BS2 Exam5: Cardiovascular, cholesterol, and lipid pharm 10/29 ASYNCH
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Diuretic
Respiratory infections
What do diuretics do?
- act on the kidneys
- increases excretion of sodium and water to decrease the volume of fluid on the vascular system
- "water pill"
hypertension, congestive heart failure
Diuretics are use by pts with
Thiazides, loop, and potassium-sparing diuretics
What are the classifications of diuretics?
Thiazide diuretics
- inhibits sodium reabsorption thus retaining more water in the nepheron
- used to treat hypertension
Loop diuretics
- act on loops of henle
- inhibit reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the nephron and the water that follows these electrolytes
Potassium sparing diuretics
- not as strong as thiazide and loop
- prevent the secretion of postassium into the distal tubule
What are the ADRs of diuretics?
- fluid depletion (decrease in the blood volume, causes increase in CO)
- electrolyte imbalance (hyponatremia: low sodium; lypokalemia: low potassium
- thiazides are a common cause of erectile dysfunction
What are the rehab considerations for pts taking diuretics?
- monitor vital signs
- check for weakness, fatigue, confusion, moodchanges
- encourage med compliance
Sympatholytic; increase
Beta blockers are a ____ agents. They inc/dec sympathetic activity
Beta blockers act on the:
Heart by binding to receptors on heart to decrease HR and force of contraction of the heart
beta blockers
________ are used by pts who have:
- hypertension
- arrhythmias
- angina perctoris
- heart failure
- recovery from MI
Classification of beta blockers (2)
- Cardioselective (binds to B1 receptors)
- Nonselective (binds B1 and B2)
Beta blockers - cardioselective ADR
- orthostatic hypotension
- decreased maximal exercise capacity (20-30bpm)
- psychotropic effects (depression, lethargy, decreases libido)
- erectile dysfunction
Beta blockers - nonselective ADR
- bronchoconstriction in patients with asthma and other respiratory conditions
What are the rehab consideration for patients taking beta blockers?
- monitor vital signs
- decreased maximal exercise capacity: use RPE! (1-10 haw hard the patient is working)
- encourage med compliance
*Will a BP reading at the beginning of a PT session be accurate if the patient is taking Atenolol?
Yes! BUT IF, the pt is doing aerobic exercise, monitoring HR and BP will not provide an accurate measure of how hard the person is working as the response is blunted. Use an RPE scale to get an accurate assesment of how hard a person is workinf to keep them in the safe zone.
Beta blockers
*-olol ending drugs are:
What are vasodilators?
- acts directly on smooth muscle of blood vessels
- vasodialation decreases peripheral vascular resistance
- usually added when first line meds fail
hypertension, heart failure
Vasodilators are use by pts with:
- hydralazine (apresoline)
- minoxidil (loniten)
What are the types of vasodilators used for hypertension?
What are the types of vasodilators use in emergencies?
- hydralazine (apresoline)
- diazoxide (hyperstat)
- nitroprusside (nipride, nitropress)
Vasodilators ADR
- reflex tachycardia (incerased HR)
- orthostatic hypotension
- dizziness
- headache
- weakness
- fluid retention
- minoxidil (hair growth on face, ears, forhead)
What are the rehab considerations for pts taking vasodilators?
- monitor vital signs (orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia)
- monitor for other side effects
- avoid systemic heat such as a large whirlpool or hot tub (can cause excessive hypotension)
- exercises can cause vasodilation
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- act on regin-angiotensin system
- inhibit angiotensin converting enzyme which decreases the formation of angiotensin II
- prevents angio I from converting to angio II!!
hypertension, heart failure
ACE inhibitors are use by pts with
ACE inhibitor
*-pril
ACE inhibitors ADR
- allergic skin rash
- dry cough, persistent
- nausea
- dizziness
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARB)
- block angiotensin II receptors (blocks the harmful affects when angio I turns to angio II)
- fewer side effects that ACE inhibits
- just as effective
Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker
*-sartan
Rehab considerations for pts taking ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II blockers (ARB)
- monitor vital signs
- encourage med compliance
B. Lisinopril
Which of the following drugs prevents angiotensin I from converting to angiotensin II?
A. Propranolol
B. Lisinopril
C. Losartan
D. Minoxidil
Calcium channel blockers
- blocks calcium into vascular smooth muslce cells and cardiac muscle
- promotes vasodialation and stabilize heart rate
hypertension, angina pectoris, arrhythmias
Calcium channel blockers are used by pts who have:
Calcium channel blockers
*-ipine
Calcium channel blockers ADR
- swelling in feet and ankles
- orthostatic hypotension
- altered HR, too fast, too slow, irregular
- dizzines, headache, nausea
- increased risk of heart attacks (sudden change in BP)
Rehab considerations of pt taking calcium cancel blockers
- monitor vital signs
- avoid systemic heat (hot tub, whirlpool - may cause dizziness)
- encourage meducation complicance
- exercises can cause vasodialtion in skeletal muscle
Organic nitrates
- dialate perioheral vasculature
- venous dilation causes decreases cardiac preload
- arterial dilation causes decrease afterload
- resulrs in decreases cardiac workload and decreases cardiac oxygen demand
Angina pectoris (chest pains)
Organic nitrates are used by pts who have:
Nitrates ADR
- headache
- dizziness
- orthostatic hypotenison
- nausea
Rehab consideration for patients taking nitrates
- monitor vital signs
- have meds avalible during therapy sessions (with an increase in activity level, angina occurs chest pain, need to take at first sign)
- encourage med compliance
- avoid heat/ hot tubs
- exercise can cause vasodialtaion
Positive inotropes -Digitalis
- inhibits sodium postassium pump in cardiac cells
- sodium accumulates in cell, more calcium in cell, increases actin myosin binding = STENGTHEN CONTRACTION OF HEART
derived from foxglove plant
- digoxin (lanoxin)
- digitoxin (digitaline)
- usually parental route
Congestive heart failure
Positive inotropes - digitalis are used by pts with
Digitalis ADR
- digitalis toxicity (common)
- can be fatal
- GI signs (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
- CNS problems
- cardiac arrhythmias
- indications: heart failure
What are other positive inotropes?
Dopamine (Intropin) and Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
Rehab considerations for pts taking positive inotropes?
- monitor vital signs
- observe for early sign of digitalis toxicity
C. Calcium channel blockers such as Nifedipine
Which type of drug has a side effect of swelling in the feet and ankles?
A. Organic nitrates such as nitroglycerin
B. Positive inotropes such as digitalis
C. Calcium channel blockers such as Nifedipine
D. Beta blockers such as Metoprolol
Hyperlipidemia
*-statin
Organic nitrate
*Nitroglycerin
Hyperlipidema
- high concentration of lipids in the blood stream
- plaque on the walls leading to thrombis or infarction
- primary cause of cardiovascular disease
High density lipoproteins (HDL); Low density proteins (LDL) and VLDL (very low)
The goal is to increase______ and lower _____ and ______
Statin drugs inhibit
- Inhibit HMG-CoA reductase
- inhibits the creation of cholesterol! Good!
- decrease choledterol sytehsis, increase hepatic LDL breakdown, decrease VLDL synthesis
- CAUSE MUSCLE PAIN
primary effects of Statin
- decrease LDL, VLDL, and triglycerides
- increase HDL
Fibril acids
- decrease triglycerides
- decrease VLDL
Antihyperlipidema drugs ADR
*see pic
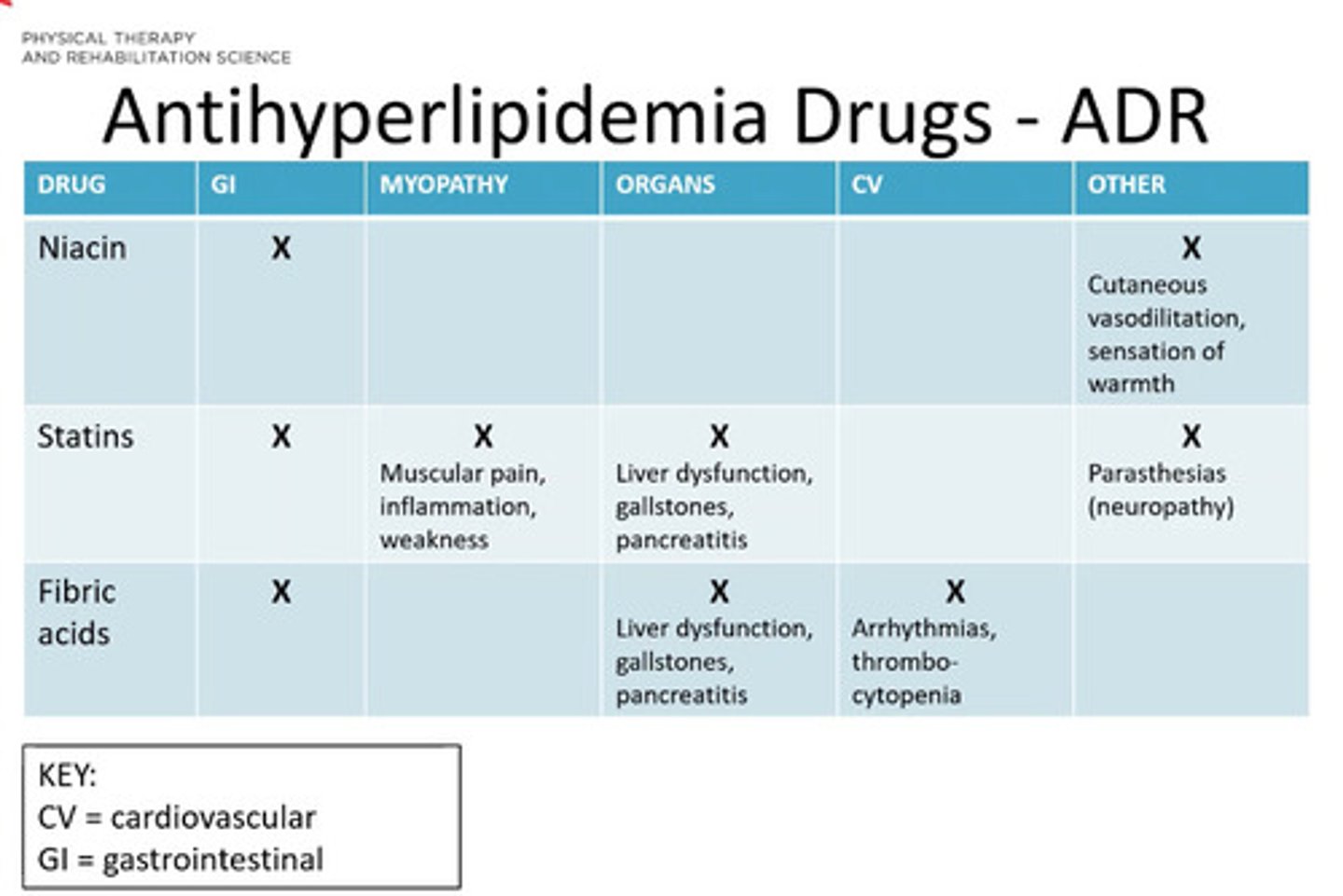
Rehab considerations for pts taking antihyperlipedmia drugs
- statin induced myopathy
- usually reversible
- encourage med compliance
- encouage lifestyle chages (diet, weight loss)
- exercise perscription
A. Atorvastatin
Which drug is MOST likely to cause muscle pain?
A. Atorvastatin
B. Niacin
C. Gemfibrozil
D. Fenofibrate