Spinal Nerves and Heart
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
ANS/ Visceral Efferent
Involuntary control of body
At least 2 neuron systems
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic systems
Preganglionic
Cell body in CNS
Axon exits CNS
Synapses to the postganglionic neuron in a ganglion
Postganglionic
Cell body in ganglion
Axon goes to smooth/cardiac muscle or glands
Sympathetic
Fight or Flight
Used if actively hunting, running…
Parasympathetic
Rest and Digest
Used if sleeping, eating, GI motility
Sympathetic Trunk
From communicating branch of spinal nerves
Postganglionic cell bodies
Sympathetic Nervous System
Preganglionic neurons:
Cell bodies in thoracolumbar region (T1-L5)
Post ganglionic neurons:
Cell bodies in visible ganglia
“Thoracolumbar” system
Preganglionic fiber→ synapse at ganglia→ post ganglionic fiber
Cervical Ganglia - Sympathetic
Cervicothoracic ganglion- ganglion close to sympathetic trunk
Ansa subclavia- connects cervicothoracic/middle cervical ganglia
Forms ring around subclavian aa
Middle cervical ganglia
Vagosympathetic trunk (29) passes through (does not synapse)
Cranial nerves to heart (22)
Abdominal nerves
Preganglionic fibers from sympathetic trunk
Major splanchnic n
Minor splanchnic n
Lumbar splanchnic n
Celiacomesenteric ganglion
to abdominal viscera
Caudal mesenteric ganglion
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Preganglionic neurons in cranial/sacral region - “craniosacral” system
Postganglionic neurons found on their target structures- not visible ganglia
*If tagged on a parasympathetic nerve, it will always be preganglionic nerve fibers
Vagus Nerve (Cranial Nerve X)
Vagus- Esophagus
Originates in medulla
3 types of nerve fibers:
Visceral sensory fibers, somatic motor fibers, and visceral motor/ parasympathetic fibers.
Visceral sensory (Vagus) nerve fibers
sends information from pharynx, larynx, trachea, esophagus, and thoracic/ abdominal viscera
Somatic motor (Vagus) nerve fibers
innervates larynx, pharynx, esophagus
Visceral motor/ parasymapthetic nerve fibers
to thoracic and abdominal organs
*preganglionic/presynaptic parasympathetic fibers
Damage to Vagus nerve
decreased gut motility
Vagus nerve
starts out as part of Vagosympathetic trunk (in carotid sheath)
Gives off recurrent laryngeal nerves
R & L recurrent laryngeal nn.
Right recurrent laryngeal n
wraps around R subclavian a
Left recurrent laryngeal n
wraps around Aortic arch/ ligamentum arteriosum
longer, more likely to get damaged- Laryngeal hemiplegia (Roarers)
Vagus nerve- more branching
Caudal to heart, divide into dorsal and ventral branches
Both vagal trunk go through esophageal hiatus
L/R ventral vagal branches
combine to make ventral vagal trunk more cranially
L/R dorsal vagal branches
combine to make dorsal vagal trunk more caudally
Heart position
The base of heart is actually the “top”
points dorsocranially
The apex of heart points ventrocaudally.
Heart spans intercoastal spaces 3-6 in a dog
angled roughly 45 degrees
Apex of heart
points ventrocaudally
made of left ventricle
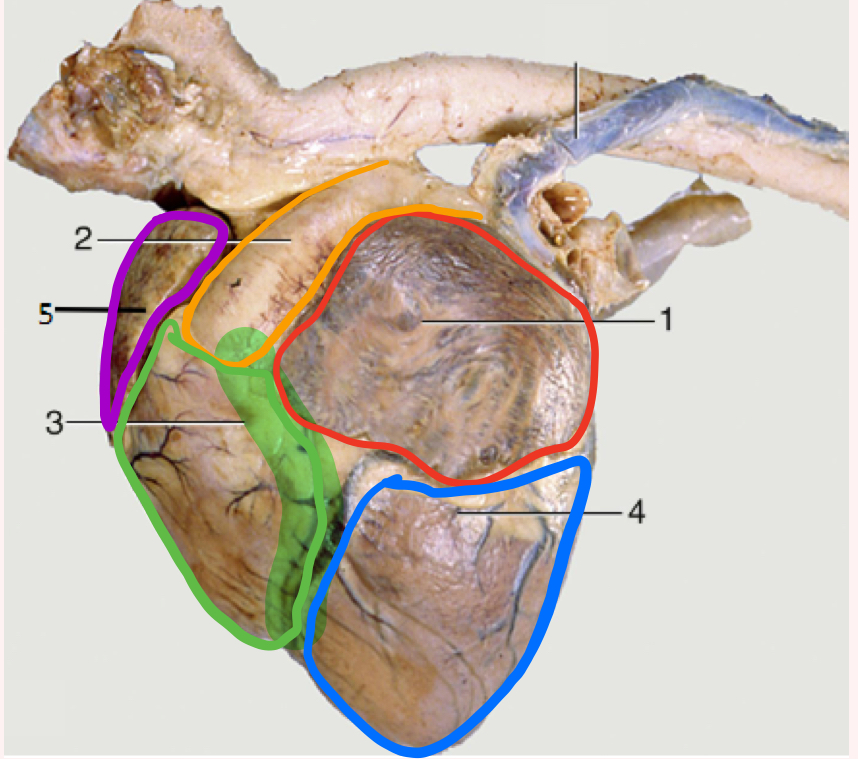
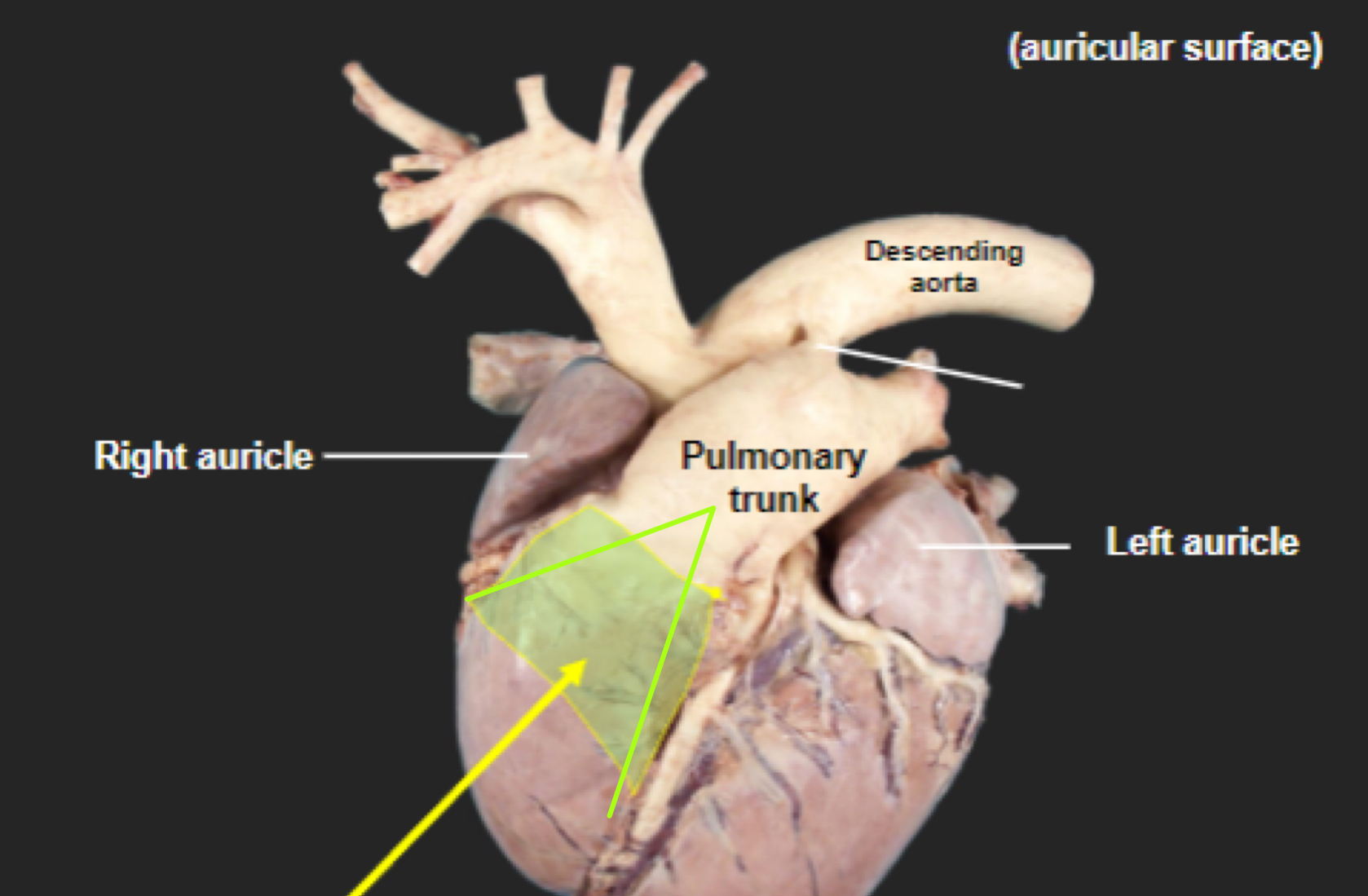
Auricular surface
Left side of heart- faces left side of chest
“Auricular” because you can see both auricles or “ears”
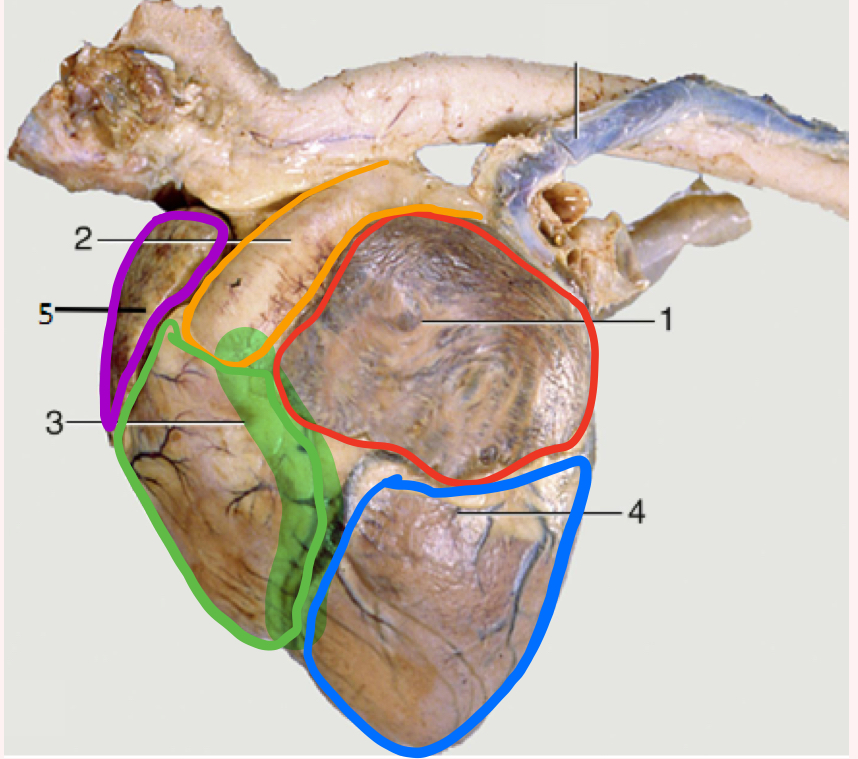
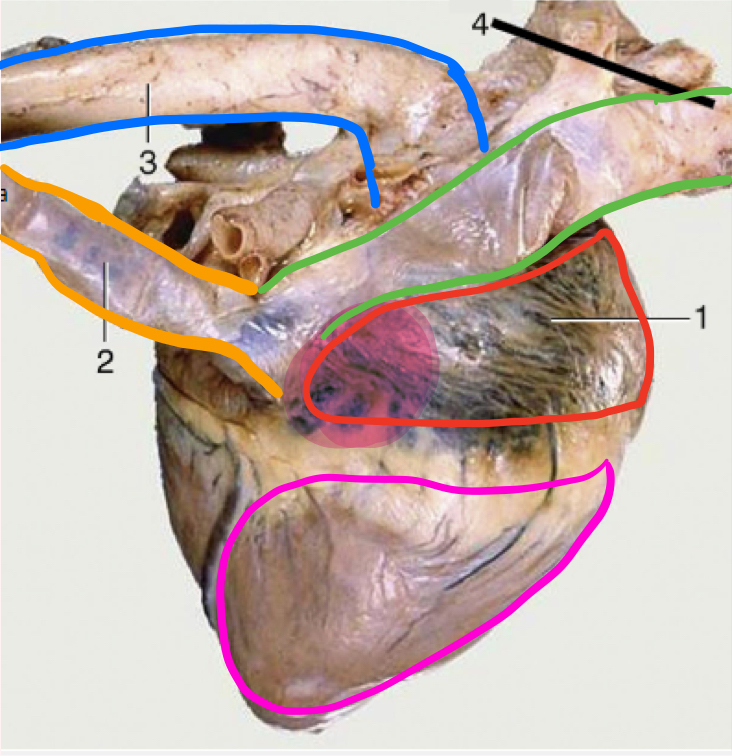
What is number 1?
Left auricle
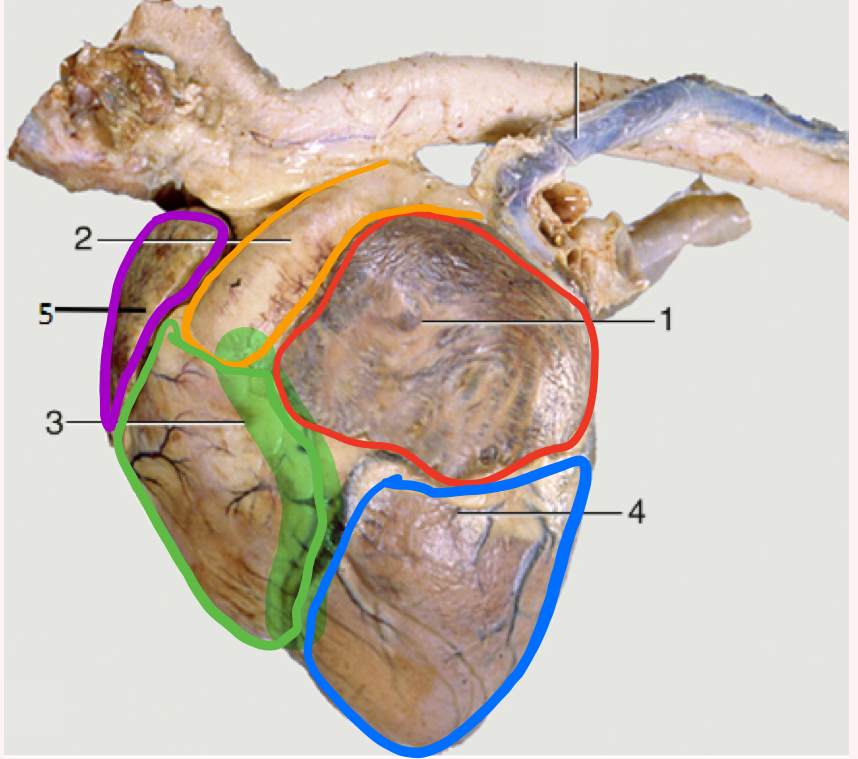
What is number 2?
Pulmonary trunk
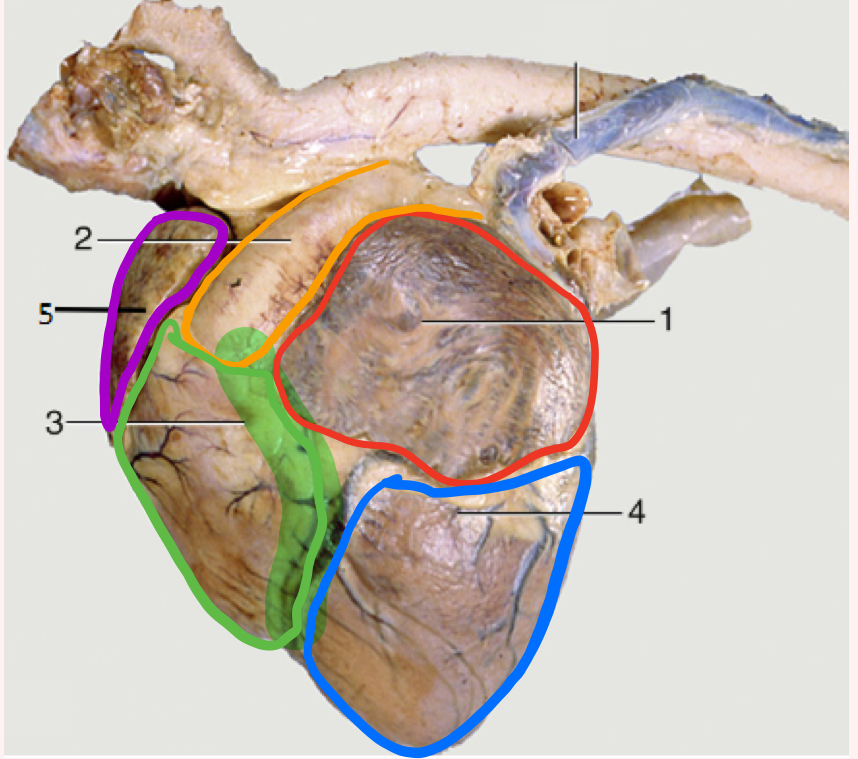
What is number 3?
Right ventricle
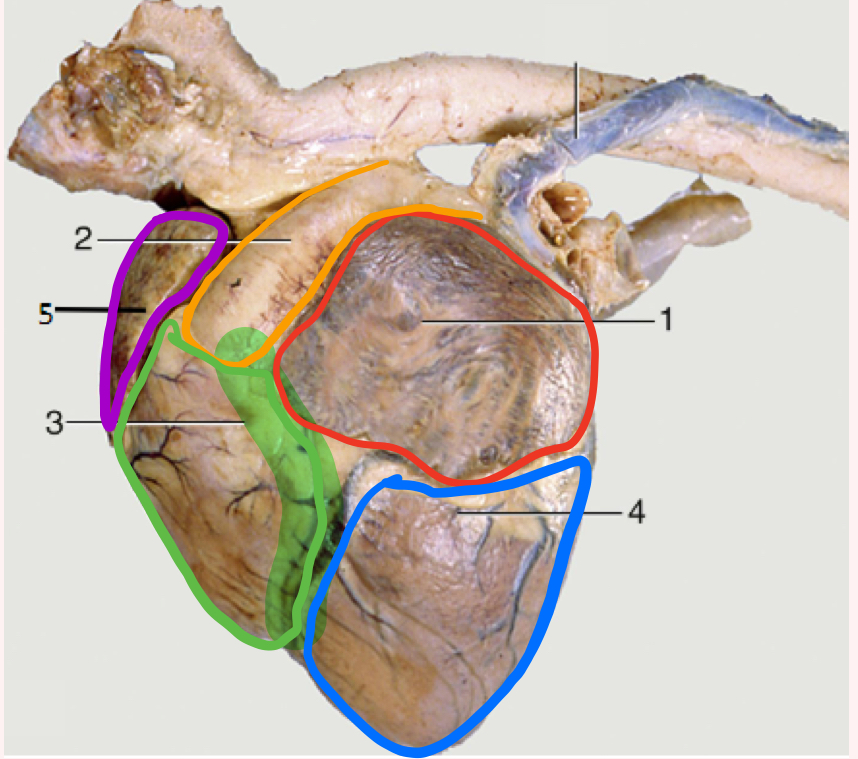
What is the highlighted portion near number 3?
Conus Arteriosus
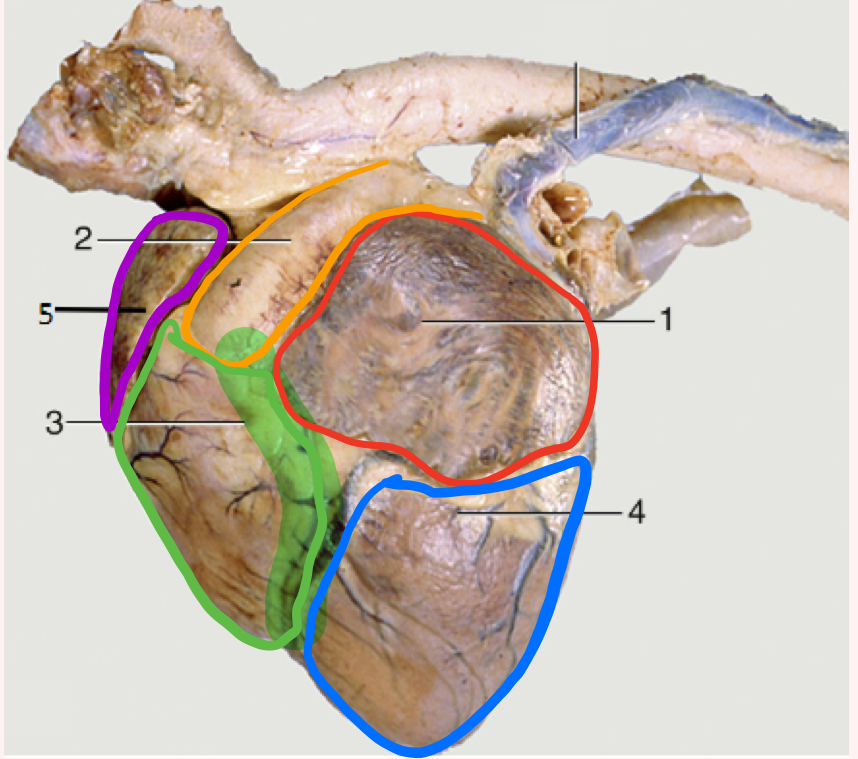
What is number 4?
Left ventricle (apex)
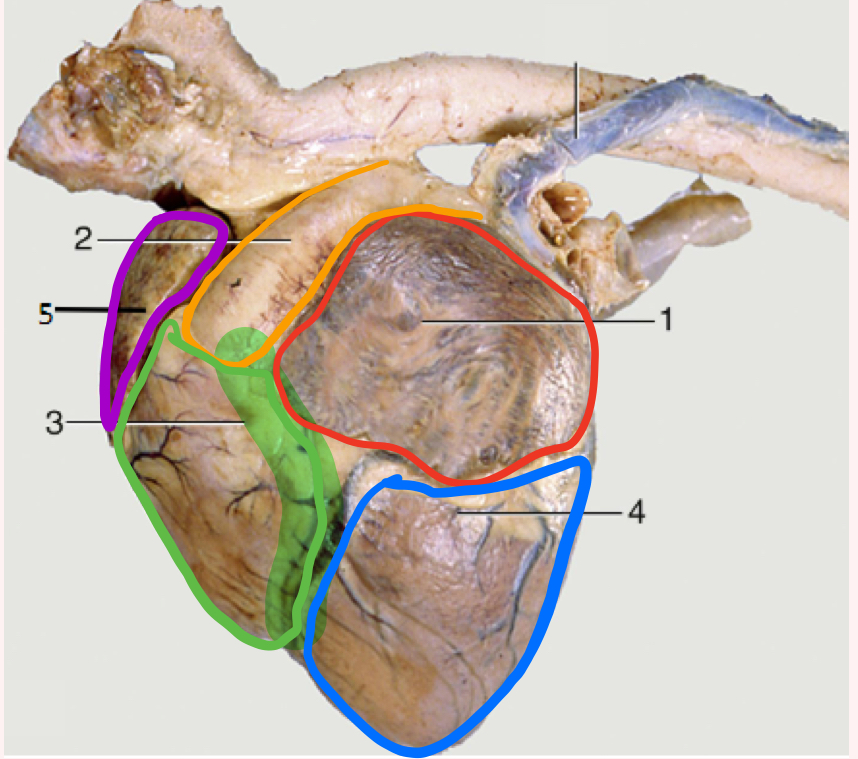
What is number 5?
Right auricle
Atrial surface
Right side of heart - right side of chest
“Atrial” because you can see right atrium really well
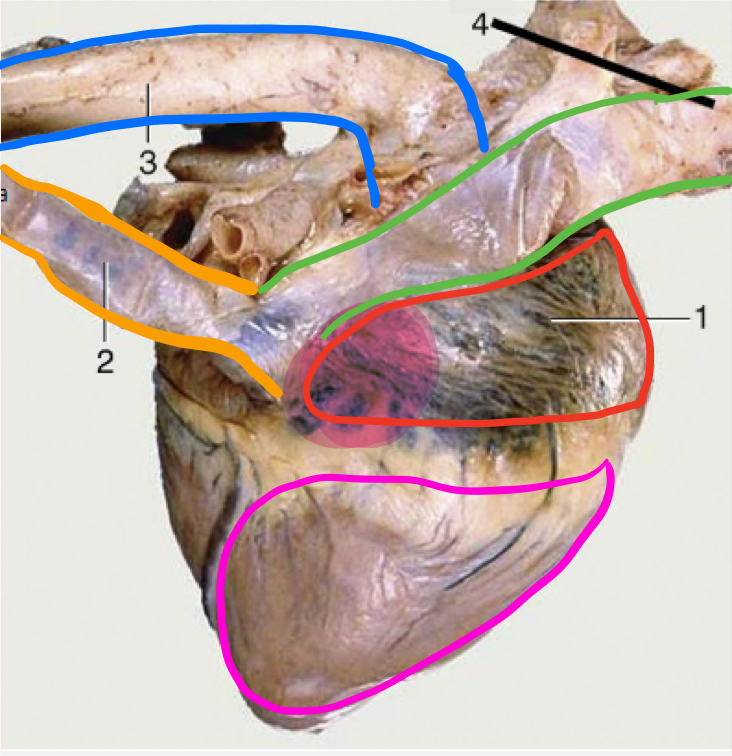
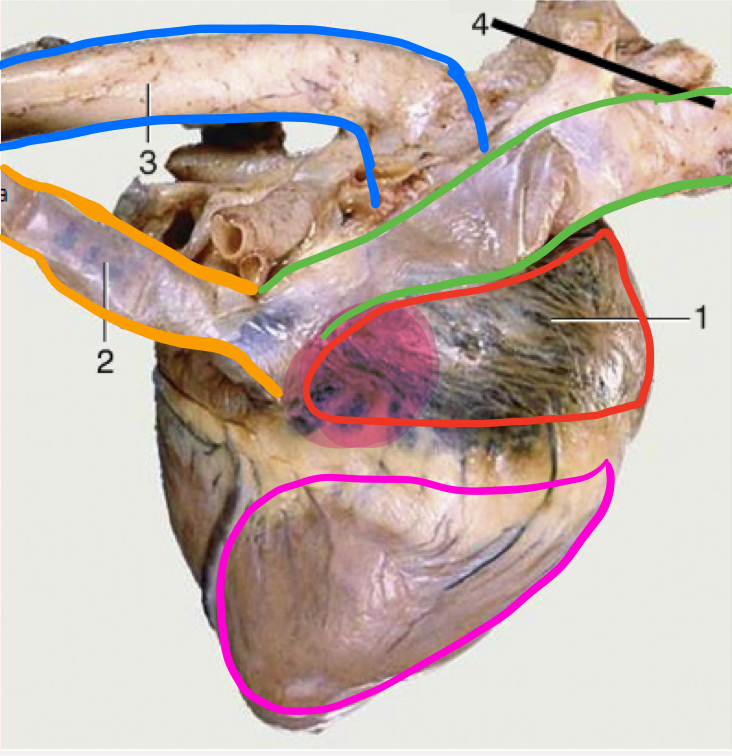
What is number 1?
Right atrium
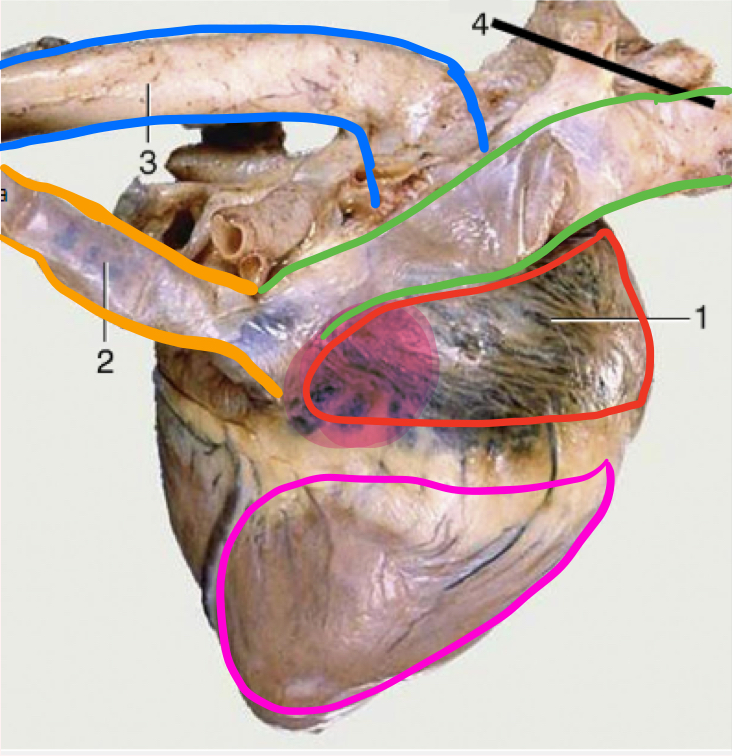
What is the portion in highlighted in magenta?
Sinus venarum
Sinus verarum
The sinus is a space, venarum refers to veins
space where cranial and caudal vena cavae drain into
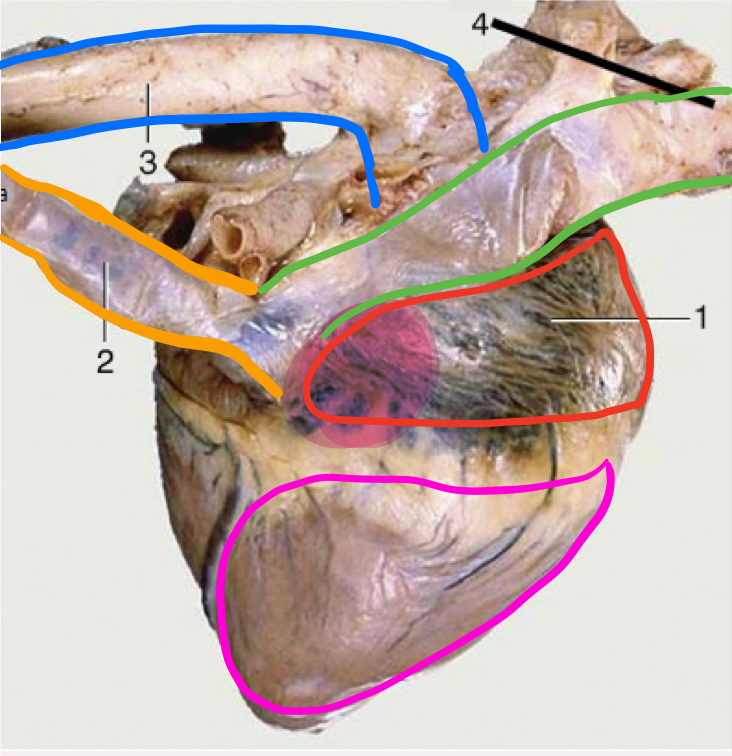
What is number 2?
Caudal vena cava
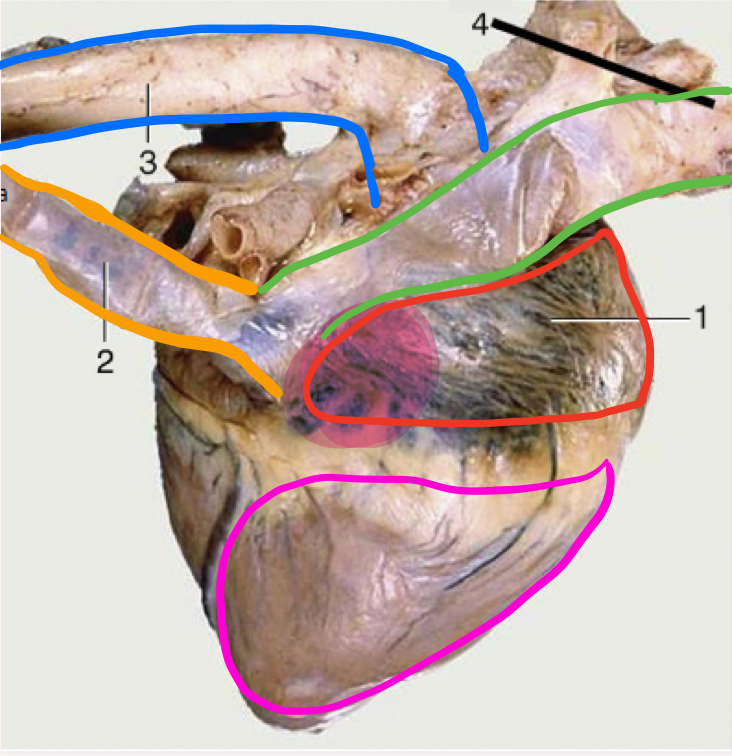
What is green?
Cranial vena cava
What is in blue?
Aorta
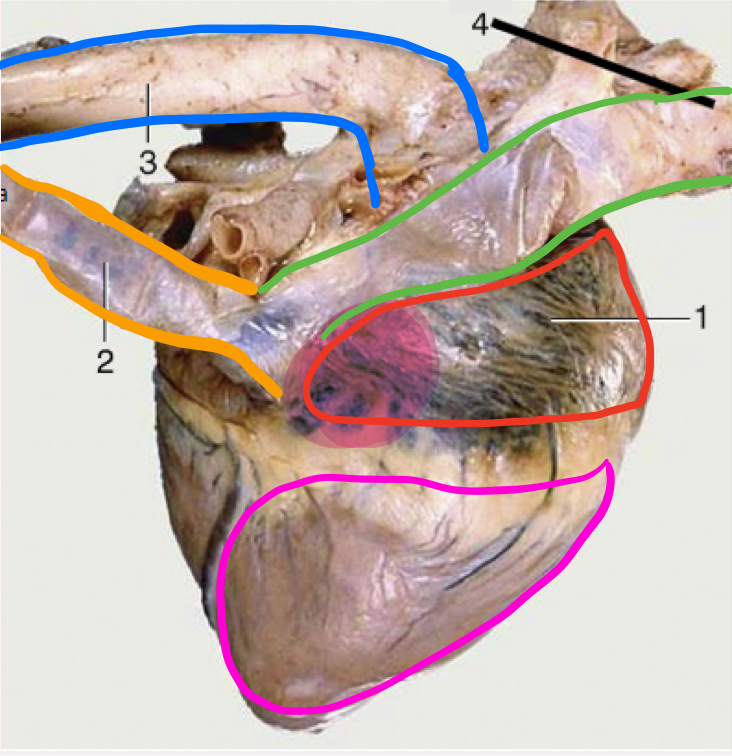
What is outlined in pink?
Right ventricle
Flow of Blood
Crainial and Caudal vena cavae drain blood into right atrium → Right atrium through right atrioventricular valve/ Tricuspid valve → Into right ventricle → right ventricle through pulmonary valve/a semilunar valve → pulmonary arteries to lungs→ Pulmonary veins from lungs into left atrium → Left atrium throught left AV valve/mitral valve into left ventricle→ left ventricle through aortic valve/semilunar valve into Aorta → Aorta → aortic arch → body
Pulmonary circulation
blood to lungs - pulmonary trunk
Systemic circulation
blood to body - aorta
Systole
ventricles contracting - blood ejected into either pulmonary or systemic circulation
Diastole
ventricles relaxing and atria contracting - blood filling ventricles
First heart sound (lubb/systole)
closure of two AV valves (tricuspid/ mitral)
blood hitting valves, closing AV valves - tricuspid (R) and mitral (L)
Second heart sound (dubb/diastole)
closure of semilunar valves (pulmonary/aortic)
blood closing semilunar valves- pulmonary (R) and aortic (L)
Valve projection - left side
Valve: P A M
Intercostal space: 3 4 5
Valve projection - right side
Valve: T
Intercostal space: 4
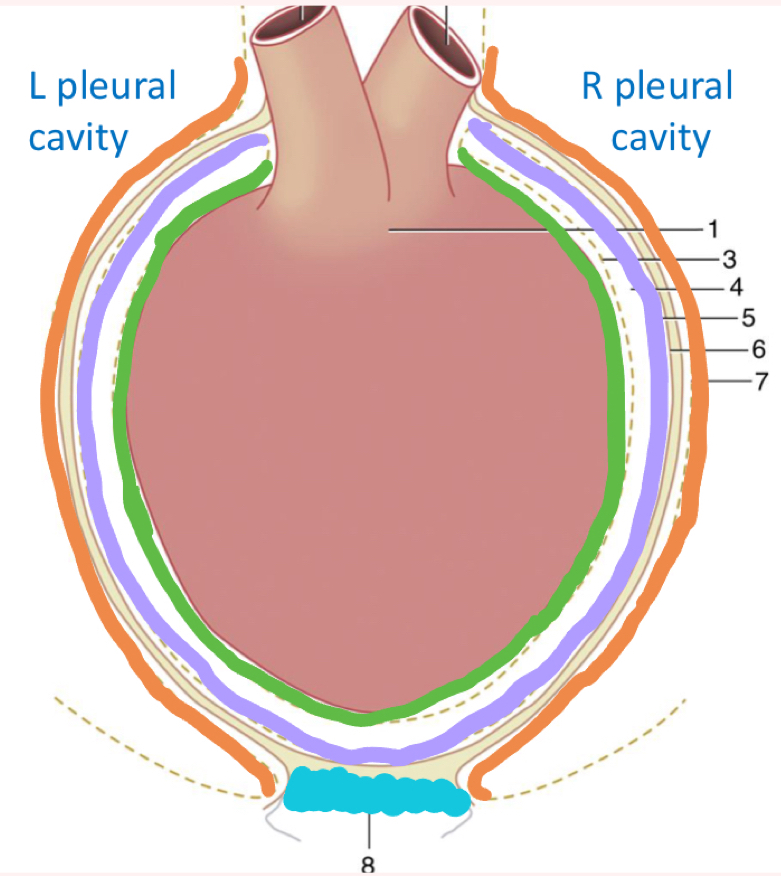
What is outlined in green?
Visceral pericardium/ epicardium
on heart, can’t get off
What is outlined in purple?
Parietal pericardium
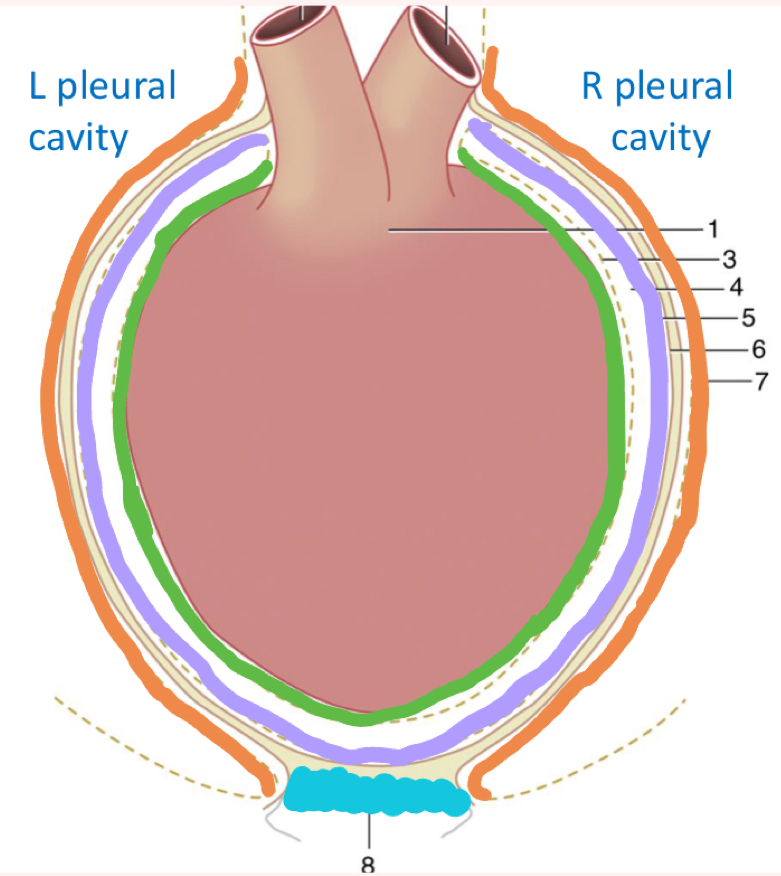
What is outline in tan?
Fibrous pericardium
Fibrous pericardium
Made of endothoracic fascia (“glue”)
Connects parietal pericardium and pericardial pleura
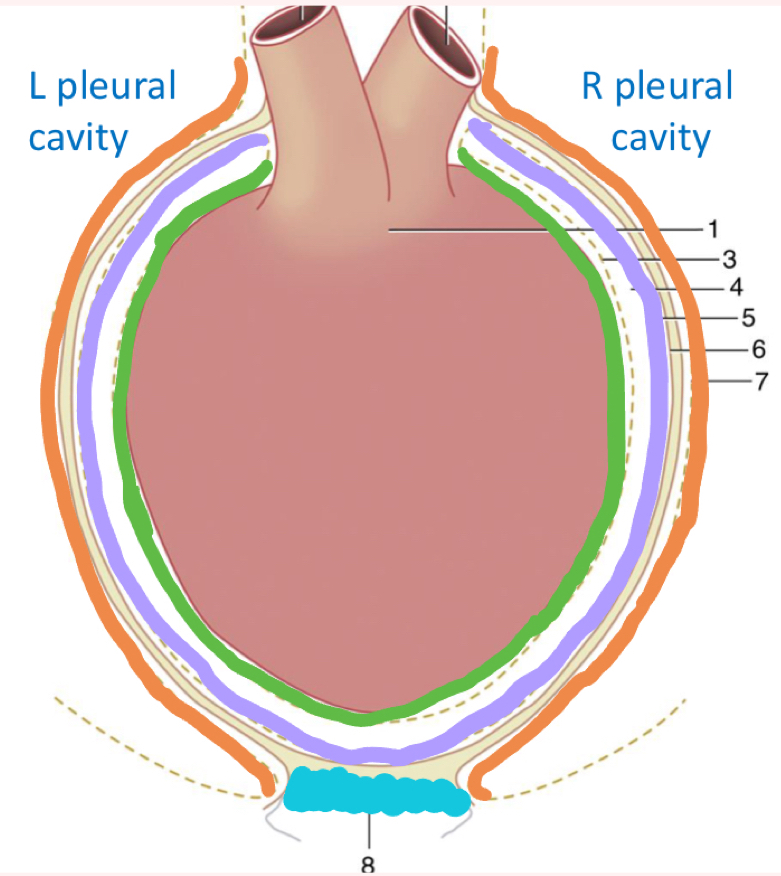
What is outlined in orange?
Mediastinal/pericardial pleura
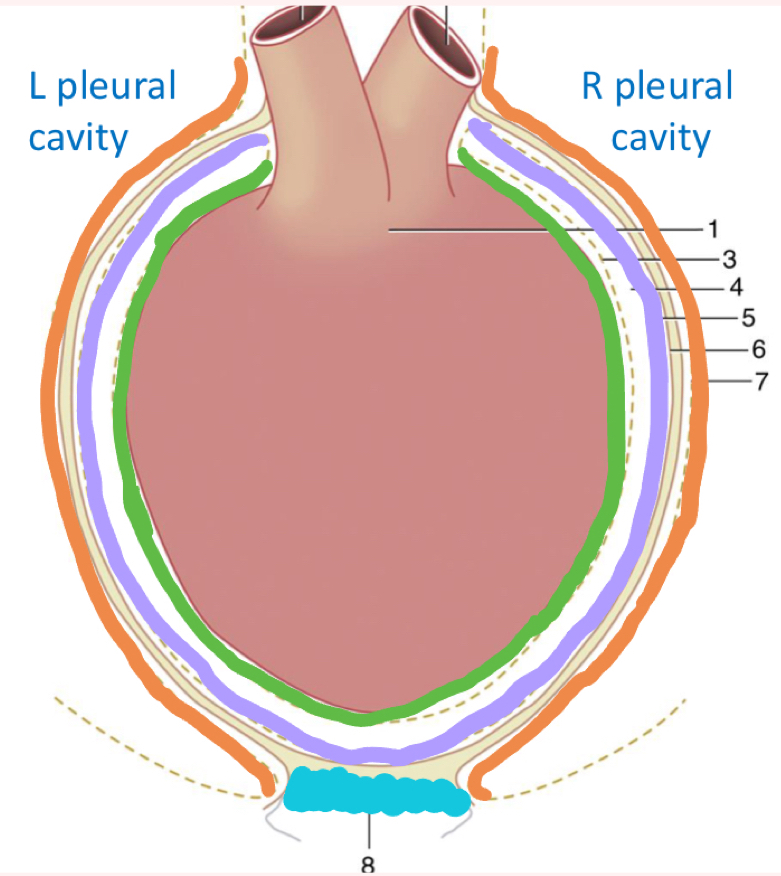
What is in blue?
Phrenicopericardial ligament
Phrenicopericardial ligament
connects diaphragm and pericardium
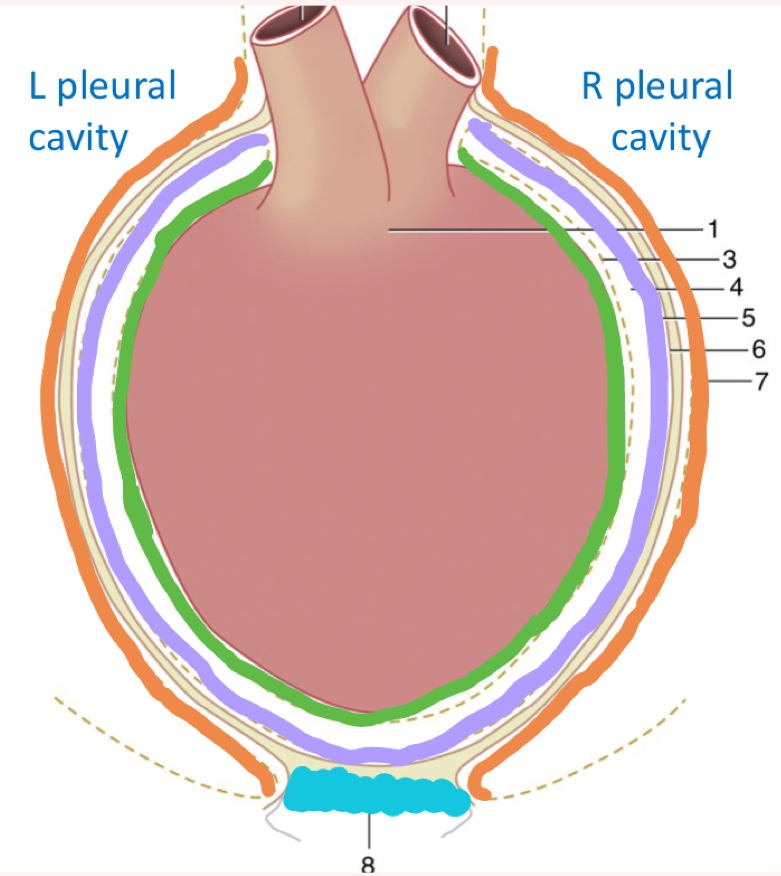
What is outlined in orange?
Pericardial/ Mediastinal Pleura
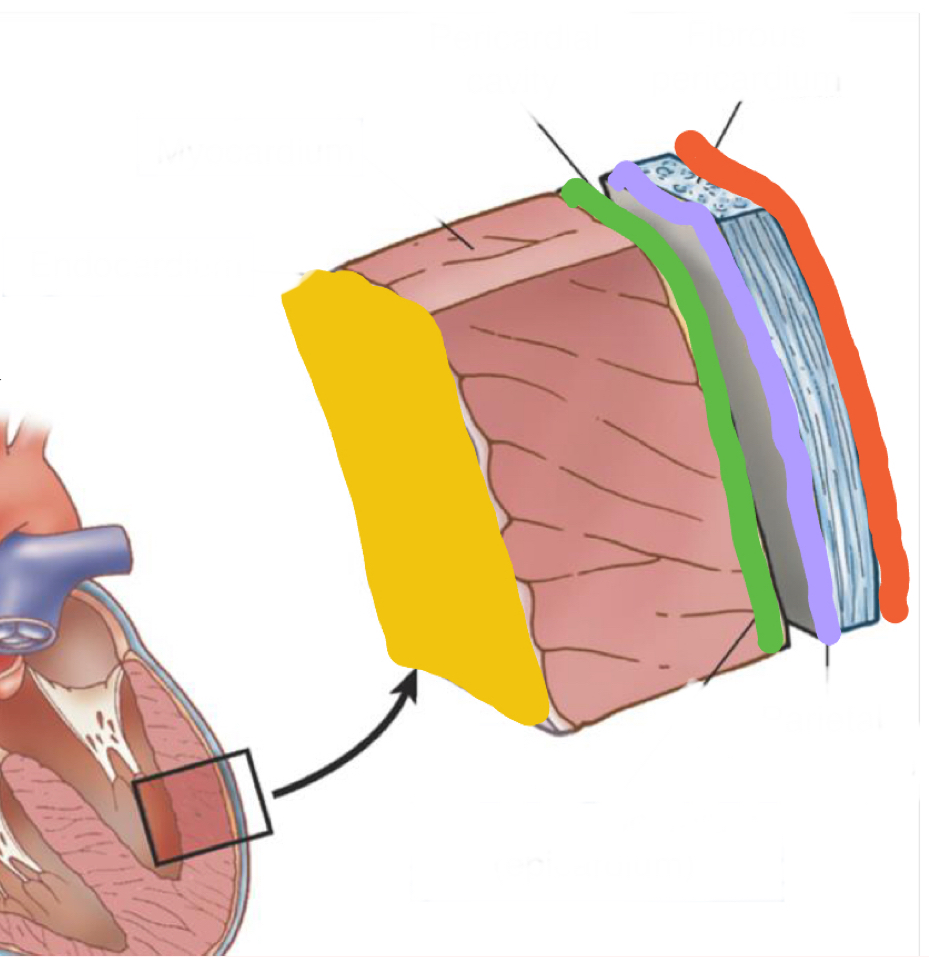
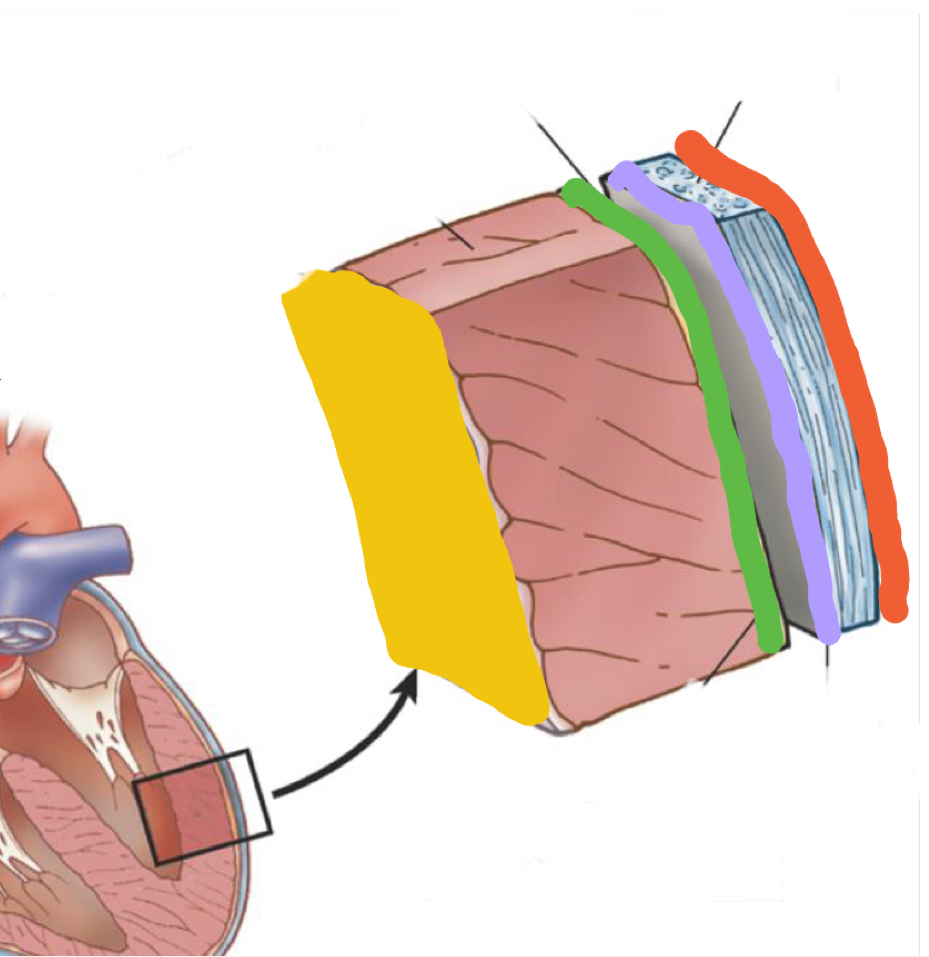
What layer is in grey?
Fibrous pericardium - endothoracic fascia
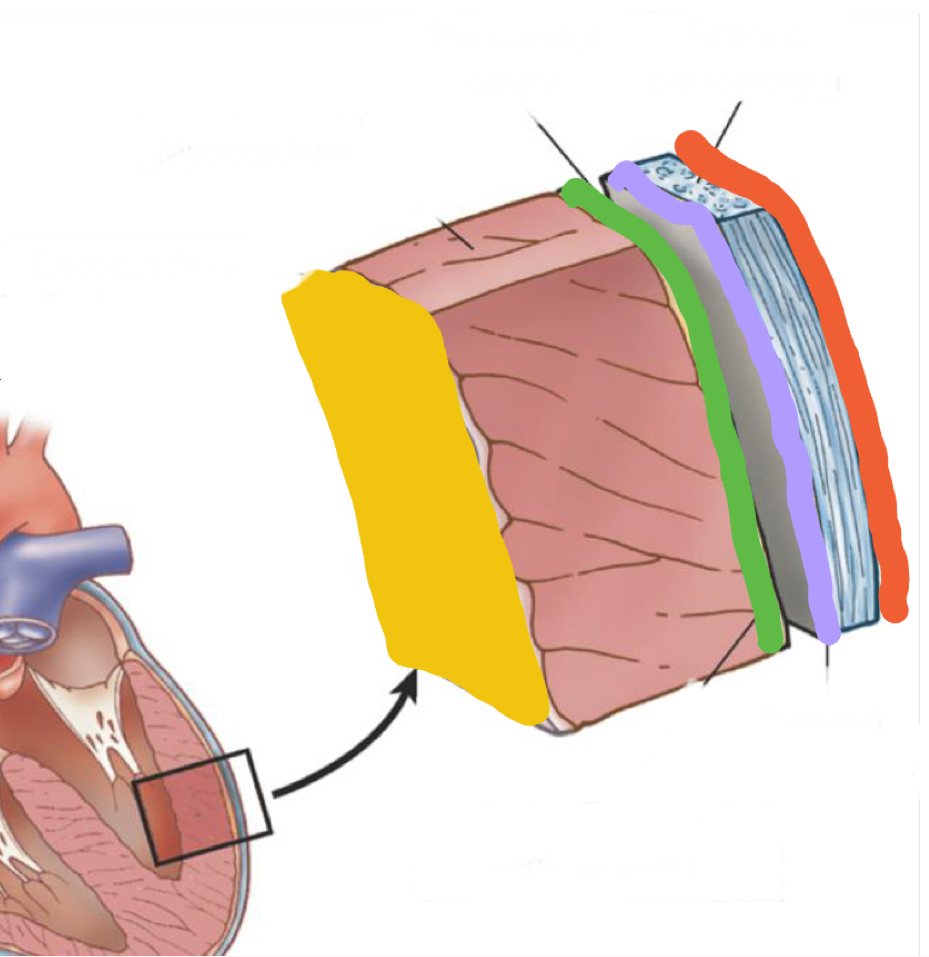
What is outlined in purple?
Parietal pericardium
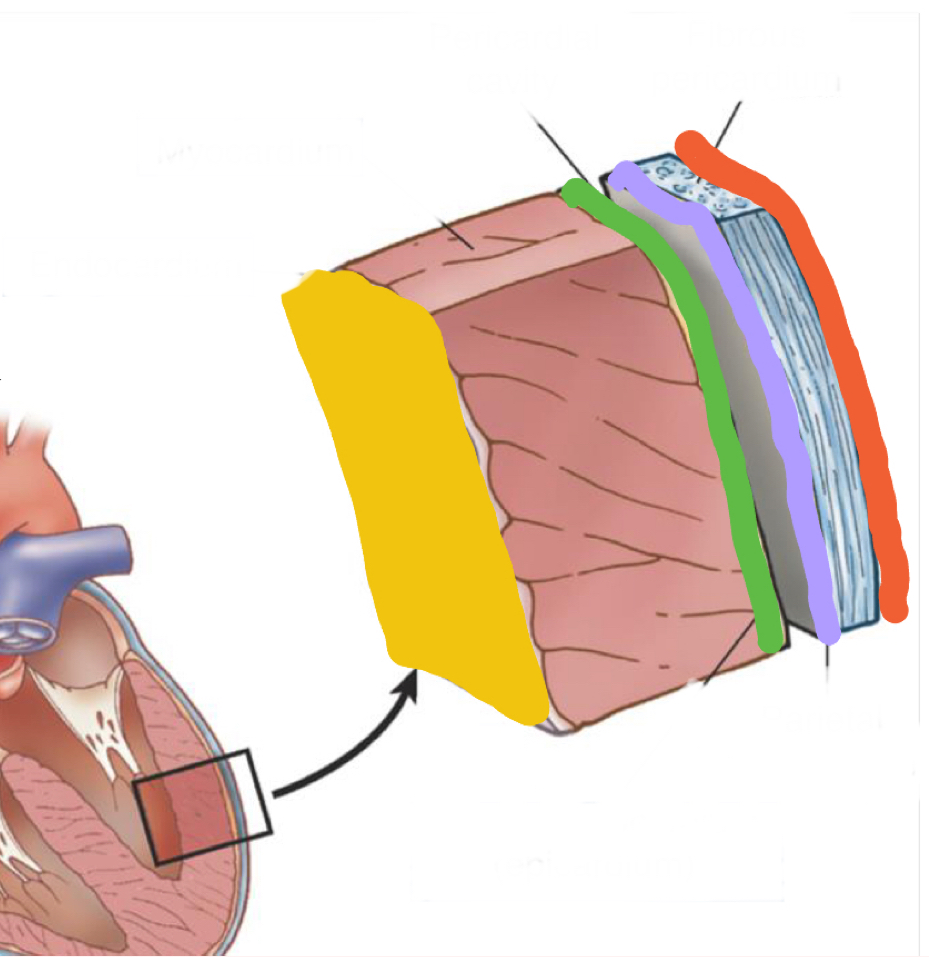
What is outlined in green?
Epicardium/ visceral pericardium
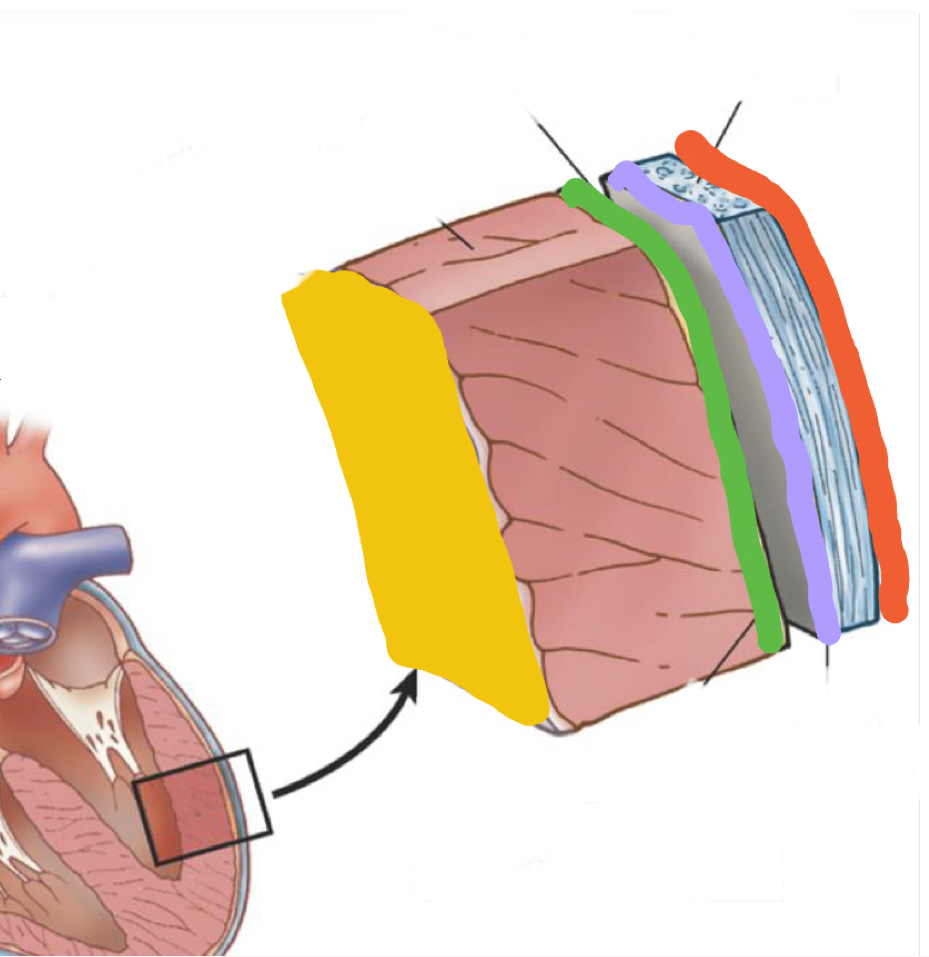
What layer is in pink?
Myocardium - heart muscle
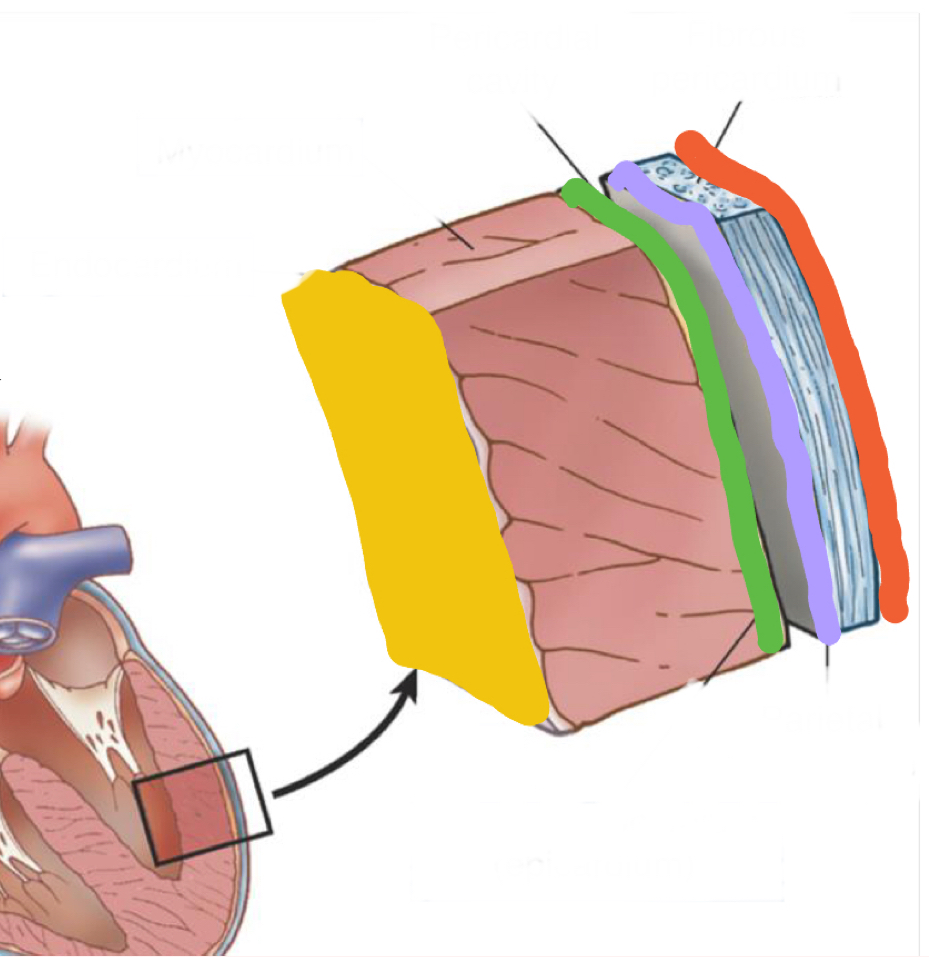
What is highlighted in yellow?
Endocardium - inner lining of heart muscle
Fibrous base
“Cardiac Skeleton”
4 fibrous rings for valves to attach to
Separates atrial mass from the ventricles
Sinoatrial nodes
pacemaker, in right atrial wall
Atrioventricular node
in interatrial septum
Atrioventricular bundle
R/L bundles straddle interventricular septum
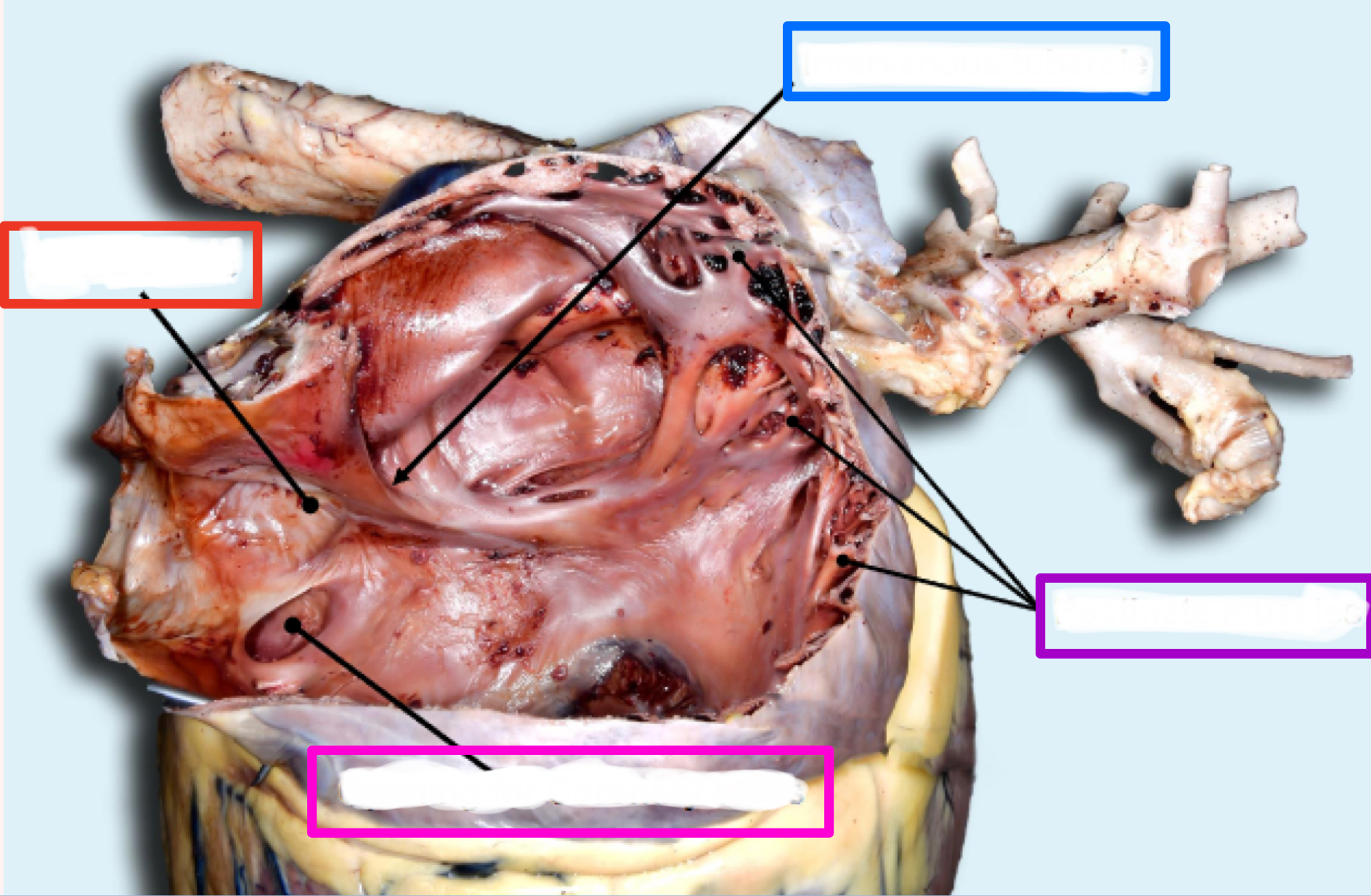
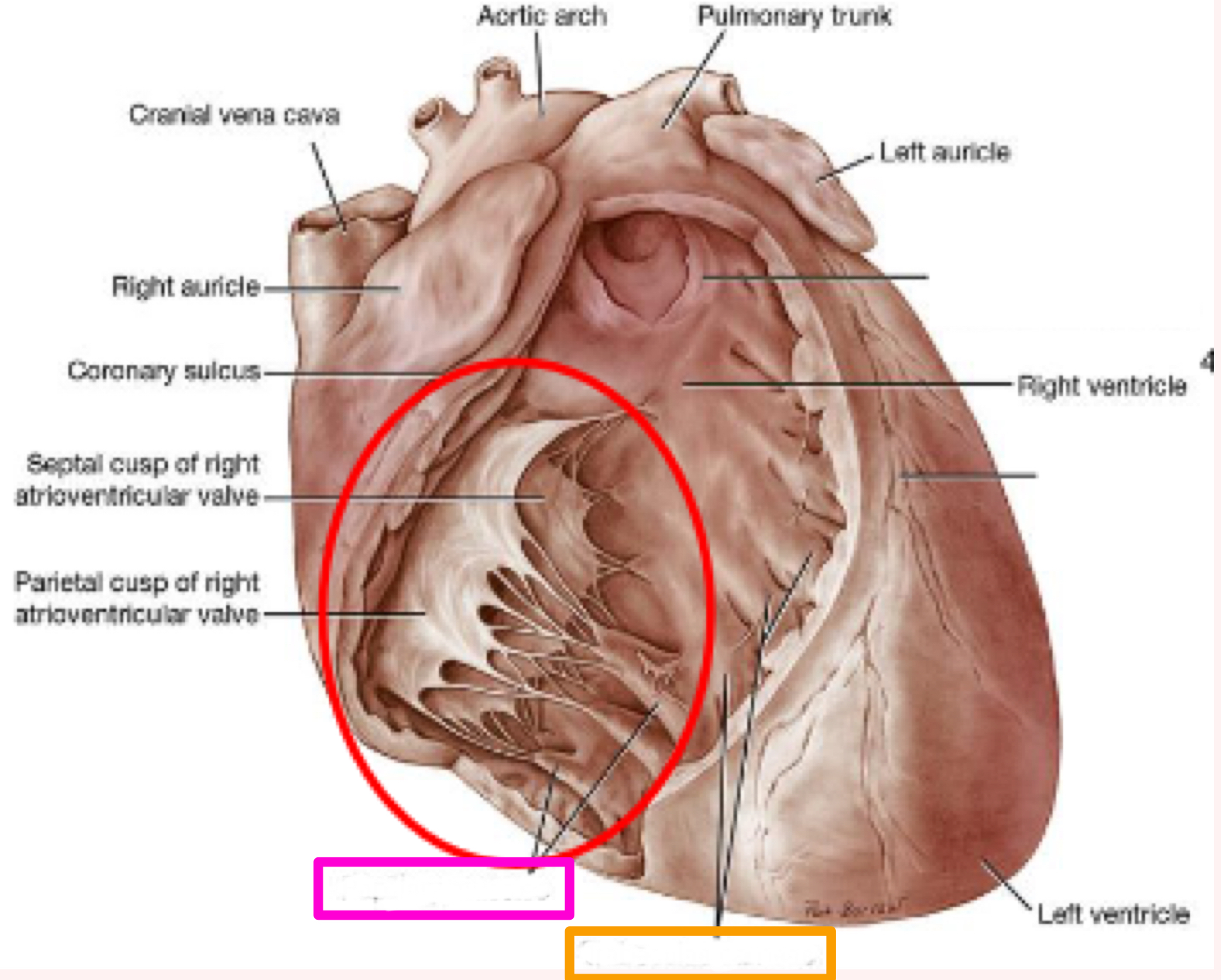
Right Atrium
Intravenous tubercle
Fossa ovalis
Coronary sinus
Pectinate muscles
RIGHT atrioventricular valve/tricuspid valve
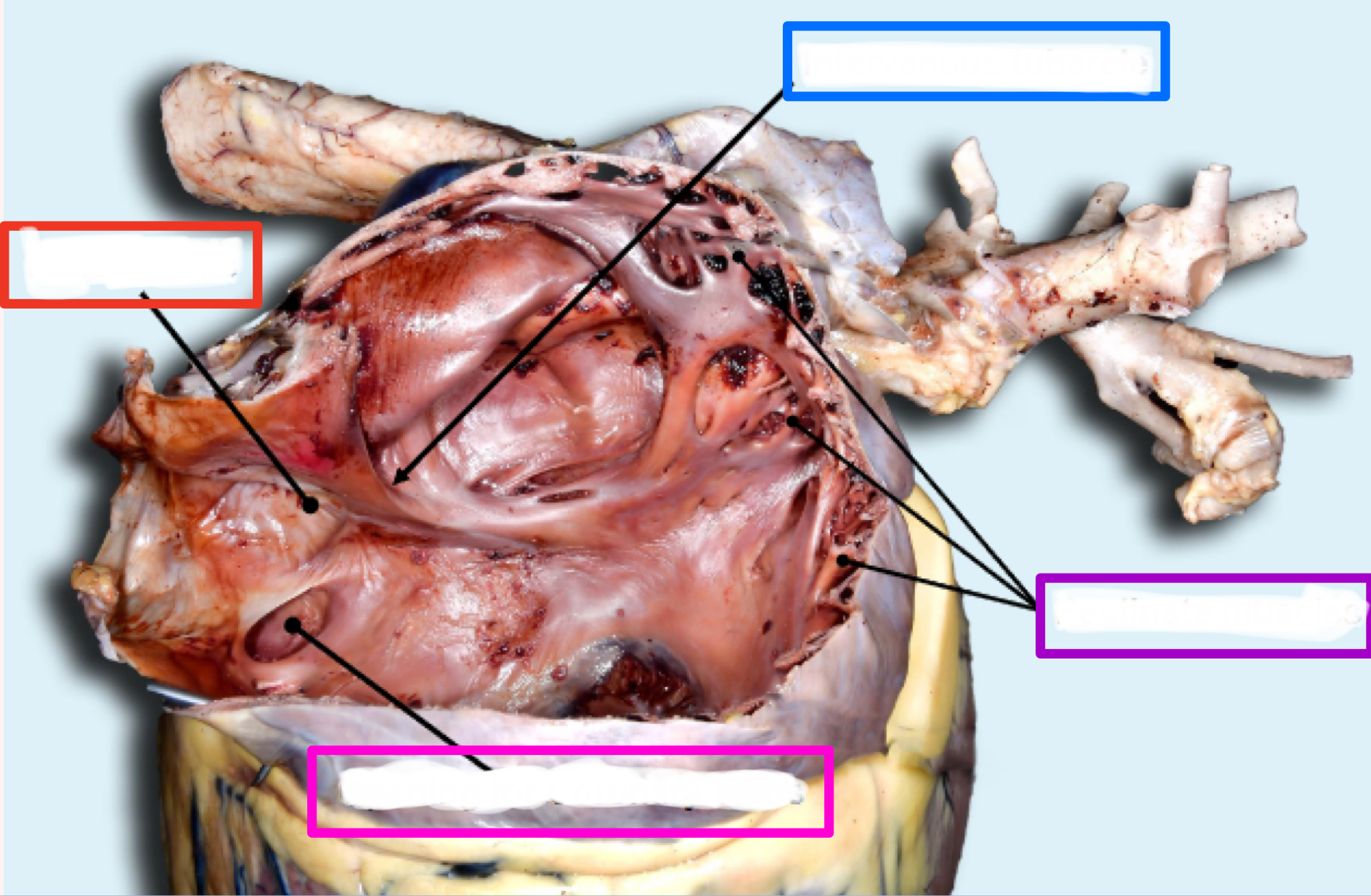
What is the structure in blue?
Intravenous tubercle
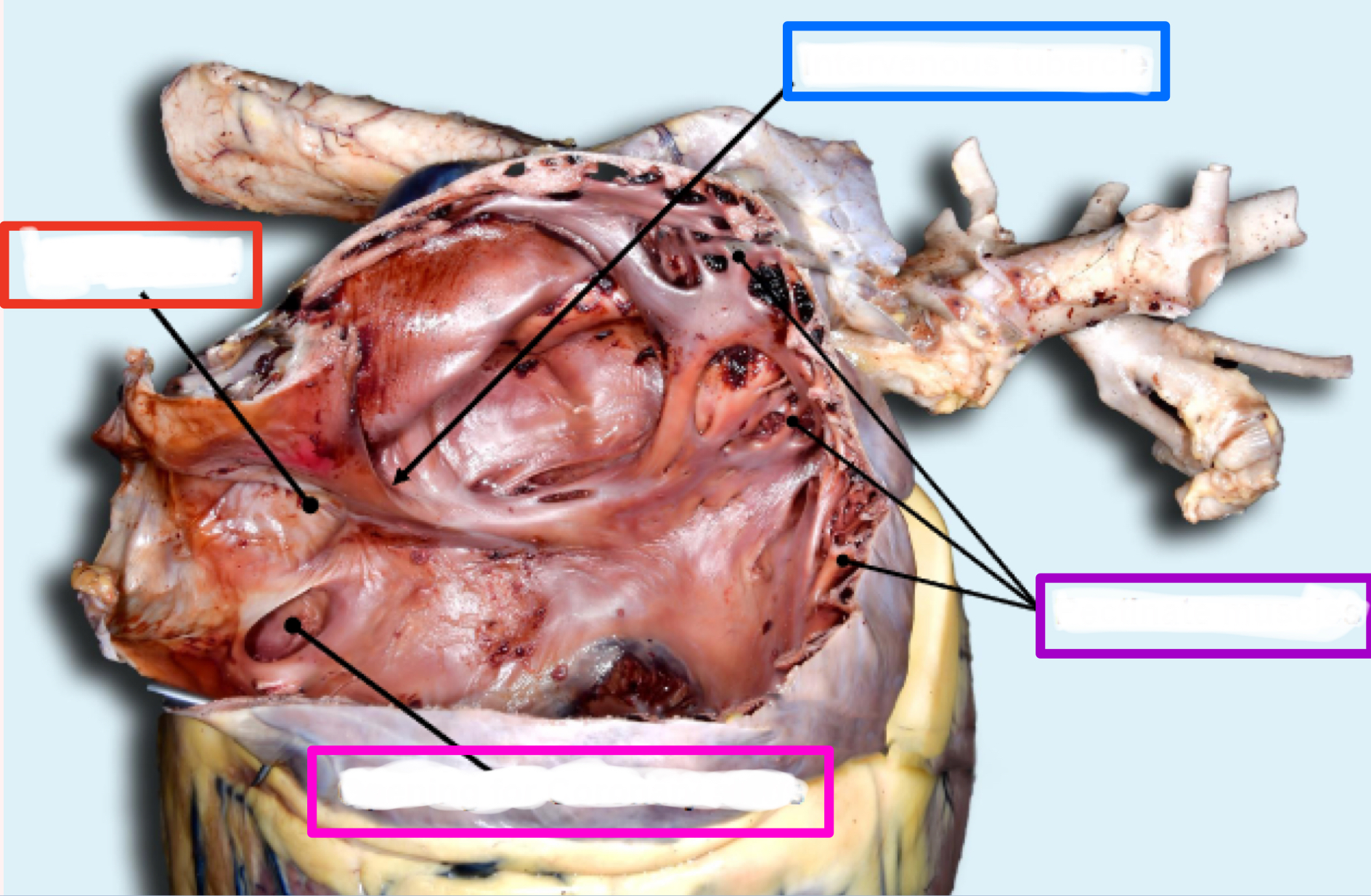
What is the structure in red?
Fossa ovalis
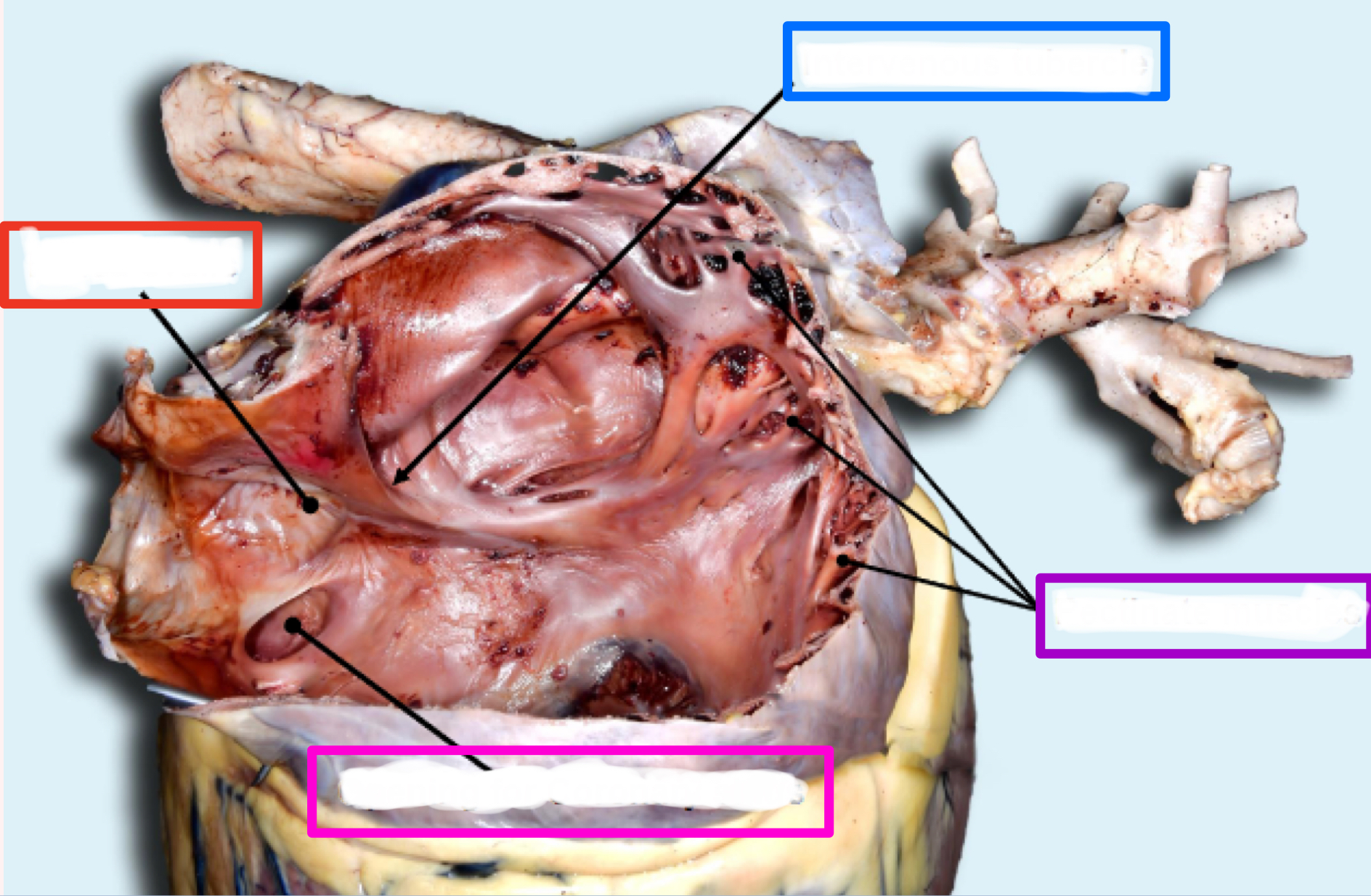
What is the structure in pink ?
Coronary sinus
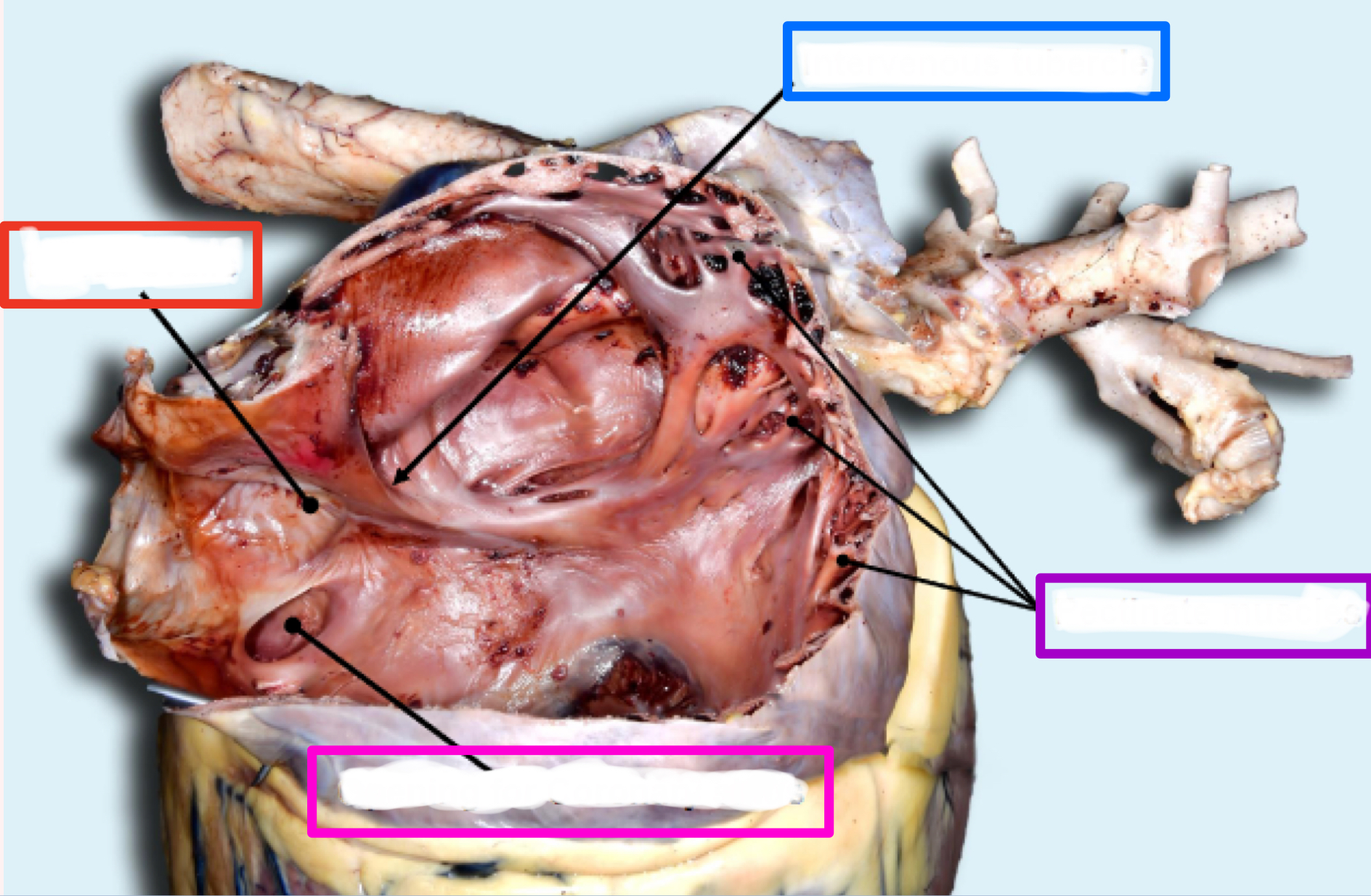
What is the structure in purple?
Pectinate muscles
Intervenous tubercle
tubercle between where two vena cavae dump blood
*only in right atrium
Fossa ovalis
closed foramen ovale between where blood was shunted between right and left atria in fetus
thin indentation
Coronary sinus
hole where dirty blood from heart is returned to right atrium
Pectinate muscles
ridges in auricles
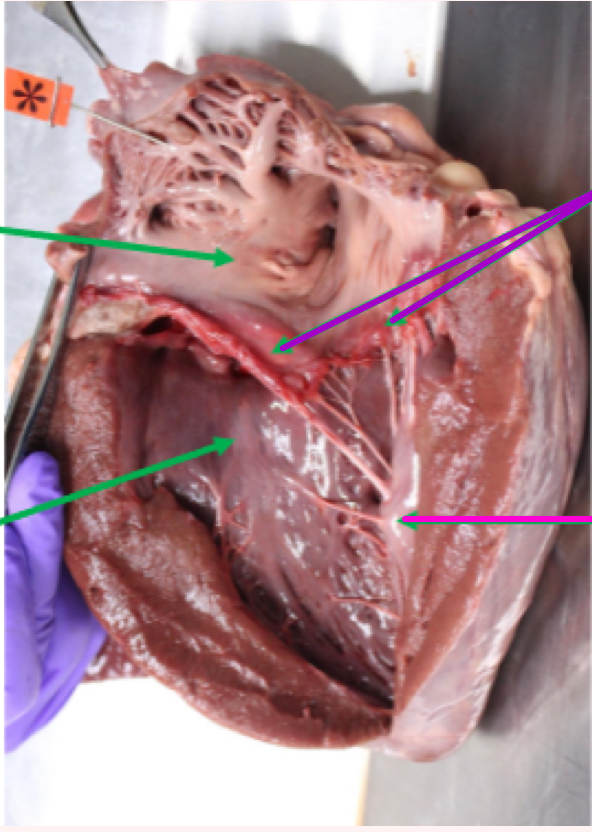
Right ventricle
Papillary muscles
Chordae tendinae
Trabeculae septomarginalis
Trabeculae carnae
Pulmonary valve - semilunar valve, leading to pulmonary trunk
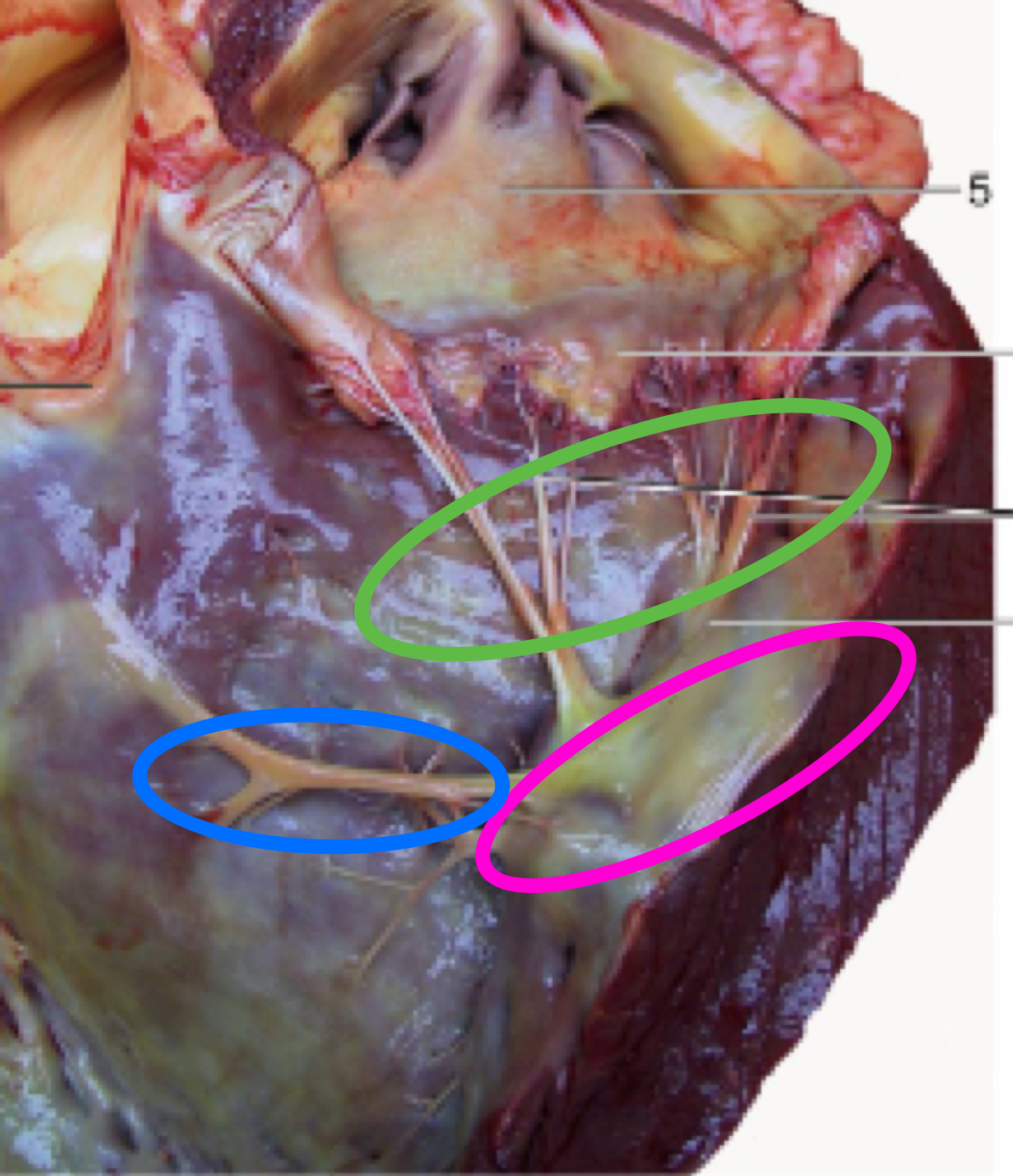
What structure is in pink?
Papillary muscles
Papillary muscles
what chordae tendinae attach to
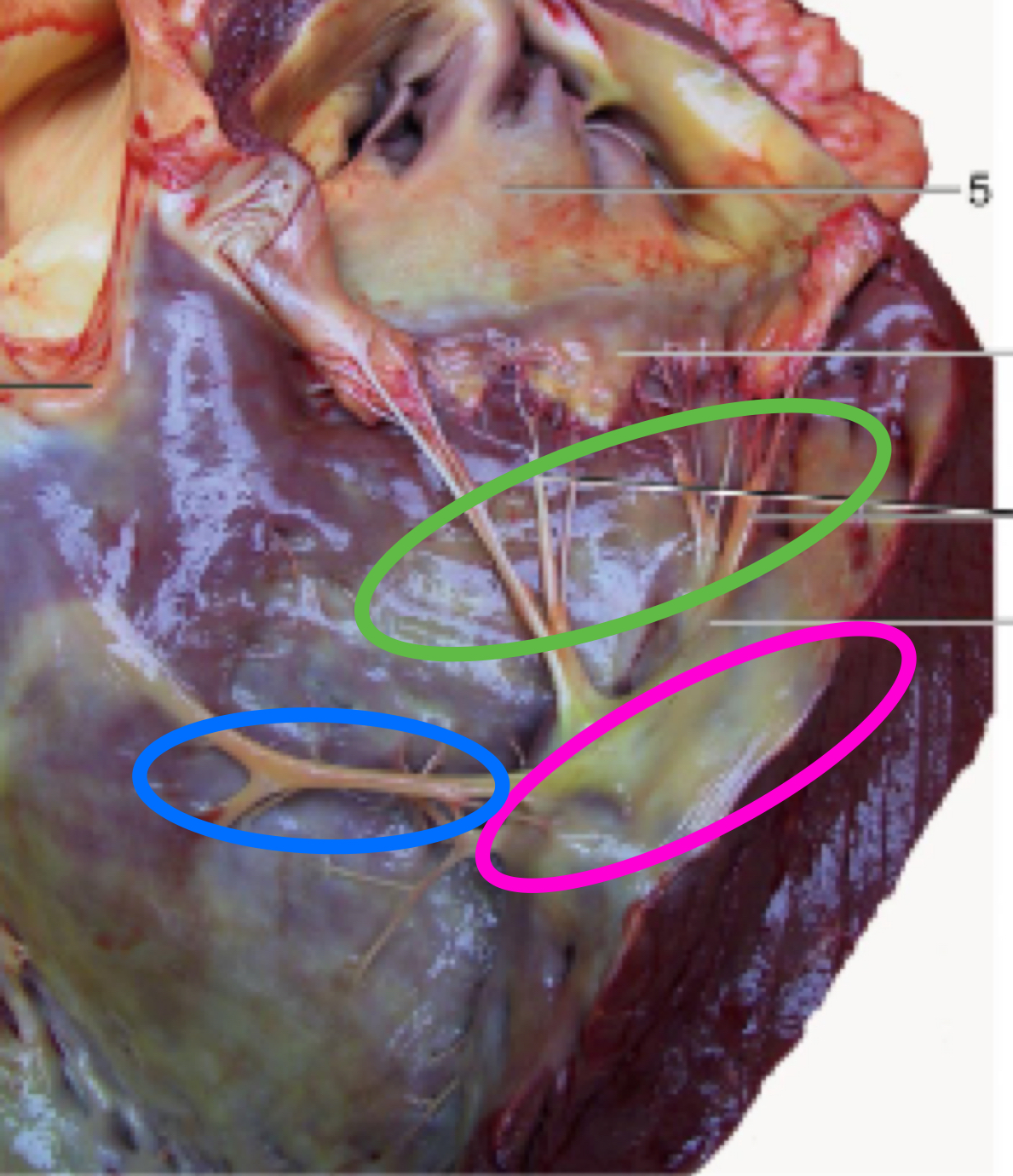
What structure is in green?
Chordae tendinae
Chordae tendinae
attach to valves
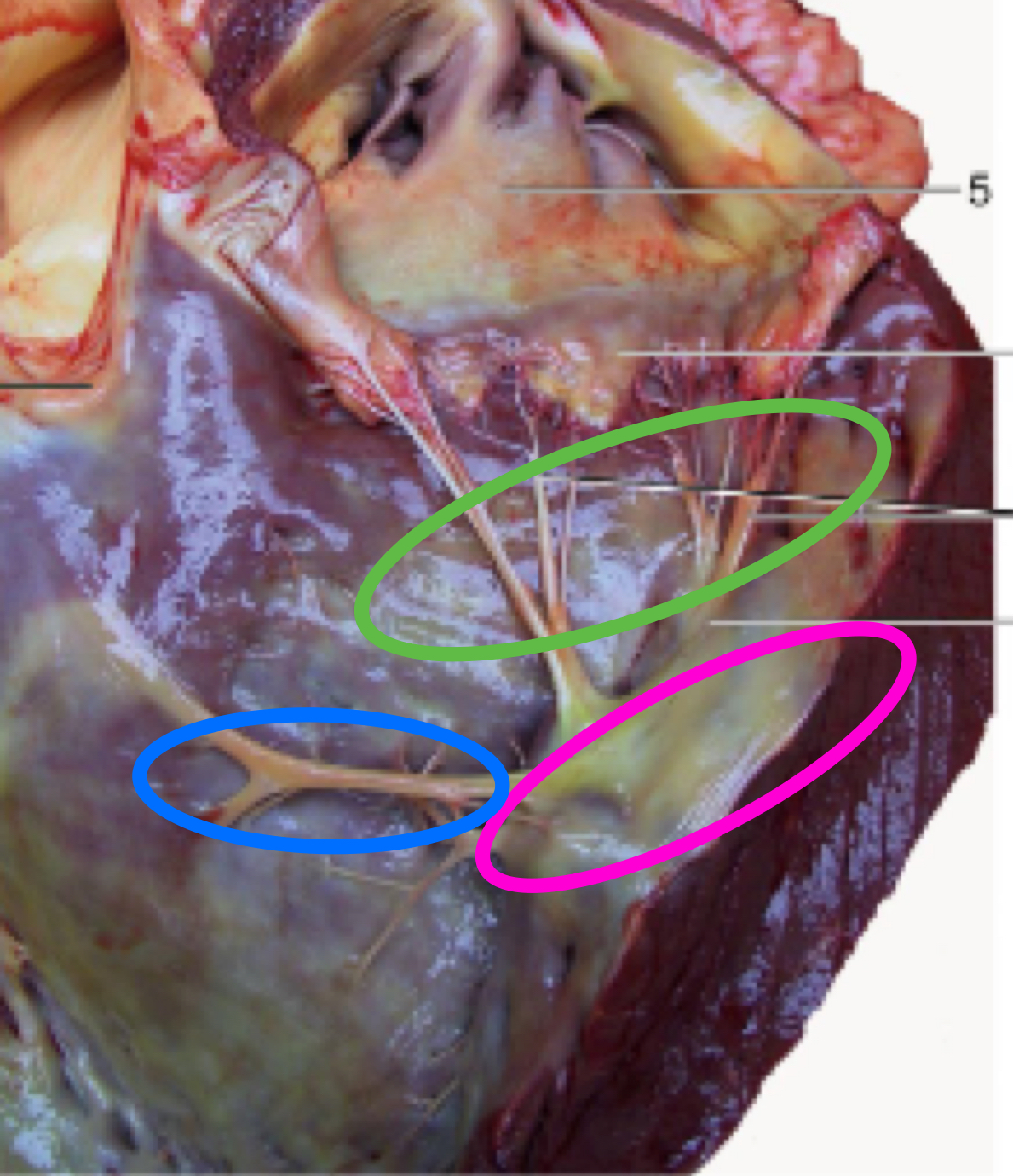
What structure is in blue?
Trabeculae septomarginalis
Trabeculae septomarginalis
nerves
cords from septum to marginal wall
Do NOT attach papillary muscles/valves
What is the structure in orange?
Trabeculae carnae
Trabeculae carnae
meat ridges
Conus arteriosus
funnel shaped part of right ventricle, leading into the pulmonary trunk
Pulmonary valve
semilunar valve
3 cusps, no sinuses
prevents backflow from pulmonary trunk into right ventricle during diastole
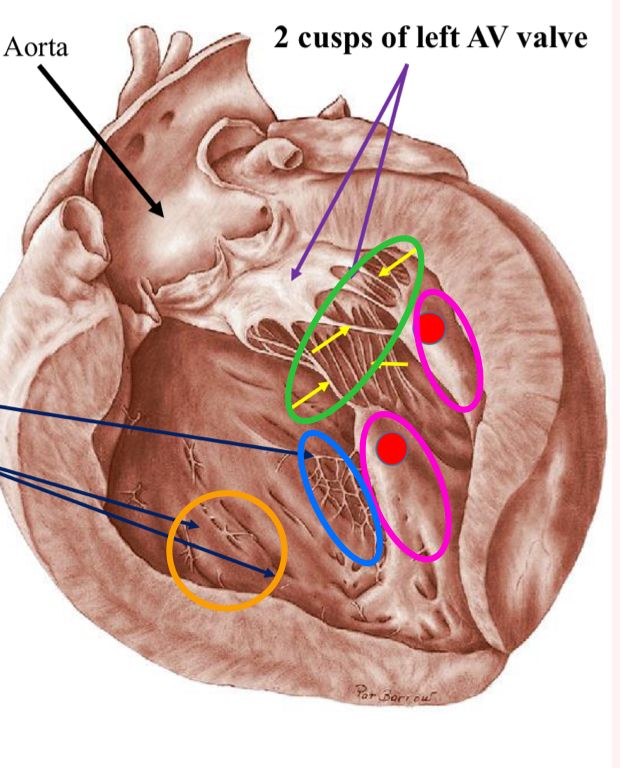
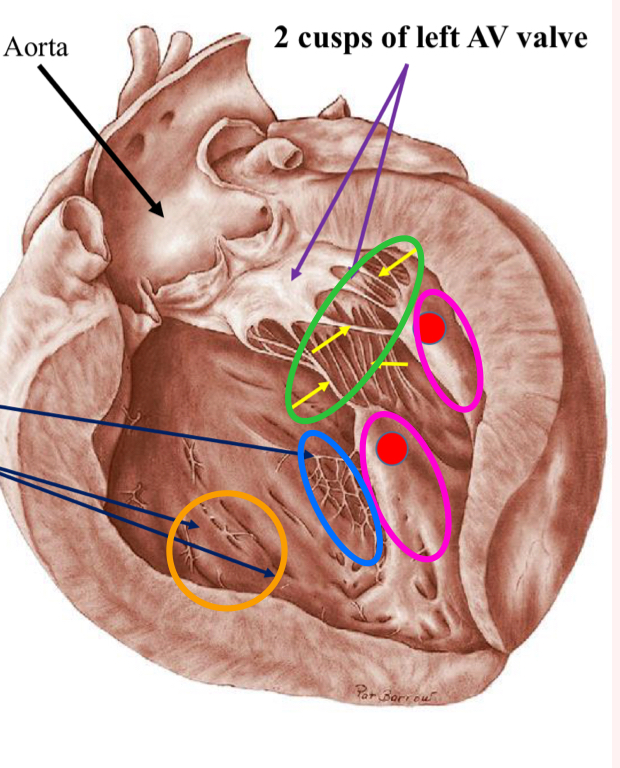
Left atrium
less complex than right
multiple openings from multiple pulmonary veins
Has an auricle
Left atrioventricular valve aka Mitral valve
Blood into left ventricle after
The purple arrows show:
Mitral valve
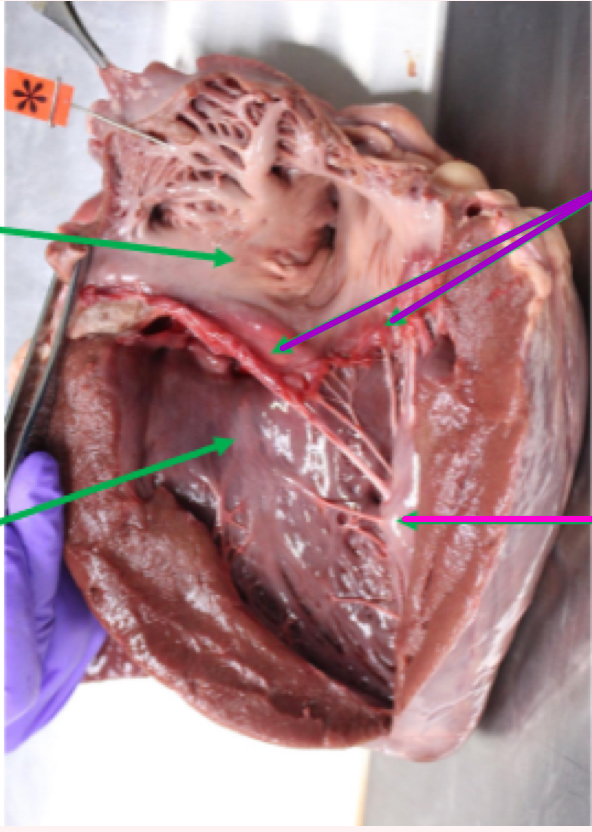
The pink arrows show?
Papillary muscles
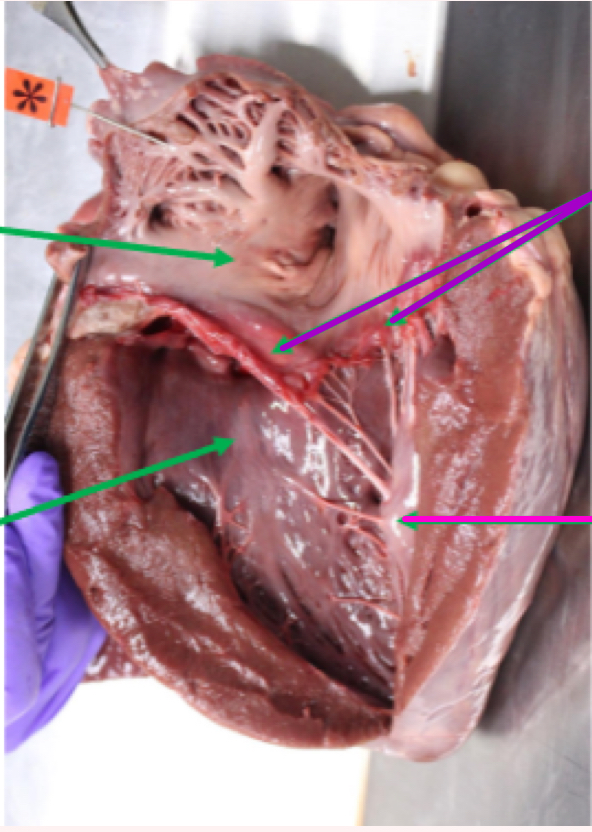
What is the tagged structure?
Pectinate muscle
Left Ventricle
Very similar to right ventricle
Thicker - needs to send blood to entire body
Apex of heart
Contains: papillary muscles with chordae tendinae, trabeculae carnae, trabecula septomarginalis
Blood through aortic valve and into aorta after
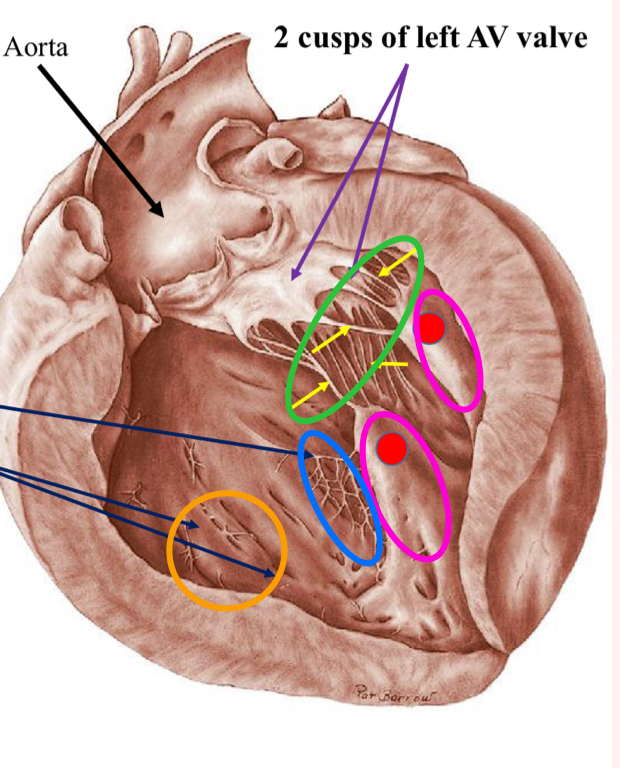
What is the structures in green?
Chordae tendinae
What are the structures in pink?
Papillary muscles
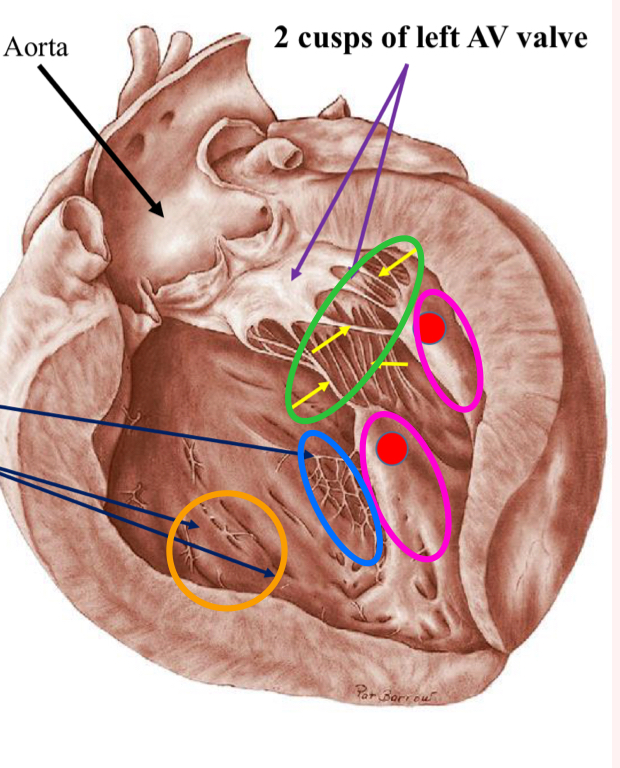
What are the structures in blue?
Trabecula septomarginalis
What are the structures in orange?
Trabeculae carnae
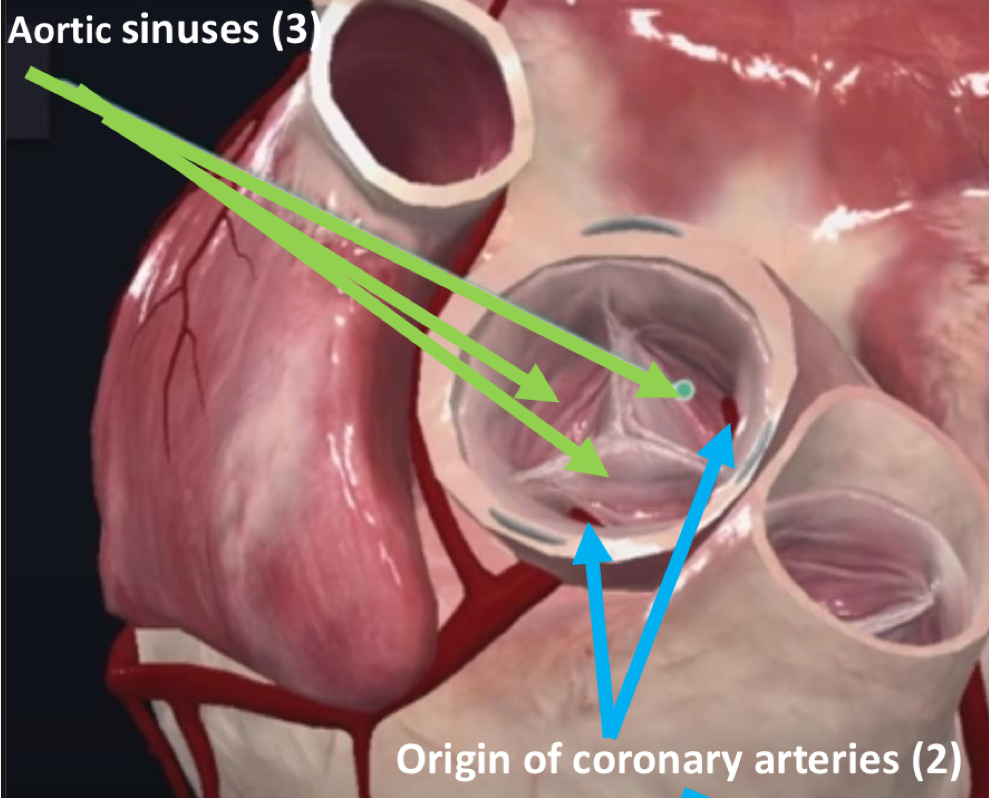
Aortic valve
Semilunar
3 cusps
2 of the cusps have Aortic sinuses
Origins of the R/L coronary arteries
Supply myocardium with nutritional blood
Heart Grooves
Coronary groove
Paraconal interventricular groove
Subsinuosal interventricular groove
Coronary Groove
separates atria and ventricles
Paraconal interventricular groove
groove next to conus arteriosus
contains paraconal interventricular branch of L coronary a
Subsinousal interventricular groove
groove on the other side
contains subsinuosal interventricular branch of L coronary a.
Coronary arteries
Supply myocardium with nutritional blood
Right coronary a
Left coronary a
Paraconal interventricular branch
circumflex branch (in coronary groove)
Subsinousal interventricular branch
Right coronary artery
no major branches
Runs in coronary groove