IB BIO DNA FLASHCARDS
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
DNA
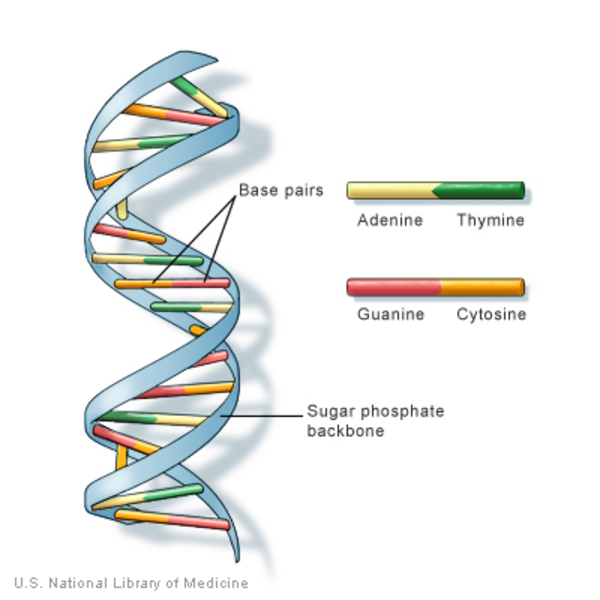
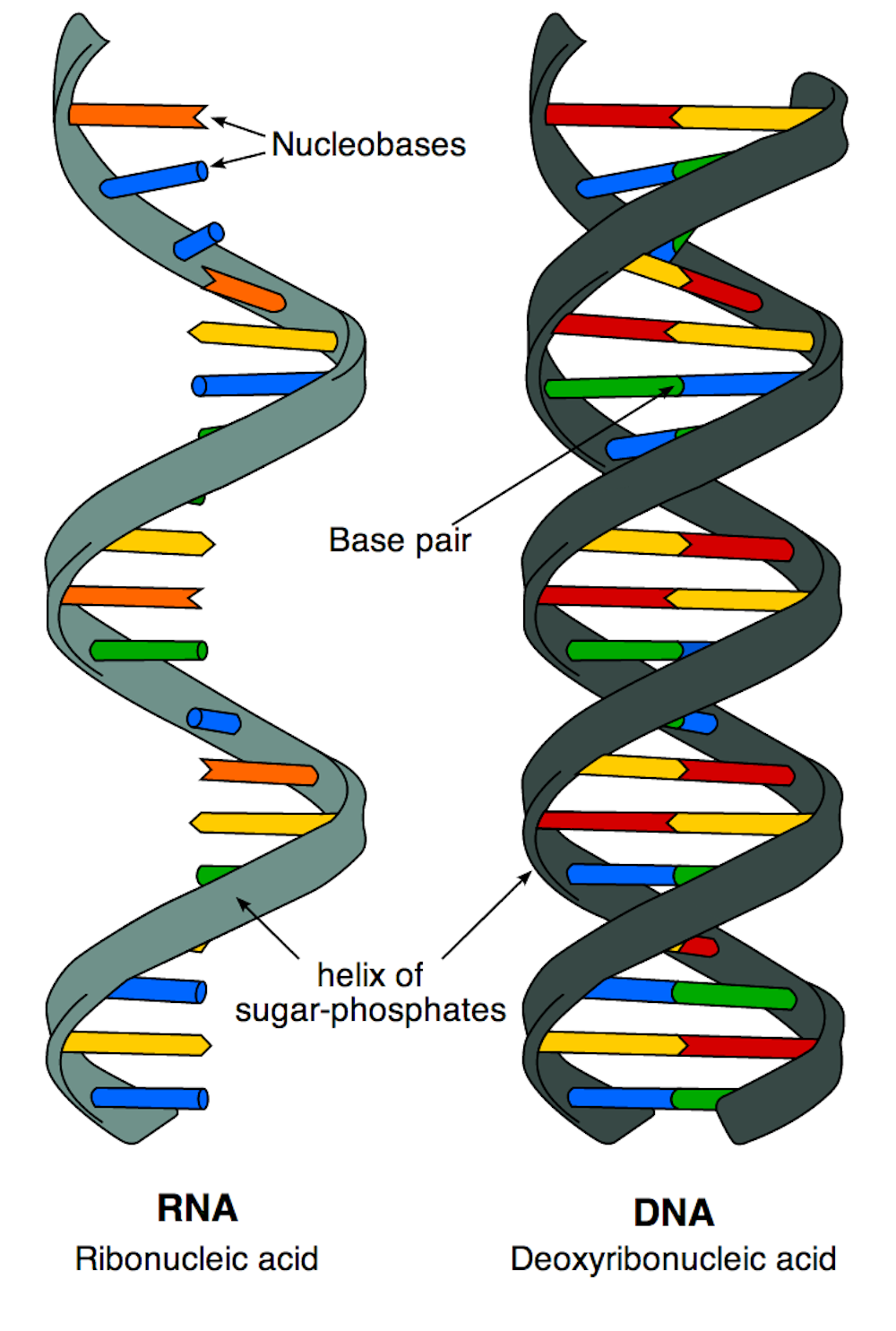
Deoxyribonucleic acid, the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for life.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, a molecule that plays several roles in the coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes.
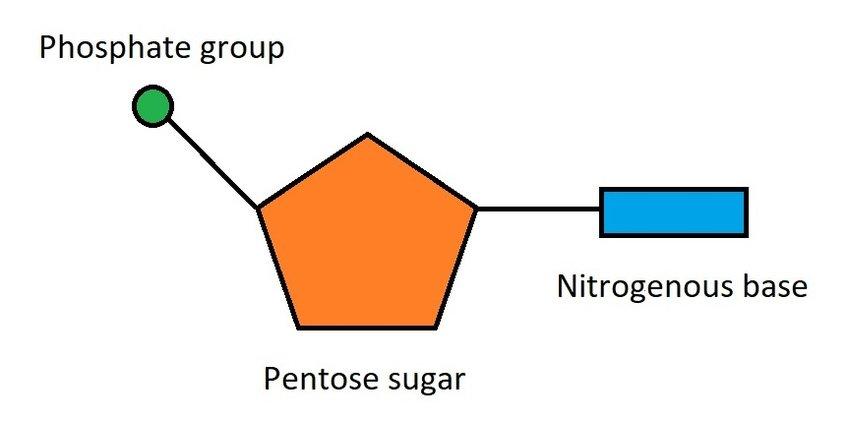
Nucleotide
The basic building block of nucleic acids, composed of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group.
Sugar-phosphate backbone
The structural framework of nucleic acids, formed from sugar and phosphate groups.
Nitrogenous base
A molecule that contains nitrogen and has the chemical properties of a base; examples include adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine.
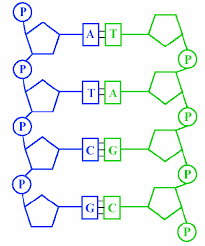
Complementary base pairing
The pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA where adenine pairs with thymine (or uracil in RNA) and guanine pairs with cytosine.
Semiconservative replication
The process by which DNA is replicated in all cellular organisms, where each new double helix consists of one old strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases.
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a pre-existing strand.
Primers
Short strands of RNA or DNA that provide a starting point for DNA synthesis.
Taq polymerase
A heat-stable DNA polymerase used in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for amplifying DNA.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A technique used to amplify a specific DNA segment by repeating cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension.
Gel electrophoresis
A laboratory method used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins according to their size and charge.
Transcription
The process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
Translation
The process by which a ribosome synthesizes proteins using mRNA as a template.
mRNA
Messenger RNA, a type of RNA that conveys genetic information from DNA to the ribosome.
Ribosomes
Molecular machines composed of rRNA and proteins, serving as the site of protein synthesis.
tRNA
Transfer RNA, a type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides on mRNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid.
Anticodon
A sequence of three nucleotides on tRNA that is complementary to an mRNA codon.
Degeneracy
The redundancy in the genetic code whereby multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
Universality
The principle that the genetic code is consistent across all known forms of life.
Genetic code
The set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins.
Point mutation
A change in a single nucleotide base pair in a DNA sequence.
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence, which can lead to altered genetic information.
Substitution mutation
A type of mutation where one base pair in DNA is replaced by another.
Insertion mutation
A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence.
Deletion mutation
A mutation involving the loss of one or more nucleotide base pairs from a DNA sequence.
Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
A variation at a single position in a DNA sequence among individuals.
Frameshift change
A mutation caused by a deletion or insertion that shifts the reading frame of the genetic message.
Mutagens
Agents that can cause mutations in DNA, such as chemicals or radiation.