Light and special relativity
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
absolute refractive index
the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium
n
sin0air/sin0material
during refraction frequency
stays constant
critical angle
angle in material that gives an angle of refraction of 90 in air
photoelectric effect
when electrons are ejected from a metal when it absorbs energy from photons of light
the refractive index of a medium increases as
the frequency of incident radiation increases
total internal reflection occurs when
the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
constructive interference
in phase crest meets crest trough meets trough giving maximum
destructive interference
180 out of phase crest meets trough giving minimum
path difference
mxwavelenght
dsin0
mxwavelenght
the central fringe (maximum) is white because at that position
the path difference for all wavelengths present will be zero, so all wavelengths arrive in phase and the central fringe will be the same colour as the source
to increase the distance between bright spots
increase the wavelength
decrease the slit separation i.e have more lines per mm
Prims
only one spectrum produced
red deviated least, violet the most
bright images
usually less widely spaced (dispersed)
Grating
many spectra produced, symmetrical about the central maximum
red deviated most, violet the least
less intense - energy divided between several spectra
central image always the same colour as the source
the principles of relativity
when two observers are moving at constant speeds relative to one another, they will observe the same laws of physics
the speed of light is the same for all observers
time dilation
a difference in a time interval as measured by two observers moving relative to each other
length contraction
the shortening of length when an object is moving
Irradiance
the power per unit area on a surface
I =
P/A
a laser is
a beam not a point source therefore does not spread out
treshold frequency
minimum frequency of electromagnetic radiation required in order to eject electrons from a particular method
work function
the minimum energy required to release an electron from a surface
amplitude
the maximum displacement of a particle way from its zero position
wavelength
the minimum distance in which the wave repeats itself
frequency
the number of wavelengths produced by a source each second
f
N/t
period
the time it takes for one complete wavelength to be produces by a source
T
1/f
speed of a wave
the distance travelled by any part of the wave each second
v
fƛ
refraction
the property of light which occurs when it passes from one medium to another
whenever light passes from a vacum to any other medium its speed
decreases
when light waves pass from one medium to another the frequency of the waves
does not change
diffraction
the bending of waves around obstacles or barriers
interference
when two sets of waves meets they combine to produce a new pattern
half-life of muons
2.2µs
if the intensity of the u.v. radiation is increased
the leaf will fall faster
high intensity white light cannot eject electrons from zinc
while low intensity u.v. radiation can
photoelectric effect
one of the main pieces of evidence for particle theory of light
Planck’s constant
6.63 × 10-34 J s
kinetic energy when an electron escapes
only appears when the energy is larger than the minimum energy
Bohr model of the atom
picture
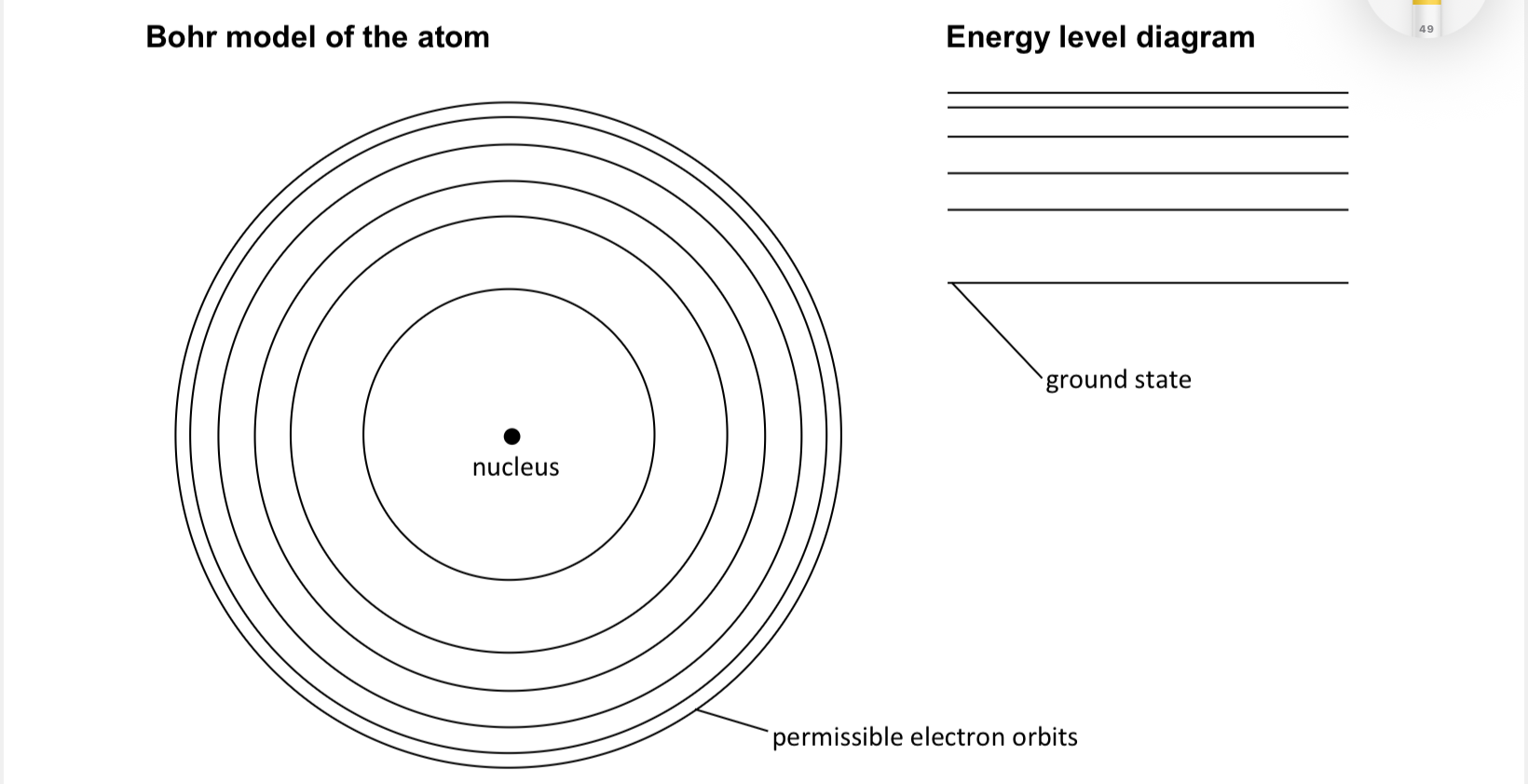
ground state of an electron
when it has lowest energy
energy levels and wavelengths
smaller jump → longer wavelength
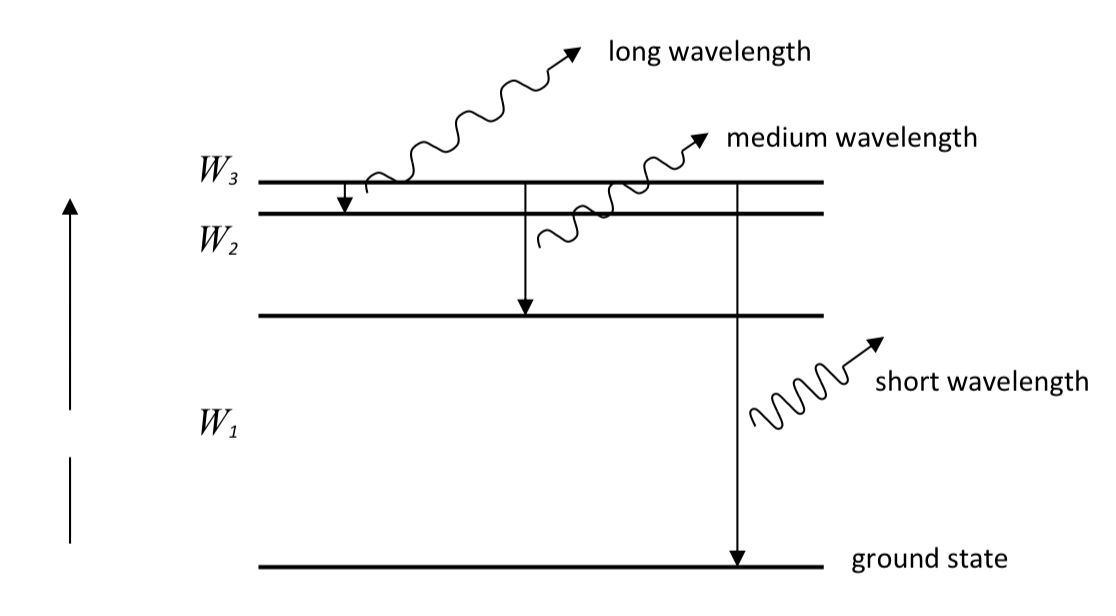
the larger the number of excited electrons that make a particular transition
the more photons are emitted and the brighter the line in the spectrum
continuous visible spectrum
consists of all wavelengths of light from violet(400nm) to red(700nm)