IBCH4 definitions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
thermodynamics
law of cons. of energy → E can be converted from 1 form to another but not destroyed/created (total E remains constant)
heat (Q) in (J) → form of thermal E, transferred between objects because of temp. diff.
conduction, convection, radiation
temp. (T) in (K) → measure of avg. kinetic energy of particles
how much heat has been transferred → measured by temp. change
heat capacity (c) in (J/kg K) → amt. of E needed to raise temp. of substance by 1 degree
specific heat capacity → amt. of heat E needed for 1 unit of mass of substance to cause inc. of one unit in temp.
open/closed/isolated systems
open → allows transfer of heat/matter in/out of system
closed → allows transfer of only heat
isolated → doesn’t allow transfer of heat/matter
endo/exo
exothermic reaction gives out heat, warming mixture (heat lost to surroundings) (ΔH<0)
endothermic reaction takes in heat, cooling mixture (heat gained from surroundings) (ΔH>0)
standard enthalpy change of combustion/formation
standard enthalpy change of combustion (∆Hc) is heat E released when 1 mol of pure substance is completely burnt in excess O2 under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of formation (∆Hf) is heat change at constant production of 1 mol of pure substance from its elements in standard states under standard conditions
can see these values in data booklet + when writing reaction equation can use fractions
measurement uncertainty in calorimetry
heat transfer due to calorimeter not being 100% insulated
reactions rarely immediate → heat lost while reaction takes place
heat absorbed by calorimeter (e.g. can)
standard heat capacity not exactly same for sol. and water
experiment not under standard conditions
fossil fuels
crude oil → HC + sulfur, nitrogen etc, refined to petroleum etc
coal → combustible sedimentary rock with high amt. C, HC
natural gas → naturally occurring mixture of gaseous HC (mainly methane, little bit of other higher alkanes)
cheap/efficient, found in large amounts, reliable, infrastructure exists alr
non-renewable, produces GG → global warming, pollution (NOx, SOx), isn’t found everywhere
biofuel
= fuel produced over short timespan from biomass (renewable E source)
biological carbon fixation → production of organic compounds from CO2 (photosynthesis)
bioethanol → ethanol produced by fermentation of glucose/biomass, used as fuel/fuel additive
biodiesel → produced in transesterification reaction
renewable, reduced GG, sustainable (many plant mats+waste can be used), economic security (reduced dependency on imported oil)
high cost, possible deforestation as demand inc., monoculture may result in reduced biodiversity, food products diverted to produce biofuel, use of agricultural land/water/fertiliser/pesticides for growing crops
specific energy
= amt of heat E released per mass of fuel (kJ/kg) (enthalpy/molar mass)
larger HC → lower volatility bc stronger dispersion forces
affects how HC interact with oxygen + type of combustion
longer HC chain → greater tendency of fuel to undergo incomplete combustion, which releases poisonous CO and produces less specific E when compared to same HC’s complete combustion
collision theory
chem. reaction only occurs when → collisions between molecules have enough E to break bonds in reagents, molecules collide w/ proper orientation, new bonds form
change in concentration (c) or amount (n) of reactant/product with time (t)
r/v = ∆/c∆t (absolute value) in mol/dm3 s
if half mass → half volume produced
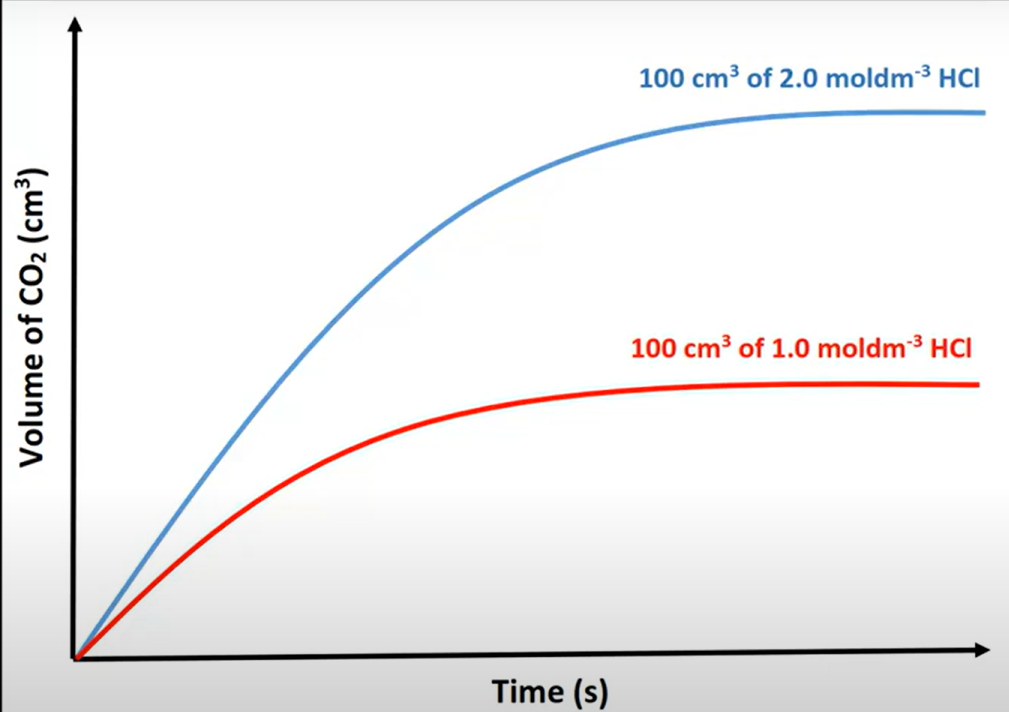
if less V but same c → slower but reaches same volume
avg rate measures over particular time interval (usually slower)
instantaneous rate measures at particular time from gradient (e.g. initial, 10hr…)
factors affecting RoR
concentration / mixing
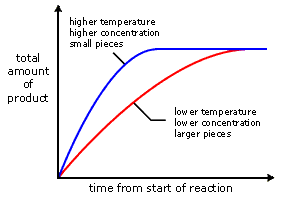
mixing or inc. c inc. freq. of collisions between particles → greater RoR
pressure
inc. pressure forces particles closer tog. → inc. collision rate → inc. RoR (only gases)
temperature
inc. in temp. → inc. velocity of particles → greater Ek → more collisions → greater RoR
catalyst (= inc. RoR but remains chemically unused at end of reaction)
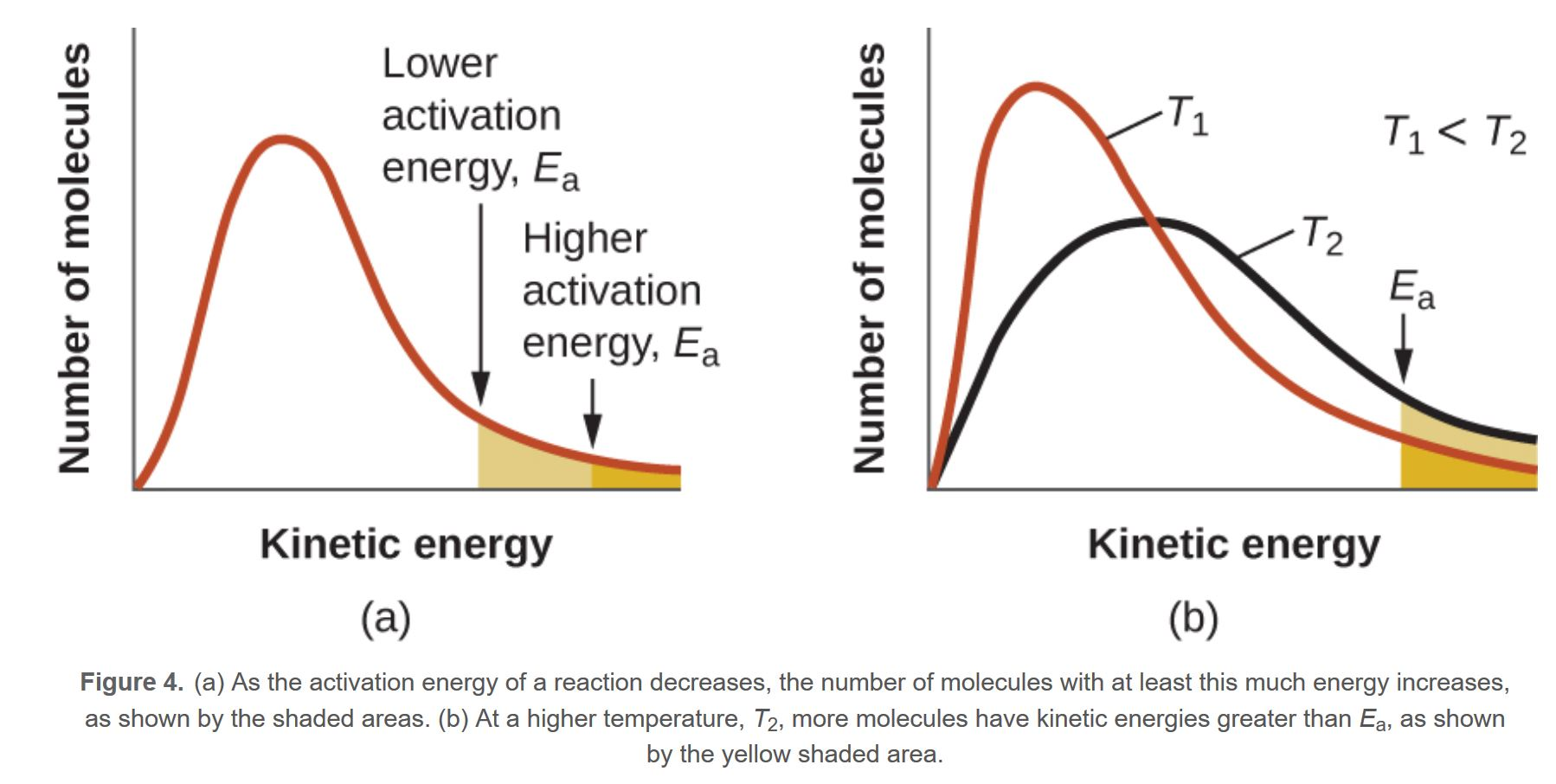
provide alt. pathway for reaction w/ lower Ea
temp. has no effect on Ea. slower tend to have greater Ea
light
VIS/UV radiation breaks bonds in reactant molecules (some rates can be inc.)
silver halides…are photosensitive + undergo partial decomp. in light
particle size
dec. size inc. SA of solid substance → more freq. collisions → greater RoR
dynamic equilibrium + equilibrium constant
only in closed systems!
macroscopic properties don’t change → amt./concentrations/densities of reactants/products same
at microscopic lvl → particles continue to take part in forward/reverse reaction (rates of these equal)
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
Kc (equilibrium constant) expression = [C]^c[D]^d/[A]^a[B]^b is constant at given temp.
[] = concentration
only for homogeneous equilibrium!
if Kc<1 → equilibrium at reactant’s side (more reactants)
if Kc=1 → equal amt. of reactants/products
if Kc>1 → equilibrium at product’s side (more products)
deduce Kc equilibrium, use it to find expression for reactions w/ diff. coefficients
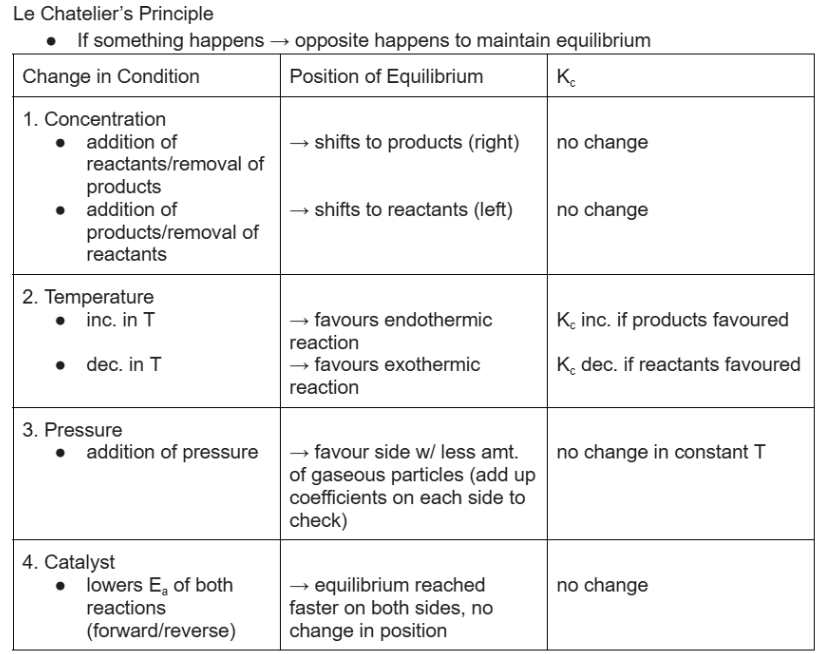
le chatelier’s principle
arrhenius + BL acids/bases
Arrhenius acids and bases:
acid → any species that inc. concentration of hydrogen ions/protons in (aq) sol.
base → any species that inc. concentration of hydroxide ions in (aq) sol.
doesn’t take into account reactions w/o water
Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases
acid → any species capable of donating a proton
base → any species capable of accepting a proton
conjugate acid of BL base → species formed after base accepts a proton
conjugate base of BL acid → species formed after acids donates a proton
e.g. NH3 + H2O → NH4⁺ + OH⁻
strong/weak acids/bases
strong acids/bases dissociate/ionise completely (irreversible)
result in weak conjugate bases/acids
strong acids → HCl, HNO3, H2SO4 (diprotic acid, donates 2H), HI (hydroiodic), HBr (hydrobromic)
strong bases → group 1 hydroxides e.g. NaOH, KOH
weak acids/bases dissociate/ionise partially (equilibrium)
result in stronger conjugate bases/acids
weak acids → organic acids, salicylic acid, ethanoic acid
weak bases → NH3 (ammonia), amines e.g. aminoethane, CO22- (carbonates), HCO3- (hydrogen carbonates)
if dissociation not complete → less OH ions produced
check pH, conductivity, amt. of H3O ions produced to distinguish strong/weak