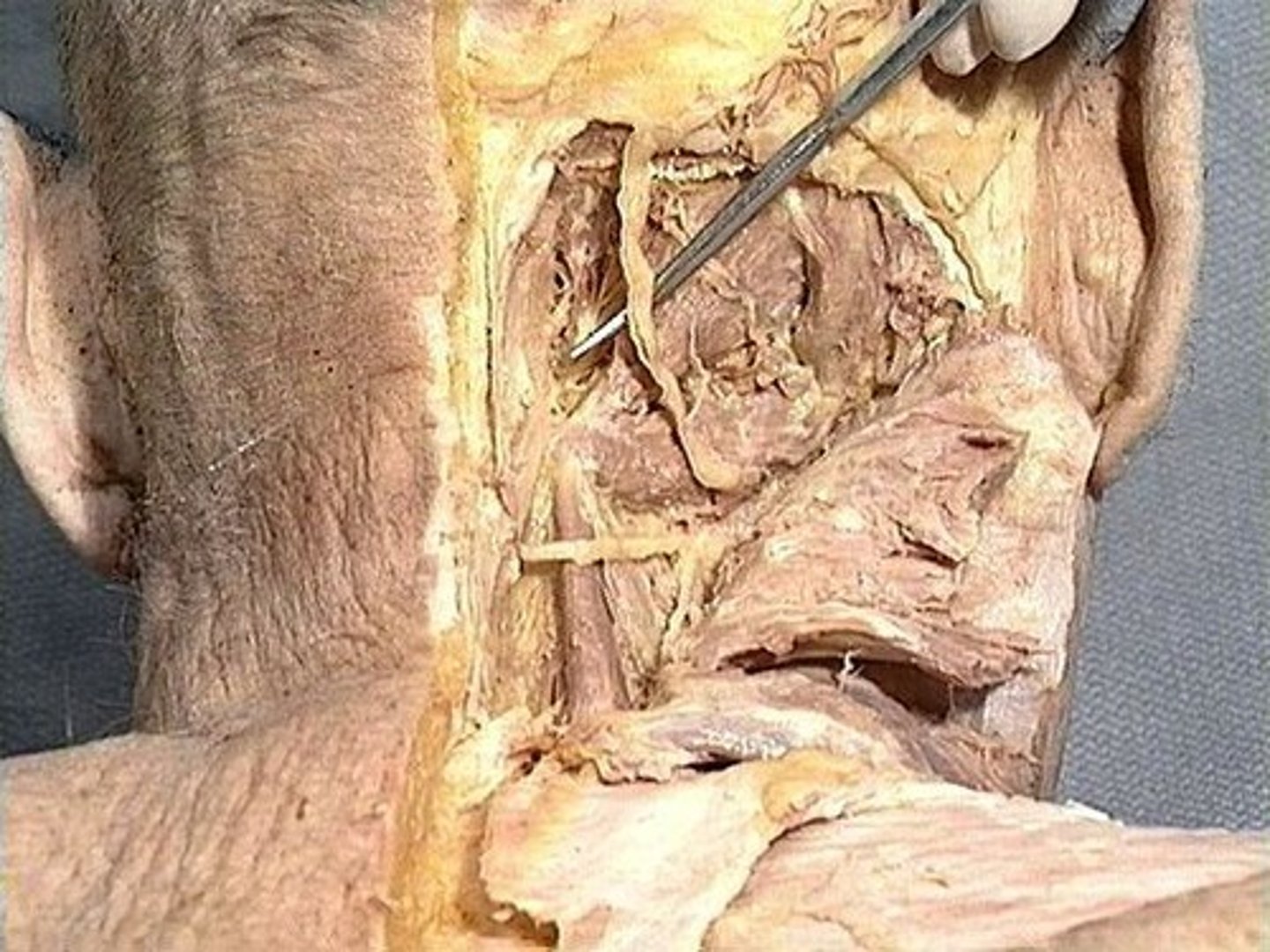
lesser occipital nerve
greater auricular nerve
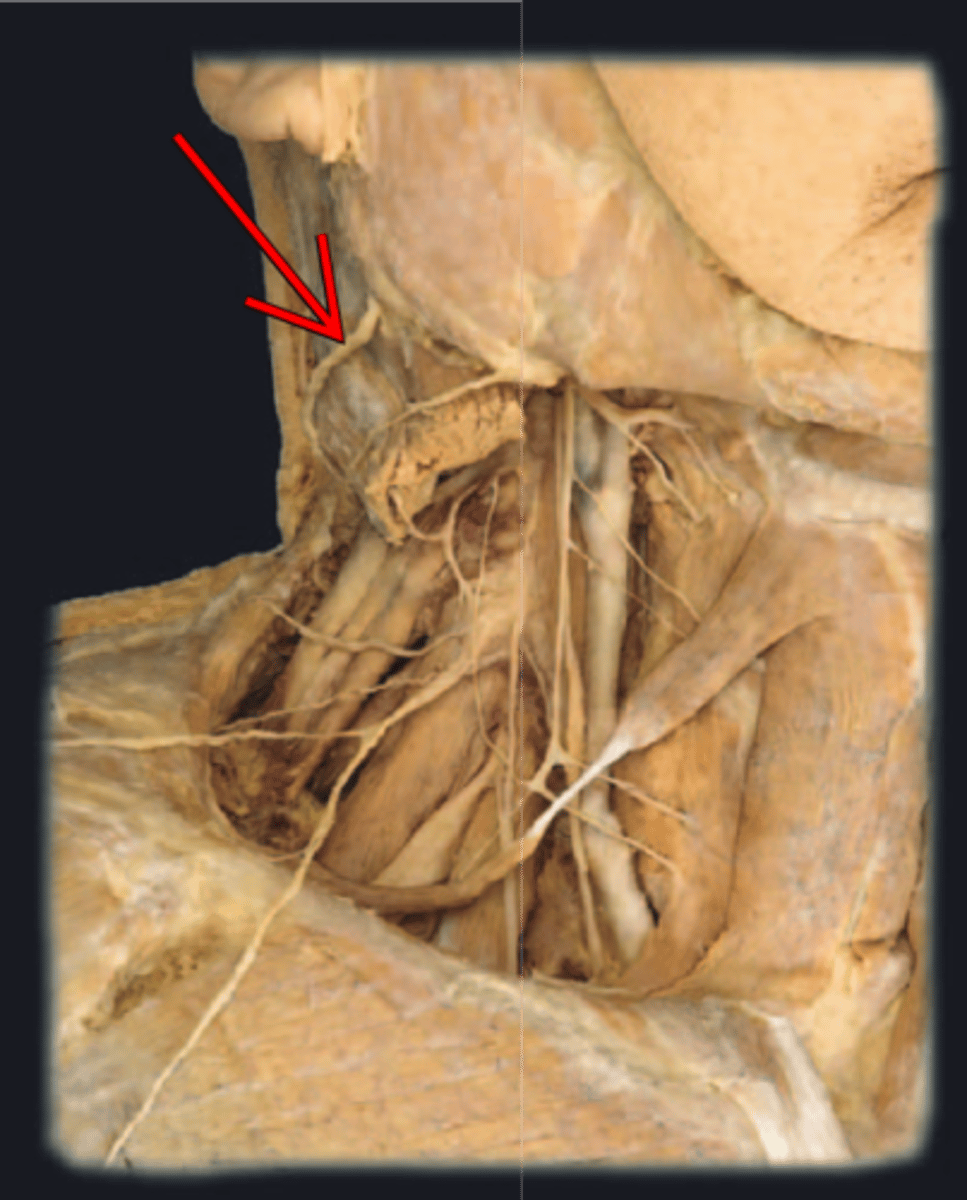
transverse cervical nerve
posterior cutaneous rami of thoracic spinal nerves
lateral cutaneous rami of thoracic spinal nerves
posterior brachial cutaneous nerve
medial brachial cutaneous nerve
lower lateral brachial cutaneous nerve
lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve
iliohypogastric nerve
cluneal nerves
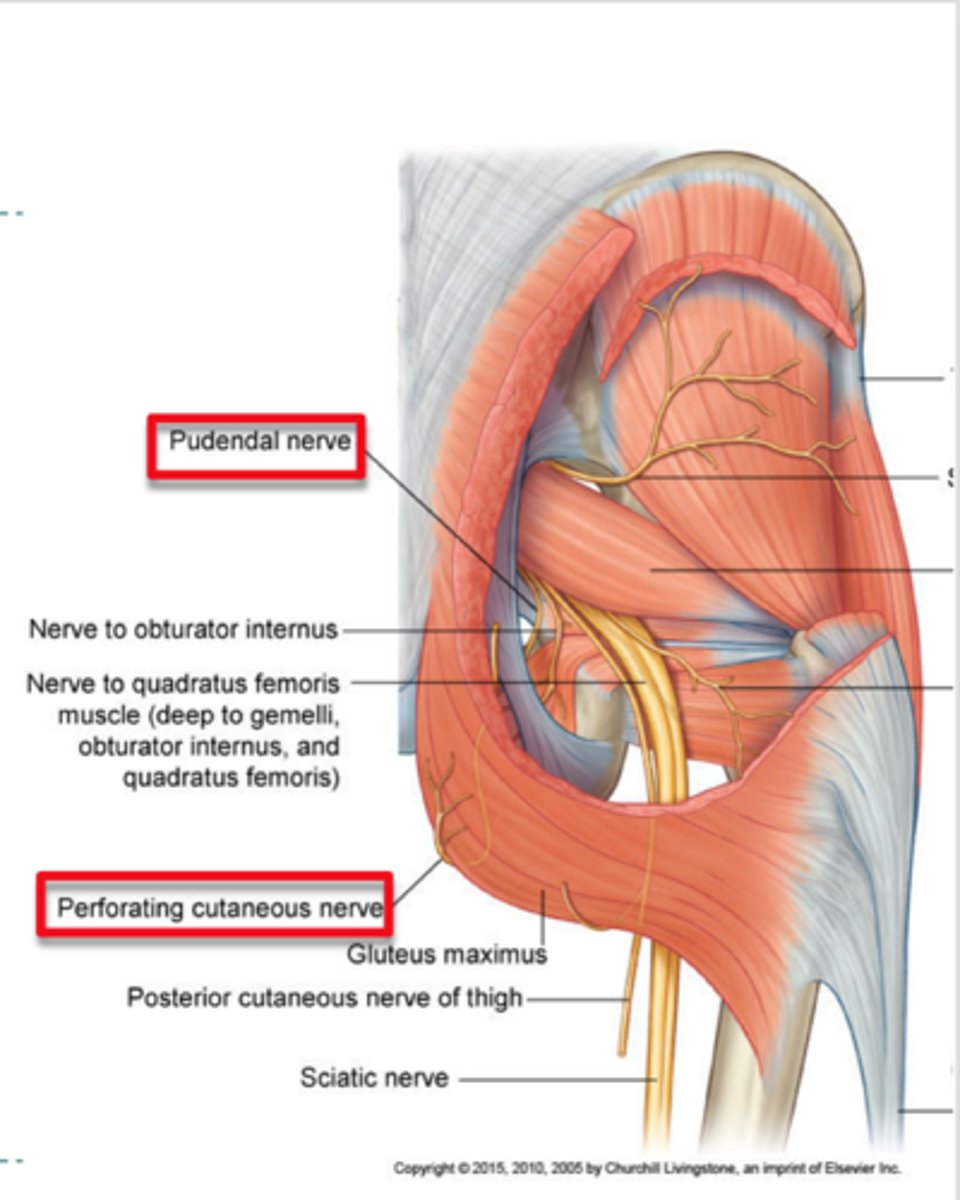
perforating cutaneous nerve

lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
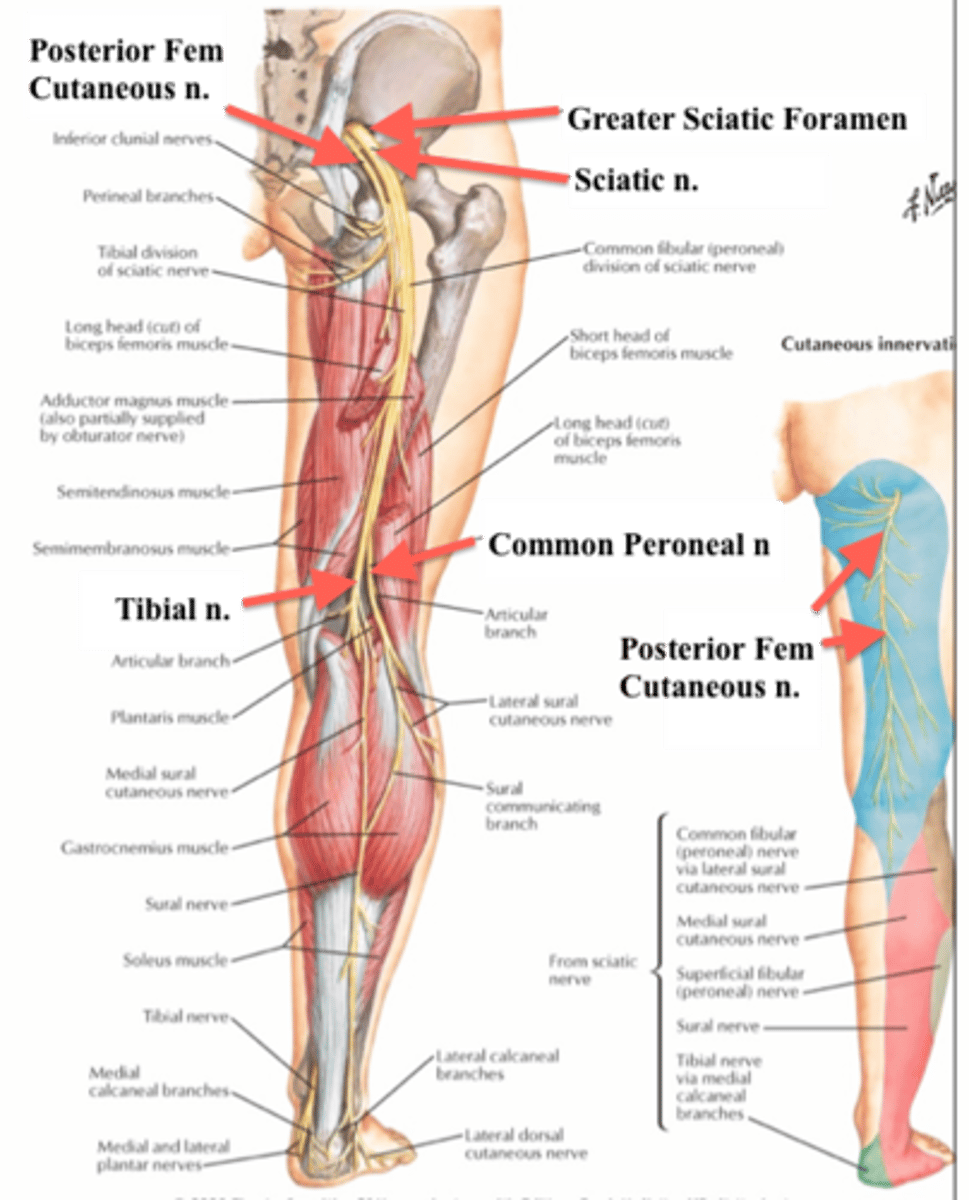
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
lateral sural cutaneous nerve
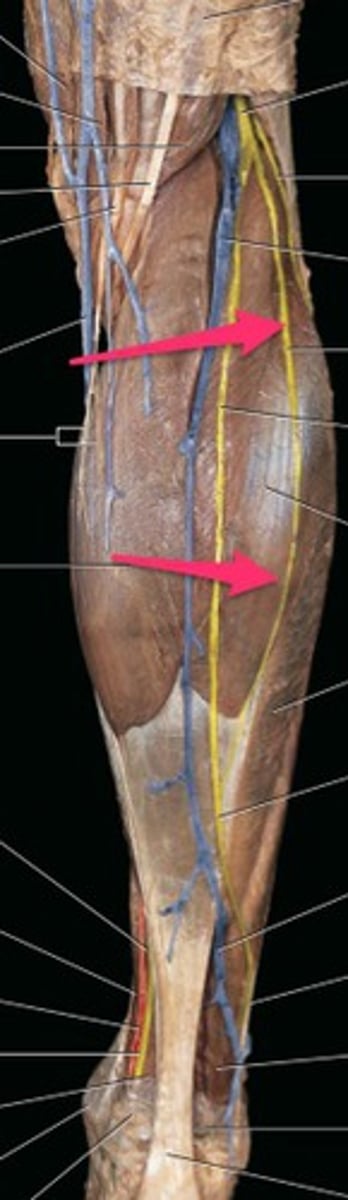
medial sural cutaneous nerve
calcaneal nerve

sural nerve
Nerve of the lower leg that supplies impulses to the skin on the outer side and back of the foot and leg.
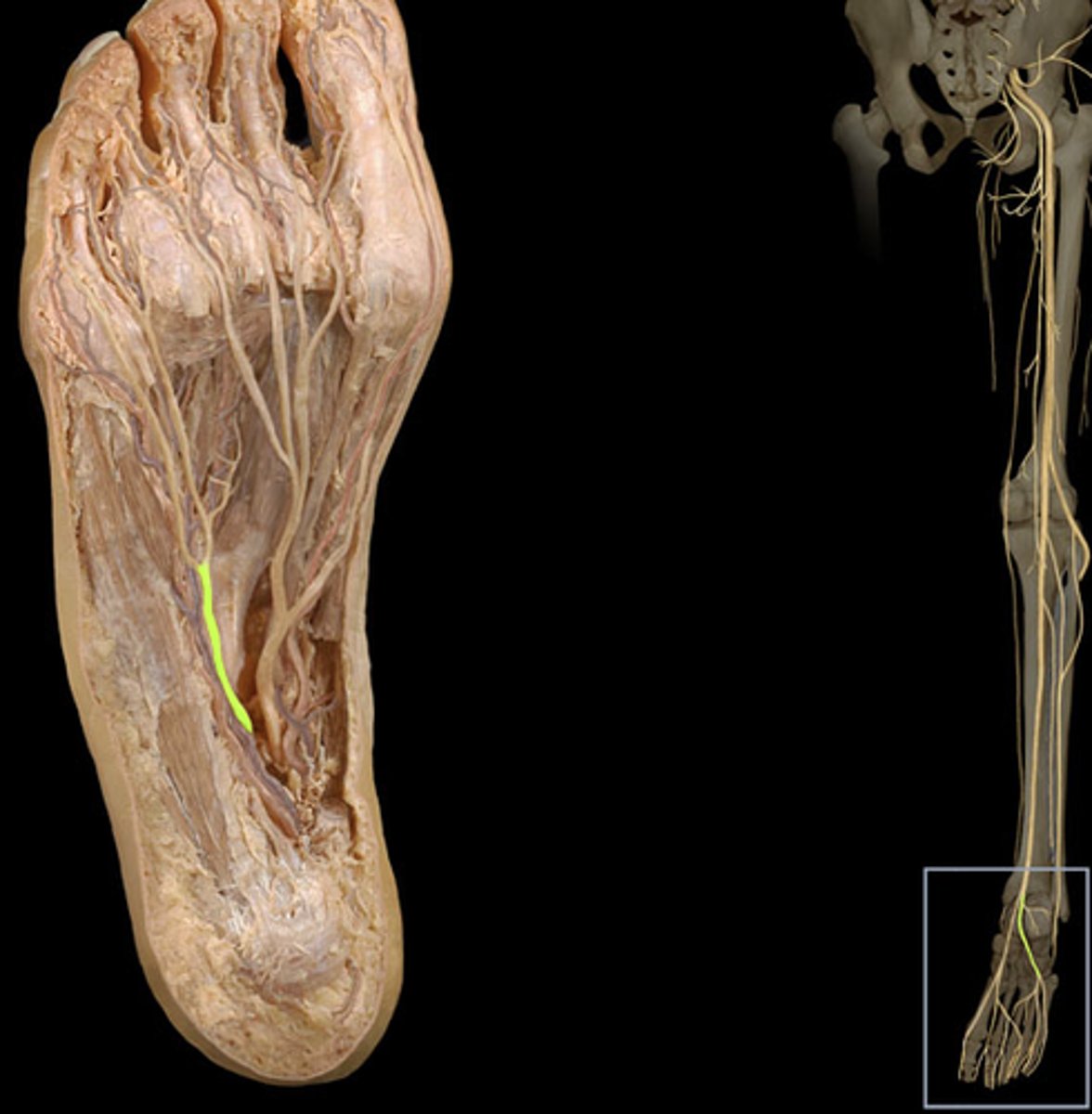
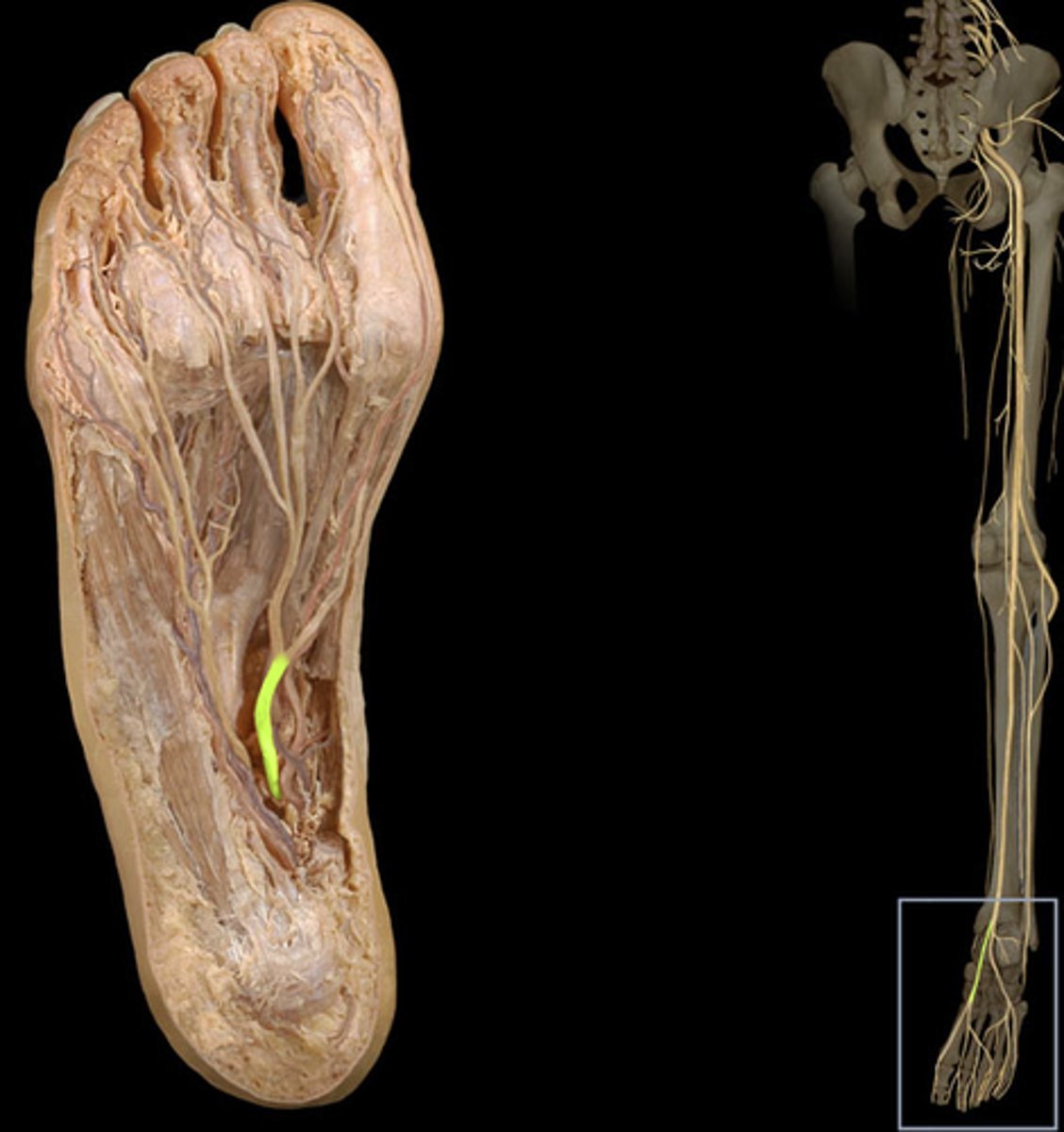
lateral plantar nerve

medial plantar nerve
yes
Are dermatomes more CNS?
peripheral
What kind of injury are cutaneous nerves?
myotomes
a group of muscles receiving innervation from a single spinal cord segment or spinal nerve; the muscle equivalent of dermatome testing
motor neuron pools
-clusters of motor neurons in longitudinal columns
-correlate to muscle spinal level innervation
yes
Are some muscles most associated with 1 spinal level?
C1/2 myotome
cervical flexion
C3 myotome
cervical sidebending
C4 myotome
scapular elevation (shrug)
C5
what myotome is shoulder abduction?
C6 myotome
elbow flexion, wrist extension
C7 myotome
elbow extension, wrist flexion
C8 myotome
thumb extension or finger flexion
T1 myotome
5th finger abduction
L2
what myotome is hip flexion (adduction)?
L3
what myotome is knee extension?
L4 myotome
ankle dorsiflexion
L5 myotome
great toe MTP extension
s1
what myotome is eversion or plantarflexion?
S2 myotome
plantarflexion or knee flexion
action potentials
How do neurons transmit information?
The target of the information
What must be considered regarding neurons?
yes
Do the action potentials for motor commands or sensory info look the same?
true
t/f one nerve is composed of many neurons and one nerve can carry several types of information
autonomic nervous system
-the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
-motor system that innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, organs
sensory (afferent)
What other component does it have?
heart rate, digestion, body temperature, pupillary dilation or constriction, dilation or constriction of arteries/arterioles, salivation and secretion of glands, bowel and bladder function, sexual response
What does the ANS influence?
general somatic afferents (GSA)
-Sensations from skin, skeletal muscle, tendon, and connective tissue
-feeling cold results in contraction of smooth muscle in superficial arteries to conserve body heat
general visceral afferent
what is sensory feedback to the ANS?
cortical inputs from hypothalamus
fight or flight response; arousal
special sensory afferents
seeing and smelling food cooking, resulting in increased salivation