CHM2210 Exam 2
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
chiral
carbon w/ 4 different substituents
enantiomers
pair of molecules who are mirror images of each other
diastereomers
pair of molecules who are NOT mirror images of each other
R/S
assigned by priority, has to do with chirality
R
approaching from the top, chirality
S
approaching from the bottom, chirality
fischer projections
chiral C in center, substituents coming from center; wedges are horizontal, dashes are vertical, if H is horizontal flip S/R
meso
when a chiral C has a plane of symmetry, it is achiral and _____
racemic mixture
50% (R) and 50% (S)
pro-chirality
one step away from being chiral, re and si can be assigned in place of R/S
specific rotation
observed rotation divided by (grams/solvent) times length in dm (1 dm = 10cm)
enantiomer composition
observed rotation over rotation of pure enantiomer
enantiomeric excess
specific rotation (low) over specific rotation (high)
addition
type of rxn where reactants are added together
elimination
type of rxn where something is removed from the rctnt, can be E1 or E2
substitution
type of rxn where some of the starting rctnt is swapped out, can be SN1 or SN2
rearrangement
type of rxn where the rctnt is changed to a more stable form
homolytic
single electron, free-radical mechanism
heterolytic
electron pairs, ionic (polar) mech
high temperature
favors entropy (delta s)
low temperature
favors enthalpy (delta h)
large K/rate
favors product
small K/rate
favors reactant
Ea
activation energy, larger = slower, RDS is slower
sterics
orientation of the molecule as they collide
nucleophilic
e- rich, attacks electrophiles
electrophilic
e- poor
nucleophilic attack
proton transfer

carbocation rearrangement
delta g neg high t
endothermic, ΔS up, T up
delta g neg
exothermic, ΔS up, T up
delta g pos
endothermic, ΔS down, T up
delta g pos high t
exothermic, ΔS down, T down
SN2
substrate; methyl > 1 > 2 »» 3 (3 doesnt happen)
SN2
nucleophile; very important
SN2
LG; important
SN2/E2
solvent; polar, aprotic
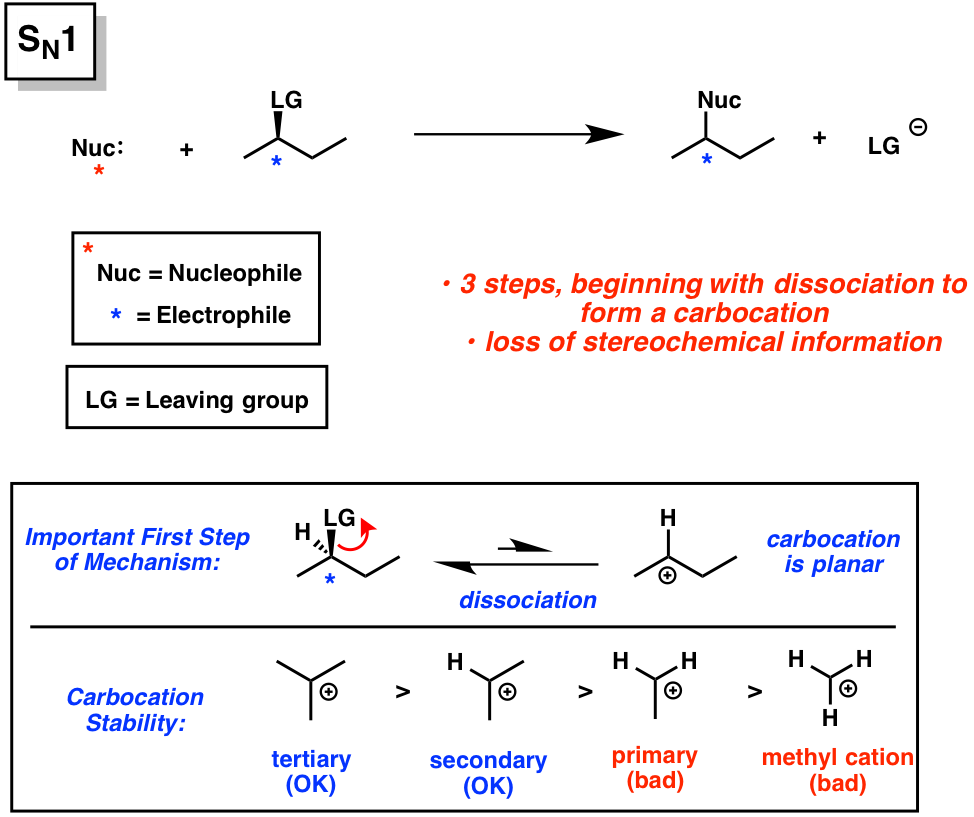
SN1
substrate; 3 > 2 »»1
SN1
nucleophile; irrelevant
SN1
LG; critical
SN1/E1
solvent; polar, protic
nucleophile
the better ________ usually has a negative sign, larger better if in same column and goes hand in hand with basicity
leaving group
the better the _______, the faster the reaction; conjugate base of strong acids make a good ________________
polar aprotic
this kind of solvent cannot donate protons and is usually h-bonded
polar protic
this kind of solvent can donate protons (has free valence e-) and is usually h-bonded
allylic
C double bonded to C; both SN1 and SN2
vinylic
halide double bonded to C; no SN1 or SN2
zaitsev’s rule
the more substituted an alkene, the more stable; tetrasub most stable
hoffman product
when a bulky base is used, this product is preferred to zaitsev’s
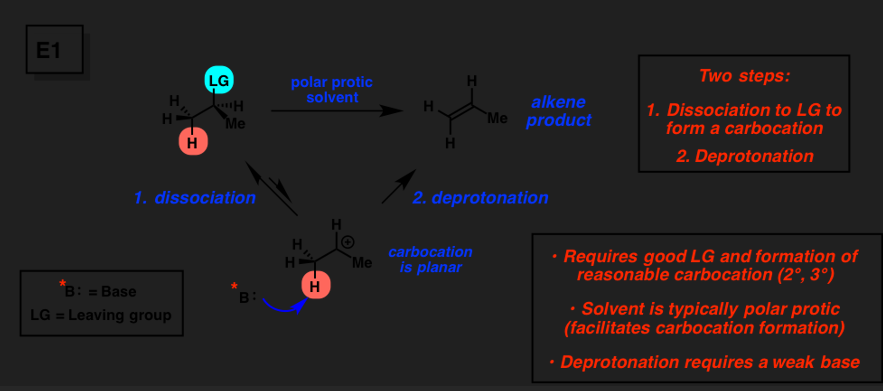
E1
2-step elimination method
E1
substrates; 3 > 2 » 1
E1
base; weak/moderate base
E1
no antiperiplanar required, high temp
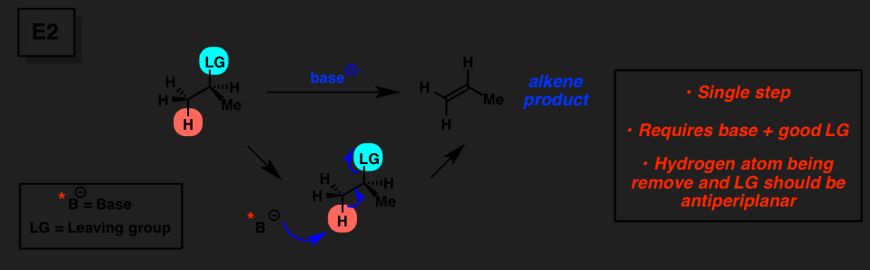
E2
1-step elimination method
E2
any substrate is good
E2
base; strong base
E2
LG and H+ (proton) has to be anti peri-planar (180 degrees) to each other, low temp
methyl substrate
this substrate only does SN2
SN2
strong nucleophile, 1
E2
weak nucleophile, strong base
E2
strong nucleophile, strong base 2 and 3
SN2
strong nucleophile, weak base
SN1/E1
weak nucleophile, weak base
SN2
if negative charge on less electronegative atom, it is a _______ rxn
E2
if large in size, weak nucleophile; can be strong base good for a _________ rxn
strong nuc, strong base
OH-, K-O-, R2N-, MeO-, EtO-
strong nuc, weak base
K-NH2 (amines), R-S-, CN-, N3-, I-, H2S, R-SH, halides
weak nuc, strong base
Kot-Bu, LDA, DBN, DBU (bulky bases)
weak nuc, weak base
H2O, K-OH (alcohols), carboxylic acids, MeOH, EtOH
bulky base
strong base, weak nucleophile; hoffman product preffered
concerted
means single step
degree of unsaturation
equal to amount of double bonds and rings
degree of unsaturation
[(2*number of C)+2-H-X+N]/2
cis
H are on same side of alkene
trans
H are on opposite side of alkene
E
high priority groups on different sides
Z
high priority groups on same side
markonikov’s rule
C-X bond forms on more substituted carbon, or C w/ least H
anti-mark
C-X bond forms on less substituted carbon, or C with most H
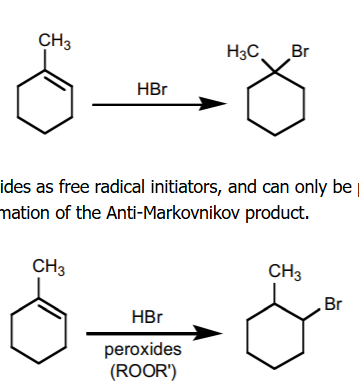
hydrobromination
alkene + H-X leads to a markonikov product, alkene + HBr/ROOR leads to an anti-mark product
halogenation
X2 added, w/ H2O ads an -OH
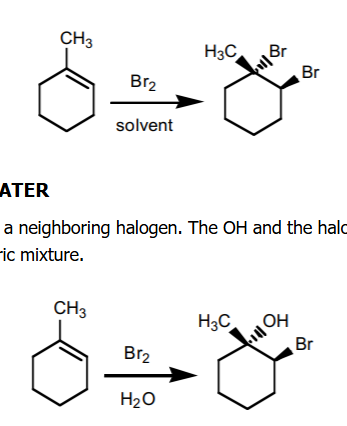
hydration
acid; H3O+ or H2SO4 adds OH, mark product; to avoid rearrangement, HgOAC/H2O, same product; react w/ BH3 THF to get anti-mark
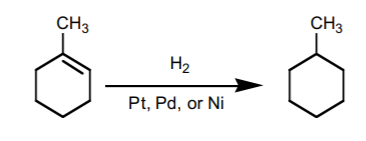
hydrogenation
H2/Pt/C addds two H groups; cis/syn, react with MCPDA for two line/wedge attach to O (removes the alkene)
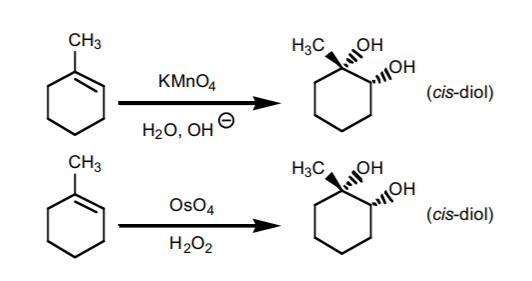
dihydroxylation
OsO4/NaHSO4 yields H and OH cis, can react with KMnO4/NaOH when basic pH, cis-1,2-diol forms
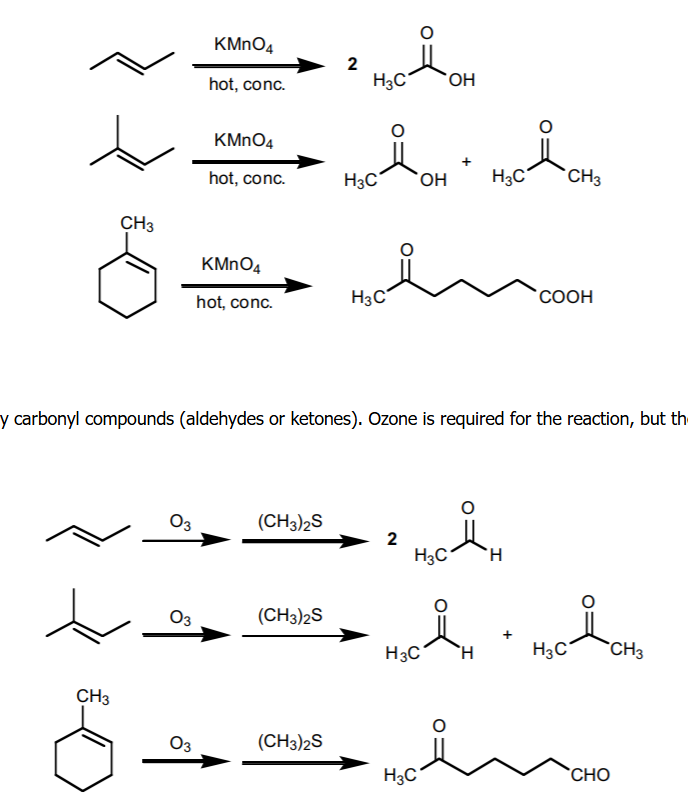
cleavage
O3/ZnH+ yields an aldehyde or ketone, when KMnO4 is acidic/neutral yields carboxylic acid
carbene
makes cyclic alkenes by KOH
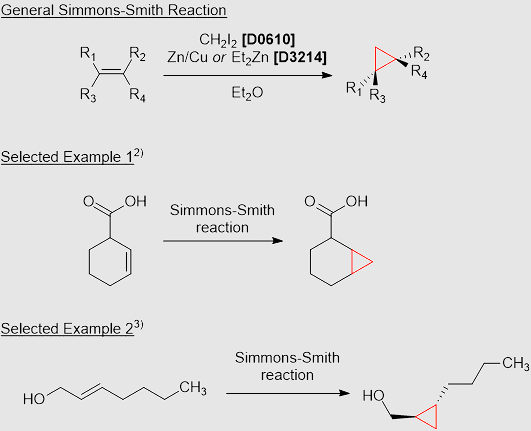
simmons-smith
H2I2/ZnCu or Et2O yields cyclic alkene
SN1
SN2

E2
E1
hydroboration
BH3 THF yields H and OH both cis