PSYC 190 - Autism & Vaccination
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
(VIDEO 3.42) Alternative to spanking
tie children’s behaviors to natural consequences
ex: a child who doesn’t do their homework → doesn’t get to go out
experts suggest that we should use other techniques like positive reinforcement, praising and rewarding kids for positive outcomes
teach the child through repeated examples that when they do something bad they should be encourage to talk
help the kid imagine alternative ways to behave in the future, so they have different ways to respond
(VIDEO 4.42) What is psychological health?
is absence of mental illness as defined by criteria like those laid out in the DSM-5
functioning at or near one’s personal best with an ability to thrive in one’s personal & professional activities
(VIDEO 4.42) Criticism on the DSM-5
scientist have argued that mental disorders exist on a spectrum rather than an all or none kind of thing
have many different causes rather than being clear cut entities
thinking about mental health and disorders on a spectrum acknowledges the variability between patients
(VIDEO 4.43) What is autism?
According to the DSM-5 it has two main components
1. deficit in behaviors related to social communication, such as not effectively reciprocating other’s emotions, problems with non-verbal behaviors during social interaction etc.
2. exhibit movements that are highly repetitive, very restricted or otherwise unusual given the context
now referred to autism as a spectrum disorder (ASD)
Individuals much show symptoms in early childhood, even if those symptoms are not recognized until later
(VIDEO 4.43) Why has attention on Autism increased?
first paper on autism estimated that it affected between 2-4 children in 10,000 (0.4%)
current numbers from the CDC is 1 in 68
after the original estimate in the 1940s, it took another 20 years till autism was included in the international diagnostic systems
(VIDEO 4.43) Hans Asperger
1940s another syndrome was described by a scientist names Hans Asperger
these children exhibited some of the social delays found in autistic children but also had relatively high IQs and were often highly verbal
(VIDEO 4.44) How fast has Autism increased?
CDC estimates that autism prevalence has more than doubled between the years 2000 and 2010
from 1 in 150 to 1 in 68
some have called it the fastest growing developmental disability
(VIDEO 4.44) Study by King and Bearman
found that in California many individuals received a new diagnosis of autism when new versions of the DSM were published
¼ of the change in diagnoses can be explained by this
(VIDEO 4.44) Penn State University Study
team of geneticists at Penn found that as diagnoses of autism rose from the year 2000 to 2012, the rate of other similar diagnoses decreased in equal amounts (like intellectual disability)
about 65% of the increases can be attributed to the change in diagnoses
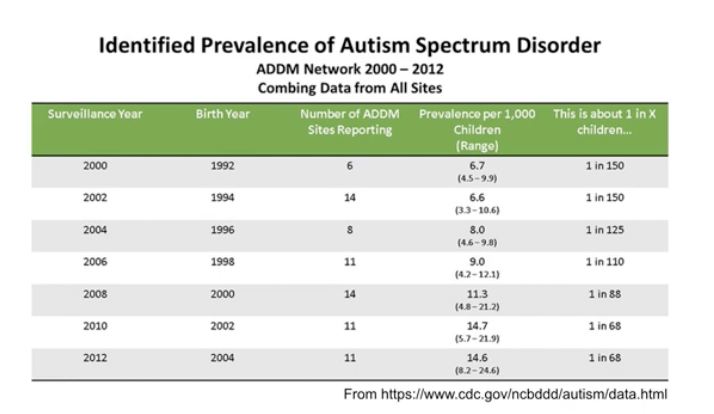
(VIDEO 4.44) Money spending for ASD
California spends between 8-10 billion dollars a year helping educate students with disabilities
some states use ‘census based model of funding’
other states use ‘cost-based model’
(VIDEO 4.44) What is census based funding?
where the state assumes that all schools will have roughly the same percentage of kids with disabilities and therefore distribute funding to schools according to how many total students they have
(VIDEO 4.44) What is cost-based funding?
where they only get funds if their students have established diagnoses
(VIDEO 4.44) How much variability between kids is likely due to genetic variation versus environmental factors?
heritability estimates for autism are quite variable across studies
the plain old concordance rate in autism diagnoses for identical twins is very high → about 60 to 65% and sometimes more
as for heritability → the rate is as high as 90% (this considers twins raised together or apart)
(VIDEO 4.44) Journal of the American Medical Association (study)
researchers found a high concordance between autism in identical twins as high as 77% in male twins
this rate of overlap may have been due to shared environment, specifically the researchers calculated only 37% heritability estimate
concluded that shared environment explained a 55% of variability
(VIDEO 4.45) How long have vaccines been around?
have been around since the late 1700s when they were developed for the small pox (mostly eradicated disease)
as of 2012 → according to the WHO there existed vaccines for 25 different types of infection
(VIDEO 4.45) What is a vaccine?
technically its a dead purified or severely weakened version of a pathogen that’s known to cause a disease
scientists isolate, weaken it or neutralize this pathogen
they grow copies of this version by injecting them into chicken eggs, although alternative methods are being developed
not full-blown strains of the disease you never actually experience the illness
(VIDEO 4.45) What happens when you are vaccinated?
these weakened copies of the disease are entered into the bloodstream
they work by taking advantage of the body’s natural defenses within the immune system
whenever you encounter any kind of germ or pathogen your immune system reacts to counter the disease immune cells called lymphocytes → respond by producing antibodies
(VIDEO 4.45) What are antibodies?
specifically tailored to that particular disease
these antibodies hang around for months or even years and are ready to attack the real live version of the disease if it ever pops up
(VIDEO 4.45) Why are vaccines not fully effective?
each person’s body produces antibodies in different ways with varying degrees of effectiveness
(VIDEO 4.45) Why should you get vaccinated even if they aren’t 100% effective?
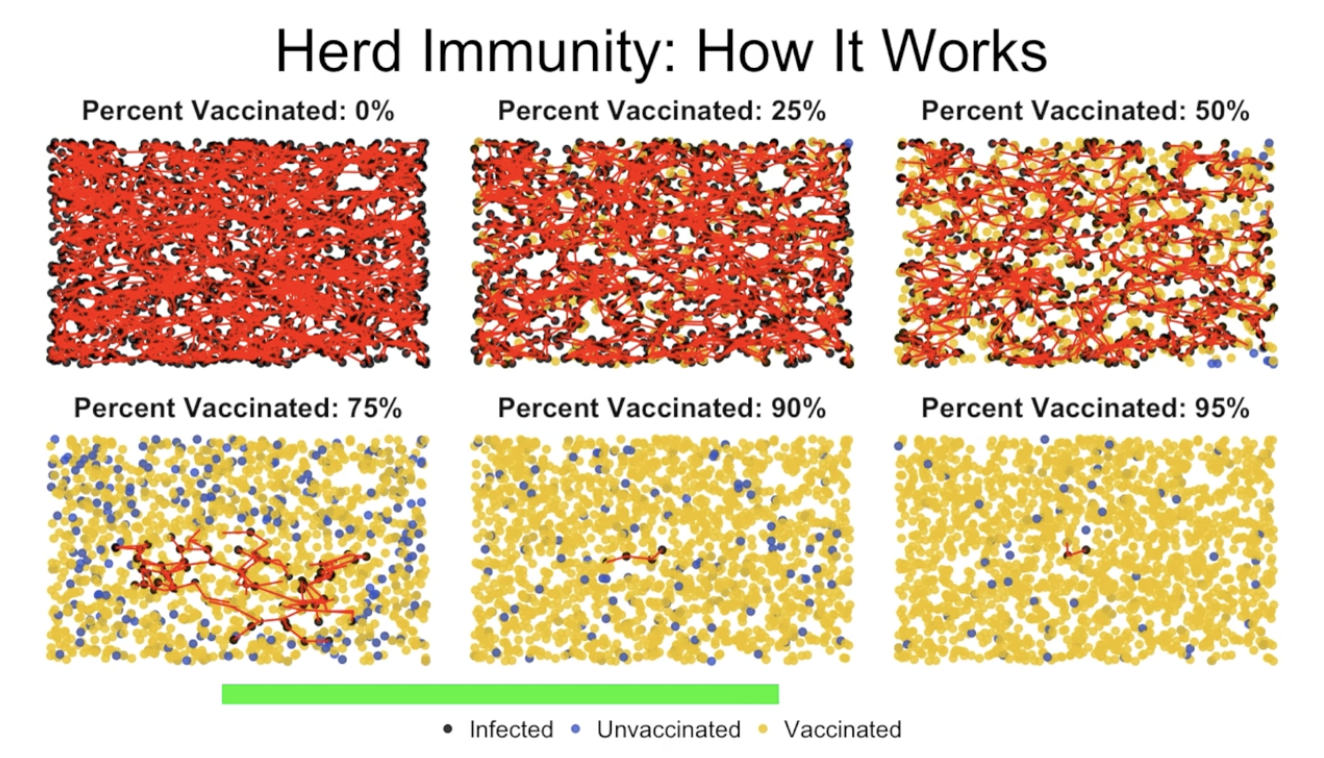
herd immunity
the idea that in a group or herd where not every individual is 100% immune from a disease, its still possible for 100% of people to be protected
(VIDEO 4.45) Herd immunity & Edmund Helmer
(VIDEO 4.45) Measles & the vaccine
1963 before the vaccine was first introduced over 500,000 Americans were infect each year
right now despite a larger US populations we only have 60 deaths per year
most of these are travelers from other countries where vaccination may not be as prevalent
(VIDEO 4.45) Who is least likely to get vaccinated?
federal programs have worked to eliminate differences in access
the least likely to get vaccinated actually come from relatively affluent & educated families
parents intentionally choose not to vaccinate
in some places parents are allowed to refuse vaccination for their child on the basis of ‘personal belief’
(VIDEO 4.46) Polio & Vaccines
a disease causing paralysis in about 1 in 200 cases
as recently as 1988 it affected 350,00 people a year which was reduced to 74 in 2015
(VIDEO 4.46) Why do some parents choose not to vaccinate?
of those who choose not to vaccinate about 50% believe that diseases like measles, mumps, rubella are not serious
50% believe child’s own defenses can fend off infections
they fear that vaccines may do more harm than good
some vaccination is perceived to be contrary to the religious beliefs or their view that individuals should have the right to control what happens to their bodies
deep distrust of the science behind vaccination since some of it is funded by big pharmaceutical companies
these companies have an interest in making money
(VIDEO 4.46) WHO & Measles
350 children/day die from measles
in the last 15 years
dropped 79% in 15 years
20,000,000 deaths have been prevented in the last 15 years
(VIDEO 4.46) Effects of Vaccines
5 to 15% of kids develop a temporary fever after vaccination and about 5% develop a rash
(VIDEO 4.47) Where did the connection between vaccines & autism start?
a scientific report published in a highly respected mainstream journal
1998 → increasing autism diagnoses were entering into public awareness
partly because diagnostic criteria has changed with the publication of the DSM-5
(VIDEO 4.47) Andrew Wakefield & researchers
published a 1998 paper by Wakefield (a gastroenterologist & medical researcher)
in this paper the researchers claim to show evidence for a connection between the combined measles, mumps, rubella vaccine and a new disease that they claim to have discovered called Autistic oculitis (form of bowel disease)
published in the Lancet (one of the world’s most prestigious medical journals)
(VIDEO 4.47) What did Andrew Wakefield claim?
argued that parents should still vaccinate their children & vaccines were safe when given individually
the risk came from the combination
(VIDEO 4.48) Thimerosal (compound)
ingredient of vaccines
commonly used at the time as a preservative
chemically similar to methyl mercury which is a known neurotoxin
(VIDEO 4.48) How did scientist react to Wakefield’s study?
2004 → 10 of Wakefield study’s original authors (not including Wakefield) issued a statement retracting the paper
2010 → the article was retracted by the editorial team of the Lancet
investigation by the British General Media Council (GMC) which revealed four main findings and led to Wakefield losing his medical license
(VIDEO 4.48) Four main findings of the investigation by GMC
1. Wakefield drew blood from typically developing children at his child’s birthday, without ethical approval
2. subjected autistic children to medical tests (colonoscopy & lumbar puncture) without approval
3. failed to disclose a patent for his own vaccine that was meant to compete with the MMR Vaccine
4. treated children with experimental drug without ethical approval
5. failed to disclose a second conflict of interest - > received about $100,000 to act as a consultant to lawyers representing parents of autistic children who believed their problems were caused by vaccinations
(VIDEO 4.48) Studies on MMR & Autism not funded by pharmaceutical companies & other countries
blockbuster study (2005) → Japanese scientists found no reduction of ASD after separation of MMR into single doses after the MMR was discontinued
Denmark 1992 → thimerosal was removed from all vaccines and found that the rates of autism diagnoses did not change instead found the opposite
2017 → University of North Carolina Chapel Hill focused on siblings where one had autism and see if they could predict whether the other siblings would have autism
found that the brains of those with autism were significantly larger than those typically developing
(VIDEO 4.48) Pregnancy & autism
some studies state exposure to certain environments during first trimester as a possibility rather than vaccines