Week 1 Fundamentals of IHC
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the most frequently utilised Ab for IHC?
IgG and IgM
Why are monoclonal Ab immunochemically identical?
They are produced by the same plasma cell
What is the product of combining plasma cells and tumour cells called?
Hybridoma
Compare between mAb and pAb.
mAb:
unique specificity
lower sensitivity
unlimited supply
lower titre
lower batch to batch variability
lower robustness to staining conditions variability
pAb:
lower specificity
higher sensitivity
limited supply
higher titre
higher batch to batch variability
higher robustness to staining conditions variability
What is the most widely used enzyme? Why?
HRP
small size→not hinder the Ab binding
easily obtainable in a highly purified form→min contamination
stable
List the visualization systems from least sensitive to the most sensitive.
direct IHC, indirect IHC, PAP, ABC, LSAB, polymer technology, tyramide
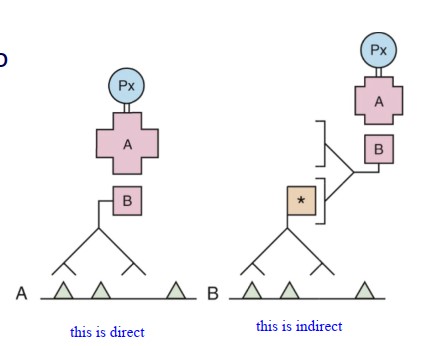
What label is more commonly used in direct IHC?
fluorochrome
When will we use direct IHC?
frozen sections of skin and renal biopsies
What does PAP reagent consist of?
HRP and Ab against HRP
What is the principle behind ABC?
avidin and biotin has high affinity
What is the difference between ABC and LSAB? Why is LSAB better than ABC?
streptavidin replaces avidin
streptavidin has fewer bg staining, more stable, higher sensitivity
What is the advantage of polymer method?
avoid biotin→no need to block endogenous biotin→less false +ve and less errors due to less steps
How to reduce non specific Ab binding?
Preincubation with normal serum that is the same species as the 2nd Ab→proteins within can occupy the charged tissue components
We have to block endogenous peroxidase after 1st Ab application. Why?
H2O2 may damage some epitopes→less signals
What is optimal dilution?
The finest conc that gives the best contrast between specific Ag and non specific bg staining
How do we know the specific Ag is really what it is?
use isotype Ab
add 2nd Ab directly
What is the difference between specific -ve control and non specific -ve control?
specific uses tissues without the Ag and normal Ab to detect Ab cross reactivity to cells
non specific uses pt tissue that doesn’t contain tumour and diluent to replace Ab to detect bg staining
What is the most widely used Ag retrieval method?
HIER
What are some possible problems that IHC can encounter?
wrong Ab selection
false +ve
false -ve
What are some possible reasons for false +ve?
bg staining
endogenous enzymes
too high Ab conc
pigment mistaken for +ve signals
drying artefact
pseudospecific signal
What are some possible reasons for false -ve?
poor fixation
too low Ab conc
incorrect Ag retrieval