Skin Integrity & Wound Care
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
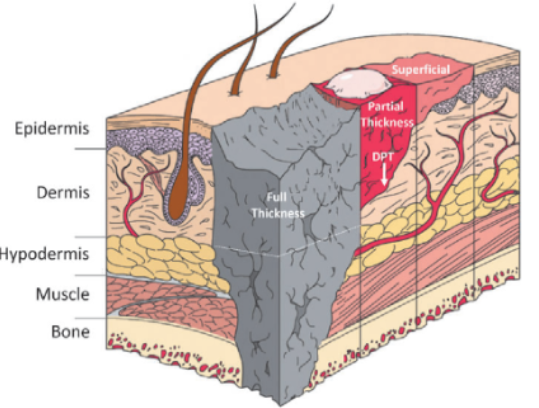
Partial Thickness Wound
Epidermis + part of dermis
inflammatory response
epithelial proliferation
resurfacing
Full Thickness Wound
extends to dermis —> hypodermis
hemostasis
inflammatory response
proliferation
remodeling - scar tissue forms
Primary Intention
edges are approximated (close together)
sutures aid this
Secondary Intention
Edges left open
Wound bed fills with granulation tissue
Once filled, epithelialization occurs across surface
Scar tissue form
*Greater risk for infection
Tertiary Intention
wound intentionally left open for days
closed later after infection resolves or drainage decreases
Granulation Tissue
should be:
Surface - pink, red, moist
Edges - clean & intact
Hemorrhage
External Hemorrhage - direct visualization of bleeding
Internal Hemorrhage
Hematoma - localized collection of blood under tissues (24-48 hours postop)
Infection
2nd most common HAI
Presents in 2-3 days up to 30 days
Risks: dirty wounds + underlying conditions
Dehiscence
partial or total separation of wound layers
greatest risk 3-11 days post-op
Triggers: Out of Bed activity, coughing
Increase in drainage —> infection
Patients at greater risk: DM, infection, poor nutrition, obesity
Evisceration
total separation + protrusion of visceral organs (SURGICAL EMERGENCY)
DO NOT push organs back in
moist gauze
NG suction
Fistula
abnormal connection/passageway between 2 structures
Serous
clear & watery
Purulent
thick, yellow, green, tan, or brown
Serosanguineous
pale, red, watery mixture
Sanguinous
bright red, bloody
Debridment
remove non-viable tissue
Dressing Change Best Practice
Know
ordered dressing type
if drains are present
what equipment is needed
Pre-medicate w/ Anelgesics (timed so pain med works during the change)
Review prior assessments (compare progress or decline)
eMAR & Handoff report
Measure & Photograph (often weekly)
Securement of Dressings
Use skin barrier wipes so tape doesn’t destroy skin
“Picture framing” is outdated—cover the whole dressing instead
Remove tape with the direction of hair; if not possible, push the skin away rather than pulling tape upward
Jackson Pratt (JP)/Hemovac
Constant, low pressure vacuum to remove & collect
Empty when 50% full or once per shift
Chart COCA (Color, Odor, Consistency, Amount)
Concerns w/ Drainage
Sudden increase or decrease in drainage
Foul smell
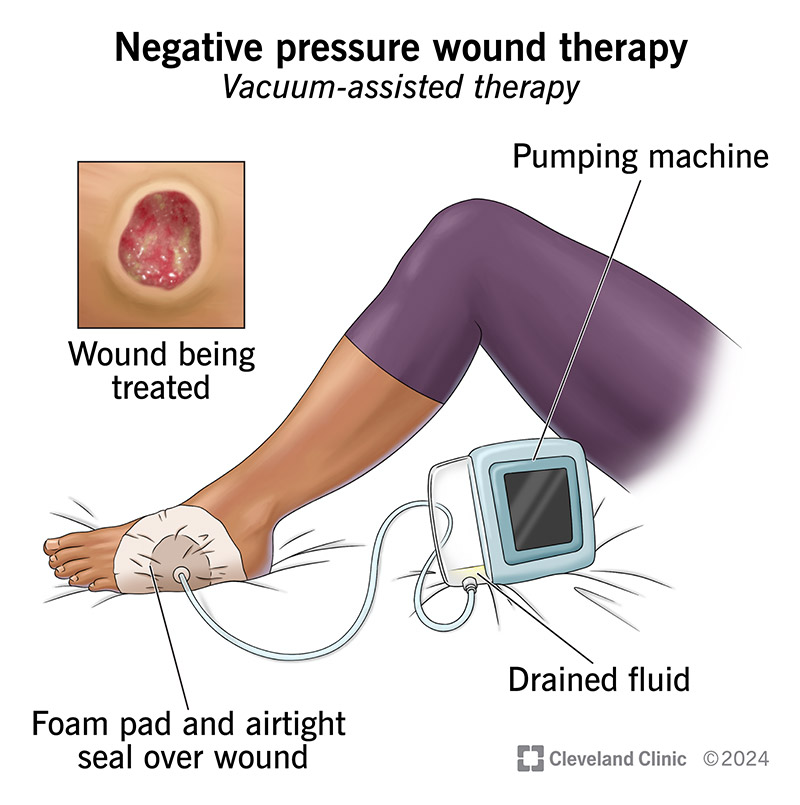
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
NEGATIVE PRESSURE WOUND THERAPY (Wound VAC)
Pulls wound edges together
Removes fluid and exudate
Reduces edema
Promotes angiogenesis (new blood vessels)
Increases granulation tissue formation
Diabetic Ulcers
limb amputations (10x greater prevalance)
slow wound healing
neuropathy - loss of sensation in hands & feet
Decreased
bloodflow
angiogenesis
Increased
inflammation
circulating glucose
PVD: Venous
wet, weeping, edematous edges
develops above ankle
PVD: Arterial
pulses faint
skin cool to touch
minimal or no edema
clear demarcation (well-defined, punched out areas)
Pathogenesis of Pressure Ulcers
Pressure Intensity - ischemia, blanching
Pressure Duration
Tissue Tolerance
Bony Prominences
Medical Device Locations
Frequency of Assessment for Pressure Ulcers
Acute care: admission, within 8 hrs, then q24–48 hrs & ANY CHANGE IN CONDITION
ICU: admission + q24 hrs
Long-term care: admission + weekly OR with client change
Home care: admission + every visit