Cog Neuro
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
1
New cards
Neurons
cells in the nervous system that communicate with one another to perform information-processing tasks
2
New cards
Glia
Cells that support the functionality of the neurons by providing physical support, supplying nutrients and enhancing neuronal communication.
3
New cards
Cell Body (soma)
The part of a neuron that coordinates information-processing tasks and keeps the cell alive.
4
New cards
Dendrites
The part of the neuron that receives information from other neurons and relays it to the cell body.
5
New cards
Axon
The part of a neuron that transmits information to other neurons, muscles or glands.
6
New cards
Myelin Sheath
An insulating layer of fatty material made up of glial cells.
7
New cards
Synapse
The junction or region between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites or cell body of another.
8
New cards
Sensory Neurons
Neurons that receive information from the external world and and convey this information to the brain vis the spinal cord.
9
New cards
Motor Neurons
Neurons that carry signals from the spinal cprd to the muscles to produce movement.
10
New cards
Interneurons
Nerons that connect sensory neurons, motor neurons or other interneurons.
11
New cards
Resting Potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neurons cell membrane.
12
New cards
Action Potential
An electric signal that is conducted along the length of a neuron's axon to a synapse.
13
New cards
Refractory Period
The time following an action potential during which a new action potential cannot be initiated.
14
New cards
Terminal Buttons
Knoblike structures that branch out from an axon.
15
New cards
Cognitive Neuroscience
the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition with a specific focus on the neutral substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain.
16
New cards
Why Neuroscience matters?
Humans (and animals) are biological systems
The basic assumption of all modern neuroscience and psychology: Mental functions are the product of activity in the nervous system
The basic assumption of all modern neuroscience and psychology: Mental functions are the product of activity in the nervous system
17
New cards
What does the nervous system do?
Receives sensory information from the environment
Integrates and processes information
Regulates internal functions
Produces motor actions
Integrates and processes information
Regulates internal functions
Produces motor actions
18
New cards
Levels of Observation:
Genes & DNA - make up
Cells - basic units of structure/function
Tissues - groups of cells of same kind
Organs - structures composed of more than one tissue, work together to perform specific function
Systems - groups of organs that work together to perform specific function
Body
Cells - basic units of structure/function
Tissues - groups of cells of same kind
Organs - structures composed of more than one tissue, work together to perform specific function
Systems - groups of organs that work together to perform specific function
Body
19
New cards
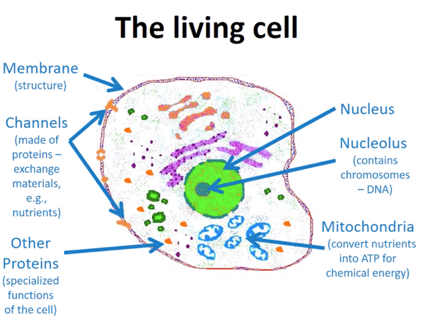
Structure of a living cell:
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Channels
Other proteins
Membrane
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Channels
Other proteins
Membrane
20
New cards
How many cells are there in the brain?
170 billion - 85 billion neurons, 85 billion glia cells
21
New cards
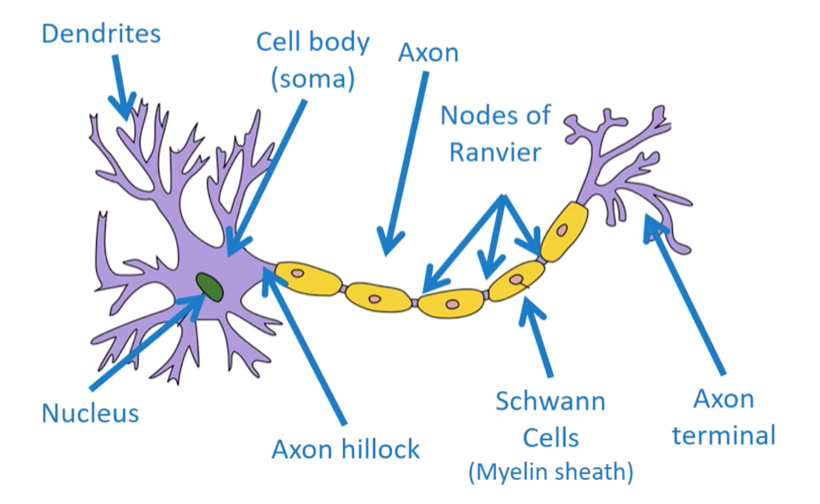
The structure of a neuron:
Nucleus
Cell Body (Soma)
Dendrites
Axon
Axon Hillock
Myelin Sheath
Axon terminal
Cell Body (Soma)
Dendrites
Axon
Axon Hillock
Myelin Sheath
Axon terminal
22
New cards
Axon Hillock
Receives inputs from different cells and sends them along the axon.
23
New cards
Axon Terminal
forms synapses with dendrites of other neurons
24
New cards
Communication WITHIN a synapse is...
Electrical
25
New cards
Communication BETWEEN synapses are...
Chemical
26
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit information across the synapse to a receiving neuron's dendrites.
27
New cards
Receptors
Parts of the cell membrane that receive neurotransmitters and initiate a new electrical signal.
28
New cards
Spacial Summation
when the dendrites are stimulated from various neighbouring cells.
29
New cards
Temporal Summation
one cell repeatedly trying to stimulate a cell
30
New cards
Action Potential
Electricity:
most single atoms have an electric charge, charged atoms are called ions
An overall difference in charge between nearby areas creates an electric potential (aka voltage)
Chemistry:
Diffusion - particles diffuse to equate concentrations across space
most single atoms have an electric charge, charged atoms are called ions
An overall difference in charge between nearby areas creates an electric potential (aka voltage)
Chemistry:
Diffusion - particles diffuse to equate concentrations across space
31
New cards
What is multiple sclerosis?
Autoimmune disease where one's own immune system damages the myelin sheath.
32
New cards
Type of neuron in the cerebellum?
Purkinje cell
33
New cards
Type of neuron in hippocampus?
Pyramidal cell
34
New cards
Type of neuron in Retina?
Bipolar cell
35
New cards
Motor neuron disease is...
a family of diseases in which motor neurons degenerate and die, leading to weakness, paralysis and eventually death
36
New cards
Synaptic Transmission
Communication BETWEEN neurons
37
New cards
EPSP
Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential
38
New cards
IPSP
Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential
39
New cards
Excitatory Signal
tells neurotransmitter to fire
40
New cards
Inhibitory Signal
tells neurotransmitter NOT to fire
41
New cards
Glutamate
most common excitatory neurotransmitter\
important for learning and memory
too much -> seizures/migraines
OCD
important for learning and memory
too much -> seizures/migraines
OCD
42
New cards
GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid)
most common inhibitory neurotransmitter
counteracts glutamate
regulates and prevents over-excitation
GABA deficiency -> seizures, tremors, insomnia/increased responsiveness to stress
Increased risk of anxiety disorders and phobias
counteracts glutamate
regulates and prevents over-excitation
GABA deficiency -> seizures, tremors, insomnia/increased responsiveness to stress
Increased risk of anxiety disorders and phobias
43
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Regulates motor control
Excitatory in synapses between neurons and skeletal muscles
Inhibitory in synapses between neurons an the heart
important for attention, learning, memory, arousal...
too much -> role in depression
deficiency -> alzheimer's disease -> degeneration of cholinergic neurons
Excitatory in synapses between neurons and skeletal muscles
Inhibitory in synapses between neurons an the heart
important for attention, learning, memory, arousal...
too much -> role in depression
deficiency -> alzheimer's disease -> degeneration of cholinergic neurons
44
New cards
Dopamine
Important role in movement, motivation
Tied to addiction
too much -> inked to schizophrenia
deficiency -> tremors, difficulty initiating and stopping movement -> parkinsons disease
Tied to addiction
too much -> inked to schizophrenia
deficiency -> tremors, difficulty initiating and stopping movement -> parkinsons disease
45
New cards
Serotonin
regulates mood, appetite, sleep
involved in arousal and aggression
involved in cognitive functions -> learning and memory
involved in arousal and aggression
involved in cognitive functions -> learning and memory
46
New cards
Endorphins
chemicals that act within the pain pathways and emotion centres of the brain
47
New cards
Agonists
drug that mimics or increases the action of a neurotransmitter
48
New cards
Antagonist
Drug that blocks the effect of a neurotransmitter
49
New cards
Block reuptake agonists:
Prozac (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) & Cocaine (blocks dopamine, norepinephrine & serotonin reuptake)
50
New cards
Increase production of neurotransmitter agonist:
L-dopa (precursor of dopamine, used for parkinson's)
51
New cards
Increase neurotransmitter release agonist:
Amphetamines (stimulate release of dopamine and norepinephrine)
52
New cards
Agonist - Blind and activate post-synaptic receptors:
Nicotine (activates Ach receptors)
Cannabis (activates CB1 cannabinoid receptor - anandamide)
Cannabis (activates CB1 cannabinoid receptor - anandamide)
53
New cards
Antagonist - prevent release of neurotransmitter:
Botulinum Toxin (prevents ACh vesicles from fusing with membrane)
54
New cards
Antagonist - bind to post synaptic receptor and block it:
Haloperidol (prevents dopamine from activating receptors by blocking them; used to treat schizophrenia)
55
New cards
Nervous System
an interacting network of neurons that conveys electrochemical cells throughout the body -> the bodys command centre
56
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
part of the nervous system that is composed of the brain and the spinal cord
57
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
part of nervous system that connects the central nervous system to the body's organs and muscles
"outside the brain and spinal cord"
"outside the brain and spinal cord"
58
New cards
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
nerves that convey information into and out of the central nervous system
important for forming movements
attached to bones/tendons that allow us to move
important for forming movements
attached to bones/tendons that allow us to move
59
New cards
Automatic Nervous System (ANS)
set of nerves that carry involuntarily and automatic commands that control blood vessels, body organs and glands.
60
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
A set of nerves that prepare the body for action in a threatening situation.
increases arousal
survival related action
***FOUR F'S***
increases arousal
survival related action
***FOUR F'S***
61
New cards
Parasympathetic Nervous system
a set of nerves that help the body return to a normal resting state
reduces arousal
reduces arousal
62
New cards
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems act in a _________ manner...
CO-ORDINATED
63
New cards
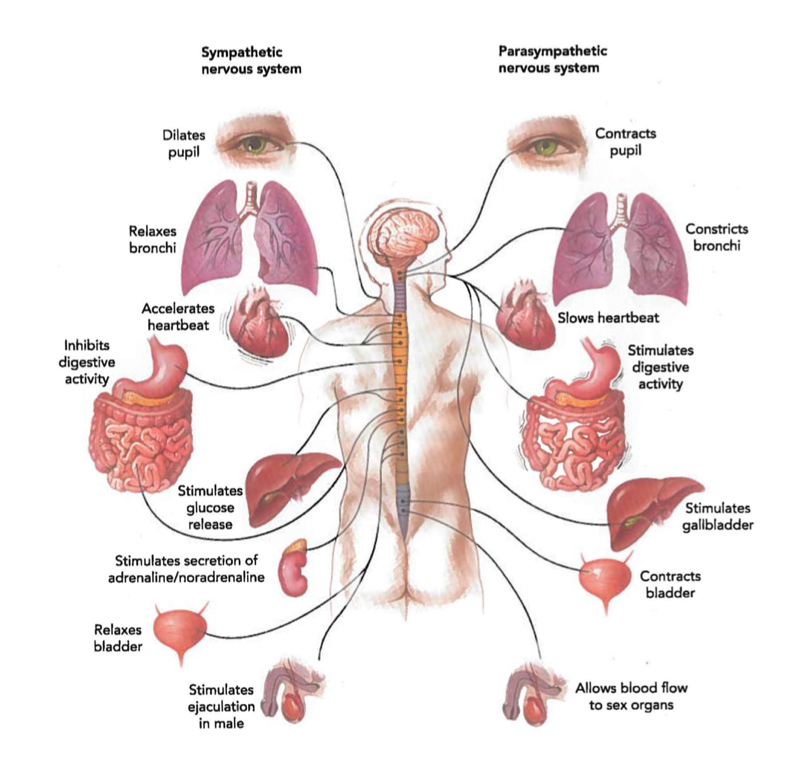
SYMP vs PARASYMP
- eyes
- bronchi
- heartbeat
- digestive activity
- glucose release/gallbladder
- adrenaline??
- bladder
- sex organs?
- eyes
- bronchi
- heartbeat
- digestive activity
- glucose release/gallbladder
- adrenaline??
- bladder
- sex organs?
64
New cards
Central Nervous System Terminology: 4 Legged Mammal
- Front
- Back
- Above
- Below
- Front
- Back
- Above
- Below
Front - rostral/anterior
Back - caudal/posterior
Above - dorsal
Below - Ventral
Back - caudal/posterior
Above - dorsal
Below - Ventral
65
New cards
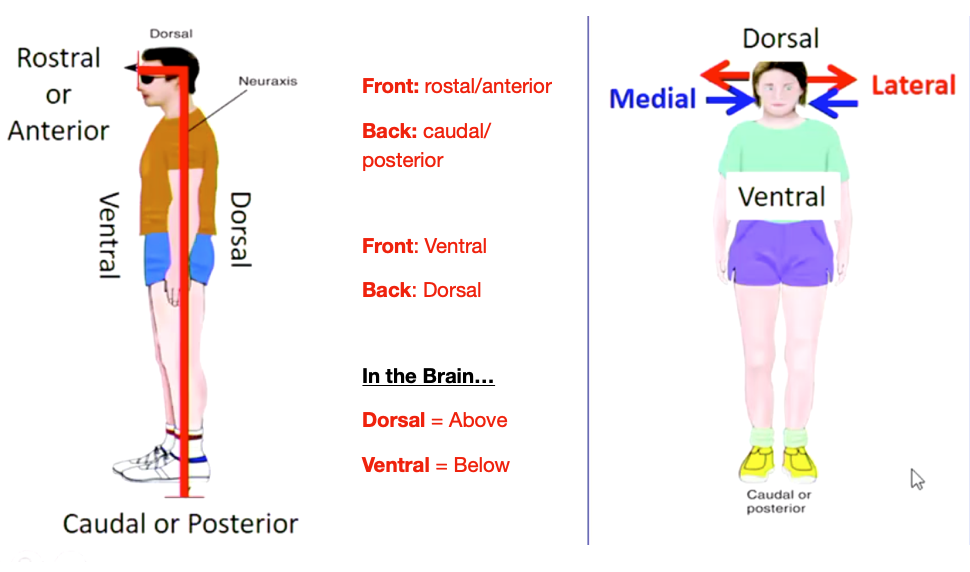
Central Nervous System Terminology: 2 Legged Mammal (Human)
- Front
- Back
- Front
- Back
- Front
- Back
- Front
- Back
Front - rostral/anterior
Back - caudal/posterior
Front - Ventral
Back - Dorsal
Back - caudal/posterior
Front - Ventral
Back - Dorsal
66
New cards
Central Nervous System Terminology: In the Brain
- Above
- Below
- Above
- Below
Above - Dorsal
Below - Ventral
Below - Ventral
67
New cards
Spinal Column
- made up of tiny bones
- vertebrae protect the spinal cord
- vertebrae protect the spinal cord
68
New cards
Spinal Reflexes
Simple pathways in the nervous system that rapidly generate muscle contractions
69
New cards
Hindbrain
An area of the brain that coordinates information coming into and out of the spinal cord.
70
New cards
Dorsal horn location and function...
back of spinal cord
receives sensory information
receives sensory information
71
New cards
Ventral horn location and function...
Front of spinal cord
sends signals to thee body to initiate motor movement
sends signals to thee body to initiate motor movement
72
New cards
Gray matter (cortex)...
where the cell bodies are in the brain (dendrites)
73
New cards
White matter...
where myelinated axons are in the brain
74
New cards
Left/Right function in the brain...
Left control right side of body
Right controls left side of body
Right controls left side of body
75
New cards
Left/Right function in the spinal cord...
Left controls left side of body
Right controls right side of body
Right controls right side of body
76
New cards
Dorsal/Ventral Horn effect whether one has difficulty with....
Paralysis (ventral)
Sensation (dorsal)
Sensation (dorsal)
77
New cards
Folds within the brain allow for more...
cortex
78
New cards
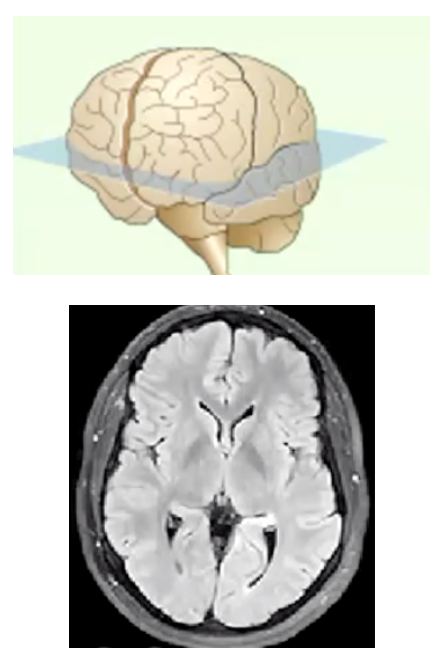
Name the view/slice of the brain...
Horizontal/Axial/Transverse
79
New cards
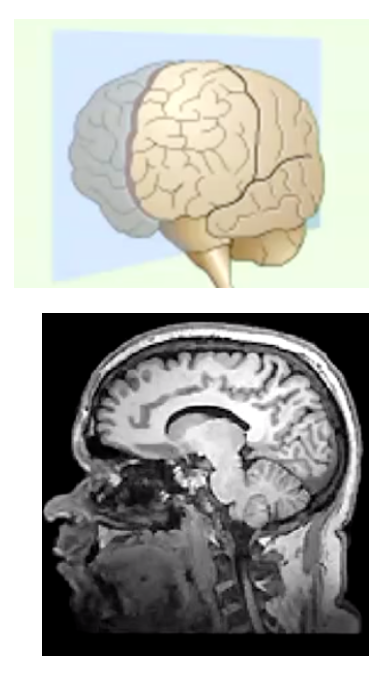
Name the view/slice of the brain...
Sagittal
80
New cards
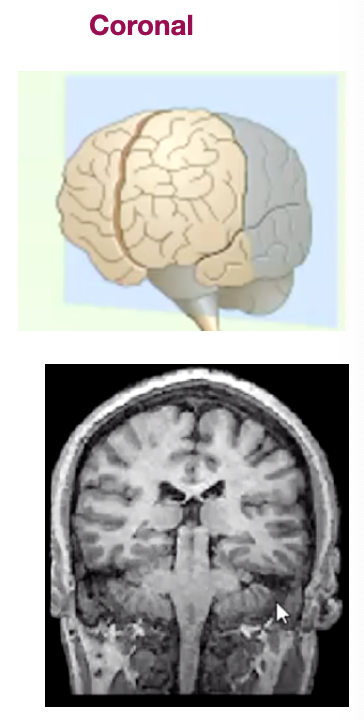
Name the view/slice of the brain...
Coronal
81
New cards
The 3 major divisions of the brain are....
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
82
New cards
Hindbrain
an area of the brain that coordinates information coming into and out of the spinal cord
83
New cards
The hindbrain is phylogenetically ancient means that....
it was the first developed part of the brain (in terms of evolution)
84
New cards
The 4 parts to the hindbrain are...
Pons
Medulla
Reticular Formation
Cerbellum
Medulla
Reticular Formation
Cerbellum
85
New cards
Medulla
an extension of the spinal cord into the skull that coordinates heart rate, circulation and respiration
vital to survive -> damage can cause heart and lungs to stop
vital to survive -> damage can cause heart and lungs to stop
86
New cards
The term "brain stem dead" means....
There has been damage to the medulla
87
New cards
Reticular Formation
regulates sleep/wake cycle & arousal levels
88
New cards
cerebellum
controls fine motor skills
89
New cards
Pons
relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
90
New cards
Midbrain
Important to coordinate the basic functions related to perception and action
91
New cards
Tectum
spatial orienting to an environment
92
New cards
In the tectum, the SUPERIOR colliculi is responsible for...
visual orientation
93
New cards
In the tectum, the INFERIOR colliculi is responsible for...
auditory orientation
94
New cards
Tegmentum
movement, arousal and pleasure seeking
95
New cards
Substantia Nigra
part of tegmentum
high level of dopamine can give it a dark colour
plae colour -> parkinsons
high level of dopamine can give it a dark colour
plae colour -> parkinsons
96
New cards
Forebrain
highest level of the brain - both literally and figuratively
split into the cerebral cortex and the subcortial structures
split into the cerebral cortex and the subcortial structures
97
New cards
Cerebral cortex
outermost layer of the brain - visible to the naked eye and split into two hemispheres
98
New cards
Subcortial structures
areas of the forebrain housed under the cerebral cortex near the very centre of the brain
99
New cards
Basal Ganglia
plans initiation of intentional movements
100
New cards
Thalamus
relays and filters information from the senses to the cortex (except smell)