Atoms, Molecules, and Chemical Bonds in Biology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the four classes of biological macromolecules?
Proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), carbohydrates (polysaccharides), and lipids.
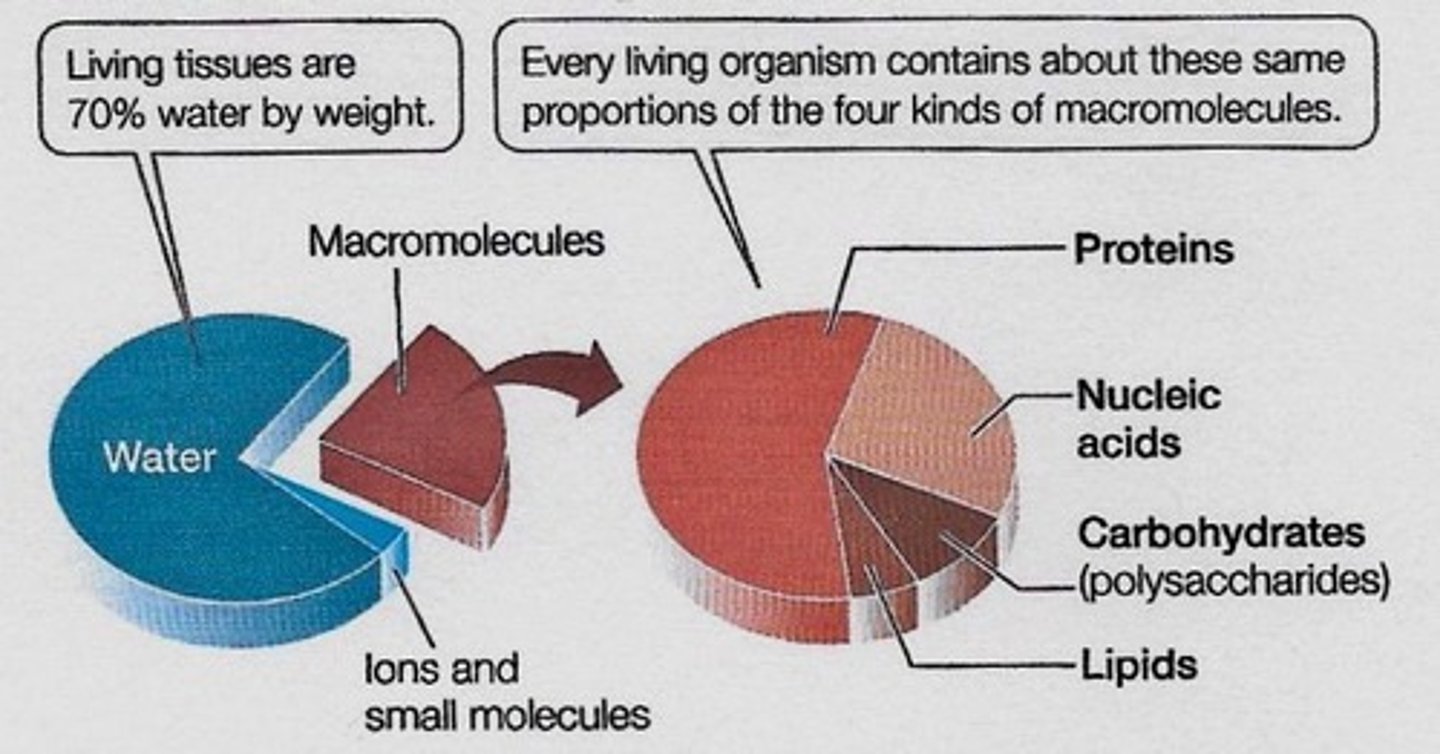
What percentage of living matter is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen?
96% of all living matter.
What is an element?
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions.
How many naturally occurring elements are there?
92 naturally occurring elements.
What are the three subatomic particles that make up an atom?
Protons, electrons, and neutrons.
What defines the atomic number of an element?
The number of protons in an atom.
What is the atomic mass of an atom with 3 protons, 3 electrons, and 4 neutrons?
7 Da (3 protons + 4 neutrons).
What is the difference between atomic mass and atomic weight?
Atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons, while atomic weight is an average mass based on the mix of isotopes.
What is the structure of an atom?
Protons and neutrons are clustered in the nucleus, while electrons surround the nucleus in an electron cloud.
What are valence electrons?
Electrons in the outermost energy level that determine the chemical properties of an element.
What is a chemical bond?
The interaction between two atoms in a molecule.
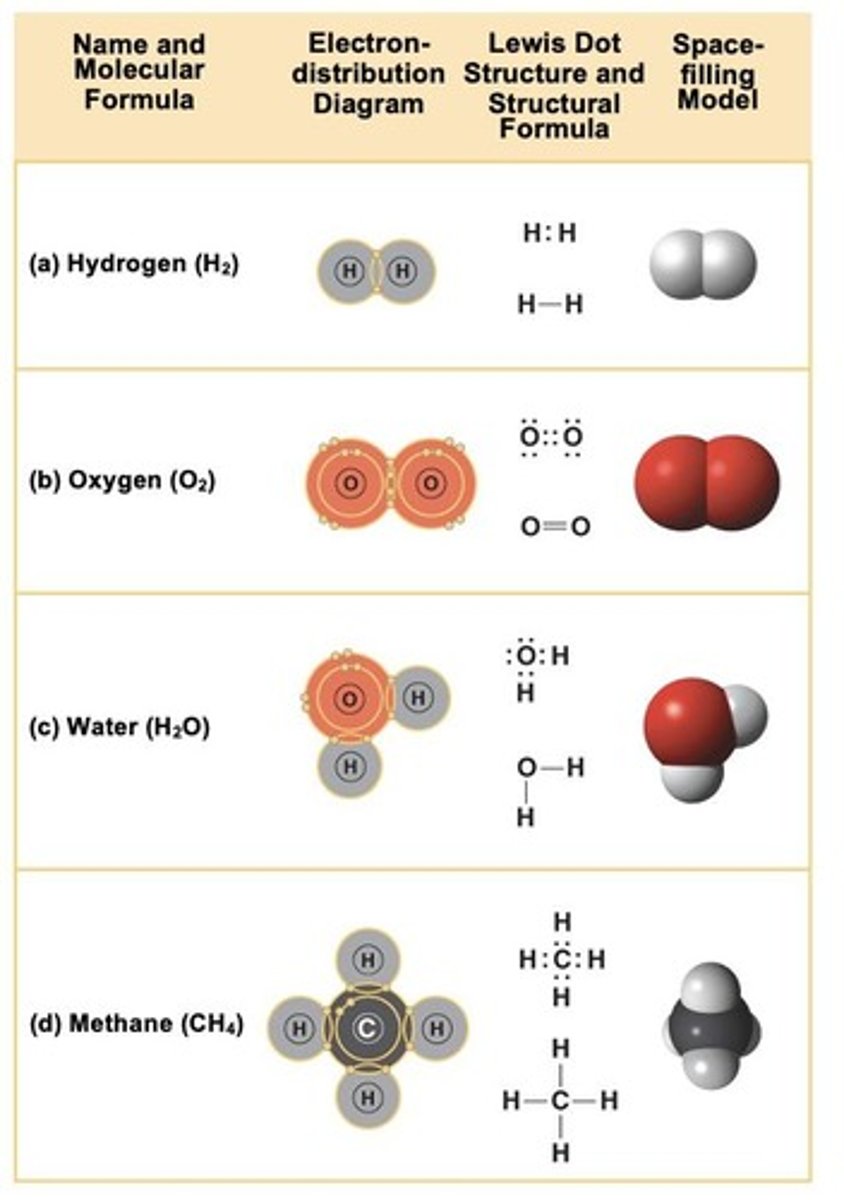
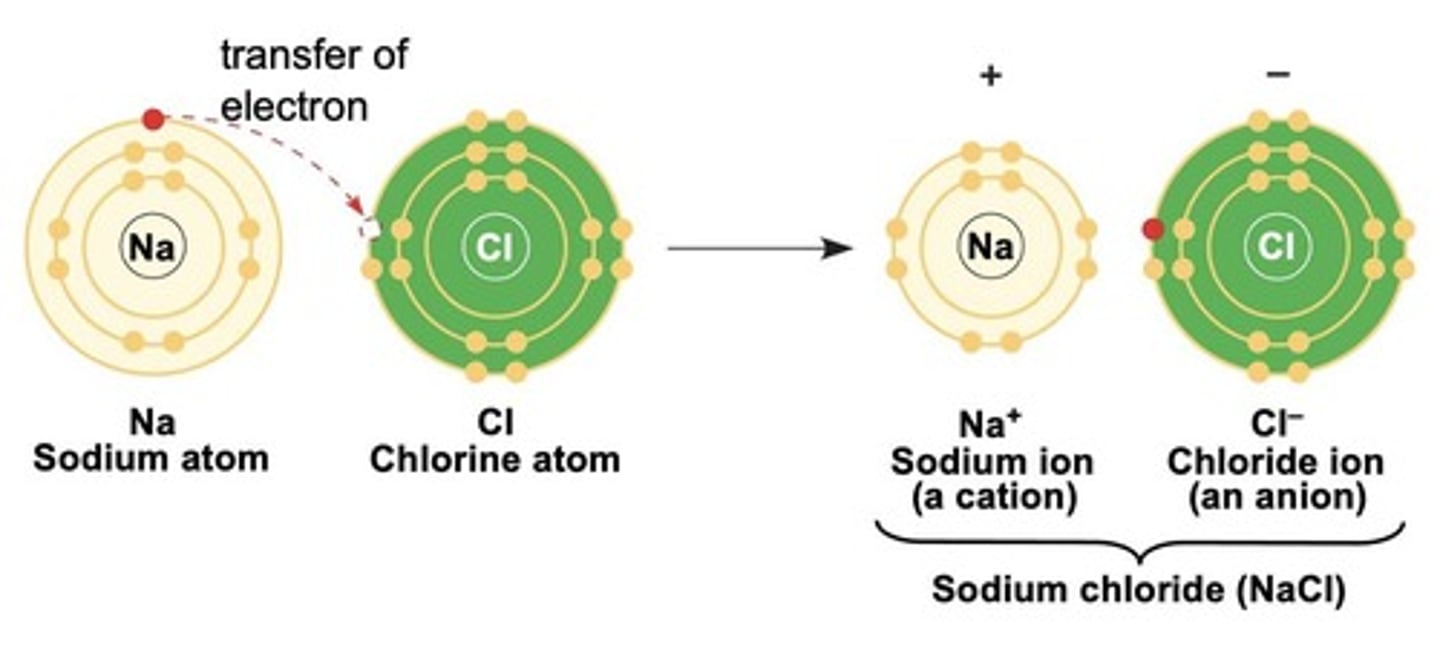
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds involve sharing electrons.
What is a cation?
A positively charged ion.
What is an anion?
A negatively charged ion.
What is reductionism?
The process of breaking things down into smaller components for easier study.
What are emergent properties?
Properties that arise at higher levels of organization and are not present in individual components.
Give an example of an emergent property.
The combination of sodium and chlorine to form sodium chloride, which is edible.
What is the most stable configuration of an atom?
An outer energy shell filled with electrons.
What happens to elements without a full valence shell?
They are chemically reactive and tend to combine with other atoms.
What is the significance of the periodic table's rows and columns?
Rows correspond to filling different energy levels, and columns have elements with similar chemical properties due to the same number of valence electrons.
What is the atomic mass of carbon's most common isotope?
12 Da, with an atomic weight of 12.01 due to isotopes.
What is the role of electrons in determining an atom's chemical behavior?
The chemical behavior is mostly determined by the valence electrons.
What is the electron cloud?
The region surrounding the nucleus where electrons are located.
How do electrons fill energy levels?
Electrons fill lower energy levels before higher ones.
What is the bonding capacity of carbon?
Carbon can form 4 bonds.
What is a common example of covalent bonding?
Methane (CH4), where carbon shares electrons with hydrogen.