Heart disorders 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Part 2
Normal heart function (refresher)
Ischaemic heart disease*
Myocardial infarction*
Heart failure
Valvular heart disease
Rheumatic heart disease
Infective endocarditis
Pericarditis
Cardiomyopathies
Myocarditis
Heart tumours
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
Understand the difference between rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, risk factors aetiology, pathogenesis and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of infective endocarditis
Be aware of relevant clinical guidelines relating to dental treatment in patients with the above conditions.
Understand the difference between acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
(Q) State the difference between acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
Acute rheumatic fever; Acute, immunologically mediated, multi-system inflammatory disease following group A beta-haemolytic streptococcal infection
[Acute, immunologically mediated, multi-system inflammatory disease]
Rheumatic heart disease: Valvular disease resulting from chronic valve damage as a result of acute rheumatic fever AKA rheumatic valve disease
Term NOT used to describe the “carditis- inflammation in heart- seen in acute rheumatic fever
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
(Q) Define acute rheumatic fever, its causes & epidemiology.
[Acute, immunologically mediated, multi-system inflammatory disease]- AUTOIMMUNE DISORDER
Follows group A streptococcal pharyngitis.
Rare in UK because of improved diagnosis / treatment
15 million in developing countries / poor Western populations
Commonly children 5-15 years
Characterised by delayed, chronic, inflammatory changes in primarily the heart, blood vessels, joints, subcutaneous tissue and CNS – 10 days to 6 weeks post-infection
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
(Q) Describe the process of acute rheumatic fever (PATHOGENESIS)
Hypersensitivity reaction
Combined ANTIBODY and T-CELL response- Immune responses to group A strep (pharyngitis)*
ANTIBODY RESPONSE
Antibodies directed against the M proteins of streptococci
Antibodies Cross-react with self-antigens in heart and other systems)
T CELL RESPONSE
CD4+ T cells specific for streptococcal peptides
React with self proteins (heart and other systems)
Produce cytokines that activate macrophages
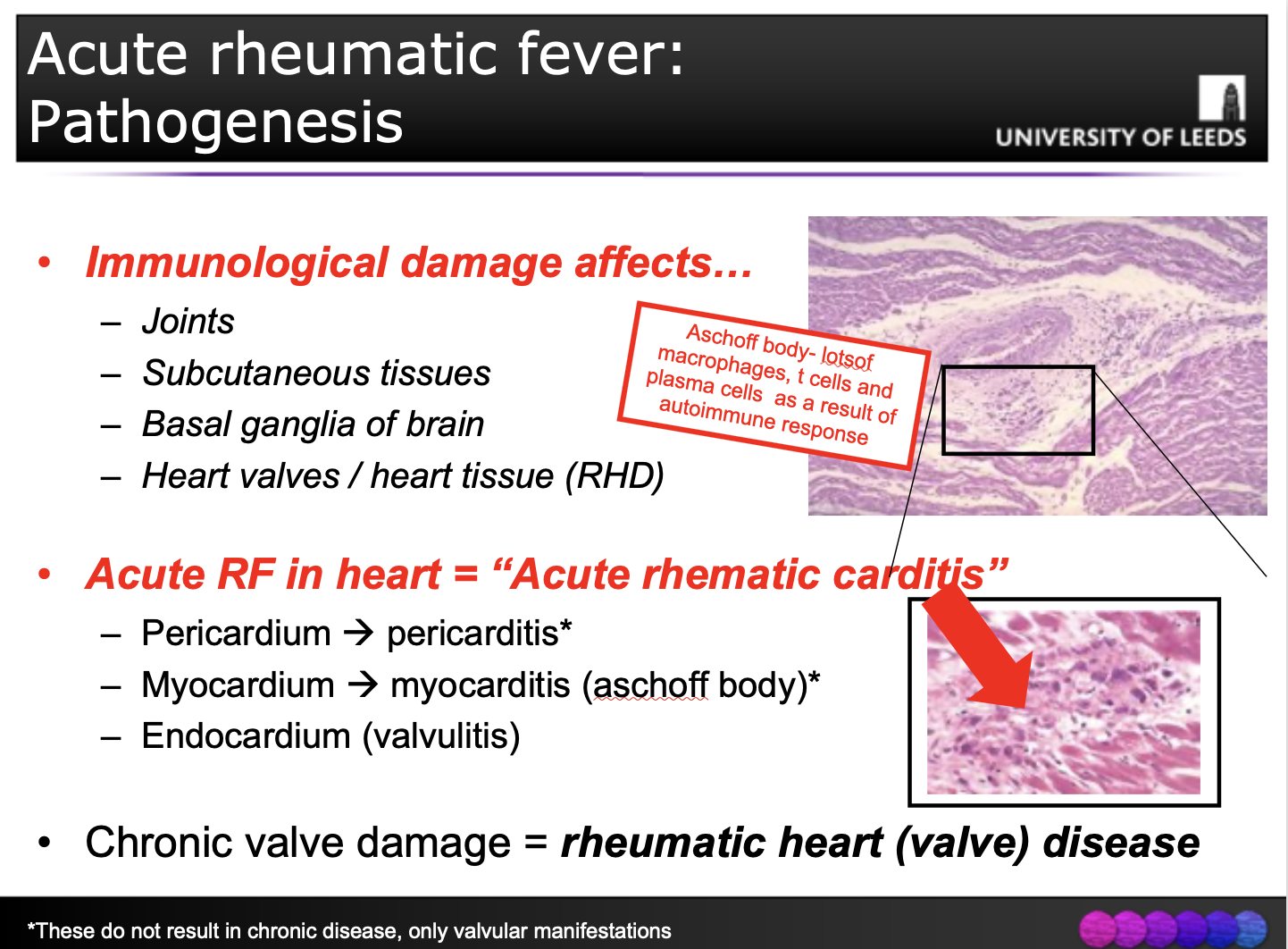
(Q) Describe pathological features of acute rheumatic fever.
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
(Q) State the clinical features of acute rheumatic fever including the diagnosis criteria.
Characterized by systemic symptoms / signs
Migratory polyarthritis of the large joints
Pancarditis
Subcutaneous nodules
Skin lesions
Sydenham chorea (involuntary purposeless movements)
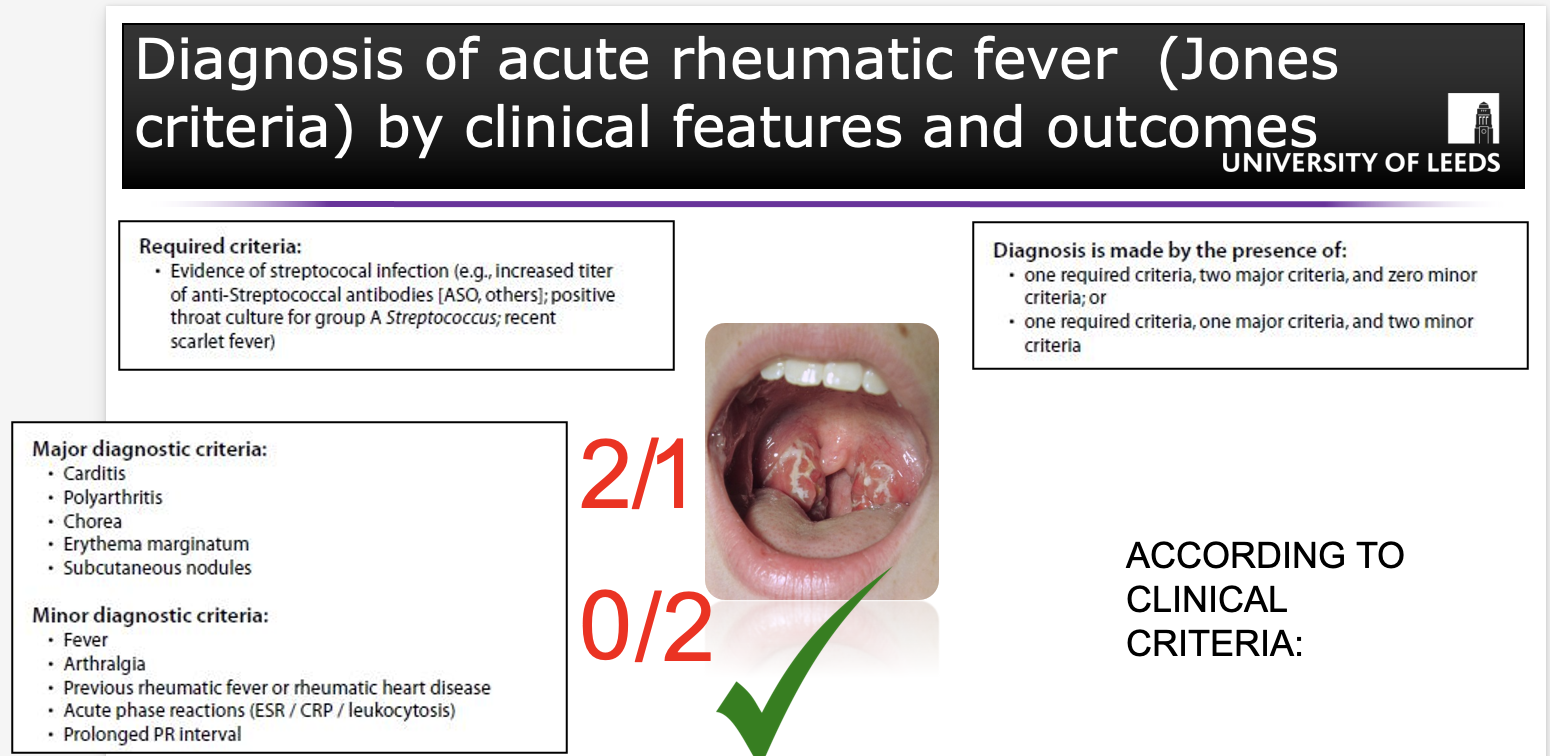
Diagnosis by Jones criteria
Evidence of a preceding group A streptococcal infection
Two of the major manifestations
One major and two minor manifestations (non-specific signs e.g. fever, arthralgia, or elevated blood levels of acute-phase reactants)
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER USING JONES CRITERIA
Presence of streptococcal infection- look for streptococcal antibodies or do a throat swab.
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
(Q) State the MAJOR manifestations/ clinical features of acute rheumatic fever.
10 days to 6 weeks after infection
Major manifestations of acute rheumatic fever are carditis and arthritis
Migratory polyarthritis
One large joint after another becomes painful and swollen for a period of days and then subsides spontaneously, leaving no residual disability.
Acute (pan)carditis – “Acute rheumatic carditis”
Pericardial friction rubs, tachycardia, and arrhythmias.
Myocarditis can cause cardiac dilation that may culminate in functional mitral valve insufficiency or even heart failure
1% of affected individuals die of fulminant RF involvement of the heart.
Know and be able to describe the definition, epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, pathological features and key clinical features (including diagnostic criteria) of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
(Q) Define acute rheumatic fever.
Increased vulnerability to reactivation – recurrent episodes
Valve damage is cumulative and permanent (RHD)
Can develop cardiac hypertrophy (esp. RV), dilation and heart failure
Arrhythmias (esp. atrial fibrillation)
AETIOLOGY: Result of chronic valvular damage
Thromboembolic complications due to atrial dilation / fibril.
Infective endocarditis (coming up!).
Surgical repair or prosthetic replacement of diseased valves
Describe the aetiology, epidemeology, clinical features, and process of rheumatic heart disease (pathology)
(MITRAL STENOSIS!)
Rheumatic heart disease, only cause of mitral stenosis as a result of acute rheumatic fever.
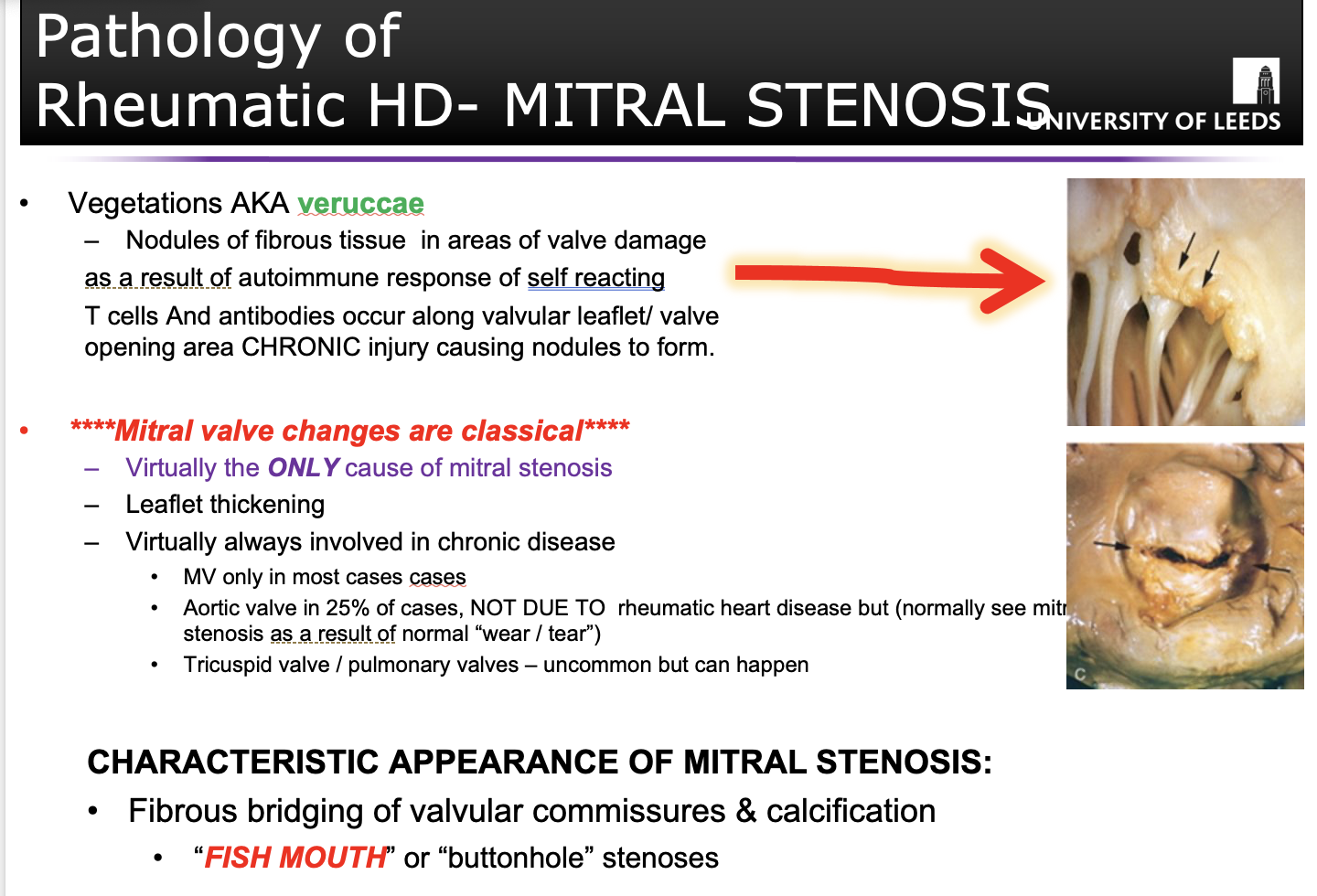
Differentiate between the following:
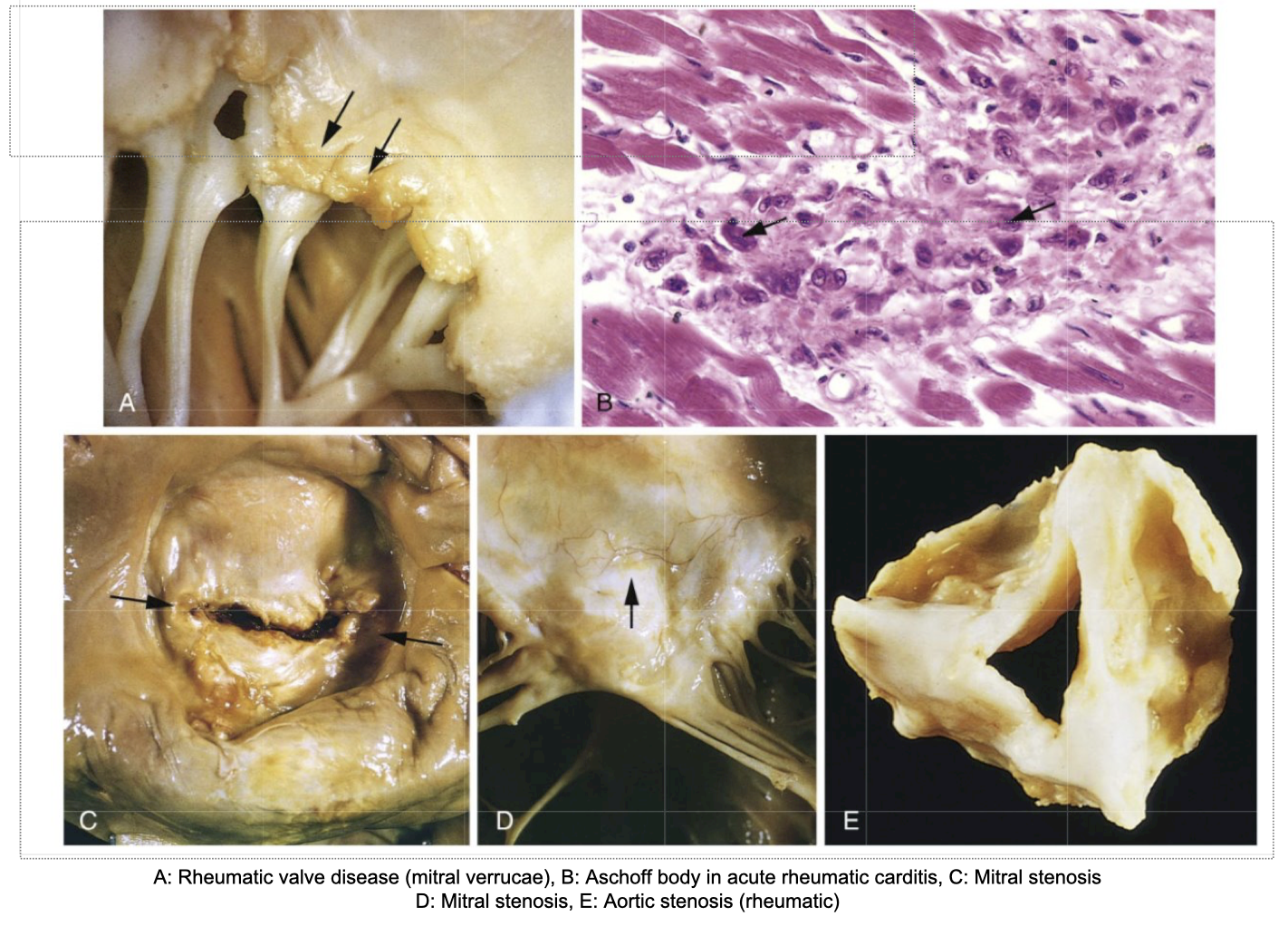
A: Rheumatic valve disease (mitral verrucae)
B: Aschoff body in acute rheumatic carditis, C: Mitral stenosis
D: Mitral stenosis,
E: Aortic stenosis (rheumatic)
(Q) Define endocarditis.
Endocarditis: Inflammation of the endocardium” of the heart
Prototypical lesion = “vegetation” on valves
2 main forms of endocarditis:
Infective endocarditis
Clinically important
Non-infective endocarditis (not need to know much about this)
Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE)
Endocarditis of SLE
(Q) Define infective endocarditis.
Infective endocarditis: Clinically serious infection!!!
Occurs as a result of
the Colonization / invasion of heart valves or heart chamber endocardium by a microbe
The vegetations of infective endocarditis are a……
Mixture of thrombotic debris and organisms
Destroy underlying cardiac tissues
Aorta, aneurysmal sacs, blood vessels, prosthetic valves can also be infected
Most cases caused by bacterial infection
- Fungi / other classes can also cause
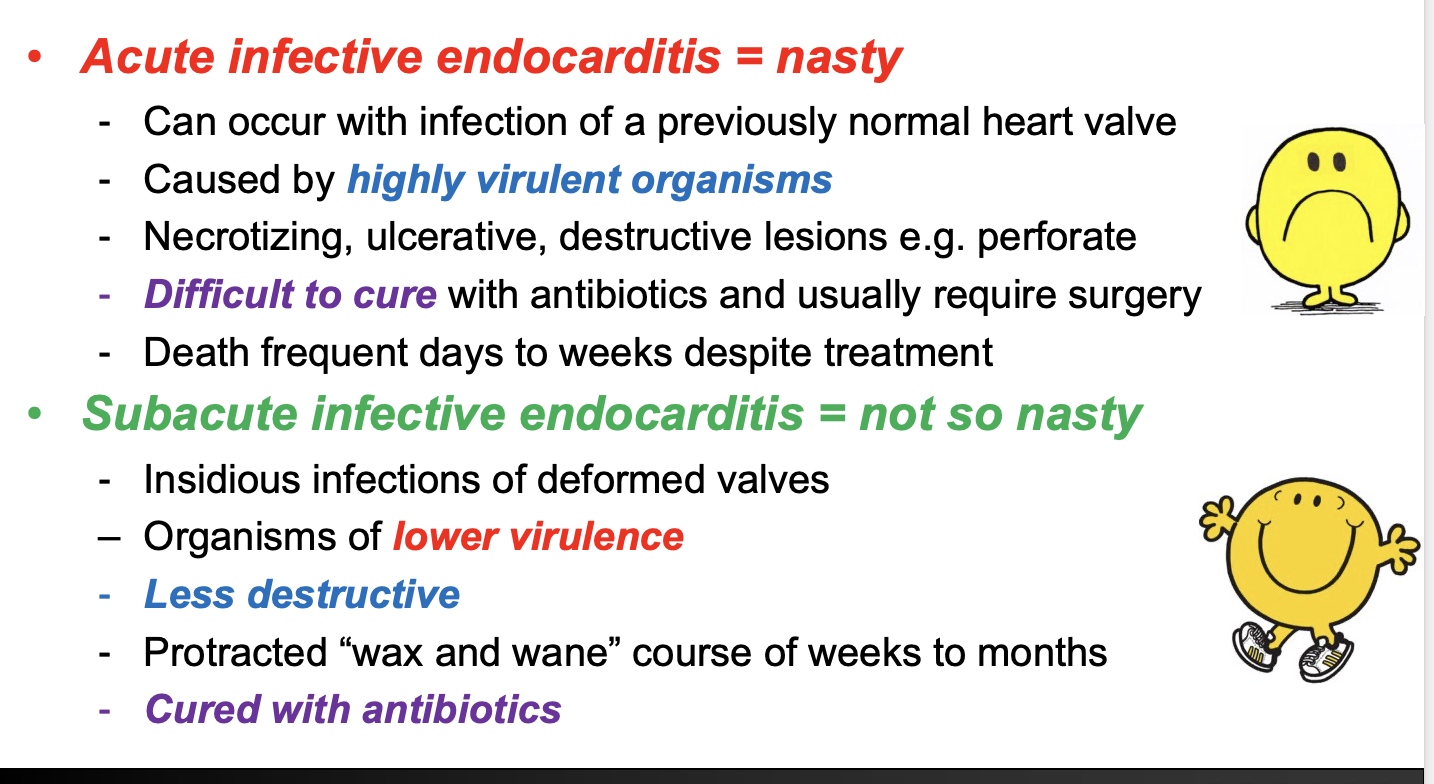
(Q) Describe the difference between the 2 subtypes of infective endocarditis.
Acute infective endocarditis = nasty
Subacute infective endocarditis = not so nasty
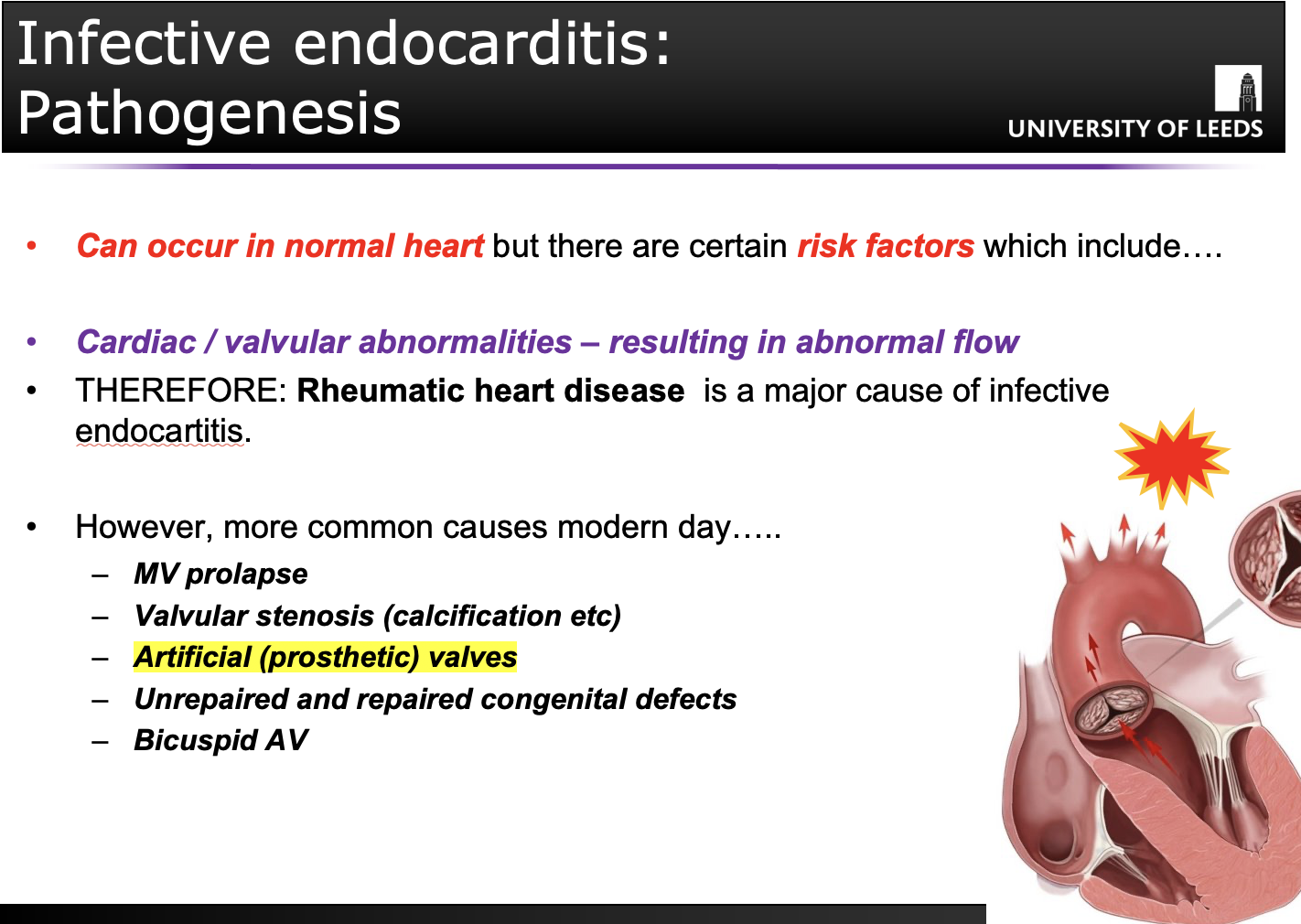
(Q) State the 2 contributory factors which cause infective endocarditis
Organisms present in bloodstream to cause infection
Cardiac vascular abnormality resulting in abnormal flow, promoting adherence and growth
(Q) State the possible causes of infective endocarditis.
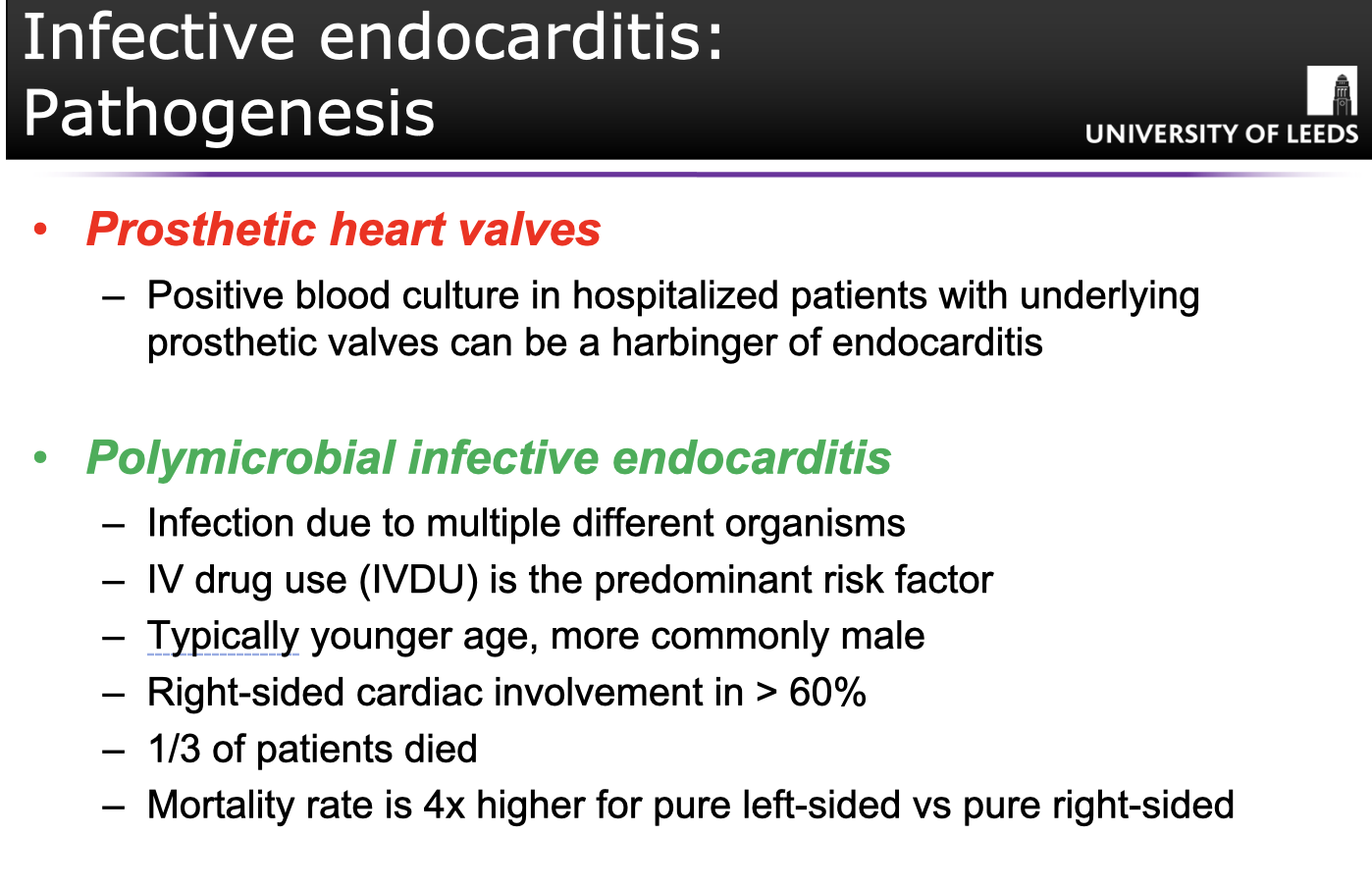
(Q) Describe 2 key risk factors of infective endocarditis. (factors which make people more vulnerable to infective endocarditis)
(Q) State the risk factors for the development of infective endocarditis.
*Anything that affects blood flow through heart will put you at risk of infective endocarditis.
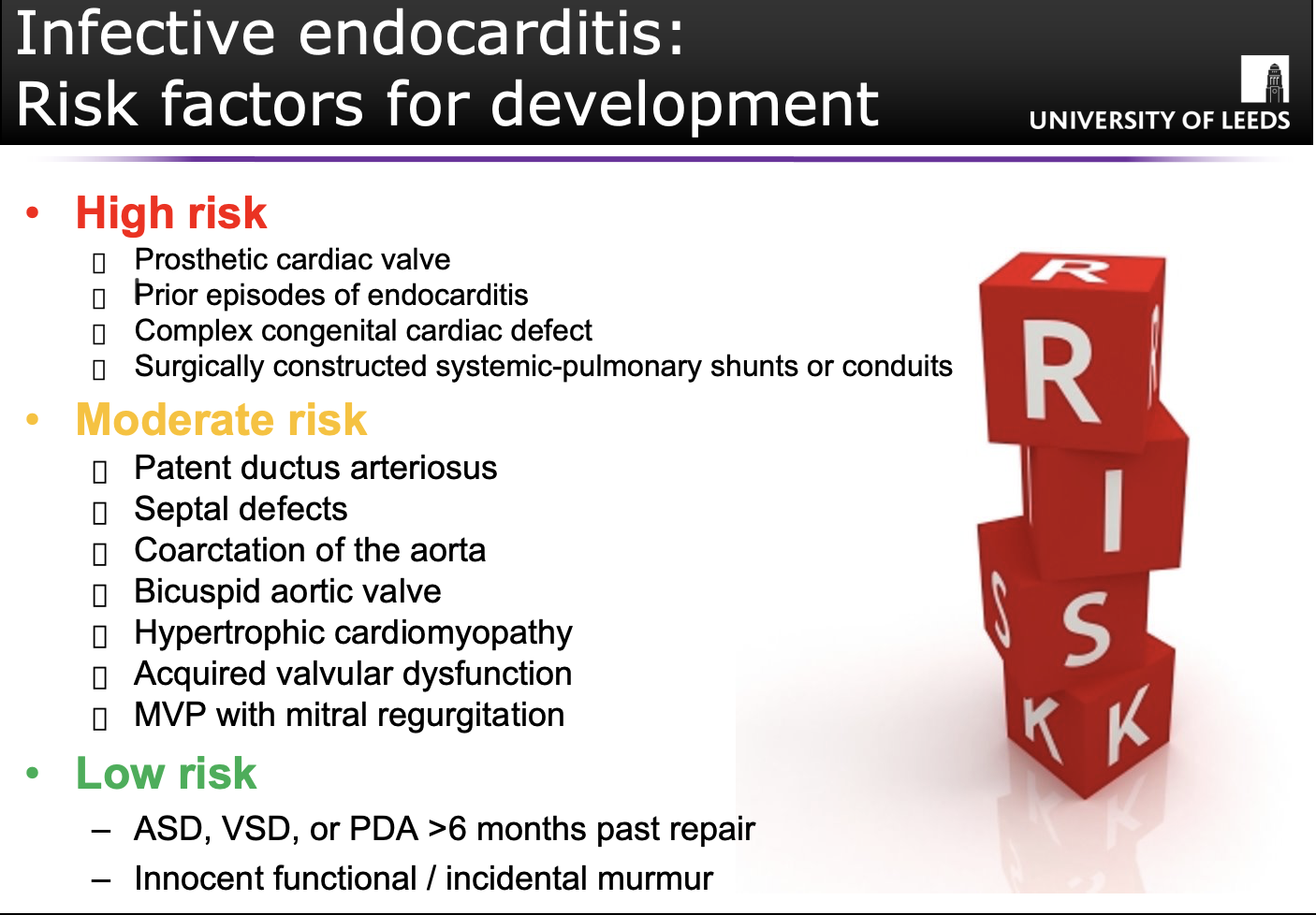
(Q) How do organisms mainly bacteria get into the bloodstream to cause infective endocarditis?
Most common organisms involved:
s. viridans
s. aureus
s.epidermis
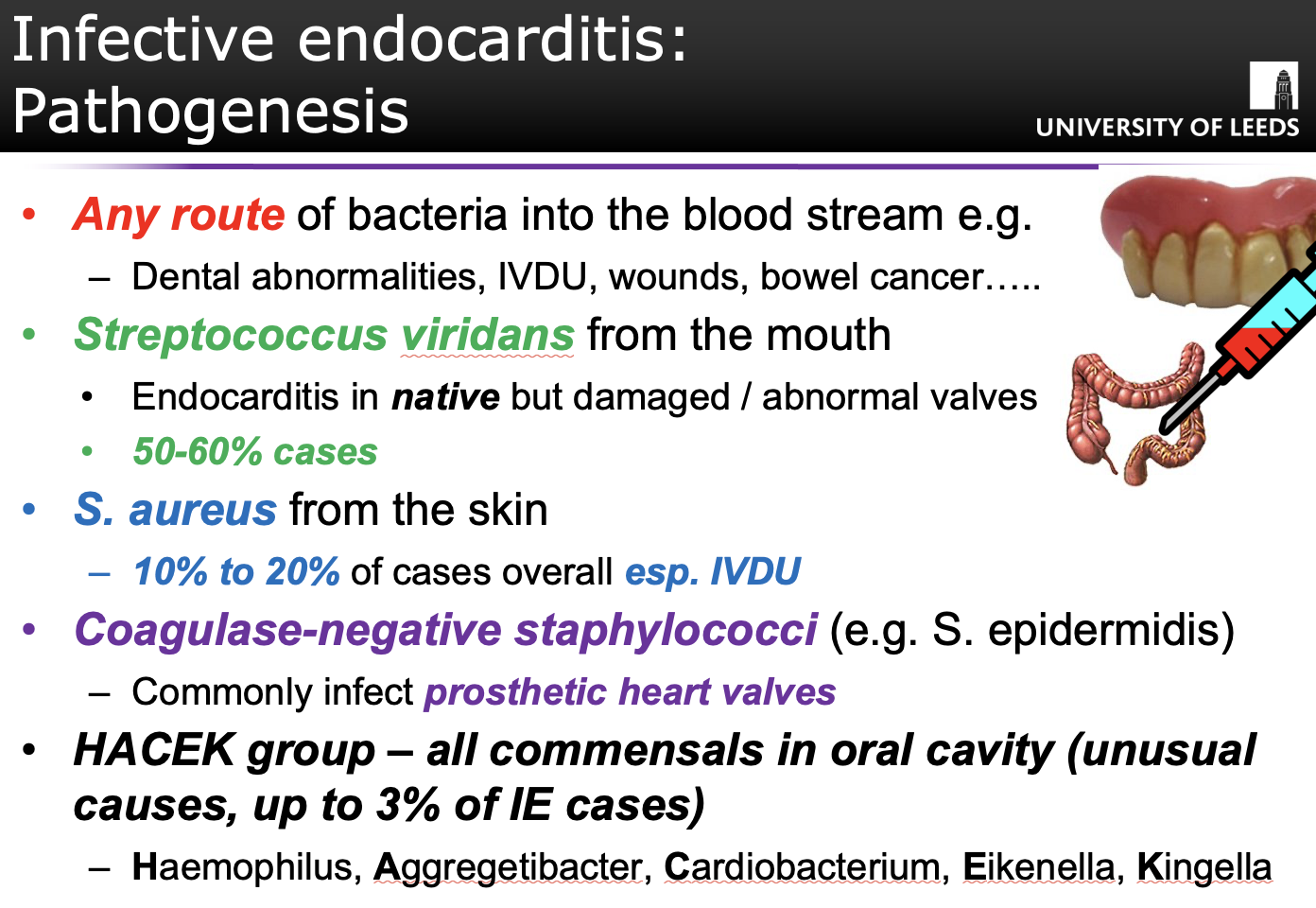
(Q) What is culture negative endocarditis?(5-10% of cases)
When you suspect endocarditis but cannot isolate causative agent (5-10% of cases)
Sometimes patients are given antibiotic therapy suppressing infection detected in the blood.
Deeply embedded organisms within enlarging vegetation
Organisms that fail to grow in normal blood cultures
- Coxiella burnetiid
- Chlamydia spp.
- Bartonella spp.
- Legionella.
(Q) Describe the pathological features of infective endocarditis.
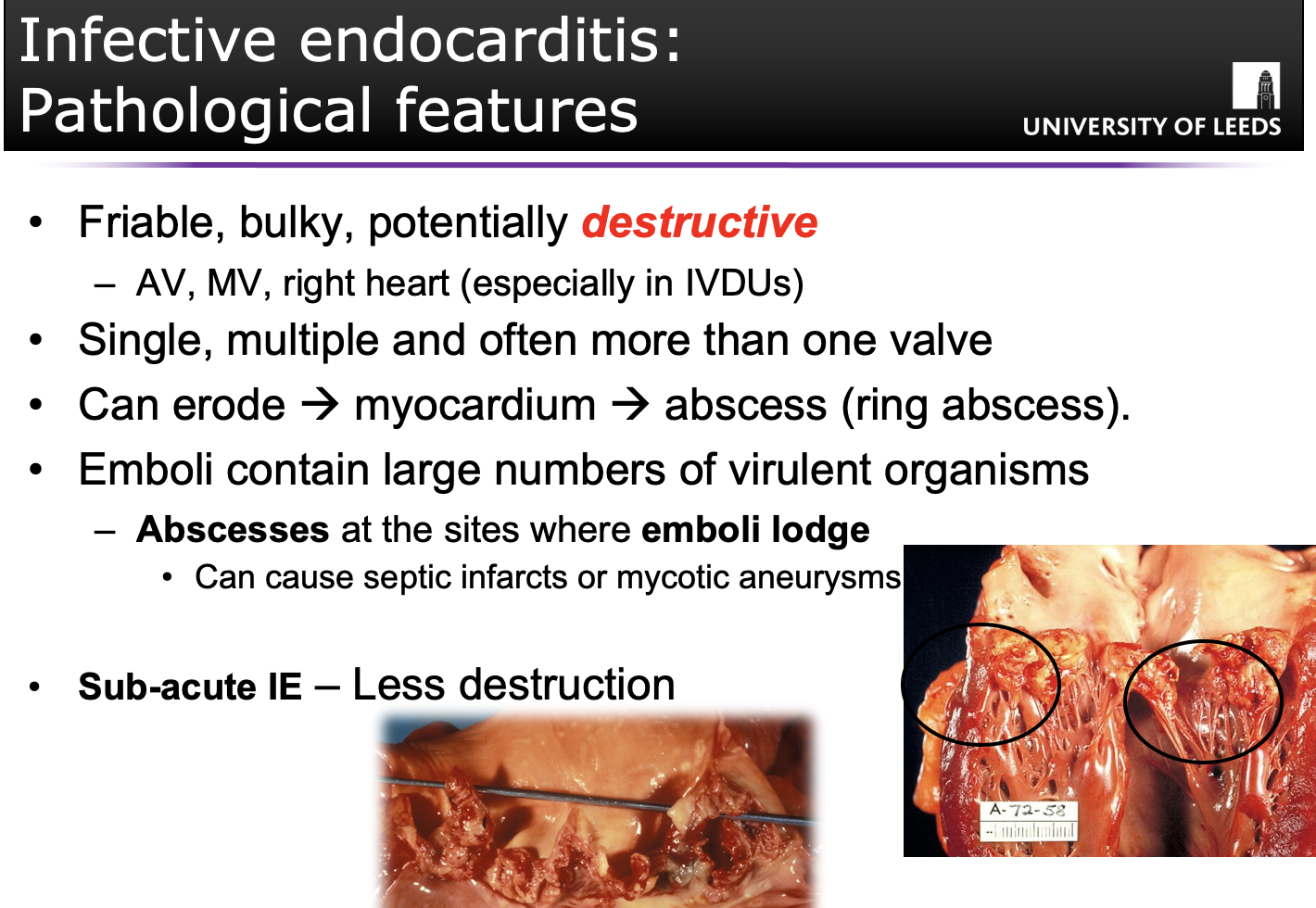
(Q) State the clinical features of infective endocarditis.
New heart murmur + fever = infective endocarditis!
Until proven otherwise
Patients can present with acute illness and the classic features of a new/changing heart murmur and fever
Infective endocarditis: Diagnosed using Duke Criteria

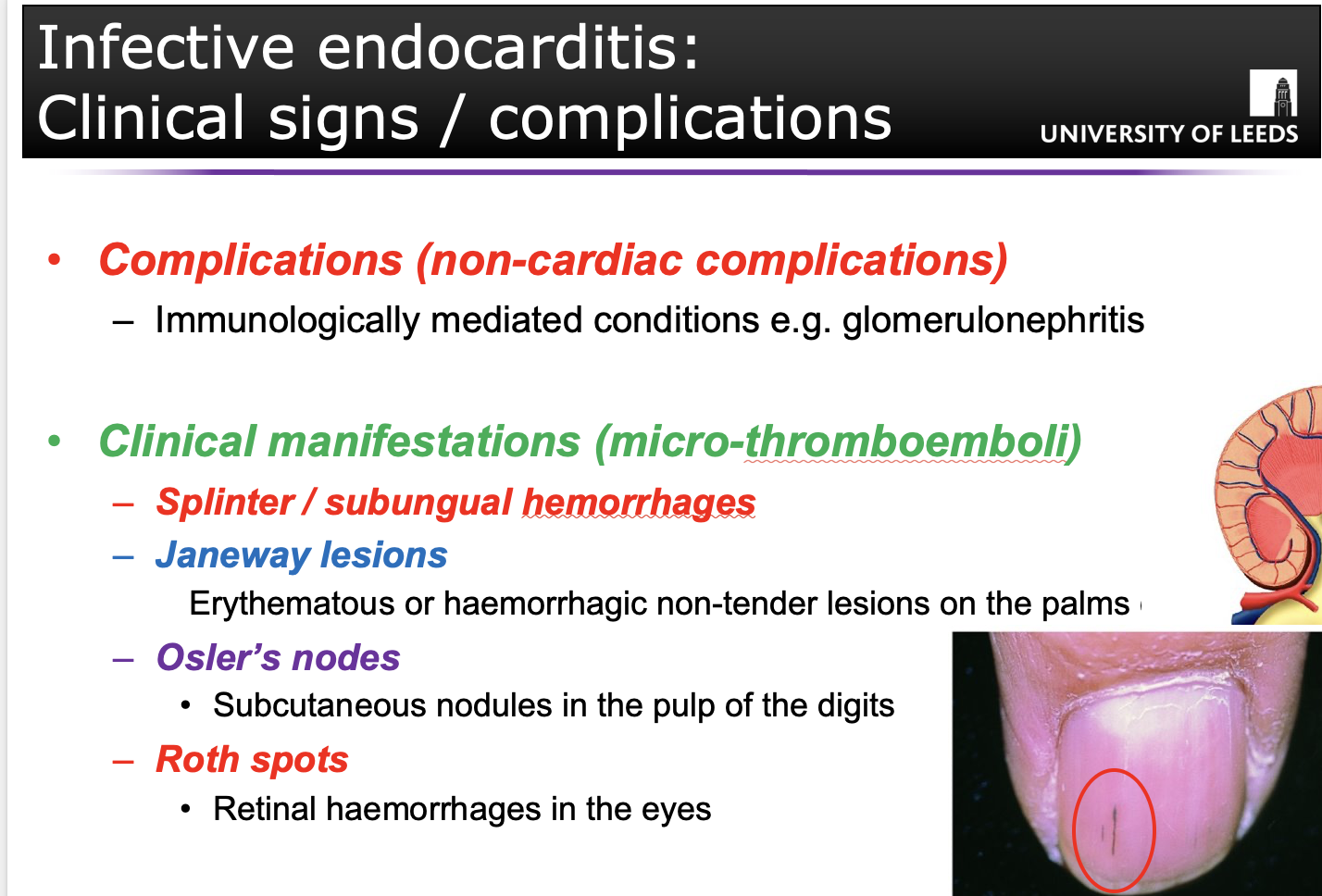
(Q) State the clinical signs and complications of infective endocarditis.
JANE WAY LESION:
F – Fever
R – Roth spots
O – Osler’s nodes
M – Murmurs
J – Janeway Lesions
A – Anaemia
N – Nail (splinter) haemorrhage
E – Emboli (septic)
(Q) State the treatment for infective endocarditis.
Organisms protected within vegetation so difficult to treat
High concentrations of IV antibiotics for approx 4-6 weeks
- Adjusted according to culture results
- Penicillin common (or alternative broad spectrum if allergic)
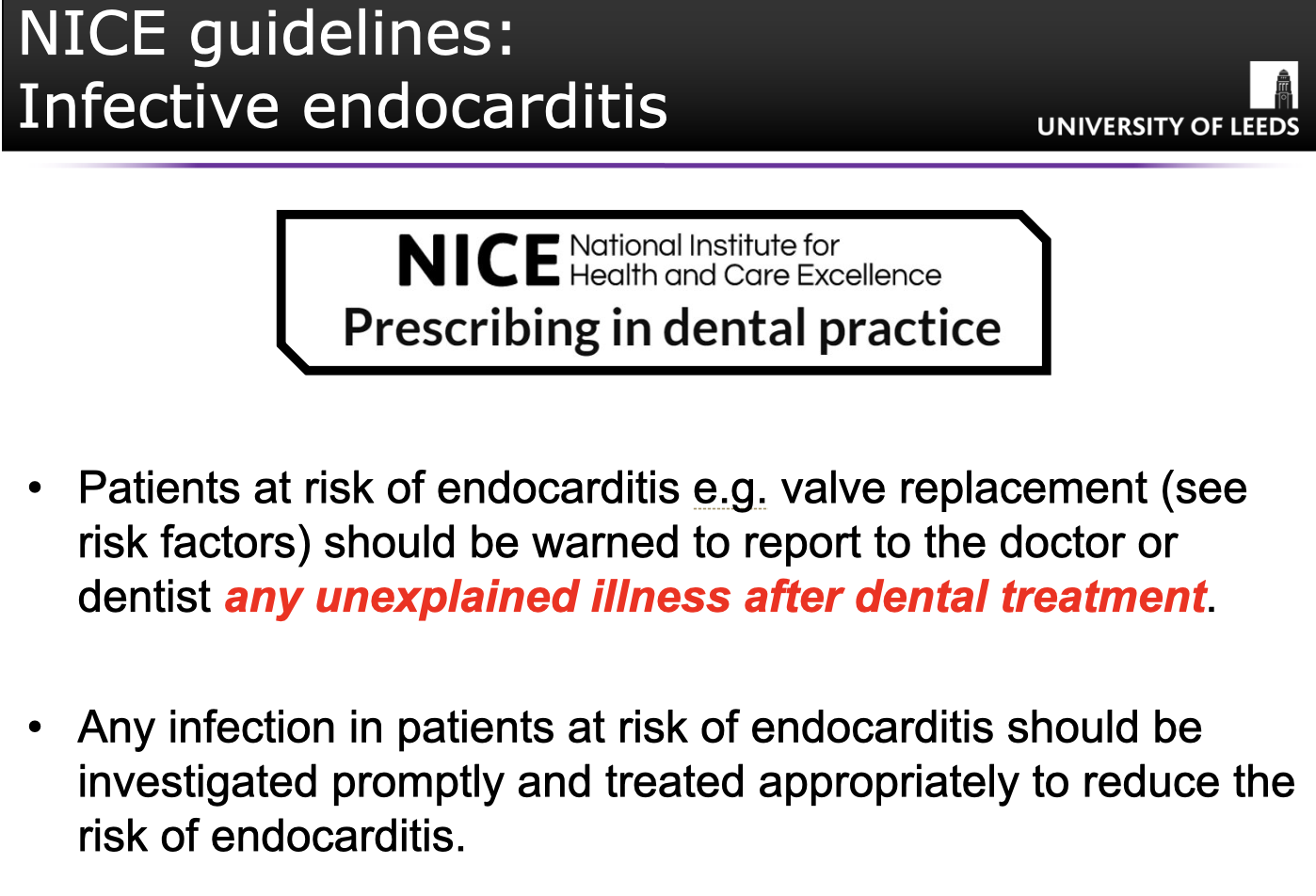
NICE GUIDLINES FOR PREVENTION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARITIS:
Reduction of oral bacteria- maintain high standards of oral hygiene as reduces need for prevention.