Mcgraw Hill Chapter 6 Integumentary System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
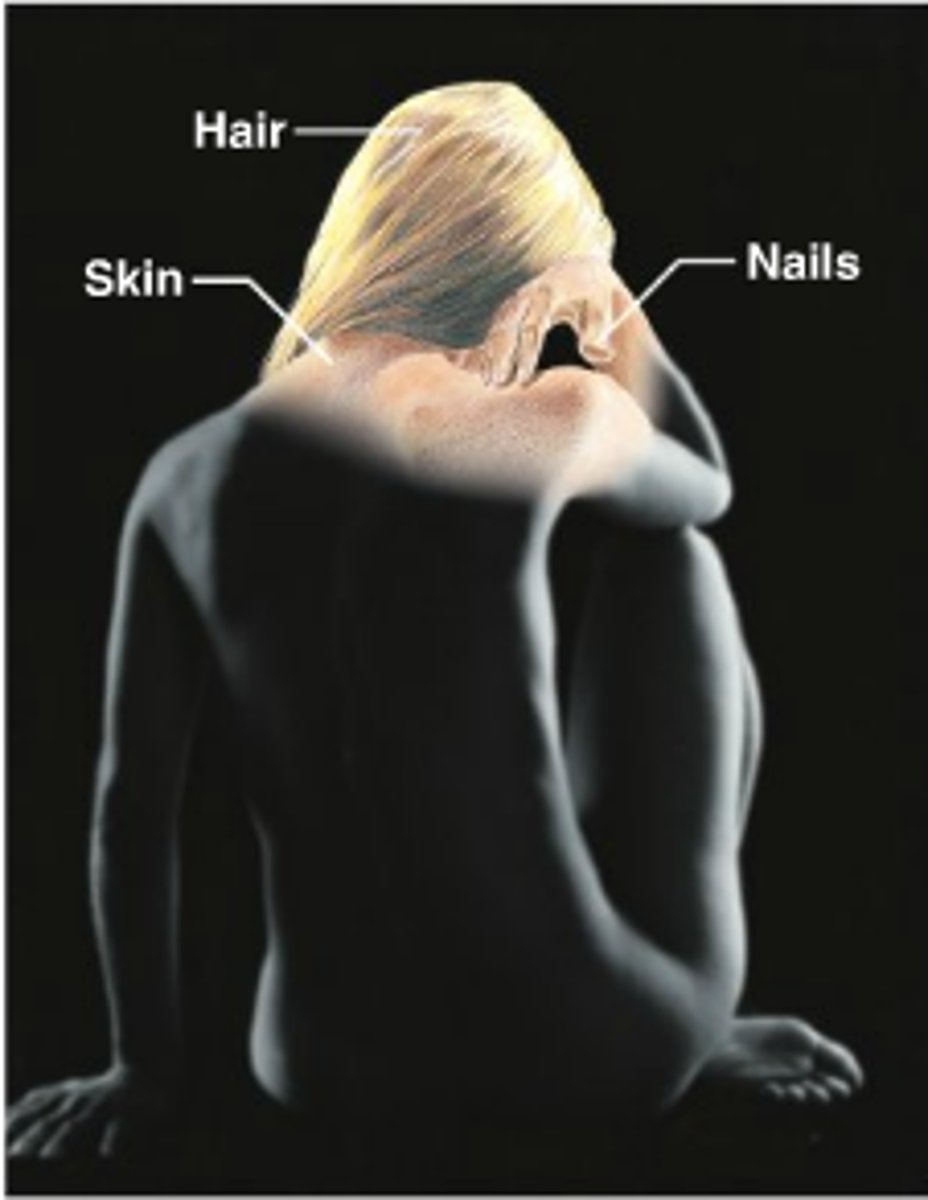
integumentary system is made up of
skin
hair
nails
sweat glands
sebaceous glands
layers of integument
epidermis and dermis
the cutaneous membrane is
the most superficial region (skin)
the epidermis is
stratified squamous epithelium
the epidermis function is
absorption and secretion
protection from abrasion of stem cells
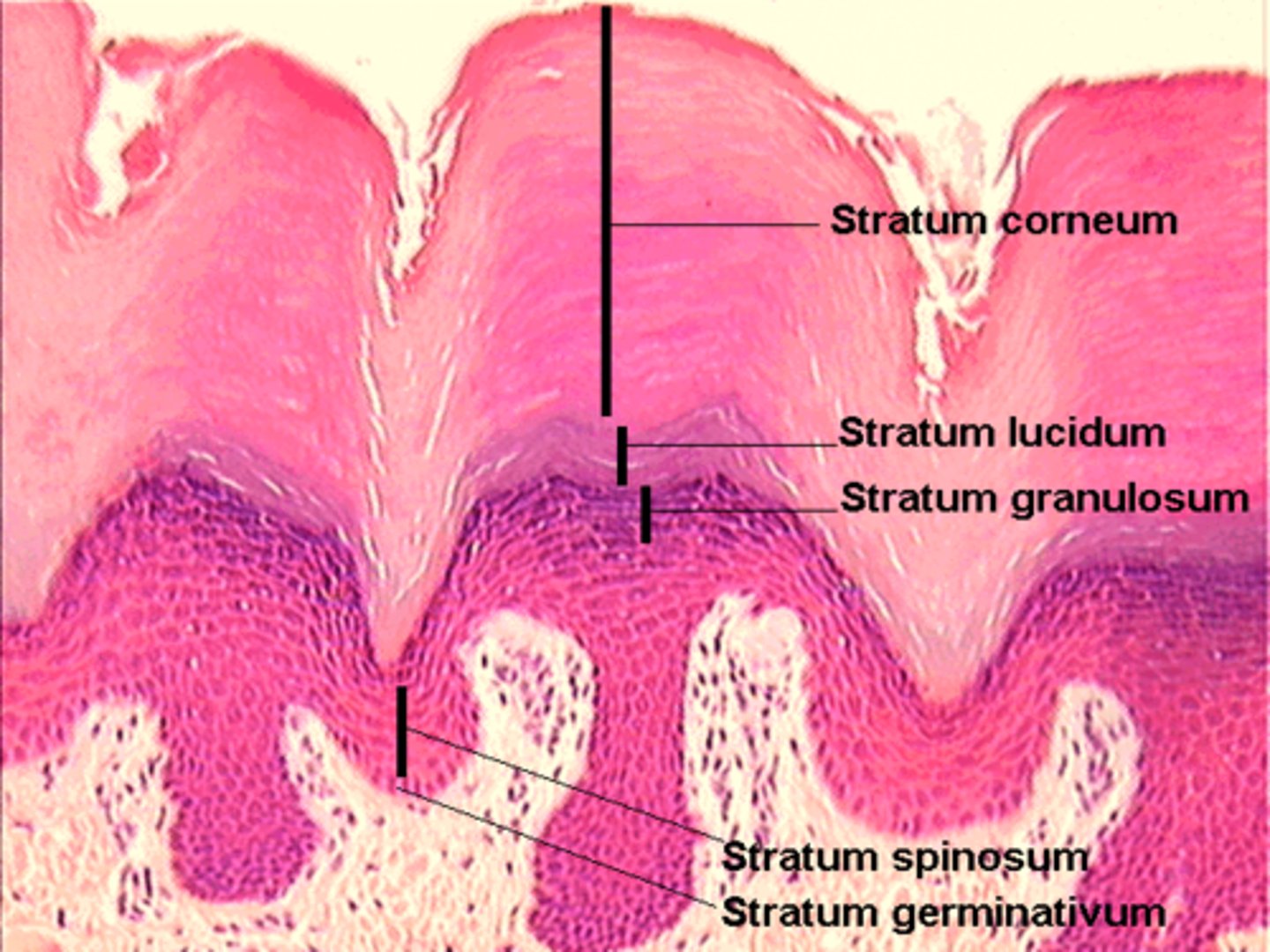
layers of epidermis in order from deep to superficial
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum
stratum corneum
stratum basale
living layer
mitotic division of keratinocytes
melanocytes and tactile cells
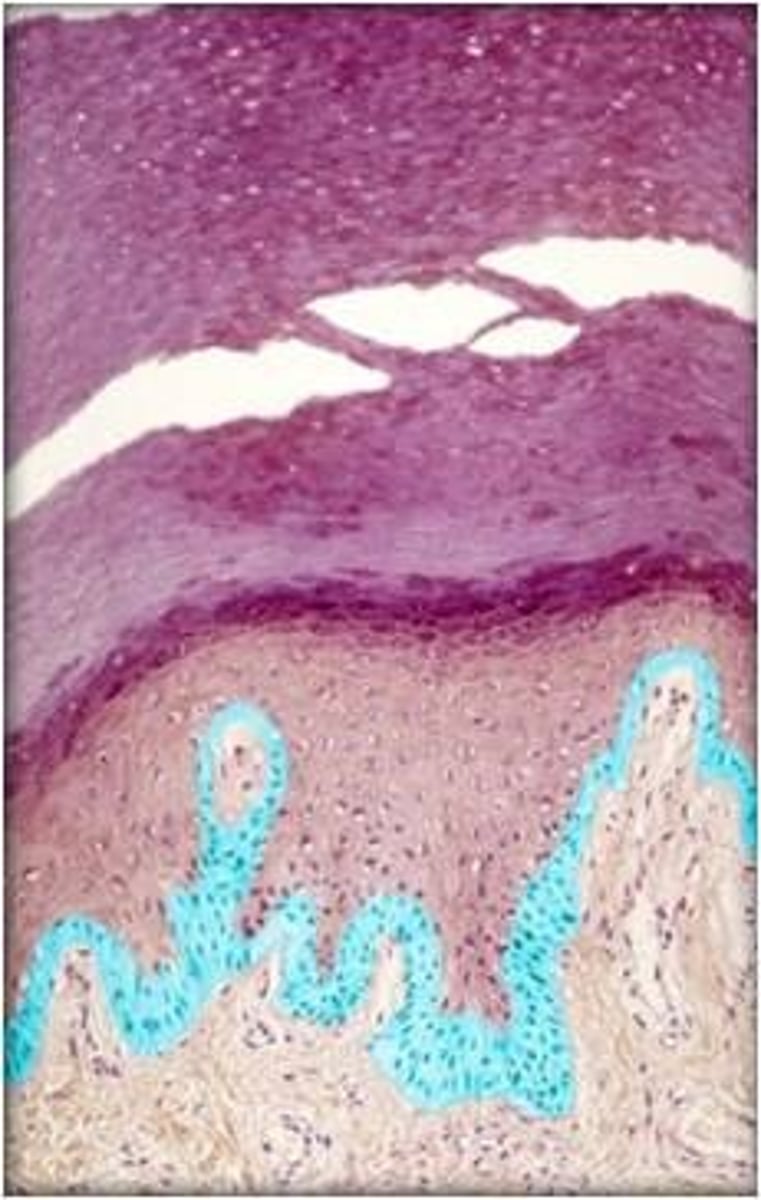
stratum spinosum
has epidermal dendritic cells fight off infection
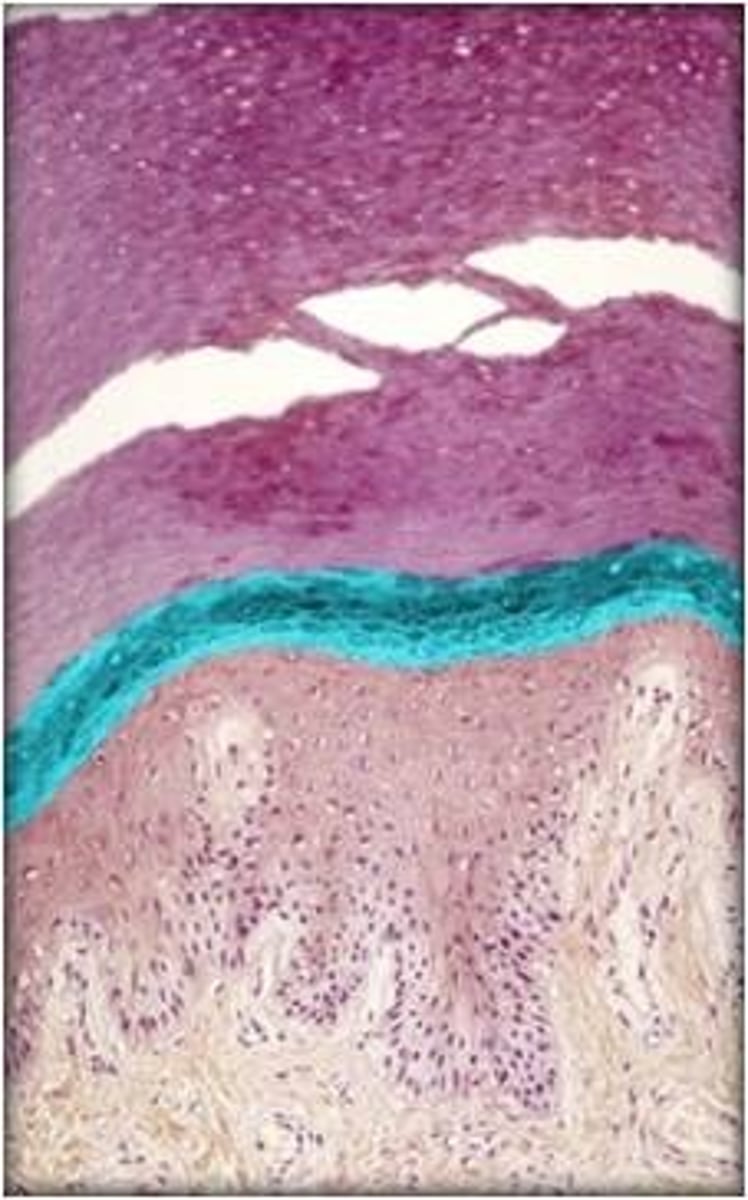
stratum granulosum
keratinocytes go through keratinization
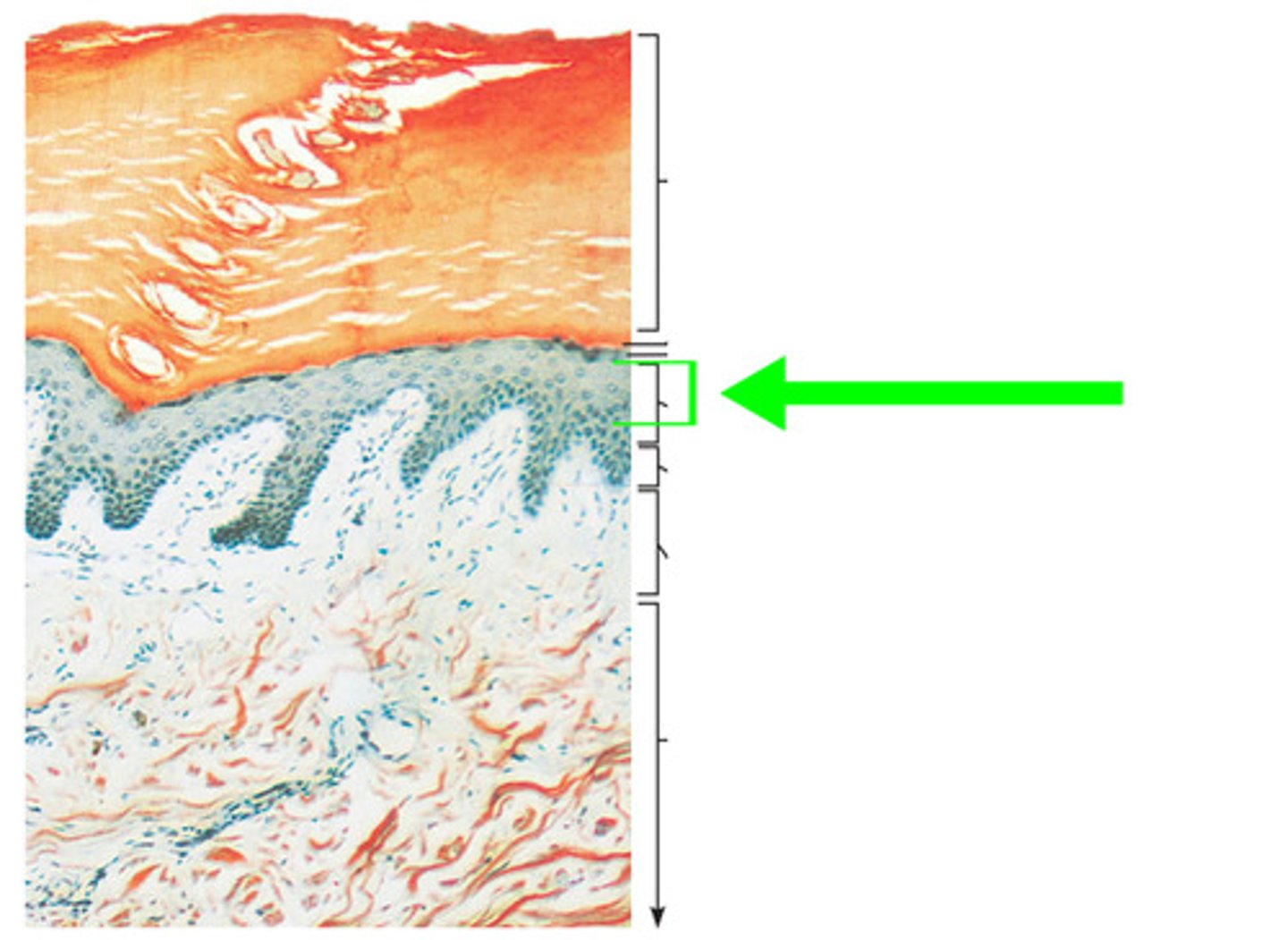
stratum lucidum
found only in the thick skin
translucent layer of of eledin protein that fills the cell
stratum corneum
outermost layer of epidermis
20/30 layers dead keratinocytes
protects against abrasian
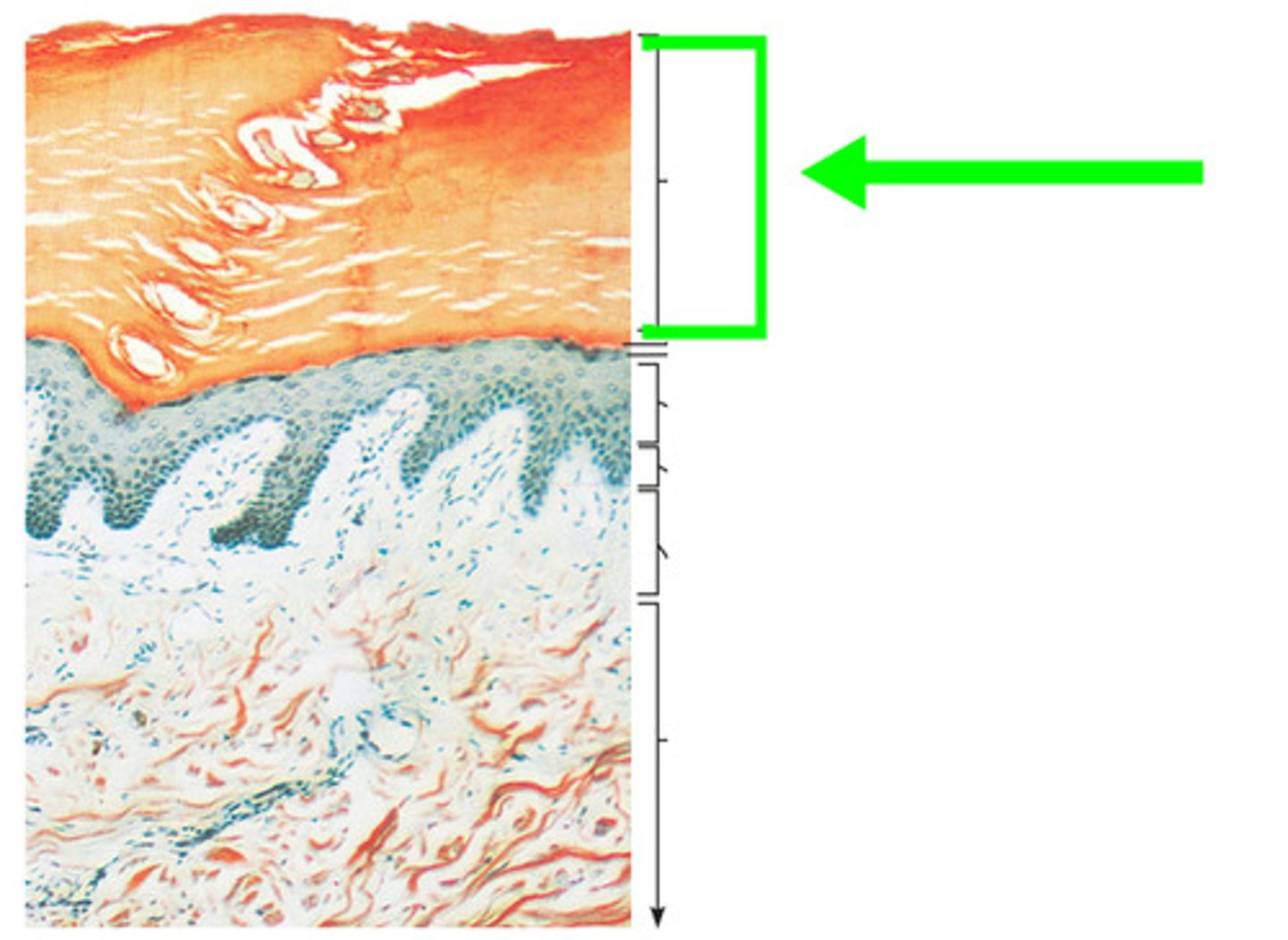
how long does it take for keratinocytes to go from stratum basale to the superficial surface and stratum corneum
25-45 days
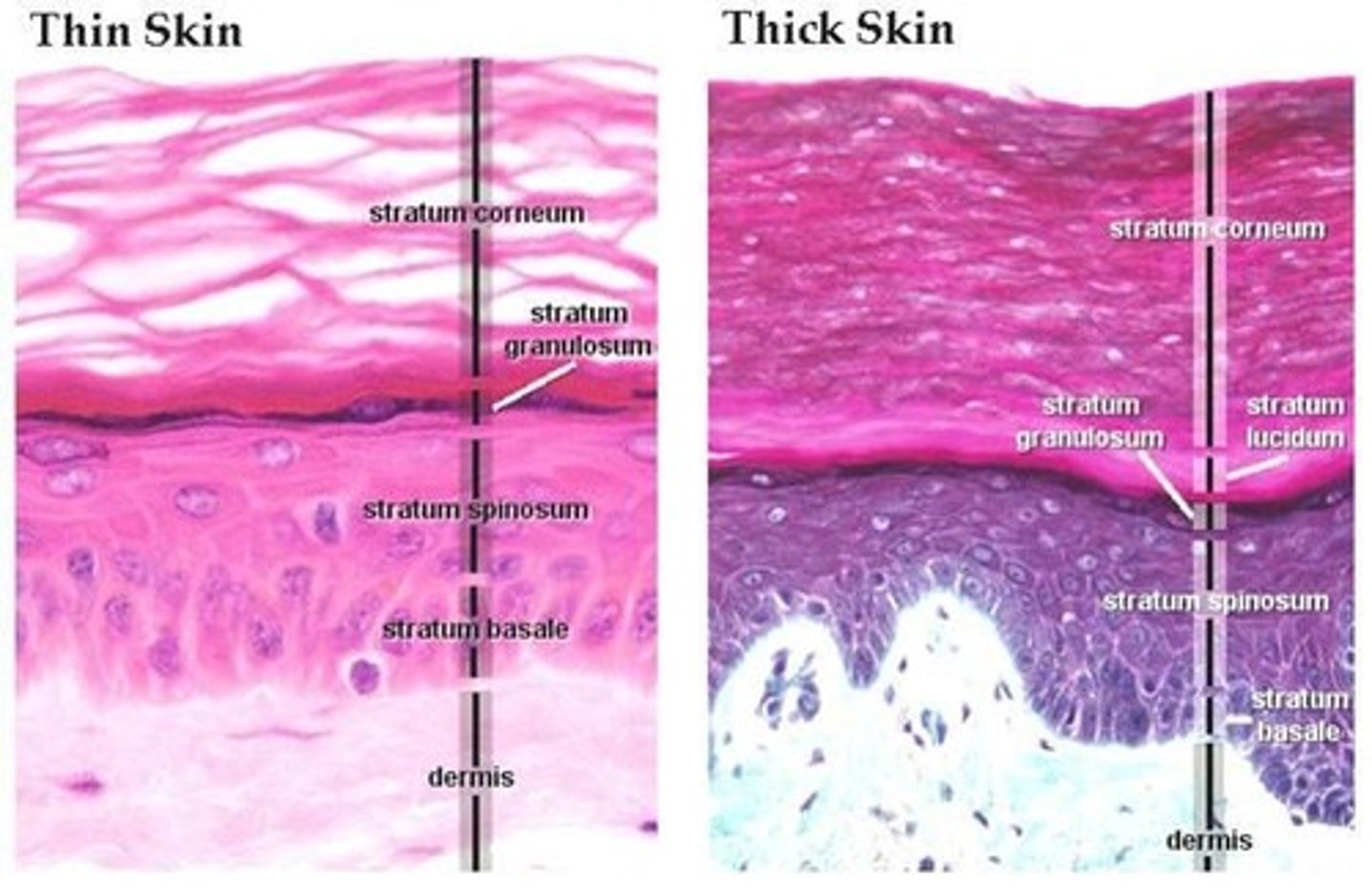
difference between thick and thin skin
thick skin is only in palms of hands and soles of feet and have 5 layers of epidermis
thin skin is everywhere else and only has 4 layers of epidermis
what contributes to skin color
comes from melanocytes being more active in making more melanin from UV light
hemoglobin brings more oxygen to blood making it more red
carotene yellow orange pigment from vegetables
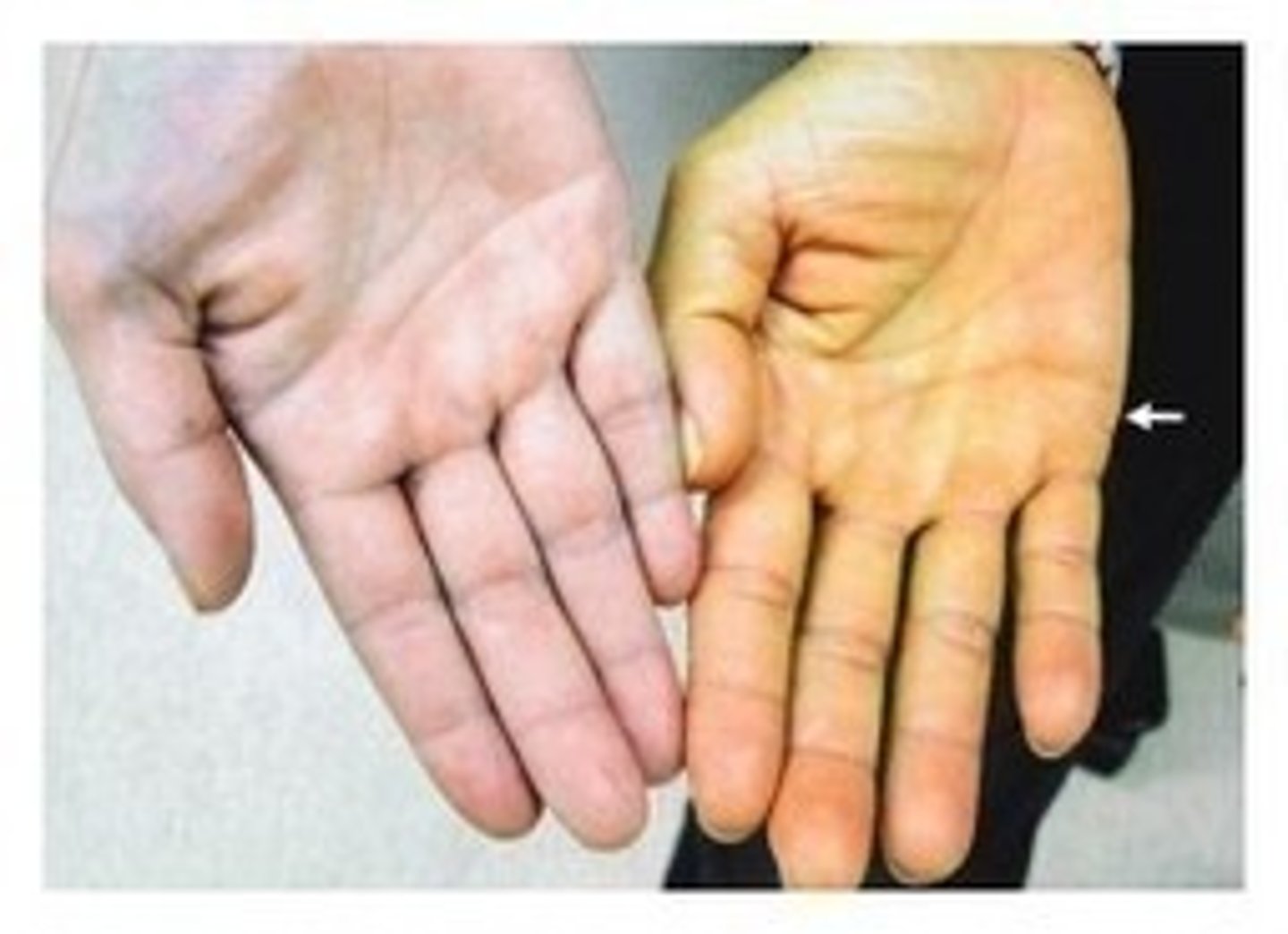
skin color changes from diagnostic value
cyanosis- blue oxygen deficiency
polar- pale decrease in blood flow
hematoma- bruising clots of blood under skin
erythema- blush increased blood flow
jaundice- yellowing from bilirubin release
common skin markings inlcude
nevus- mole overgrowth of melanocytes
freckles- increased spot of melanocyte activity
hemangiomas- birthmarks discoloration of benign blood vessel tumors
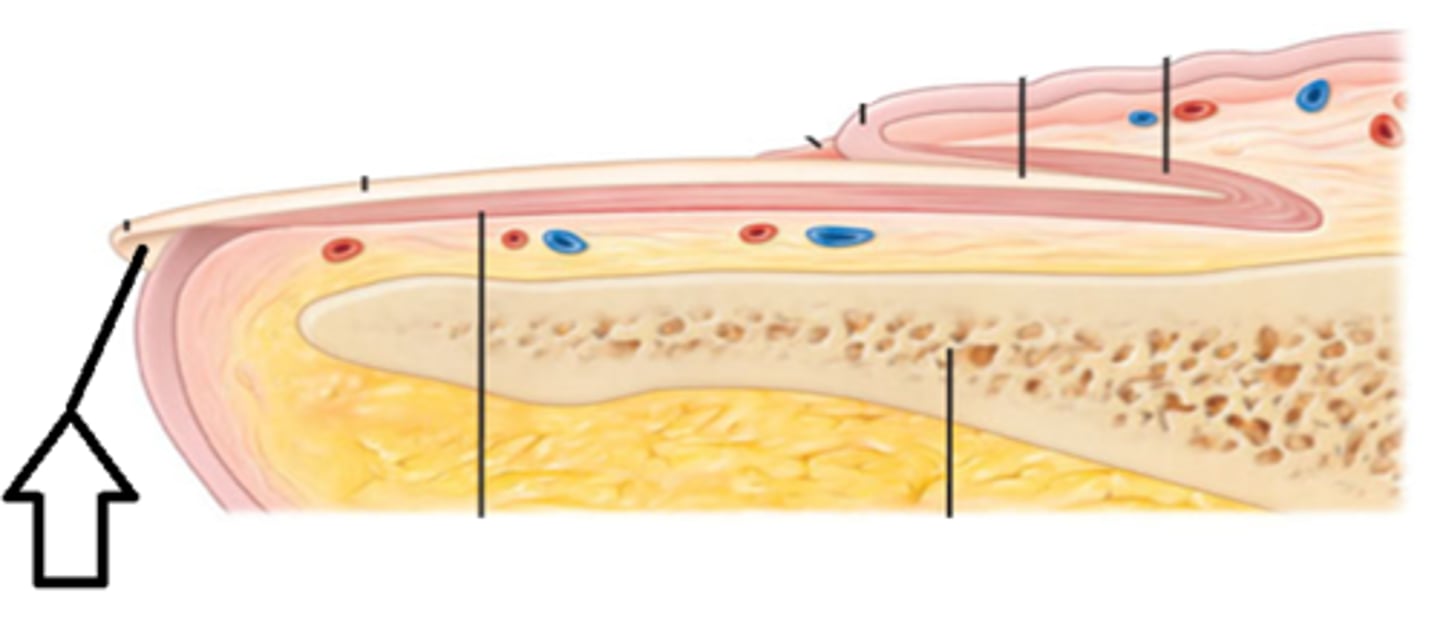
epidermis structure
Avascular dead outer layer
nourished by diffusion from capillaries of papillary layer of dermis
composed of cells arranged into strata (layers) and
separated from dermis by basement membrane
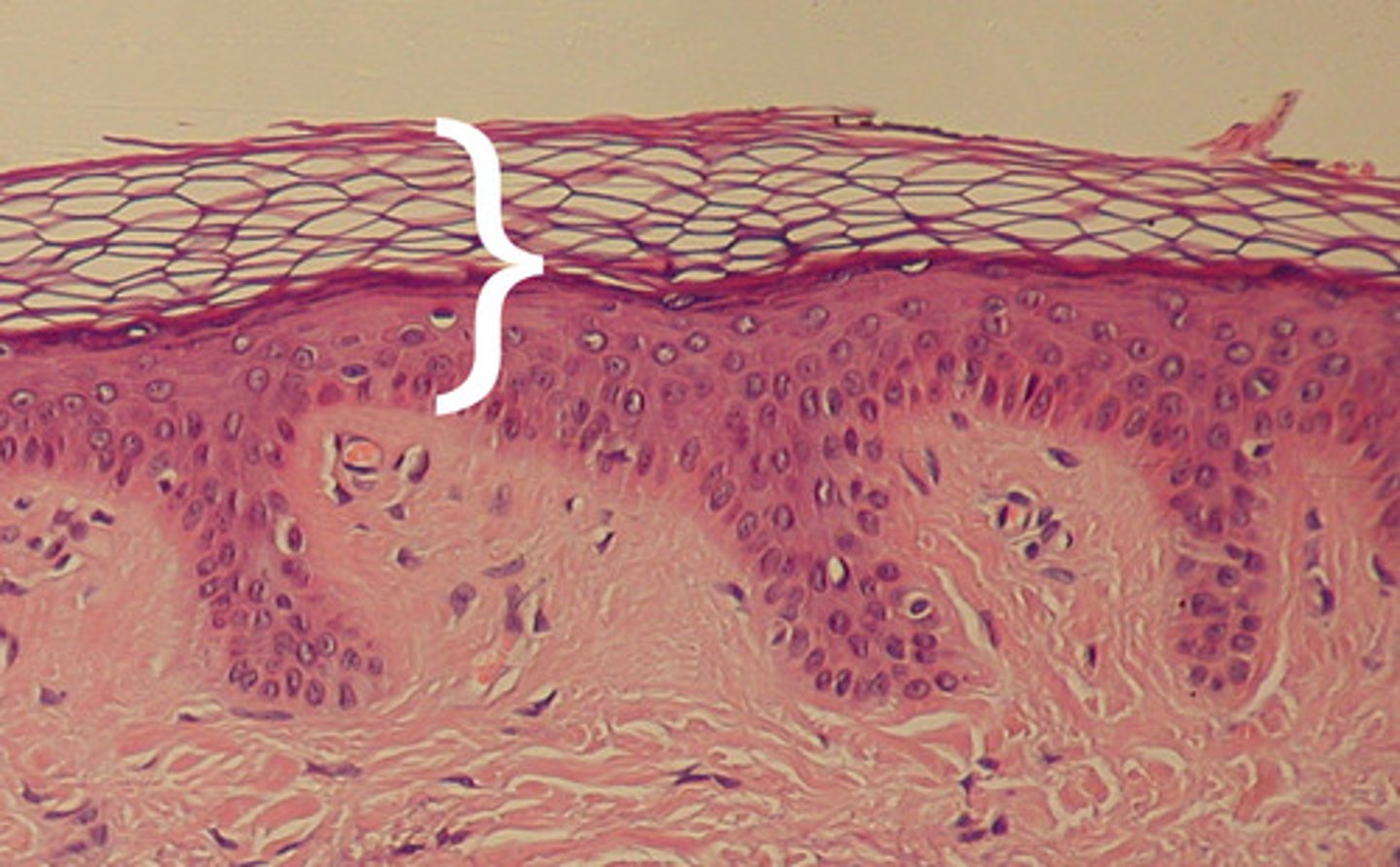
Dermis structure
vascular layer below epidermis
made of connective tissue layers
collagen and elastic fibers
sweat glands hair follicles
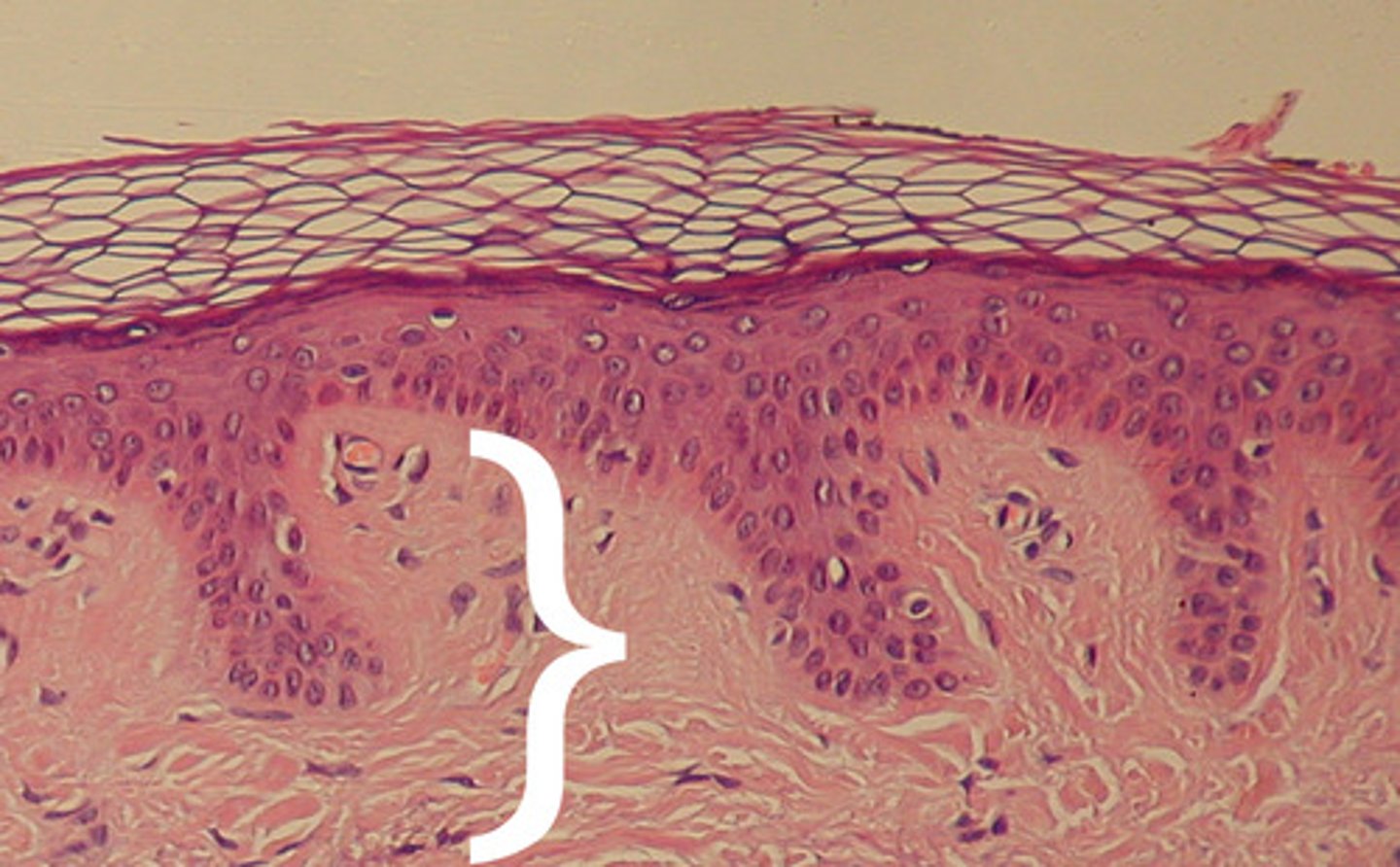
layers / structures found in the dermis
has hair follicles
nail roots in papillary layer
has papillae connecting to epidermal ridges
sebaceous glands
sweat glands
reticular layer of dense irregular ct has elastic and collagen fibers
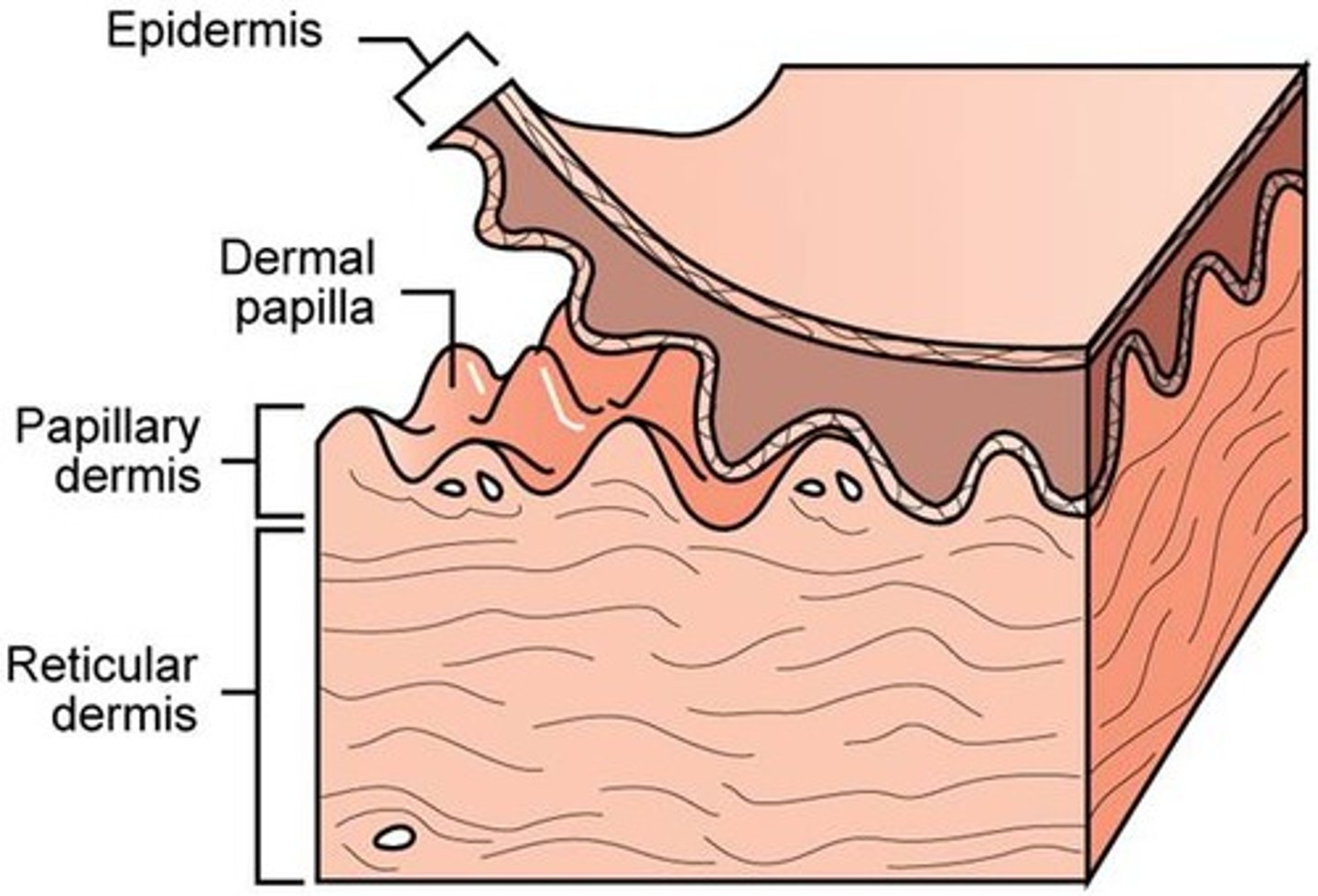
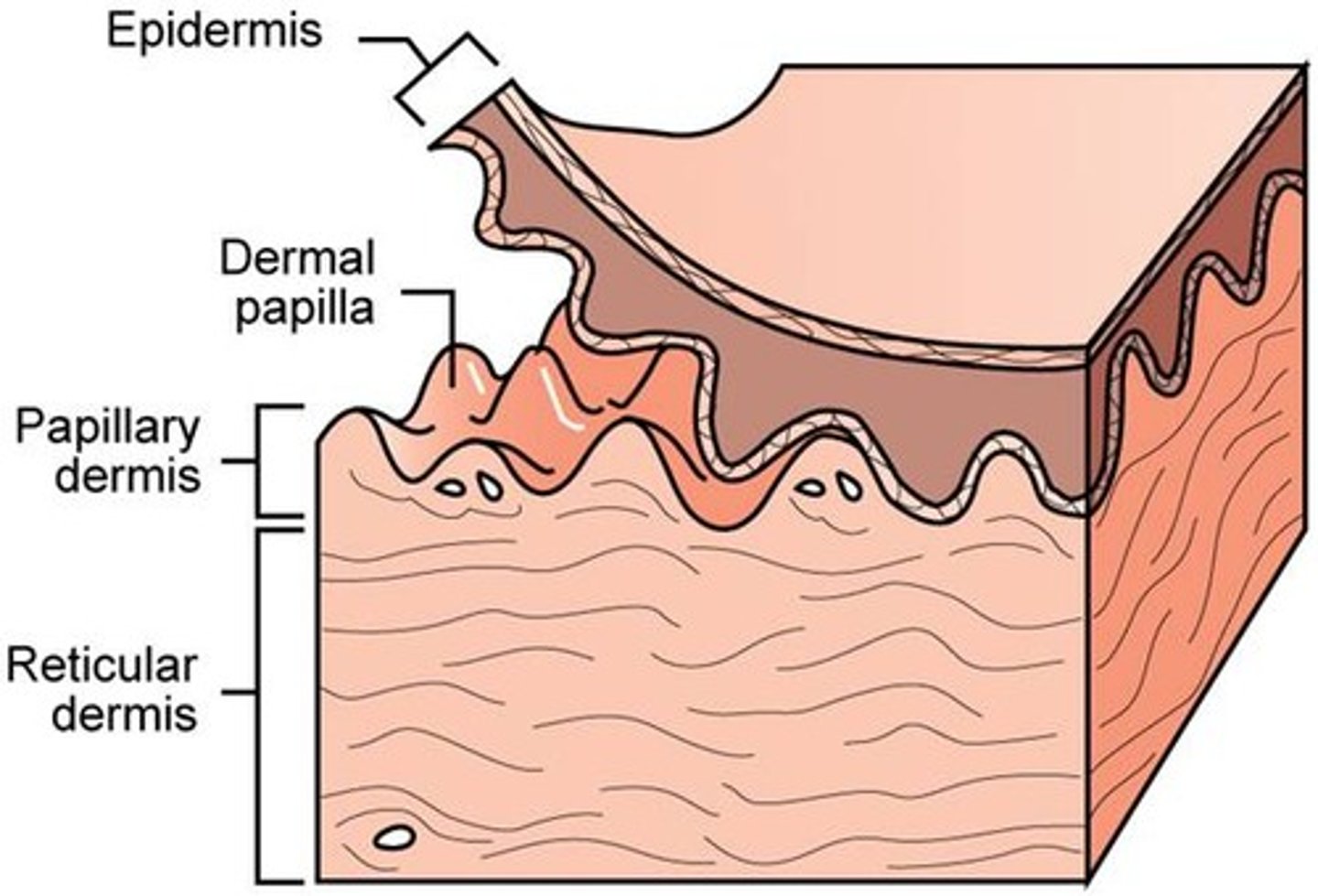
purpose of dermal papilla
increase surface area b/w dermis and epidermis
increase amount of oxygen exchange
nourish avascular epidermis
give fingertips grasp
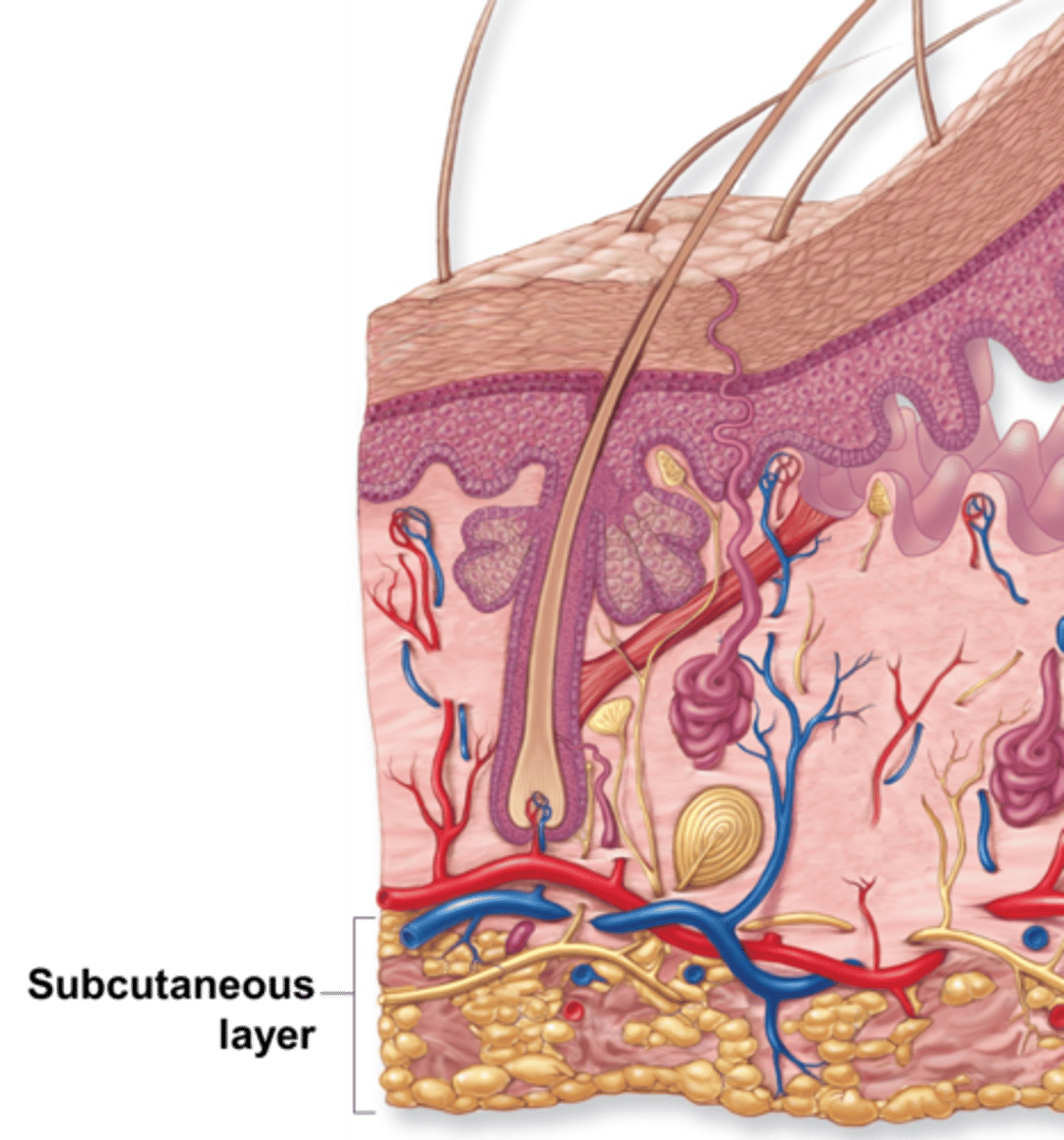
subcutaneous layer is
NOT part of the integument
below dermis
called hypodermis
drug injection site
highly vascularized increase rapid absorption
made of areolar and adipose ct
function of integumentary system
protection
prevention of water loss
metabolic regulation
secretion/absorption
immune function
sensory reception
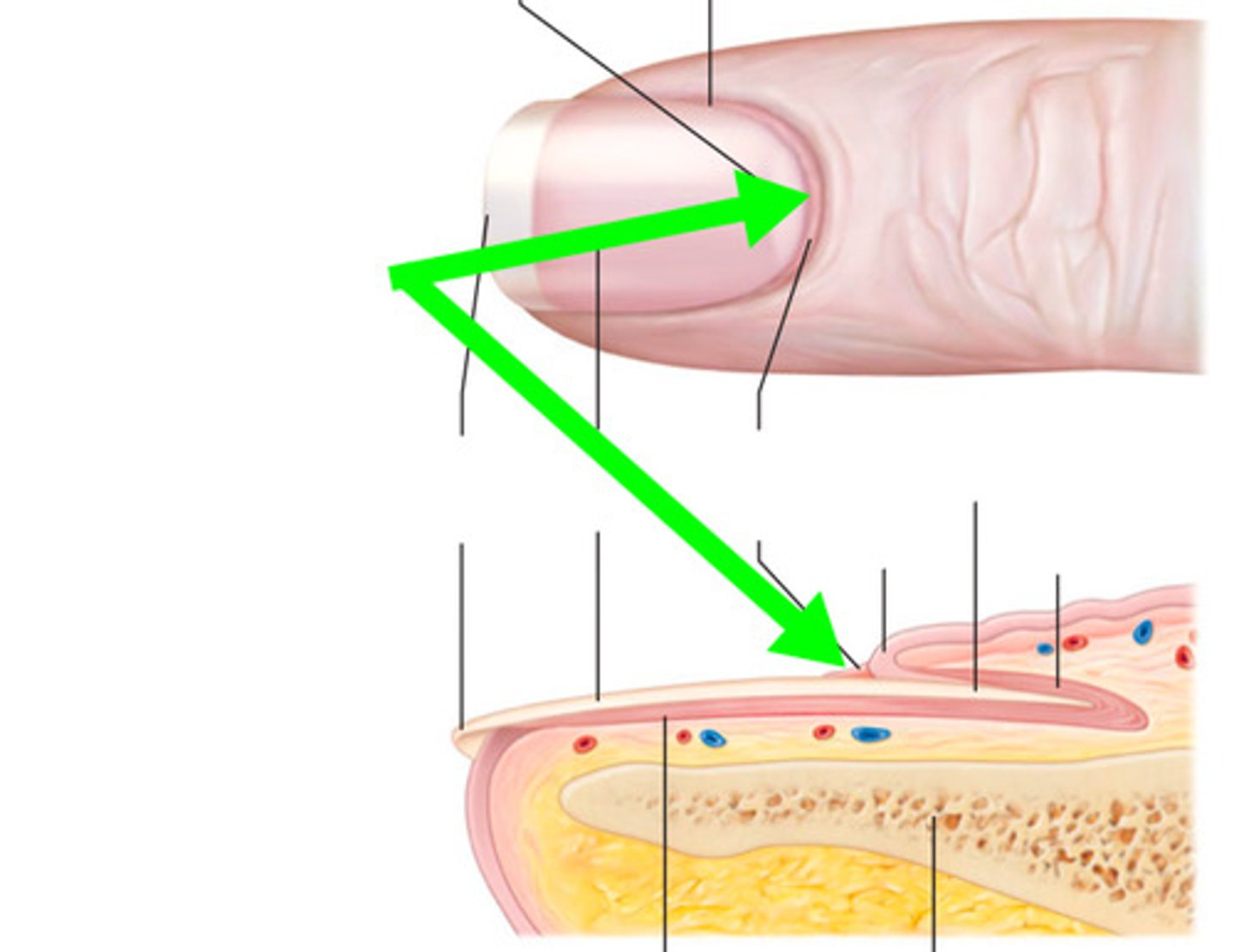
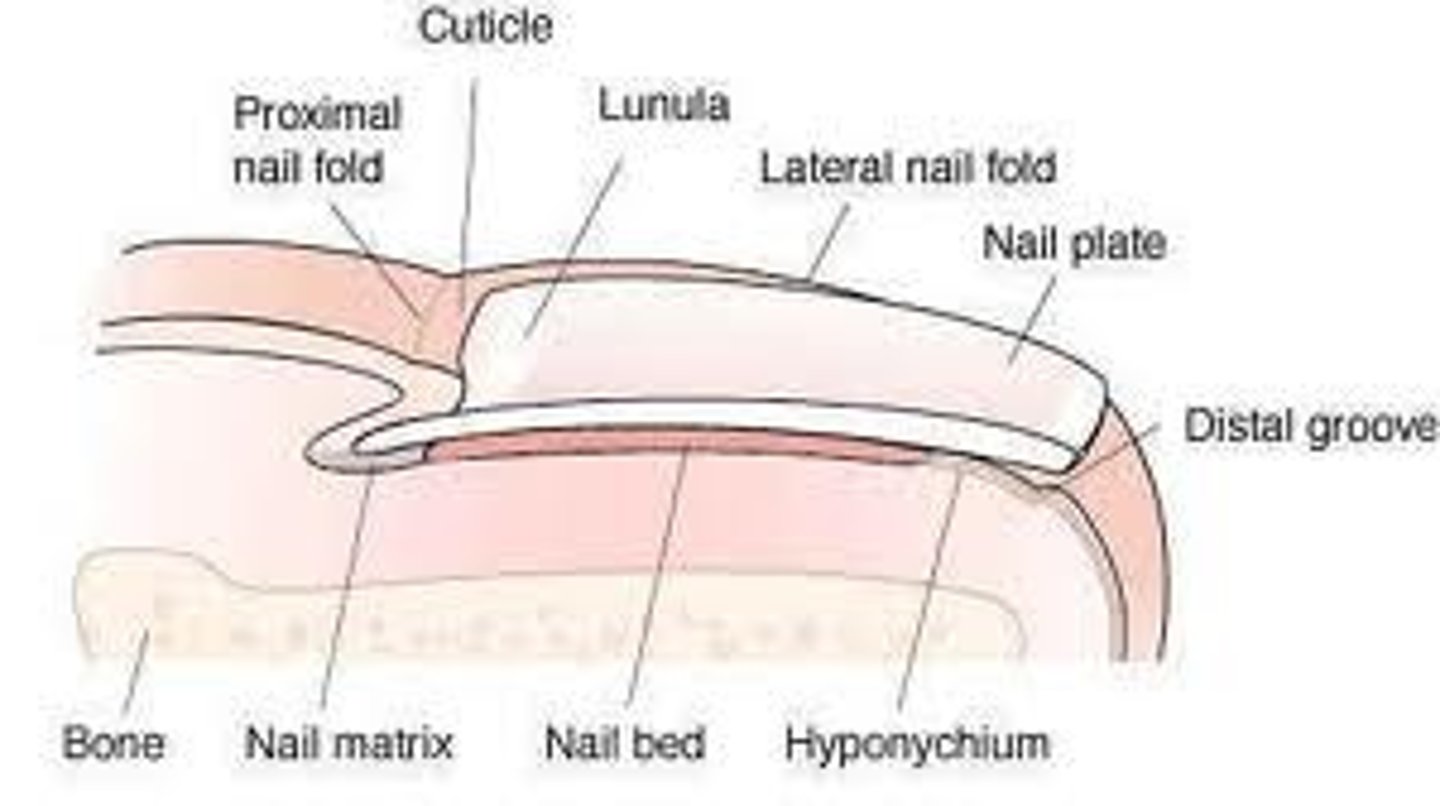
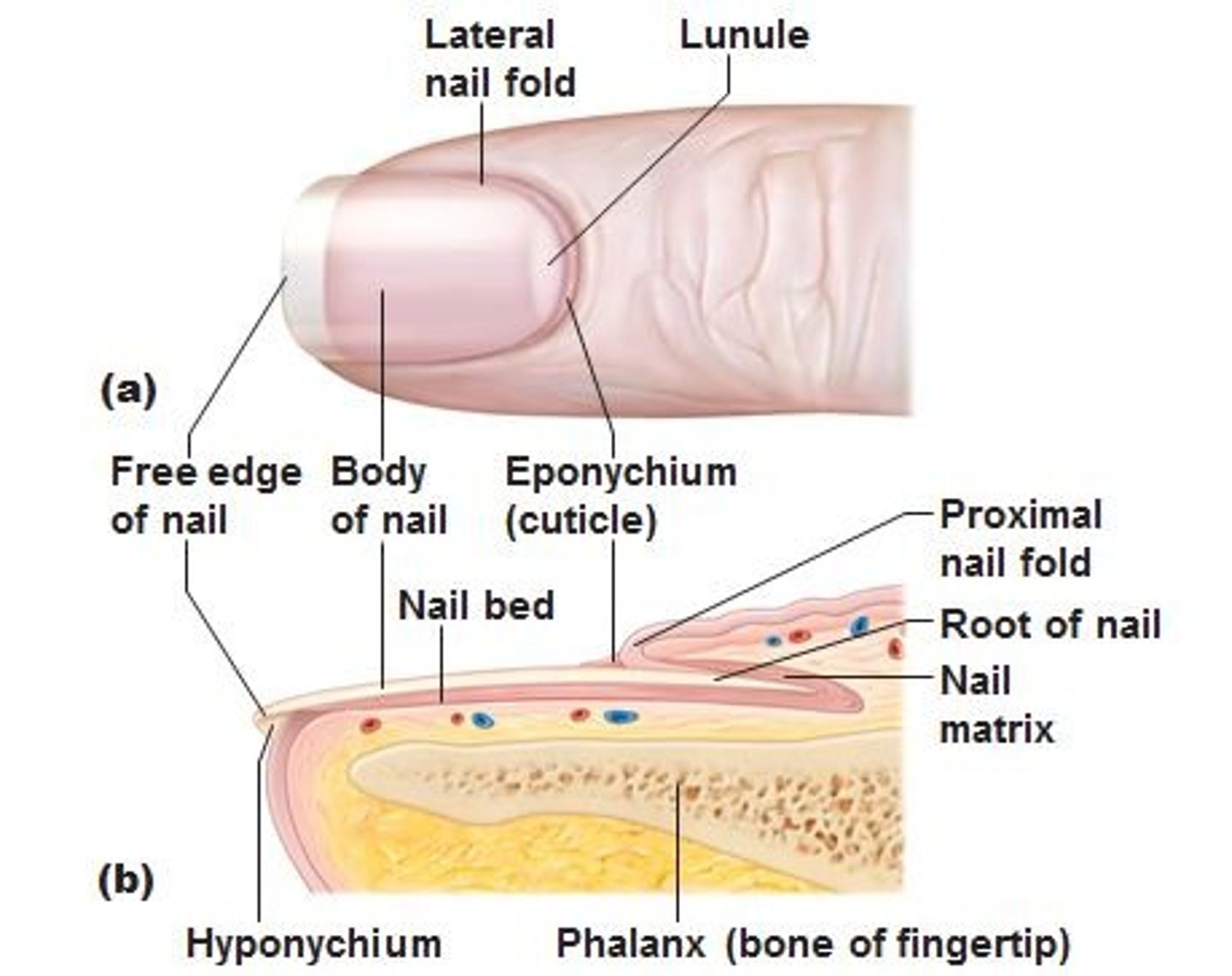
structure / function of eponychium
cuticle
overlines nail root
protects epidermis from bacteria
thickened skin layer at base of nails
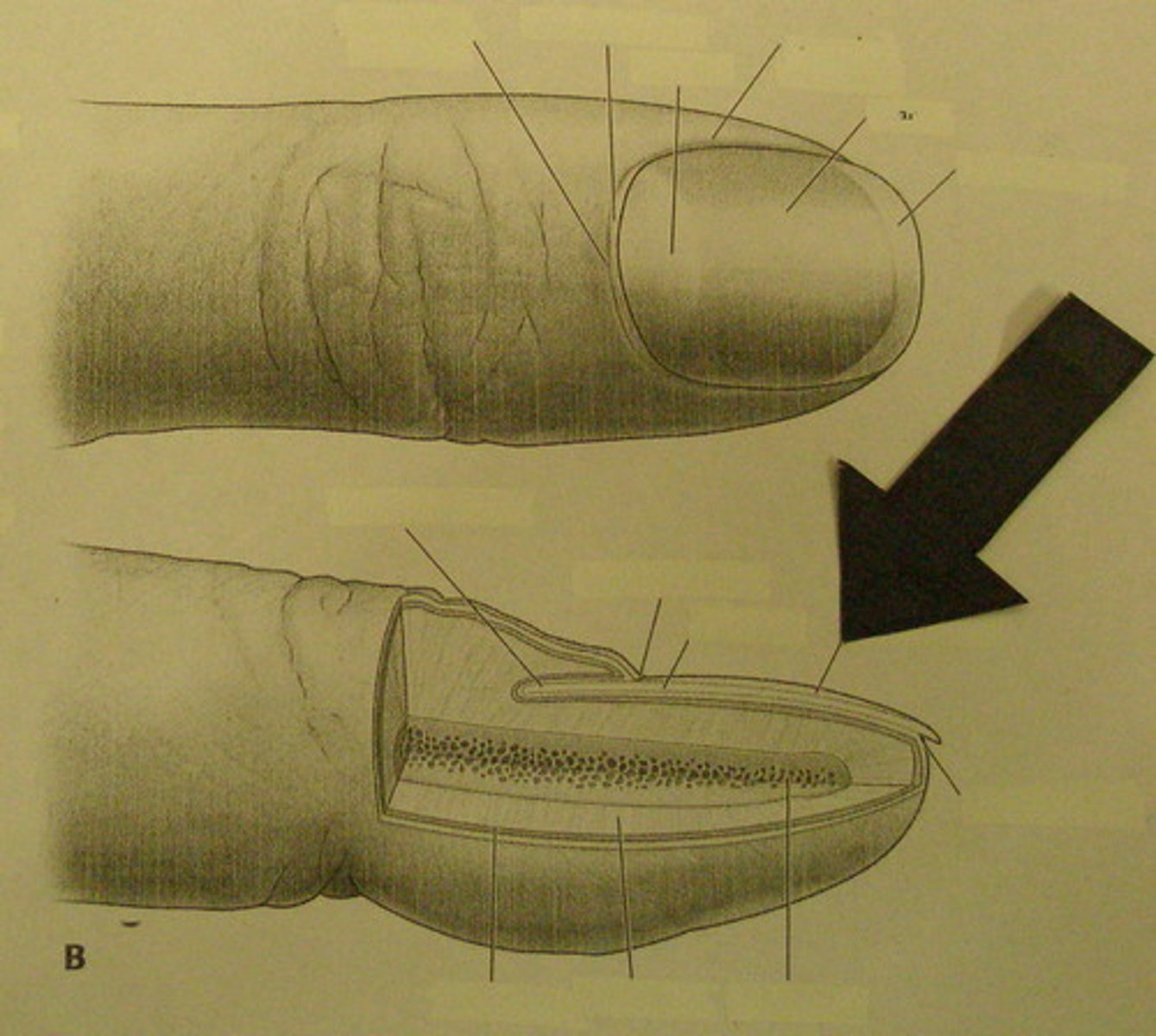
structure / function of free edge of nail
aid in grasping of fingers
protect digits
distal edge white part

structure / function of nail bed
epidermal layers deep to nail plate
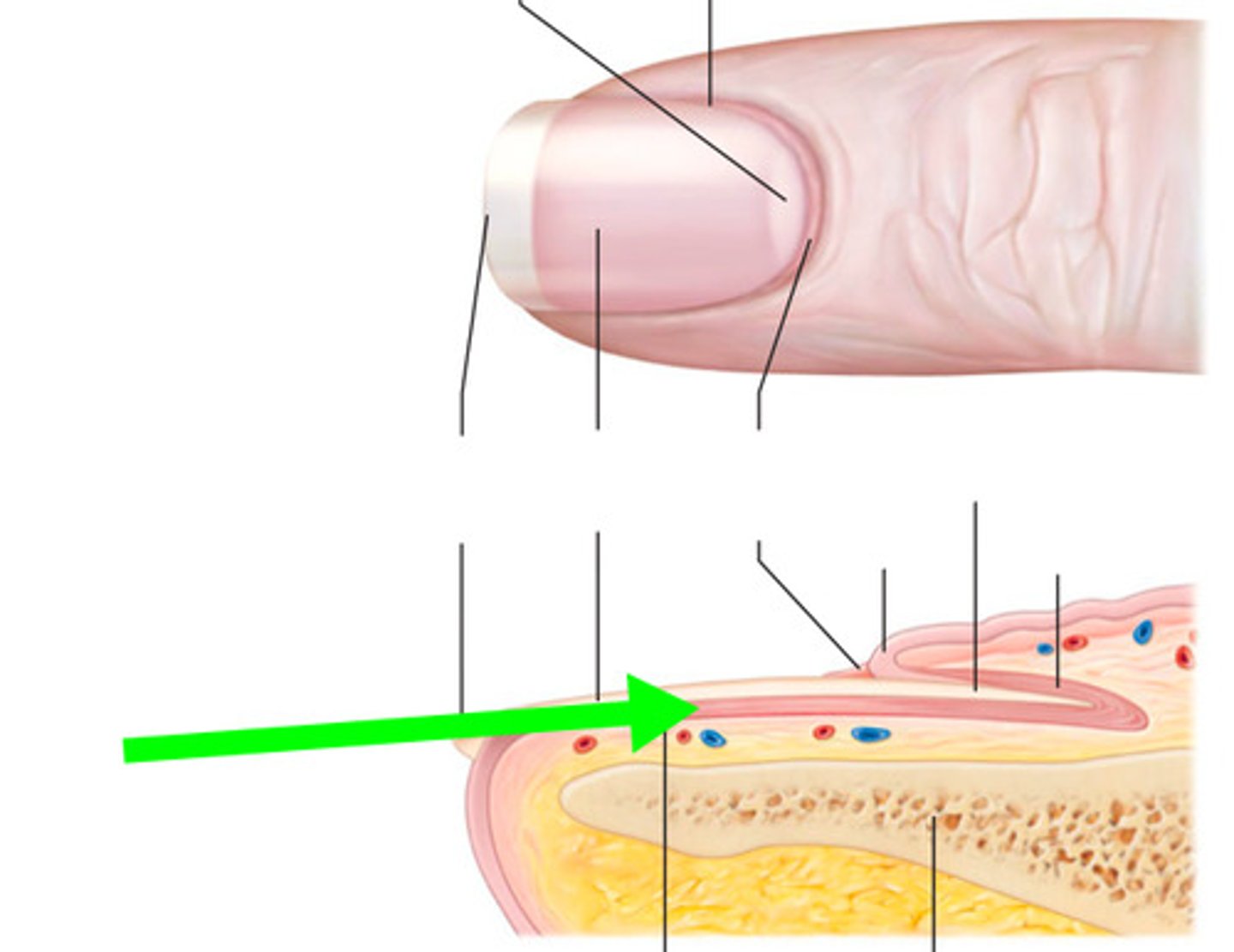
structure / function of nail body
layer of compact high keratinized epithelial cells
protect digits
pink part
structure / function of nail matrix
mitotic cells correspond to stratum basale
growth zone of nail
structure / function of nail root
smallest part
in nail plate under the nail
growth of nail
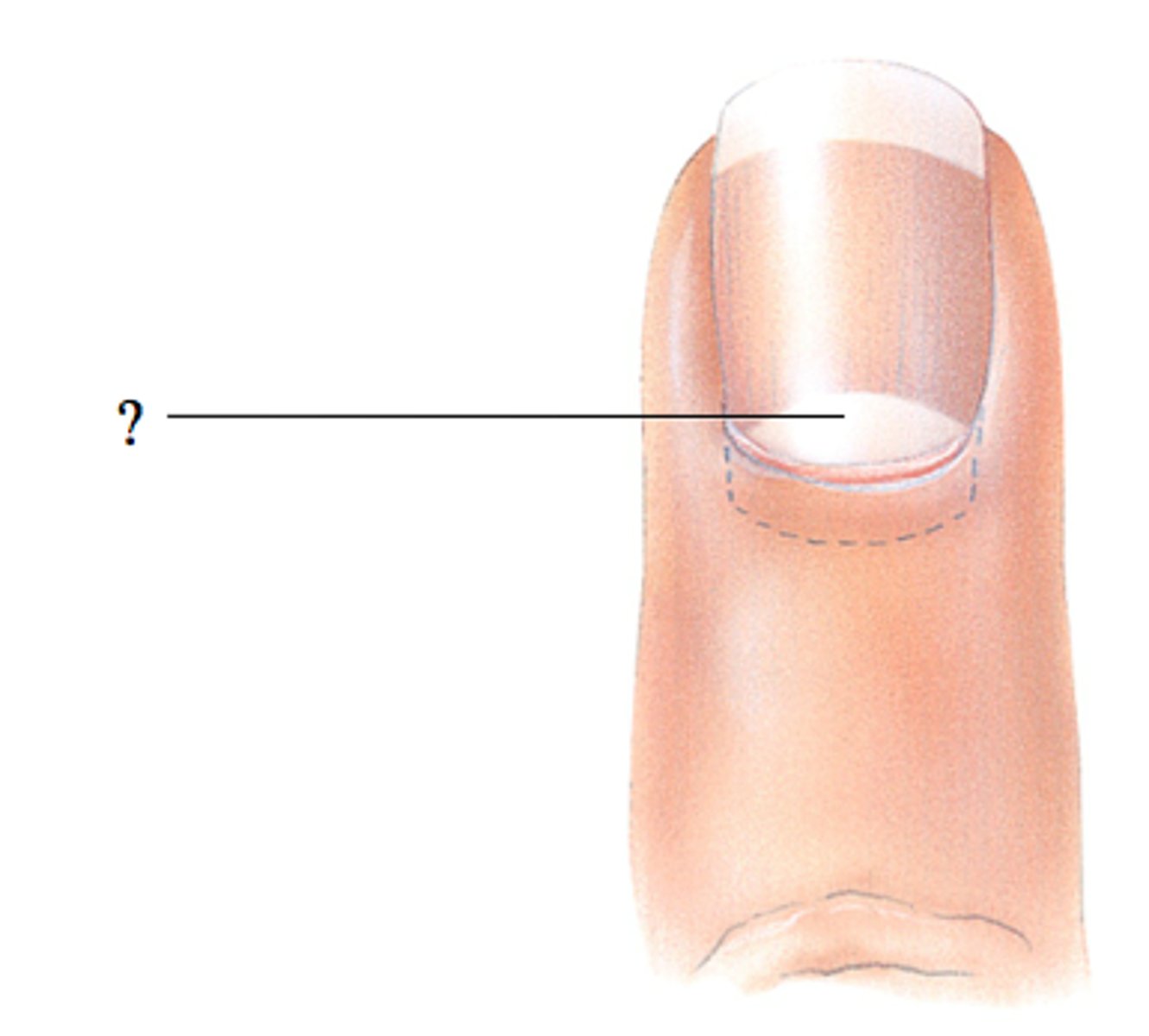
structure / function of lunula
part of nail matrix
crescent shape at bottom of nail
shapes outermost part of nail
strcuture / function of nail folds
folds of skin overlapping nail
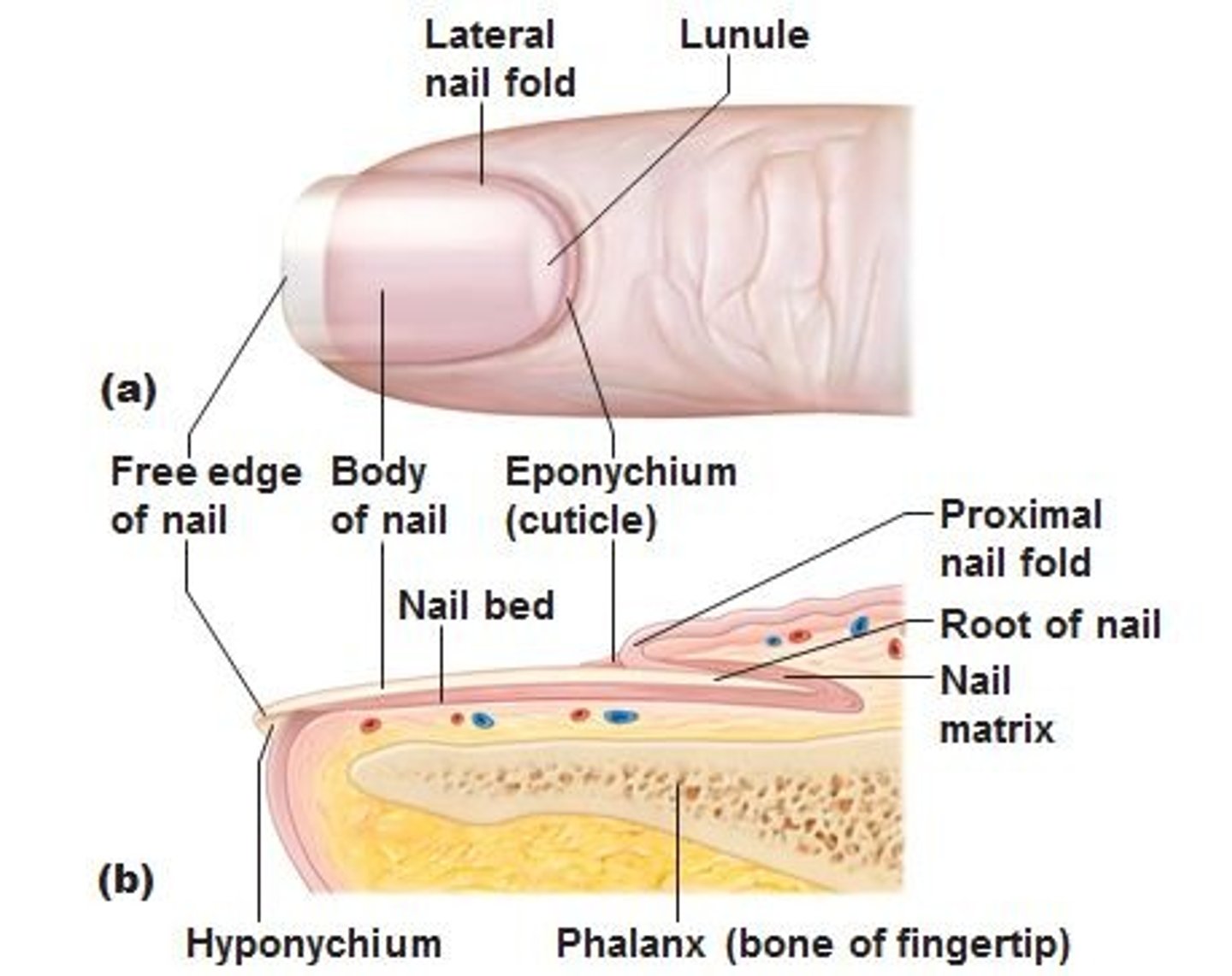
structure / function of hyponychium
thickened stratum corneum under where free nail edge hangs
functions of hair (6)
protection
facial expression
heat retention
sensory reception
visual identification
chemical signal dispersal
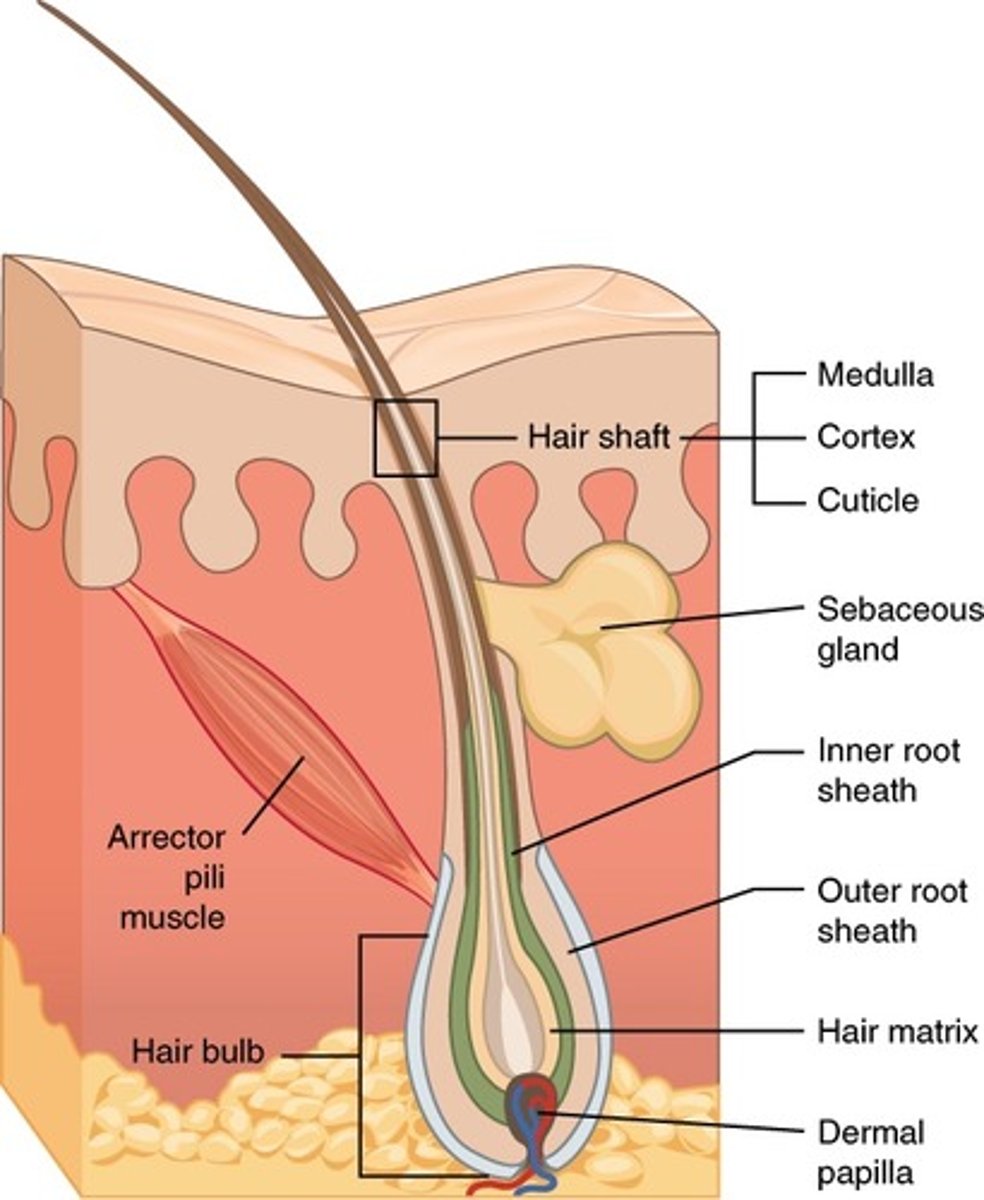
structure of hair bulb
surrounds hair papilla
made of ct
only living region of epithelial cells
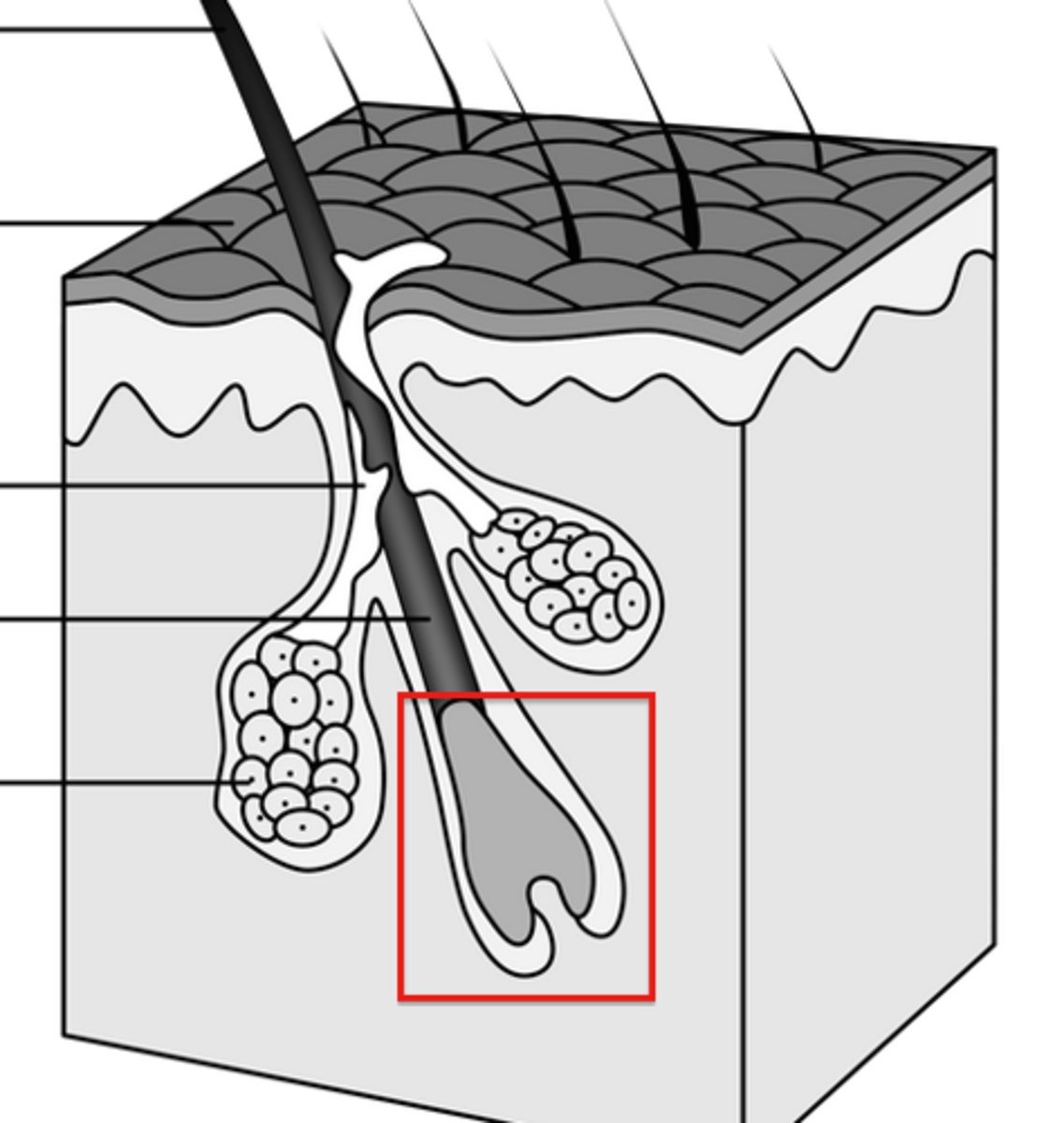
structure of hair root
zone of hair from bulb to skin surface
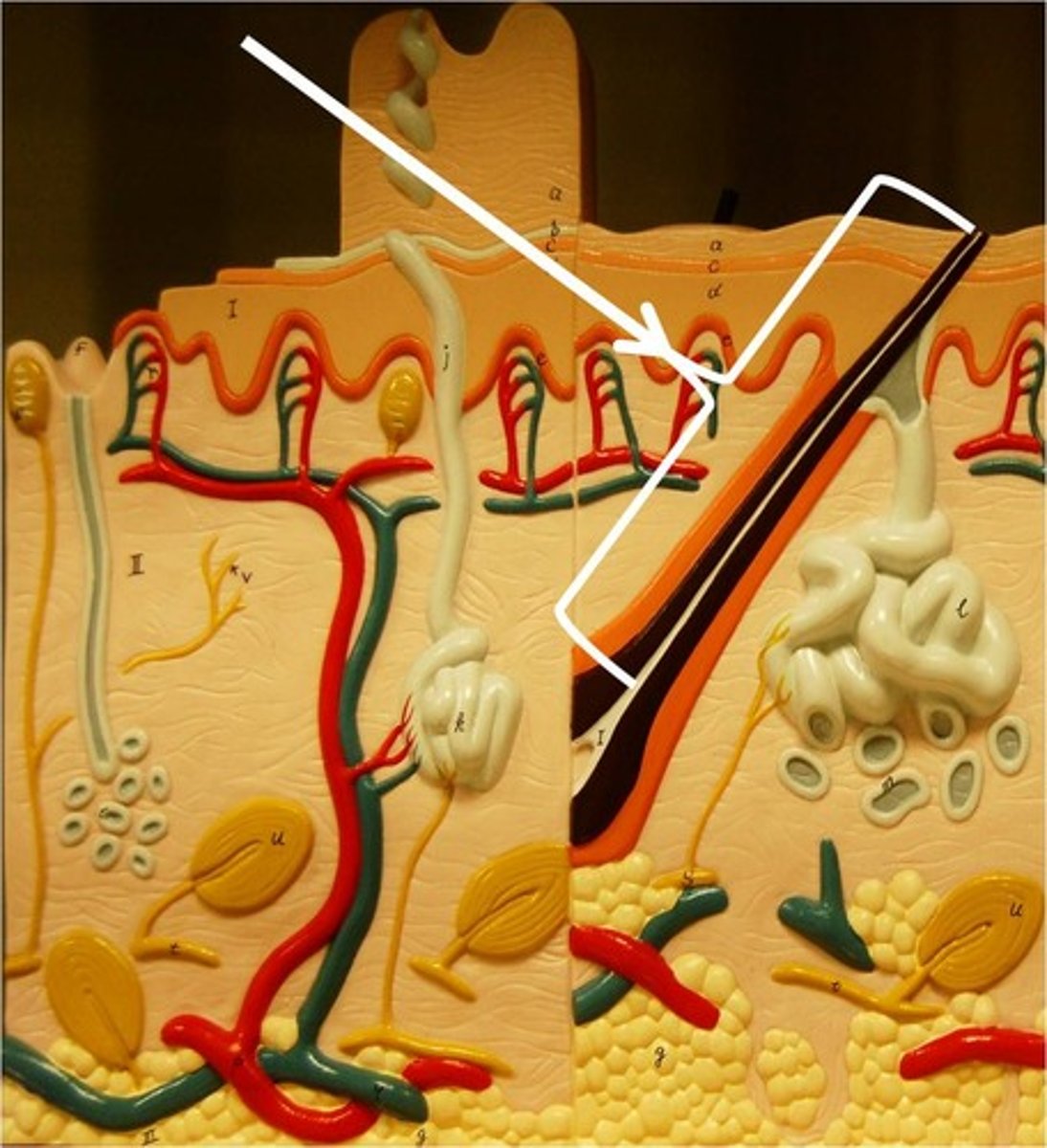

structure of hair shaft
portion of hair beyond skin surface no nerve endings
has cuticle
medulla
cortex
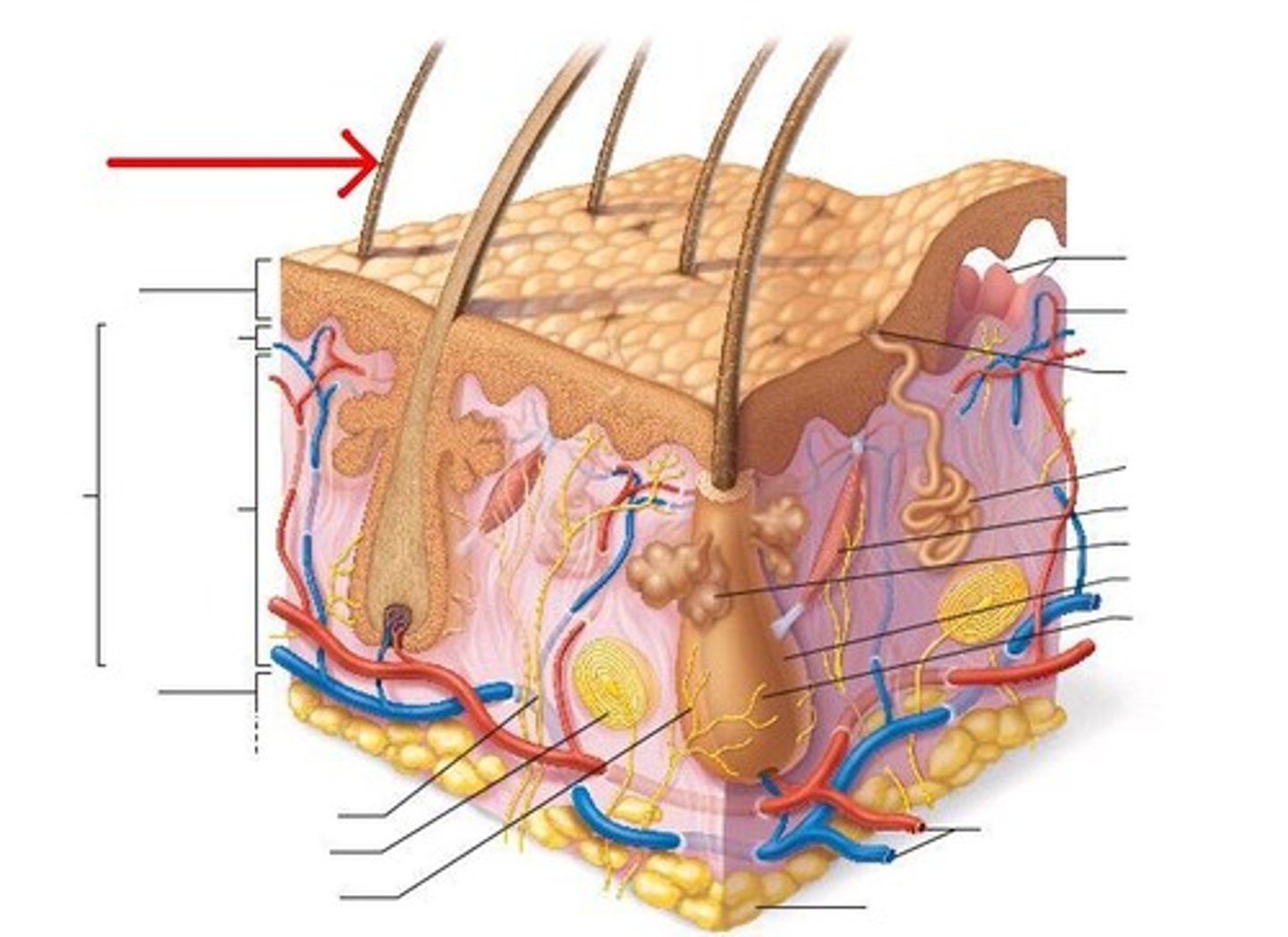
image of hair coretex medulla epithelial root sheath connective tissue root sheath
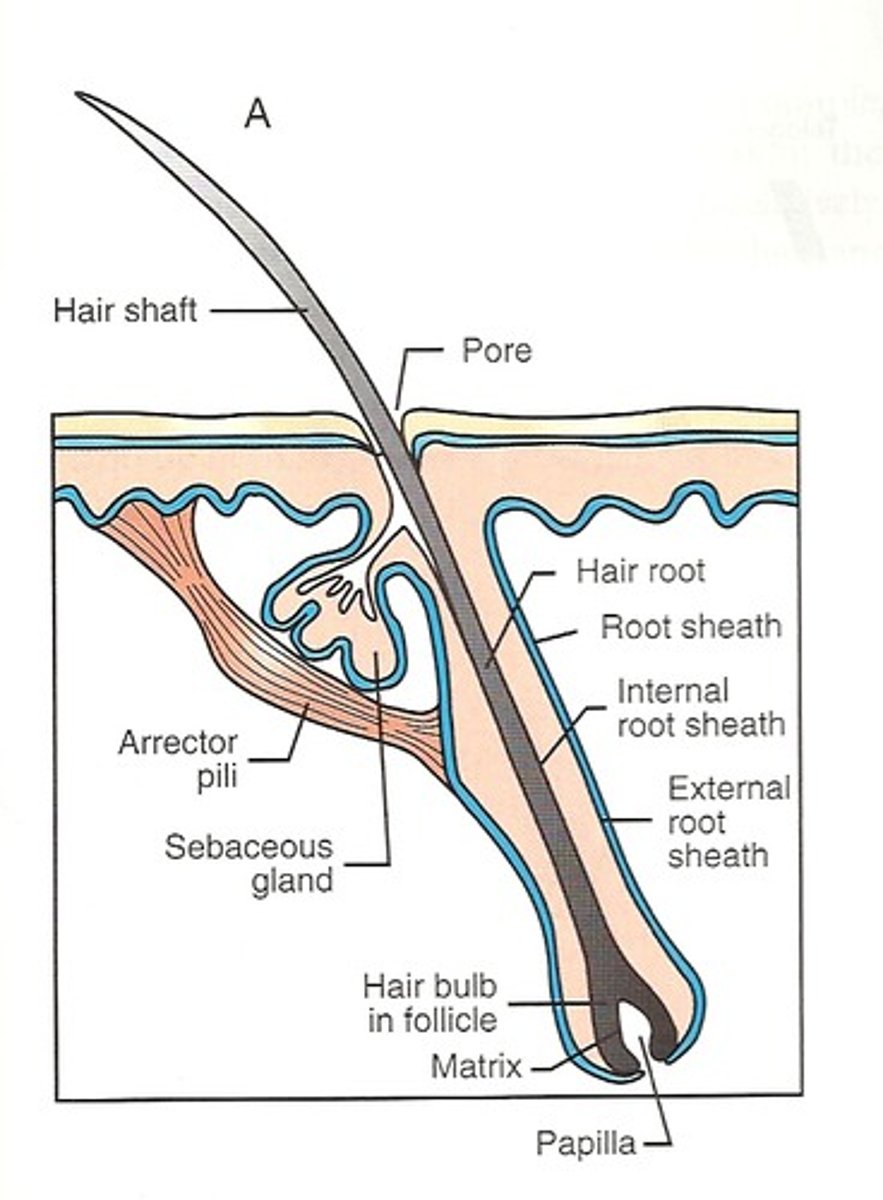
arector pili muscle
ribbons of muscle from hair follicle to dermal papillae causing goosebumps bc of hair elevation contractions
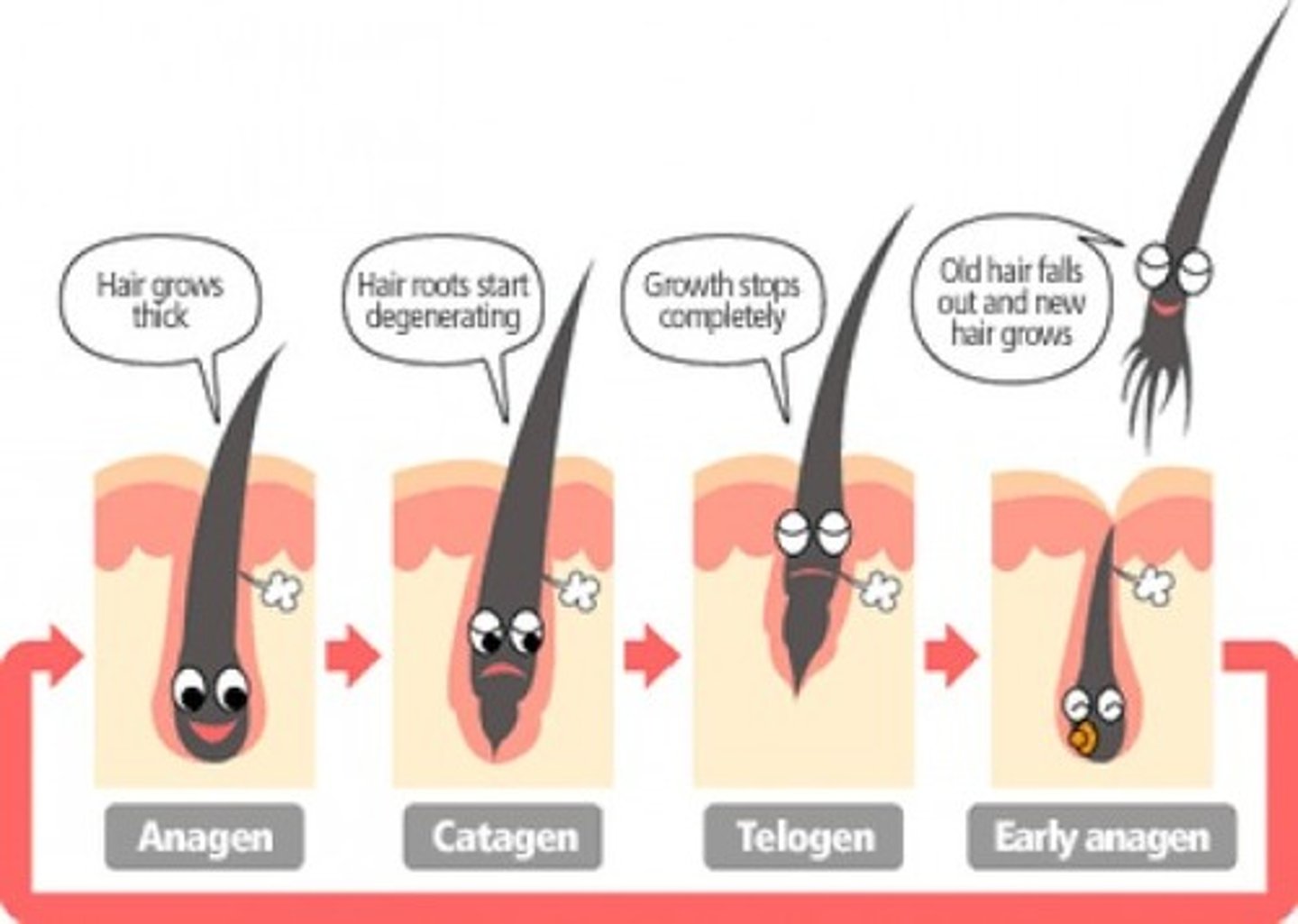
Stages of hair growth
Anagen (Growth stage)
Catagen (Transition/regression stage)
Tetagen (Final resting stage)
basis for hair color and texture
hair color- synthesis of melanin lightening w age to gray
hair texture- circle is straight, oval is wavy, flat is curly

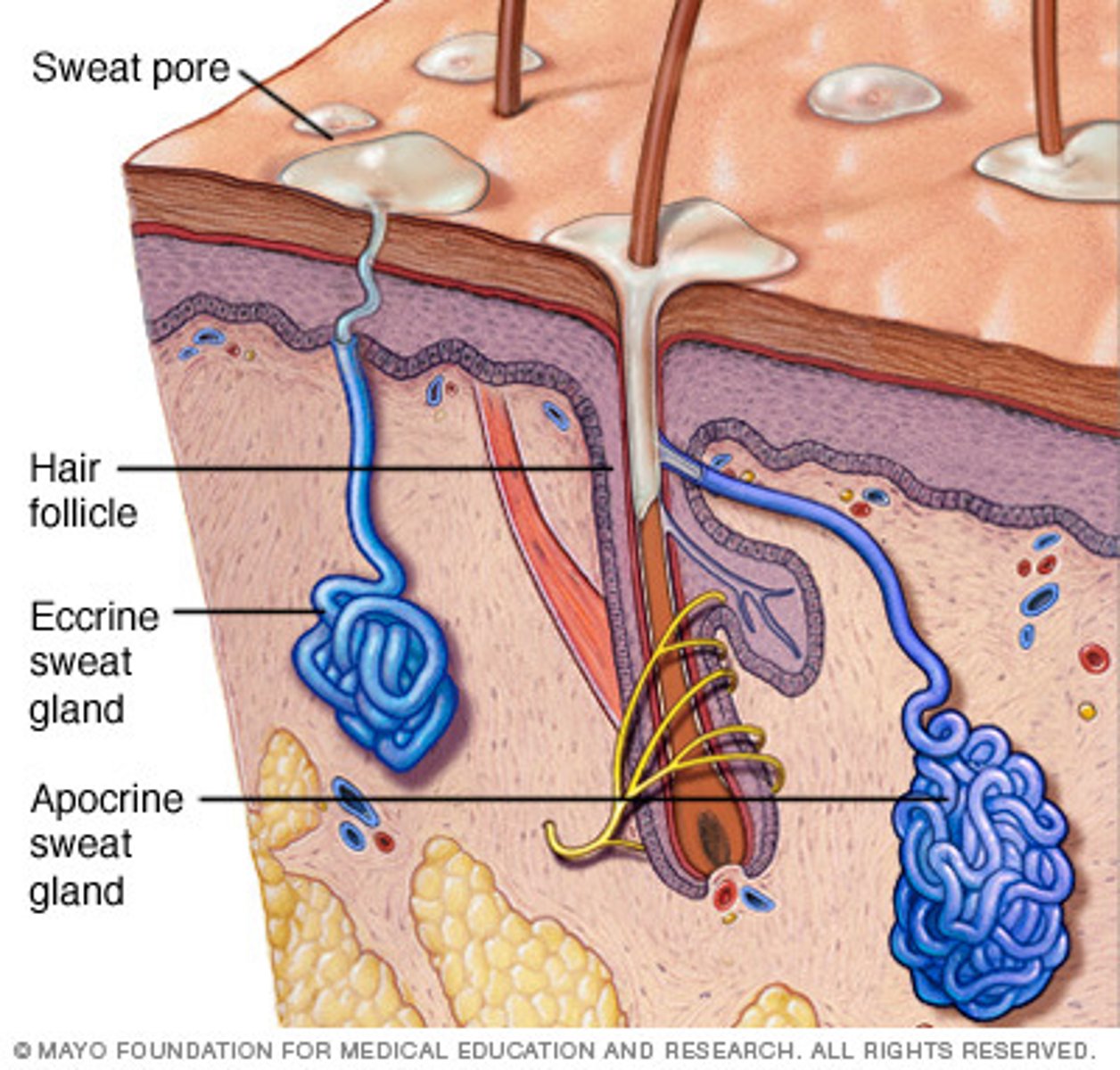
types of sweat glands
merocrine sweat glands- thermoregulation sweat on surface of skin
apocrine sweat glands- body odor during adolescence
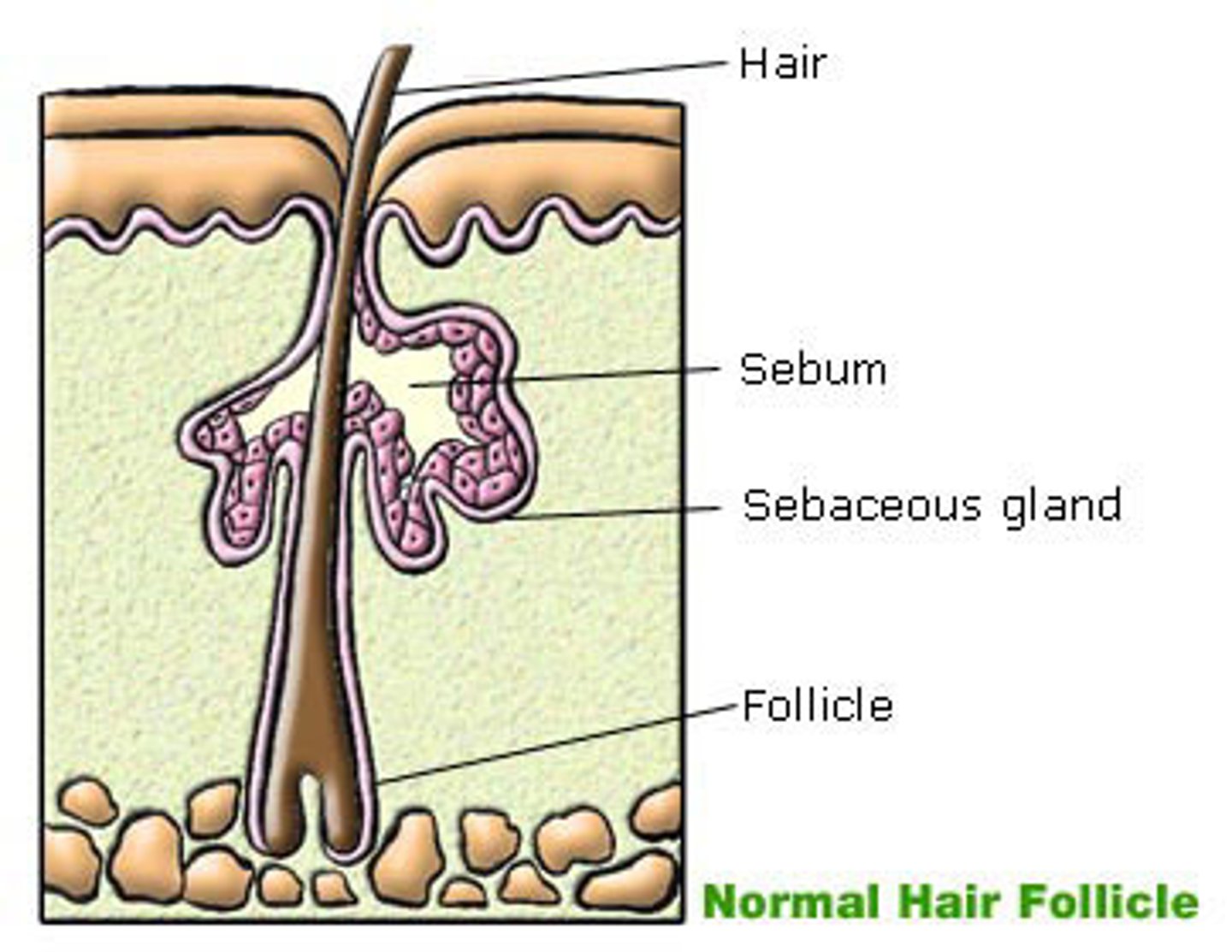
function / location of sebaceous glands
they secrete oil
lubricate cover hair follicle and skin with sebum for protection
ceruminous glands
modified apocrine sweat gland
located in external ear canal
secretes cerumen (earwax)
mammary glands
modified apocrine sweat glands of breasts that produce milk
regeneration is
replacement of damaged/dead cells with same type of cell restoring function
fibrosis is
gap filled with scar tissue bc collagen makes fribroblasts
functional activity is NOT restored
third degree burns are determined by
invasion of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer
needs skin grafts
severe scarring
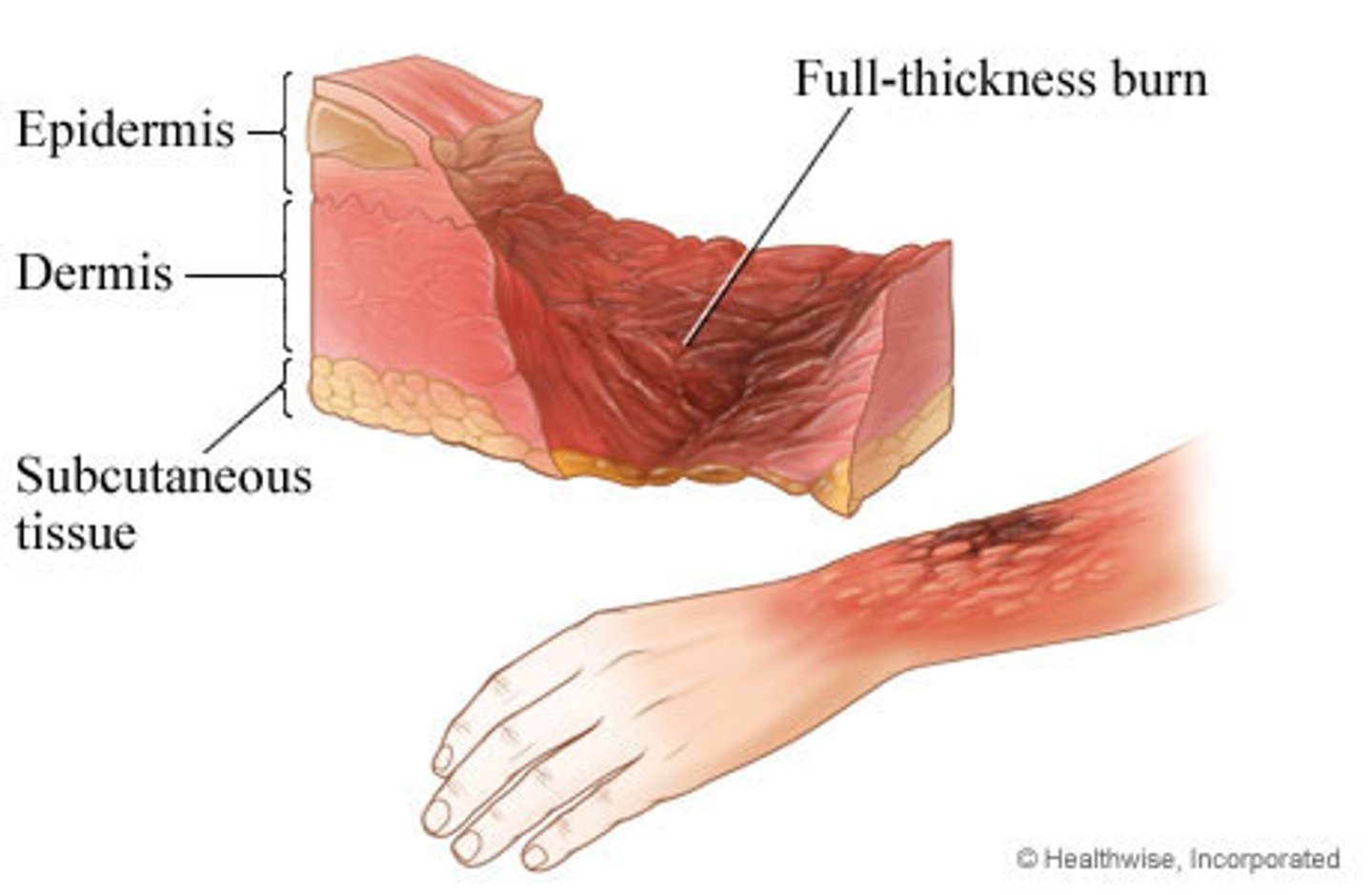
burns are dangerous and disrupt the body's homeostatic mechanisms by
causing dehydration from water loss
infection and sepsis
no protective barrier
electrolyte imbalance
slows thermoregulation
treatments of burns include
managing fluids
relieve swelling
remove dead tissue
control infection
increase caloric intake
skin grafting for third degree burns
effects of aging on the integumentary system
1 decrease in number of stem cell activity
2 decrease in collagen fibers
3 elastic fibers lose elasticity-crease lines make wrinkles
4 decrease in immune response bc dendritic cell lower and hair follicles make few to none
5 UV radiation damages DNA in epidermal cells causing skin cancer
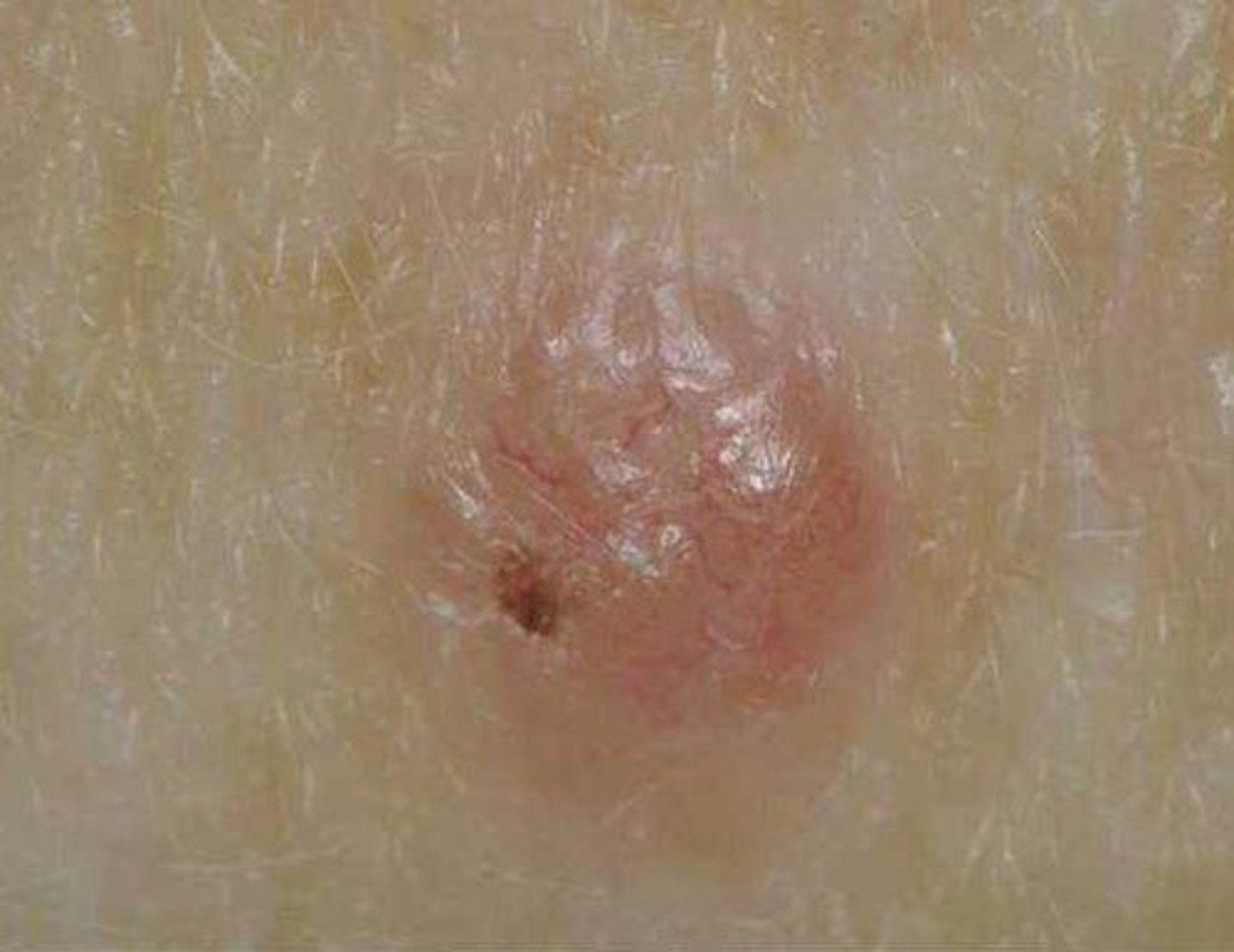
basal cell carcinoma
Most common form of skin cancer
Originates in stratum basale due to mutations caused by overexposure to UV radiation
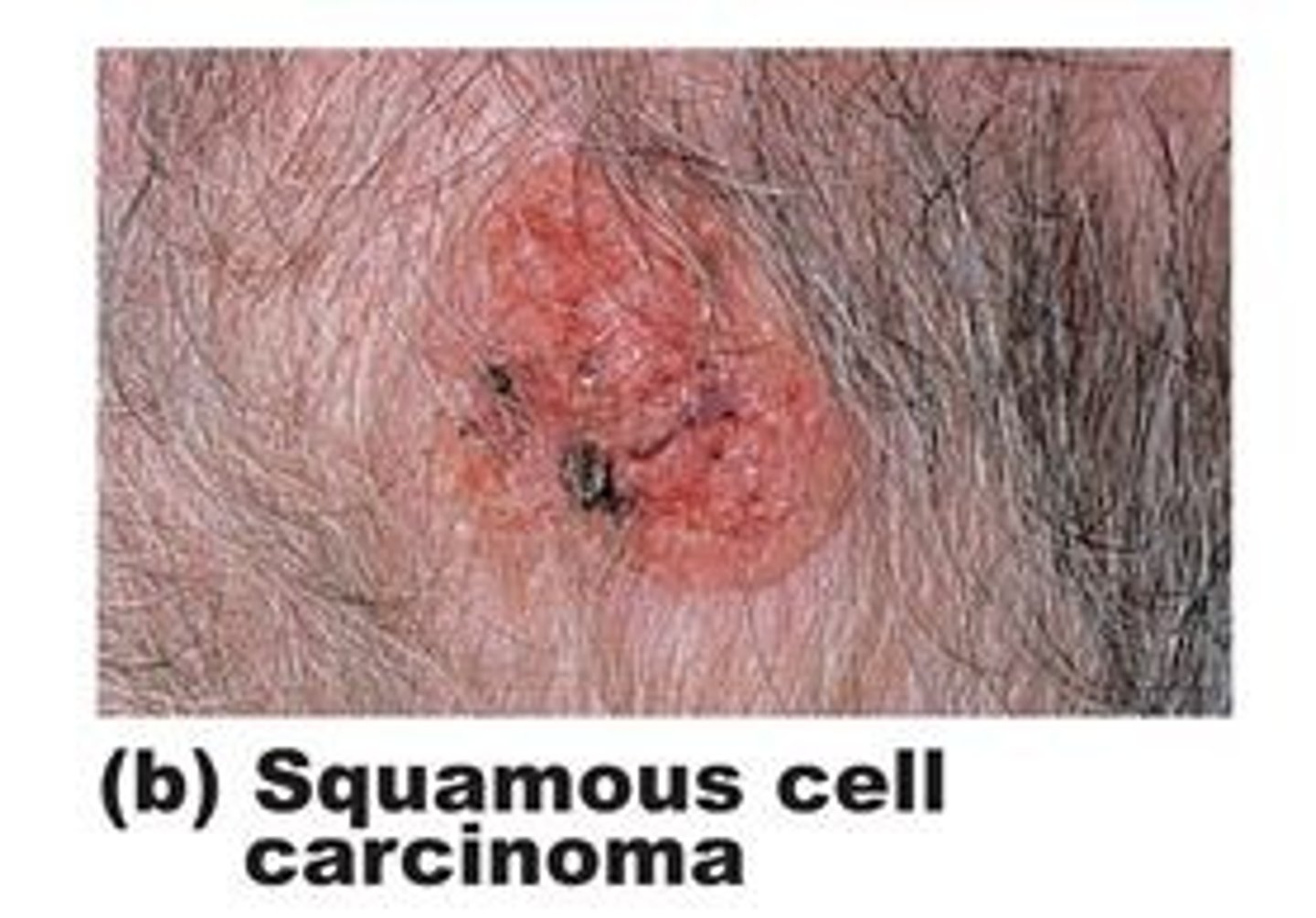
squamous cell carcinoma
Type of skin cancer more serious than basal cell carcinoma
uncontrolled overgrowth of abnormal squamous cells
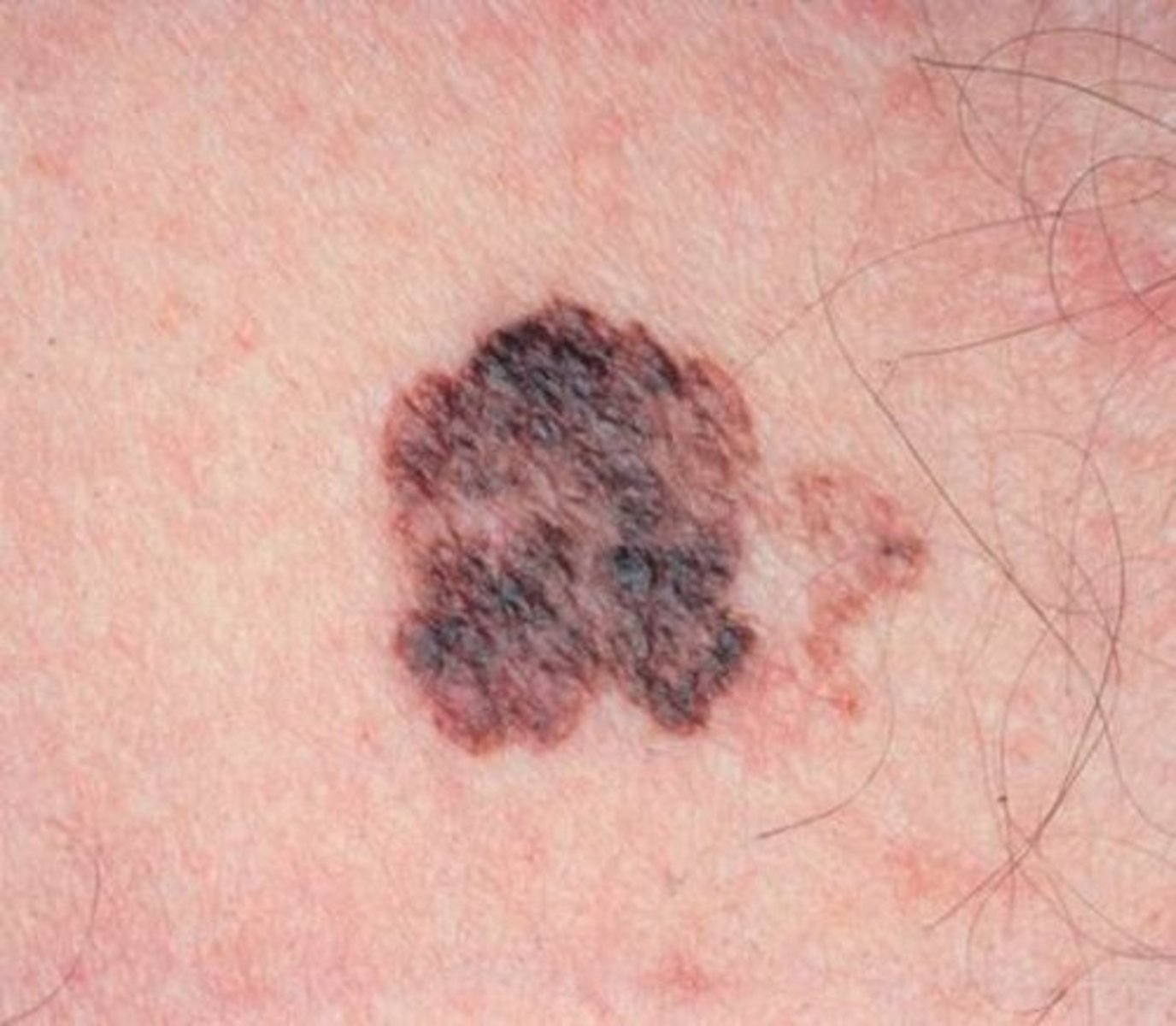
malignant melanoma
Most serious form of skin cancer; often characterized by black or dark brown patches on the skin
caused by melanocytes
Clinical View: UV Radiation , Sunscreens, and Sunless Tanners
sun makes UV radiations
sunscreen blocks UVA/B rays
sunless tanner stains skin no increase in melanin
*Clinical View: Nail Disorders
nails show overall health
brittle nails- separate nail plate bed
ingrown nails- nail digs into skin
yellow nail syndrome- growth/thickening slows
onchomycosis- fungal infection
Beau's lines- temp interference w/ nail growth
*Clinical view: Acne and treatments
acne- plugged sebaceous ducts
during puberty
increase activity of gland secretion
blocks pores
treatments- salycilic acid, antibiotics, vitamin A, benzoyl peroxide
Clinical View: Burns
death caused by heat radiation chemicals sunlight
threat to life from fluid loss and dehydration infection
*Clinical view: Botox and wrinkles
botox- treatment for wrinkles of facial muscle expression
blocks nerve impulses to facial muscles
injected to superficial facial muscles temporary
muscles regain function