Chemistry - Atomic Structure Y7
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What are atoms?
An atom is the smallest particle of an element.
What is an element?
A substance only made from type of atom.
Exam Question: What is hydrogen ONLY made up of?
Hydrogen atoms.
Exam Question: What is hydrogen oxide ONLY made up of?
Hydrogen and oxygen atoms
Exam Question: What is hydrogen carbonate ONLY made up of?
Hydrogen, carbon and oxygen atoms.
What is the periodic table?
It is the table which groups all of the elements into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) which have something in common.
What charge do protons have?
Positive charge.
What charge do neutrons have?
Neutral charge.
What charge do electrons have?
Negative charge.
In an atomic model, where are the electrons located?
The electron rings around the nucleus and bordering the atom.
In an atomic model, where are the protons and neutrons located?
Inside the nucleus which is in the middle of the atom, joined together.
What is the rule with the amount of electrons in each ring?
Every electron ring can only contain UP TO the amount of electrons in the said row of the periodic table.
How many electron rings will you draw in an atomic model of a certain element?
You will draw the same amount of electron rings corresponding to the row of the element on the periodic table.
Exam Question: How many electrons can the first electron ring go up to?
2
Exam Question: How many electrons can the second and third electron ring go up to?
8
What is the collective name for protons, neutrons and electrons?
Sub-atomic particles.
What is the mass number of an element inside a periodic table box? (Size)
The bigger number.
What does the mass number show in relation to the subatomic particles.
The number of protons + neutrons
What is the atomic number inside a periodic table box? (Size)
The smaller number.
What does the atomic number show in relation to the subatomic particles.
The number of protons and electrons. (NOT COMBINED)
What four things do periodic table boxes contain?
Mass number
Atomic number
Chemical symbol
Name of element
How do you calculate the number of protons in an element?
The atomic number. (p)
How do you calculate the number of neutrons in an element?
The mass number subtracted by the atomic number.
How do you calculate the number of electrons in an element?
The atomic number. (e)
What does every chemical in the periodic table have which represents it?
A chemical symbol.
What case does the first letter of a chemical symbol must be?
Capital.
What case does the second letter (if there is one) of a chemical symbol must be?
Lowercase.
Exam Question: How would you write ‘gold’ as a chemical symbol?
Au
What is a chemical formula?
It is how we represent compounds using elements and numbers to show how many of each element is used in a compound.
Example: What is the chemical formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
What is a compound?
It is made of more than one type of atom chemically joined.
How are compounds different to elements?
It is different to elements because elements are only one type of atom and compounds are multiple.
What are there more of: compounds or elements?
Compounds.
Why are there more compounds than elements?
Because you can combine elements to make more possible compounds than the fixed amount of elements.
What is a chemical property?
A chemical property is how a chemical reacts to another chemical.
What is a physical property?
A physical property is a characteristic of a substance that can be measured or observed without a chemical reaction.
What are some examples of chemical properties?
Flammability, toxicity and acidity,
What are some examples of physical properties?
Colour, magnetism, boiling/melting points and atomic structure
What is a mixture?
It is two or more elements or compounds that are mixed together and NOT chemically joined.
What is the difference between a mixture and a compound?
A compound is two or more elements chemically joined, whereas a mixture is not chemically joined.
What is the different between a mixture and a compound in terms of a particle model?
The particles in a compound are joined together whereas in a mixture they will not be.
What is the different between an element and a compound in terms of a particle model?
The particles in an element will only be one type of particle whereas a compound will have more than one different type of particle.
In a chemical formula, what do the little numbers represent?
The amount of atoms of a certain element in the compound.
In a chemical formula, if there are no little numbers, how many of each element are there?
It will be split equally with one atom of each element in the compound.
When naming compounds, which element comes first?
The element furthest to the left of the periodic table.
What if, when naming compounds, all the elements are in the same column? Then, which one will come first?
The lower one in the same column will come first.
What happens to the second element when naming compounds?
It changes the end of its name into -ide.
What happens if there are three elements and one of them is oxygen when naming compounds?
The second element changes the end of its name to -ate instead of adding oxygen into the compound.
Is there a rule on how much of an element gets chopped off to add the suffix?
No; it’s just what sounds best.
Exam Question: What is the compound name for Calcium + Carbon + Oxygen
Calcium Carbonate.
Exam Question: What is the compound name for Copper + Sulphur + Oxygen?
Copper Sulphate.
Exam Question: What is the compound name for KO2
Potassium Dioxide.
Exam Question: What is the compound name for FeCO.
Iron Carbonate.
Exam Question: What is the chemical formula for Iron Carbonate?
FeCO
Exam Question: What is the chemical formula for Hydrogen dioxide?
HO2
Exam Question: What is the chemical formula for Potassium sulphide?
KS
Exam Question: What is the chemical formula for Zinc Fluoride?
ZnF
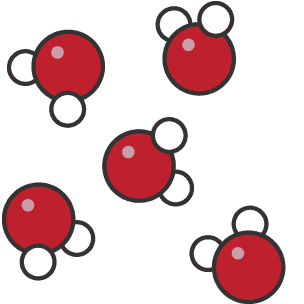
Exam Question: What does the image show? Element, compound or mixture?
Compound
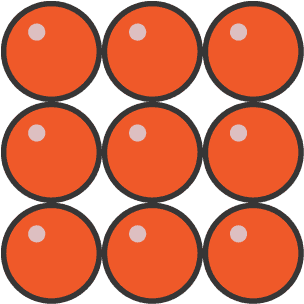
Exam Question: What does the image show? Element, compound or mixture?
Element
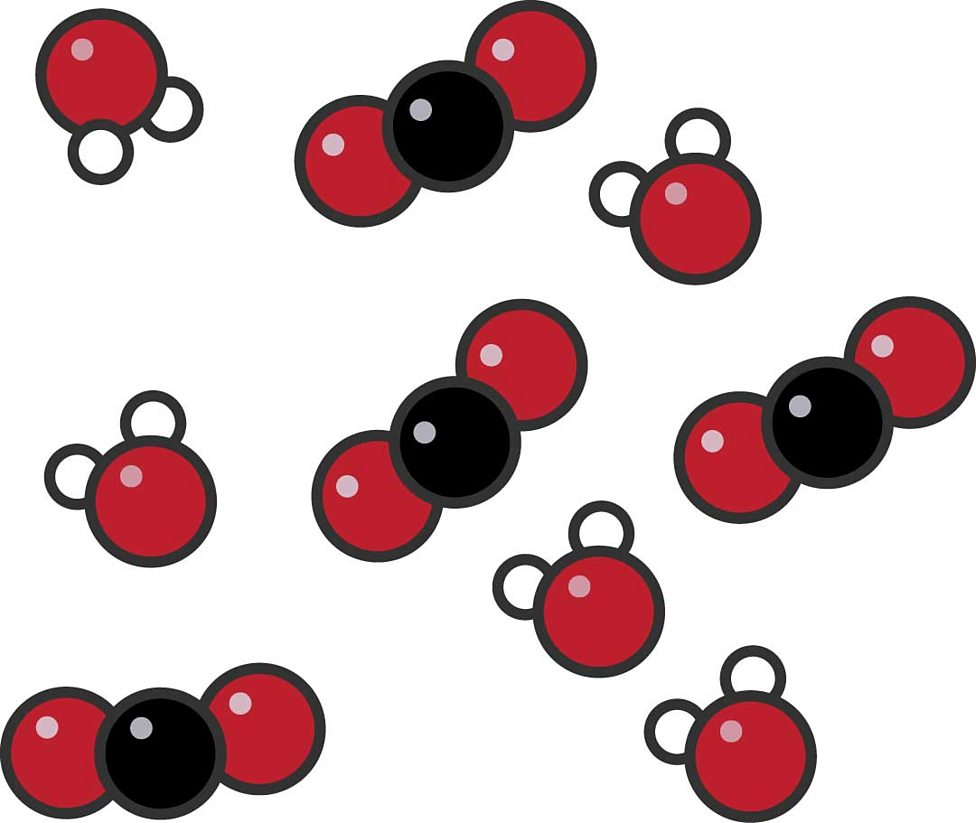
Exam Question: What does the image show? Element, compound or mixture?
Mixture.
Key word definition: Pure
A single substance made of one type of particle.
Key word definition: Molecule
Two or more atoms chemically bonded
Key word definition: Chemical bond
The link between atoms in molecules and compounds.
Key word definition: Reaction
Another word for chemical change.
Key word definition: Reactant
The substance(s) you start with in a chemical reaction.
Key word definition: Product
The substance(s) you make after a chemical reaction.
Key word definition: Chemical equation
An equation to show what happens during chemical reactions: Reactants —> Products.
Key word definition: Mixture
A pure substance with more than one type of particle in it NOT CHEMICALLY JOINED.
Key word definition: Chemical change
A change in which one or more new substances have been produced by rearranging particles from the reactants.
Key word definition: Physical change
A change in which movement and arrangement of particles change but the particles themselves remain the same substance.
What is made in a chemical reaction?
A new substance.
What are the four ways we can tell if a chemical reaction has taken place or not?
Colour Change
Temperature Change
Gas produced
New substance production
Why is rolling a ball of clay into a square not a chemical reaction?
Because it is still the same piece of clay.
Why is boiling water not a chemical reaction?
Because it is still the same water in a different state of matter.
Why is mixing salt and water not a chemical reaction?
Because a mixture and not a new substance was made.
Why is burning something a chemical reaction?
Because there would be a temperature change from the fire, colour change from the fire and a gas would be produced from the fire.