Lab 7 – Control of Growth: UV Radiation, Antibiotics, and Conjugation
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering ultraviolet radiation, DNA damage and repair, antibiotic classes, mechanisms, testing methods, and bacterial conjugation concepts from Lab 7 lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
Non-ionizing, short-wavelength (4–400 nm), high-energy radiation used to control microbial growth.
UV-A
The longest-wavelength subdivision of UV light; least damaging to DNA.
UV-B
UV radiation with wavelengths of 280–315 nm; moderately damaging.
UV-C
UV radiation of 100–280 nm; most damaging, especially around 254–260 nm.
Pyrimidine Dimer
Covalent linkage of adjacent thymine or cytosine bases in DNA caused by UV exposure.
Thymine-Thymine Dimer
Most common pyrimidine dimer; kinks DNA and blocks polymerase activity.
SOS Repair System
Bacterial emergency pathway that excises UV-induced dimers and replaces them with new pyrimidines.
Endospore UV Resistance
Protection afforded by acid-soluble proteins and repair enzymes within bacterial spores.
Biofilm UV Protection
Physical shielding provided by multicellular bacterial communities that reduces UV penetration.
Natural Antibiotic
Antimicrobial metabolite produced by bacteria or fungi to inhibit nearby competitors.
Semi-Synthetic Antibiotic
Drug whose core active moiety is natural but whose side chain (R-group) is chemically modified (e.g., ampicillin).
Synthetic Antibiotic
Completely laboratory-made antimicrobial, such as sulfonamides.
Beta-Lactam Moiety
Four-membered ring common to penicillins and related antibiotics; inhibits cell-wall synthesis.
Bactericidal Antibiotic
Drug that kills bacteria outright.
Bacteriostatic Antibiotic
Drug that halts bacterial growth, relying on host immunity to clear infection.
Narrow-Spectrum Antibiotic
Agent effective against a limited group (usually one Gram category) of bacteria.
Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic
Agent effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria; risks disrupting normal microbiota.
Selective Toxicity
Property of targeting microbes without harming host cells; high for penicillin, low for polymyxin B.
Penicillin
First commercial antibiotic; natural beta-lactam that blocks peptidoglycan cross-linking.
Ampicillin
Semi-synthetic penicillin derivative with a broader spectrum than penicillin G.
Sulfonamide
Synthetic antibiotic class that inhibits folic-acid synthesis in bacteria.
Cell-Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
Antibiotics like penicillin that block peptidoglycan formation.
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Agents such as tetracycline that target bacterial ribosomes.
Membrane Disruptors
Antibiotics like polymyxin B that compromise bacterial cell membranes.
DNA/RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Drugs such as ciprofloxacin (DNA gyrase) or rifampicin (RNA polymerase) that stop nucleic-acid replication or transcription.
Kirby-Bauer Method
Standardized disk-diffusion assay on Mueller-Hinton agar for qualitative antibiotic sensitivity testing.
Zone of Inhibition
Clear area around an antibiotic disk where bacterial growth is prevented; measured in millimeters.
E-Test
Strip diffusion method that provides a gradient of antibiotic concentrations to determine MIC quantitatively.
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Lowest antibiotic concentration that visibly inhibits bacterial growth in vitro.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Movement of genetic material between unrelated cells (conjugation, transformation, transduction, transposons).
Conjugation
Direct plasmid transfer from donor to recipient bacterium via a sex pilus, producing recombinants.
Transformation
Uptake of free DNA from the environment by competent bacteria.
Transduction
DNA transfer between bacteria mediated by bacteriophages.
Plasmid
Small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule carrying non-essential genes such as antibiotic resistance.
Sex Pilus
Surface appendage used by donor bacteria to initiate plasmid transfer during conjugation.
Recombinant Cell
Recipient bacterium that has acquired and incorporated foreign genetic material.
Streptomycin Resistance Gene (strᵣ)
Chromosomal determinant in E. coli Strain I that confers streptomycin resistance.
Ampicillin Resistance Gene (ampᵣ)
Plasmid-borne determinant in E. coli Strain II that confers ampicillin resistance.
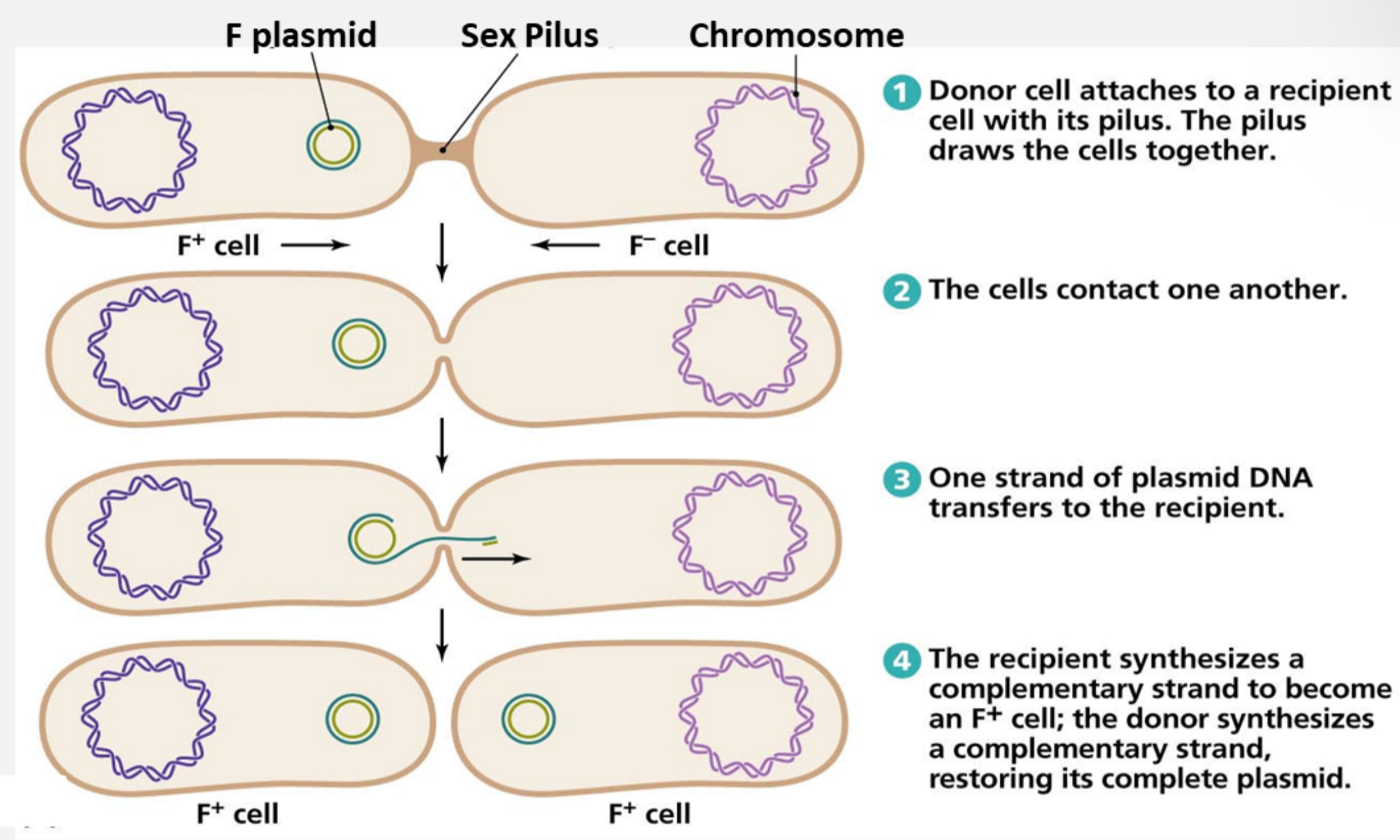
What is the process of this picture shown
bacterial conjugation
This results in a recombinant cell.
•Biofilms bring bacteria closer together making it easier to transfer genes.