Action potential graph
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
1a
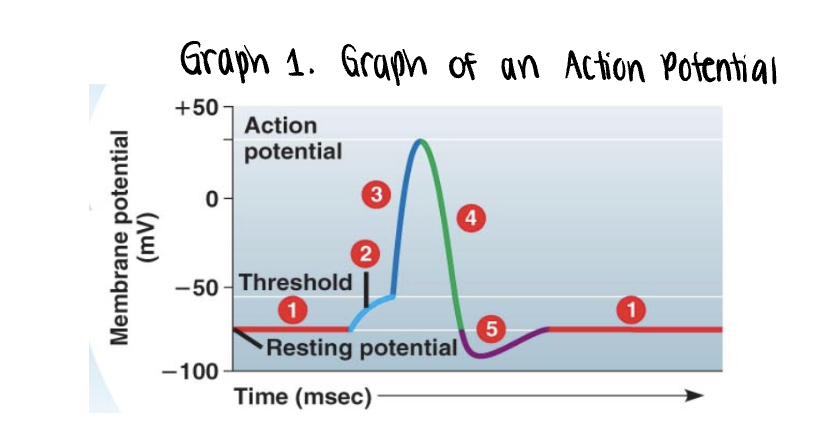
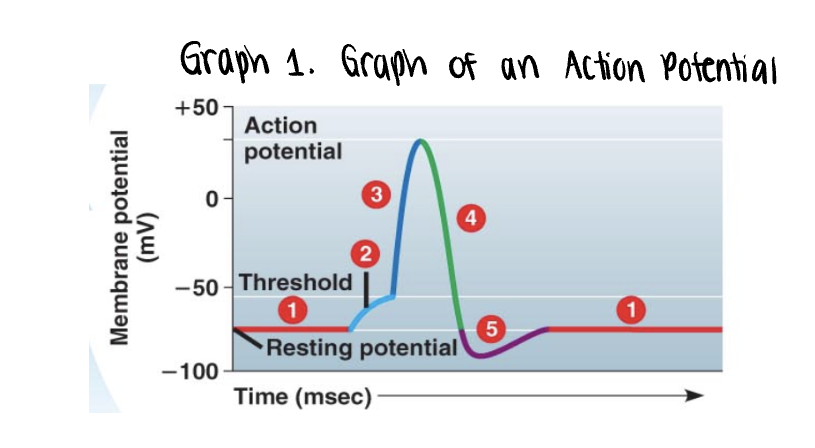
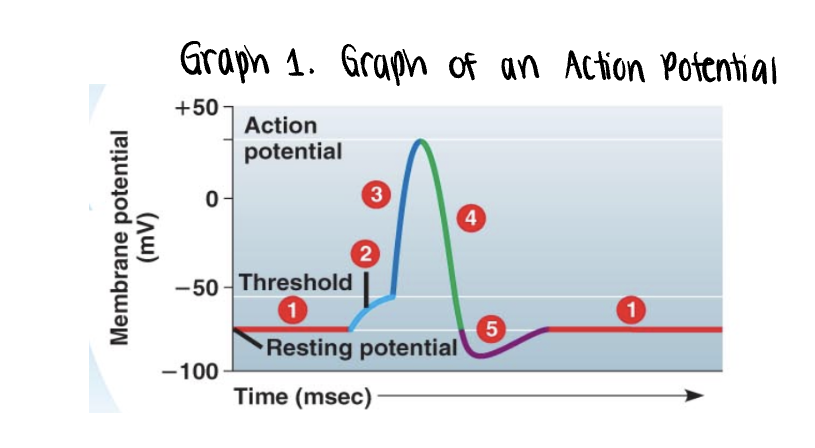
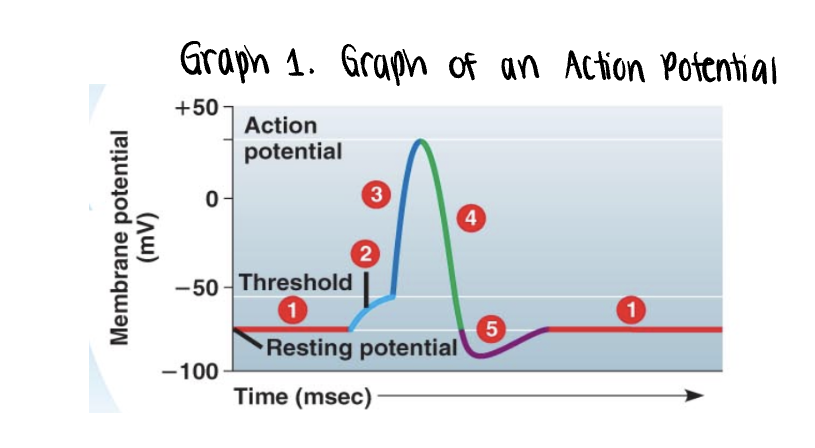
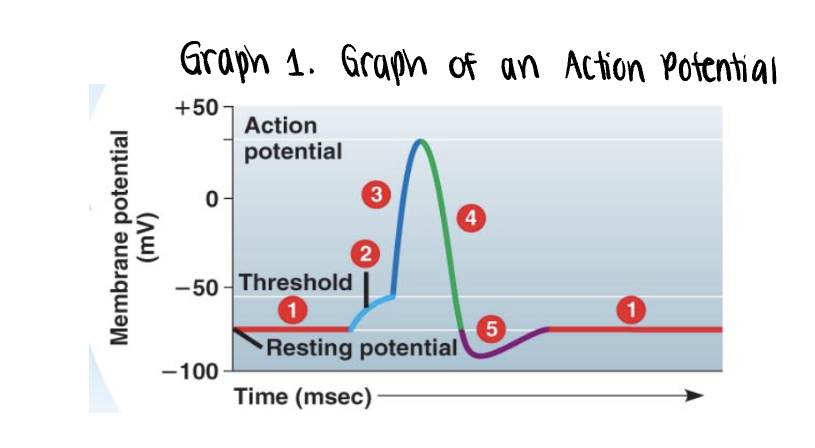
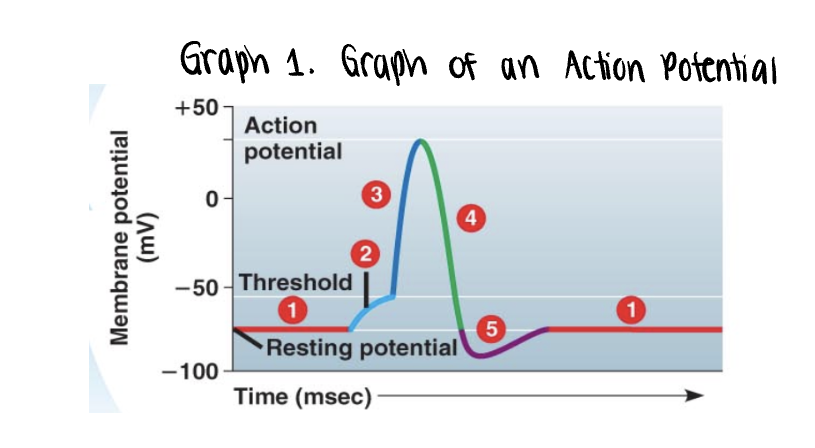
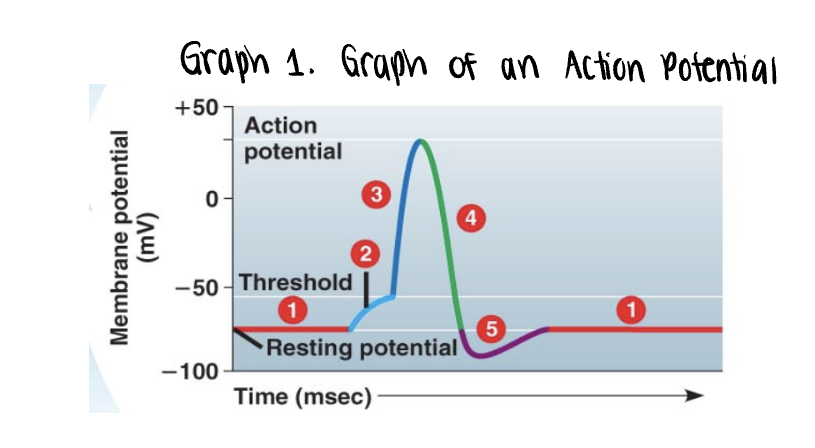
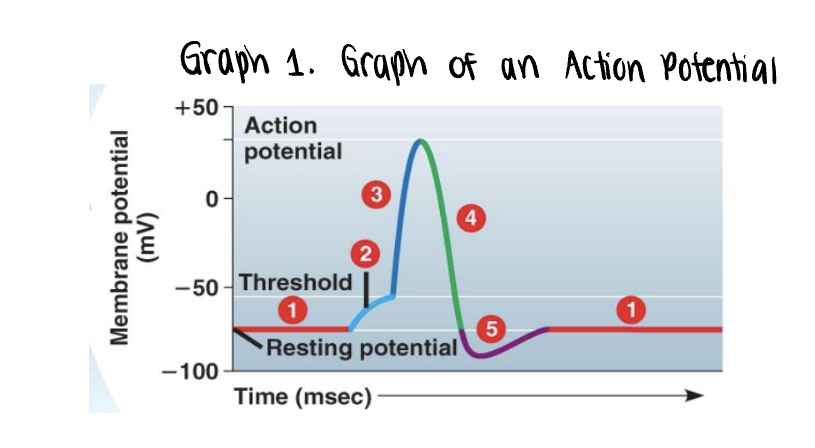
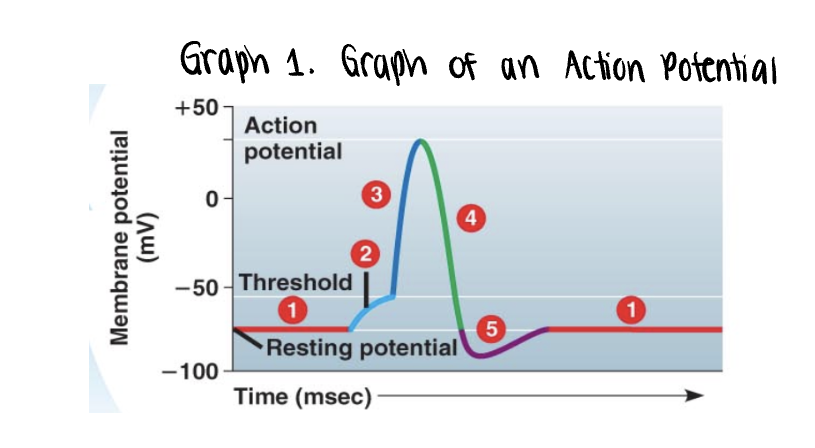
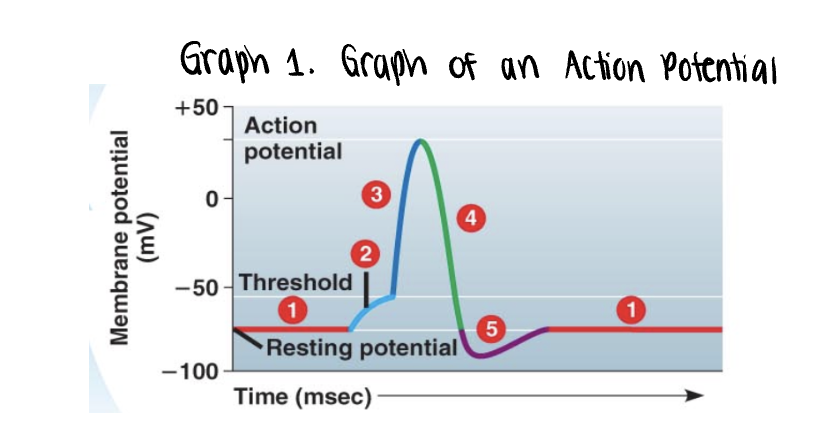
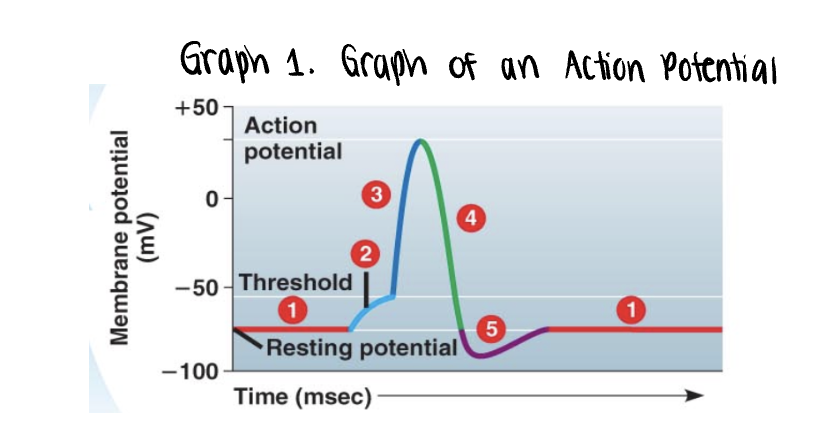
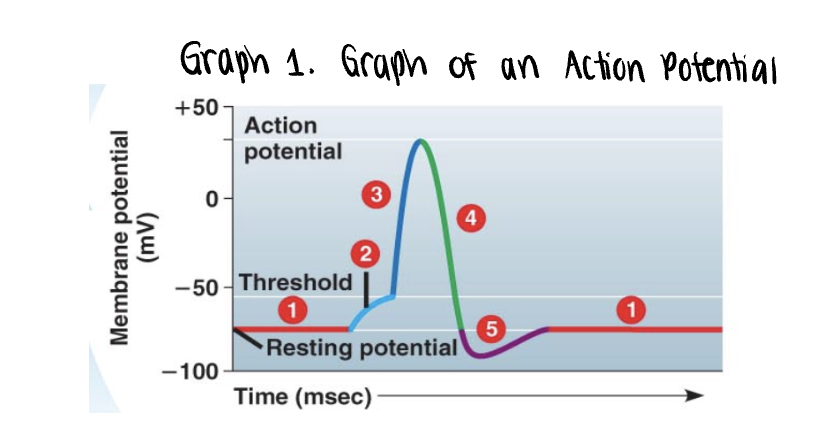
the graph stars at the membranes resting potential ______mV
both voltage gated Na+ y K+ gates remain ______
the graph stars at the membranes resting potential (-70mV)
both voltage gated Na+ y K+ gates remain closed
2
_______ is applied
this triggers the ______ of a few ___ ____ Na+ gates
if it is strong enough, the voltage rises to what is called the _______ (_____mV)
stimulus is applied
this triggers the opening of a few non voltage Na+ gates
if it is strong enough, the voltage rises to what is called the threshold (-55mV)
3
once the ______ is reached, the _____ potential is triggered
voltage gated ___+ channels open, allowing even more ___+ to diffuse into the cell
the membrane polarity is reversed abruptly (______) —→ becomes more positvely charged
as more ___+ moves into the axon, the voltage soars to its peak (approximately ____mV)
once the threshold is reached, the action potential is triggered
voltage gated Na+ channels open, allowing even more Na+ to diffuse into the cell
the membrane polarity is reversed abruptly depolarization —→ becomes more positvely charged
as more Na+ moves into the axon, the voltage soars to its peak (approximately +35mV)
4
the peak voltage triggers _____ and inactivation of the voltage gated __+ channels
meanwhile the voltage gated K+ channel ______, allowing K+ to ______ out
membrane rapidly _________ as voltage drops back down
___+/___+ pump will also assist in _____ process by actively pumping 3 ___+ out of the axon for every 2 ___+ into the axon
______ takes approx 0.001s or 1ms. this time frame is known as the _______ period. an impulse ______ be activated during this time
4
the peak voltage triggers closing and inactivation of the voltage gated Na+ channels
meanwhile the voltage gated K+ channel opens, allowing K+ to diffuse out
membrane rapidly repolarizes as voltage drops back down
Na+/K+ pump will also assist in repolarization process by actively pumping 3 Na+ out of the axon for every 2K+ into the axon
repolarization takes approx 0.001s or 1ms. this time frame is known as the refractory period. an impulse cannot be activated during this time
5
a very brief undershoot of the resting potential (__________) results because K+ channels close slowly
a very brief undershoot of the resting potential (hyperpolarization) results because K+ channels close slowly
6
the membrane then returns to its ______ potential
the membrane then returns to its resting potential