Stonehenge to Hubble Exam 1
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
How many stars are visible to the unaided human eye on a clear night from a dark place?
about 3,000
Astronomy (origin/definition)
ORIGIN: greek word: astron (meaning star)
MEANING: science that studies the nature of stars and all celestial bodies in the Universe
Why is astronomy important?
gives is PERSPECTIVE about our place in the Universe
What kind of science is astronomy?
quantitative
put these numbers is scientific notation:
a) 9,760,000
b) 0.003642
a) 9.76 x 10^6
b) 3.642 x 10^-3
most of the universe is _________
empty
traveling far in space means _____________________
traveling back in time
the observable Universe is ___________, but the Universe itself may not be.
finite
Cosmology
study of the universe as a whole
what is science?
systematic observation of natural events and conditions in order to discover facts --- then formulate laws and principles based on these facts
technology vs. science
science does NOT equal technology
-technology comes from Greek word for craftmanship
-science is a system of observing and experimenting to acquire knowledge and create theories about natural phenomena
technology is the ___________ of science for human purposes
application
(T/F) science is a moral system
FALSE
What is the Scientific Method? (4)
1. OBSERVE basic facts about nature
2. develop a THEORY that explains known facts
3. use the theory to make PREDICTIONS about new phenomena
4. perform EXPERIMENTS to test the predictions. If the experiments disagree with the predictions, the theory is wrong!! and must be discarded or modified
what is a scientific theory?
a carefully constructed proposition that
-accounts for all known data relevant
-makes specific and quantitative predictions
(usually expressed in mathematical form)
Properties of a Scientific Theory
1. account for all known relevant data
2. lead to simplification
3. no tested with current knowledge
4. must make predictions for new phenomena
5. make definite and falsifiable predictions
6. can never be proven TRUE, just not yet innocrrect
7. simple as possible
When a new scientific theory is enunciated, experimenters should:
a. perform a series of tests with more and more precision each time to verify that the theory can explain already known phenomena
b. carefully examine the credentials of the scientist proposing the theory to know if they should believe it or not
c. try to interpret existing data in the framework of the new theory
d. perform experiments to test whether the predictions of the theory regarding new phenomena are correct
d. perform experiments to test whether the predictions of the theory regarding new phenomena are correct
science is a product of ________
nature
what is a Pseudoscience? (give examples)
a claim presented as scientific but not adhering to the scientific method
ex. astrology, crystal energy
What does Carl Sagan look for in scientific theories?
1. independent confirmation
2. substantive debate
3. no "authorities"
4. more than one hypothesis
5. quantification
6. shortened hypothesis
7. falsifiable hypothesis
Occam's Razor
when faced with 2 hypotheses, use the one that is simpler
ad hominen (fallacy)
attacking arguer
argument from authority (fallacy)
assigning merit to arguer, not argument
appeal to ignorance (fallacy)
the claim that whatever has not been proved false must be true
observational selection (fallacy)
counting the hits and forgetting the misses
small number statistics (fallacy)
misunderstanding stats, not using enough subjects
non sequitur (fallacy)
premise is irrelevant to the conclusion
post hoc, ergo propter hoc (fallacy)
it happened after so it was caused by... WRONG
correlation vs. causation
correlation does not equal causation
ex. divorce rates in comparison to per capita consumption of margarine
Imagine the composition of the Earth's atmosphere as a football field. Most of the atmosphere is nitrogen. So, starting from the goal line, nitrogen takes you
all the way to the 78 yard line. And most of what's left is oxygen. Oxygen takes you to the 99 yard line. Most of what remains is the inert gas argon. Argon brings you within 3 1/2 inches of the goal line. That's pretty much the thickness of the chalk stripe. And how much of the remaining three inches is
carbon dioxide? One inch. You are told carbon dioxide has increased in the last 50 years. Do you know how much it has increased, on our football field? Three-eighths of an inch -- less than the thickness of a pencil. Yet you are asked to believe that this tiny change has driven the entire planet into a
dangerous warming pattern.
What is the fallacy here?
a. he doesn't have the authority (not a scientist)
b. analogy is incorrect
c. non sequitur: conclusion doesn't follow the premise
d. global warming is too complex to discuss in simple terms
c. non sequitur: conclusion doesn't follow the premise
Science is the ________ search for _____ knowledge about the ________ world
honest, true, real
What was astronomy used for in ancient times? (3)
1. finding direction (travel, communication)
2. keeping time (harvest, migrations)
3. ritualistic
most ancient astronomical sites are megalithic. what does this mean?
made from large stones
Where will the sun rise tomorrow (as seen from Pittsburgh)? ----beg. of sept.-----
somewhere north of east
in the northern hemisphere, the shortest day is the _____ ______ . the longest day is the _______ _______ .
winter solstice is shortest
summer solstice is longest
the sun rises exactly east from any specific location on what 2 days of the year?
spring and autumn equinoxes
From any specific location, the sun rises in the South east in ______ and North east in _______
south east in winter
north east in summer
What is the Goseck Circle?
-in Goseck, Germany
-built around 5000 BC
-earliest known structure with a recognizable astronomical alignment
-marks the winter solstice (left opening sunset, right opening sunrise)
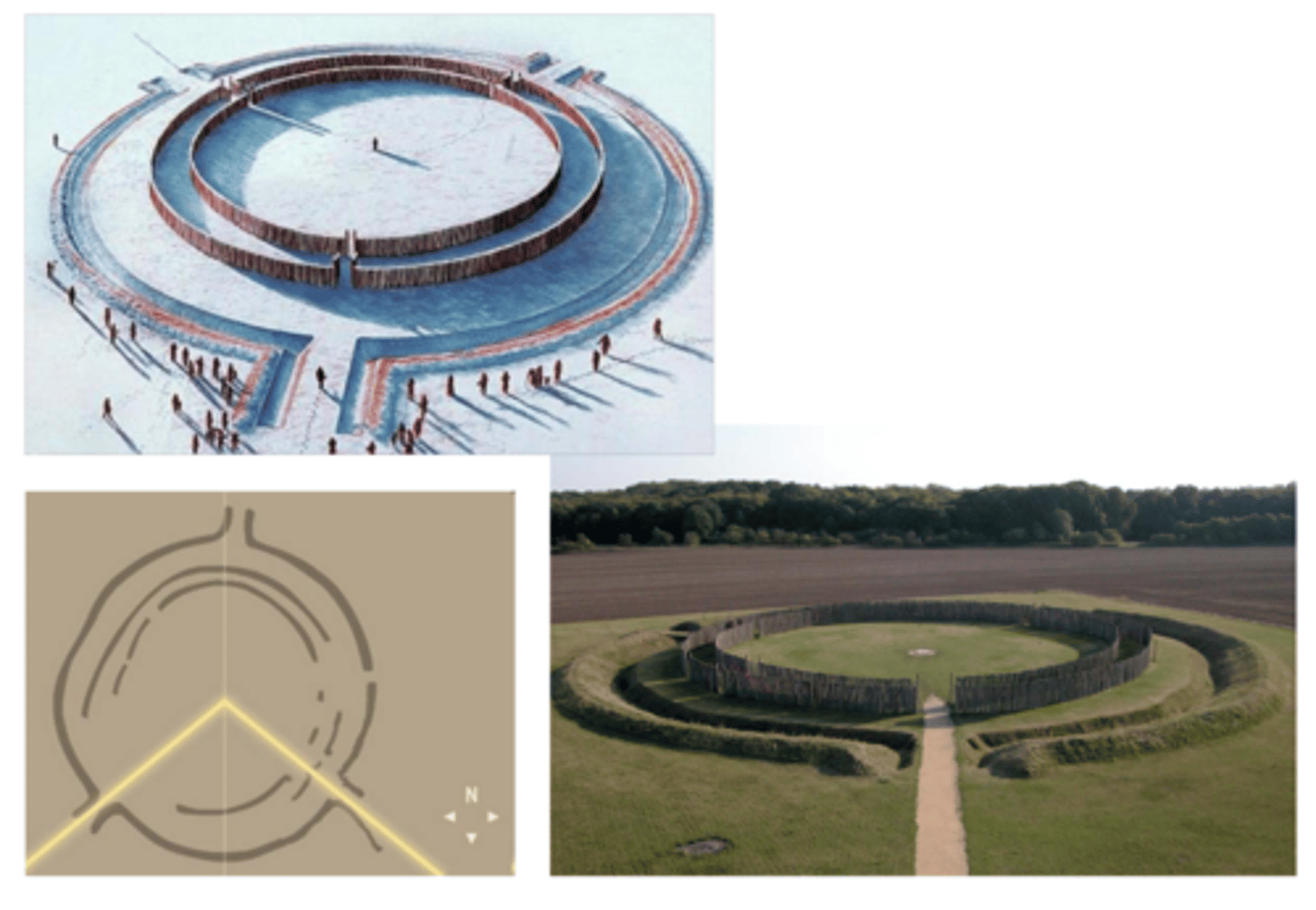
What is Stonehenge?
-megalithic ruin near Wiltshire, UK
-built during the Bronze Age
-horseshoe of trilithons pointed to sunrise on summer solstice
Given how little we know about sites like Stonehenge, do you think that it's justified to build complex hypotheses about its purpose?
Yes, as long as there is data available to falsify the hypotheses.
What is Avebury Henge?
another megalithic monument south of Stonehenge (in the UK)
What is Newgrange?
a tomb (passage grave) in Ireland
-set in a large mound with a narrow slit
-slit illuminates the central tomb at sunrise on the winter solstice
What are the Mayan Temples?
-central america
-Mayans could predict eclipses
-writing on temples reveals great concern for astronomical events
-snake shadow appears on El Castillo temple during spring and fall equinoxes
Which Chinese dynasty recorded 6 lunar eclipses and 1 solar eclipse between 1400-1200 BC?
Shang dynasty
The earliest reliable records of supernovae are _______
Chinese
Babylonian astronomy focused on... (4)
-numbers
-5 naked eye planets
-charting star/planet postions
-calendar of 360 12-hour days with 12 30-day months
Thales of Miletus (3)
-orderly universe that could be understood
-suggested that natural phenomena may have common cause
BIRTH OF SCIENTIFIC THOUGHT/TRADITION
Anaximander
-performed 1st recorded science experiment
-1st to discuss infinity (said earth floats free and still in center of infinite)
FIRST MODEL OF UNIVERSE
Anaximander used a sundial (gnomon) to mark the
seasons of the year and mark the solstices and
equinoxes. He measured the length of the
gnomon's shadow at different times. When do you
think the gnomon's shadow at noon will be the
shortest?
June 21st (shortest shadow = longest day)
Where will the Sun rise on December 21st (as seen from Pittsburgh)?
somewhat south of east
Who is Pythagoras?
-"all is number"
-introduced concept of cosmos (order)
-earth may be round
-5 regular solids/Pythagorean theorem
What did Plato do for astronomy?
trick question, he was a douche
-denied reality of the material world, which is fine
-but said this reality was right and told people that if they didn't agree they were wrong
HIS IDEAS WERE HARMFUL TO SCIENCE
Eudoxus
-detailed theory for planetary motion
-earth was center of this motion
Aristotle
-expanded on Eudoxus' geocentric model
-first detailed arguments for spherical earth
broke from scientific thought
is it possible to see a full moon during the day?
no, full moon means the moon and sun are 180 degrees away from each other. thus, it's impossible to see both at the same time
How often do we see solar eclipses?
about twice a year
When does a solar eclipse appear?
when the moon lies directly between the Sun and the Earth
Aristarchus
-first person to to say the Sun may be at the center of the universe, Copernicus would rediscover this later
-estimated Earth, Moon and Sun size/distance comparison
Parallax in a heliocentric universe
nearby stars should move with respect to more distant ones (as Earth moves around the Sun, stars seem to move)
Hipparchus
-cataloged stars with unprecedented accuracy
-created magnitude system to measure star brightness (Still used)
INTRODUCED EPICYLCES
Ptolemy
refined geocentric universe model to track star and planet motion with great accuracy
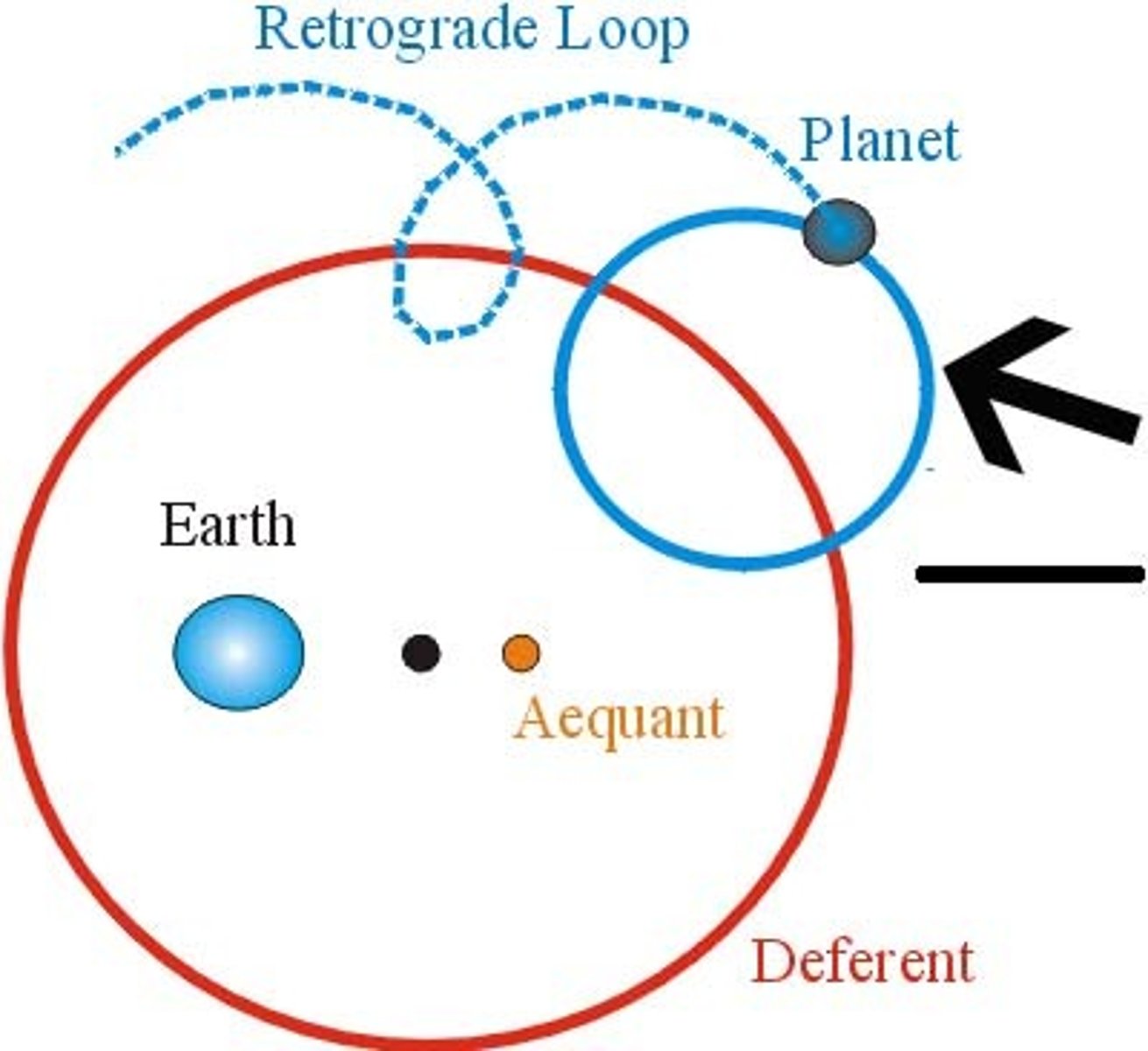
What is an epicycle?
the apparent motion the sun, moon and planets as the earth moves around the sun
Which Greek philosopher loved circles? Which Greek astronomer applied circles to his map of he universe?
Plate, Ptolemy
a scientific theory can never be proven ______. it must be _______ .
true, falsifiable
(T/F) a scientific theory should NOT be taken seriously if it contradicts other, well-accepted theories
FALSE
Who made the first recorded observations of supernovae?
ancient Chinese astronomers
(T/F) In the Northern hemisphere, the Sun rises towards the Southeast between the fall and spring equinoxes.
True
Homeopathy can be described as a ______________ because its basic rules have not changed despite the lack of evidence for its effectiveness.
pseudoscience
what is the best thing to do if you develop a theory that can't be tested with current tech?
work toward developing new tech that could test your theory
Looking out from the largest trilithon to the Heel Stone at Stonehenge, one looks toward ______________
sunrise on the summer solstice
_______ _________ were the first to try to understand the universe.
greek philosphers
Eratosthenes
-earth must be spherical
-paid someone to walk and measure (he found diameter of earth)
difference in shadows between two cities when sun was ""directly overhead" both at the same time
(Syene vs. Alexandria)
through the Dark and Middle ages, what ruled thought?
religion (christianity)
political fragmentation of the Middle Ages allowed for ____________ __________ to dominate all parts of society
Christian dogma
Which religion continued Greek tradition of scientific thought through the Middle Ages?
Islam, though ideas eventually returned to Europe
Dante Alighieri
saw the universe as layers from hell (center of earth) to heaven (outermost layer, past other planets)
INFLUENCED DIRECTLY BY ARISTOTLE
What is significant about Brunelleschi's dome?
switch from Godliness to "humanism"
-new techniques were credited to specific people
What did the printing press do?
allowed knowledge and ideas to spread faster and wider
Martin Luther
a theologian who openly criticized Catholic dogma
(caused church people to become paranoid)
Who is the reason for the double meaning behind "revolution"?
Copernicus
Copernicus was on par with the Ptolemaic system, what didn't he like about it? What did he want to learn more about?
-wanted to apply heliocentric idea
-why do planets have different motions
Tycho Brahe
said the heavens aren't perfect
In a newspaper interview, a scientist claims that some experimental evidence proves her theory.
She is phrasing her results in a common manner, but her intended meaning is probably to:
(a) describe experimental results that verify her theory beyond any doubt.
(b) state that the experiment falsifies a previous theory but does not falsify her theory.
(c) use a pre-conceived notion about Nature rather than remaining dispassionate about her
theory.
(d) construct a working hypothesis
(e) make a judgment based on her intuition.
b) state that the experiment falsifies a previous theory but does not falsify her theory.
(T/F) Science is concerned with the basic rules of Nature and Technology with their application
to practical matters.
True
Individual archaeological sites may not necessarily have an astronomical purpose because ...
their astronomical alignments may have been accidental
Astronomy is a science whereas astrology is not, in part because ...
astrological predictions are ambiguous
(T/F) I have developed a theory for the formation of stars. My next step should be to strive to prove
the theory
False, you must first PREDICT
What are the two basic principles of the Ptolemaic System?
-geocentrism
-circular motion (epicycles, deferent)
Why did Ptolemy create his geocentric and uniform system of epicylces, deferents, etc?
to understand the observed retrograde motion of planets
What is the Commentariolus?
Copernicus' ideas written:
-earth is center of moon rotation
-all celestial bodies don't revolve around 1 object
-distance of sun and earth is nothing compared to other stars
-earth's motion causes apparent retrograde motions of other planets
etc...
What is the reason for retrograde motion?
faster moving Earth
overtakes the slower moving
outer planet
-the position of
the planet against the stars
seems to loop
(planet in question is brighter looking during "loop")
humanism
shift from God to man
In order to consider the Copernicus'
heliocentric system as a successful
scientific theory, it must...
A) Make falsifiable predictions for
phenomena that have not been
observed yet.
B) Reproduce the existing
observations of the planets.
C) Explain the orbital paths of a
majority of the planets.
D) Be in accordance to the teachings
of Aristotle.
A) Make falsifiable predictions for
phenomena that have not been
observed yet.
Tycho Brahe is known for...
-discovery that heavens were not perfect
-really good math (taken by Kepler)
-lots of tech
Measuring angles with fingers...
1 finger =
fist =
pinky to thumb =
1 finger = 1-1.5 degrees
fist = 10 degrees
pinky to thumb = 20 degrees
Tychonic System (HYBRID)
(mix of Ptolemy and Copernicus)
-earth around sun
-other planets around earth
Who asked Kepler to help him with findings?
Tycho Brahe
What is Kepler's Mysterium Cosmographicum?
idea that 5 known regular solids were nested in each other and spaced out all 6 (known) planets
(T/F) Kepler and Tycho had a great relationship and Kepler never took any of Tycho's work.
FALSE, they fought but needed each other and when Tycho died, Kepler took some of his intricate mathematical findings
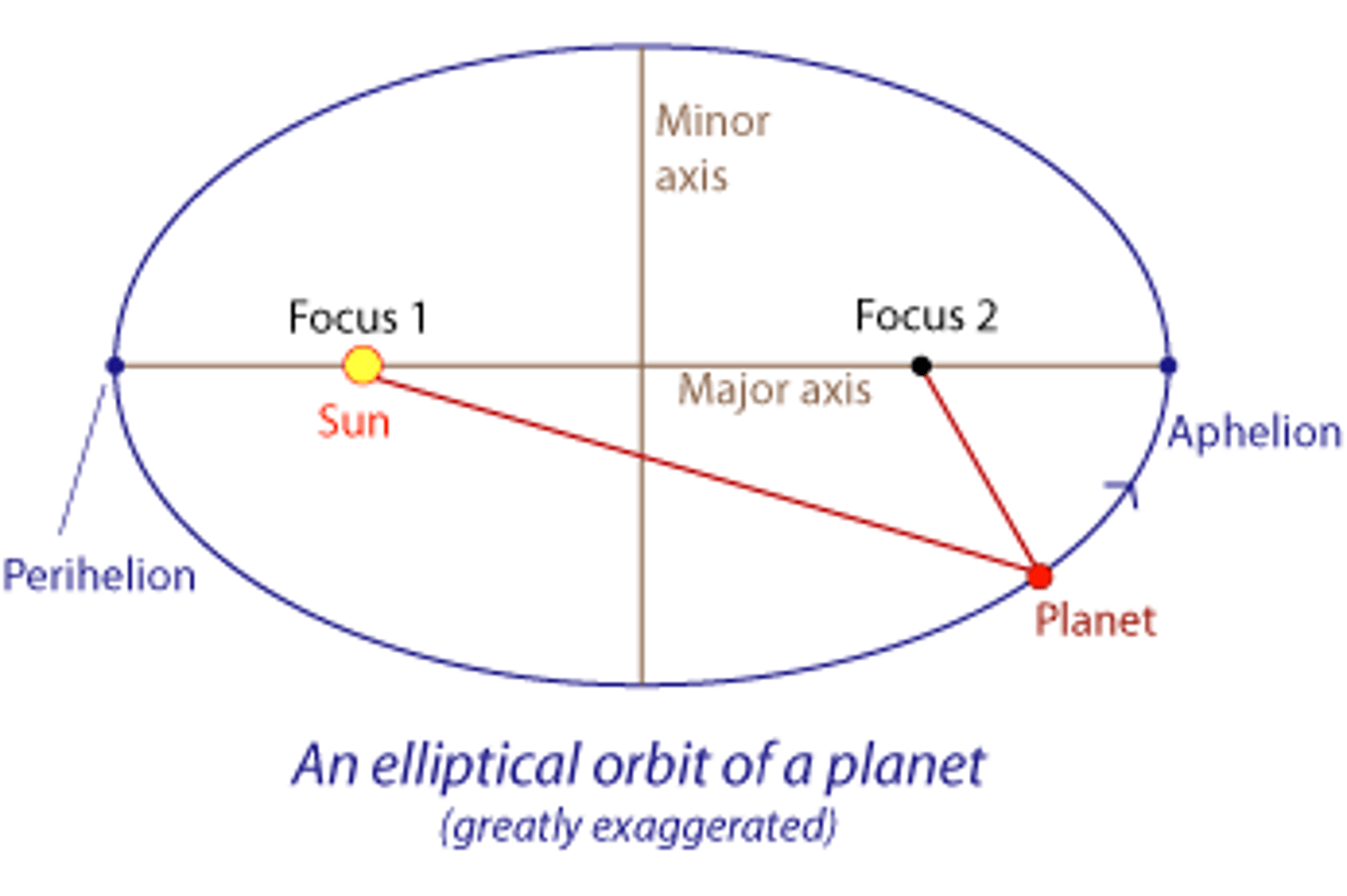
Kepler's First Law of Planetary Motion
The orbits of planets are ellipses with the sun at one focus
d1 + d2 = constant (always 2(semi-major)