Finance Management
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
1
New cards
When is it comes to things that makes a business successful, what is the most important factor?
Customer satisfaction
2
New cards
Which part of the Value Creation Process does the financial person focus on?
Investment Decisions
3
New cards
Aside from investments, what other decisions does a financial manager make for a corporation?
Accessing financial capital in terms of debt and equity
4
New cards
What is a debt holder?
Someone who invested in the company and still needs to be paid the principle and interest by the company
5
New cards
What are the owners of the corporation?
The focus of the financial manager. These are the people who are the equity owners once the debt holders have been accounted for
6
New cards
Describe the flow in the Value Creation Process that involves financing decisions
Financial Markets (Stockholders and Bondholders) → Corporation
7
New cards
Describe the flow in the Value Creation Process that involves investment decisions
Corporation → Factor Market (Land, Labor, and Physical Capital)
8
New cards
Describe the flow in the Value Creation Process that involves dividends and interest
Corporation → Financial Markets (Stockholders and Bondholders)
9
New cards
Describe the flow in the Value Creation Process that involves profits
Product Market (Customers)
10
New cards
Describe the flow in the Value Creation Process that involves products or services
Factor Market (Land, Labor, and Physical Capital) → Product Market (Customers)
11
New cards
Investment decisions are also sometimes called ______
Operating decisions
12
New cards
What is supposed to be the outcome of making operating decisions?
To increase internal capital (resource allocation), also by acquisitions and divestitures. This in turn should also increase expected cash flows.
13
New cards
What happens alongside the operating decisions?
The financing decisions
14
New cards
What is the outcome of financing decisions?
Focusing on improving capital structure (debt and equity), as well as managing risk and the payout policies. Results in decrease cost of capital.
15
New cards
Which branch in the role of finance involves valuation and monitoring?
Operating decisions and performance evaluation
16
New cards
Which branch in the role of finance involves strategy formulation and implementation?
Financing decisions
17
New cards
What is the number one goal of financial management?
Maximizing shareholder wealth
18
New cards
What are some special qualities about shareholders?
They are residual claimants and the owners of a corporation
19
New cards
What payments need to happen prior to the shareholder receiving money?
* Supplier paid
* Wages to workers paid
* Interest to bondholders paid
* Taxes paid
* Wages to workers paid
* Interest to bondholders paid
* Taxes paid
20
New cards
What are firms constantly interacting with?
Financial Markets
21
New cards
What does IPO stand for?
Initial Public Offering
22
New cards
What is IPO?
It’s when investors in the market give money to the firm, then the firm gives securities to the investors.
23
New cards
If a company is successful, what two things can it generate profits and cashflows through?
Debt and Equity
24
New cards
Cashflows are returned to ____ and debt repayments to ____
Equity holders and debt holders
25
New cards
Aside from paying equity and debts, what third payment happens between firms and financial markets?
Tax payments to the government
26
New cards
Cash flows from the firm must _____ the cash flows from the financial markets
Exceed
27
New cards
What is capital budgeting?
The process of determining exactly which assets to invest in and how much to invest
28
New cards
What are the four steps, in order, of the decision making process for investments?
1. Identification
2. Evaluation
3. Selection
4. Implementation
\
29
New cards
Describe the Identification step in Investment Projects
Finding out opportunities and generating investment proposals
30
New cards
What type of investments fall under the identification step?
* Required
* Replacement
* Expansion
* Diversification
* Replacement
* Expansion
* Diversification
31
New cards
Describe the evaluation step in Investment Projects
Estimating the project’s relevant cash flows and appropriate discount rate
32
New cards
What type of investments fall under the evaluation step?
* Expected cash-flow stream
* Discount rate
* Discount rate
33
New cards
Discount rate is also sometimes known as ____
Cost of capital
34
New cards
Describe the selection step in investment projects
Choosing a decision making rule (accept / reject criteria)
35
New cards
List the types of investments that fall under the selection step
* Net present value
* Profitability index
* Internal rate of return
* Payback period
* Profitability index
* Internal rate of return
* Payback period
36
New cards
Describe the implementation step in investment projects
Establishing an audit and a follow-up procedure
37
New cards
List the types of investments that fall under the implementation step
* Monitor the magnitude and timing of cash flows
* Check if the project still meets the selection criterion
* Decide on a continuation or abandonment
* Review previous steps if failure rate is high
* Check if the project still meets the selection criterion
* Decide on a continuation or abandonment
* Review previous steps if failure rate is high
38
New cards
Money received in the future is _____ than money received today
less
39
New cards
Define opportunity cost
Rate of return sacrificed on the next best alternative
40
New cards
What is the formula for finding the future value FV of an investment of PV dollars today
FV = PV\*(1+r)^t
41
New cards
What is the present value
The amount of money you would need to invest today in order to duplicate some future dollar amount
42
New cards
What excel formula allows you to calculate the number of periods it will take for a future value to be achieved?
NPER
43
New cards
What is the formula for calculating payments of an amount with an interest rate?
PMT
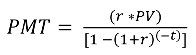
44
New cards
What rule is usually used for forecasting the benefits and costs of an investment project?
Net Present Value (NPV)
45
New cards
What is the formula for Net Present Value (NPV)?
NPV= C0 + C1/(1+r) +…+ Ct/(1+r)^t
46
New cards
What condition needs qualifies a project to be accepted when using NPV?
If NPV > 0, the the project will increase shareholder value and should be accepted
47
New cards
What is an independent project?
Acceptance or rejection is independent of the acceptance or rejection of other projects
48
New cards
What is a mutually exclusive project?
Can accept “A” or you can accept “B” or you can reject both -- you cannot accept both
49
New cards
What is the payback period?
The number of periods required for the sum of the project’s expected cash flows to equal its initial cash outlay
50
New cards
What are some of the consequences of the payback period?
* Penalizes long-term projects
* Difficult to know who decides the period
* Ignores cashflows after the period
* Difficult to know who decides the period
* Ignores cashflows after the period
51
New cards
What is the internal rate of return?
It is the discount rate that makes the net present value of the project equal zero
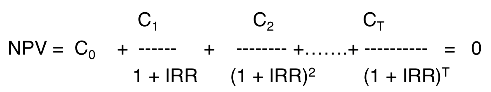
52
New cards
What is the criteria for an acceptable project using the internal rate of return?
The IRR needs to be greater than the cost of capital
53
New cards
What is the profitability index?
It is the present value of an investment’s future cash flows divided by its initial cost
54
New cards
What is another name for the profitability index?
Benefit / cost ratio
55
New cards
How do you calculate the profitability index?
(CF + NPV) / CF
56
New cards
What is the criteria for accepting the profitability index?
PI > 0 means you accept the project
57
New cards
What are some of the issues with IRR?
* Multiple IRRs can exist
* Scale issue
* Timing issue
* Scale issue
* Timing issue
58
New cards
What happens to cause multiple IRRs?
There is more than one change of sign of the cashflows (positive to negative and negative to positive)
59
New cards
What is the crossover rate?
NPVa = NPVb
60
New cards
What two evaluation methods will generally give the same decision?
NPV and IRR
61
New cards
Why would NPV and IRR not produce the same outcomes?
1. Non-conventional cashflows (flow signs change more than once)
2. Mutually exclusive projects
1. Initial investments are substantially different
2. Timing of cash flows is substantially different
62
New cards
What is the most popular capital budgeting method?
IRR and NPV
63
New cards
What is the difference between discounted and undiscounted payback periods?
Undiscounted means that the payments shown already are adjusted to incorporate the time value of money, whereas discounted means you need to make that adjustment
64
New cards
If you want to determine the amount of capital expenditures a company made during the previous year, you should find the company’s most current ____ and look under the caption ________
cash flow statement; cash flow investments
65
New cards
When combining investment IRR, the combined IRR will be _____ the two individual IRRs
between
66
New cards
Conventional cash flows must be ______ for the NPV and IRR methods to be consistent in accept / reject decisions
independent
67
New cards
What are the two principle for recording relevant cash flows:?
1. Record cash flows when the money actually moves
2. Cash flows that are different in both scenarios (accepting or rejecting an investment) are relevant to the decision, and those that are the same are irrelevant
\
68
New cards
Define Sunk Costs
Something you’ve already spent -- not relevant for decision making
69
New cards
Define test marketing costs
These are the marketing research expenses expended
70
New cards
Define erosion costs
Taking away costs from an existing location -- Cash flow transferred to a new project from sales and customer of other products of the firm
71
New cards
Define Opportunity Costs
Lost revenues from alternative uses of the asset
72
New cards
What kind of an expense is depreciation?
Non-cash
73
New cards
How do you calculate the after-tax cash flow (ATCF)?
ATCF = (revenue - costs - depreciation)(1- tax) + depreciation
74
New cards
What is working capital?
Changes in the current assets that are the result of the investment decision -- this is relevant to the decisions
75
New cards
What is working capital considered (directionally) at the start and end of a project?
Start: cash outflows
End: cash inflows
End: cash inflows
76
New cards
What are the three groups to consider when making cash flow estimates?
* Price, volume
* Variable costs
* Fixed costs
* Capital expenditure
* Working capital
* Variable costs
* Fixed costs
* Capital expenditure
* Working capital
77
New cards
What are the factors to consider with Price, Volume?
* Competition from existing products
* Competition from technological advances
* Values to customer
* Competition from technological advances
* Values to customer
78
New cards
What are the factors to consider with variable costs?
Labor, material, energy
79
New cards
What are the factors to consider with fixed costs?
Marketing (sales, advertising), information technology, accounting management
80
New cards
What are the factors to consider with capital expenditure?
Property, plant and equipment
81
New cards
What are the factors to consider with working capital?
Inventory, accounts payable, accounts receivable
82
New cards
What does the operating margin consist of?
Revenues (price, volume) and costs (variable and fixed)
83
New cards
What does the operating cash flow consist of?
The operating margin and taxes
84
New cards
What does the capital requirement consist of?
Capital expenditure, working capital (accounts receivable/payable, inventory)
85
New cards
What does the free cash flow consist of?
Operating cash flow and capital requirement
86
New cards
What does the cost of capital consist of?
Cost of debt and cost of equity
87
New cards
What does the net present value (NPV) consist of?
Free cash flow and cost of capital
88
New cards
The goal of the company is to ______ free cash flow and _______ cost of capital
maximize; minimize
89
New cards
What is a nominal return?
The percentage change in the amount of money you have
90
New cards
What is the real return?
The percentage change in the amount of stuff you actually buy
91
New cards
What is the Fisher Effect?
1 + Nominal = (1+Real) \* (1+Inflation)
92
New cards
Describe the two methods you can use to account inflation and estimation of cashflows
1. Express cash flows in real terms and discount them at the real interest rate
2. Convert real cash flows to nominal cash flows by allowing them to grow at rate of inflation and discount them at the nominal rate
\
93
New cards
Cost of capital is expressed in ______ terms
Nominal
94
New cards
Depreciation is expressed in ______ terms
Nominal
95
New cards
When is it important to account for inflation/
When dealing with long horizons and high inflationary times
96
New cards
How can you do sensitivity analysis?
Ask what if questions:
* Target Market Share
* Cost overrun
* Inflation
* Competition
* Discount rate
* Valuable options
\
\
* Target Market Share
* Cost overrun
* Inflation
* Competition
* Discount rate
* Valuable options
\
\
97
New cards
What are the steps?
1. Identify each key variable and the probability distribution associated with it
1. Base case
2. Revenues
3. Growth
4. Operating Margin
5. Working Capital
2. Draw one outcome for each variable
3. Estimate PV and IRR
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 many times (\~5000)
5. Use the distribution of NPV to answer the following questions:
1. What is the likelihood that this will be a bad project?
2. What is the worst case and best case scenarios?
3. Can you try to build linkages in the simulations?
98
New cards
What is the most preferred technique for capital investment analysis?
Net Present Value (NPV)
99
New cards
Capital budgeting must be done on an _____ basis
Incremental
100
New cards
In regards to capital budgeting, what costs are ignored and what costs are considered?
Sunk costs are ignored; opportunity costs and side effects are considered