Water and Solutions (Including Water Hardness)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
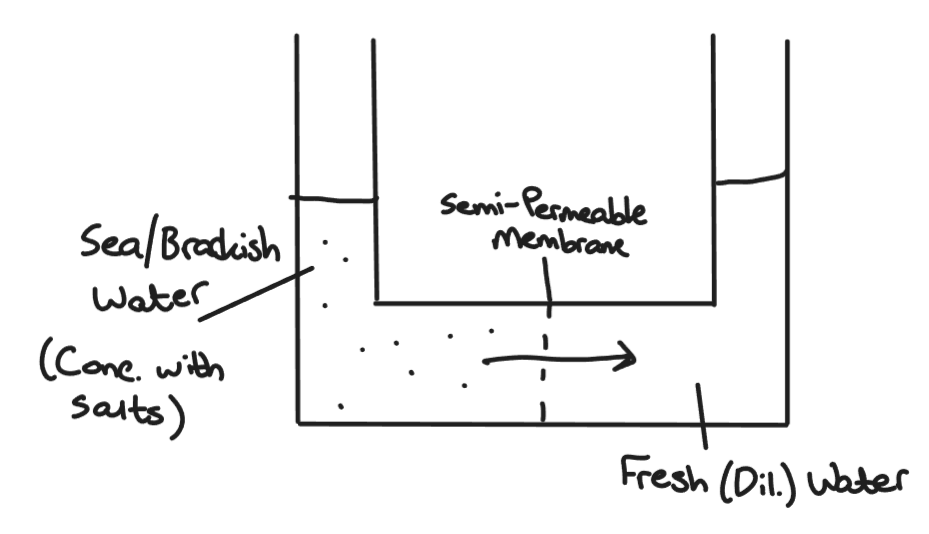
The purification of Brackish and Sea Water, including diagram
Brackish and Sea Water can be purified by Reverse Osmosis. Normal osmosis occurs when water moves from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution. In this case it is the opposite, hence Reverse Osmosis
Substance | Solubility (including exceptions) |
|---|---|
Group 1 and Ammonium Salts | |
Nitrates | |
Chlorides | |
Sulfates | |
Carbonates | |
Hydroxides | |
Hydrogen Carbonates |
Substance | Solubility (including exceptions) |
|---|---|
Group 1 and Ammonium Salts | Soluble |
Nitrates | Soluble |
Chlorides | Soluble except Silver and Lead Chlorides |
Sulfates | Soluble except Lead, Barium, and Calcium Sulfates |
Carbonates | Insoluble except Group 1 and Ammonium Carbonates |
Hydroxides | Insoluble except Group 1 and Ammonium Hydroxides |
Hydrogen Carbonates | Soluble |
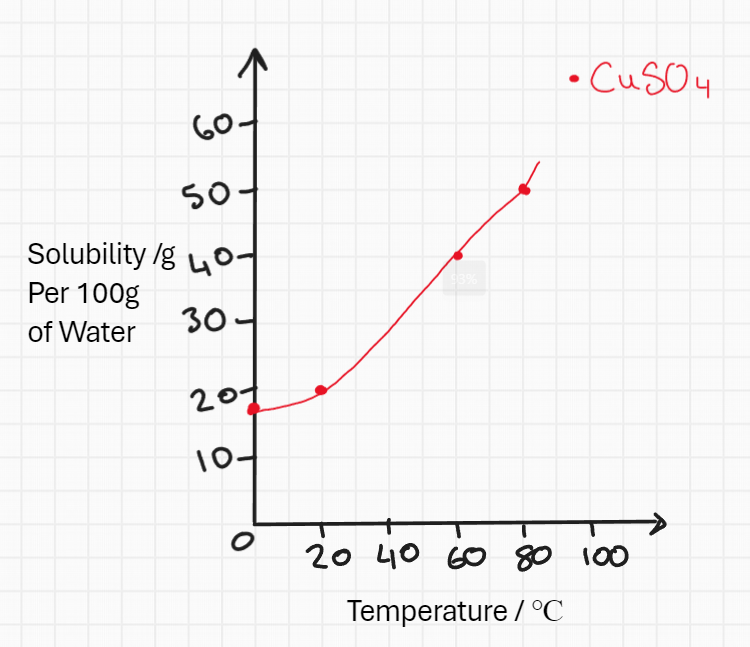
Answer the following questions by referring to the solubility curve
How much copper (II) sulfate will dissolve in 100g of water at 55℃?
What would you see when a saturated solution of copper (II) sulfate is heated from 80℃ to 20℃?
How much copper (II) sulfate will dissolve in 20g of water at 30℃?
37.5g
30g of CuSO4 crystals will appear
4.8g
Efflorescence
The loss of water of crystallisation from a hydrated salt to the atmosphere on exposure to air
Deliquescence
The ability of a substance to absorb water vapour from the air and dissolve in it
Hygroscopic
The ability of a substance to absorb water vapour from the air but doesn’t dissolve in it
Testing for the presence of water
Check whether the liquid turns anhydrous copper sulfate (white powder) into hydrated copper sulfate (blue crystals)
Testing for the purity of water
Check whether the melting point of the water is 0℃ and the boiling point is 100℃
Element | (Reacts with cold water / reacts with steam / unable to react with water) | Products of the reaction with water |
|---|---|---|
Potassium | ||
Sodium | ||
Calcium | ||
Magnesium | ||
Aluminium | ||
Zinc | ||
Iron | ||
Lead | ||
Copper | ||
Silver |
Element | (Reacts with cold water / reacts with steam / unable to react with water) | Products of the reaction with water |
|---|---|---|
Potassium | Reacts with cold water | Potassium Hydroxide and Hydrogen |
Sodium | Reacts with cold water | Sodium Hydroxide and Hydrogen |
Calcium | Reacts with cold water | Calcium Hydroxide and Hydrogen |
Magnesium | Reacts with steam | Magnesium Oxide and Hydrogen |
Aluminium | Reacts with steam | Aluminium Oxide and Hydrogen |
Zinc | Reacts with steam | Zinc Oxide and Hydrogen |
Iron | Reacts with steam | Iron Oxide and Hydrogen |
Lead | Unable to react with water | / |
Copper | Unable to react with water | / |
Silver | Unable to react with water | / |
The chemical and word equation for the reaction between Chlorine and Water
Cl2 + H2O → HOCl + HCl
Chlorine + Water → Hypochlorous Acid + Hydrochloric Acid
The test for chlorine
Add a damp blue litmus paper. Since the water on the paper will react with the chlorine, it will form hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid
The hydrochloric acid will first turn the litmus paper from blue to red since it’s an acid
The hypochlorous acid will then turn the litmus paper from red to white (bleaching it) since it’s a bleach
Hard water
Hard water is water which doesn’t easily lather with soap. Hard water is formed when solid impurities of Calcium or Magnesium dissolve in it
The difference between hard and soft water
Hard water forms scum (a white precipitate) when soap is added
Soft water forms lather (a frothy white solid) when soap is added
The difference between permanent and temporary water hardness
Permanently hard water cannot be removed by boiling whilst temporarily hard water can
The 2 compounds that form temporary hardness in water
Calcium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate
The 2 compounds that form temporary hardness in water
Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate and Magnesium Hydrogen Carbonate
The substance which converts neutral water into acidified water, causing it to dissolve calcium carbonate
Carbon Dioxide
The chemical equation of the dissolving of calcium carbonate by acid rain
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 → Ca(HCO3)2
or
CaCO3 + H2CO3 → Ca(HCO3)2
The reason why temporary hard water can be removed by boiling
Since Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate (one of the compounds which cause temporary hardness) can decompose by heat to form Calcium Carbonate, water and carbon dioxide
The chemical formula of soap
NaSt (Sodium Stearate)
The chemical formulae of scum
CaSt2 (Calcium Stearate) or MgSt2 (Magnesium Stearate)
The reactions between the 2 types of temporary hard water and soap
Ca(HCO3)2 + NaSt → NaHCO3 + CaSt2
Mg(HCO3)2 + NaSt → NaHCO3 + MgSt2
The reactions between the 2 types of permanent hard water and soap
CaSO4 + NaSt → Na2SO4 + CaSt2
MgSO4 + NaSt → Na2SO4 + MgSt2
The 3 methods of water hardness removal
Boiling (temporary hardness only)
Adding washing soda, Na2CO3
Distillation