proped credit 1
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
write basic clinical examination methods
inspection
palpetetion
percrussion
cuscultation
what is history
anamnesis
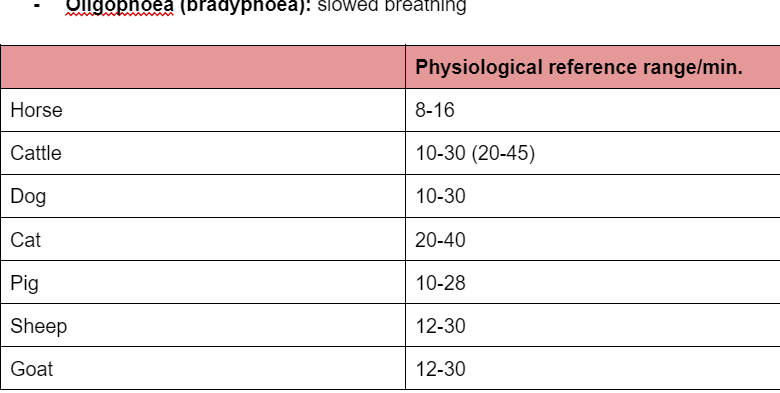
Reference range of breathing rate in cattle is
10-30
we usually examine pulse rate of dog on
femoral artery
write places of examination of skin elasticity
neck
sholder back
sheep: upper eyelid
primary lesions are
macula, visicula, pustula
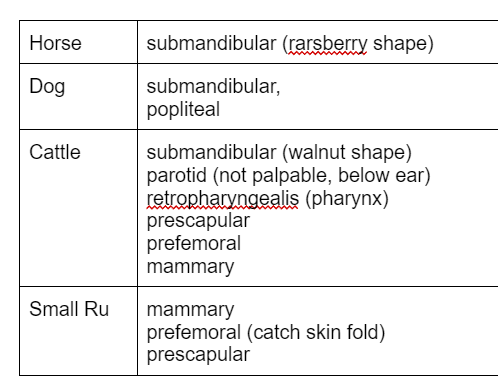
Lymph node i goat
prescapular
prefemoral
mammary
1 more (scrotal)
write 2 breeds of brachyocephalic dog
pug
tibetian spanial
write classification of breath sound
breathing sound over nasal cavity
luryngial breah sound
trachea breathing
over thorax
abnormal patological breath sound isnt
eructation
lung border horse
16 ics- 11ics
what is positive venous pulse

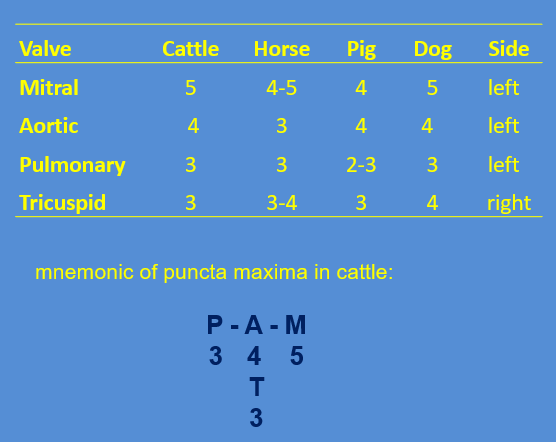
in which intercostal space do we usually examine haert in cattle
4-6 icss
what is FIRDA
riquency
intensity
rythm
demarcution
adventitius sound
describe P wave og ECG

write classification of endocardial murmurs
organic murmus - diasolic and systolic
INORGANIC murmurs
reference range of breathing horse
8-16
which sighs of heart beat do you examine

where are the puncta maxima in cattle

typical signs of hypotermia are

types consistency
hard
elastic
doughy
haert percussion in horse

which signs of paranasal cavities do you examine

lung of dog

range of pulse horse
8-16
noral capllary refill time
1-2 s
general status include
behaviour
posture
nutritional state
signalment include

which signs examin on skin

lymph node examination

which types of arrythmias of heart do we reveal by ECG

parameters of breathing do you examine
Rate, Rhythm type depth
symmetry of thoracic wall movments, dyspoea
puncta maxima horse

abnormal patological breathing sound
crackle
special examination methods
RTG
ECG
ultrasound
endoscopy
labrascopy
examine pulse rate horse
facial artery
examine cattle
mandibular
prescapular
prefemoral
mammary
retropharyngeal
secondery lesions
•scurf
•erosions:
•excoriation:
•ulcer
•crust (scab)
•scar:
wart:
eupnoe and ration between inspiration and expiration in cattle
eupnoe - normal physiological breathing rythmic
cattle 1:1,2
Disease
inability to perform physiological functions at normal levels even though nutrition and other environmental requirements are provided at adequate levels
PROPEDEUTICS
basic methods of clinical examination and examination of the symptoms of the disease and its classification by origin and interdependencies – semiotics (symptomatology)
SYNDROME
-
PATHOGNOMIC SYNDROME
a group of symptoms which occur at a certain disease
-
typical syndrome for each particular disease
COMPLETE DIAGNOSIS
should include three parts
1. the specific cause
2. the abnormality of structure or function produced by the causative agent, and which is inimical to normal processes
3. the clinical manifestation of that abnormality produced by causative agent
Types of restrain
physical
mechanical
chemical
phychological
percussion sounds
resonant – the sound emitted by organs containing air (normal lungs)
tympanic – drum-like sound emitted by an organ containing gas under pressure (rumen or caecum)
dull – solid organs (heart or liver)
principal auscultatory sounds
quality – characteristic for each system
location – anatomical position
frequency – normal / increased / decreased / stopped
intensity – normal / increased / decreased / extinct
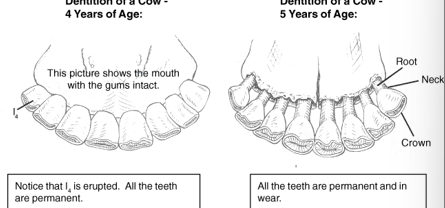
Age on cow
at 3 years of age first premolar teeth fall out
age on horse

Dog age
tartar on teeth
General status of animal
behaviour / general appearance
-2. coma – recumbency with unconsciousness
-1. dull – sluggish reactions, apathetic
0. bright – normal responses to external stimuli
1. excited – increased responsiveness
2. restlessness – more intensive locomotion
3. mania – vigorous abnormal movements
4. frenzy – dangerous abnormal locomotion (attack)
posture
regular – physiological posture – anatomically dependent
irregular
nutritional state (body condition)
very poor –
poor –
average –
good –
excellent –
obesity –
EXAMINATION OF TPR
breathing rate per minute
insepction
auscultation
pulse rate per minute
body temperature at least per minute
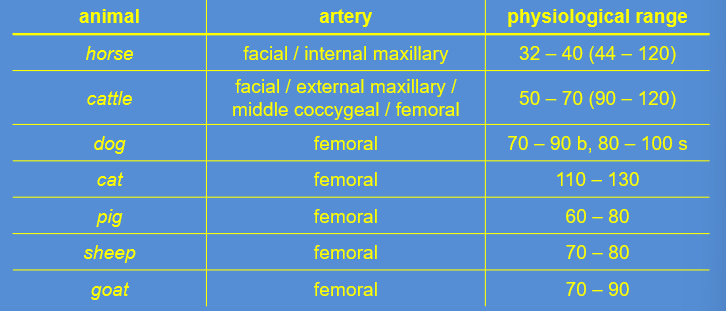
palpetation of arteries in animals + range
horse
cattle
dog
cat
pig
sheep
goat
60 sek
horse — 32 - 40
cow — 50 - 70
sheep — 70 - 80
goat — 70 - 90
pig — 60 - 80
dog — 70 - 90
cat — 110 - 130
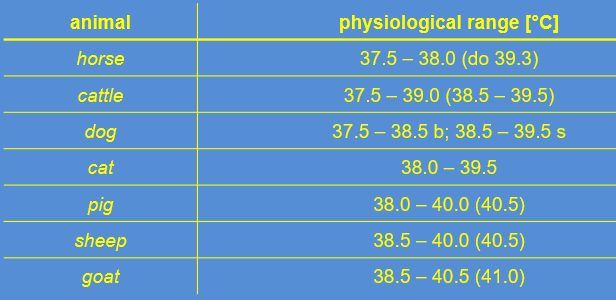
Temperature of animals
horse
cattle
dog
cat
pig
sheep
goat
horse — 37.5 - 38
cow — 37.5 - 39
sheep — 38.5 - 40
goat — 38.5 - 40.5
pig — 38 - 40
dog — 37.5 - 38.5
cat — 38 - 39.5
breathing range
horse — 8 -16
cow —10 - 30
sheep— 12 - 30
goat— 12 - 30
pig — 10 - 28
dog — 10 - 30
cat — 20 - 40
Palpebral fissure
eyelids + eyeball = gap between eyelids
exophtalmos
Eyeball
•size
•position
direction of the visual axis
sclera
colour
surface
Iris
•colour
•pigment pattern
•shape
•reaction of the pupil
VISIBLE MUCOUS MEMBRANES
•palpebral conjunctiva
•nasal mucous membrane
•mucous membrane of oral cavity
•mucous membrane of the vagina
or prepuce
wow lymph nodes
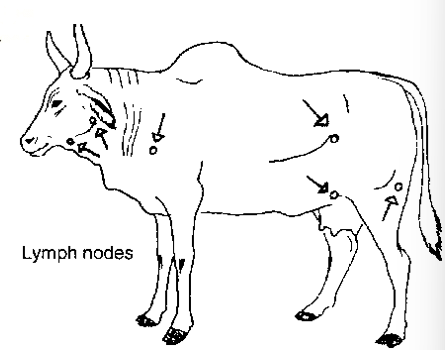
lymph in animal
paranasal sinuses
•Maxillary
•Frontal
•Ethmoidal
•Sphenopalatine
Examination:
Inspection
Palpation
Percussion
Auscultation
Radiography
Larynx - trachea
Examination:
•Inspection
•Palpation
•Auscultation
•Endoscopy
Palpation of the thorax
To detect:
•Fractured ribs
•Wounds
•Subcutaneous emphysema/oedema
•Thoracic pain
Sound has three principal characteristic
•Frequency
•Intensity
•Duration
Types of air flow and sounds produced
laminar
turbulent
Evaluation of the breath sounds
•Acoustic characteristics
•Timing in the respiratory cycle
•Anatomical location of adventitious sounds
•Areas of absence of sounds
Abnormal breath sounds
–Discontinuous sounds – crackles
short
Non-musical
Interrupted
–Continuous sounds – wheezes
Continuous
Whistling
Musical
Squeking
Horse lung

cow lung

Dog lungs

Tachycardia
Bradycardia
Tachycardia
over 70 in resting adult cattle
over 100 in young cattle
over 120 per minute in calves
at the heart rates over 120 - 140 a minute the second heart sound becomes practically inaudible: lublublub
bradycardia
less than 50 per minute
Rhythm
regular
irregular
Valves in animals
EXAMINATION OF PERIPHERAL CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
1) Inspection
2) Examination of arteries
3) Examination of capillaries
4) Examination of veins
Examination of arteries
frequency
rhythm
quality

EXAMINATION OF CAPILLARIES
vessels of the eye
fullness
colour
extent
Palpation - capillary refill time
normal: 1 – 2 seconds
dehydration: 2 – 4 seconds
severe dehydration, heart weakness, shock: 5 – 6 seconds
Heart location
location against the chest inside the left elbow at the:
horse: 3rd to 6th intercostal space
cow: 3rd or 4th intercostal space
dog: 4th or 5th intercostal space
Percussion of the heart D

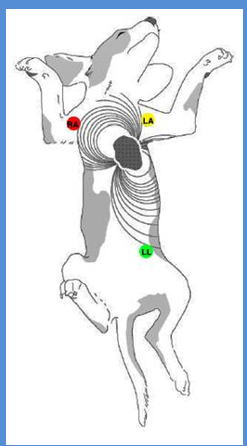
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY – ECG
electrocardiograph provides a time / distance recording of the changes in electrical potential generated in the heart – it evaluates the electrical activity of animal´s heart
ECG can determine the rate, rhythm and nature of cardiac depolarization and repolarization
ECG is the curve traced by an electrocardiograph. Also called cardiogram .
the P PR QRS T- wave
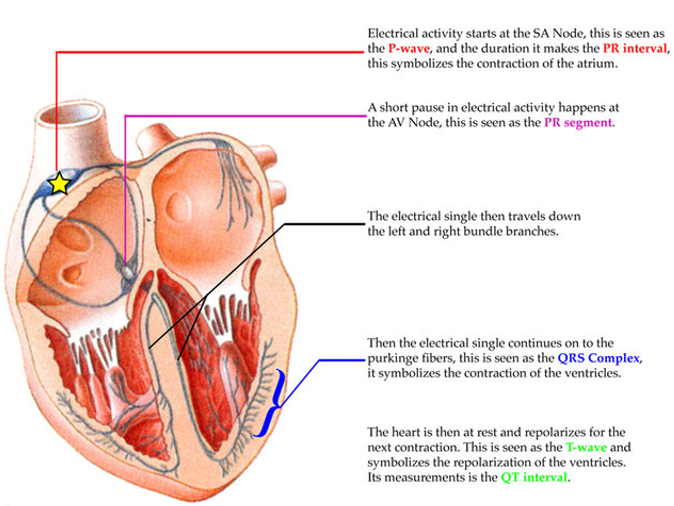
the P PR QRS T- wave part 2
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM = P Q R S T
P wave - excitation (depolarization) spreading from sinoatrial node and causing contraction of the atria
in the horse, ox and dog,it is positive and sometimes it may be diphasic
P interval corresponds to the time taken for depolarization of the ventricles to occur and is followed by QRS (ventricular) complex
Q wave - small and negative
R wave - more pronounced and positive
S wave - negative, similar Q
T wave – positive, isoelectric period that follows QRS complex representing repolarization of the myocardium during the last stages of ventricular systole
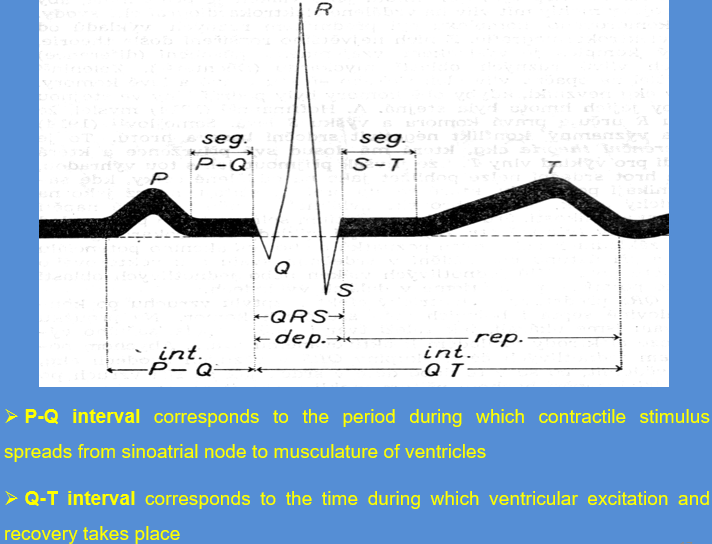
Characteristics of normal sinus rhythm
rate 50–70 beats per minute
rhythm regular
P wave normal
PR interval
QRS complex
T wave
duration of one cycle is 1.5 s
Heart blocks diagnosis (3)
incomplete heart block:
extended P-R interval, irregular failure of ventricles - absent QRS complex
almost complete heart block:
P waves more frequently than irregular QRS complex
complete heart block:
rapid P waves - atrial flutter, continuous sequence of small modulation in atrial fibrilation
What wave does:
Hypercalcemia +Hypocalcemia
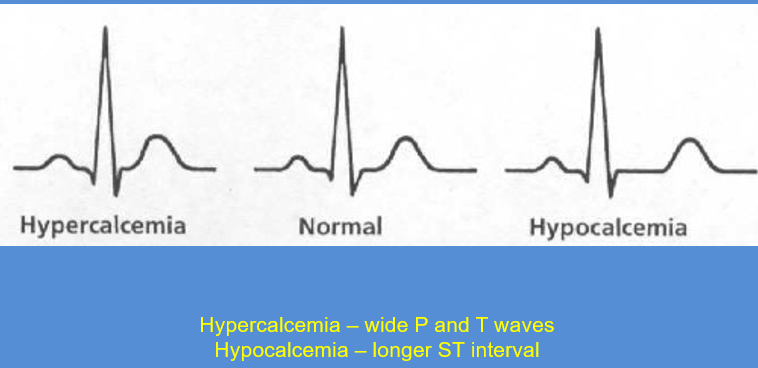
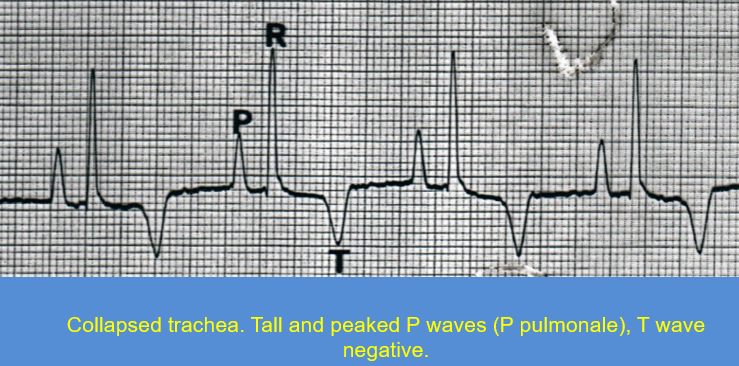
What wave does:
collapsed trachea
Ultrasound colours
Liquid is black
Solid airless tissues white