Genetics Final Exam Question Bank
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is the probability of producing a child that will phenotypically resemble either one of the two parents in the cross A1A2 B1B3 C2C4 D1D4 x A1A1 B3B3 C2C2 D4D4 if alleles of each gene show incomplete dominance and the four genes are unlinked?
a. 1/16
b. 1/8
c. 1/4
d. 1/2
e. 1
B
If a couple has 5 children, what is the chance that 4 are females and 1 is a male?
a. 5/32
b. 1/4
c. 3/8
d. 1/2
e. 3/4
A
You flip a fair coin six times. What's the chance of getting at least one Head?
a. 1 − (1/36)
b. 1/64
c. 64/63
d. 1 − (1/26)
e. 1/4
D
4. If you roll 2 dice, what’s the probability of rolling an even on one and an odd number on the other?
a. 1/2
b. 1/3
c. 1/4
d. 1/5
e. 1/6
A
5. In pea plants, smooth seeds (S) is dominant to wrinkled seeds (s), and tall plants (T) is dominant to short plants (t). A true-breeding tall, smooth plant (TTSS) is crossed with a true-breeding short, wrinkled plant (ttss). The F₁ offspring are then crossed to the short, wrinkled parent. What proportion of the progeny are expected to be homozygous for short and wrinkled?
a. 1/20
b. 1/16
c. 1/8
d. 1/4
e. 1/2
D
In corn, having ligules (L) is dominant to liguleless (l), and green leaves (G) is
dominant to white leaves (g). When a testcross is performed with a plant that has
ligules and green leaves, all the offspring had one of the two following phenotypes:
EITHER plants with ligules and green leaves OR liguleless plants with green
leaves. What is the most likely genotype of the parent plant that has ligules and green leaves?
a. LLGG
b. LlGG
c. LLGg
d. LlGg
e. It cannot be determined.
B
Recall that in Mendel's peas, yellow is dominant to green, and round is dominant to
wrinkled. Parent plants where one is homozygous for yellow and wrinkled peas
and the other is homozygous for green and round peas produce an F1 generation.
The F1 plants self-fertilize. One of the F2 pods contains 10 peas.
What is the chance that all 10 peas are green and round?
a. (1/16)10
b. (9/16)10
c. 1 – (1/1610)
d. (1/4)10
e. (3/16)10
E
A male and female couple went to see a genetic counselor because each had a
sibling with cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis is caused by a rare recessive disease
allele (100% penetrant), and neither member of the couple nor any of their four
parents is affected. The pedigree is shown here.
What is the probability that the child of the couple will have cystic fibrosis?
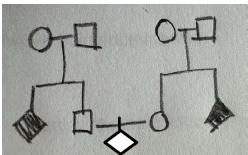
a. 1/4
b. 1/3
c. 2/3
d. 1/9
e. 3/4
D

C
Staring with the parental cross AAbbCC × aaBBcc, what proportion of the F2
offspring is expected to be homozygous for at least one of the three genes?
a. none of them
b. 1/8
c. 1/64
d. 63/64
e. 7/8
E
In daisies, flower color is determined by two genes, A and B. For a plant to make
colorful flowers, it must have at least one dominant allele at both loci (A and B). If
a plant is missing the dominant allele at either locus, the flowers are white. Two
white-flowered plants are crossed. One is homozygous AA and the other is
homozygous BB. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of colorful to white
flowers in the F2 generation? What kind of inheritance is this?
a. 13 white: 3 colorful. This is dominant epistasis.
b. 15 colorful: 1 white. This is reciprocal dominant epistasis.
c. 15 white: 1 colorful. This is reciprocal dominant epistasis.
d. 7 colorful: 9 white. This is recessive epistasis.
e. 9 colorful: 7 white. This is reciprocal recessive epistasis
E
Achondroplasia is a form of dwarfism in humans. It is caused by a mutant allele of
the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 gene (FGFR3) that produces an overactive
protein. Having one copy of the mutant allele results in dwarfism. Two copies of the
mutant allele results in death before birth. The mutant FGFR3 allele is completely
penetrant. If two people with achondroplasia have a child together, what is the
probability that their child will also have achondroplasia?
a. 1
b. 0
c. 2/3
d. 1/2
e. 3/4
C
A certain disease is caused by a dominant mutant allele. (The wild-type allele is
recessive.) However, the penetrance of the disease is 50%. Two individuals known
to be heterozygotes have a child that survives. What is the probability that the child
exhibits the disease? [Assume dominant homozygotes survive with the disease]
a. 1/4
b. 3/4
c. 1/8
d. 3/8
e. 1/2
D
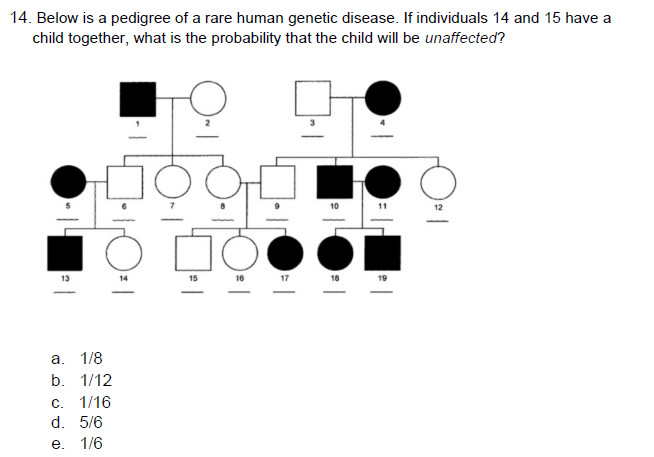
D
A woman who is a heterozygote for X-linked colorblindness (she is not
colorblind) has a daughter with a man, and the man is not colorblind. Their
daughter has a son with a man who is not colorblind.
What is the chance that their son will be colorblind?
a. 0
b. 1/8
c. 1/4
d. 1/3
e. 1/2
C
16. The pairwise map distances for four linked genes are as follows:
B-C = 15 m.u.
C-D = 2 m.u.
B-D = 13 m.u.
A-B = 5 m.u.
A-C = 10 m.u.
A-D = 8 m.u.
What is the order of these four genes?
a. BADC
b. BACD
c. BCAD
d. BCDA
e. BDCA
A
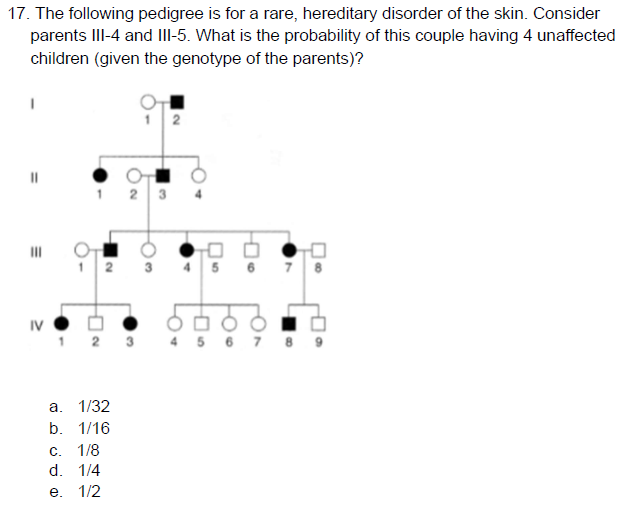

B
In humans, the genes for red-green color blindness (C = normal, c = colorblind)
and hemophilia A (H = normal, h = hemophiliac) are both X-linked and only 3 map
units apart. Both color blindness and hemophilia are rare conditions. A normal
daughter has a normal mother (and the mother is NOT a carrier for either disease)
and a hemophiliac and colorblind father.
What is the percent of the daughter’s sons that will be either hemophiliac or
colorblind (but not both).
a. 1.5 %
b. 3.0 %
c. 48 %
d. 50 %
e. 97 %
B
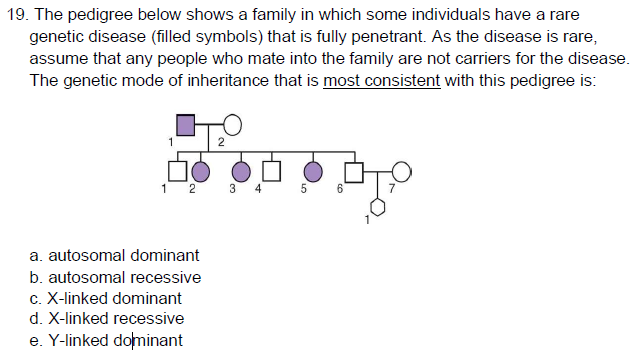
C

What is the chance that the child (indicated by the hexagon shape) will have the
condition?
a. 0
b. 1/2
c. 1/4
d. 1/8
e. 1/16
A
Suppose you used a DNA synthesizer to generate the two short, single-stranded DNA molecules called DNA #1 and DNA #2. You add DNA 1 and DNA 2 to a reaction tube containing DNA polymerase and the four radioactive dNTPs. After DNA polymerase is allowed to work for a few hours, what will be the sequences of the single-stranded DNA molecules that contain radioactive nucleotides? (Remember DNA polymerase requires a primer, a template, and 4 dNTPs. Assume that in the reaction tube, 10 bp of complementary sequence is sufficient for stable base-pairing.)
DNA 1 3′ GTCCCACTTGATATA 5′
DNA 2 5′ TTGCCAGGGTGAACT 3′
a. 5' AACGGTCCCACTTGATATA 3' and 5' TATATCAAGTGGGACCGTT 3'
b. 5' CTACTACGGATCGGGCGA 3' and 5' CCAGTCCCGATCCGTCTAA 3'
c. 3' AACGGTCCCACTTGATATA 5' and 3' TATATCAAGTGGGACCGTT 5'
d. 5' CTACTACGGATCGGGACTGG 3' and 5' CCAGTCCCGATCCGTAGTAG 3'
e. 3' AACGGTCCCACTTGA 5' and 5' CAGGGTGAACTATAT 3'
C
Assume that a wild-type sequence is 5' AGCCTAC 3'. Which sequence could be produced by a transversion?
a. 5' ATCCTAC 3'
b. 5' AGCCCAC 3'
c. 5' AGCCTGC 3'
d. 5' AGTCTAC 3'
e. 5' AGCCGCCGCCGCCTAC 3'
A
Nitrous acid removes an amine group from cytosine (C) to change it to uracil (U), which pairs with adenine (A) instead of guanine (G). What type of mutation would this cause?
a. Substitution of A-T base-pair with G-C (A-T → G-C)
b. Substitution of C-G base-pair with T-A (C-G → T-A)
c. Deletion leading to a frameshift mutation
d. Slipped mispairing leading to a trinucleotide repeat
e. Substitution mutation known as a transversion
B
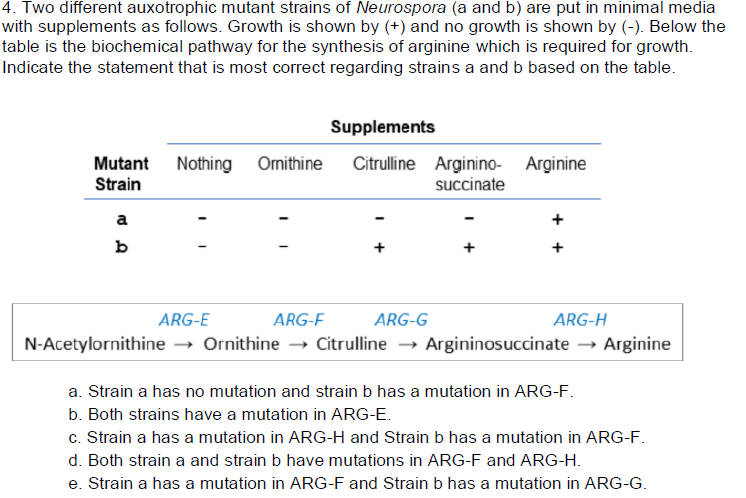
C
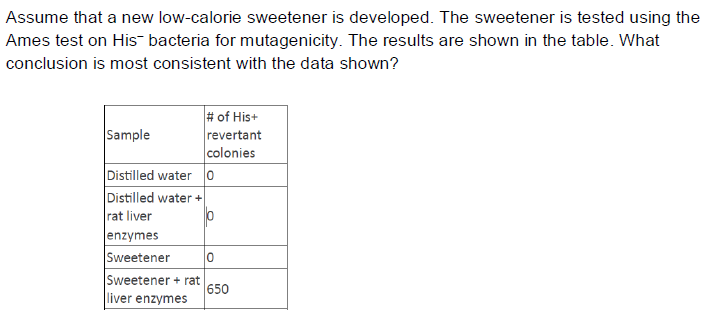
a. The sweetener is not mutagenic.
b. Rat liver enzymes are highly mutagenic.
c. The sweetener is not mutagenic but can be converted by the liver into strong mutagens.
d. The sweetener is mutagenic but can be converted by liver enzymes into strong
mutagens.
e. The sweetener and its conversion products are equally mutagenic.
C
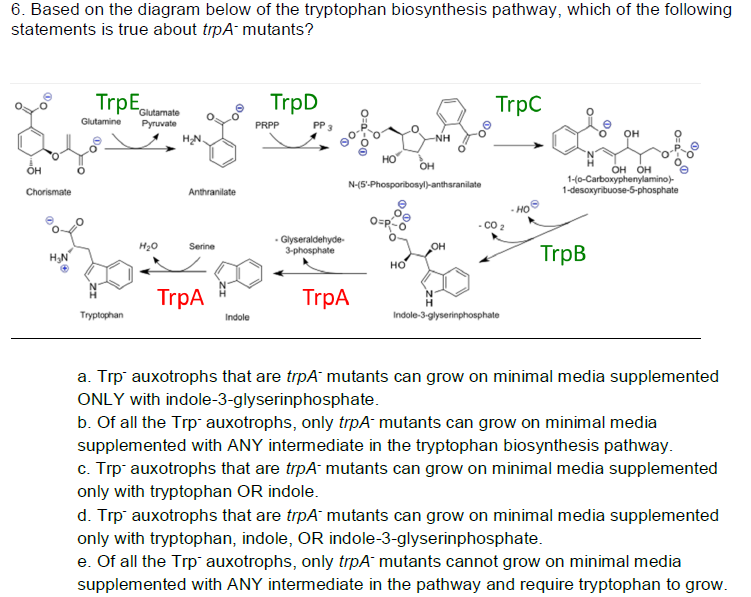
E
A gene encodes a protein that is 900 amino acids long. Three nonsense mutant alleles exist: His20X, Ala560X, and Leu890X. [His20X, for example, means that the histidine amino acid, which the 20th amino acid in the wild-type protein, is now a stop codon (X).]
Suppose that you KNOW that one of these mutant alleles causes a loss of function, one causes a gain of function, and one appears to have no effect on protein function at all. For each of these effects on protein function, assign the MOST likely allele.
a. Loss of function: His20X; Allele with no effect: Leu 890X, Gain of Function: Ala560X
b. Loss of function: Leu 890X ; Allele with no effect: His20X, Gain of Function: Ala560X
c. Loss of function: Leu 890X ; Allele with no effect: Ala560X, Gain of Function: His20X
d. I can’t predict the effect on function.
A
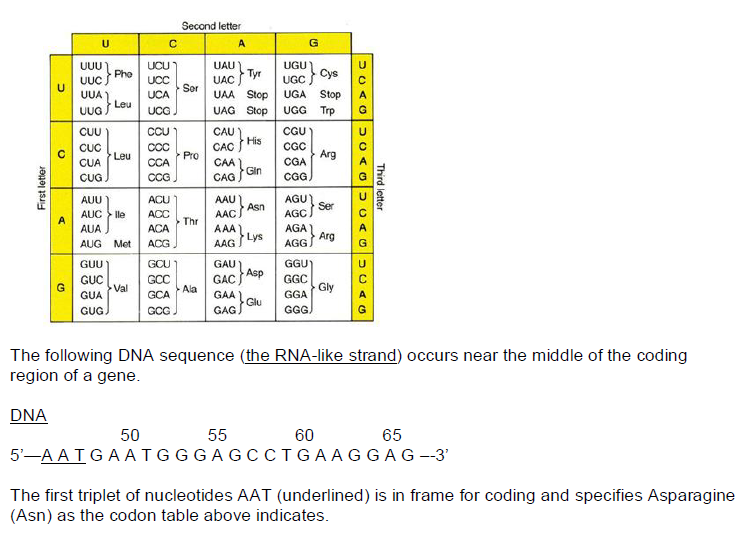
8. Which of the following DNA mutations is likely to result in a shorter than normal protein?
a. A→G at position 50
b. G→A at position 53
c. C→A at position 58
d. All the above
e. None of the above
B
9. Which of the following DNA mutations is likely to result in no change in the protein?
a. Insertion of a G after position 54
b. A→G at position 61
c. Deletion of G at position 53 AND Insertion of a G after position 54
d. A→G at position 50
e. Answer Choices C and D
E

10. You have made random-sequence synthetic RNA molecules that contains only U and C, and which contain three times as much U as C. You use these RNAs to perform in vitro translation. How many different amino acids would you find in the resulting polypeptides? And at what frequency would you expect to find Proline (Pro) in the resulting polypeptides?
a. 6; 1/16
b. 4; 1/16
c. 6; 12/64
d. 4; 12/64
e. 4; 36/64
B
11. The following DNA sequence is part of one exon and contains the beginning of a gene’s open reading frame (ORF).
5' ATGCCTGAATCAGCTTTA 3'
How many amino acids does this sequence encode?
a. 18
b. 7
c. 6
d. 5
e. 4
C
Would a tRNA with an anticodon sequence 3’ UUA 5’ normally exist for making proteins?
a. Yes; it specifies a stop codon
b. Yes; it specifies only one amino acid (Leu)
c. No; it specifies more than one amino acid (Asn or Lys)
d. No; it specifies more than one amino acid (Phe or Leu)
e. Not enough information to answer this
C
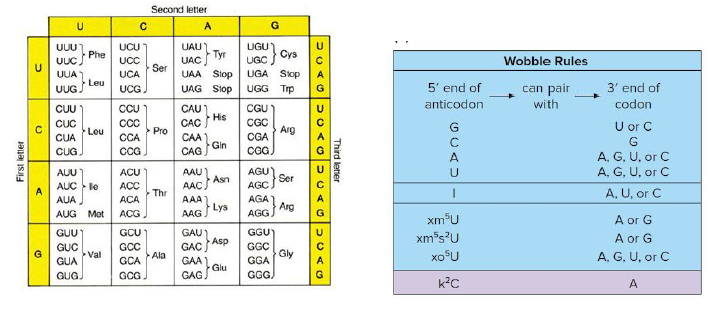
E.coli is known to have two duplicated genes for a tRNA with the anticodon 3′AUG5′. In one strain of a bacterium, both of the genes have mutated into a tRNA with the anticodon 3’ AUxm5s2U 5’ instead. What is true about bacteria with the mutant tRNA anticodon?
a. All proteins produced by these bacteria will be unable to incorporate tryptophan.
b. Bacteria that use the mutant tRNA will have proteins shorter than usual.
c. Their mutant tRNA codes for more than one amino acid.
d. Their mutant tRNA can suppress more than one stop codon.
e. None of the above
D
How might a splice site mutation that causes an unspliced intron (the intron stays in) affect the RNA transcript or protein?
a. The protein encoded by the mutant gene could have fewer than the normal number of amino acids.
b. The protein encoded by the mutant gene could have more than the normal number of amino acids.
c. The mRNA could be longer than normal.
d. The mutant protein could have a normal function.
e. All of the above
E
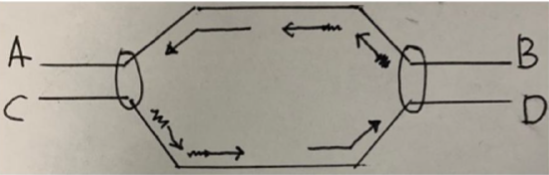
Based on the image below, which letters represent the 5' ends of the DNA template?
a. A & B
b. A & C
c. A & D
d. B & C
e. B & D
C
What information is NOT present in a cDNA library of all the mRNAs in red blood cells?
a. Poly-A-Tail
b. Exon sequences
c. Intron sequences
d. UTR (untranslated region) sequences
e. Codon sequences
C
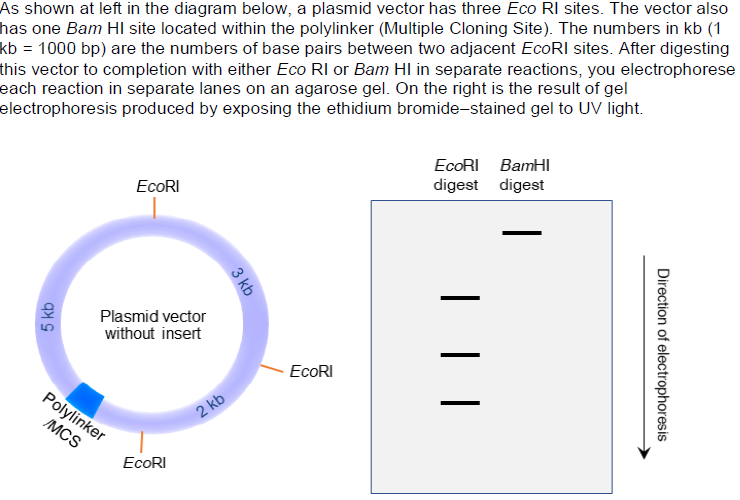
What are the sizes of DNA fragments in the four bands from top to bottom?
a. 10 kb; 8 kb; 7 kb; 5 kb
b. 5 kb; 7 kb; 8 kb; 10 kb
c. 10 kb; 5 kb; 3 kb; 2 kb
d. 2 kb; 3 kb; 5 kb; 10 kb
e. None of the above
C
To estimate the genome size of a newly discovered plant, you digest one copy of its genomic DNA with the restriction enzyme Rsa I, which has a 4 bp recognition site. The genome is cut into about 100,000 fragments. Which is your best estimate of the size of this plant’s genome?
a. 25,000 bp
b. 6,400,000 bp
c. 25,600,000 bp
d. 400,000 bp
e. 400,000,000 bp
C
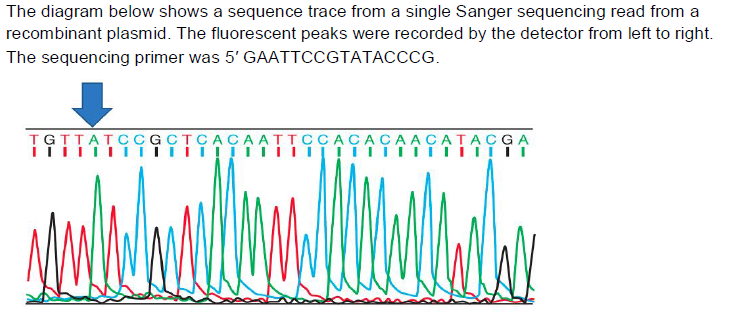
19. Which DNA molecule, when it passed by the detector, made the A peak indicated by the large arrow?
a. 5′ TGTTA
b. 5′ AGCATACAACACACCTTAACACTCGCCTA
c. 5′ GAATTCCGTATACCCGACAAT
d. 5′ ACAAT
e. 5′ GAATTCCGTATACCCGTGTTA
E

In what way would the sequence trace look different if you accidentally left the dideoxyC (ddCTP) out of the reaction?
a. The C peaks would be absent.
b. There would be no peaks at all.
c. Only the C peaks would be present.
d. Only the first seven peaks at left would be present.
e. The C peaks would be higher.
A
1. D21S11 is an SSR locus on chromosome 21 whose repeat unit is 5′ TCTA. The diagram below shows one DNA strand of an allele with 5 copies of the repeat unit in underlined bold. Which pair of sequences could be used as PCR primers to amplify any allele of this SSR locus?
5′ …CTCTAGTTTAGGCCTTAATCTATCTATCTATCTATCTAGGTTCCAAACCACTGGGC… 3′
a. 5′ TCTATCTATCTATCTATC and 5′ ATCTATCTATCTATCTAT
b. 5′ TCTATCTATCTATCTATC and 5′ GCCCAGTGGTTTGGAACC
c. 5′ CTCTAGTTTAGGCCTTAA and 5′ CGGGTCACCAAACCTTGG
d. 5′ TCTATCTATCTATCTATC and 5′ TAGATAGATAGATAGATA
e. 5′ CTCTAGTTTAGGCCTTAA and 5′ GCCCAGTGGTTTGGAACC
E
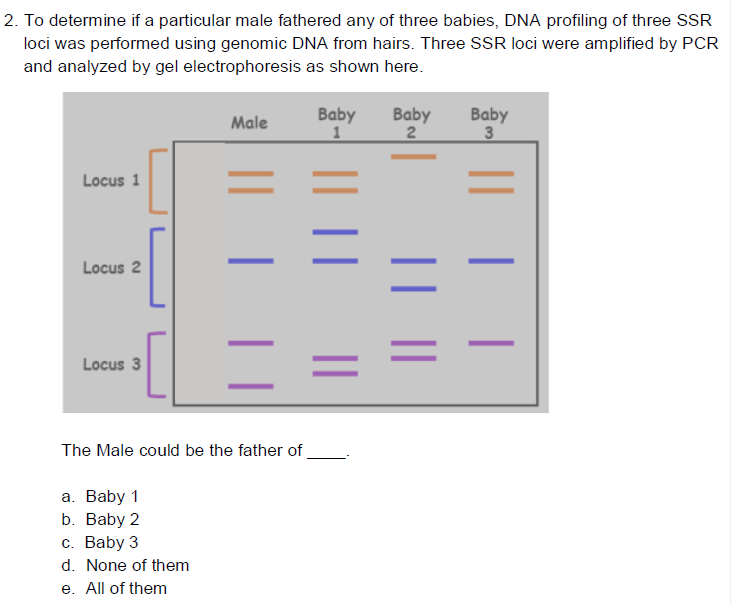
C

E
Let’s say a gene suffers from an “inversion” mutation in the underlined sequence below. What is the new mutant sequence?
5’-ATGCCTGAATTTGAATGCCTGCACCGGTATAG-3’
a. 3’-ATGCCTGAATTTGAATGCCGGTGCAGGTGCAGGTATAG-5’
b. 5’-ATGCCTGAATTTGAATGCCCCACGTGGTATAG-3’
c. 3’-ATGCCTGAATTTGAATGCCCCACGTGGTATAG-5’
d. 5’-ATGCCTGAATTTGAATGCCGGTGCAGGTATAG-3’
e. 5’-ATGCCTGAATTTGAATGCCGGTATAGGGTGCA-3’
D
Which of these is an example of a SNP locus?
a. Individuals with fragile X syndrome have 200 or more CGG repeats in the untranslated region of the FMR-1 gene.
b. A base pair substitution in the GLI3 gene makes a nonsense mutation that can cause polydactyly.
c. The most common cystic fibrosis allele has a deletion of three base pairs in the coding region of the CFTR gene.
d. Individuals with Huntington disease have more trinucleotide repeats in the coding region of the HD gene than normal individuals.
e. A two nucleotide base-pair insertion in an exon of a gene results in a truncated protein, which is nonfunctional.
B
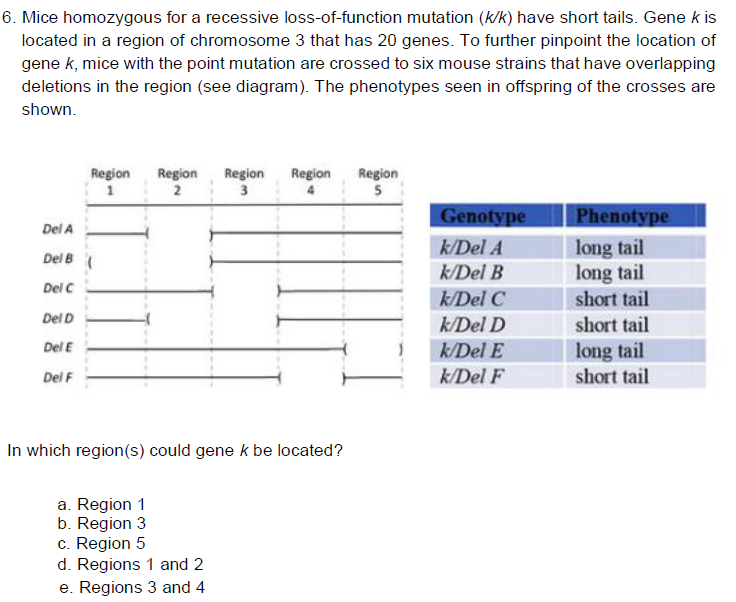
E
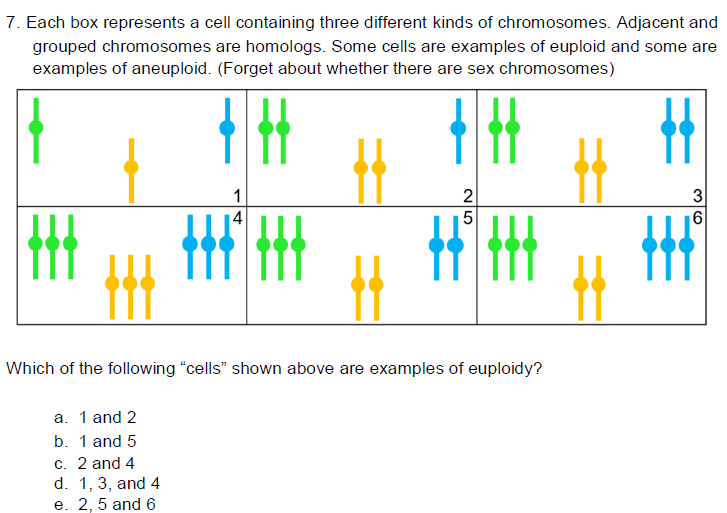
D
An Aaaa tetraploid plant undergoes self-fertilization. At least one dominant A allele is required for the dominant phenotype. What proportion of the progeny will show the dominant phenotype?
a. 1/16
b. 1/2
c. 3/4
d. 35/36
e. 1
A couple has a son that is XYY. What event in meiosis could have resulted in the extra Y chromosome in the child?
a. Nondisjunction in meiosis II in the father can generate YY gametes.
b. Nondisjunction in meiosis I in the father can generate XY gametes.
c. Nondisjunction in meiosis I in the mother can generate XX gametes.
d. Nondisjunction in meiosis I in the father can generate YY gametes.
e. Nondisjunction in meiosis II in the mother can generate XY gametes
A
What do the activator proteins bound to an enhancer do so that transcription can occur?
a. They bind RNA polymerase II at the TATA box.
b. They interact with insulator-binding proteins to form TADs dynamically.
c. They either stabilize the interaction of the basal complex proteins with the promoter or bind to co-activators that clear nucleosomes from the promoter.
d. They stabilize the contacts between histones and DNA so that the chromatin around the promoter becomes more compact.
e. They either destabilize the interaction of the basal complex with the promoter or bind to co-repressors that maintain nucleosomes and close chromatin near the promoter.
C
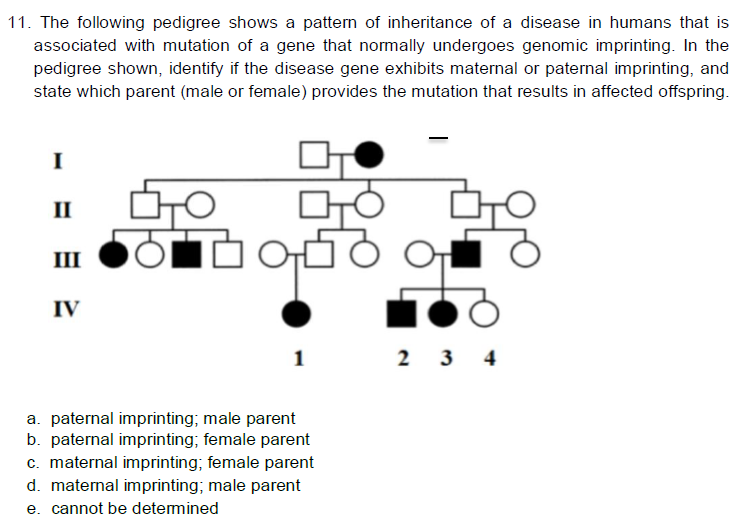
C
You are studying a region of a chromosome and observe an unusually high number of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) activity associated with the histones.
What would you predict about the transcriptional activity of a gene in this region?
a. Since the DNA becomes more accessible to transcription factors and RNA polymerase, there would be less gene transcription.
b. Since the DNA becomes inaccessible to transcription factors and RNA polymerase, there would be more gene transcription.
c. Since histone acetyltransferases remove acetyl groups from histone tails, gene transcription would be reduced as the chromatin becomes more condensed.
d. Since histone acetyltransferases add acetyl groups to histone tails, gene transcription would increase as the chromatin becomes more accessible.
e. Since acetyl groups added to histone tails tighten the interaction between histones and DNA, the gene in this region would be less actively transcribed.
D
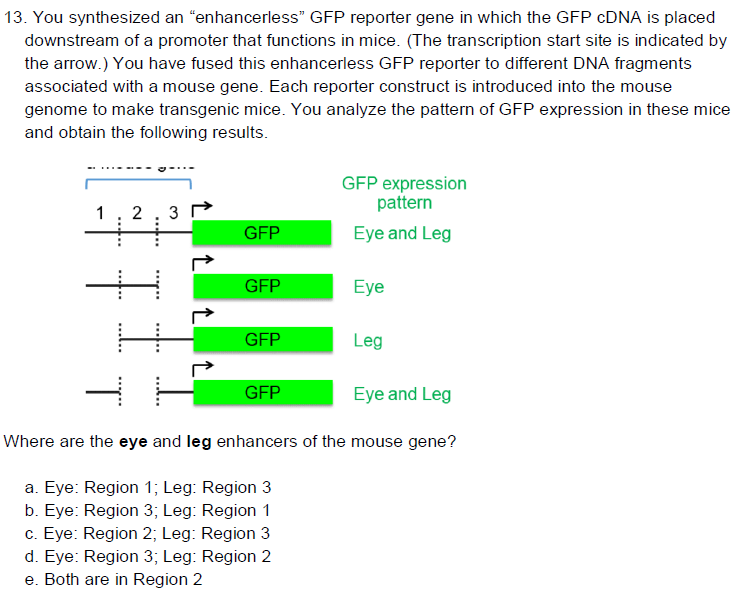
A
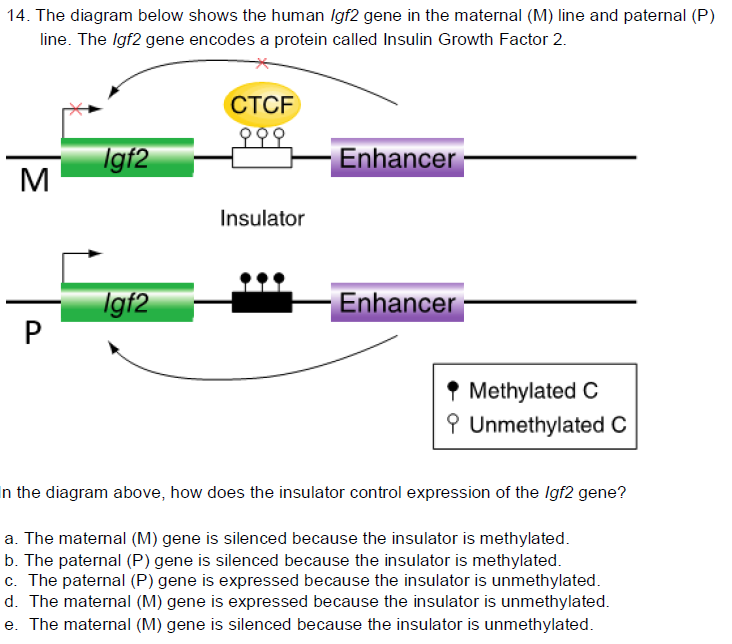
E
The X-linked FMR-1 gene contains a trinucleotide (CGG) repeat region. Expansion of this region results in fragile X syndrome. Suppose you are male who carries a single FMR-1 allele with 15 (CGG) repeats. You design two PCR primers, each 20 nucleotides long, that flank the repeat region immediately on both sides. What is the expected size (in base pairs) of the PCR amplification product?
a. (15 repeats × 3) + 20 = 65 bp
b. (15 × 3) + 20 + 20 + 15 = 100 bp
c. (15 repeats × 2) + 20 + 20 = 70 bp
d. (15 repeats x 3) + 20 + 20 = 85 bp
e. 2 (15 repeats x 3) + 20 + 20= 130 bp
D
Common red clover, Trifolium pratense, is a diploid with 14 chromosomes per somatic cell. What would be the somatic chromosome number of a trisomic variant and a triploid variant of this species, respectively?
a. 14; 28
b. 14; 42
c. 15; 21
d. 42; 14
e. 21; 15
C
The coding sequence of the green fluorescent protein gene (GFP) is placed under the control of an enhancer active in neurons. When this transgene is introduced into flies, GFP will be expressed in
a.
all cells in the early embryo and then GFP will be silenced.
b.
all fly cells that have the transgene.
c.
all cells in the late embryo after neurons form.
d.
all neuron cells or a subset of neurons.
e.
all fly cells that do not have the transgene.
D
What is one main advantage for using CRISPR/Cas9 for genome editing over other methods?
a. Without CRISPR/Cas9, DNA molecules introduced into cells could never recombine into the genome by homologous recombination.
b. CRISPR/Cas9 makes knockins and knockouts efficiently by introducing therapy genes into patient cells with viral vectors.
c. CRISPR/Cas9 is so efficient for making knockouts and knockins that you don’t need to use embryonic stem cells to grow a clone of a single rare cell that has undergone homologous recombination.
d. CRISPR/Cas9 makes double-strand breaks at nonspecific sites in DNA, which promotes homologous recombination at many sites.
e. CRISPR/Cas9 makes all somatic cells behave like embryonic stem cells (ES cells).
C
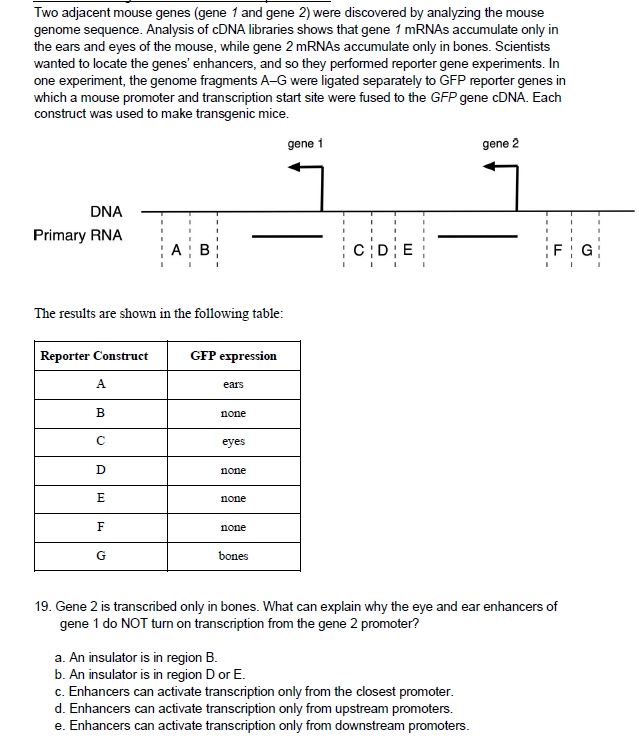
B
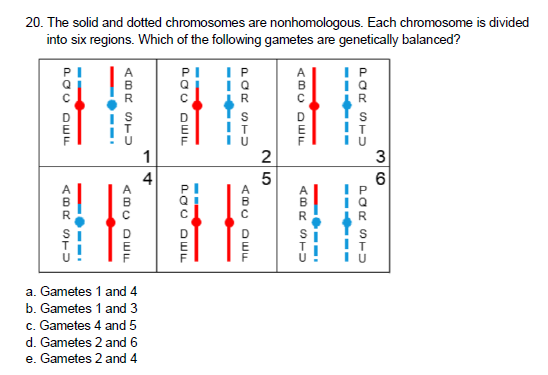
B