Chapters 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 - Enzymes, Carbohydrates, Metabolism, Aerobic Met., Lipids & Membranes, Lipid Metabolism
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
1
New cards
Characteristics of enzymes
- Increase reaction rates
- Obey the laws of thermodynamics (no effect on Keq)
- Catalyze the forward and backward reactions of reversible rxns
- Usually present in low concentrations because they are not consumed
- Transition state of reacting substrates bound in enzyme active sites
- Obey the laws of thermodynamics (no effect on Keq)
- Catalyze the forward and backward reactions of reversible rxns
- Usually present in low concentrations because they are not consumed
- Transition state of reacting substrates bound in enzyme active sites
2
New cards
Characteristics shared between chemical catalysts and enzymes
Both catalyze chemical reactions without altering themselves, they accelerate the rate of rxn but do not alter the equilibrium
3
New cards
Enzymes: Carry out specific reactions at moderate temperature, much larger, require unique "active site"
Chemical catalysts: Accelerate wide variety of chemical reactions and most of them need additional input of energy
4
New cards
Emil Fischer
"Lock and Key"
5
New cards
Koshland
Variation of lock and key but with "induced fit" to take into account conformational flexibility
6
New cards
Category 1 of Enzyme: Oxidoreductases
Catalyze redox reactions
7
New cards
Category 2 of Enzyme: Transferases
Catalyze the transfer of groups from one molecule to another. Common prefix "trans-"
8
New cards
Category 3 of Enzyme: Hydrolases
Catalyze breakage of chemical bonds with the addition of water. Ex: peptidases
9
New cards
Category 4 of Enzyme: Lyases
Catalyze reactions in which groups are removed to form a DOUBLE BOND or are added to one
10
New cards
Category 5 of Enzyme: Isomerases
Intramolecular rearrangements
11
New cards
Category 6 of Enzyme: Ligases
Catalyze bond formation between two substrate molecules. Energy supplied by ATP hydrolysis. Common term "synthetase"
12
New cards
Turnover number
Quantity of substrate in moles converted to product per second by one mole of enzyme
13
New cards
Enzyme activity
Measured in international units. One IU is the amount of enzyme that produces 1 micromole of product per minute
14
New cards
Specific activity
IU per milligram of protein. 'katal'
15
New cards
Katal
transformation of 1 mole substrate to product per second
16
New cards
Slope =
Km/Vmax
17
New cards
Irreversible inhibition
Inhibitor binds covalently to enzyme and inactivates it. ex: Mercury and silver bind to the sulphahydryl group of protein
18
New cards
Reversible inhibition
Inhibitor is bound through noncovalent bonds, can dissociate. Competitive and noncompetitiveC
19
New cards
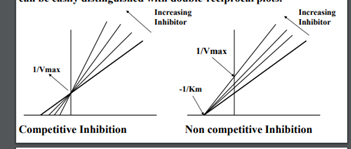
Competitive inhibition (reversible)
Competitive inhibitor closely resembles the true substrate, it binds to active site and forms enzyme-inhibitor complex. This interferes with product formation and results in a decline in enzymatic activity
20
New cards
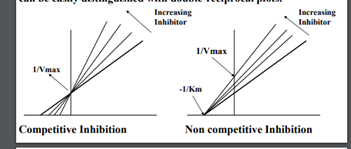
Noncompetitive inhibition (reversible)
Inhibitor binds at an allosteric site, does not interfere with binding of enzyme to active site. Brings about conformational changes.
21
New cards
Enzyme catalysis factors:
1. Proximity and strain
2. Electrostatic effect - dipoles of active site and substrate
3. Acid base catalysis - side chain interference, protons
4. Covalent catalysis - Unstable covalent bond that forms between enzyme and substrate which forms product
2. Electrostatic effect - dipoles of active site and substrate
3. Acid base catalysis - side chain interference, protons
4. Covalent catalysis - Unstable covalent bond that forms between enzyme and substrate which forms product
22
New cards
Cofactors
1. Metal ions: Transition metals and alkaline metals. Transition most often involved in catalysis due to their electronic structure
2. Coenzyme: Derived from vitamins
2. Coenzyme: Derived from vitamins
23
New cards
Enzyme regulation:
1. genetic control
2. covalent modification
3. allosteric regulation
4. compartmentation
2. covalent modification
3. allosteric regulation
4. compartmentation
24
New cards
The enzyme catalyzing the transfer of amino group to form a double bond will be classified under....
Lyases
25
New cards
Km
Michaelis constant. Substrate concentration at half the maximum velocity. Smaller Km = higher affinity to substrate and ES formation
26
New cards
Specificity constant
High SC = low Km and high affinity = high kinetic efficiency (turnover number)
27
New cards
What are the most abundant molecules in nature?
Carbohydrates. Major components: C, H, O
28
New cards
General chemical formula for carbohydrates:
Cn(H20)n
29
New cards
Clockwise rotation: +, D
Counterclockwise rotation: -, L
30
New cards
Reaction order: 1 molecule, 1st order
a
31
New cards
Reaction order: 2 molecule, 2nd order
2a (unimolecular) or 2O (unimolecular) or 2(a+b) (bimolecular). NOT O2
32
New cards
Pseudo first order reaction
1 molecule + H2O - second order reaction behaving like first order
33
New cards
Uncompetitive inhibitor can only bind to...
ES complex
34
New cards
position of hydroxyl group on carbon 1 determines...
a or B anomer. Down is alpha
35
New cards
Mutarotation
a and B forms of monosaccharides can easily be interchanged when dissolved in water. Produces equilibrium mixture of a and B forms
36
New cards
Oxidation of aldehyde group...
Aldonic acid
37
New cards
Oxidation of terminal CH2OH group (not aldehyde)
Uronic acid
38
New cards
Oxidation of both aldehyde and terminal CH2OH group...
Aldaric acid
39
New cards
Reduction of aldehyde and ketone group yield..
sugar alcohols. Ex: reduction of D-Glucose yields D-Glucitol/D-Sorbitol
40
New cards
Monosaccharides are linked together to form disaccharide glycoside with....
glycosidic linkages
41
New cards
Glucose, also called Dextrose
Eyes and brain rely heavily on this source of energy
42
New cards
Fructose, also called Levulose
Present in large quantity in fruits and semen
43
New cards
Galactosemia
Lack of enzyme required for metabolism of galactose. Can cause mental retardation and cataracts and liver damage
44
New cards
Disaccharides
Maltose, Lactose, Cellobiose, Sucrose
45
New cards
lactose reducing or nonreducing
reducing
46
New cards
Maltose and cellobiose...
do not exist freely in nature
47
New cards
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose, a-1,4 glycosidic linkage. Intermediate product of starch hydrolysis
48
New cards
Cellobiose
Glucose + Glucose. B-1,4 glycosidic linkage
49
New cards
Sucrose reducing or nonreducing
Non-reducing
50
New cards
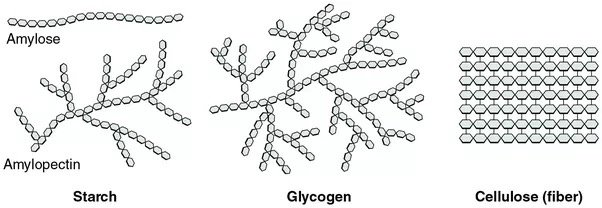
Amylose - linear
Glycogen & amylopectin - branched
51
New cards
Amylose: a-1,4 glycosidic
Amylopectin: a-1,4 and a-1,6 glycosidic linkages
52
New cards
Glycogen is found majorly in...
liver and muscle cells
53
New cards
D(-) prefix on monosaccharide means...
Its molecular arrangement is similar to D-Glyceraldehyde and it rotates light anticlockwise
54
New cards
D-Glucitol (D-Sorbitol) is formed from D-Glucose as a result of ....
Reduction
55
New cards
Oxidation of aldehyde group in D-Glucose forms....
Gluconic acid
56
New cards
Level of increased branching:
Amylose < Starch < Glycogen
57
New cards
Three stages of catabolism
1. Stage 1: Proteins digested to their fundamental parts (amino acids, sugars, fatty acids).
2. Stage 2: Further reduced to form Acetyl CoA.
3. Stage 3: Acetyl CoA is completely oxidized to form CO2 and water through the CAC and ETC.
2. Stage 2: Further reduced to form Acetyl CoA.
3. Stage 3: Acetyl CoA is completely oxidized to form CO2 and water through the CAC and ETC.
58
New cards
A significant amount of energy is produced when electrons move from NADH to oxygen during
electron transport chain
59
New cards
Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis are controlled by three hormones:
Insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine. ALL of these are mediated by secondary messenger molecule Cyclic AMP
60
New cards
when glucose molecules enter cells, they are phosphorylated
Phosphorylation is catalyzed by hexokinase in the presence of ATP-Mg2+ complex (co-substrate)
61
New cards
Fate of pyruvate
Aerobic conditions: Pyruvate converted to Acetyl CoA then goes through the CAC to form CO2.
Anaerobic conditions: Pyruvate to lactic acid with formation of NAD . Alcohols are produced in yeast & bacteria
Anaerobic conditions: Pyruvate to lactic acid with formation of NAD . Alcohols are produced in yeast & bacteria
62
New cards
Regulation of glycolysis:
1. Hexokinase is inhibited by Glucose-6-phosphate.
2. PFK-1 is activated by Fructose-2,6-biphosphate and fructose-6-phosphate, and AMP. Inhibited by Citrate, ATP
3. Pyruvate kinase is activated by Fructose 1,6-biphoaphate, AMP and inhibited by Acetyl coA and ATP
2. PFK-1 is activated by Fructose-2,6-biphosphate and fructose-6-phosphate, and AMP. Inhibited by Citrate, ATP
3. Pyruvate kinase is activated by Fructose 1,6-biphoaphate, AMP and inhibited by Acetyl coA and ATP
63
New cards
Glucagon and glycolysis:
inhibits synthesis of fructose-2,6-biphosphate
64
New cards
Insulin and glycolysis:
Promotes synthesis of fructose-2,6-biphosphate
65
New cards
End product of first stage of glycolysis
2 GAD-3-P
66
New cards
Enzymes that play role in regulation of glycolytic pathway
Hexokinase, PFK-1, Pyruvate kinase
67
New cards
Mechanism of regulation of gluconeogenesis
4 enzymes
68
New cards
Citrate synthase
Stimulated by substrates acetyl coa and oxaloacetate.
Inhibited by citrate and succinyl coA, NADH and ATP
Inhibited by citrate and succinyl coA, NADH and ATP
69
New cards
Isocitrate dehydrogenase ***primary regulator of CAC***
Stimulated by ADP and NAD.
Inhibited by NADH and ATP
Inhibited by NADH and ATP
70
New cards
a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Stimulated by low conc. NADH and inhibited by high concentration NADH
71
New cards
The process in which oxygen is used as final electron acceptor
aerobic respiration
72
New cards
Components of ETC are located....
inner mitochondrial membrane. Organized in four complexes
73
New cards
Complex 1
NADH dehydrogenase complex. Transfers e- from NADH to UQ. FMN to FMNH2, then to iron sulfur centers and eventually UQ
74
New cards
Complex 2
Succinate dehydrogenase. Transfers electrons from succinate to UQ
75
New cards
Complex 3
Cytochrome bc1 complex. Transfers electrons from reduced coenzyme Q (UQH2) to cyt C
76
New cards
Complex 4
Cytochrome oxidase. Reduction of Oxygen to form H2O. Contains copper
77
New cards
Antimycin inhibits....
Cyt b (complex 3)
78
New cards
Rotenone and Amytal inhibit...
NADH dehydrogenase (Complex 1)
79
New cards
CO inhibits...
cyt oxidase (complex 4)
80
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
Process by which the energy generated by the ETC is conserved by the phosphorylation of ADP to yield ATP
81
New cards
As electrons pass through the ETC, protons from the matrix are transported...
to the intermembrane space. create proton gradient between the matrix and intermembrane space
82
New cards
How many molecules of NADH are generated during CAC?
3
83
New cards
How many molecules of glucose are generated from one molecule of glucose during CAC?
2, transport process is 1 so 1 net
84
New cards
Lipid classes:
1. Fatty acids
2. Triacylglycerols
3. Wax esters
4. Phospholipids (phosphoglycerides & sphingomyelin)
5. Sphingolipids
6. Isoprenoids
2. Triacylglycerols
3. Wax esters
4. Phospholipids (phosphoglycerides & sphingomyelin)
5. Sphingolipids
6. Isoprenoids
85
New cards
Fatty acids
Naturally occurring ones are usually cis.
86
New cards
Triacylglycerols
Esters of glycerol with three fatty acid molecules. Neutral fats. Less oxidized than glycogen, so they release more energy. They also take up much less space. Poor conductor of heat provides insulation in low temperatures
87
New cards
Sphingolipids
Ceramides (precursors for glycolipids). Found in nerve cells and cell membranes
88
New cards
Isoprenoids
Terpenes and steroids
89
New cards
mixed terpenoids
Vitamin E, UQ, Vitamin K, cytokinins
90
New cards
Saturated fatty acids are likely to form solids because they have a higher melting point.
Unsaturated fatty acids have lower melting point because they do not pack easily because of their double bonds
91
New cards
Trans unsaturated fatty acids behave like saturated fatty acids because of
configuration. They are able to bend and pack. In cis form, this bending is inhibited
92
New cards
When triacylglycerols are esterified, what happens?
Neutralizes the charges
93
New cards
Glycolipids
Bind to bacterial toxins, bacteria, and plasma membranes
94
New cards
Lipoproteins
Blood plasma, transports lipid molecules like triacylglycerols, phospholipids, cholesterol from one organ to anotherLip
95
New cards
Lipid-soluble antioxidants
Carotenoids. Found in lipoproteins
96
New cards
Triacylglycerols are digested in small intestine by..
pancreatic lipase. forms fatty acids and monoacylglycerol
97
New cards
Monoacylglycerols are transported across the plasma membrane of intestinal wall and converted to triacylglycerols
Glucagon and epinephrine bind to initiate lipolysis
98
New cards
Carnitine
Transports acetyl CoA into the matrix
99
New cards
Lipogenesis precursors
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate
100
New cards
Fate of glycerol after lipolysis
transported to liver to form glucose or a lipid