ecosystems of the planet
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
ecosystem
living and non-living components in an environment and the interrelationships that exist between them
abiotic
non-living component (e.g. soil, water, sunlight)
biotic
living component (plants, animals, bacteria)
where deserts are found
in discontinuous bands [1] around Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn [1]. Often found in continental interiors [1]. Examples are Sahara desert in northern Africa and the Arabian Peninsula [1]
where tropical rainforests are found
in discontinuous bands [1] between Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn with a main focus on the equator [1]. Tropical rainforests are found in South America, central Africa, and northern Australia [1].
where temperate rainforests are found
in a discontinuous band [1] found only above the Tropic of Cancer [1] found across northern Europe and the north of North America
major tropical rainforests around the world
Amazon, Central American, Congo River Basin, Madagascan, South East Asian and Australasian
major coral reefs around the world
Great Barrier Reef, Red Sea Coral Reef, New Caledonia Barrier Reef, Mesoamerican Barrier Reef, Florida Reef, Andros Coral Reef
coral reefs are found where the water is clear and shallow
allows sunlight to reach the coral and photosynthesise
humans farm arable crops in temperate grassland regions
arable crops rely on sunlight and rain to help them grow and photosynthesise. humans eat the arable crops
inuits use caribou skin to remain warm in polar regions
inuits rely on caribou skin to insulate them and allow them to survive harsh weather conditions
trees quickly remove nutrients from the soil in tropical rainforests
trees rely on nutrients found in the soil to survive. due to the many trees in the rainforest there is a lot of competition for the nutrients
latitude
how close you are to the equator
continentality
how close you are to the sea
altitude
how high you are above the sea level
GAC (global atmospheric circulation)
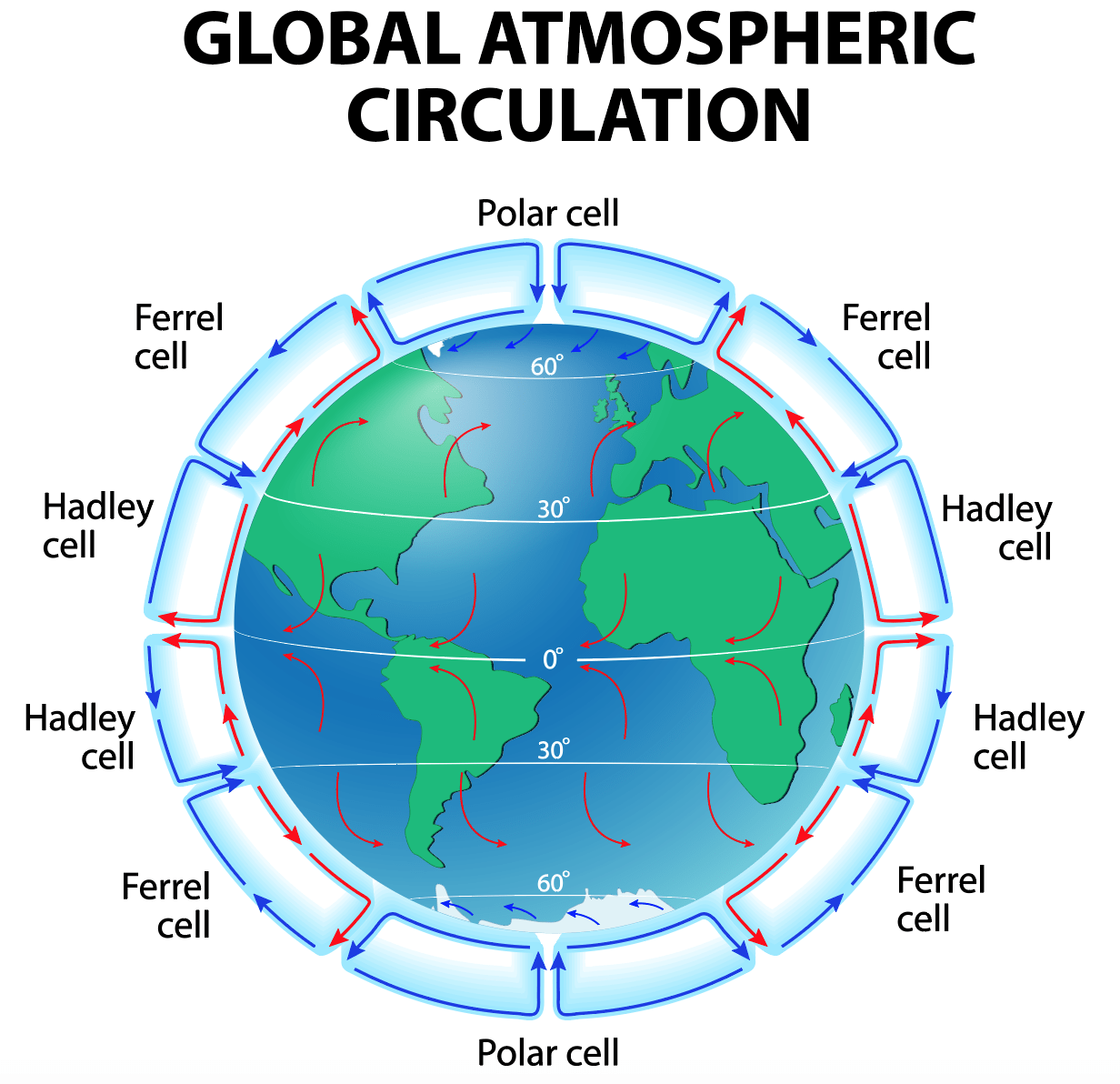
convection rainfall
occurs when the sun’s energy heats the surface of the earth and at the equator the sun’s heat is more concentrated.
causes air to warm and rise and water to evaporate. the air cools and condenses to form clouds
if process continues rainfall will occur