Psychology 202 Exam 1: UW Madison - Addington
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
243 Terms
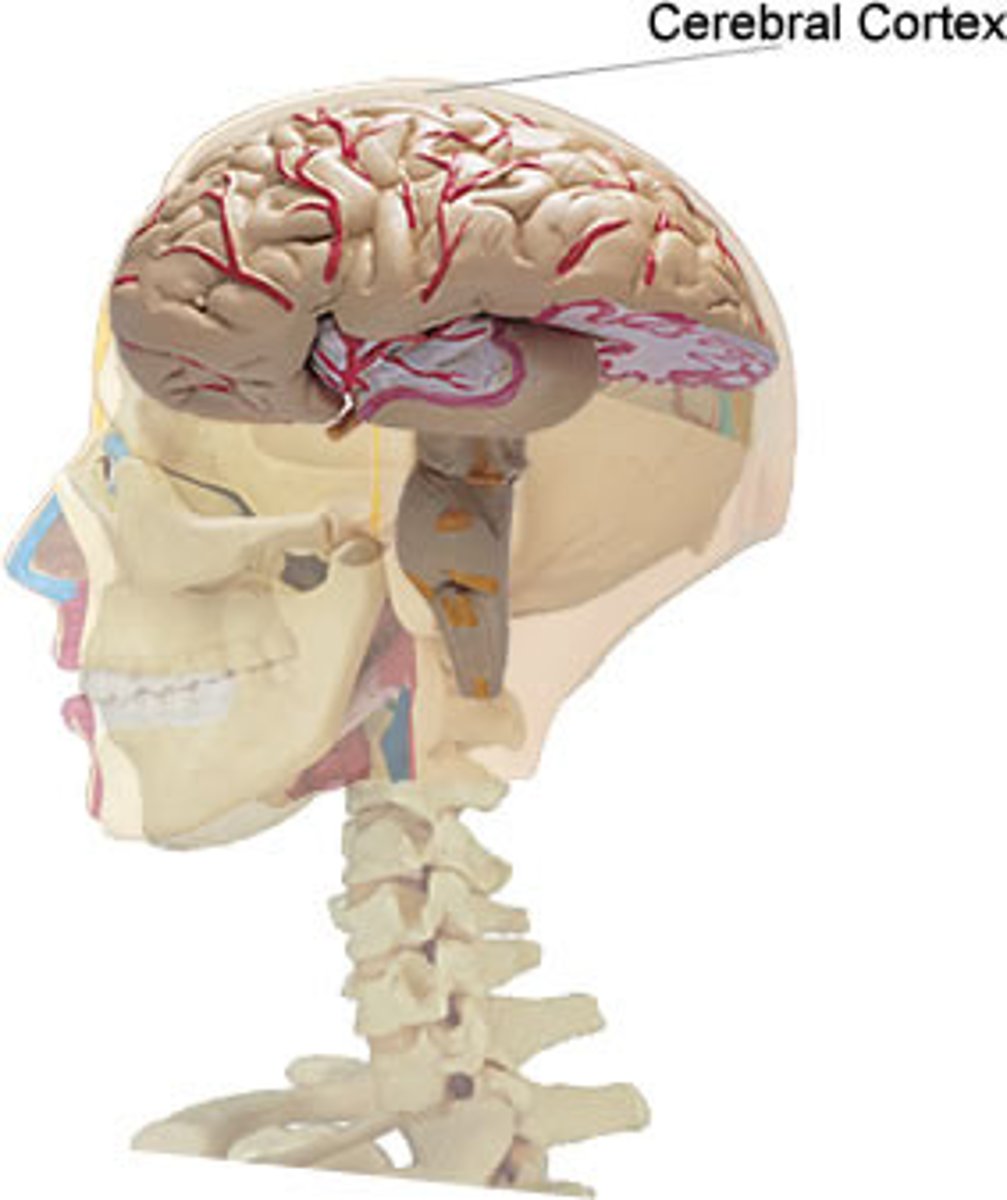
Cerebral cortex
-The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
-thought & planning
-contains the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobe
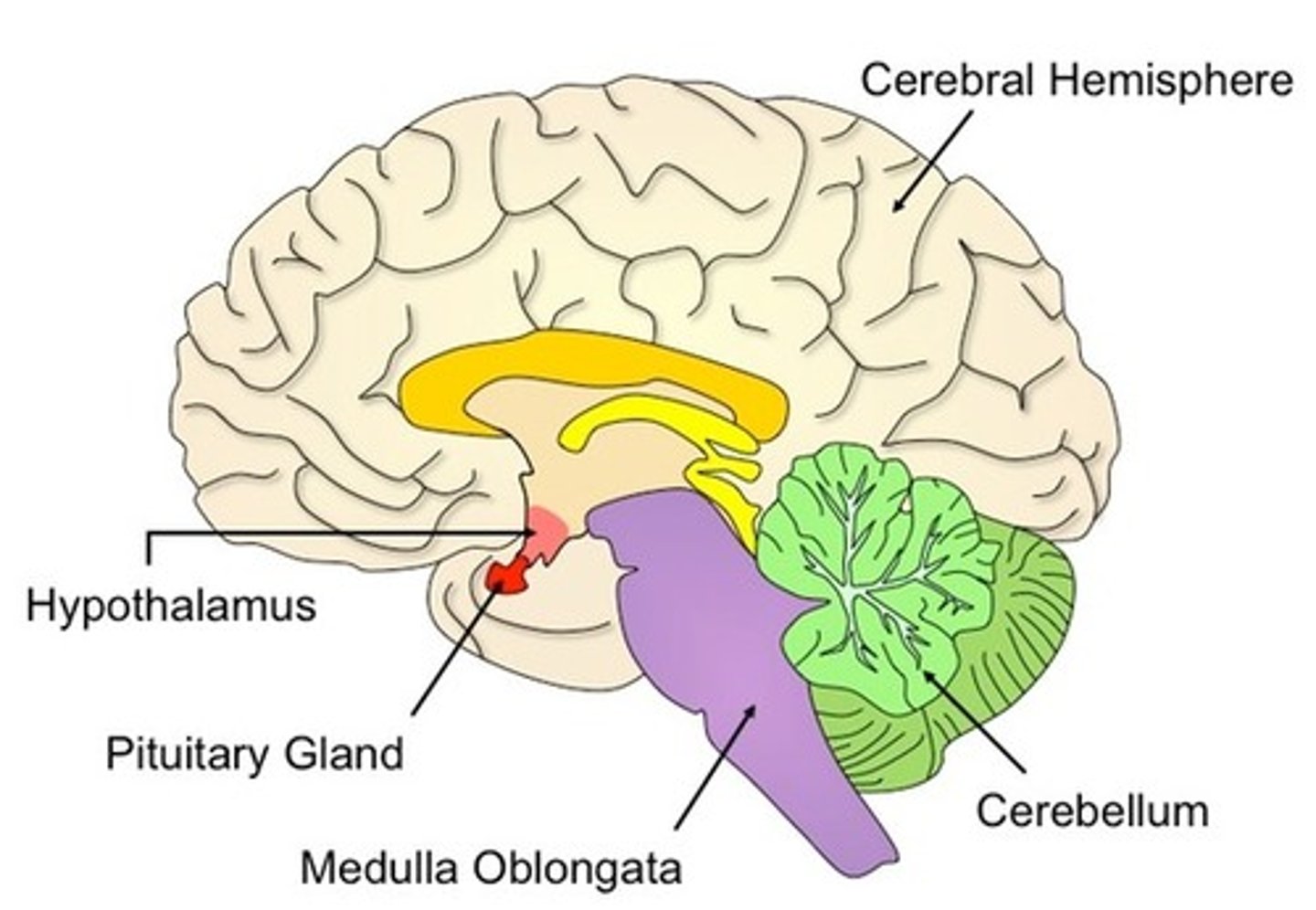
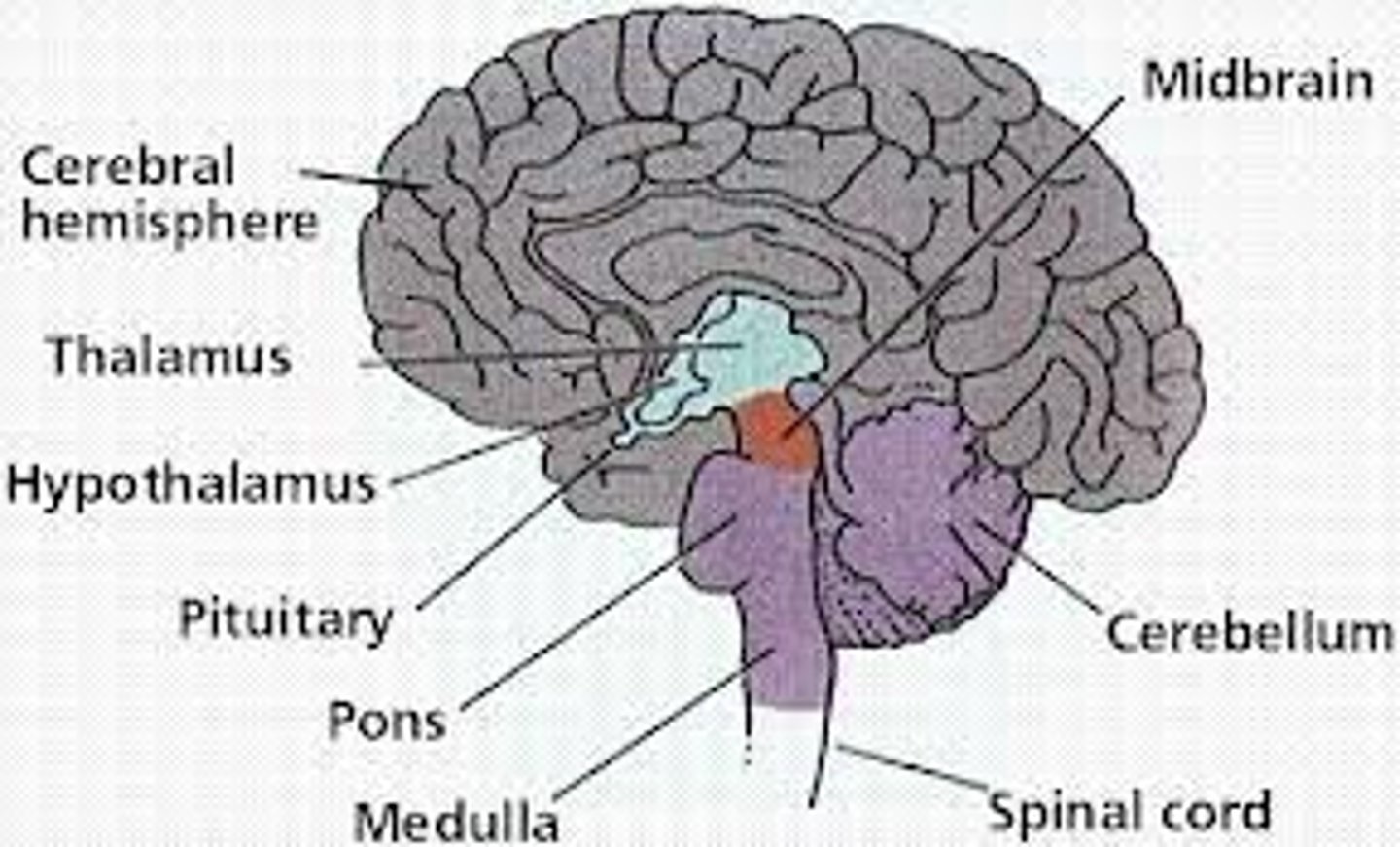
Hypothalamus
-A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature)
-Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland
-Linked to emotion and reward.
-Part of the limbic system
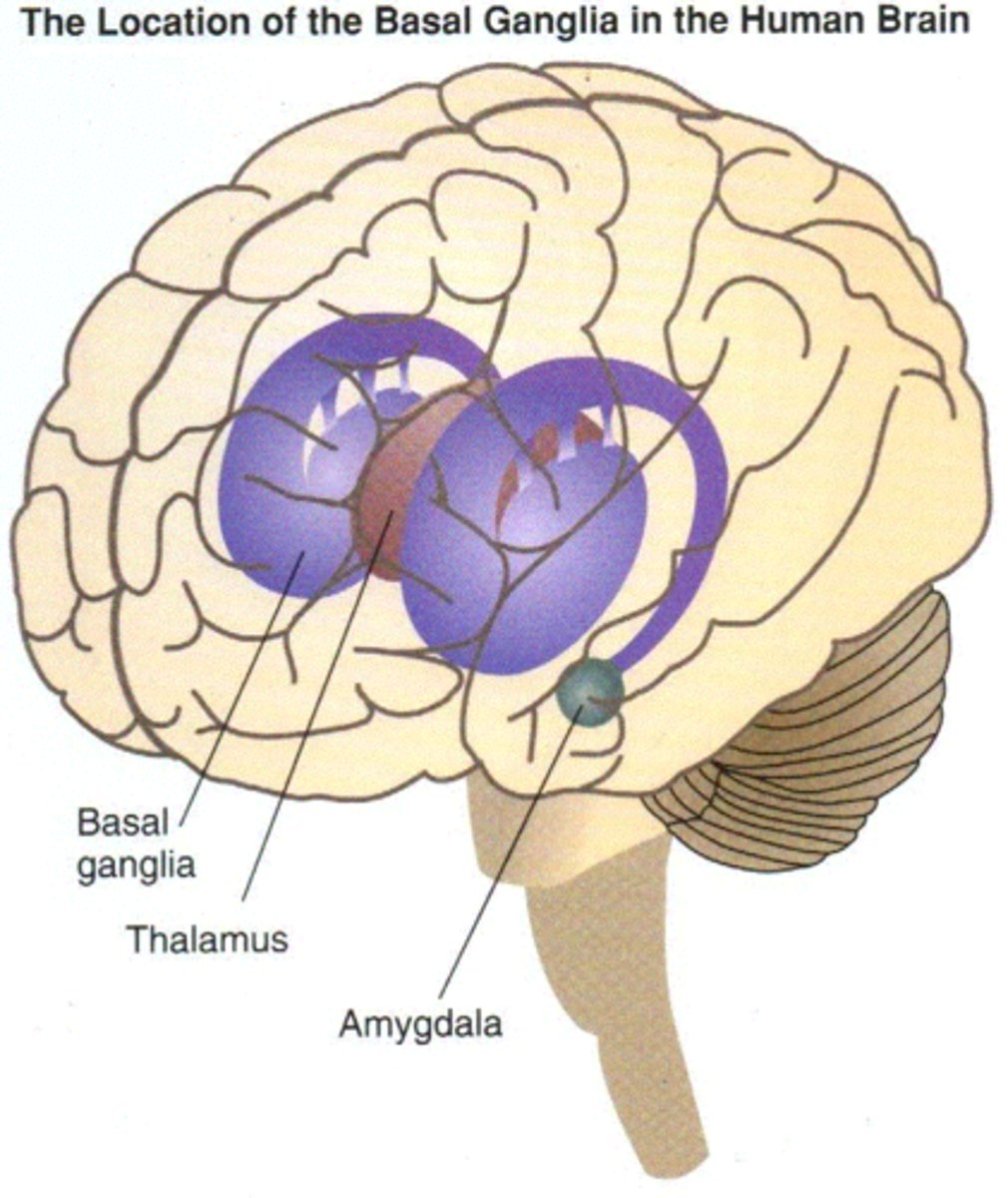
Amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotion
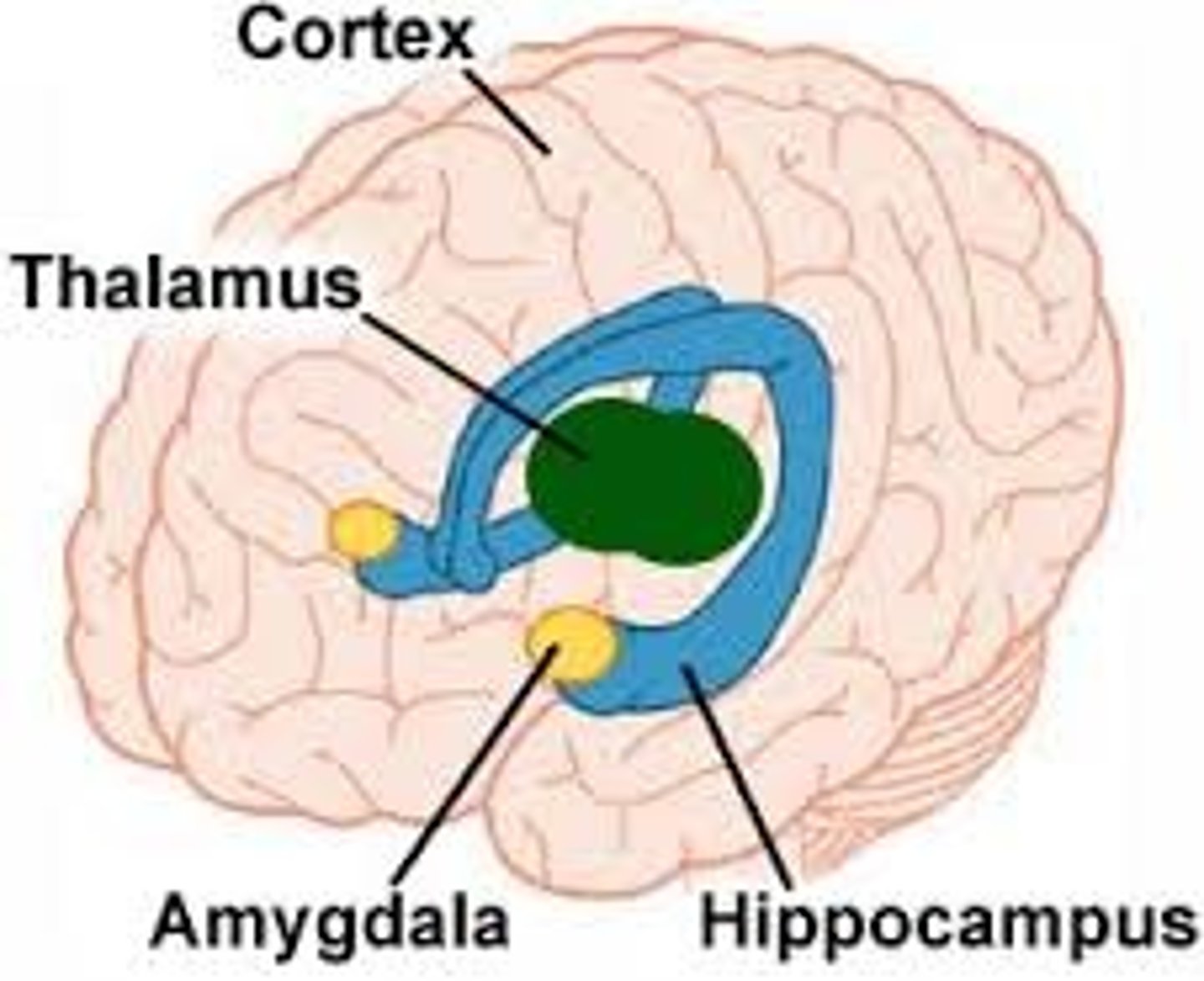
Hippocampus
-A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage
-Easy way to recall: If you see a hippo walking into class you will surely remember that memory for awhile
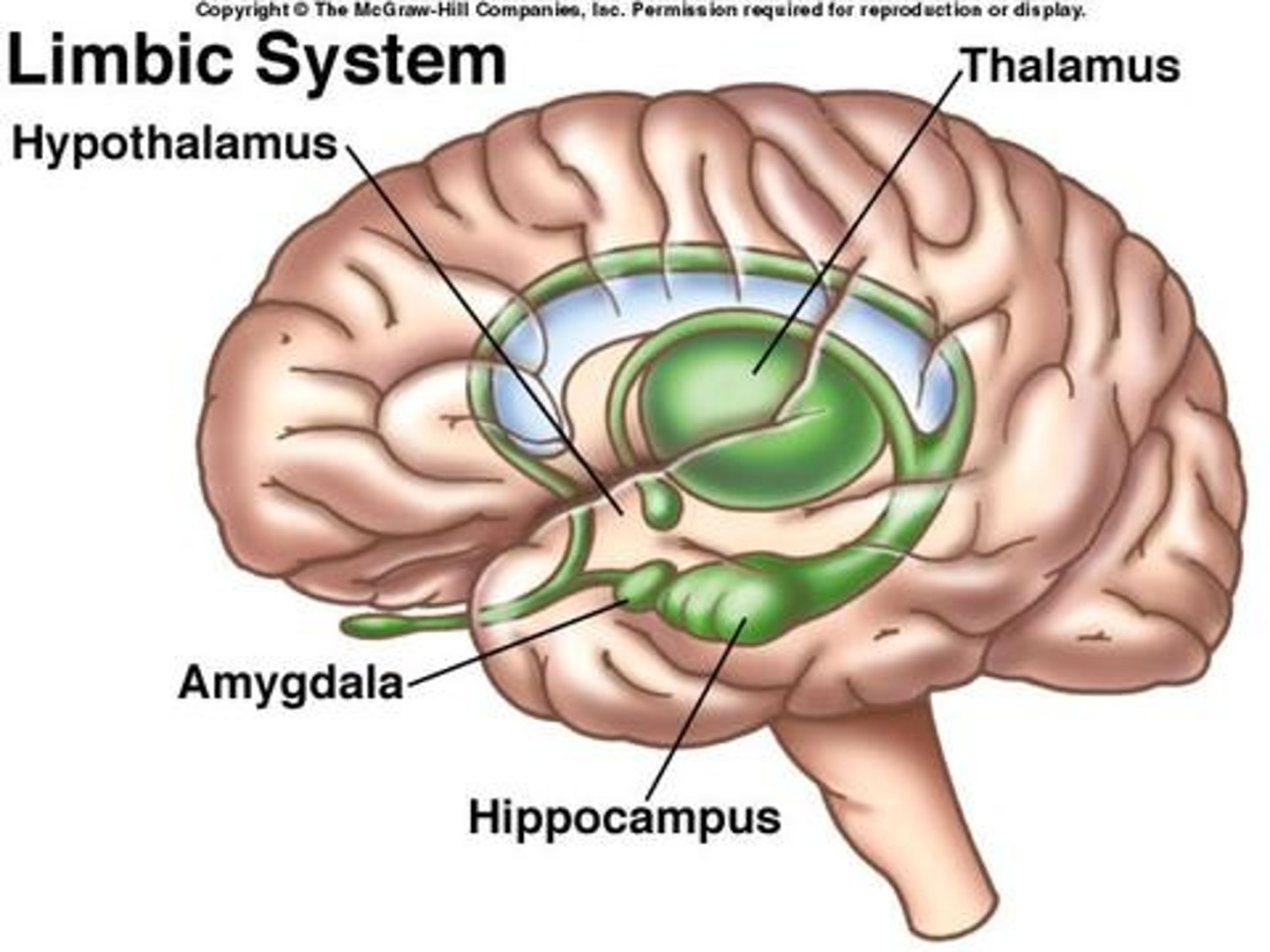
Thalamus
-the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem
-directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
-part of the limbic system
-essentially the gateway to the cortext
Basal ganglia
-a set of subcortical structures that directs intentional movements
-part of the limbic system
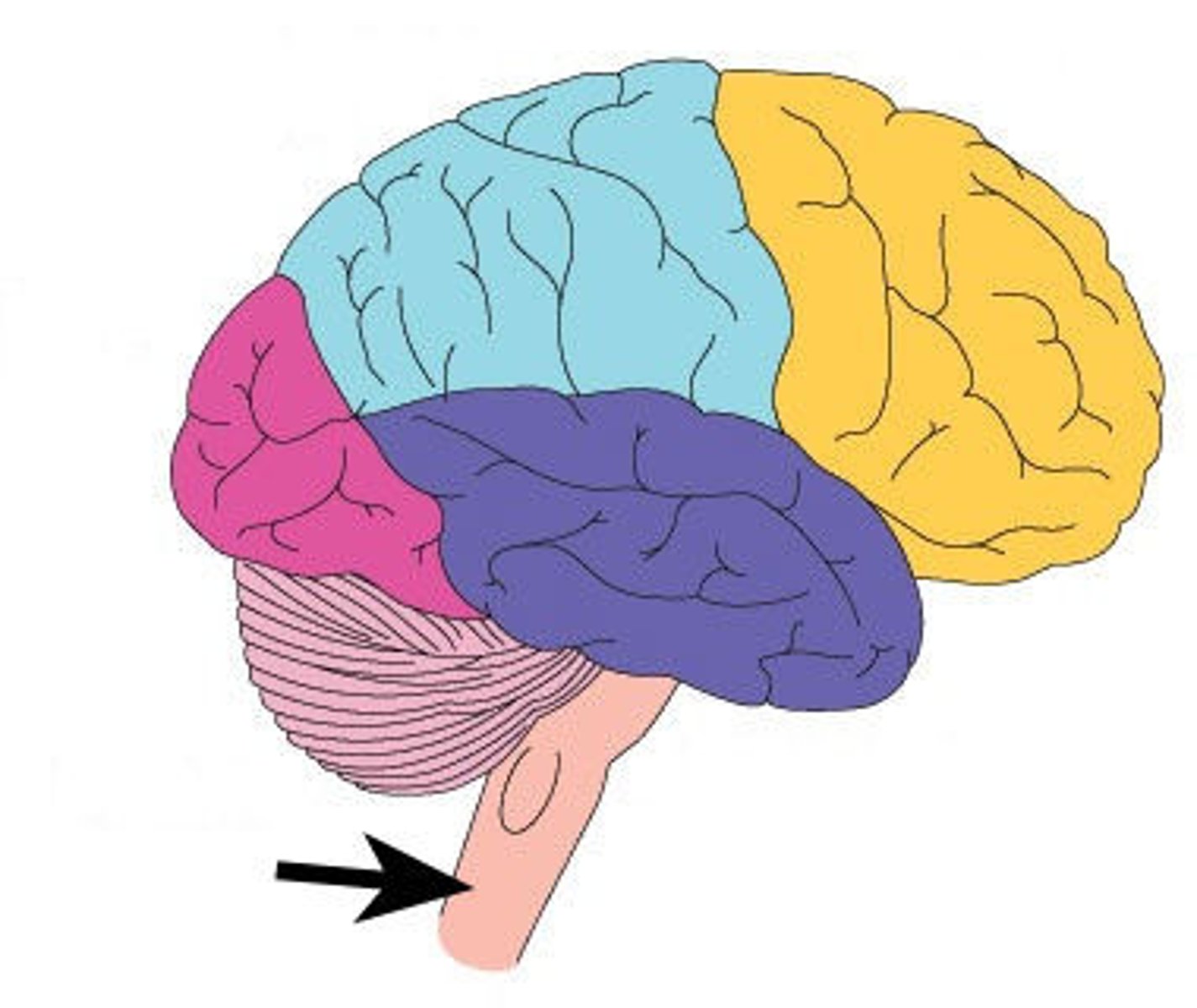
Brain stem
-Connection to spinal cord
-Filters information flow between peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain.
Limbic system
A doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres
-associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex
-Includes the hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, thalamus, pituitary gland, and basal ganglia
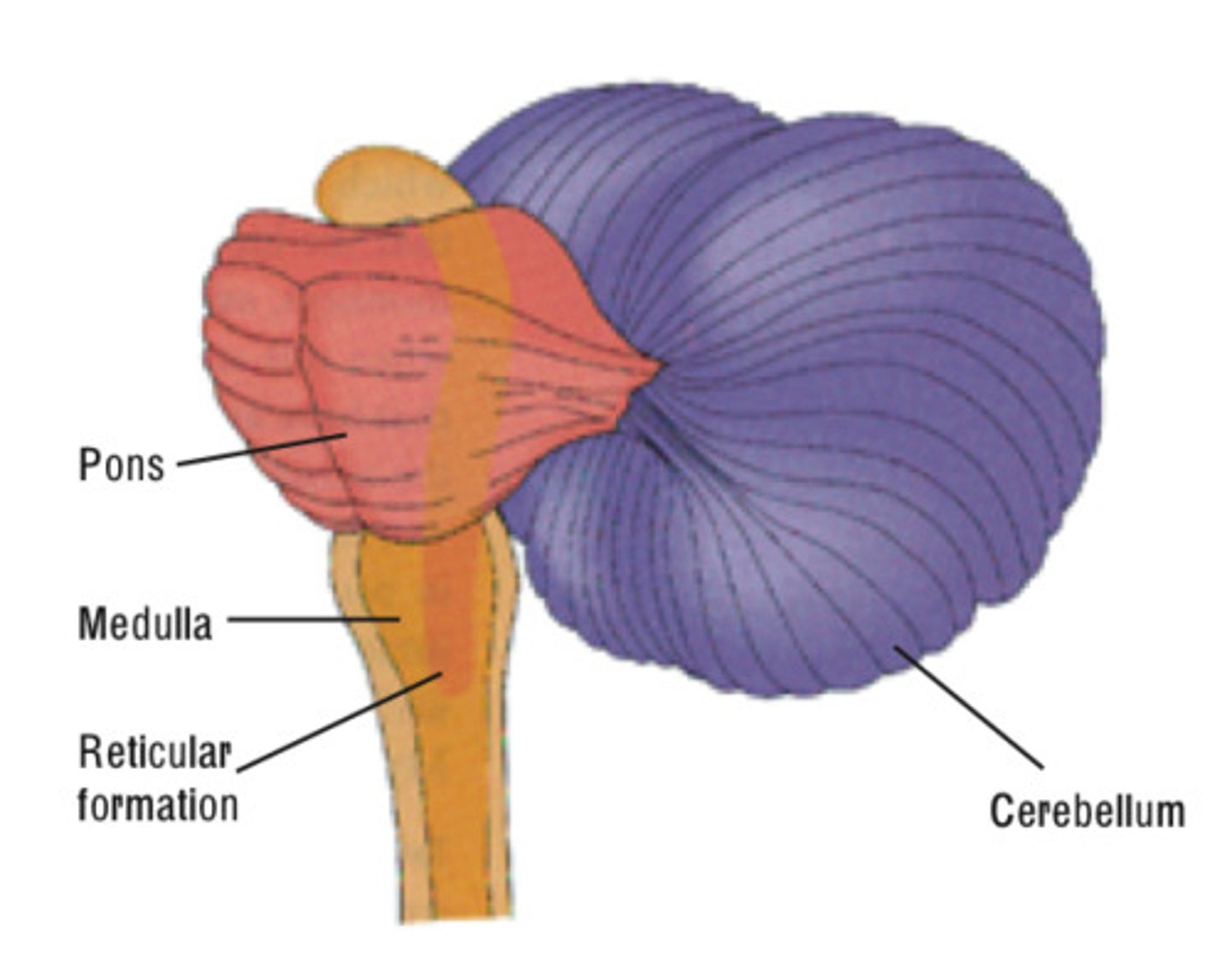
Pons
-A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
-sleep, arousal, facial expressions
-connects the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
Meta-analysis
-a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
-larger view of replication
-example: math ability & gender
Occlusion
-helps you detect depth
-whether or not objects are in front, behind, or obscuring other objects
D2 receptors
-The dopamine receptors that the original antipsychotics bound to
-regulate self-control in frontal lobe
-Important point: might harm the individual's ability to make a good decision, perhaps to steal money from a parent to be able to afford a drug again
3 types of neurons
sensory, motor, interneurons
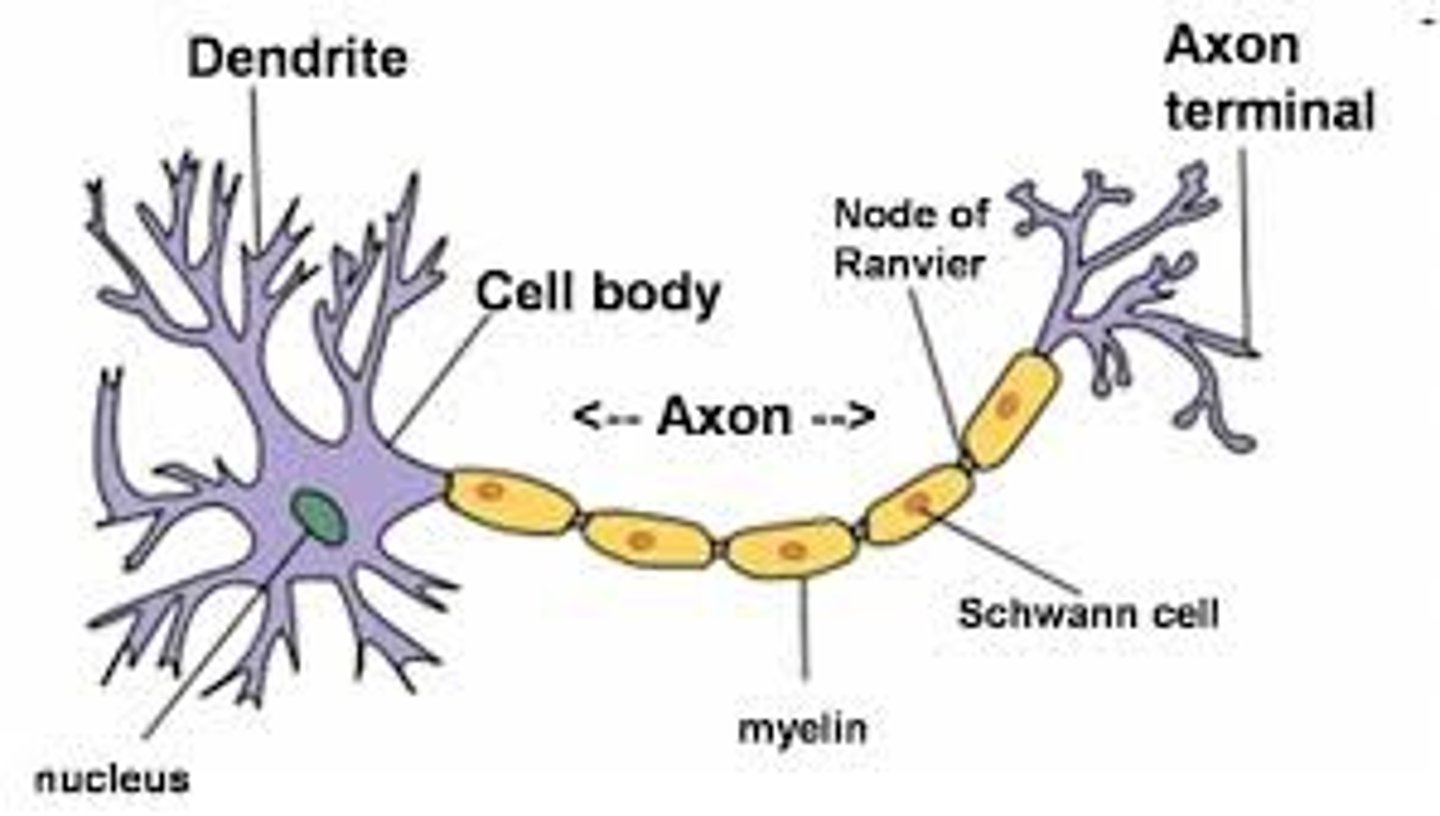
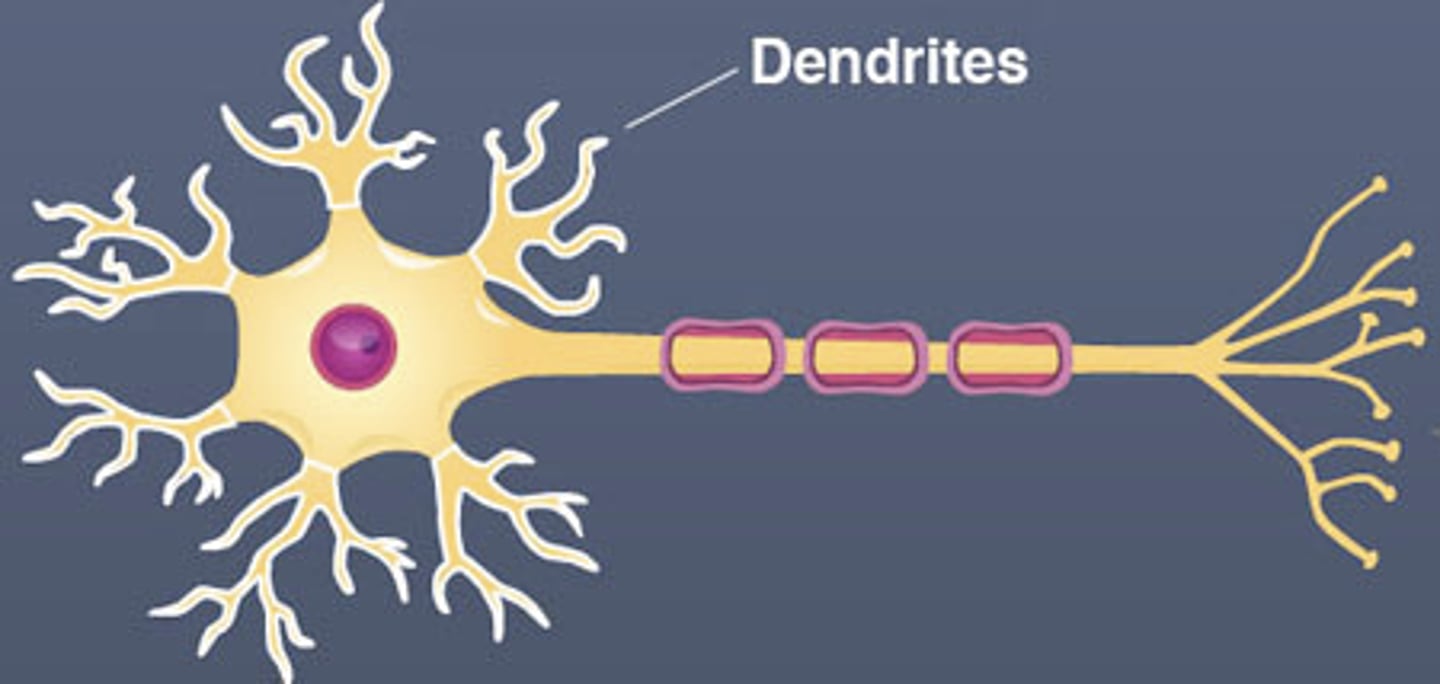
Myelin sheath
-A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons (insulation)
-enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next
Sensory neurons
-neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
-afferent
-incoming information to the CNS
Motor neurons
-neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
-efferent
-outgoing information from CNS to muscles
Interneurons
-Central nervous system neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
-Essentially connect sensory, motor, and other neurons
Main components of a Neuron
-Cell body
-Dendrites
-Axon
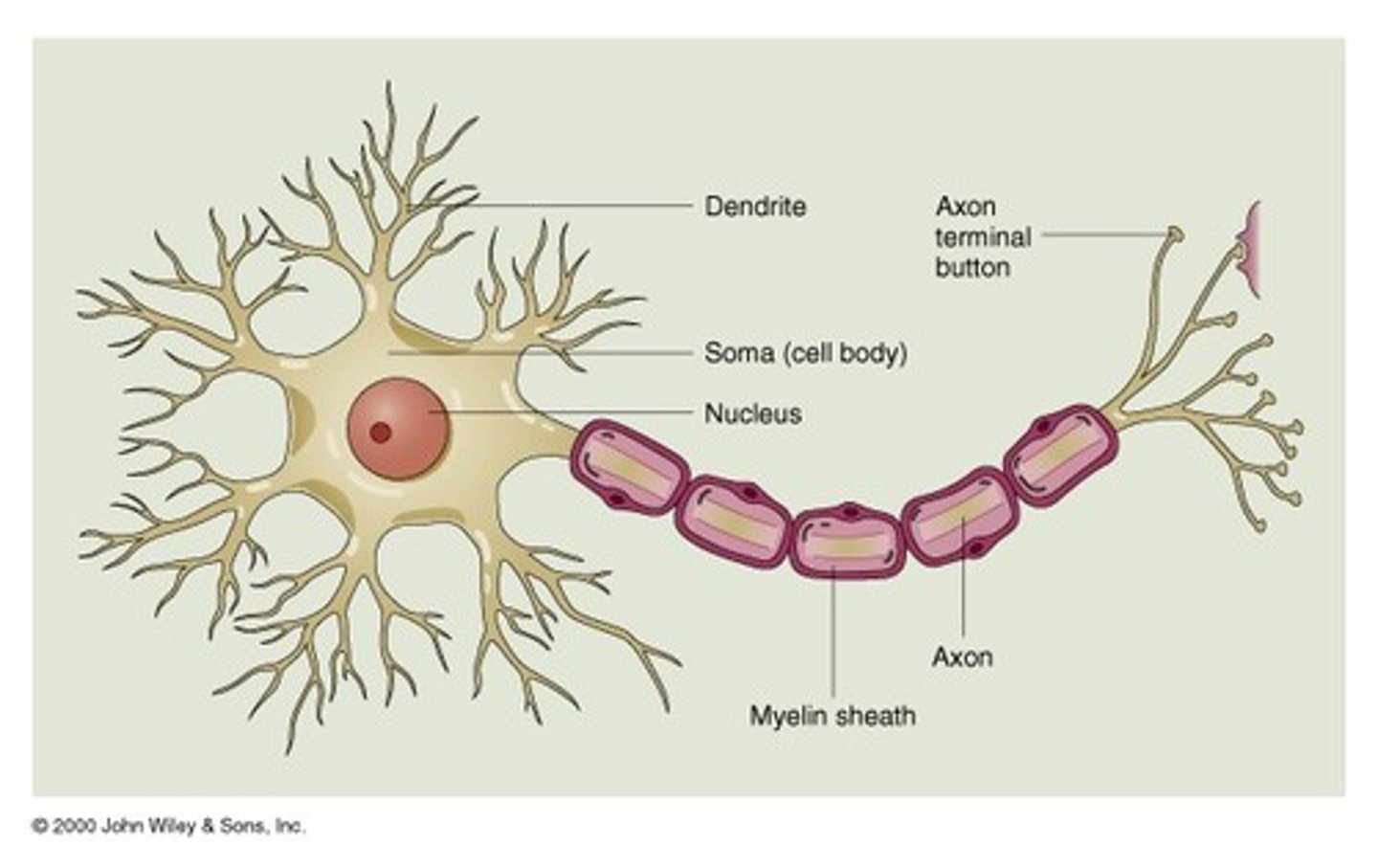
Cell body
-Largest part of a typical neuron
-contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
-integrates information
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information
Axon
-messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
-transmits information
-contains axon terminal and synapse
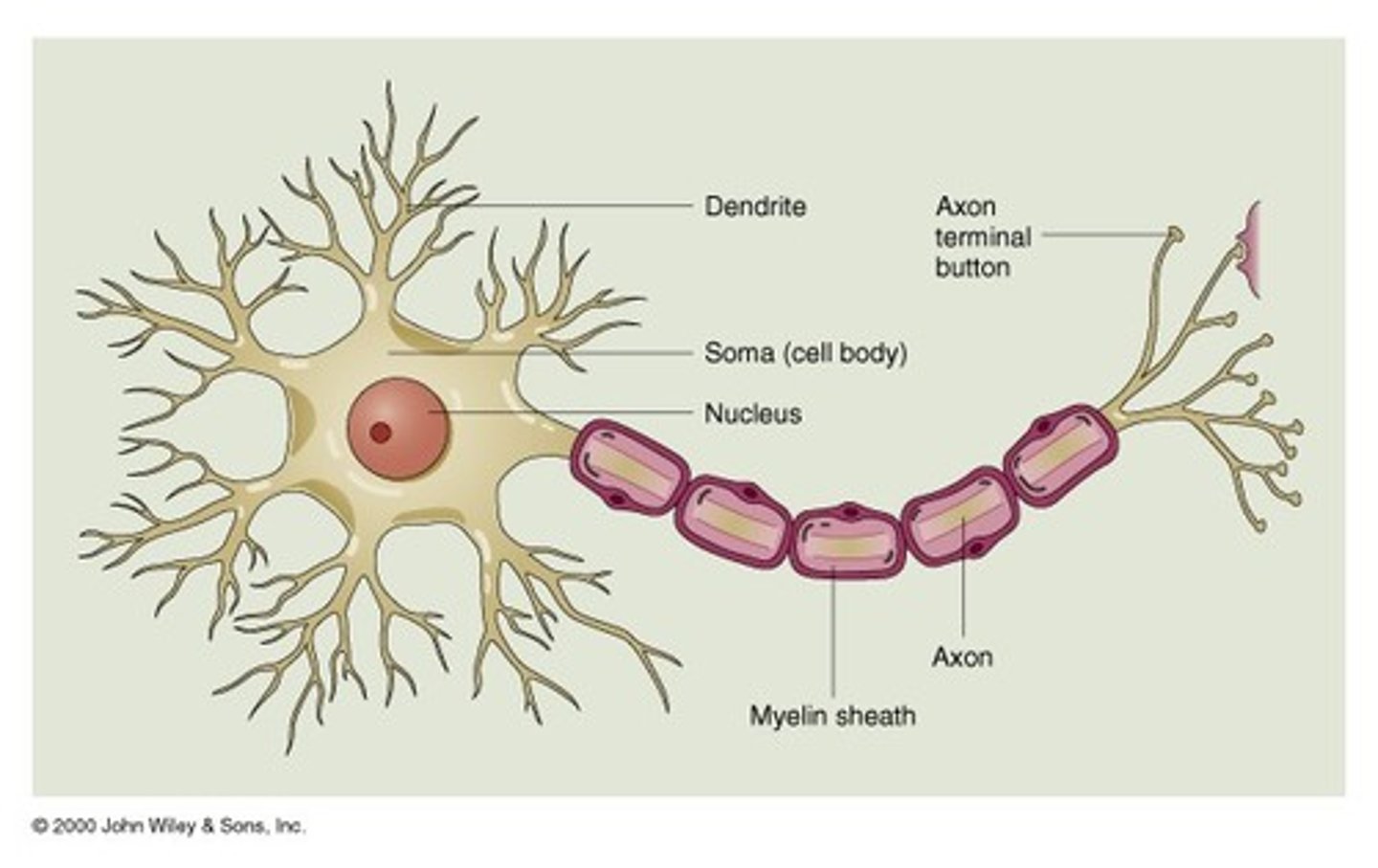
Axon terminal
-The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
-outgoing information
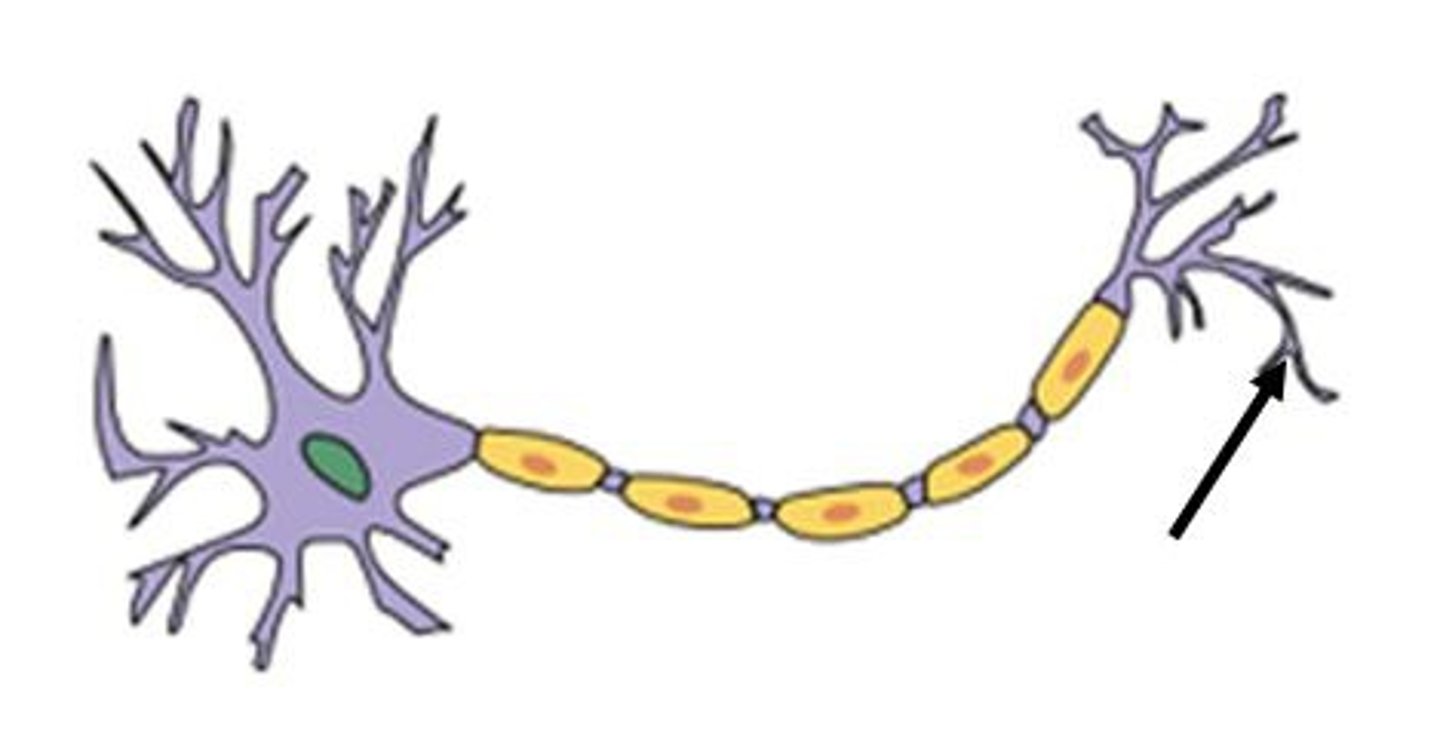
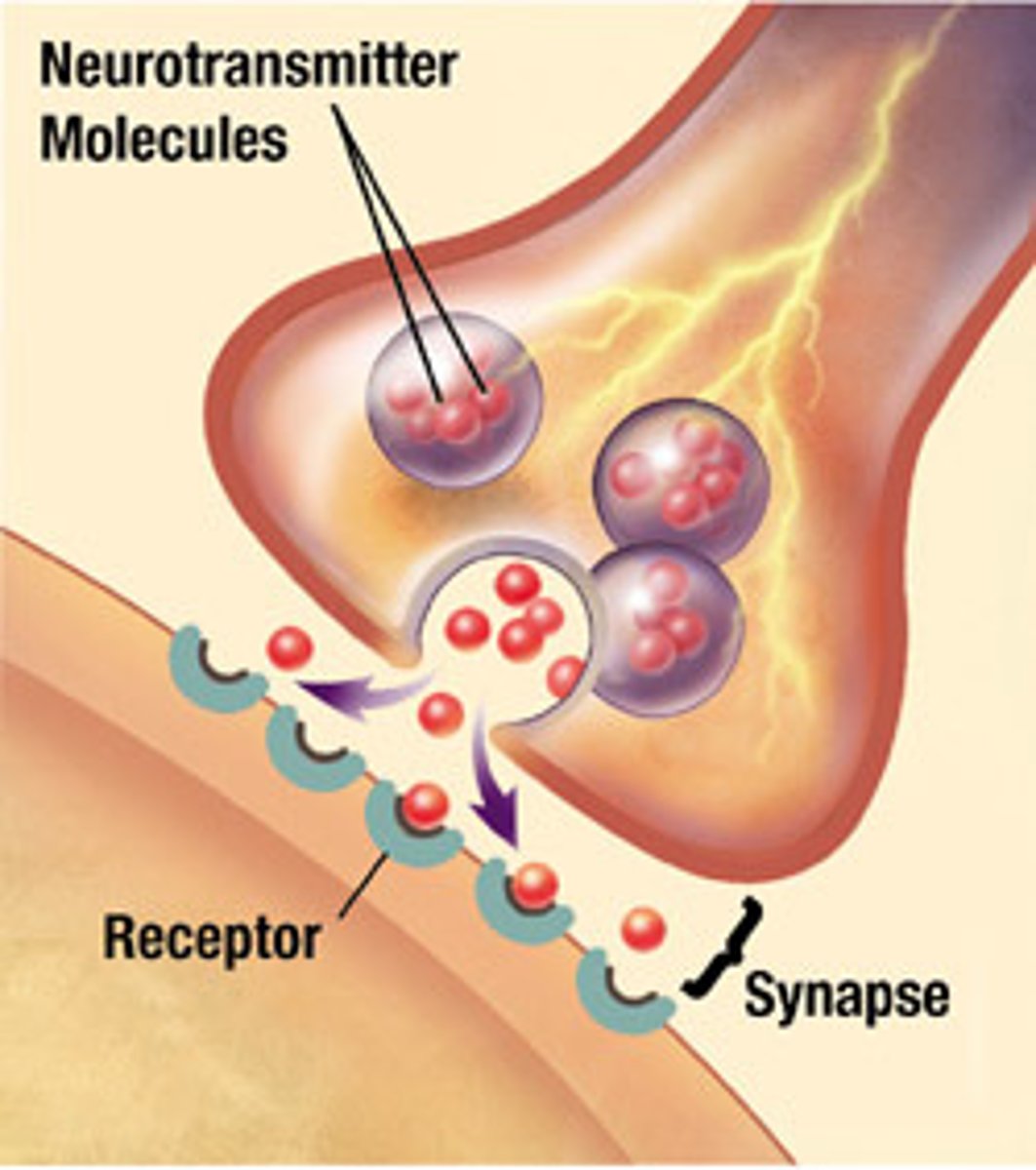
Synapse
-the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
-incoming/receiving
Glial cells
-cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
-formation of blood-barrier and myelin sheath
-supply nutrients to neurons
-support structure
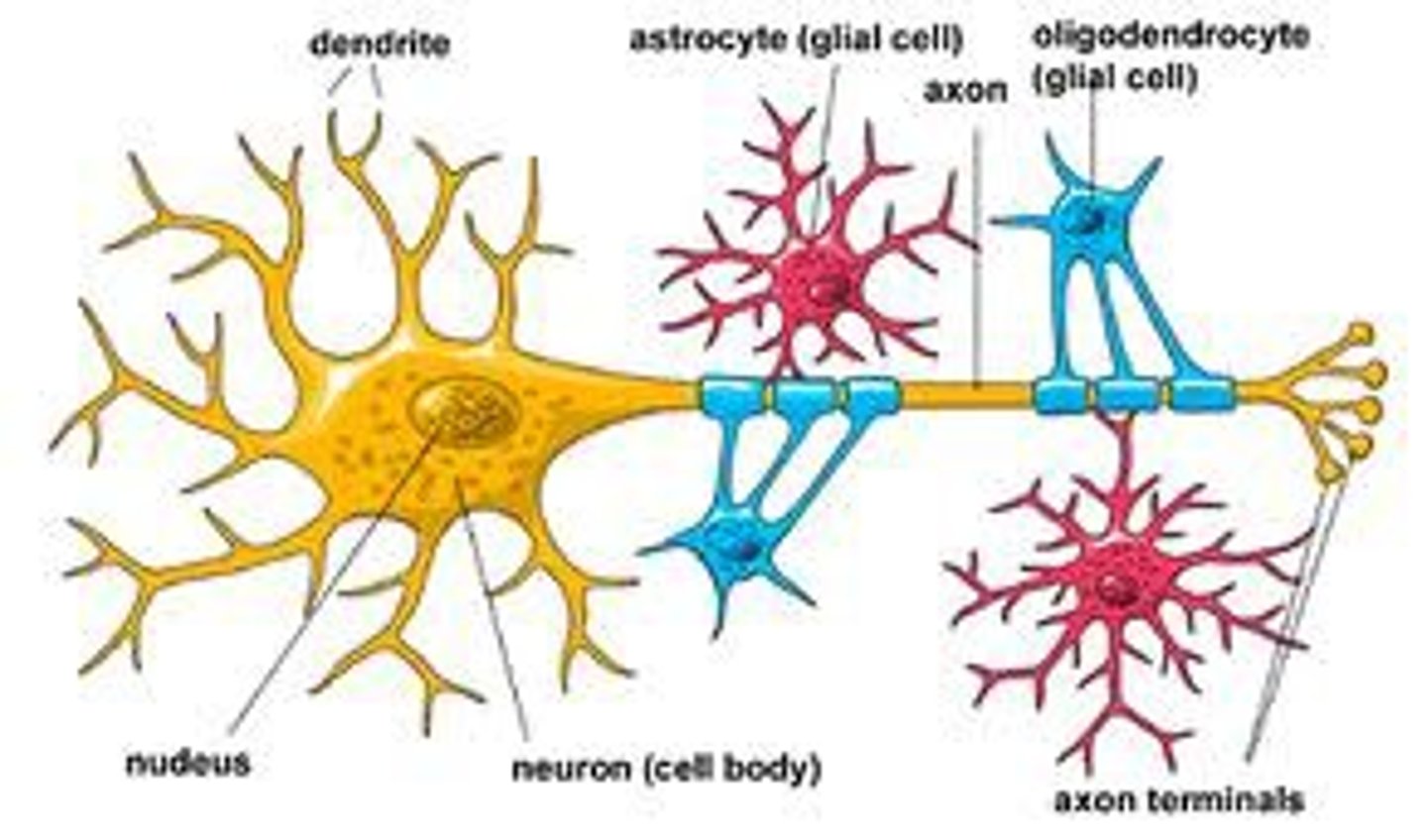
Histology
the study of the microscopic structure of tissues
EEG (electroencephalogram)
-amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface
-waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
Nervous system
-the network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body
Central Nervous System (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
PET scan (positron emission tomography)
-brain-imaging technique that reveals activity in various parts of the brain, based on patterns of blood flow, oxygen use, and glucose consumption
Lesions
removal or destruction of part of the brain
fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
-type of MRI that reveals which parts of the brain are most active during various mental activities
-using magnetism to track the flow of oxygen
Division of the nervous system
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
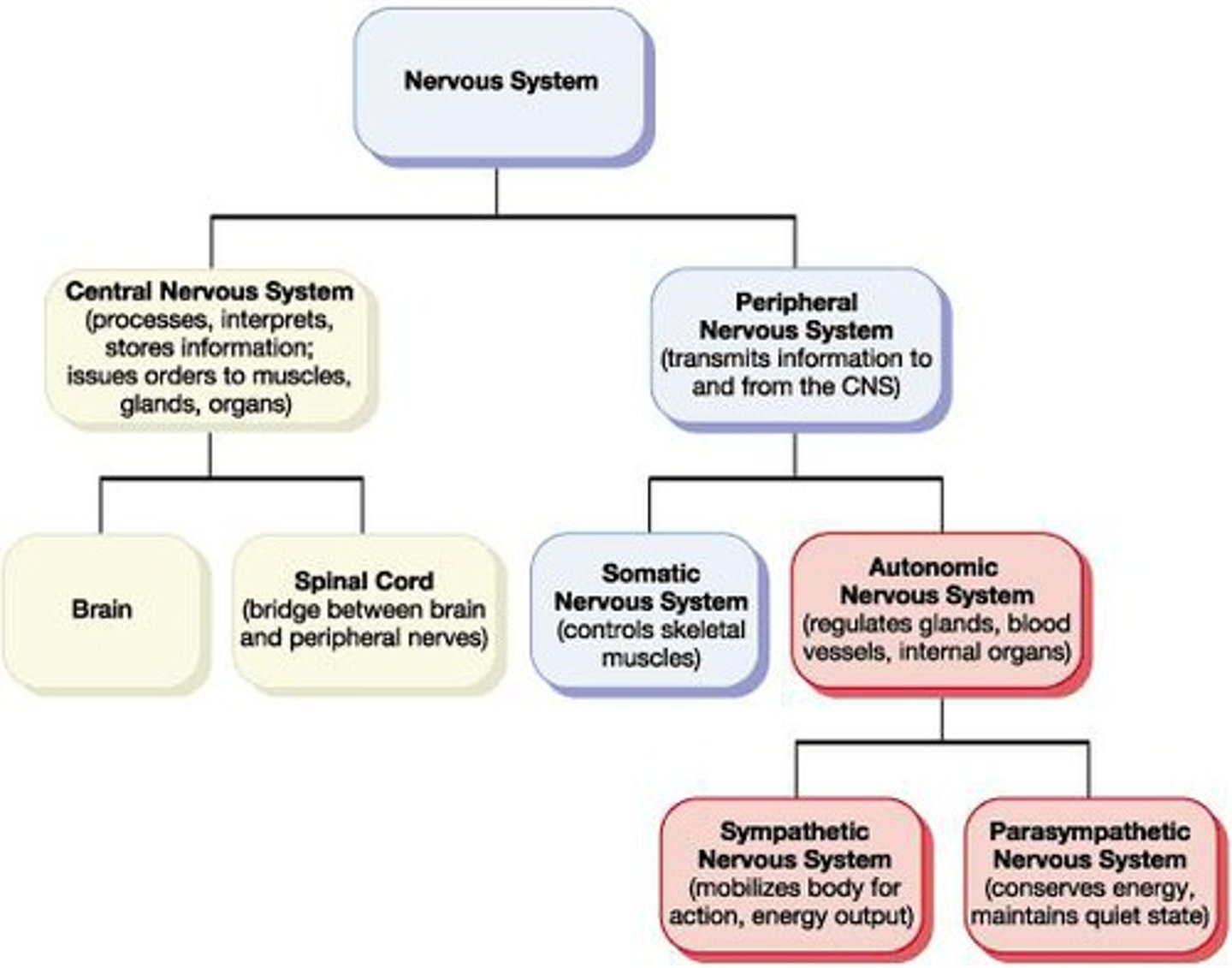
Division of the Peripheral Nervous System
somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
Division of the automatic nervous system
sympathetic and parasympathetic
Threshold for an action potential is reached when ...(4-step process)
1. Sodium channels are activated and sodium ions move into the neuron
2. The interior of the neuron becomes more positively charged than the exterior
3. Potassium channels are activated, and potassium ions move out of the neuron
4. The interior of the neuron becomes more negatively charged than the exterior
Limitation of experimental method
participants know they are in a research study resulting in possibly skewed results
Reliability
-consistency of measurement
-the consistency of a measure, including test-retest, interrater, inter-method, and internal consistency
SSRIs
-selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
-agonist
-treat depression, anxiety, OCD, eating disorders
-Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil
Damage to the midbrain would most likely result in...
changes in pain perception
Which of the following is an accurate match between a division of the autonomic nervous system and a bodily function or state?
1.Sympathetic; constricts pupils
2.Sympathetic; stimulates immune response
3.Parasympathetic; induces rapid heart beat
4.Parasympathetic; stimulates digestion
ANSWER: 4
In a meeting with the psychology professor, Steph reports having a hard time staying awake during lectures and sometimes experiencing the feeling of uncontrollably falling asleep while sitting at a desk. Steph's sleepiness may be due to the cells firing slowly in the
reticular formation
The idea that a person's dominant hemisphere influences their creativity or ability to think logically is
a popular myth about lateralization
How do drugs classified as SSRIs, such as Prozac, alter neuronal communication?
They increase the effectiveness of the neurotransmitter serotonin by blocking its reuptake into the axon terminal.
In hopes of better understanding how glia affect brain repair, Dr. Jennings develops a special mouse lacking specific types of glia. In her experimental design, Dr. Jennings injures the brain of this special mouse and monitors neuronal repair. What is Dr. Jennings likely to observe?
Cell debris from damaged neurons is not cleared
Tarik is designing a new race car video game. To create the illusion of depth, how should Tarik design the backdrop in relationship to the first-person driver?
Show distant objects traveling with the first-person driver; show closer objects moving in the opposite direction of the driver.
Our primary method for localizing sound in the horizontal plane is
to compare the arrival time of sound at each ear
Why is it inaccurate to say that daydreaming is a "total waste of time"?
We often think about past experiences and plan our future when the DMN is active during daydreaming
While hanging up a picture, Joy hits her thumb with a hammer, causing agonizing pain. Joy immediately puffs out her cheeks and blows air onto her thumb over and over again. Her roommate Bethany laughs and then remarks, "Are you drying nail polish or hoping to blow away the pain?" However, Joy's thumb does in fact feel better. Why?
She is activating a competing sensory pathway, which dilutes the amount of pain information getting to the brain.
Azul studies for her upcoming molecular biology midterm. She starts by making an outline of her textbook chapters and then begins studying her lecture notes. Azul's brain is likely to show _____ wave activity
beta
Persis is a summer intern at a new video game software company, Generation Z Gamers. She is working on three-dimensional landscapes for a new role-playing video game Submarine Adventures. As her supervisor, what advice can you give Persis to help her create the illusion of three dimensions?
Converge parallel lines at the horizon to create a linear perspective
Jordan typically has at least three cups of coffee throughout the day. She decides to cut her coffee habit "cold turkey," but experiences severe lethargy despite having a good night's sleep. Jordan is experiencing
Withdrawal symptoms
How does the input of olfactory information to the brain differ from other sensory input pathways?
Direct connections to the thalamus are not made before information reaches the cortex.
Tasha runs a daycare center. She places birthday hats on a group of children to celebrate 1-year-old Chantal's birthday. Tasha notices that when Chantal passes by a mirror she grabs for the hat by reaching for the mirror instead of reaching for her own head. Tasha picks up the baby and helps her find her hat. What aspect of consciousness has Chantal not yet reached?
Self-awareness
Consider the following scenarios. Which person displays characteristic signs of a persistent vegetative state?
1.Sienna is learning to walk after her automobile accident; however, she still cannot communicate and suffers significant cognitive impairment.
2.Anil is in a coma; his mother is hopeful because he occasionally opens his eyes and sometimes even smiles or cries, but Anil's doctors tell her that these actions are random.
3.Brian is in a persistent state of unconsciousness; he cannot be awakened and does not respond to painful stimuli.
4.Muriel was in a deep coma; she now squeezes her mother's hand when she hears her voice, but she cannot yet open her eyes or speak
ANSWER: 2
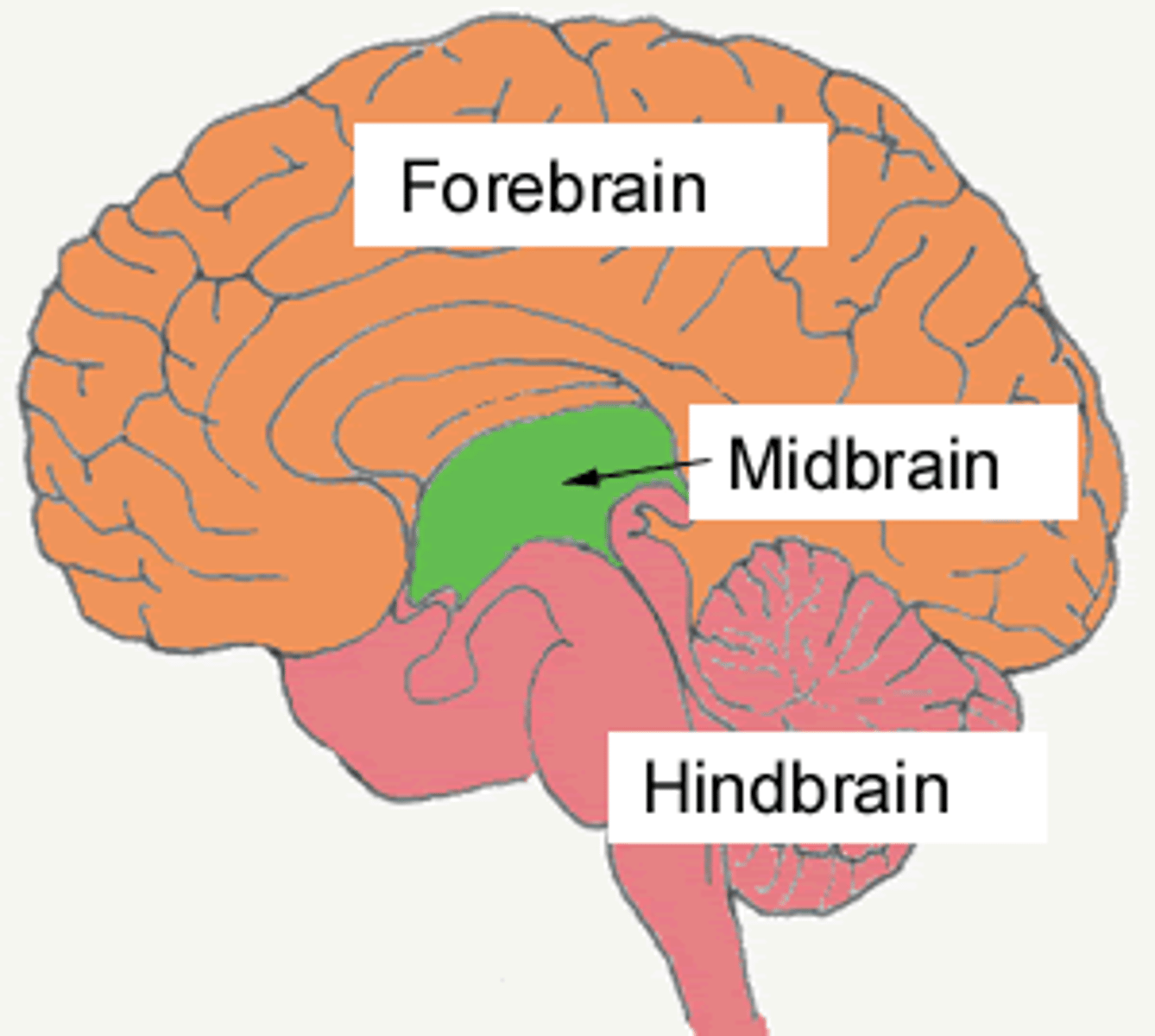
Forebrain
-largest and most complicated region of the brain, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and cerebrum
-critical for complex cognition, emotional, sensory, and motor functions
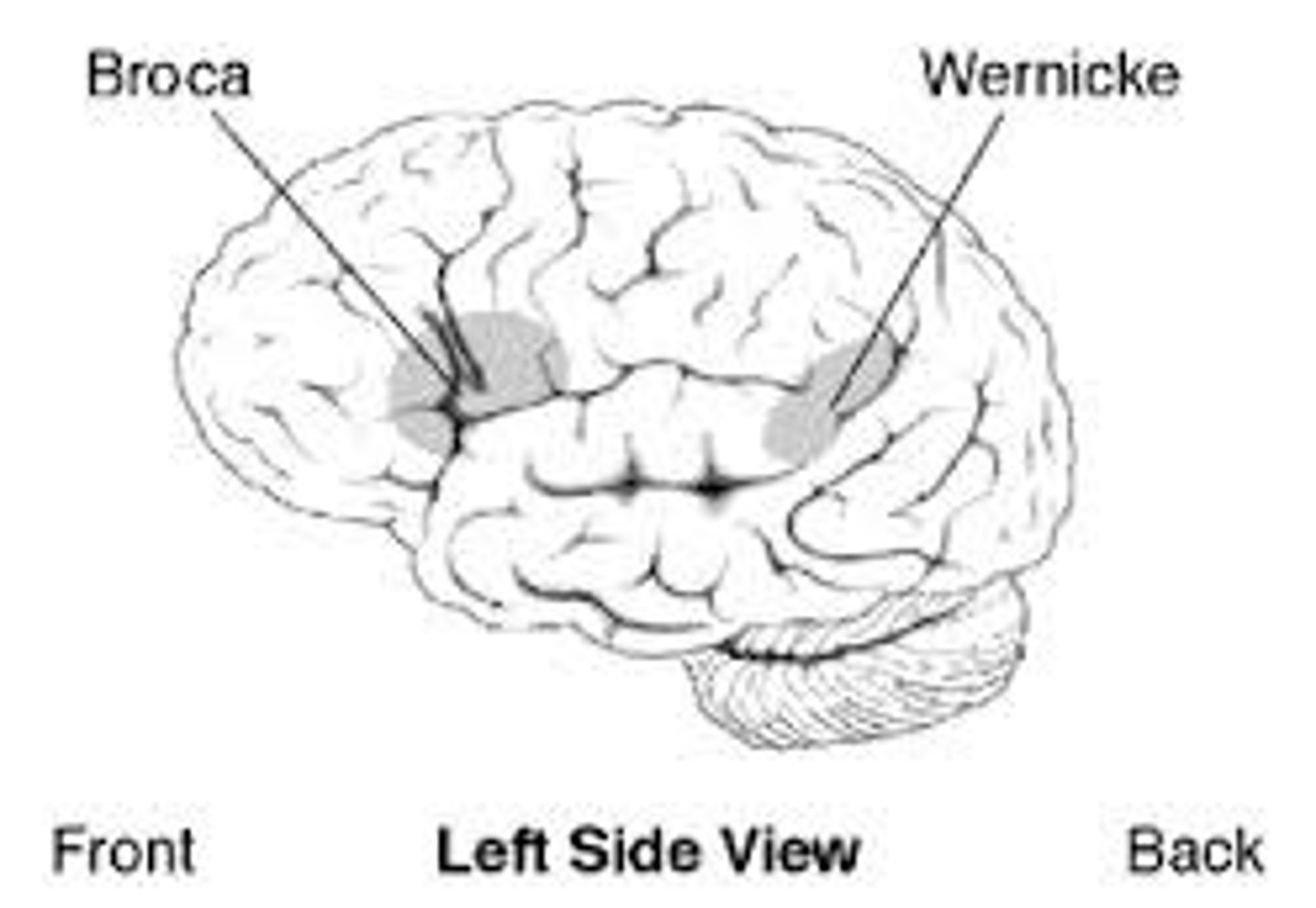
Broca's area
-Controls language expression/prodcution
- an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
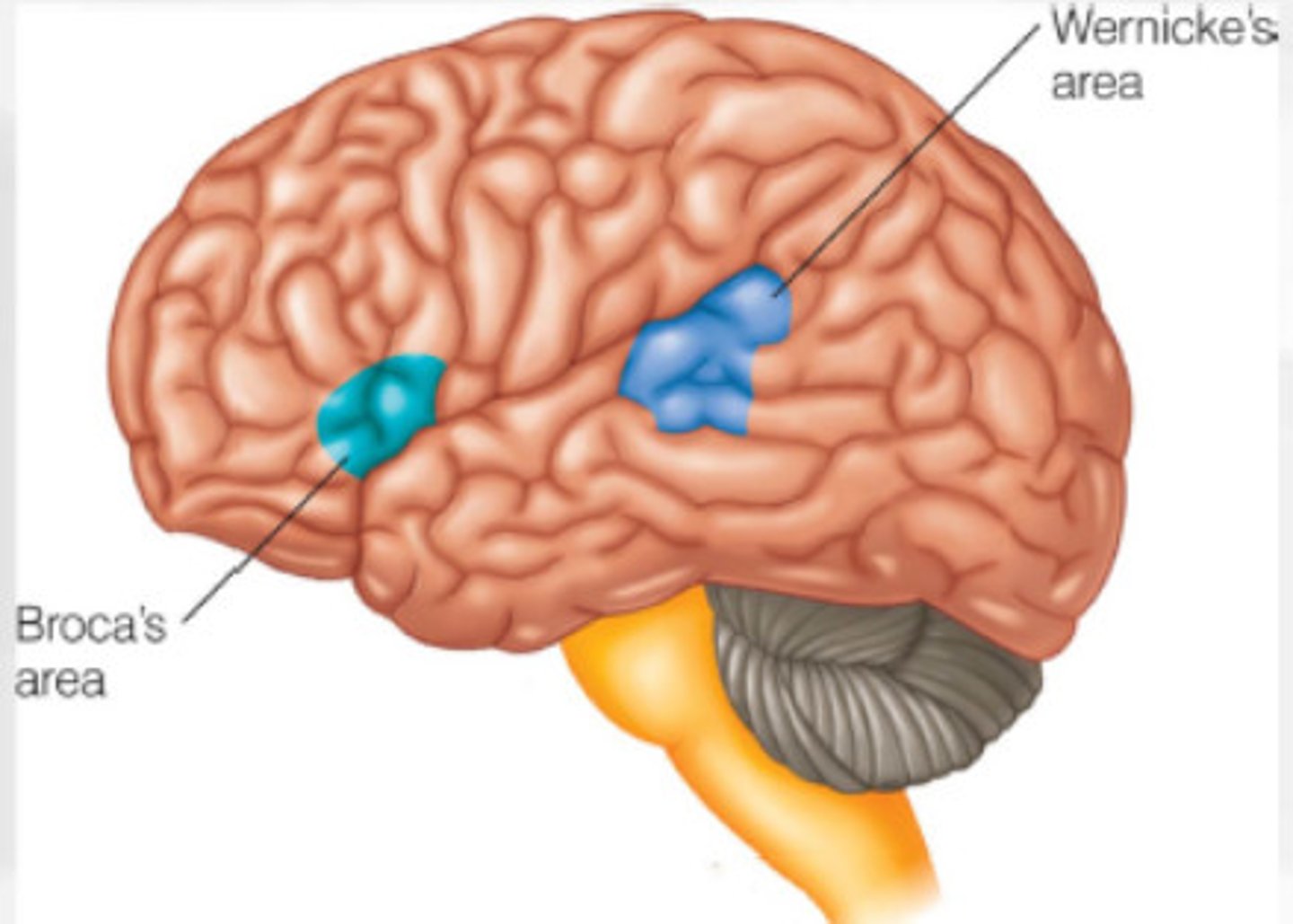
Wernicke's area
-controls language reception
- a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
Parts of the brainstem include...
-Medulla
-Pons
-Reticular Formation
-Cerebellum
Double-blind procedure
-research strategy in which neither subjects nor experimenters know which subjects are in the experimental or control groups
-considered the "gold standard"
-requires a placebo
Placebo
-a fake drug used in the testing of medication
-example: sugar pill
Operant conditioning
-a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher
-pairs behavior and response
Classical conditioning
-type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
-pairs two stimuli
Operationalization
-the process of assigning a precise method for measuring a term being examined for use in a particular study
-first step is to identify the concept to be measured clearly (such as violence in video games)
-second step is the quaintirgaives measures of the concept (such as the measures to tell a violent video game from a non-violent video game)
Confounding variable
-factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment
-situational confounds (such as noise in a laboratory during an experiment) the is an issue faced by the experimental method
Independent variable
-the experimental factor that is manipulated
-the variable whose effect is being studied
-controlled
Dependent variable
-measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested
-emphasis on MEASURABLE effect
Cross-sectional study
-a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another
-used to asses the normal behaviors associated with age
-subject to the cohort effect (generational effects of having been born at a particular point in history)
Cohort effects (generation effects)
-refer to differences between age groups (or cohorts) caused by unique characteristics or experiences other than age
Survey
-a technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group
-results are often influenced due to surveys being self-reported
Sample
a subset of the population
Measure
a method for describing a variable's quantity
Peer review
a review of research by people with similar professional qualification prior to publication
Third variable
-a variable that is responsible for a correlation observed between two other variables of interest
Control group
-In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment
-contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment
Descriptive methods
-case study
-survey
-naturalistic observation
(DON'T SHOW CAUSE/EFFECT)
-include case studies, surveys, and naturalistic observations
Science
-An organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world
-learning about reality through systematic observation and experimentation
William James
Functionalism
Example of opioids
-heroin
-oxy
-morphine
Sigmund Freud
-psychologist who developed psychoanalysis
-Believed strongly that unconscious drives and desires guided people's actions
-psychodynamic theory
Abraham Maslow
Hierarchy of needs; humanistic psychologist
Opioids
-activate receptors that usually respond to endorphins, increase dopamine activation, dual activation of dopamine and opiate receptors (which is why it is so addictive)
-very addictive
-heroin, oxy, morphine
Ivan Pavlov
-discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell
-behavorism
Uric Neisser
-cognitive psychology
-cognitive revolution
Objectivity
-treating facts without influence from personal feelings or prejudices
Confirmation bias
-a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
Critical thinking
the ability to think clearly, rationally, and independently
Theories
a set of facts and relationships between facts that can explain and predict related phenomena
Biological and evolutionary psychology
Investigates the connections among mind, behavior, and biological processes, and asks how our evolutionary past continues to shape our behavior
Cognitive Psychology
investigates mental processes, including reasoning and thinking, problem solving, memory, perception, mental imagery, and language
Social and personality psychology
asks how our behavior is affected by the presence of others; recognizes that behavior varies around averages and that individual differences often interact with environments
Developmental psychology
investigates the normal changes in behavior that occur across the lifespan of an individual
Clinical psychology
-studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
-promotes general well-being
Longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
Mixed longitudinal study
A method for assessing age-related changes that combines the cross-sectional and longitudinal approaches by observing a cross-section of participants over a shorter period than is used typically in longitudinal studies.
Validity
-the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
***both reliability and validity are not subject to be dependent upon each other
Circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle
How does jet lag affect circadian rhythms?
largely caused by air travel across one or more time zones
Examples of sleep disorders
-*sleep terrors
-nightmares
-*insomnia
-*narcolepsy
-cataplexy
-*sleep apnea
Sleep terrors
-sleep disturbance characterized by an episode of increased physiological arousal, intense fear and panic, frightening hallucinations, and no recall of the episode the next morning
- typically occurs during stage 3 or stage 4 NREM sleep
-also called night terrors.
Insomnia
-recurring problems in falling or staying asleep