Integumentary System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Stratum basale
Deepest layer of epidermis (closest to dermis)
Gets nutrients from dermis
Growing keratinocytes and melanocytes
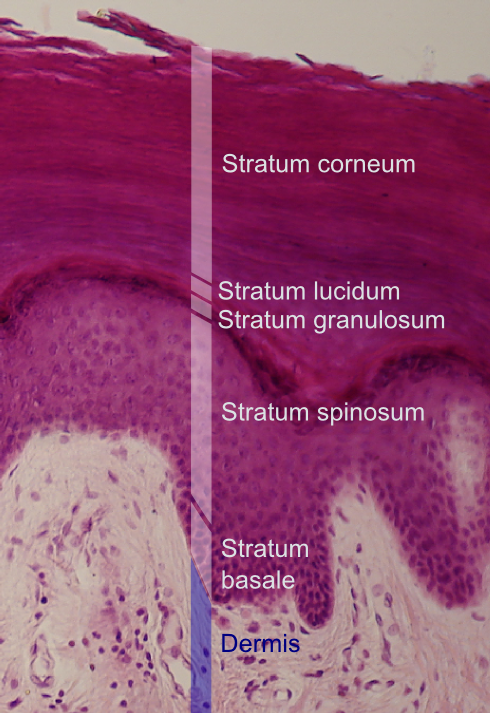
Stratum spinosum
Bundles of pre-keratin substances in cells
Limited mitosis
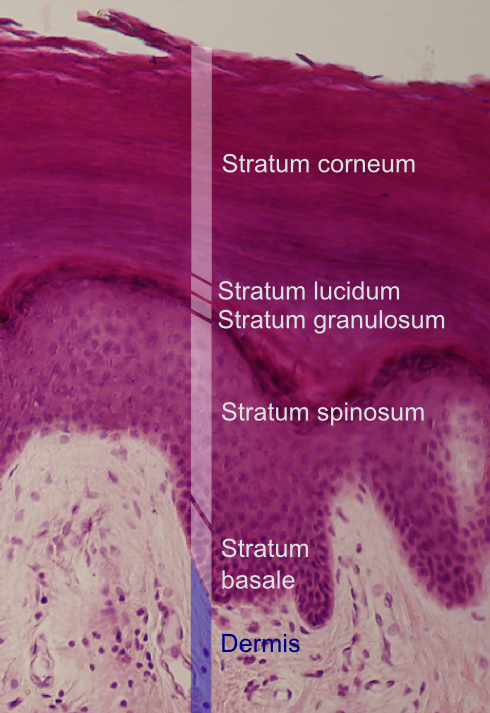
Stratum granulosum
Cells flatten and organelles deteriorate
Contains fibers of kertain and shriveled nuclei
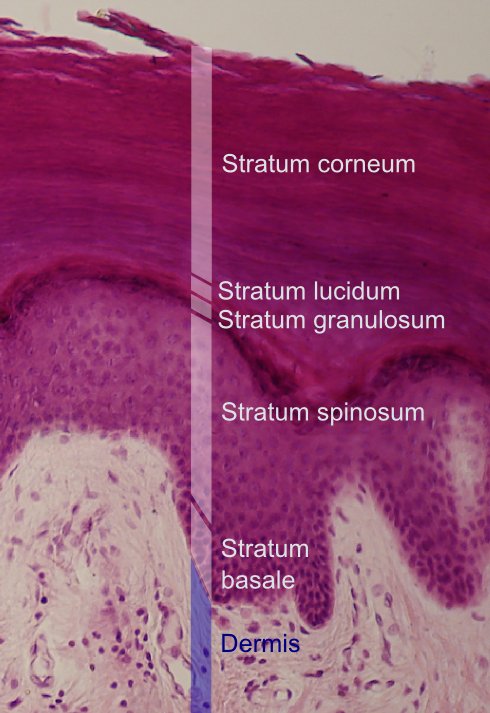
Stratum lucidum
Thin, clear layer
Only exists in lips, palms, soles
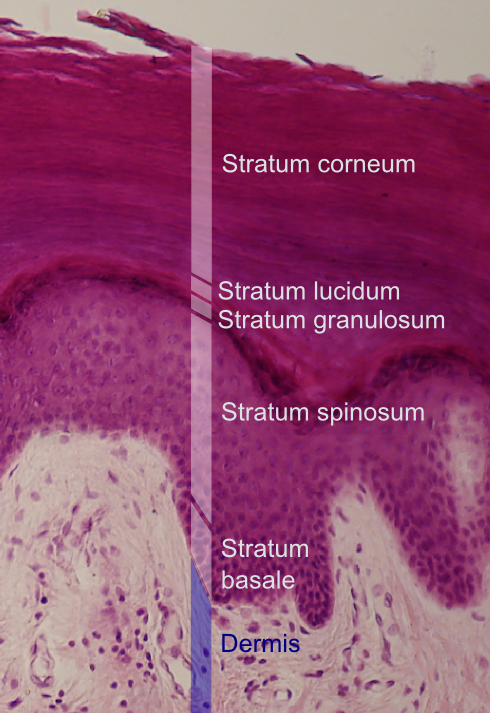
Stratum corneum
20-30 cell layers thick (uppermost layer)
Keratinized, dead, and flattened cells connected by desmosomes
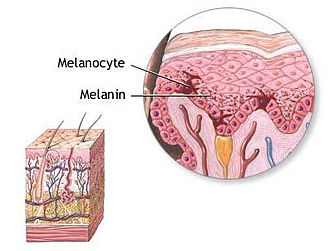
Melanin
Gives hair and skin color
Produced by malnocytes in stratum basal
Protects from bacterial/viral and can activate lympathic system
Keratinocytes
Produces keratin (fibrous protein)
Keratin provides a waterproof, protective layer
Kertainization occurs which hardens layers
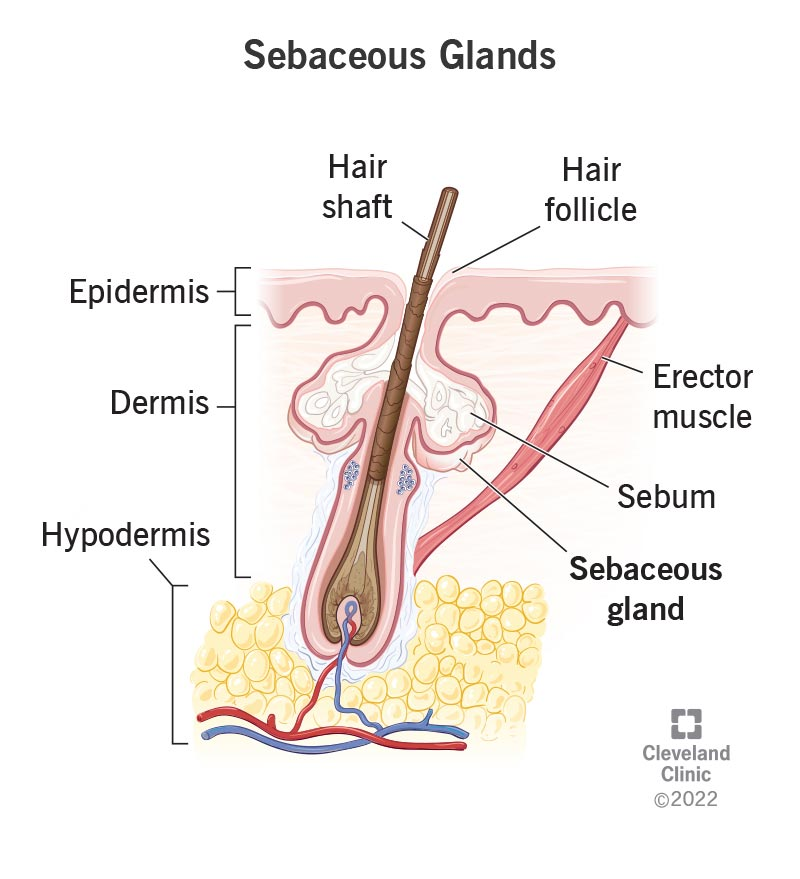
Cutaneous glands
Exocrine (release secrtion on skin surface)
Consists of sebaceous and sweat glands
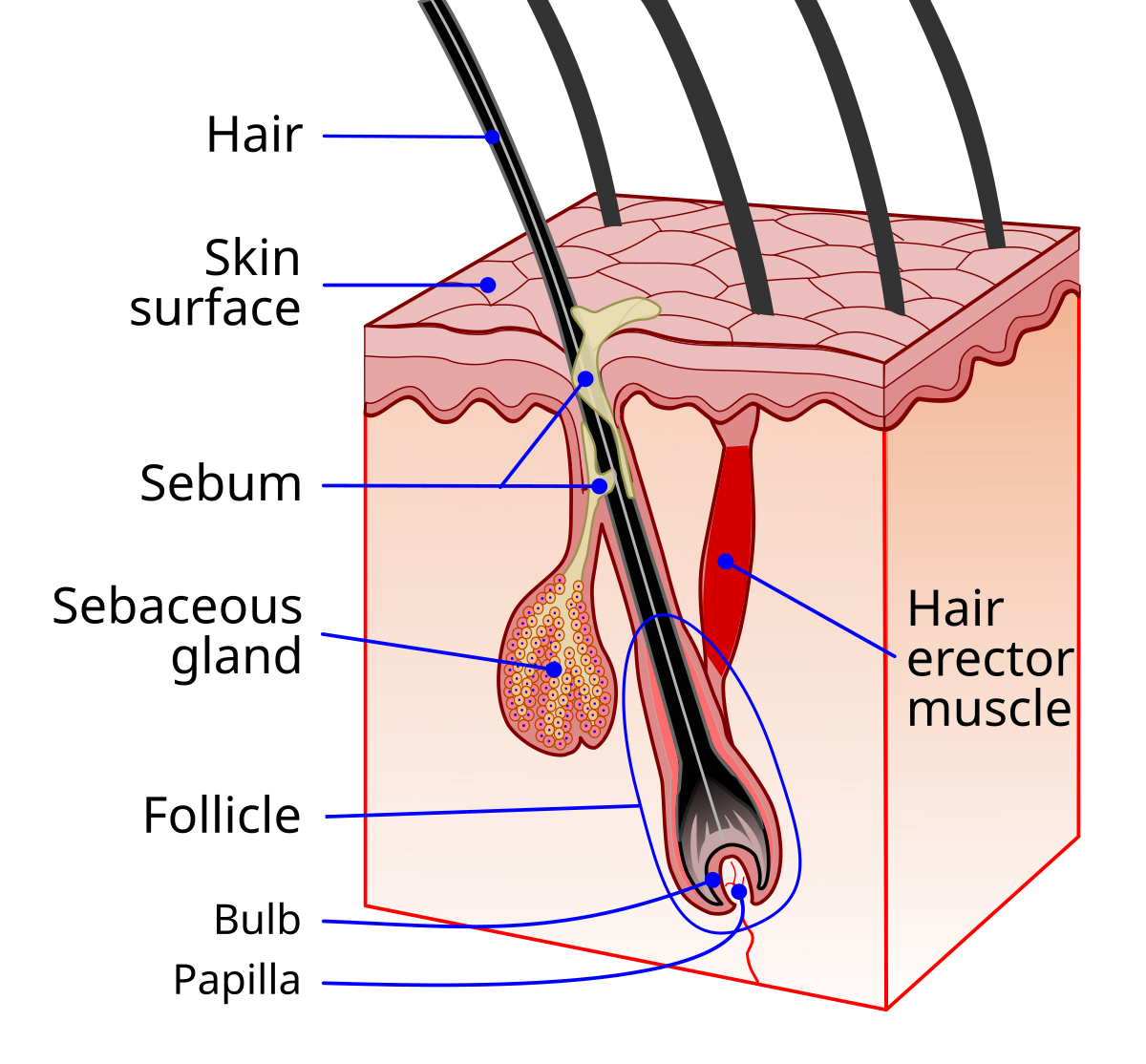
Sebaceous (oil) glands
Releases sebum (oil + fragmented cells) on hair follicles
Found everywhere except for palms of hands and feet
Lubricates skin, keeps hair from becoming dry
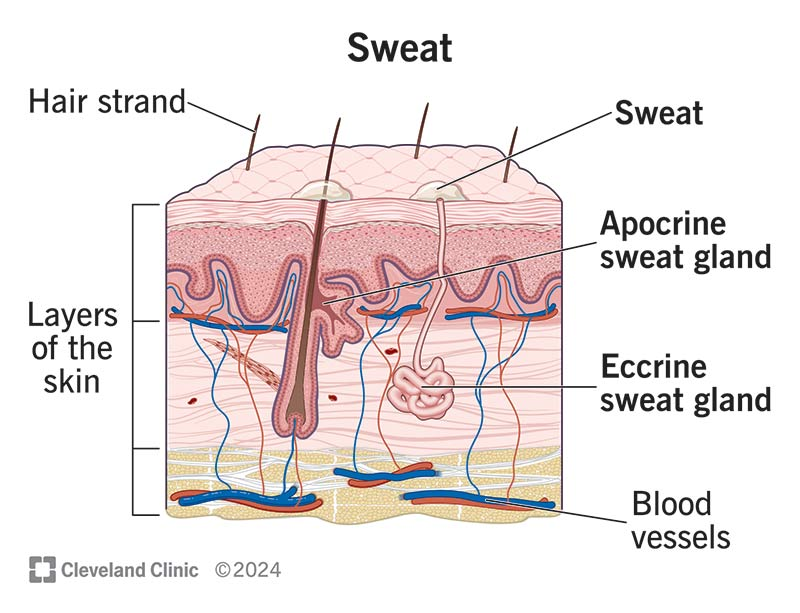
Eccrine sweat glands
Produce sweat (water, salts, metabolic waste)
Found everywhere except for palms, soles, forehead
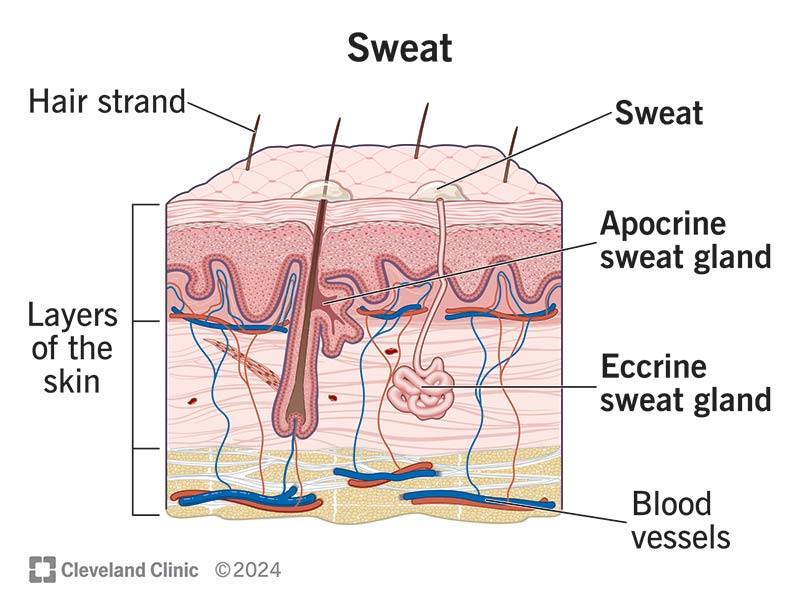
Apocrine sweat glands
Found in armpits and genital areas
Release sweat on hair follicles (sweat is milkly, yellowish)
Hair
Fastest growing cells
Consists of root, shaft, bulb, follicle
Protects from particles and provides insulation
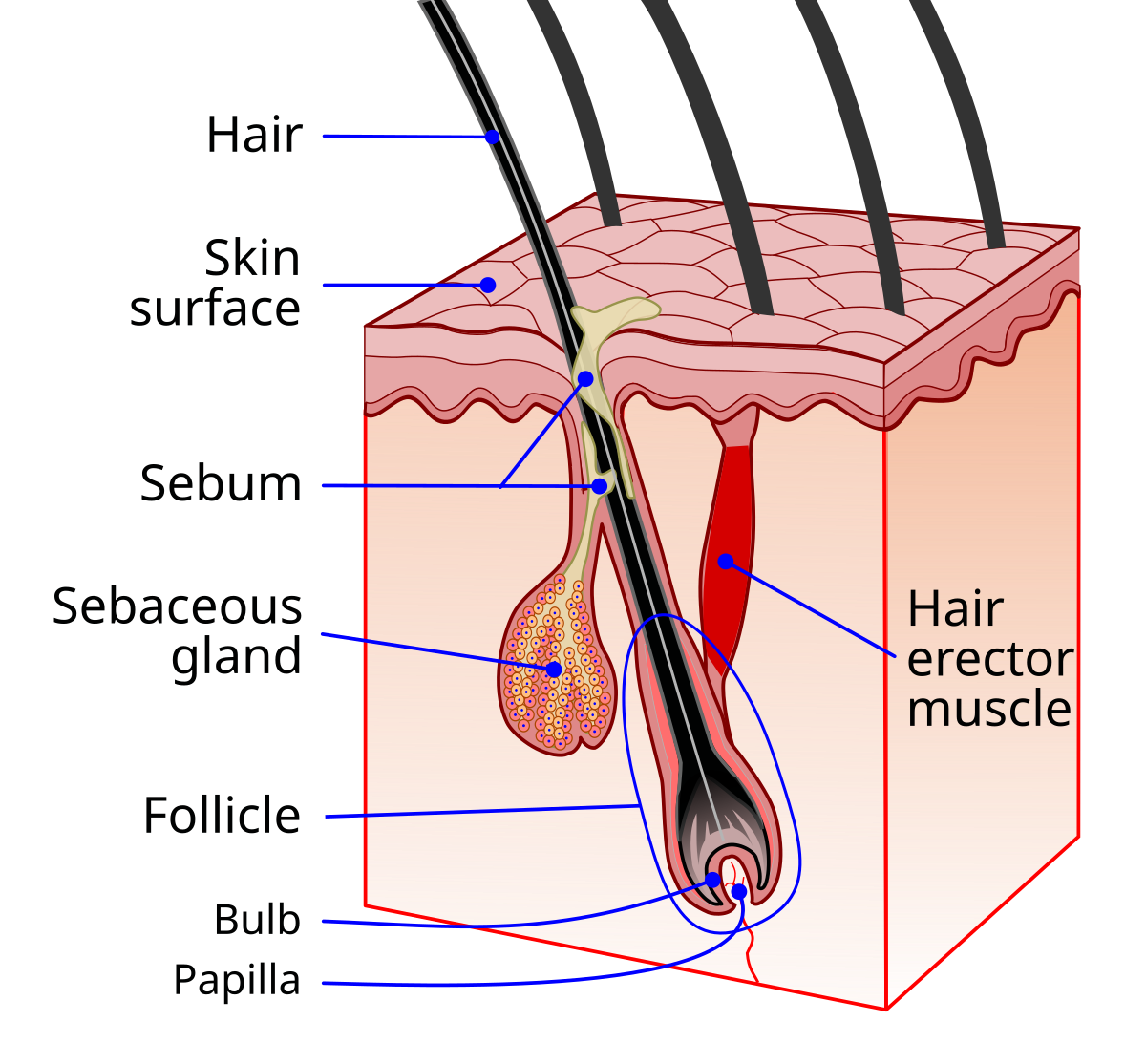
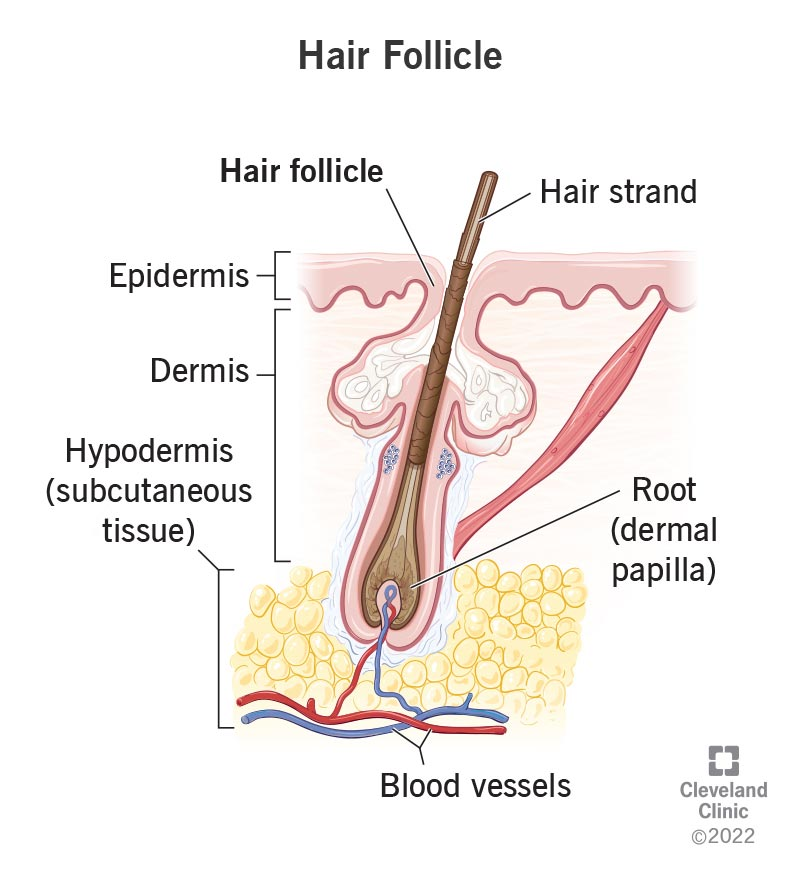
Hair bulb
Deepest part of follicle
Supplied blood by dermal region
Part where new hair cells are made (hair matrix) and pushes them upward
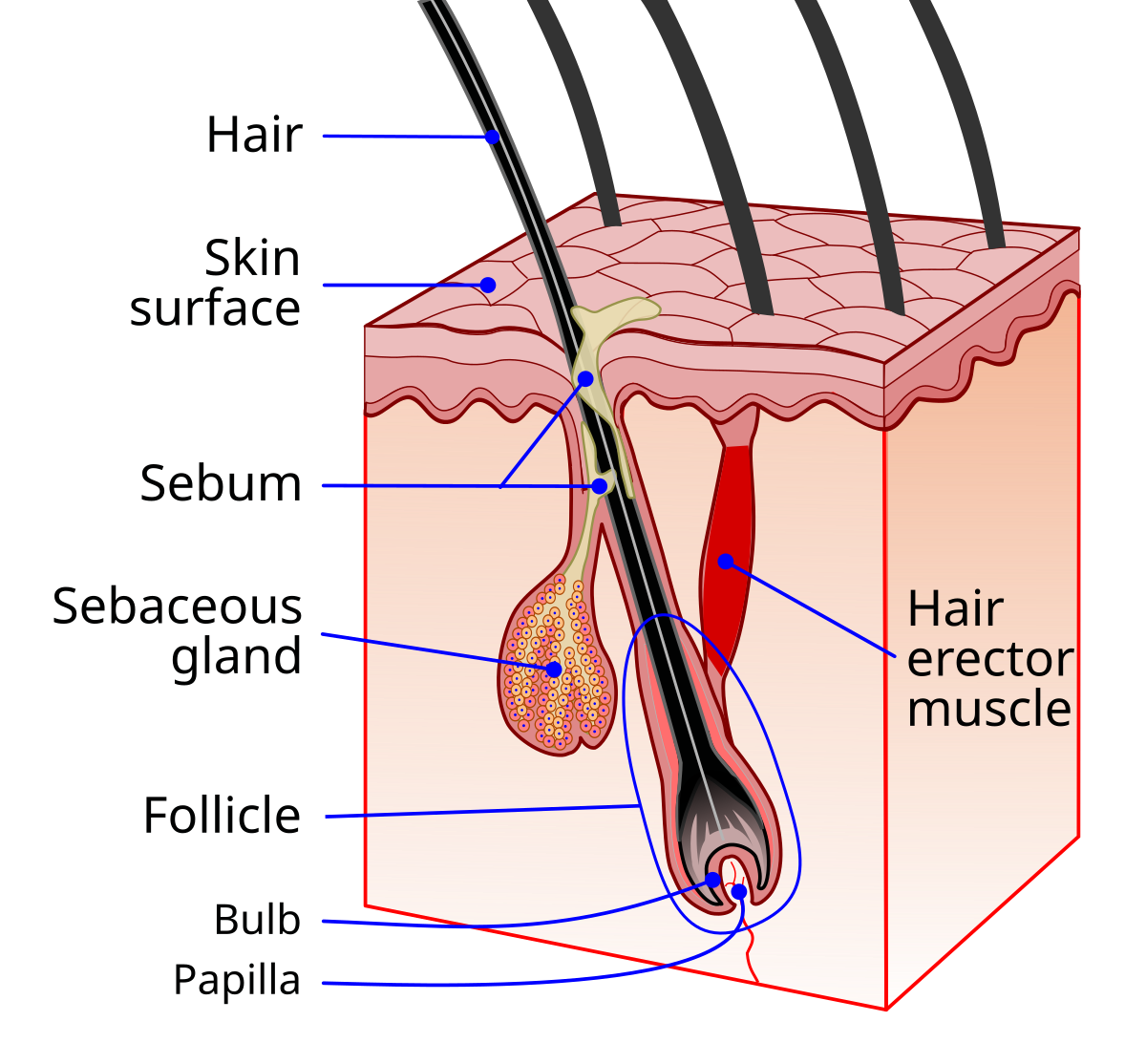
Hair follicle
Composed of epithelial root sheath and fibrous sheath
Anchors hair into skin
Extends from epidermis into dermis and hypodermis
Hair shaft
Cells become keratinized + die to form shaft
Consists of core called medulla and outer cortex layer surrounded by cuticle
Cuticle keeps hair part
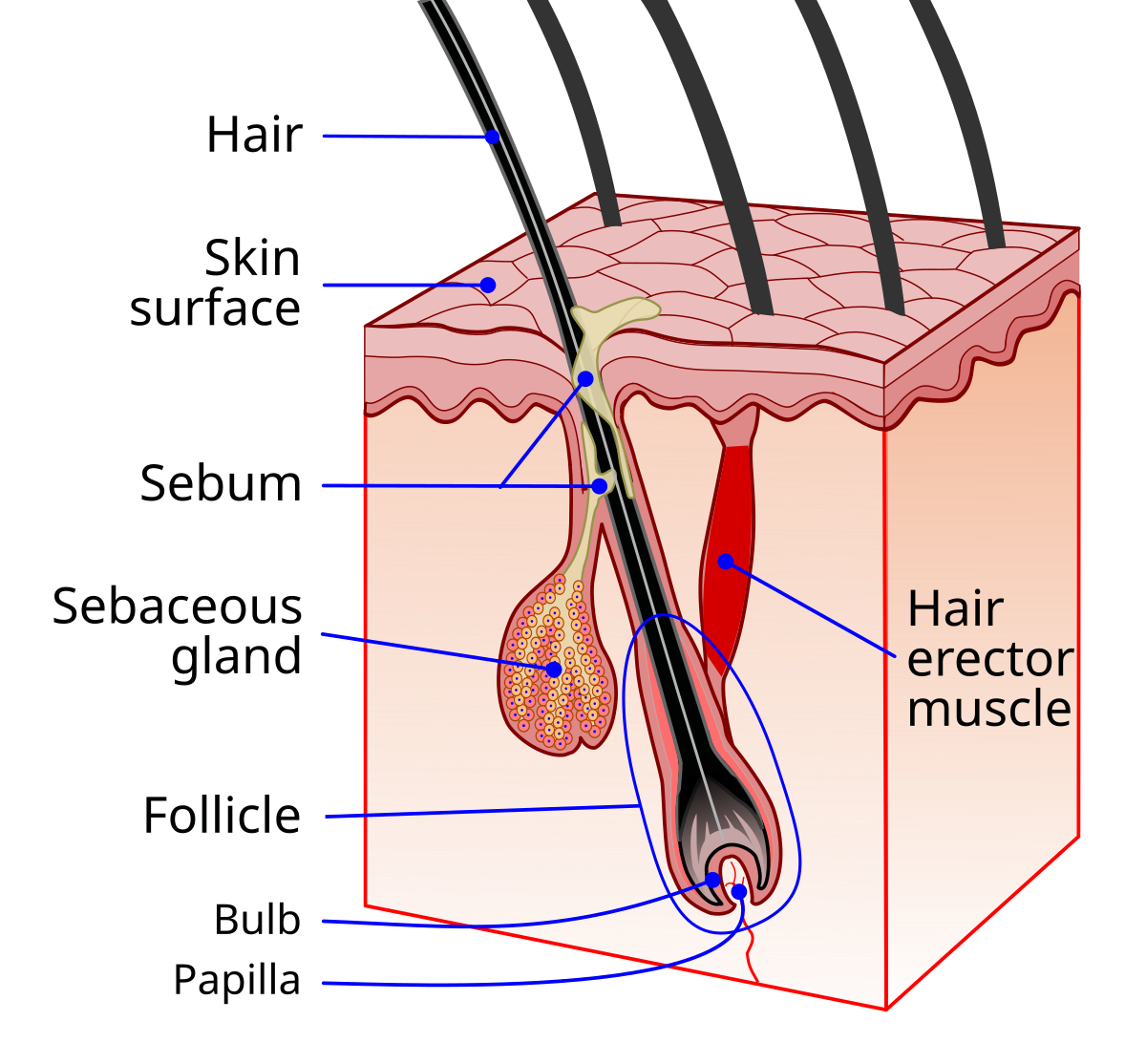
Arrector pili muscle
Connects hair to hair follicle
Pulls hair upright when cold or frightened (goose bumps)
Sits in dermis layer
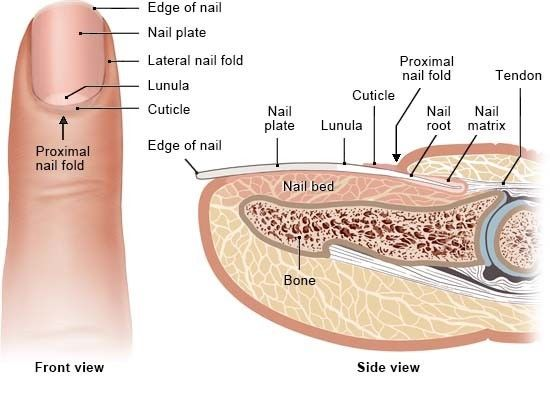
Nails
Heavily keratinized and scalelike modification of epidermis
Includes free edge, body (attached portion), nail folds, cuticle (proximal edge)
Grows from nail matrix
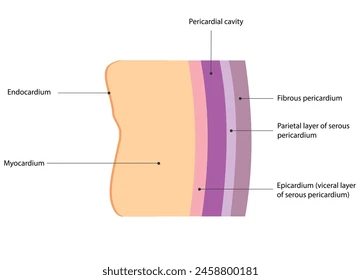
Serous (serosa) membrane
Double membrane, containing simple squamous epithelium + areolar (loose) CT
Lines body cavities not open to exterior
Secretes serous fluid (lubricant)
Peritoneum (abdominal cavity), pleurae (around lungs), pericardia (around heart)
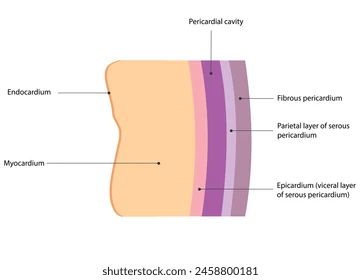
Parietal layer
Lines walls of body cavities
Outer layer of serous membrane
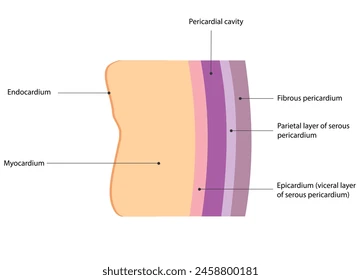
Visceral layer
Covers outside surface of organs themselves
Inner layer of serous membrane
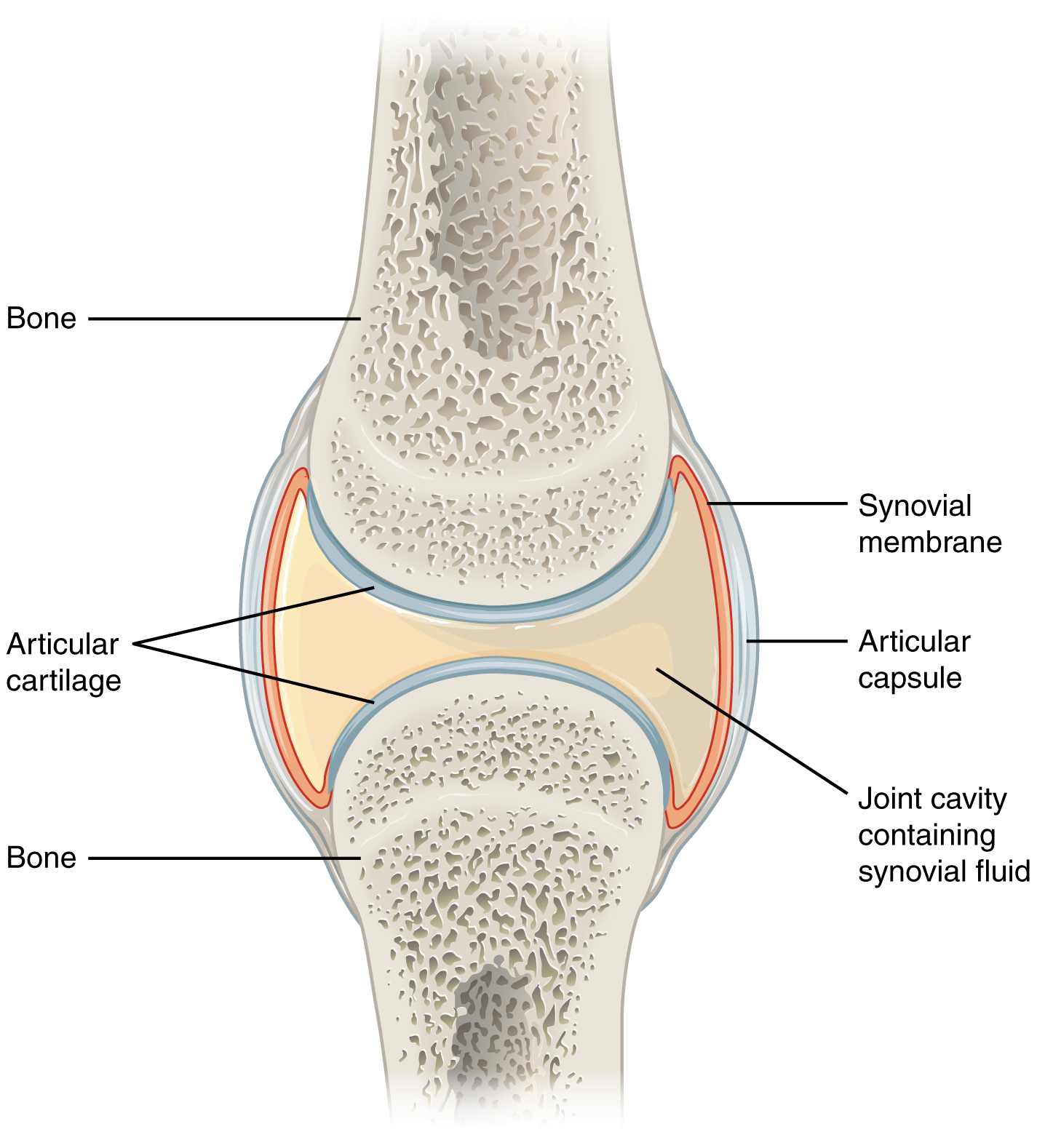
Synovial membrane
No epithelial tissue, only areolar CT
Surrounds + cushions major body joints/organs
Secretes synovial fluid (lubricate joints)
Bursae (small sacs) lined with membranes
Dermis layer
Under epidermis, above hypodermis
Two major regions: papillary and reticular layer
Made of connective tissue (collagen + elastic fiber)
Helps supply nutrients, has pain/touch receptors
Genetically predetermines fingerprints
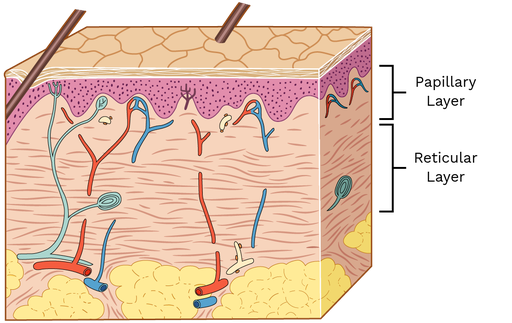
Reticular layer
Deepest layer of dermis
Comprised of dense irregular CT
Blood vessels, sweat/oil glands, lamellar corpuscles (deep pressure receptors)
Papillary layer
Upper layer of dermis
Areolar CT
Papillae, pain receptors, Meissner’s corpuscles (touch)
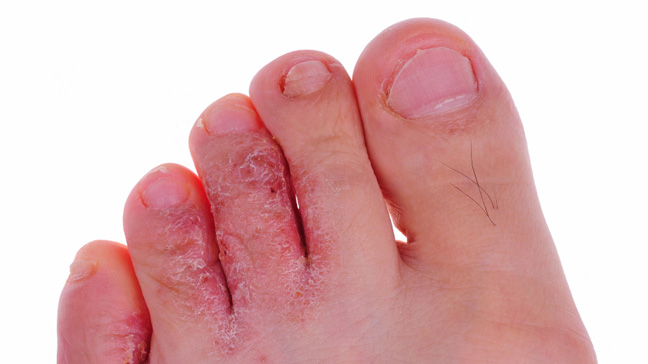
Athlete’s Foot
Caused by Tinea pedis (fungal infection)
Itchy, red peeling skin between toes
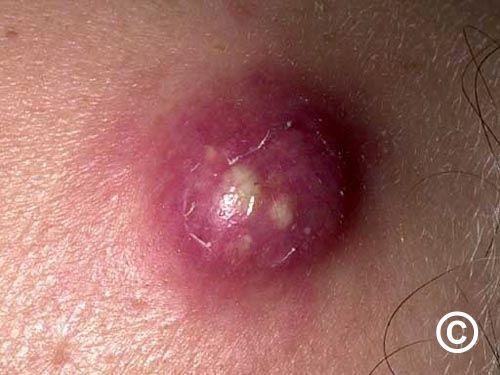
Boils (furnucles) and carbuncles
Boils caused by inflammation of hair follicles
Carbuncles are clusters of boils caused by bacteria infection
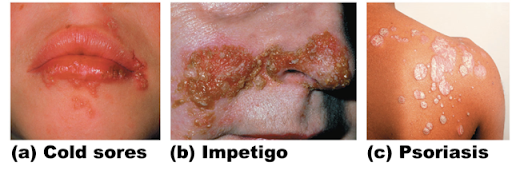
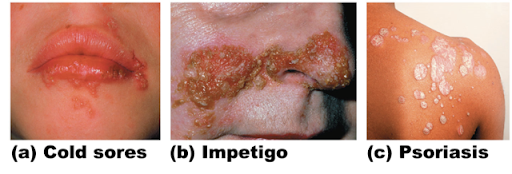
Cold sores (fever blisters)
Caused by virus
Blisters and itching
Frequency/growth can be increased by exposure to sun/heat
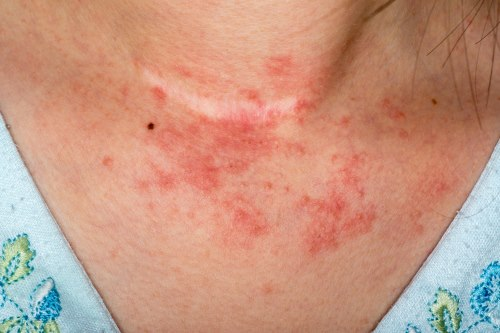
Contact dermatitis
Caused by exposure to chemicals that provoke allergic reactions
Impetigo
Caused by bacterial infection
Pink, fluid filled raised lesions around mouth/nose
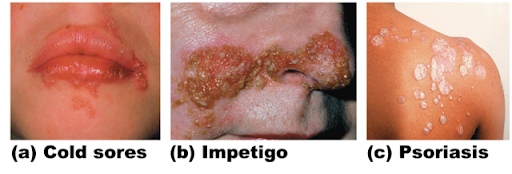
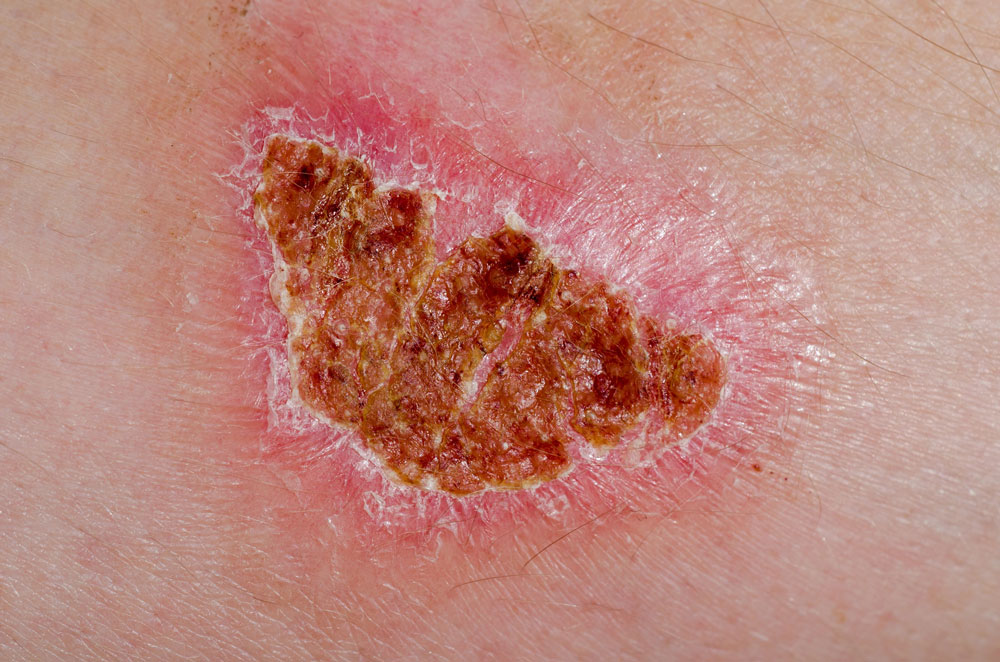
Psoriasis
Triggered by trauma, infection, hormonal changes, or stress
Red, epidermal lesions covered with dry, silvery scales
Itch, burn, crack, bleed
First-degree burn (superficial)
Superficial burn
Only epidermis is damage
Skin is red and swollen (sunburn)

Second-degree burn (partial-thickness)
Partial-thickness burn
Epidermis + superficial part of dermis is damage
Skin is red, painful, blisters (can regrow epidermis)
Third-degree burn (full-thickness)
Destroys epidermis + dermis
Burned area is painless (no pain receptors)
Needs skin grafts (regeneration not possible)
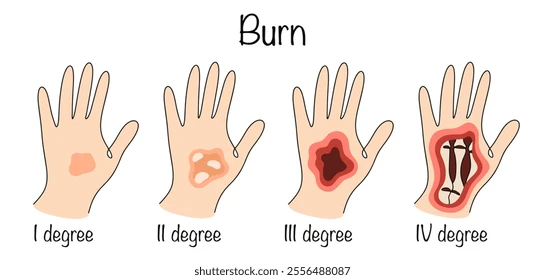
Fourth-degree burn (full-thickness)
Extends to deeper tissue (bone, muscle, tendon)
Appears dry/leathery
Amputation is possible and sometimes required
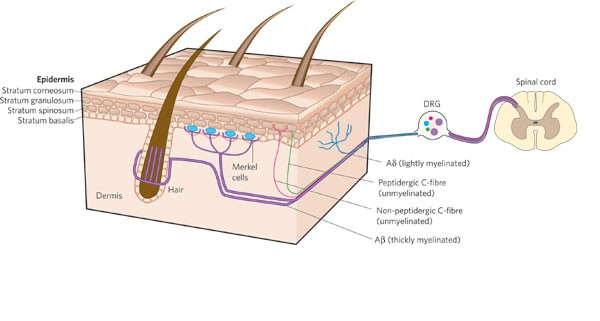
Nociceptors
Free nerve endings for pain
Found in skin, joint capsules, blood vessels, bone coverings
Detects temperature, mechanical damage, chemicals
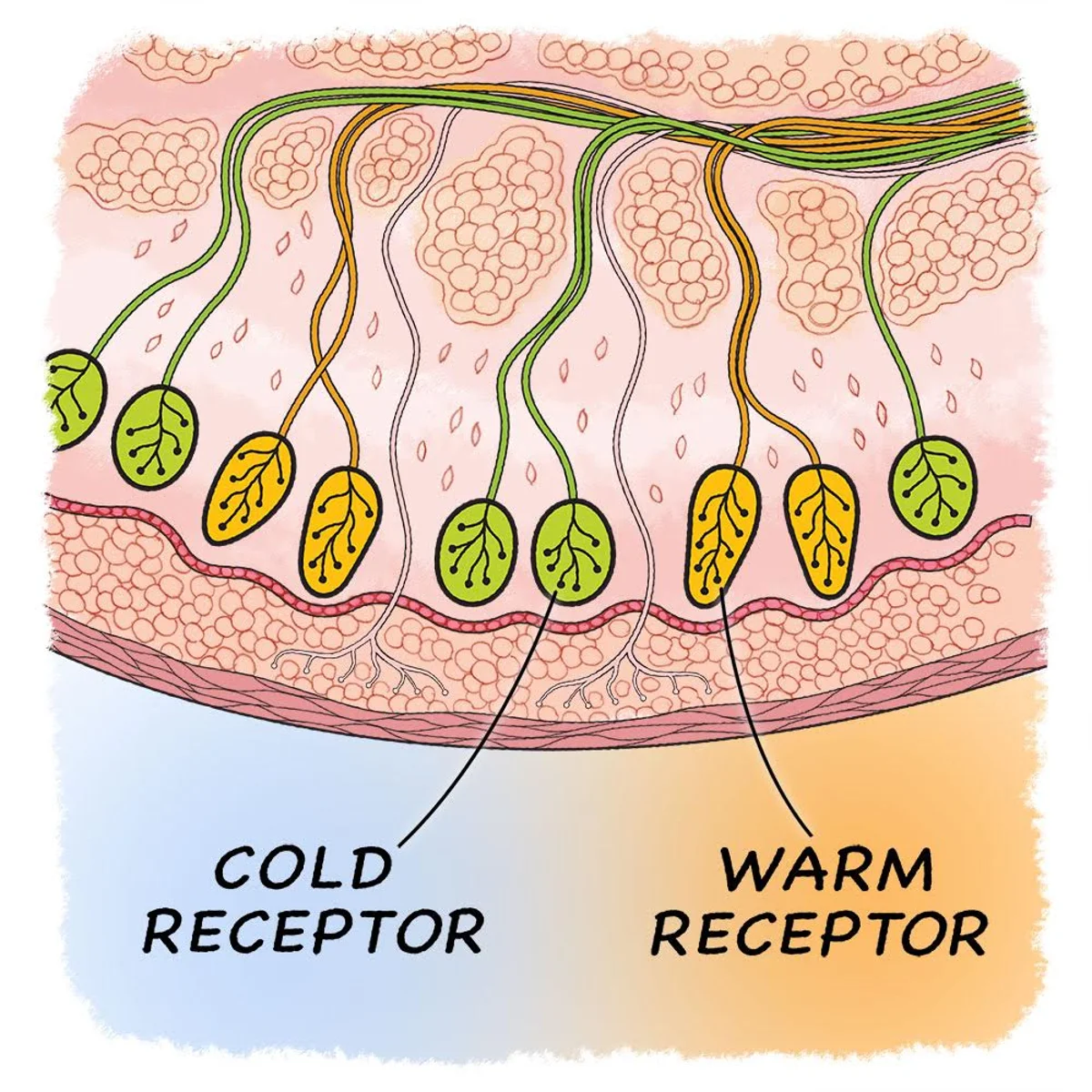
Thermoreceptors
Free nerve endings in dermis, skeletal muscles
Cold and hot receptors (detects changes in temperature)
Mechanoreceptors
Sensitive to stretching, compression, twisting
Consists of tactile receptors (sensitive to touch) and root hair plexus (hair displacement)
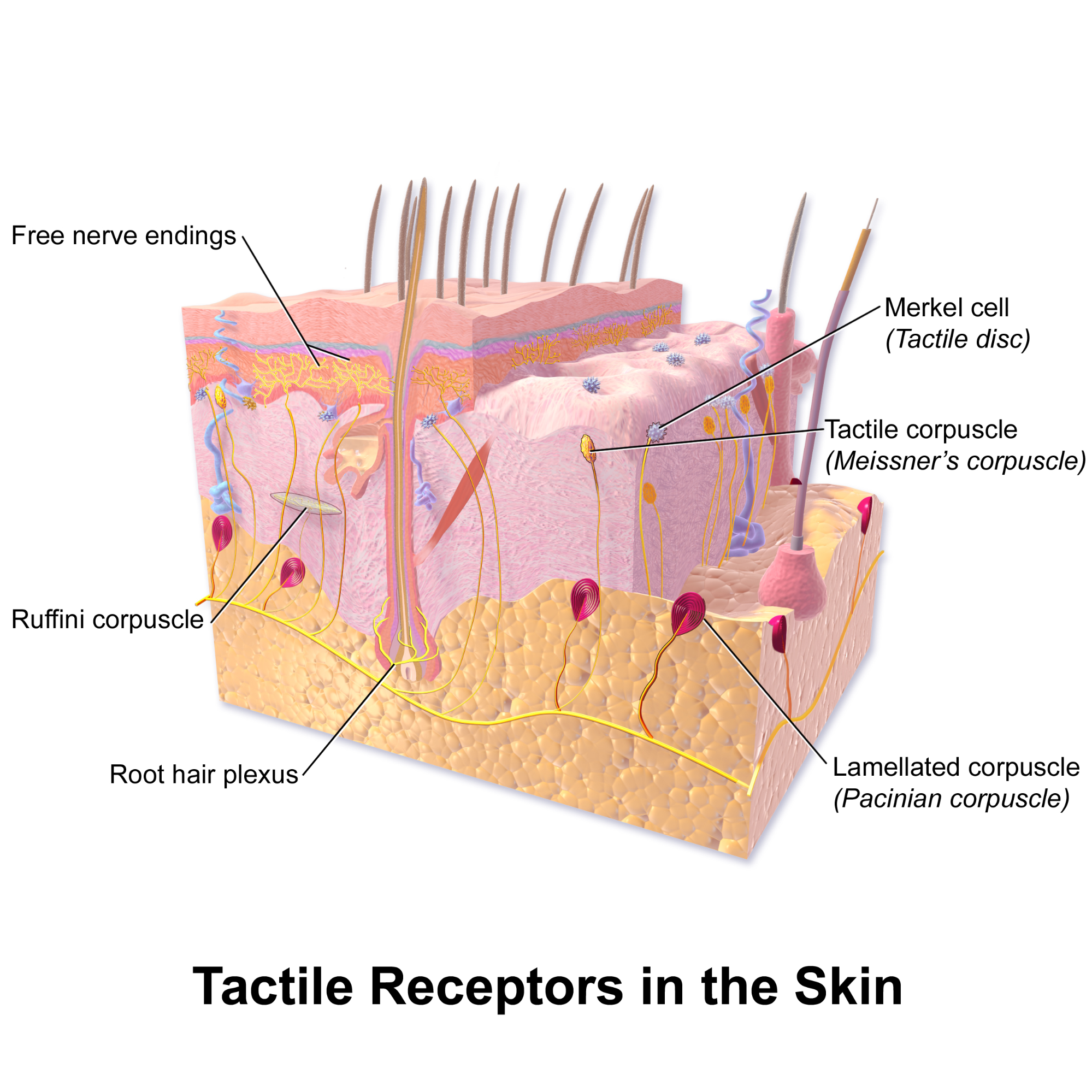
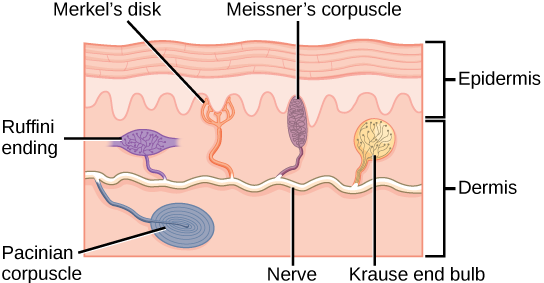
Merkel’s disc
Fine touch and pressure
High % in hairless areas
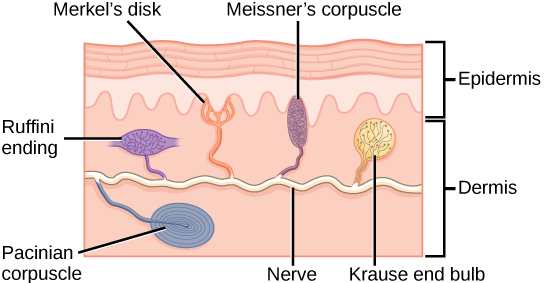
Meissner’s corpuscles
Deep pressure
Found in fingers, genitalia, joint capsules, messenterie
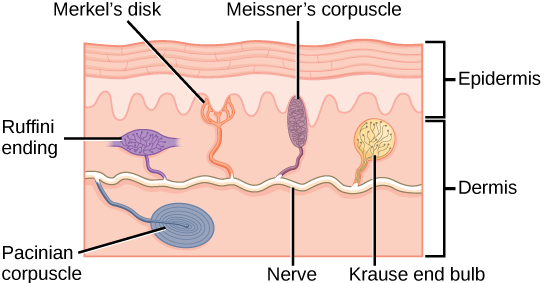
Ruffini corpuscles
Pressure and distribution of skin
Found in deepest layers of dermis