Gas Exchange and Circulation
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I recommend you use paper for the diagram questions and that you draw the diagrams before filling in. I took the diagramds from lecture BIO 201 Lecture 22 Gas Exchange and Circulation (Creighton University)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What does a true circulatory system consist of?
Blood vessels
One or more hearts to generate hydrostatic pressure
Blood (or hemolymph) that moves through vessels
What are the 5 important processes of circulating blood?
Move respiratory gases
Move nutrients and wastes
Distribute hormones and immune system-cells
Distribute heat
Provide hydrostatic pressure
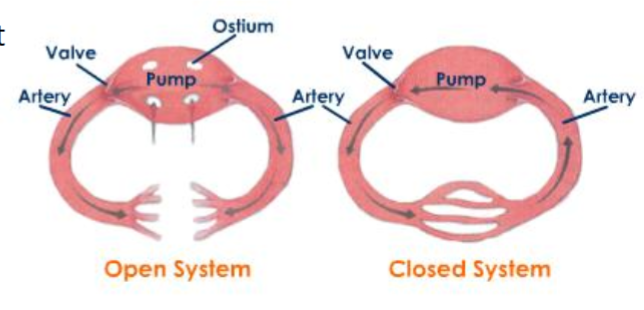
What are the two circulatory systems?
Open or closed
Where do vessels empty into in an open circulatory system?
Sinus (open, fluid filled spaces)
After vessels empty into the sinus, what re-enters the vessel/heart system?
Hemolymph
What animals contain an open circulatory system?
most invertebrates
In a closed circulatory system, where does blood stay during transit?
in vessels
What is a benefit of the closed circulatory system?
more percise delivery to needy tissues
What animals contain a closed circulatory system?
all vertebrates
Draw the open vs closed circulatory systems
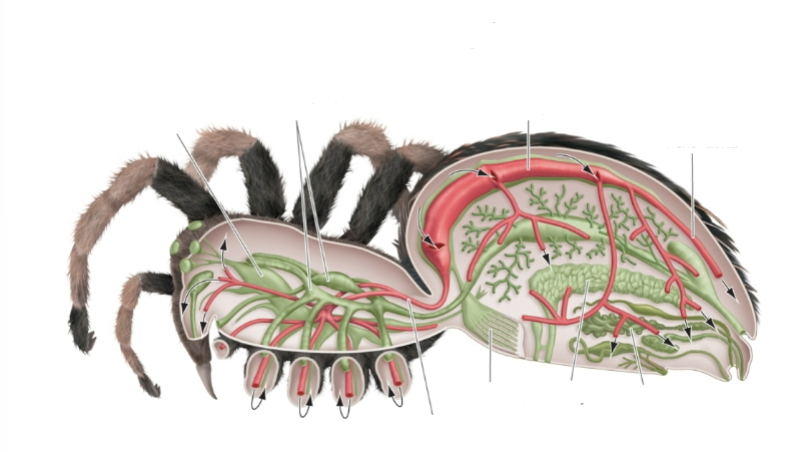
Label this spiders circulatory system
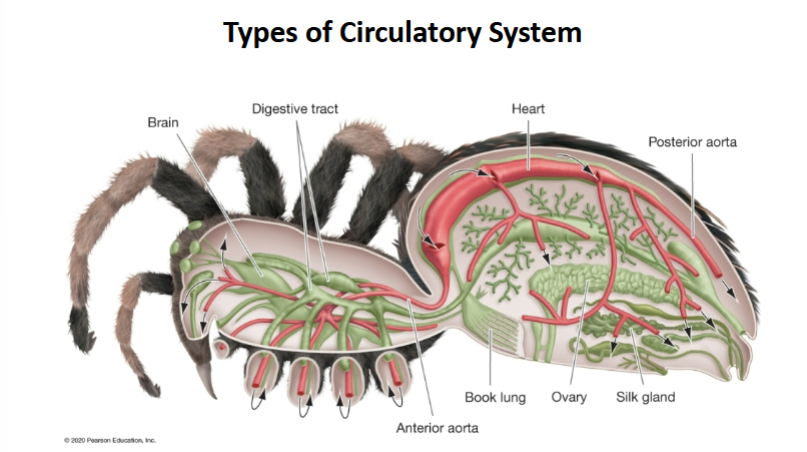
Open systems where metabolic rates are ____ (sessile, slower-moving animals)
lower
Closed sustem for metabolic rates that are ____ (mobile, active and/or predatory animals)
higher
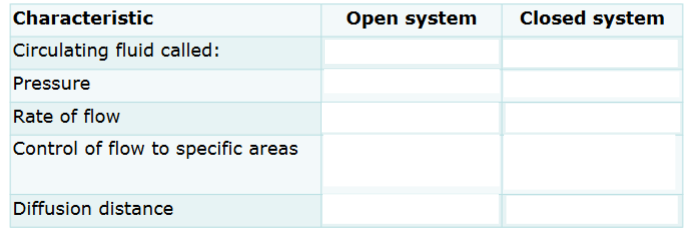
Fill this in
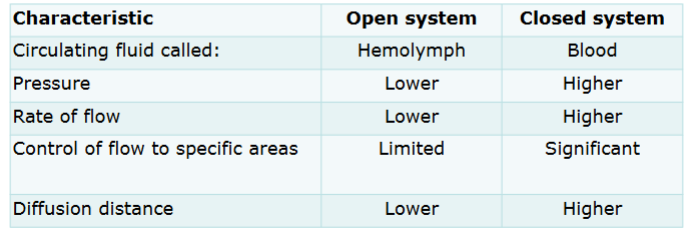
Do arteries carry blood towards or away from the heart?
Away
Arteries are large in diameter and thick-walled. What are the flow rates and pressure?
Highest flow rates, highest pressure
What are arterioles compared to arteries?
smaller versions with variable diameters
Do veins carry blood away or towards the heart>
towards
What are the flow rates and pressure in veins?
high flow rates, lowest pressure
What are vennules compared to veins?
thinner walled
What are venules compared to arterioles?
slightly larger
How many cells thick are capillaries?
1 cell thick
What do capillaries allow?
gas exchange between vessels and tissues
Capillaries are the ____ with the ____ flow.
Narrowest, slowest
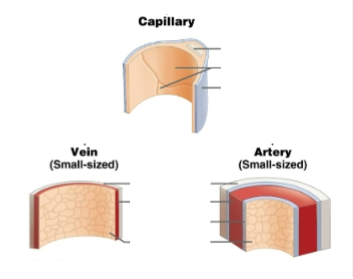
Fills this in
What does the heart do?
Pumps to generate pressure
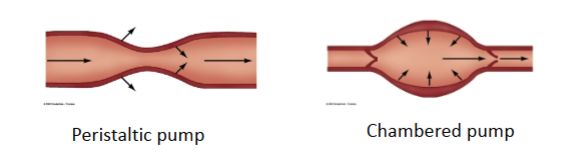
Peristaltic pumps -
part of blood vessels and limited to lower pressures
Chambered pumps -
specialized structures with one-way valves and can generate higher pressures
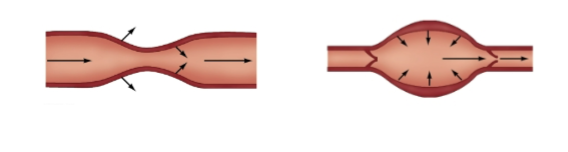
Label these pumps
How many ventricles do all vertebrate hearts have?
one or two
What is the main purpose of the ventricles?
Generate main pressure for circulation
How many atria do ventricles have?
one or two
What does the atria do?
help fill ventricles
What kind of valves are in the heart?
one-way
What do one-way valves help with?
keeping blood flowing in the correct direction
What differs between vertebrate groups? Hint: heart
number of chambers and number of circulatory circuits
How are gasses carried through blood vessels?
by blood
When blood exits the heart and travels to the lungs/gills, what does it pick up and what does it get rid of?
gains O2 and loses CO2
What is it called when blood exits the heart and travels to the lungs/gills to pick up O2 and drop off CO2?
pulmonary circuit
When oxygenated blood leaves the lungs and returns to the heart to pump to the tissues, what is it called?
systemic circuit
How many circuits and chambers do fishes have?
1 circuit, 2 chambers
how many circuits and chambers do amphibians, turtles, lizards, and snakes have?
2 circuits, 3 chambers
how many circuits and chambers do crocadilians, birds, and mammals have?
2 circuits, 4 chambers
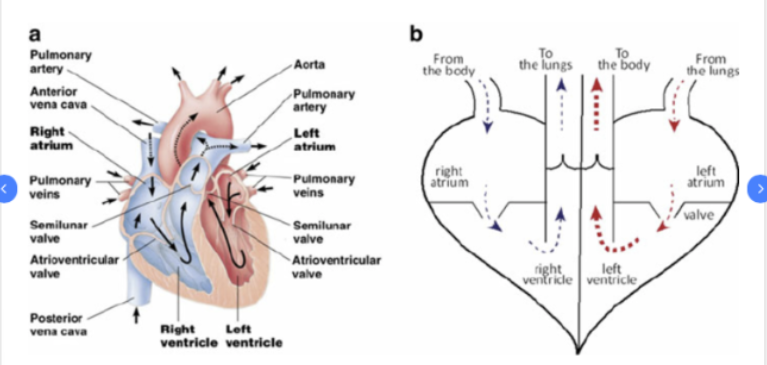
Left atrium and the left ventricle move blood through which circuit?
systemic circuit
Right atrium and right ventricle move blood throguh which circuit?
pulmonary circuit
Atrioventricular (AV) valves allow blood from where to where?
atria to ventricles
Semilunar (SL) valves allow blood from where to where?
ventricles to arteries
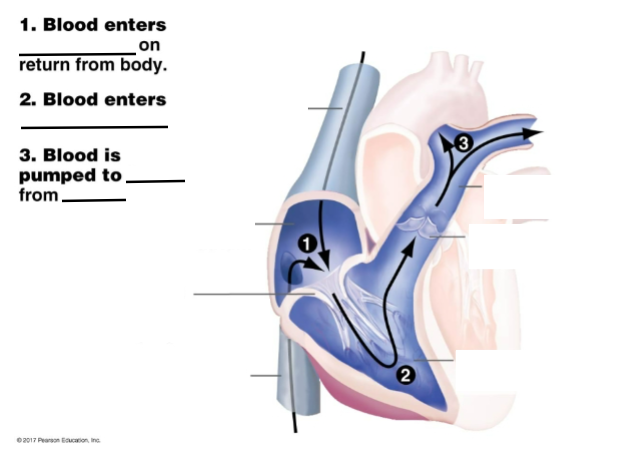
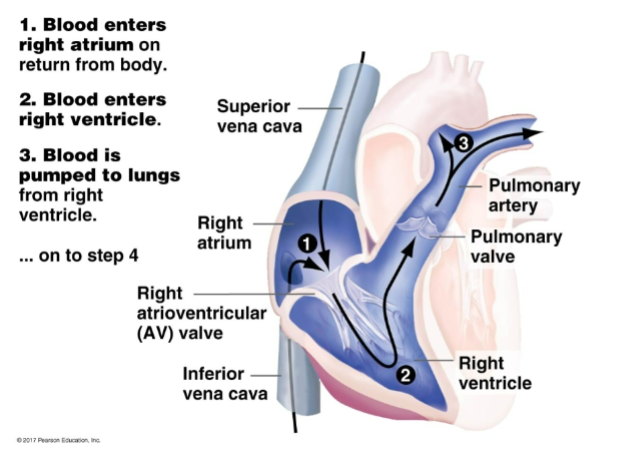
Fills in the steps and diagram
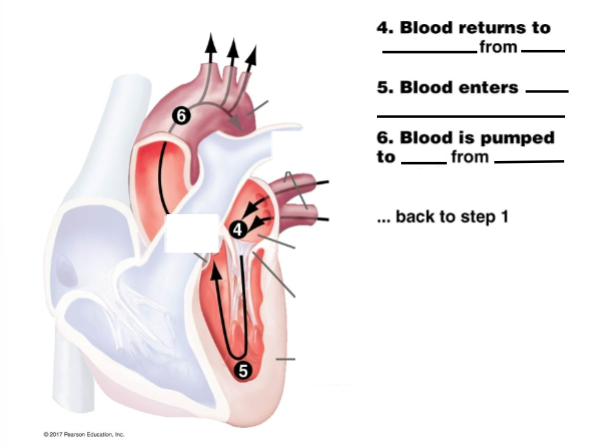
Fill in the steps and diagram
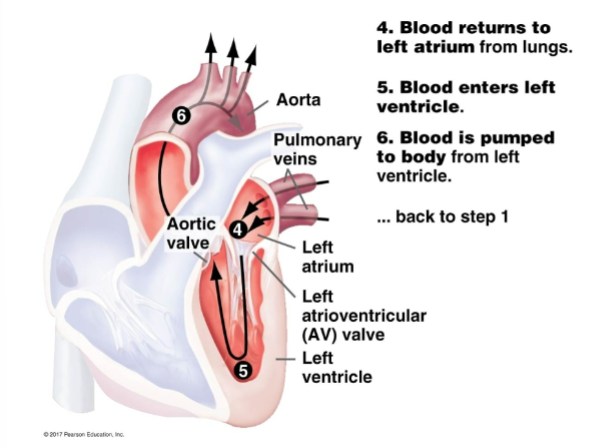
With no help from a photo, draw the full blood flow through the circulatory system of a mammal. Word bank: Lungs, Body, Right Atrium, Left Atrium, Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Artery, Pulmonary Veins, Superior Vena Cava, Aorta, AV valves, SL valves
What is the contraction of the heart?
Systole
What is the relaxed stage of the heart?
diastole
How is contraction of the heart triggered?
electrical signals
What is the primary pacemaker of the heart?
sinoatrial node
What influences the frequency (heart rate) of the heart?
nervous and endocrine systems
Contraction of the two atria followed by contraction of the two ventricles =
cardiac cycle
Step 1. of the Cardiac cycle
Sinoatrial node generates an electrical signal
Step 2. of the Cardiac cycle
Signal spreads to the atrial muscle cell and the atria contract, blood is ejected to the ventricles
step 3. of the cardiac cycle
Signal spreads to the atrioventricular (AV) node and is delayed before passing to the ventricles
Step 4. of the cardiac cycle
Signal spreads to the ventricles and causes them to contract. The atria relaxes and the ventricle empties toward the arteriesS
Step 5 of the cardiac cycle
ventricles relax
What barriers must O2 and CO2 cross to pass between air and blood inside the lungs?
Capillary wall, Extracellular Fluid, and Epithelial cells
How is most carbon dioxide transported from tissues to the lungs?
As bicarbonate ions (HCO3-)
Constricted blood vessels keeps you ____.
warm
Dialated blood vessels keeps you ____.
cold
By picking up hydrogen ions, hemoglobin prevents the blood from becoming too ____.
acidic
What promotes oxygen release from hemoglobin?
a decrease in pH
The Bohr shift on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve is produced by changes in ____.
pH
Key aspect of cooperative binding by hemoglobin
permits rapid uptake of oxygen in the lungs and greater delivery of oxygen once blood reaches capillaries in the body’s tissues
How many polypeptide chains does Hemoglobin have?
four
What does each heme group on Hemoglobin contain?
one iron ion
How many O2 molecules can bind to a hemoglobin molecule?
four
Blood returns to the heart via
pulmonary veins
from pulmonary veins, blood flows to the
left atrium
from the superior vena cava, blood flows to the
right atrium
from capillaries of the abdonimal organs and hind limbs, blood flows to the
inferior vena cava
What is the function of the left ventricle?
pumps oxygenated blood around the body via systemic circulation
What event of the cardiac cycle occurs when systolic blood pressure is measured?
ventricles contract, carrying blood into the aorta, and blood flows into the relaxed atria