bio test 2 (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:51 PM on 10/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
1
New cards
plasma membrane
outer layer of cell
2
New cards
cytoskeleton
internal protein network for support/transport
3
New cards
cytosol
jelly like fluid in the cell
4
New cards
cytoplasm
the space between the nucleus and plasma membrane
5
New cards
organelles
perform cellular functions
6
New cards
endomembrane system
organelles connected by membranes or exchange membrane bound transport vesicles
7
New cards
organelles job
protein production pathway
8
New cards
nucelus
contain DNA
DNA is instructions to build proteins
surrounded by nuclear envelope
"double membrane"- contains pores
DNA is instructions to build proteins
surrounded by nuclear envelope
"double membrane"- contains pores
9
New cards
nuclear envelope
membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
10
New cards
mRNA
messenger RNA
"photocopy" of DNA instructions
"photocopy" of DNA instructions
11
New cards
nucleolus job
produces ribosome subunits
12
New cards
ribosome job
protein synthesis
13
New cards
if ribosome is free in cytoplasm then
the proteins are used in the cytosol
14
New cards
if ribosomes is bound to the rough ER then
the proteins are exported from the cell
15
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum
membrane network
lined with ribosomes
lined with ribosomes
16
New cards
rough ER main functions
modifies proteins
eliminates faulty proteins
produce membrane
eliminates faulty proteins
produce membrane
17
New cards
ER lumen
continuous space within nuclear envelope
18
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
enzymes
synthesize lipids
- fatty acids, phospholipids, steroids, detoxify drugs
metabolize carbs
store Ca2+ = muscle contractions
synthesize lipids
- fatty acids, phospholipids, steroids, detoxify drugs
metabolize carbs
store Ca2+ = muscle contractions
19
New cards
golgi complex
processes and distributes product from the ER
produces polysaccarides
layers of flat membrane sacs
vessicles to and from the golgi
- more golgi = more secretion
produces polysaccarides
layers of flat membrane sacs
vessicles to and from the golgi
- more golgi = more secretion
20
New cards
lysosomes
membrane bound organelle that contains digestive enzymes
21
New cards
autophagy
digesting dysfunctional organelles
22
New cards
mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell
produces ATP - adenosine triphosphate
generates body heat
produces ATP - adenosine triphosphate
generates body heat
23
New cards
chloroplasts
captures suns energy
24
New cards
endosymbiosis meaning
inside-together-life
25
New cards
endosymbiosis in mitochondria and chloroplasts
both have 2 membranes
both have DNA - circular shape
both have their own ribosomes
both have DNA - circular shape
both have their own ribosomes
26
New cards
microfillaments
cell shape, movement, muscle contraction
27
New cards
intermediate fillaments
cell shape, organelle anchoring
28
New cards
microtubules
chromosome and organelle movement
flagella and cilia
flagella and cilia
29
New cards
plants vs animals
plants lack lysosomes
plants have
-cell walls
-central vacuole
-chloroplasts
plants have
-cell walls
-central vacuole
-chloroplasts
30
New cards
cell wall
provides structure and support
31
New cards
central vacuole
stores h2o, pigments, and waste
32
New cards
plant cell junctions
plasmodesmata
channels connecting plant cells
helps with diffusion of molecules in cytoplasm
channels connecting plant cells
helps with diffusion of molecules in cytoplasm
33
New cards
animal cell junctions
gap junctions
similar to plasmodemata
found in heart and animal embryonic stage
similar to plasmodemata
found in heart and animal embryonic stage
34
New cards
tight conjunctions
leakproof sheet
line digestive tract
line digestive tract
35
New cards
desmosomes
anchoring junctions
strong connection in stressed tissue
skin and heart muscle
strong connection in stressed tissue
skin and heart muscle
36
New cards
cell membranes
boundary between cell interior and membrane
enables. internal regulation- char. of life
membranes are both flexible and stable
enables. internal regulation- char. of life
membranes are both flexible and stable
37
New cards
all cells have external plasma membrane
but eukaryotes have internal as well
38
New cards
membranes have a
phospholipid bilayer
39
New cards
hydrophillic head
react well with h2o in cell
40
New cards
hydrophobic tail
keep stability in the cell
41
New cards
cholesterol
helps keep membranes more fluid @ cool temps
less fluid @ warm temps
less fluid @ warm temps
42
New cards
membranes are
selectively permeable
43
New cards
selective permeability is
when some substances can cross more easily than others
44
New cards
hydrophobic molec pass through
non-polar membranes
45
New cards
hydrophillic molec pass through
polar membranes
46
New cards
fluid mosaic model
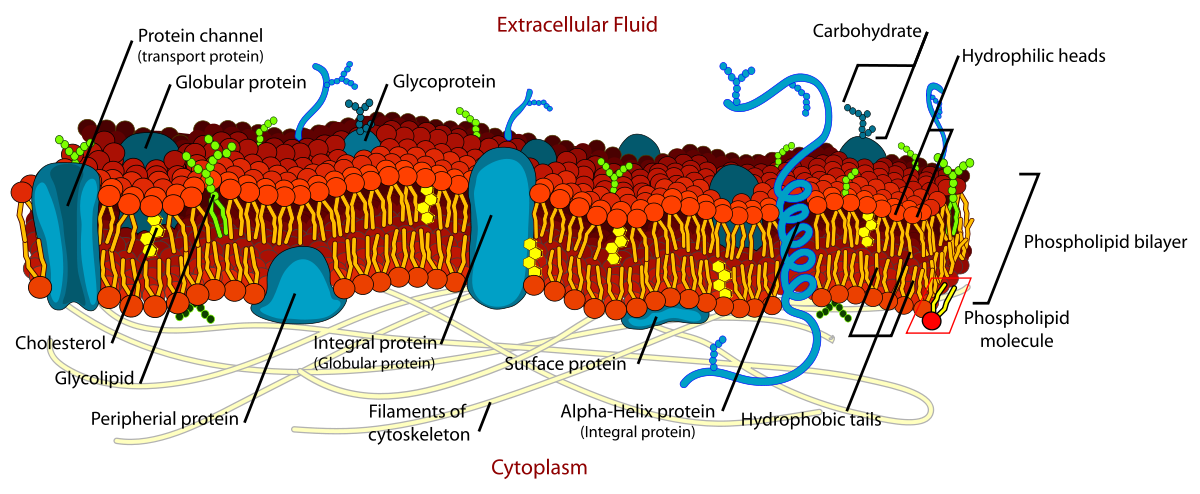
47
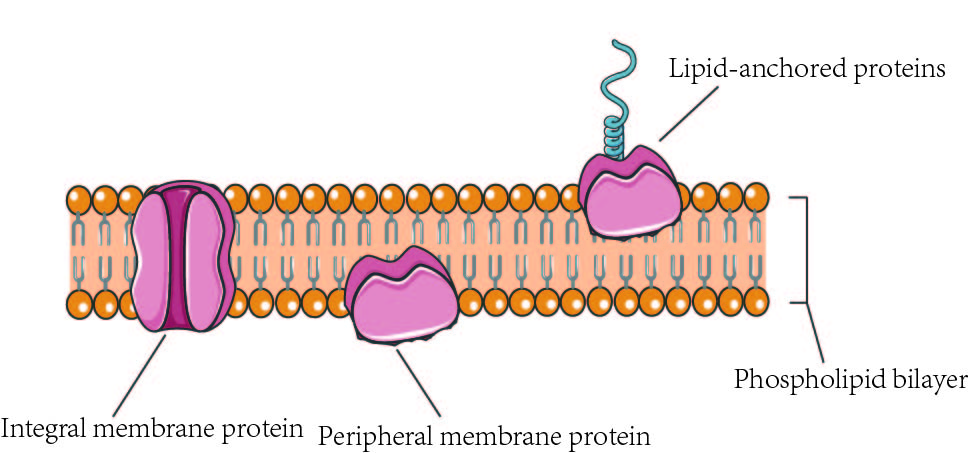
New cards
integral membrane proteins
pass into or through hydrophobic region of the membrane
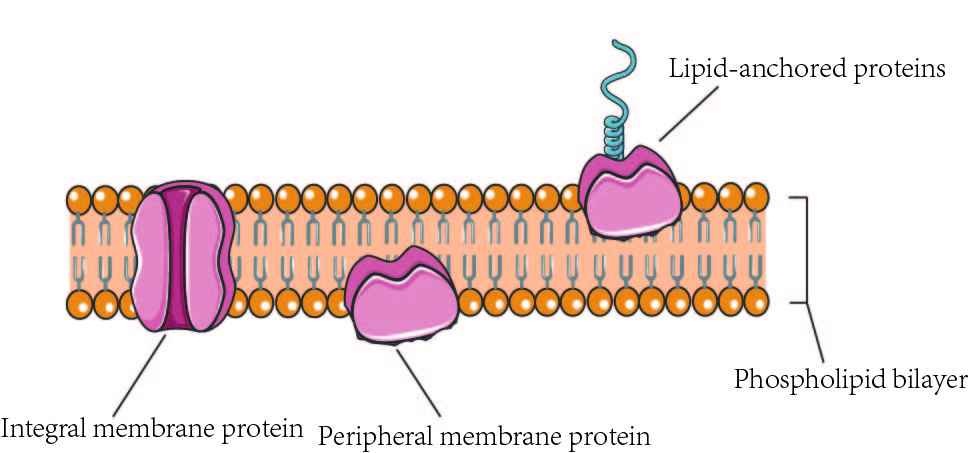
48
New cards
peripheral membrane proteins
attach to the outside of the membrane
49
New cards
membrane protein functions
transport enzymes, cell communication, physical attachment
50
New cards
glycoproteins made of
carb + protein
51
New cards
glycolipid and glycoprotein functions
used in cell identification
immunity (self vs non self)
embryonic cell sorting
immunity (self vs non self)
embryonic cell sorting
52
New cards
passive transport
not requiring cellular energy
53
New cards
diffusion
passive transport
movement from high concentration to low concentration
all molec are in constant mostion
each molec moves independently from other molec
movement from high concentration to low concentration
all molec are in constant mostion
each molec moves independently from other molec
54
New cards
factors that influence diffusion rate
size of molecule/ membrane
the concentration gradient
- larger difference in gradient = faster
temperature
- warmer = faster
elec. or pressure gradients
the concentration gradient
- larger difference in gradient = faster
temperature
- warmer = faster
elec. or pressure gradients
55
New cards
facilitated diffusion
passive transport
movement aided by membrane proteins with a channel or carrier
movement aided by membrane proteins with a channel or carrier
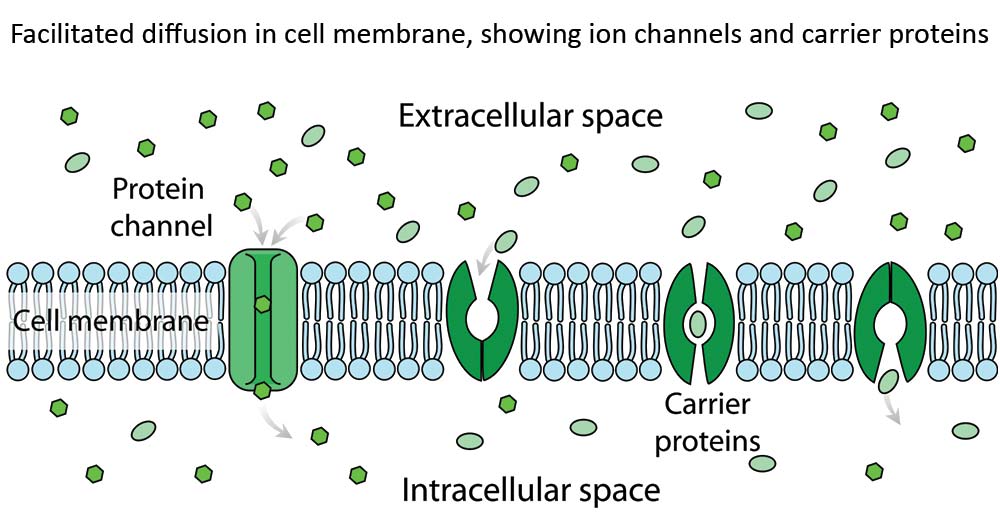
56
New cards
what needs facilitated diffusion
larger molec, polar molec, charged molec
57
New cards
aquaporin
facilitated protein for H2O
needed bc water is polar
needed bc water is polar
58
New cards
facilitated proteins have
specific shape for each substance
ex enzymes
ex enzymes
59
New cards
osmosis
movement of free H2O molec from low solute concentration to high across a semi permeable membrane
60
New cards
isotonic
same concentration on each side
no net movement on each side of cell but flow in and out
no net movement on each side of cell but flow in and out
61
New cards
hypotonic
lower concentration
62
New cards
hypertonic
higher concentration
63
New cards
cells ____ to maintain balance
osmoregulate
64
New cards
animal- lysed
exploded
hypotonic
hypotonic
65
New cards
animal- plasmolysed
shrivled
hypertonic
hypertonic
66
New cards
plant- flacid
limp
hypertonic
hypertonic
67
New cards
plant- turgid
firm
hypotonic
ideal for plant
doesnt explode due to cell wall
hypotonic
ideal for plant
doesnt explode due to cell wall
68
New cards
____ is ideal for animal cell
isotonic
69
New cards
active transport
cell expends energy for transport
up/ against concentration gradient
driven by ATP
Na+ and K+ pump
inside of cell has slight negative charge
up/ against concentration gradient
driven by ATP
Na+ and K+ pump
inside of cell has slight negative charge
70
New cards
cotransport
active transport
transport of diff solutes through common protein
transport of diff solutes through common protein
71
New cards
exocytosis
exit cell
72
New cards
endocytosis
enter cell
73
New cards
endocytosis and exocytosis functions
fuse with plasma membrane to transport larger molec
74
New cards
phagocytosis
cell eating
75
New cards
pinocytosis
cell drinking
76
New cards
receptor-mediated endocytosis
is a process by which cells absorb metabolites, hormones, proteins – and in some cases viruses – by the inward budding of the plasma membrane
77
New cards
ligand
molec that binds to the receptor
78
New cards
size of plasma membrane
8nm
79
New cards
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
80
New cards
genome
complete set of an organisms genetic information
81
New cards
gene
a segment of DNA that is the coding for polypeptides
sequence of amino acids
proteins > 1 polypeptide
sequence of amino acids
proteins > 1 polypeptide
82
New cards
humans have ___ genes
25,000
83
New cards
there is a ____ copy of genes in almost every cell
full copy
84
New cards
what is DNA's monomer
nucleotides
85
New cards
DNA structure
5 carbon sugar
phosphate group
nitrogenous base = rungs
sugar phosphate backbone
held with H bonds
phosphate group
nitrogenous base = rungs
sugar phosphate backbone
held with H bonds
86
New cards
DNA has a _____ shape
double helix
87
New cards
Purines
adenine and guanine
2 ring structure
2 ring structure
88
New cards
pyramidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil in RNA
1 ring structure
1 ring structure
89
New cards
A pairs with
T
90
New cards
G pairs with
C/U
91
New cards
differences between DNA and RNA
DNA
- double strand
- deoxyribose = H, no oxygen
- thymine
RNA
- single strand
- ribose = OH
- uracil
- double strand
- deoxyribose = H, no oxygen
- thymine
RNA
- single strand
- ribose = OH
- uracil
92
New cards
deoxyribose
5 carbon sugar
1' 2' 3' 4' 5'
1' to nitrogenous base
5' to phosphate group
3' to next nucleotide phosphate
1' 2' 3' 4' 5'
1' to nitrogenous base
5' to phosphate group
3' to next nucleotide phosphate
93
New cards
there are ____ bonds within a nucleotide
covalent
94
New cards
there are ____ bonds between nitrogenous bases
hydrogen
95
New cards
what is semiconservative replication
when the parent strand is conserved and acts as a template for the daughter strand
96
New cards
how many origins of replication do prokaryotes have
one
97
New cards
what shape are prokaryotes DNA
circular
98
New cards
how many origins of replication are there for eukaryotes
multiple
99
New cards
what shape is a eukaryotes DNA
linear
100
New cards
helicase function
unwinds DNA