AP Biology Unit 5 (Meiosis, Sexual Reproduction, Hereditary)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Assignment. Day 1: Sexual Reproduction + Meiosis Assignment. Day 2: Chromosomes and Genetic Recombination Assignment. Day 3: Sex Cell Creation, Fertilization, and Basic Genetics Assignment. Day 4: Drosophila and Non-Mendelian Inheritance Assignment. Day 5: Pedigrees
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Meiosis
cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four haploid cells, each genetically distinct from the parent cell.
important for sexual reproduction
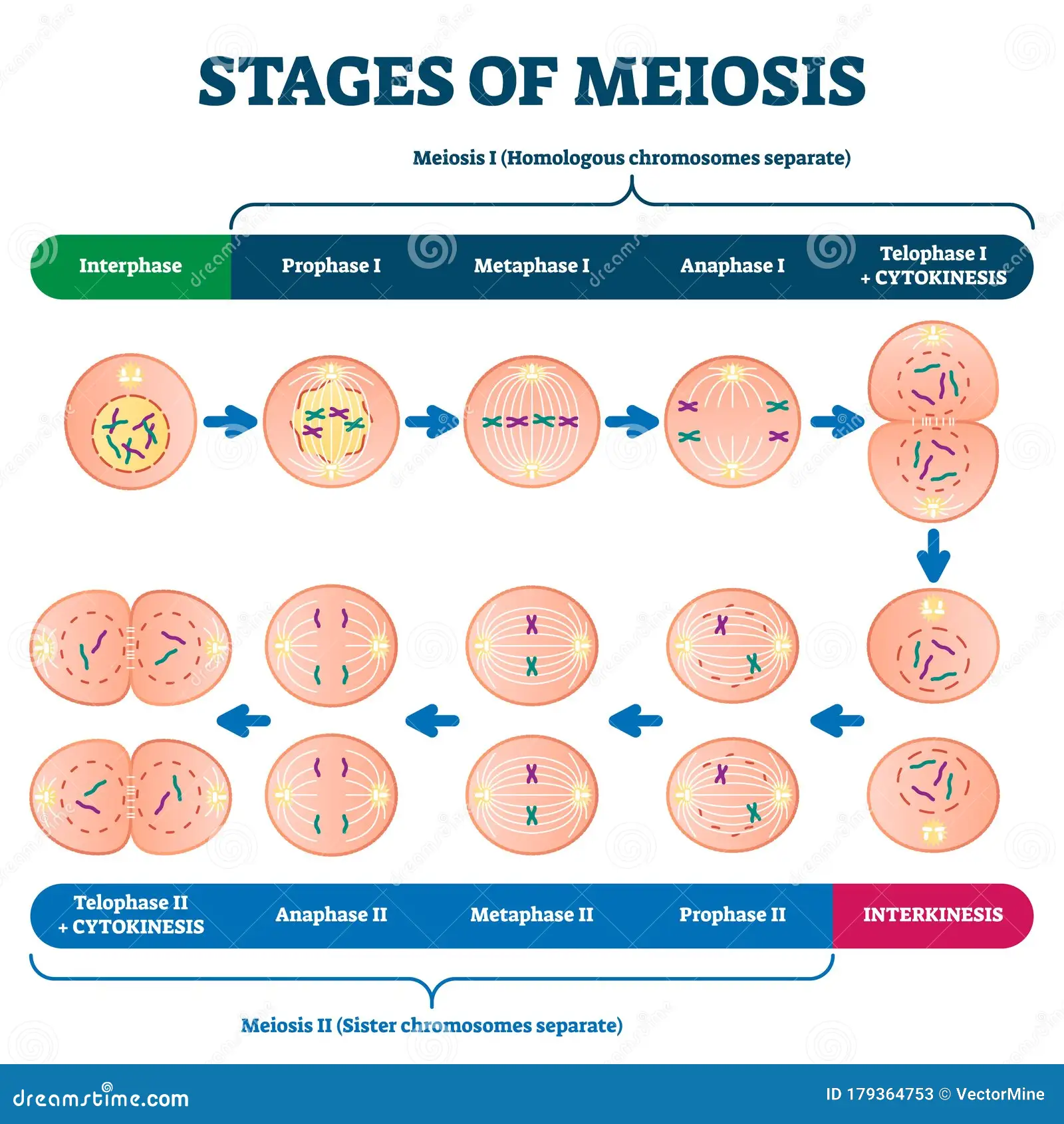
Stages of Meiosis
Prophase 1 (2 Chromosomes stick together forming a → Tetrad → Crossing Over occurs and pieces of homologs switch positions)
Metaphase 1 (independent assortment - each tetrad could align one way or the opposite, leading to the distribution of genes and traits to be irregular)
Anaphase 1
Telophase/Cytokinesis 1 (the seperation is important becuse it provides the means for cell division and the formation of idependent cells)
Prophase 2
Metaphase 2
Anaphase 2
Telophase/Cytokinesis 2 (the seperation is important becuse it provides the means for cell division and the formation of idependent cells)
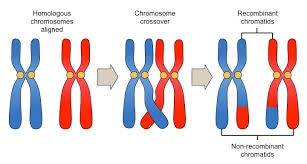
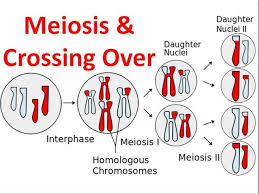
Crossing Over
2 Chromosomes stick together forming a → Tetrad → Crossing Over occurs and pieces of homologs switch positions
happens in chiasmata
chiasmata
x shaped regions where crossing over happens
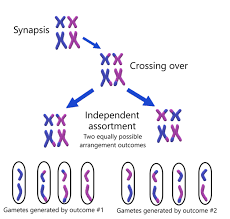
Independent Assortment
each tetrad could align one way or the opposite, leading to the distribution of genes and traits to be irregular
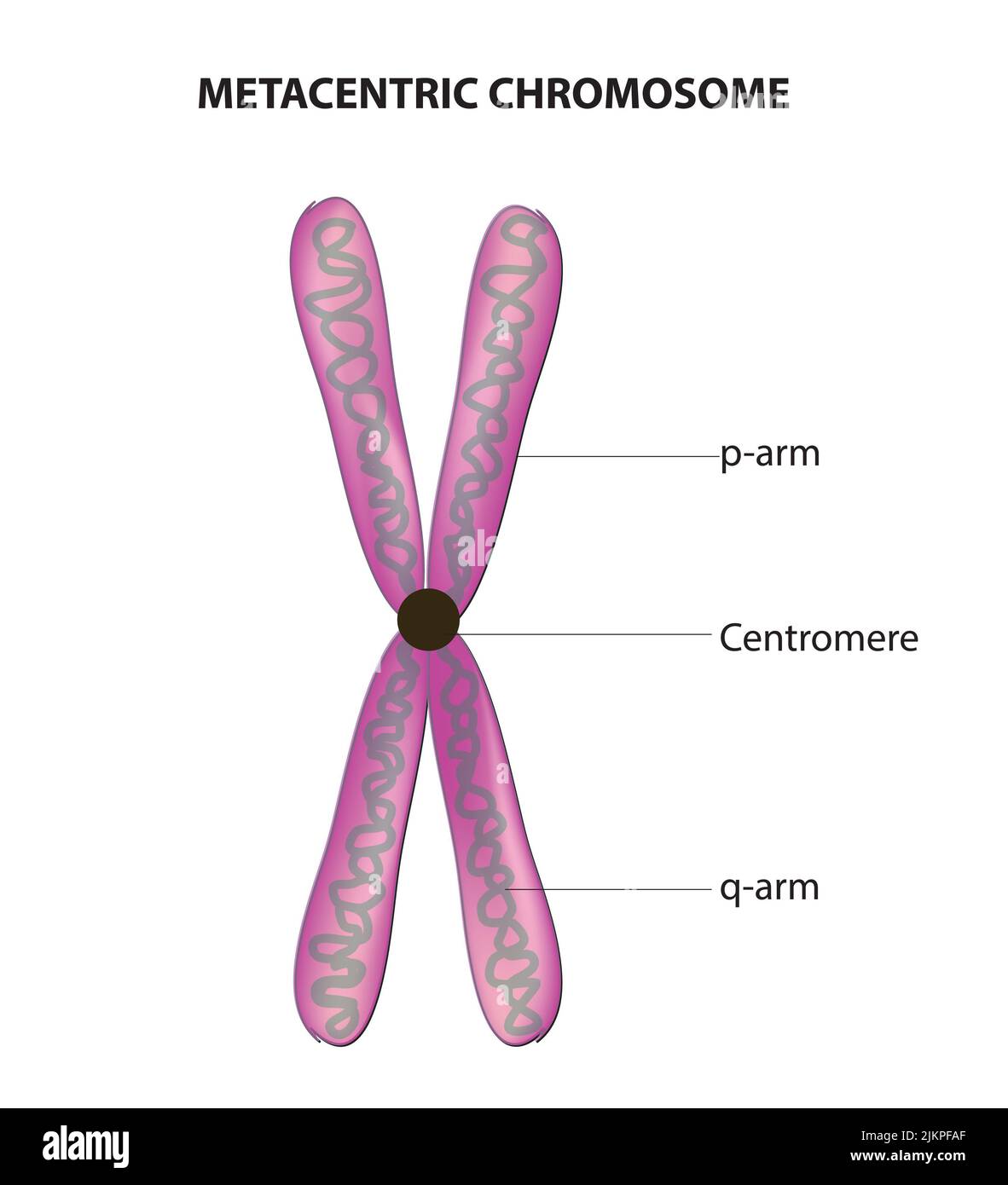
Chromosome
DNA Molecule
Made of two identical DNA Molecules (sister chromatids)
Chromosomes
Person has 46
23 from Mom + 23 from Dad
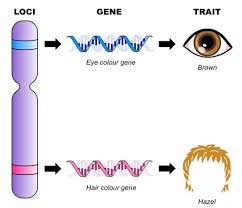
Gene Locus
1p1.11
Chromosome 1
p arm
location
heredity
transmission / sharing of traits generation → generation
variation
no identicality (inherited variation)
crossing over and independent assortment
genetics
study of heredity and inherited variation
genes
hereditary units (code) “program trains”
gametes
reproductive cells (sperm + egg)
somatic cells
allcells of the body
sexual reproduction
parent + parent = offspring (vary genetically)
asexual reproduction
single individual : passes copies of genes w/o gametes (exact copies) ((clones))
life cycle
generation → generation sequence of stages in reproductive history of an organism, from conception to its own reproduction
karyotype
displayed image of chromosome variants
homologous chromosomes (homologs)
= length = pattern = centromere position
sex chromosomes
x and y (maternal & paternal)
sets of 23
autosomes
all other chromosomes
diploid cell
cell has two chromosome sets (2n = 46 X)
haploid cell
cell has a single set of chromosomes n = 23 |
fertaalization
haploid sperm + haploid egg = zygote
zygote
fertilized egg
DNA can be seen in
chromatin
chromatid
chromosome

synapsis
DNA breaks are closed up to be ready for a non sister chromatid
synaptonemal complex
zipper structure that holds homologs together
sister chromatid cohesion
sister chromatids are 2 copies of one chromosome