52. Preparation junctions’ types. Partial crown – definition, types.
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
whats in it
require,ets of a prep junction/finishing line
types of finishing line
MARGIN finish
partial crown
types of partial crowns
advantages/disadvangtages
additional: CREATING ¾ CROWNS FOR INCISORS VS PREMOLARS/MOLARS (study on second round of essays)
require,ets of a prep junction/finishing line
must be clear, smooth, well defined
must lie on healthy tooth structure
types of finishing line
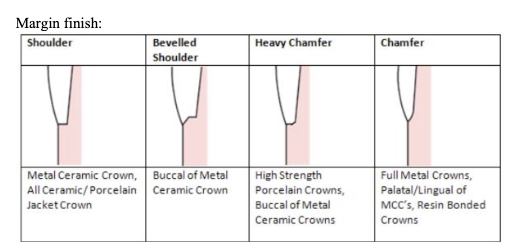
Types of finishing line:
Feathered edge – knife or chisel edge
Chamfer (quarter of a sphere or quarter of an ellipse): Chamfer with bevel
Shoulder:
- Butt shoulder
- Shoulder with bevel
- Radial shoulder. (BE SO REAL)
4. 135dc preparation junctio
margin finish
SBHC
SOME BALLS HAVE COME
adv and disadv
advantages:
:
- Saving tooth structure -
- Easy for finishing and polishing by the dentist and easy for cleaning by the patient.
- Safe for the periodontal tissue
- Easy for luting (cementing)
- Easy to adapt, because of the
visibility of the margins
- There is always an opportunity to
check the tooth vitality if necessary
Disadvantages
Poor retention in comparison to the
full anatomic crown, but still can be
used as a single crown, or as a
retainer for small FPD.
- It is not recommended as a retainer
for long FPDs, especially in the
distal area.
- Usually, there is a need of additional
retentive elements.
what is a partial crown. and types?
3⁄4 crown: is a partial coverage restoration that restores the occlusal surface(or incisal
edge), and three axial surface of the clinical crown where the buccal or facial surface
is not included
- Reversed 3⁄4 crown : is a partial coverage restoration that restores the occlusal
surface(or incisal edge), and three axial surface of the clinical crown where the lingual
surface is not included.
- Mesial 1⁄2 crown : is a partial coverage restoration that restores the occlusal
surface(or incisal edge), the mesial surface and a portion of the facial or lingual
surfaces.
- 7/8 crown : is a partial coverage restoration that restores all surfaces of the clinical
crown except the mesiobuccal cusp - used only for the maxillary first molar teeth.
¾ partial crown for premolars/molars prep as well as incisors
(unnecessary actually don’t learn)
🦷 3/4 Crown Prep – Premolars & Molars
1. Functional cusp reduction – 1.5 mm
2. Non-functional cusp reduction – 1.0 mm
3. Occlusal reduction – with a 45° phase using a conical bur
4. Axial reduction – start from lingual with a torpedo bur
5. Proximal surfaces – reduce with short needle bur, finish with torpedo bur
6. Create approximal chutes – toward the buccal side, parallel to long axis
7. Connect chutes with occlusal ditch
8. Finishing – smooth all surfaces with a carbide bur, light pressure
1. Lingual surface groove – use a small spherical bur (~0.7 mm)
2. Incisal edge reduction – with the same spherical bur
3. Lingual axial wall – shaped with a torpedo bur
4. Proximal walls – use short needle bur, avoid contact points
⤷ Finish later with enamel knife and torpedo bur
5. Create approximal chutes – toward facial (vestibular) side, parallel to facial axis
6. Connect chutes with occlusal ditch
7. Finishing – use a carbide bur, gentle strokes