Biology112 Unit 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
stimulus
produces change in variable
receptor
detects changes
Example of commensalism
Bison and birds, the bison kicks of insects and the birds eat them and have transport
barnacles and whales
Example of mutualism
Bees and flowers
some birds pick ticks off large mammals
Example of parasitism
Ticks and mammals
input
information sent along afferent pathway to control center
evolution
diversity of life evolved over time by process of mutation, selection, and genetic change
structure and function
basic units of structure define the function of all living things
information flow, exchange and storage
the growth and behavior of organisms are activated through the expression of genetic information in context
pathways and transformation of energy and matter
biological systems grow and change by processes based upon chemical transformation pathways and are governed by the laws of thermodynamics
systems
living systems are interconnected and interacting.
community
all the plants and animals in an area (not including abiotic factors)
ecosystem
includes the abiotic and biotic factors in the area

biosphere
encompases all of the ecosytems on earth
population
a group of the same species

characteristics of biotic things
maintain homeostasis, populations evolve, reproduce, excrete waste, genetic material, made of cells
what is a virus
abiotic, not made of cells, needs host to survive, reproduce not on own but hijack reproductive system of host, but has RNA and can evolve
sex reproduction and parasites
evolve to be ahead of parasites each generation
climate
long term, predictable, large geographical area (what you expect)
weather
temporary condition (what you get)
biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms (community of plants and animals in a given area)
temperate forest
Distinct seasons (we live in)

taiga/ boreal forest
conical trees, short growing seasons

tundra
cold and dry, layer of permafrost

why are the poles warming more rapidly?
a positive feedback loop, as ice melts there is less ice to reflect sunlight and the ice continues to melt
is global warming equal?
no
effects of global warming
rising sea level, extreme weather, floods, drought, famine, extinctions, forest fires
what is the effect of global warming of thunderstorms
heat causes more instability, increase the frequency and intensity of storms since the clouds are very high in the atmosphere but the hotter they are the heavier and more powerful they are
how can ice provide evidence of the change in the climate
the air bubbles contain what was in the atmosphere at the time they formed
what is the equation of exponential population growth
dN/dt = rmaxN
what is the equation for logistic population growth
dN/dt = rmax N(K - N/K)
ecological factors that increase the rate of infection of lyme disease
increase in temperature, increase in in prey abundance (prey for mice), increase in vegetation, increased precipitation (for more vegetation)
ecological factors that decrease the rate of lyme disease
decrease in temperature, increase in predators (of mice and small mammals), decrease in vegetation, decrease precipitation
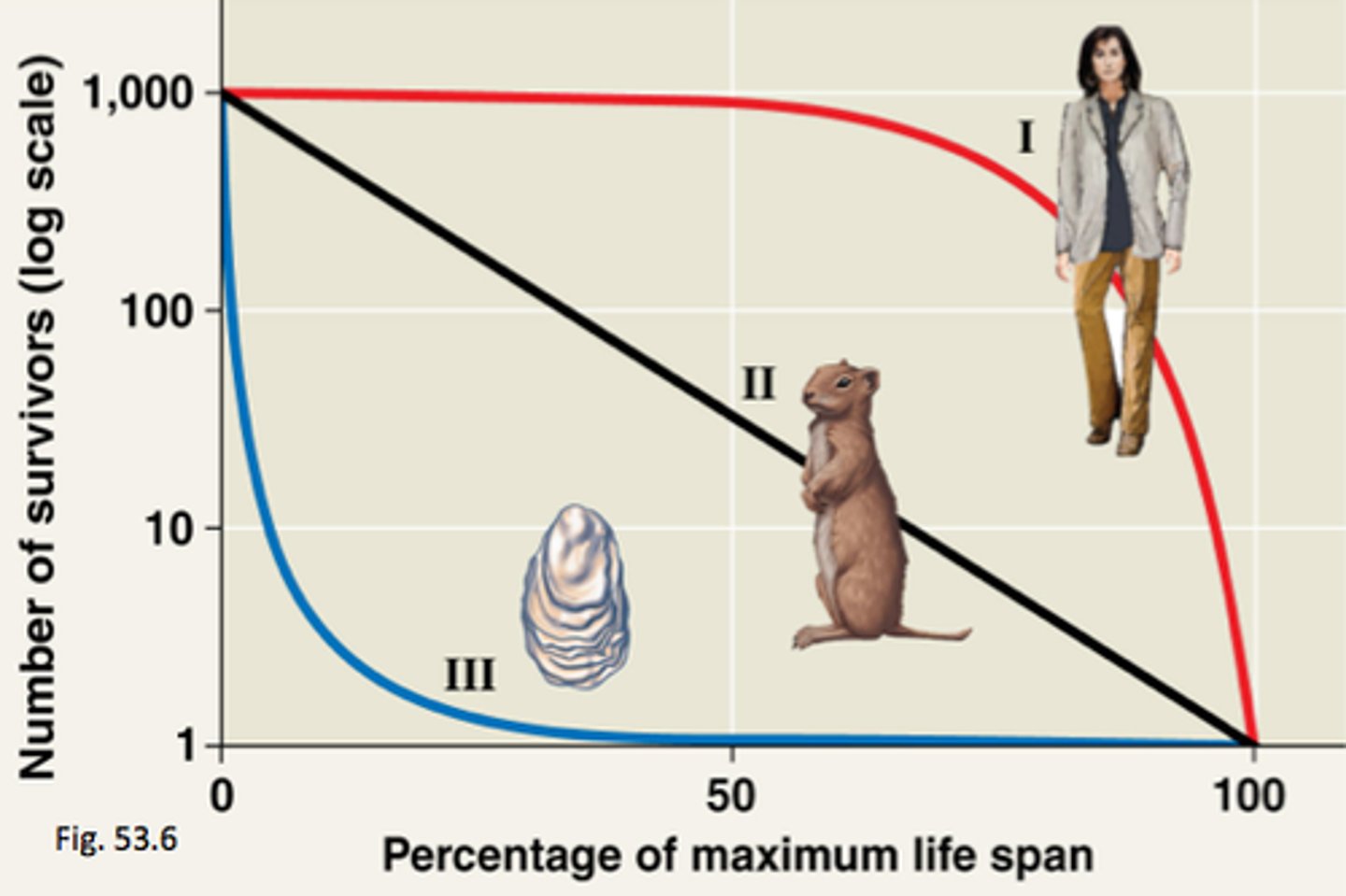
r-selected species
many offspring, little/no parental care, short life span, reproduce once, small animals like rats, insects, rabbits
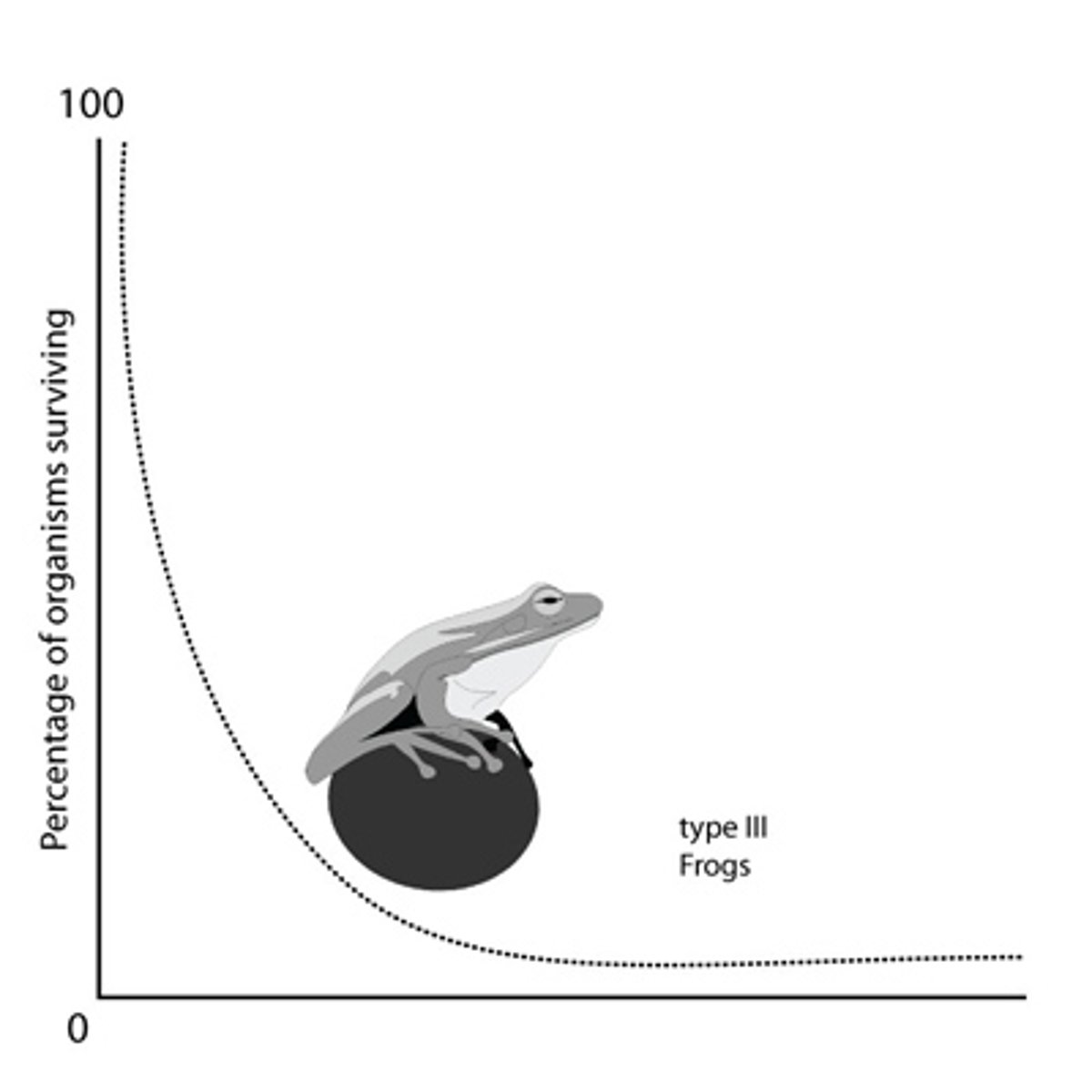
what is the survivorship of r- selected species?
type 3
K- selected species
fewer offspring, reproduce more than once, longer life span, larger like elephants (and humans)
what type of survivor ship curve are K- selected species?
type 1
afferent pathway
where the information is sent through to get to the control center (brain)
efferent pathway
flow from control center (brain) to effector
effector
gland/muscle that creates the response (trying to correct) (ex pituitary gland
give an example of positive feedback
in childbirth, the uterus contracts and sends info from the cervix from the brain, triggering the pituitary gland to release oxytocin to the blood stream which tells the uterus to contract more and theres more pressure on the cervix this process amplifies
symbiosis
close interactions between individuals of different species over an extended period of time which impact the abundance and distribution of the associating populations.
what does it mean if N>K
the population is shrinking, dN/dt is getting smaller, they are above carrying capacity, and death rates are greater than birth rates
what is dN/dt
the rate of change in a population
feedforward change
the body is anticipating a change in conditions and makes a proactive adjustment (change in set point)
example of a feedforward change
preparing for a race: heart rate increases, adrenaline is pumped
what does the body do when its cold
vasoconstriction and shiver
what does the body do when its hot
vasodilation and sweat
give examples of endotherms trying to cool down
elephants flap their large ears, rabbits release heat through ears, birds do the gular flutter where they rapidly vibrate their throats and below their beaks to cool down
Why are co2 levels lower in the summer (keeling curve)
More plants, more photosynthesis
How does the structure of bacteria borrelia help it
It’s spiral key structure allows it to burrow into cells
how do penguins (endotherm) hold heat
with layers of fat
what happens when an organism has a larger surface-area-to-volume (SA/V) ratio
they lose heat easier and gain heat easier (think of little kids getting cold hot/cold easier, they are smaller)
endotherm
an generate body temp from within (from metabolism)
higher metabolic rate
requires more calories
can lose body heat quickly
animals need to stay warm overnight so eat a lot
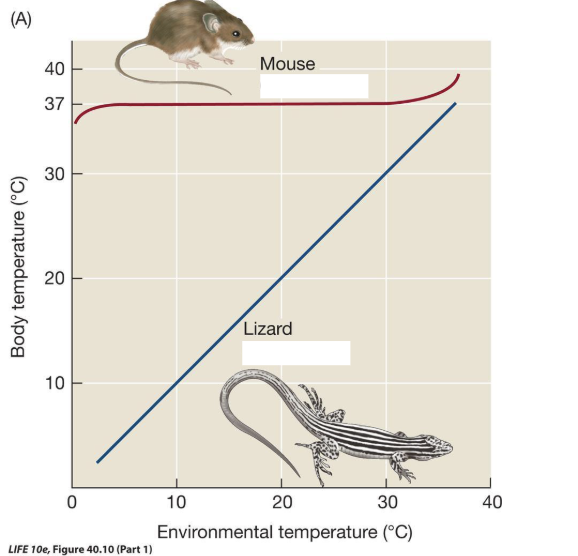
ectotherm
cant generate own heat, body temperature has a direct relationship with the environment
has to adjust behavior to maintain body temperature
snakes can go months without eating, dont need it
glycogen
storage form of glucose
glucagon
converts glycogen to glucose, released when glucose levels are low
insulin
tells body to convert glucose to glycogen
life history
pattern of an organism's survival and reproductive events throughout its lifetime
what are the 3 patterns of population distribution
uniform, random and clumped

what drives patterns of population distribution
a mix of biotic factors (living things like food availability, competition, predation, and disease) and abiotic factors (non-living environmental conditions like climate, water, and shelter)
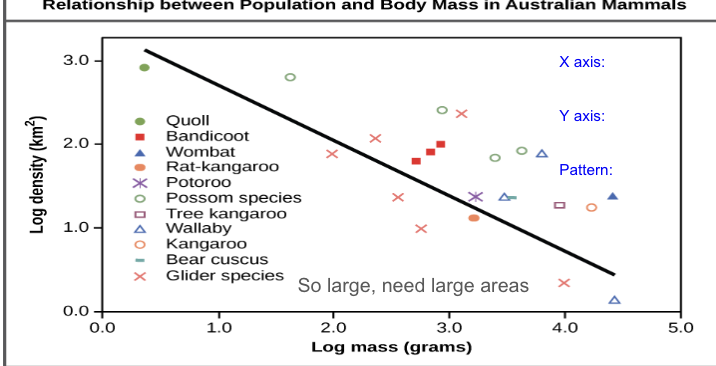
what is the relationship between population density and population size
the larger a species is, the smaller its population size is
inverse relationship
bigger animals need more space (thing elephants)