EVS AEC - 1
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards to help students review Environmental Science lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
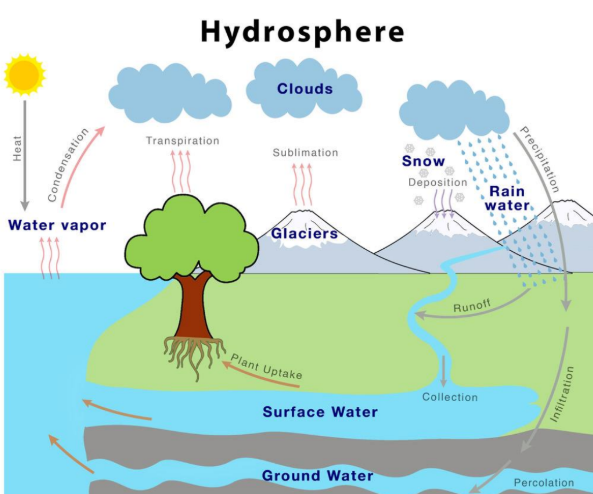
Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere comprises all of Earth's water, including oceans, lakes, rivers, glaciers, and groundwater.
Homeostasis
A self-regulating process by which a living organism can maintain internal stability while adjusting to changing external conditions.
Homeostasis Definition
Auto-regulation of a biological system that maintains equilibrium.
Grassland
A biome characterized by vast stretches of land dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants, with few trees or shrubs.
also known as prairie or savanna
Where are grasslands typically found?
in areas with moderate rainfall and and moderate to high temperatures
Land degradation
The deterioration of the quality of land resources, often resulting from human activities (like deforestation, mining, unsustainable agriculture practices, etc.)
How does land degredation manifest?
In various forms such as soil erosion, loss of soil fertility, contamination by pollutants, etc/
Fossil fuels
Natural resources formed from the remains of ancient organisms, primarily plants and microorganisms, that lived millions of years ago.
Examples of fossil fuels
Coal, oil (petrol), natural gas, kerosene and propane.
How is coal formed?
Formed from the remains of plants that were buried and put under high pressure and heat for millions of years
How is oil and natural gas formed?
Formed from the remains of marine organisms that were buried under layers of sediment and subjected to heat and pressure over millions of years.
Fossils are __________ resources?
non-renewable
What are non-renewable resources?
Finite resources that cannot be replaced within a human time scale.
Pollutants
Substances or agents introduced into the environment that cause harm or discomfort to living organisms or ecosystems.
Can be in various forms such as chemicals, particulates, biological materials, etc.
Common examples of pollutants
Carbon dioxide from vehicles
Pesticides from agriculture
Noise pollution from transportation
Soil erosion
The process where soil is displaced or washed away by natural elements like water, wind, or ice, often exacerbated by human activities, leading to land degradation and loss of fertility.
Primary productivity
The rate at which producers (like plants and algae) in an ecosystem convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis, forming organic compounds.
Foundation of energy flow in food chains and ecosystems
Hazardous waste
Any discarded material that poses a substantial or potential threat to public health or the environment due to its chemical, physical, or biological characteristics.
Examples- chemicals, solvents, pesticides, batteries, etc.
Forest ecosystem
A community of organisms that live within a forested area and interact with each other and their environment.
Biosphere
The global ecological system that integrates all living organisms and their interactions with the non-living components of Earth (like the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere)
Biomass
Organic materials derived from living or recently living organisms, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms.
These materials can be used as a source of energy (converted into biofuel)
Examples- wood, organic waste, agricultural byproducts, etc.
Lithosphere
The outermost layer of Earth's structure, includes the crust and the uppermost portion of the mantle.
Ecosystem services
The benefits humans gain from ecosystems
Includes provisioning (food, water), regulating (climate control, flood prevention), supporting, and cultural services.
These services are essential for human well-being and economic growth
Problems and challenges of hazardous waste management in India
Lack of Comprehensive Legislation: India has legislation like Hazardous Waste Management Rules (2016), the Environment Protection Act, etc. But they lack proper implementation and require stronger regulations.
Inadequate Infrastructure: India has a shortage of proper waste treatment facilities for hazardous waste, which leads to unsafe disposal methods like landfilling, burning and dumping in water bodies.
Informal Sector Involvement: As the handling of hazardous waste is usually done by informal workers in unsafe conditions, it poses even more of an environmental and health risk.
Poor Monitoring & Accountability: Weak enforcement allows illegal disposal practices.
Lack of Public Awareness: Limited understanding among citizens about hazardous waste
From an Indian perspective, is sustainable development conceivable in emerging markets?
Yes, sustainable development is conceivable in emerging markets like India, though it requires strategic efforts across multiple areas:
Optimizing Resource Use: India faces resource constraints, but sustainable practices in energy, water, and land management can drive efficient development.
Balancing Industrial Growth & Conservation: Rapid urbanization must be paired with pollution control, afforestation, and wildlife protection to avoid environmental degradation.
Ensuring Inclusive Growth: Sustainability must benefit all, especially marginalized communities, through access to education, healthcare, and skill development.
Leveraging Technology & Innovation: Digital solutions like e-governance and agritech provide opportunities for efficiency and transparency in development.
Strengthening Policy Frameworks: Existing regulations on environmental protection and urban planning need rigorous enforcement and continuous adaptation.
Building Climate Resilience: Strategies like resilient infrastructure and disaster preparedness help mitigate climate risks affecting vulnerable populations.
Encouraging Global Collaboration: International partnerships enable knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and financial support, accelerating sustainable progress.
Development Projects in India
Sardar Sarovar Dam Project
Posco Steel Plant
Arunachal Pradesh Hydroelectric Projects
Western Ghats Development
Sardar Sarovar Dam Project
Placed on the Narmada River, this is one of the largest dam projects in India
Its aim was to provide water for irrigation, drinking and hydropower water generation
But, the dam’s construction led to the ruin of forests, displacement of indigenous communities and threatened biodiversity
There has also been a decline in the population of aquatic species, disruption of river ecosystems, waterlogging, etc.
Posco Steel Plant
The Posco Steel Plant was proposed in Odisha
It could potentially destroy mangrove forests, disrupt wildlife habitats, and pollute water bodies.
Arunachal Pradesh Hydroelectric Projects
Arunachal Pradesh has had several plans for dam projects for hydroelectric development
These projects involved damming rivers and diverting water, which left to loss of biodiversity and distrubance in river flow.
These dams also submerged forests, grasslands and displaced both human and wildlife populations
Western Ghats Development
The Western Ghats are under threat due to various development projects, including infrastructure expansion, mining, deforestation, etc.
The construction of roads, highways and railways fragmented wildlife habitats
Mining activities led to soil erosion, pollution, and destruction of habitats
How is environmental studies multidisciplinary in nature?
It consists of various areas of study including: natural sciences, social sciences, humanities, engineering and technology, and health sciences
What do natural sciences consist of?
Ecology: Studies the interactions between organisms and their environment, like the flow of energy through ecosystems
Geology: Explores the Earth’s structure, composition and processes, esp those related to issues like soil erosion and other geological hazards
Chemistry: Analyses the chemical composition of environmental components such as air, water and soil.
Biology: Investigates the biodiversity, conservation and ecological roles of various species.
What do social sciences consist of?
Sociology: Examines how human societies interact with the
environment
Economics: Studies the allocation of resources, market dynamics and policies related to environmental conservation
Political Science: Analyses the political processes, institutions,
and policies shaping environmental governance
Anthropology: Explores the cultural dimensions of
environmental attitudes, practices, and perceptions
What does humanities consist of?
Philosophy: Considers ethical, moral, and value-
based questions related to the environment, sustainability, and the value of nature.
History: Traces the historical trajectories of
human-environment interactions
Literature and Arts: Provides cultural perspectives on nature, environmental themes, and the human relationship with nature
What do health sciences (like public health) consist of?
Public health investigates the impacts of environmental factors on human health
Nuclear energy
A form of power generated by nuclear reactions, most commonly through the process of nuclear fission.
What are the Environmental Impacts of Nuclear Energy?
Radioactive contamination (Chernobyl disaster)
Water pollution
Radiation exposure
Long-term storage challenges
Accidental releases
What is the importance of restoring degraded ecosystems?
Enhancing the quality of life for residents
Promoting biodiversity
Mitigating climate change impacts
Fostering resilience to environmental challenges
What is the process of restoring degraded ecosystems?
Assessment and Planning: Evaluating the extent of degradation, identifying key areas that need restoration and setting goals (urban planners, ecologists, etc.)
Ecological Restoration Techniques: Various techniques such as reforestation, wetland restoration, green infrastructure implementation, etc. are used for restoration
Community Engagement: Engaging local communities can contribute valuable knowledge, labour and support in restoration
Monitoring Progress: Continuous monitoring of the projects can help assess progress and refine strategies
Pond ecosystems
Ponds are relatively smaller, shallow bodies of standing water
They have still or slow moving water, which leads to different temperature and oxygen levels in the water
Include aquatic plants and species of fish, amphibians, etc. but they are specifically adapted to the pond
Ponds are more vulnerable to human impacts such as pollution, habitat destruction, etc.
River ecosystems
Rivers are natural flowing bodies of water that continuously move downstream
This continuous flow varies in speed and volume
Rivers offer diverse ecosystems based on depth, flow, etc.
Rivers face threats like pollution, dam construction, urban development, etc.
High Line (New York City)
A project in NYC that transformed an old elevated railway into a vibrant urban park, providing habitat for various plant species and attracting birds and insects.
What is the difference of Pond ecosystens with Rivers Size and Flow
Ponds are relatively small, shallow bodies of standing water, Rivers, on the other hand, are natural flowing bodies of water that continuously move downstream
What is the renewability difference between renewable and non renewable sources of energy
Renewable energy sources are naturally replenished on a human timescale
Non-renewable energy sources are finite and are depleted over time as they are extracted and used.
What is the Abundance Difference between Renewable and non-renewable sources of energy
Renewable energy sources are abundant and widely distributed globally.
Non-renewable energy sources are limited in quantity and distribution.
What is the Environemtal Impact difference between Renewable and non renewable sources of energy
Renewable energy sources generally have lower environmental impacts compared to non-renewable sources and produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
Non-renewable energy sources often have significant environmental consequences associated with their extraction, processing, and combustion
What are the different types of pollution that occur in metropolitan cities
Air pollution
Water pollution
Noise pollution
Soil pollution
Thermal pollution
Visual pollution
Air pollution
The presence of harmful substances in the air (such as gases, particulates, and biological molecules) which negatively impact human health and the environment.
Water pollution
The contamination of water bodies (rivers, lakes, oceans, groundwater) due to chemicals, waste, or microorganisms, making the water unsafe for consumption and harming ecosystems.
Noise pollution
Excessive or disruptive sound that negatively affects human health, wildlife, and environmental quality, often caused by transportation, industrial activities, and urbanization.
Soil pollution
The contamination of soil with toxic substances, including heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial waste, reducing soil fertility and posing health risks.
Thermal pollution
The rise or drop in water temperature due to human activities, such as industrial discharge.
Visual pollution
The degradation of the visual environment due to unattractive or disruptive elements, such as excessive advertisements, urban clutter, and poorly planned infrastructure
What are the Abiotic Features of a Grassland Ecosystem
Temperate climate with distinct seasons, Deep, fertile soils rich in organic matter and Varying water availability influences plant and animal distribution.
What are the Biotic Features of a Grassland Ecosystem?
Dominated by grass species
Home to herbivores like bison and antelope
Supports predator animals such as wolves
Rich insect life and microorganisms
Various bird species
What are the abiotic features of a grassland ecosystem?
Temperate climate with distinct seasons
Deep, fertile soils rich in organic matter
Diverse topography
Periodic fires (natural)
Open habitat with ample sunlight
What is the importance of this Grassland ecosystem
Home to diverse plant and animal species
Helps mitigate climate change by storing carbon
Prevents erosion and maintains soil health.
Aquatic food web
Describes the flow of energy and nutrients through a marine or freshwater ecosystem
Primary producers- phytoplankton (marine) and algae (freshwater); convert sunlight into energy and nutrients through photosynthesis
Primary consumers- zooplankton, small fish and some invertebrates; feed on primary producers and consumed by secondary consumers
Secondary consumers- Larger fish, predatory invertebrates and marine mammals
Tertiary consumers- Large fish, marine mammals and apex predators (dolphins, seals, sharks, killer whales); occupy higher levels of the food web, preying on secondary consumers
Decomposers- Bacteria and fungi; break down dead organisms and organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem
Primary productivity
The rate at which plants and other producers convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis
Desert ecosystems have high primary productivity than forest ecosystems (T/F)
False—forests have more sunlight, water and nutrient rich soil
The agriculture sector in India utilizes more water than industrial sector (T/F)
True—Agriculture is the largest consumer of water in India (78-80%)
Ozone at ground level is a major air pollutant (T/F)
True—Ground level ozone is a harmful pollutant through smog
Interconnected networks of food chains are called food webs (T/F)
True
Savannas are an example of mangrove forests (T/F)
False—Savannas are grassland, not mangrove forests
Mangrove forests
Coastal wetlands found in tropical and subtropical regions
Savannas
Open landscapes with scattered trees and shrubs, typically found in regions with seasonal rainfall
E-waste
Electronic waste i.e. discarded electronic devices like computers, mobile phones and televisionsEut
Eutrophication
Excessive nutrient enrichment in water bodies, often due to agricultural runoff
Leads to dense algae growth that harms aquatic life
Green energy
Energy derived from natural sources like sunlight, wind, water, etc. that doesn’t harm the environment and is renewable
Decomposers
Organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem
Organic farming
A sustainable method of farming that avoids synthetic chemicals, instead relying on natural fertilizers and ecological balance to maintain soil health
Tropical rainforest
Receive high rainfall throughout the year (200 cm or more)
Dense, evergreen trees
Rich in biodiversity, a vast range of flora and fauna
Nutrient rich soil
Found in regions like the Western Ghats and Northeast India
Thorn and scrub forests
Exist in semi-arid regions with less than 70 cm of rainfall
Short, thorny trees and shrubs
Fewer species adapted to harsher climates
Dry and less fertile soil
Common in Rajasthan, Gujarat and parts of Madhya Pradesh
Primary succession
Occurs in lifeless areas where no previous ecosystem existed, such as newly formed volcanic islands or glacial retreats
Starts with pioneer species like lichens and mosses
Secondary succession
Happens in previously inhabited areas that have been disturbed (like after a wildfire or deforestation)
Since soil is already present, recovery is faster compared primary succession
Wind energy
Harnesses kinetic energy from moving air
Clean and renewable
High initial costs but low operational expenses
Depends on wind availability
Wind farms can be expanded by adding turbines
Thermal energy
Thermal energy comes from heat sources like fossil fuels or geothermal reservoirs
Can contribute to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions
Thermal plants require continuous fuel supply
It provides consistent power
Thermal plants require extensive infrastructure
Causes of soil pollution
Excessive use of pesticides, fertilizers, etc. contaminates soil
Industrial waste from factories like chemicals, heavy metals and hazardous waste causes contamination
Improper disposal of solid waste, untreated sewage, etc. pollutes soil
Deforestation and urban expansion cause soil erosion and degradation
Mining of minerals releases harmful substances in the soil
Oil spills contaminate soil and harm plant growth and groundwater
Plastic waste management strategies
Reduce single-use plastics: Encourage reusable bags, bottles and packaging instead of disposable plastics
Efficient waste collection and segregation: Establish proper systems to separate plastic waste for recycling
Recycling: Processing plastic waste into new items or repurposing materials
Innovative tech: Advancing recycling methods like chemical recycling
Public awareness: Promoting responsible usage of plastic and its disposal
Government policies: Bans on harmful plastics and incentivising sustainable practices
National Solar Mission
Key initiative by the govt. of India to promote solar energy
Launched in January 2010
Aims to establish India as a global leader in solar power by creating favourable policy conditions for widespread adoption
Large scale solar projects, research and development, policy and financial support
Environment
All the biological and non-biological entities surrounding us
Environment Protection Act (EPA), 1986
Defines that environment consists of biotic and abiotic factors that surround us, with which we continuously interact
Resources
Anything which is useful to us or which can be transformed into a useful product
Levels of biodiversity
Genetic diversity: Genetic variability present within species
Species diversity: No. of different species present in an ecosystem
Ecosystem diversity: The variations in an ecosystem within a geographical location & its impact on human existence
Pollution
Any undesirable change in physical, chemical and biological properties of any component of environment such as water, air and soil
Types of pollutants
Biodegradable: Degraded by microorganisms
Non-biodegradable: Degraded by plastic
Components of environment
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
Atmosphere
Biosphere
Atmosphere
The layer of gases that surround a planet like Earth
Composition of Atmosphere
78% of nitrogen and 21% of oxygen
Sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Food chain
Illustrates the flow of energy and nutrients as one organism consumes another in an ecosystem
Types of ecosystems (based on occurrence)
Natural ecosystem
Man-made/ artificial ecosystems
Types of ecosystems (based on habitat)
Terrestrial ecosystems: forest, grassland, tundra, desert
Aquatic ecosystems: freshwater (river, lake, pond), marine (ocean, sea)
Tundra
A cold, treeless biome with a permanently frozen ground, minimal rain, short summers, and vegetation like mosses and lichens.
Supports wildlife like arctic foxes and reindeer.
Arctic tundra, Antarctic tundra
Food pyramid
Diagrammatic representation of the relationship of the numbers, biomass and energy content of each part of the food web
Assimilation
Digested food being changed into simpler components
Atmospheric aerosols
The suspension of particles in the atmosphere
Causes of deforestation
Urbanisation and infrastructure development
Mining
Forest fires
Logging and extraction of wood
Impacts of deforestation
Loss of biodiversity
Accelerated climate change
Soil erosion and land degradation (loss of tree roots weakens soil)
Displaces indigenous communities