enthalpy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Definition of first ionization energy
The energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous +1 ions
Enthalpy of atomization
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from its elements in its standard state.
First electron affinity
The energy released when one mole of gaseous atoms gains one mole of electrons to form one mole of 1- ions
Enthalpy of formation
the enthalpy change when one mole of substance is formed from its elements under standard conditions with all reactants and products in their standard states.
Define Bond enthalpy
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous covalent bonds are broken
Lattice Enthalpy of formation
The energy released when one mole of an ionic solid compound in its standard state is formed from its constituent gaseous ions.
In a Born-Habor cycle what is usually on the right side?
Lattice Enthalpy formation/dissociation of the compound and electron affinity
Enthalpy of hydration
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous ions dissolves in water to form one mole of hydrated ions under standard conditions.
E.g Na+ + aq → Na+ (aq) \Delta H hydration= negative
Cl-(g) → Cl - (aq)
Enthalpy of solution
The Enthalpy change when one mole of ionic compound is dissolved in water to form separate aqueous ions under standard conditions
E.g NaCl (s) → Na+ ions(aq) + Cl- ions(aq)
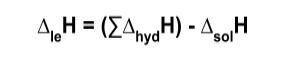
Equation with lattice Enthalpy of formation and hydration and solution
Enthalpy of lattice= sum of Enthalpy of hydration - Enthalpy of solution
Born-haber cycle
Is an Enthalpy/hess cycle composed of all the Enthalpy changes involved in the formation of 1 mole of ionic compound from its constituent elements in their standard states.
Explain the difference between the Theoretical and experimental values of lattice Enthalpy
Theoretical values assume that the compound is purely ionic
Experimental values are usually higher than the theoretical value, because the lattice Enthalpy is greater due to polarization.
So there is a large discrepancy between them
What two things affect the Enthalpy of hydration?
The size and charge of the molecule
What 2 assumptions in the perfect ionic model?
All the ions are perfectly spherical- even charge distribution
The ions display no covalent character (only electrostatic attraction)
Suggest 2 ways covalent character occurs in ions
The two ions have varying sizes
The two ions have varying charges
both cause uneven charge distribution
Explain why aluminum iodide exerts covalent character while sodium chloride doesn’t
There is a larger difference in charge between the Ag 3+ ions and the I- ions
Compared with Na+ and Cl- ions
The iodide ions have a much greater ionic radius, so the electron density is pulled towards the positive Ag 3+ cations
This causes uneven charge distribution which causes covalent character
Explain why the experimental and theoretical values of lattice energy are significantly different between calcium iodide. When theoretical=-1905 kJMol-1 experimental=-2074 kJMol-1
Because calcium iodide has polarization in the ionic bonds causing it to exhibit covalent characteristics. Causing the bonds to deform and become polarised. Therefore has a greater lattice Enthalpy. The theoretical value assumes Calcium Iodide is 100% ionic compound
Define rate of reaction
The change in concentration/amount of reactant or product per unit of time
Formula for rate of reaction
Amount of reactant used or product made divided by time
What are the 2 factors needed for collision theory
For a reaction to occur the particles must collide in the right direction and have a minimum amount of KE
Define activation energy
The minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to occur

What is the formula to work out the enthalpy of solution?
Snakes produce rice
Enthalpy of solution= Enthalpy of formation of products (aqueous ions) - Enthalpy of formation reactants of solid and solvent (H2O)
Breaking bonds is….
Endothermic
Because energy is needed to break the bonds
Making bonds is…
Exothermic
Because energy is made from forming bonds
BENDO MEXO or clapping produces a sound so forming a bond is exothermic
Define Lattice enthalpy of dissociation
The enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is broken down into its gaseous ions under standard conditions
Is lattice enthalpy of dissociation endo or exo?
Endothermic because you are breaking ionic bonds
Is lattice formation enthalpy endo or exo?
Exothermic because you are forming ionic bonds
Define Hess’s law
The enthalpy change is independent of the route taken