2.46-2.50 gas exchange
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
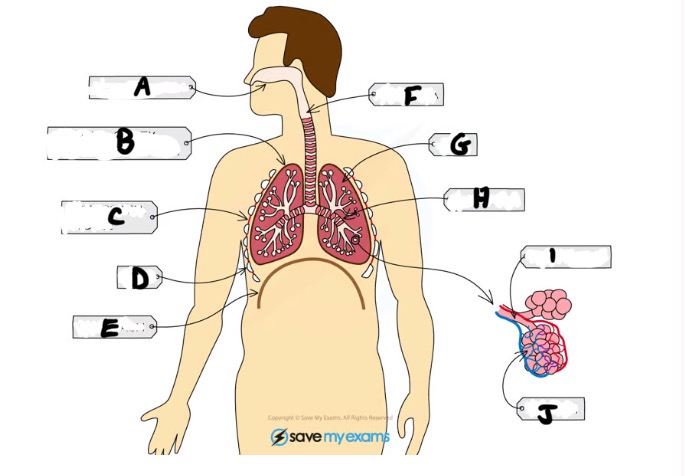
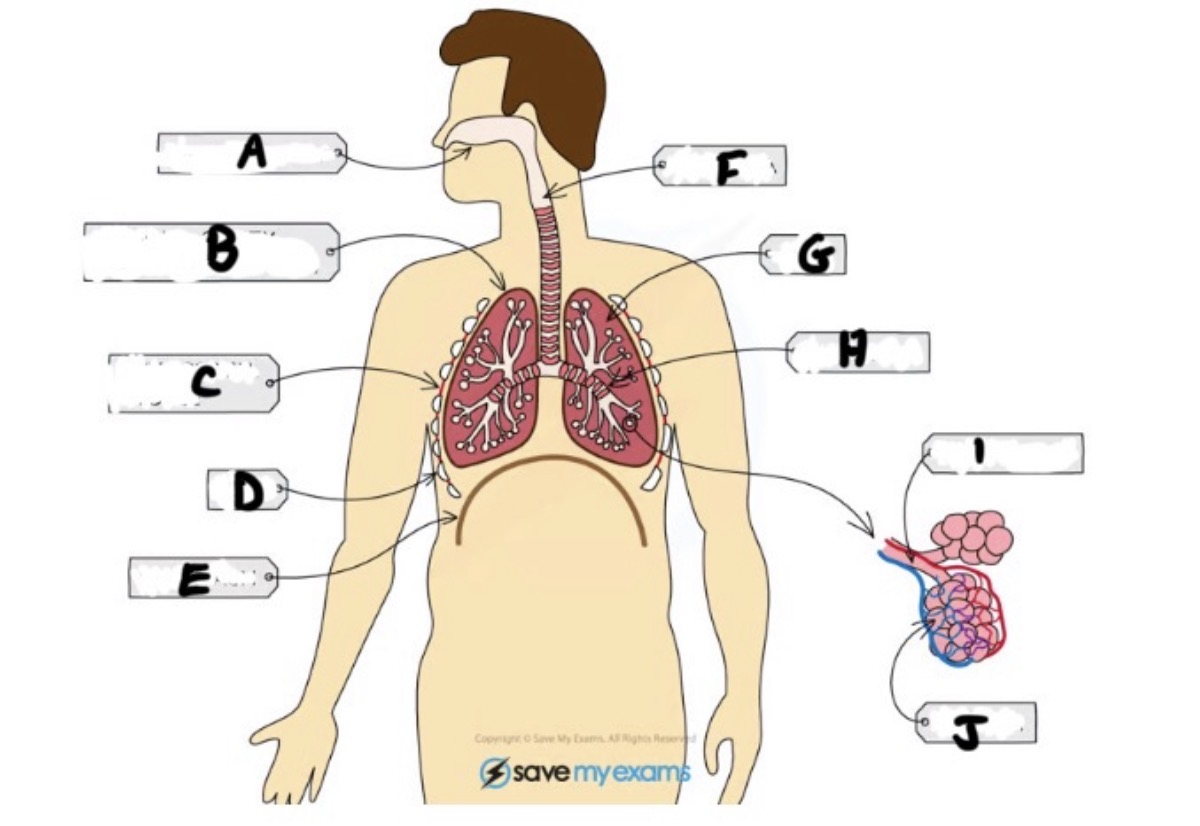
What is A and function
Nasal cavity - sense of smell, filtering out foreign particles, moistening air we breath in
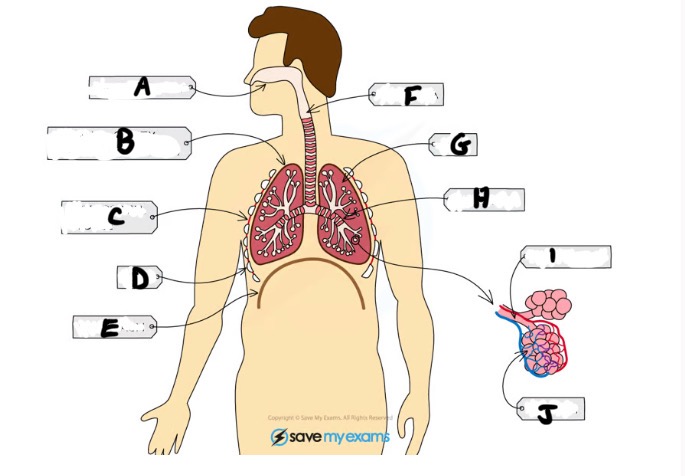
Name H and function
Bronchus - large tubes branching off from trachea (one per lung)
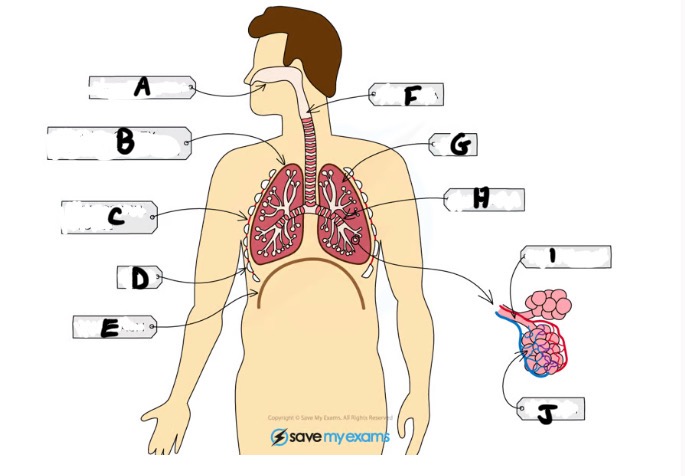
Name I and function
Bronchiole - bronchi split into smaller tubes called bronchioles connected to alveoli
Name J and function
Alveoli - tiny air sacs where gas exchange takes place
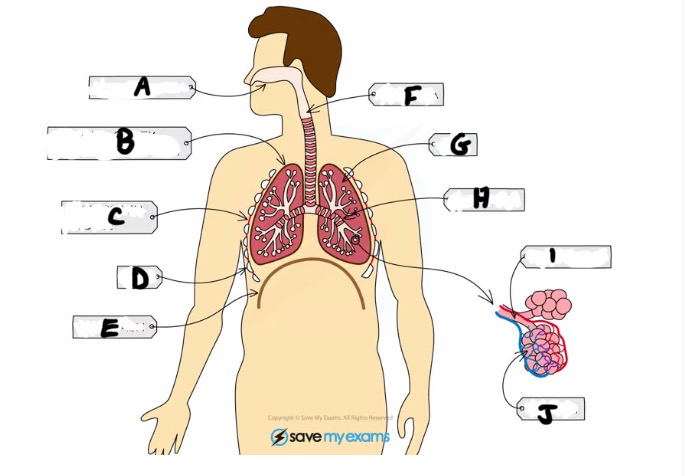
What is B and function
Pleural cavity - the fluid filled space between pleural membranes which reduces friction and allows the lungs to move freely
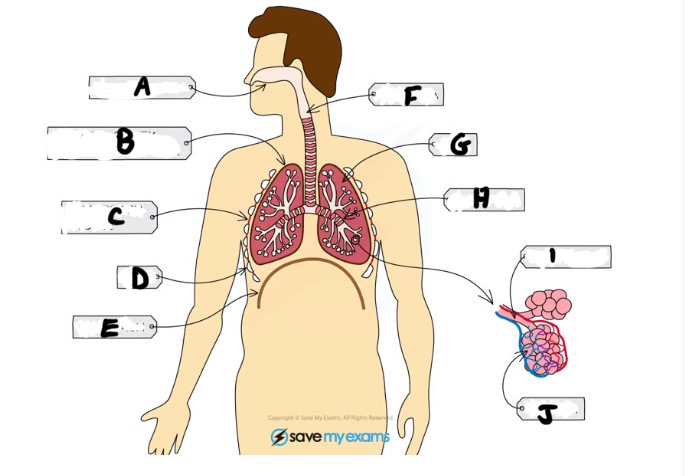
Name C and function
Intercostal muscle - muscles between ribs which control movement
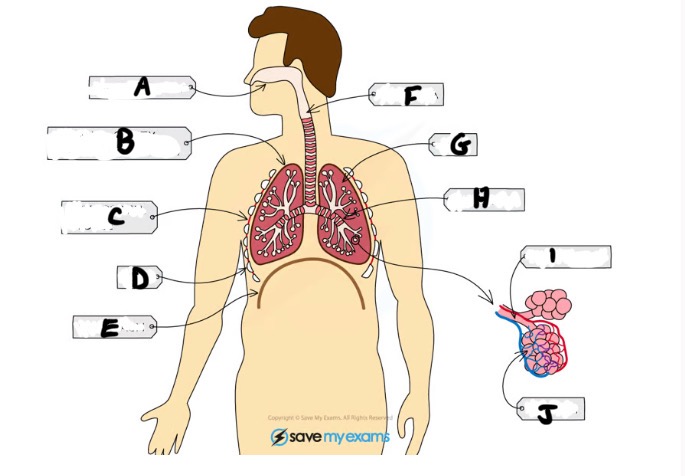
What is D and function
Ribs - protects the lungs
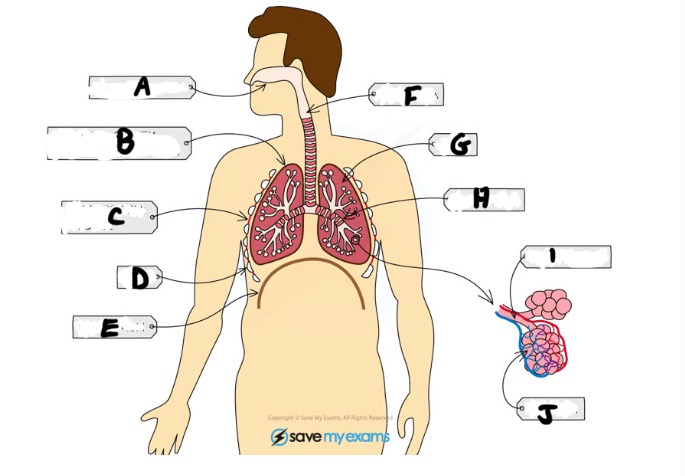
What is E and function
Diaphragm - large sheet of muscle that stretches across chest under rib cage, causes chest to expand during inhalation
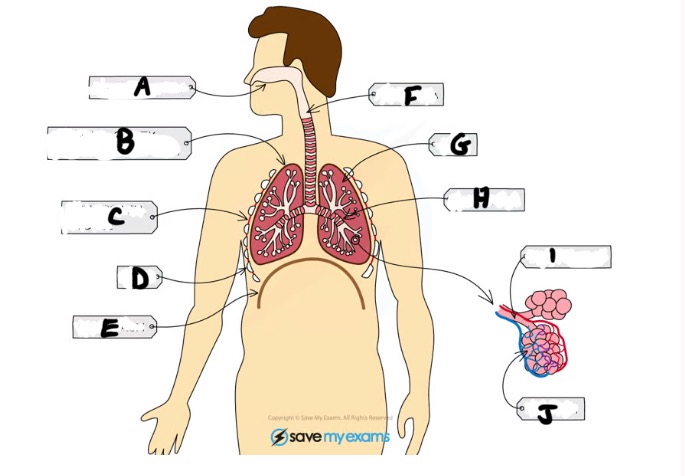
What is G
Lungs- gas exchange
Describe the contraction of the diaphragm when inhaling and exhaling
I- contract
E- relax
Direction of rib movement during inhaling and exhaling
I- upward and outward
E- downward and inward
External intercostal muscle contraction during inhalation and exhalation
I- contract
E- relax
Internal intercostal muscles contraction during inhalation and exhalation
I- contract
E- contract (only when exhalation is forced)
Lung volume during exhalation and inhalation
I- increase
E- decrease
Lung pressure during inhalation and exhalation
I- decreases (lower than atmospheric pressure)
E- increases (higher than atmospheric pressure)
What is a cavity
A space/chamber
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange by diffusion between air in the lungs and blood in capillaries?
many rounded alveolar sacs- large surface area to volume ration
Thin, single layers of cells to minimise diffusion distance
Ventilation maintains high level of oxygen and low levels of CO2 - steep concentration gradient
What harmful chemicals are in cigarettes and effects of them?
Nicotine: narrows blood vessels, increases heart rate - increased blood pressure - leads to blood clots in arteries - can result in heart attack or stroke
Carbon monoxide: binds to haemoglobin- reducing capacity of blood to carry oxygen, puts more strain on breathing system - circulatory system needs to pump blood faster - raising blood pressure and increasing risk of coronary heart disease and stroke
Tar: is a carcinogen - lung cancer, contributes to COPD (chronic bronchitis and emphysema together)
Explain how smoking causes chronic bronchitis
Tar stimulates goblet cells and mucus glands to enlarge and produce more mucus
blocking the bronchioles and leading to infections and damaging the cilia (preventing them removing the mucus)
when a smoker coughs - attempt to remove mucus
Explain how smoking causes emphysema
it is the result of frequent infection (from the build up of mucus)
The phagocytes that enter the lungs release elastase (enzyme that breaks elastic fibres in alveoli)
Alveoli is less elastic and cannot stretch - many burst- reduces surface area for gas exchange
Patients become breathless and wheezy - may need constant supply of oxygen