Mechanical Ventilation- Chapter 13 & 14
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
During mechanical ventilation of a patient with COPD, the PaO2 = 58 mm Hg and the FIO2 = 0.5. If the desired PaO2 is 65 mm Hg, the FIO2 needs to be changed to which of the following?
0.56
During mechanical ventilation of a patient with CHF, the PaO2 = 38 mm Hg and the FIO2 = 0.6. If the desired PaO2 is 60 mm Hg, the FIO2 needs to be changed to which of the following?
0.95
Thirty minutes after intubation and initiation of mechanical ventilation, a patient's PaO2 = 55 mm Hg and the FIO2 = 0.5. To what should the FIO2 be set to obtain a PaO2 of 80 mm Hg?
0.75
Calculate the pulmonary shunt fraction using the following data: Pb = 757 mm Hg; hemoglobin (Hb) = 11 g/dL; FIO2 = 0.5; PaO2 = 86 mm Hg; PaCO2 = 40 mm Hg; SaO2 = 91%; = 40 mm Hg; = 71%; respiratory exchange quotient (R) = 0.8
19%
Calculate the pulmonary shunt fraction for a patient with the following data: Pb = 760 mm Hg; Hb = 10 g/dL; respiratory quotient = 0.8; FIO2 = 0.6; PaO2 = 100 mm Hg; SaO2 = 93%; PaCO2 = 45 mm Hg; = 36 mm Hg; = 70%
26%
Calculate the pulmonary shunt fraction for a patient with the following data: CAO2 = 17 vol%; CaO2 = 16.5 vol%; = 11 vol%.
8%
PEEP therapy is indicated for patients with which of the following?
PaO2 of 100 mm Hg while receiving an FIO2 of 0.8
Which of the following patients may benefit from PEEP?
ARDS
How long after PEEP is increased should all ventilatory and available hemodynamic parameters be measured and calculated?
15 minutes
Assessing the outcome of PEEP at levels set above 15-20 cm H2O is best done using which of the following
Pulmonary artery occlusion pressure
An absolute contraindication to PEEP is which of the following
Untreated tension pneumothorax
The level of applied PEEP should be set at what point on the pressure-volume curve?
Above the upper inflection point of the deflation curve.
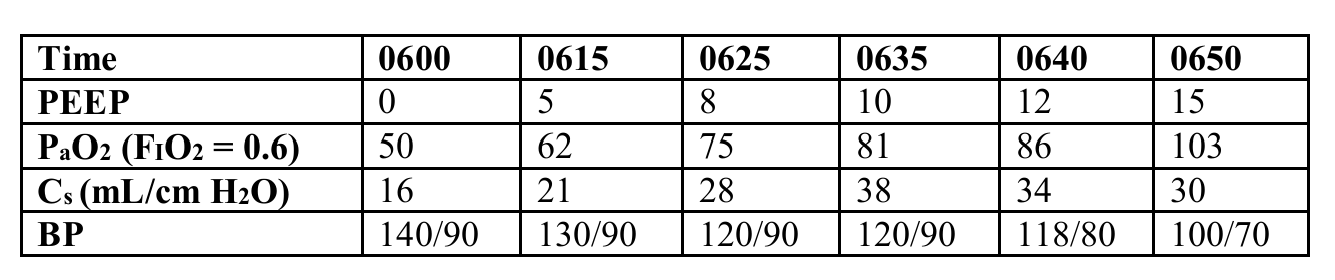
What is the optimal PEEP level given the following information?
10 cm H2O
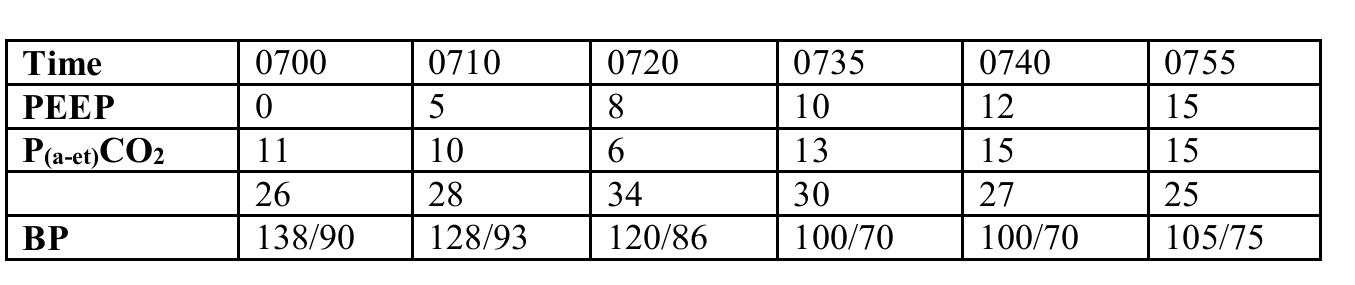
What is the optimal PEEP level given the following information?
8 cm H2O
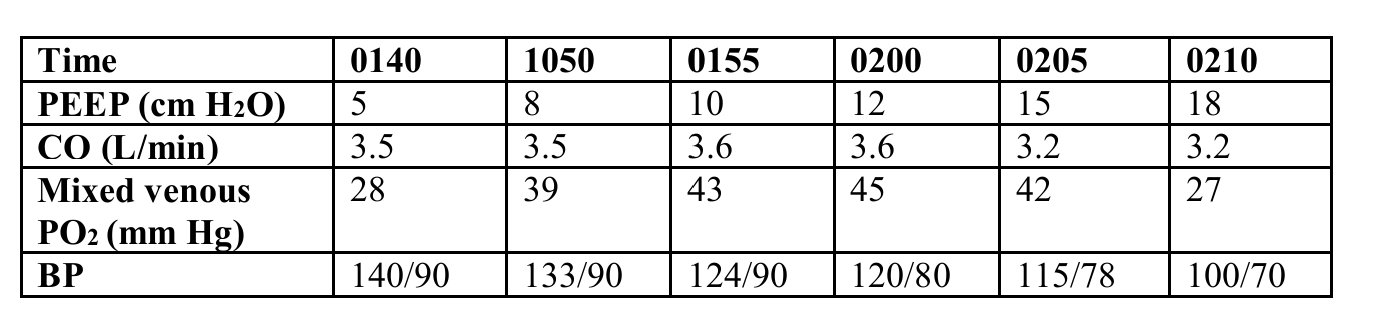
Which of the following is the most appropriate PEEP level for the patient whose information is in the table below?
12 cm H2O
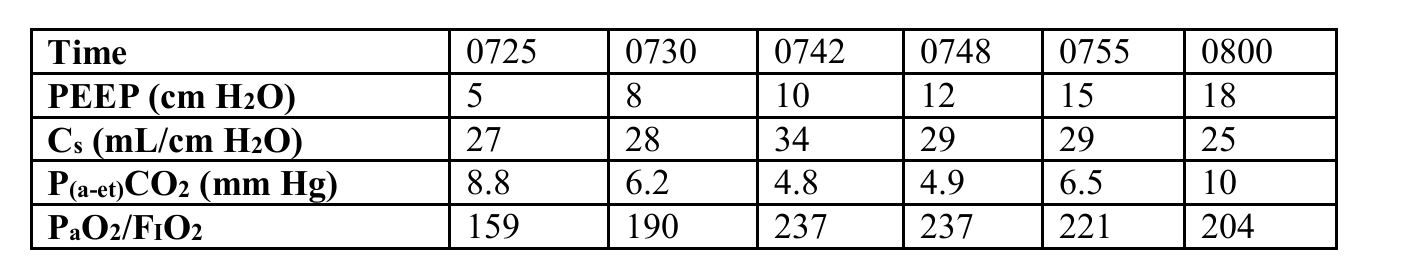
The level of PEEP that is most appropriate for a patient with the information shown below is which of the following?
10 cm H2O
A patient is being ventilated with a PEEP of 10 cm H2O and an FIO2 of 0.4. The arterial blood gas results show that the patient remains hypoxemic, and the respiratory therapist increases the PEEP to 18 cm H2O, maintaining the FIO2 at 0.4. The patient's static compliance changes from 28 to 22 mL/cm H2O just after this change. The respiratory therapist should do which of the following?
Decrease PEEP to 15 cm H2O and measure static compliance
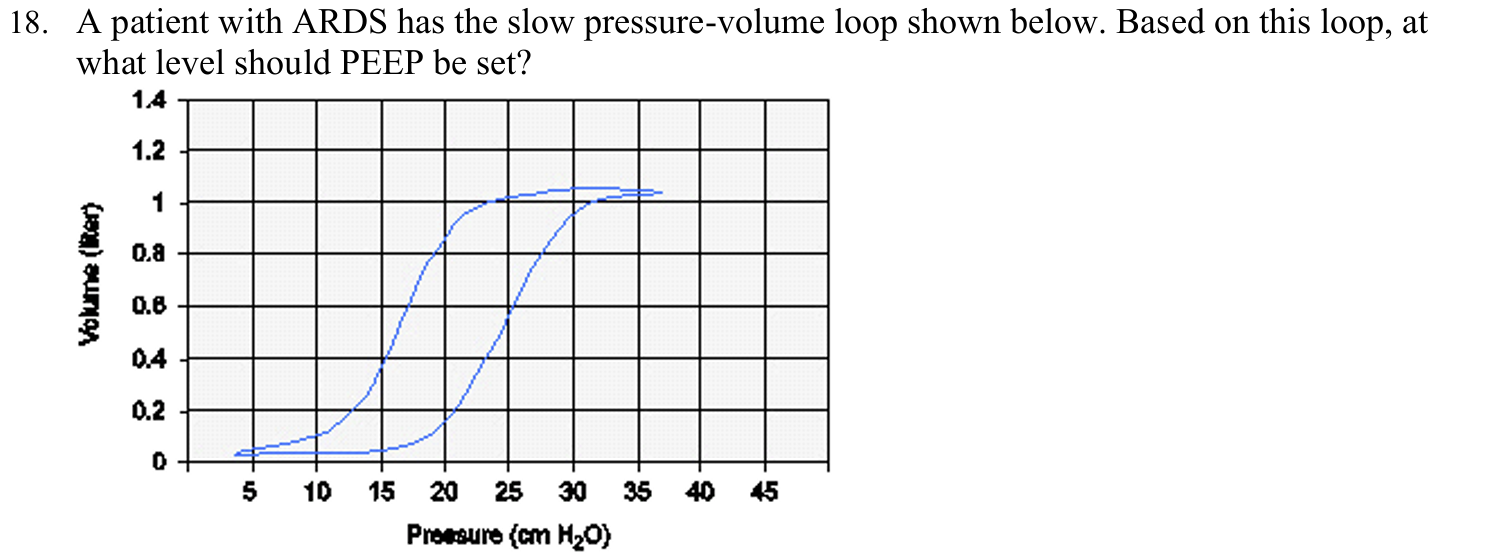
A patient with ARDS has the slow pressure-volume loop shown below. Based on this loop, at what level should PEEP be set?
22 cm H2O
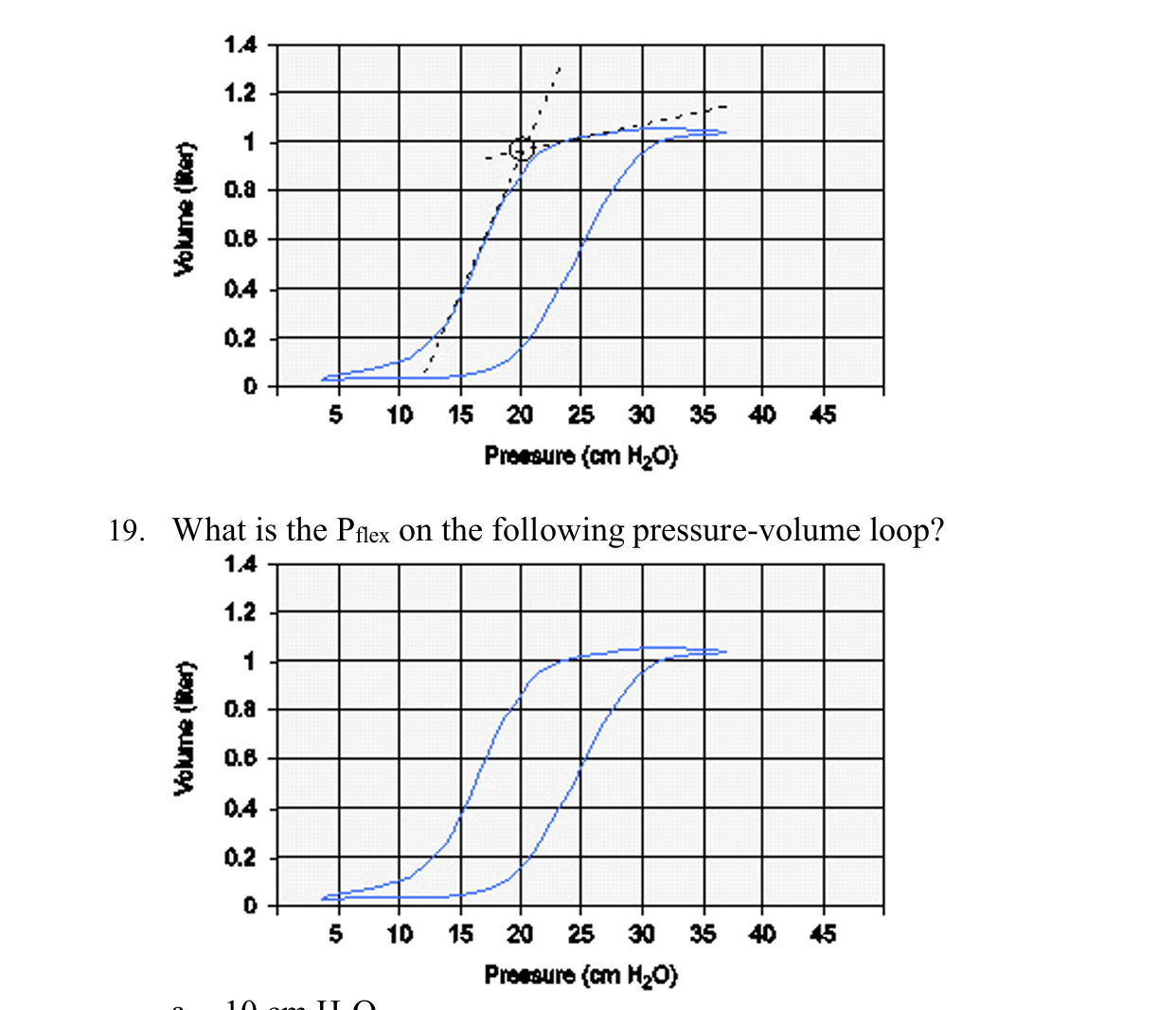
What is the Pflex on the following pressure-volume loop?
19 cm H2O
Regardless of the procedure used to establish an appropriate PEEP level, ventilating pressures should not be allowed to exceed which of the following?
Upper inflation point on the inspiratory limb (UIPi)
Despite the risk, it is still important to use PEEP, because it can prevent alveolar collapse during exhalation and reopening, even when a low VT is used. It now is theorized that it is important to use the pressure-volume loop to set PEEP
above the upper inflection point detected during deflation of the lung
During a patient case study, increasing increments of PEEP showed no significant effects until 15 cm H2O was used, at which time the PaO2 improved markedly. What point does this represent?
Alveolar recruitment probably occurred
In which ventilator mode should a patient receiving a sustained inflation technique be placed?
CPAP/spontaneous
To perform a low-flow (quasi-static) technique for determining the appropriate PEEP level, the most appropriate ventilator flow setting is which of the following
2 L/min
What should the highest pressure attained during the slow-flow (quasi-static) technique be?
45
The point on a static pressure-volume curve (SPV) where the alveoli begin to open is referred to as which of the following?
Lower inflection point on the inflation limb
The "sigmoid" shape of the static pressure-volume lung recruitment maneuver indicates which of the following?
Lung units open at different times with different pressures.
"Loose atelectasis," or compression atelectasis, is most often associated with which of the following choices
anesthesia
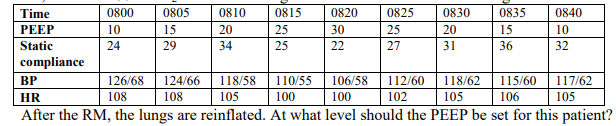
A recruitment maneuver (RM) is being performed on a patient receiving mechanical ventilation with PCV. During the maneuver the mode remains in PCV, rate = 10/min, I:E = 1:2, and PIP = 35 cm H2O. The following information is documented during the RM: After the RM, the lungs are reinflated. At what level should the PEEP be set for this patient?
12 cm H2O
The patient with which of the following assessment findings meets the criteria for beginning weaning from PEEP?
PaO2 = 95 mm Hg; FIO2 = 0.3; Cs = 30 mL/cm H2O; PEEP = 15 cm H2O
An invasively ventilated patient with ARDS is on PC-CMV, PIP = 30 cm H2O, PEEP = 12 cm H2O, FIO2 = 1.0. The patient's returned VT is 320 mL. The ABG results on these settings are: pH 7.3, PaCO2 53 mm Hg, PaO2 62 mm Hg. The patient is placed in the prone position, and after 1 hour, ABG results show: pH 7.38, PaCO2 46 mm Hg, PaO2 83 mm Hg. The respiratory therapist should do which of the following?
Keep the patient in the prone position and decrease the FIO2.
Pneumonia that was not incubating at the time of admission is one that develops a minimum of how many hours after admission?
48 hours
The type of organism that most often causes ventilator-acquired pneumonia is which of the following?
Bacteria
A patient was intubated in the emergency department just after arrival at the hospital from home. This patient develops VAP 36 hours after intubation. What type of pneumonia is this considered?
Nonhospital-acquired pneumonia
The pathogenesis of VAP involves:
1. colonization of the aerodigestive tract.
2. aspiration of contaminated secretions into the lower airways.
3. increased use of silver-coated endotracheal tubes.
4. colonization of lower airways and lung parenchyma
1,2,4
Most VAP infections are caused by which of the following?
Aerobic gram-negative bacilli
The most common gram-positive bacterium that causes ventilator-associated pneumonia is which of the following?
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are at higher risk for infection with which of the following organisms?
1. Haemophilus influenzae
2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Moraxella catarrhalis
4. Staphylococcus aureus
1,3
Patients with cystic fibrosis are at higher risk for infection with which of the following organisms?
1. Haemophilus influenzae
2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Moraxella catarrhalis
4. Staphylococcus aureus
2,4
The mortality rate for VAP depends on which of the following?
1. Length of stay on the ventilator
2. Presence of underlying disease
3. Prior antimicrobial therapy
4. Presence of a heated humidifier
2,3
Effective treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia can be ensured by diagnosis based on findings from which of the following?
Bronchial alveolar lavage
Calculate the Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score (CPIS) for a patient with the following assessments: 56-year-old female, post motor vehicle accident, intubated, and mechanically ventilated for 4 days. Static compliance is 42 cm H2O/L. Tracheobronchial suctioning reveals a moderate amount of yellow secretions; culture and sensitivity are pending. Breath sounds reveal bilateral lower lobe coarse rhonchi. Chest radiograph shows diffuse infiltrates. Partial pressure of oxygen in the arteries (PaO2) is 72 mm Hg on 40% supplemental oxygen. Patient has a temperature of 39.2° C, and white blood cell count (WBC) is 12,800 L.
CPIS = 7
A patient with which of the following CPIS criteria should be placed on empiric antibiotic therapy pending the outcome of a bronchial alveolar lavage?
CPIS = 7
Critically ill patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation have been found to have which of the following microorganisms not typically present in healthy individuals?
Gram-negative bacilli
Reasons for the shift in oropharyngeal flora in patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation with endotracheal tubes include which of the following?
Decreased mucosal immunoglobulin A
Relying on clinical findings for the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia may do which of the following?
Create multidrug-resistant organisms
The initial empiric antibiotic used to treat suspected methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a patient with late-onset VAP is which of the following?
Linezolid
The initial empiric antibiotic used to treat suspected methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a patient with early-onset VAP is which of the following?
Levofloxacin
A 63-year-old male, post head trauma, is intubated and has been mechanically ventilated for 78 hours. The respiratory therapist notes the following during ICU rounds: partial pressure of oxygen in the arteries (PaO2) is 82 mm Hg on 60% supplemental oxygen with a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 8 cm H2O; static compliance is averaging 38-41 cm H2O/L; breath sounds are diminished bilaterally. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) results are pending, but MRSA is suspected. Chest radiograph shows bilateral, patchy infiltrates. Patient has a temperature of 38.8° C, and the most recent white blood cell (WBC) count is 11,300 L. The most appropriate recommendation for this patient is which of the following?
Combination therapy with two types of antipseudomonal agents and vancomycin
Which of the following is a method to reduce the risk of VAP?
Keep patient in a semirecumbent position
A "ventilator bundle" may include which of the following?
1. Keeping the head of the bed at 30 degrees from the horizontal.
2. Changing the ventilator circuits every 48 hours.
3. Using heated humidifiers whenever possible.
4. Using noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV) whenever possible
1,4
According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN), the proposed and updated definition for VAP includes which of the following?
1. Objective data
2. Patient's family history
3. A clearly defined time criteria
4. Chest radiograph images
1,3
The main strategy for the management of VAP focuses on which of the following?
Early diagnosis and treatment
A 35-year-old patient diagnosed with ARDS is receiving PC-CMV ventilation. Based on the ABG results, the PEEP is increased from 14-16 cm H2O. Which of the following parameters should the therapist monitor immediately after the change?
Cardiac Output
Which of the following is the primary mechanics, by which PEEP increases PaO2 and improves compliance?
Recruitment of collapsed alveoli
Which of the following conditions is a potential complication when instituting PEEP?
1. Decrease in cardiac output
2. Barotrauma
3. Altered cardiac function
4. Decrease in urine output
1,2,3,4
Which of the following is an absolute contraindication to the use of PEEP or CPAP?
untreated pneumothorax or tension pneumothorax
What effect does PEEP have on PaO2 and PaCO2?
PaCO2 should remain unchanged and PaO2 should increase
The CPIS (Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score) has 6 assessment items that it scores to determine if a patient has VAP, All of the following are assessment items EXCEPT:
CT Scan
With regard to VAP, COPD patients are at increased risk from which of the following pathogenic organisms?
Hemophilus influenza
Inappropriate use of what intervention is associated with the emergence of MDR pathogens?
Antibiotics
Which of the following refers to the process of focusing the types and duration of antibiotics used to treat VAP?
Deescalating antibiotic therapy.
VAP is most commonly caused by which of the following?
Bacterial infection
Healthy individuals usually have which of the following bacteria in their upper airways?
Haemophilus sp.
If the Ca02 is 16.94% and the CO is 12.54 how much oxygen is being delivered?
2.124
What could be the most likely cause of an increased Paco2 after and increase in PEEP?
Lung over distention
Which of the following is an absolute contraindication for the use of PEEP or CPAP?
Untreated tension pneumothorax or normal pneumothorax
By which mechanism does PEEP cause increase in ICP?
Central venous pressure is increased
A 35 YOM patient diagnosed with ARDS is receving PC-CMV ventilation. Based on the ABG, the PEEP is increased from 14 to 16. What do you monitor immediately after the change?
Cardiac output