RHS Honors A&P Unit 5 Protection
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
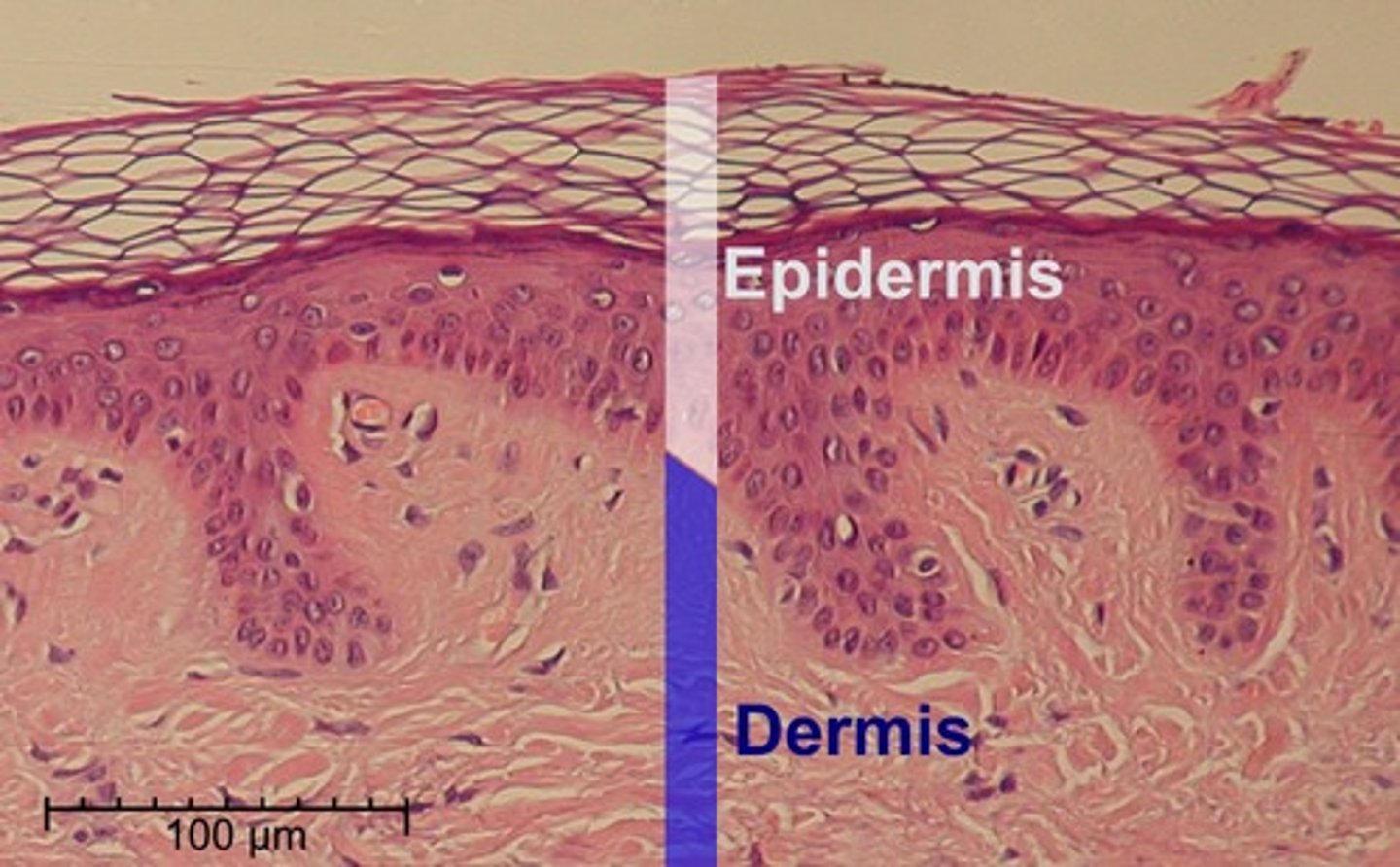
Cutaneous membrane
The skin; composed of epidermal and dermal layers
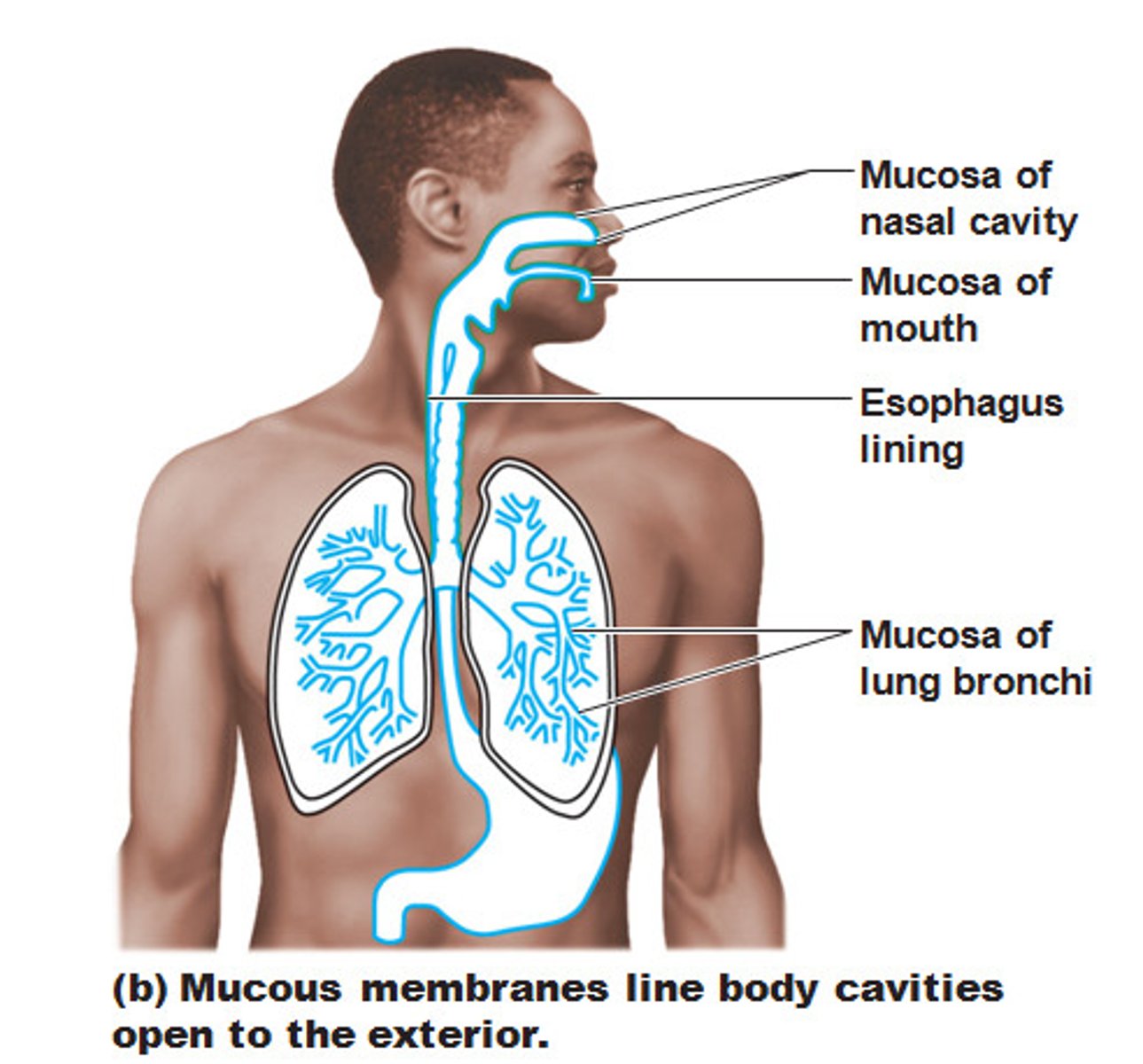
Mucous membrane
Membrane that secretes mucus that lubricates the surface of organs and keeps them moist; exposed to the exterior of the body
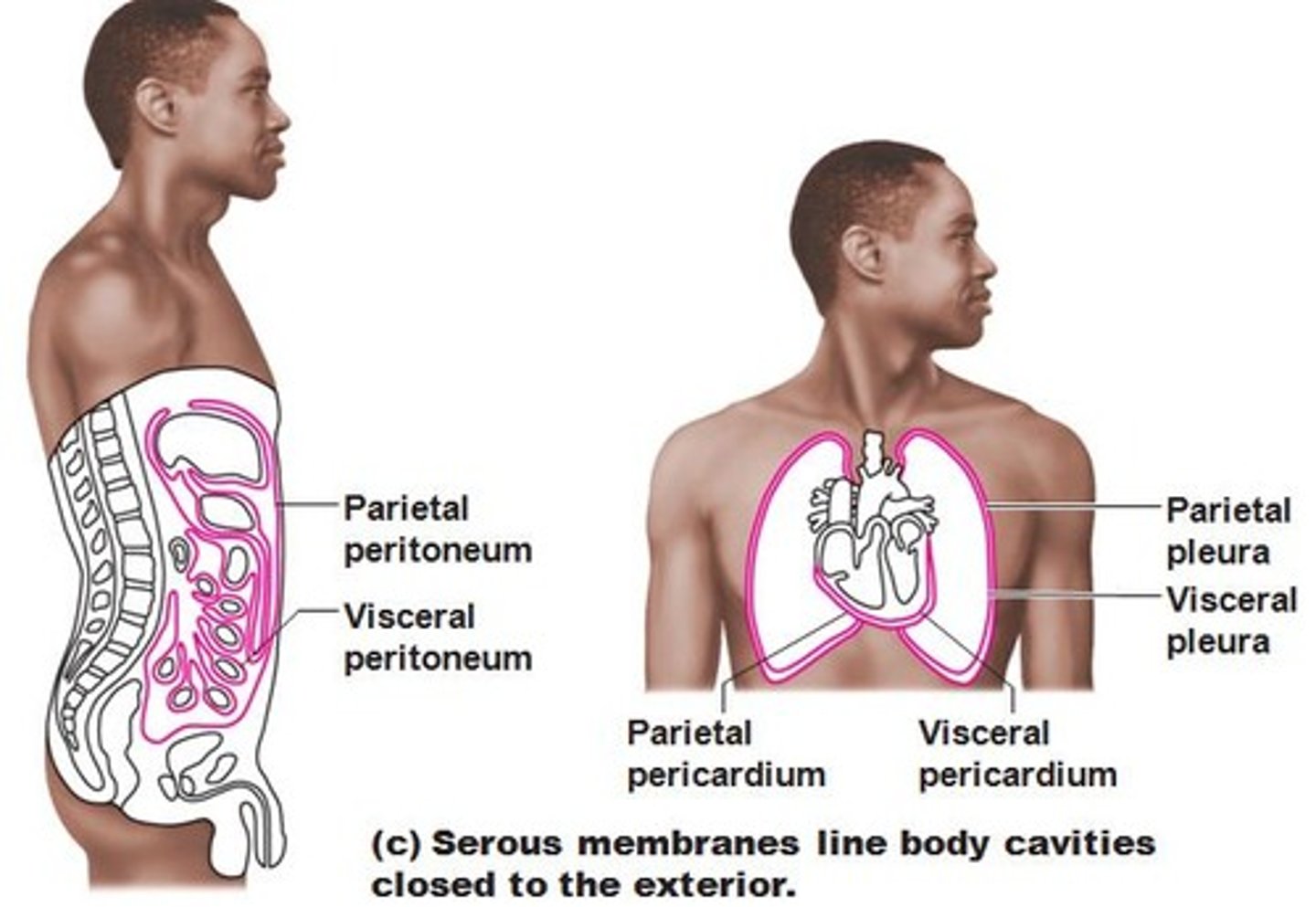
Serous membrane
Membrane that lines a cavity without an opening to the outside of the body
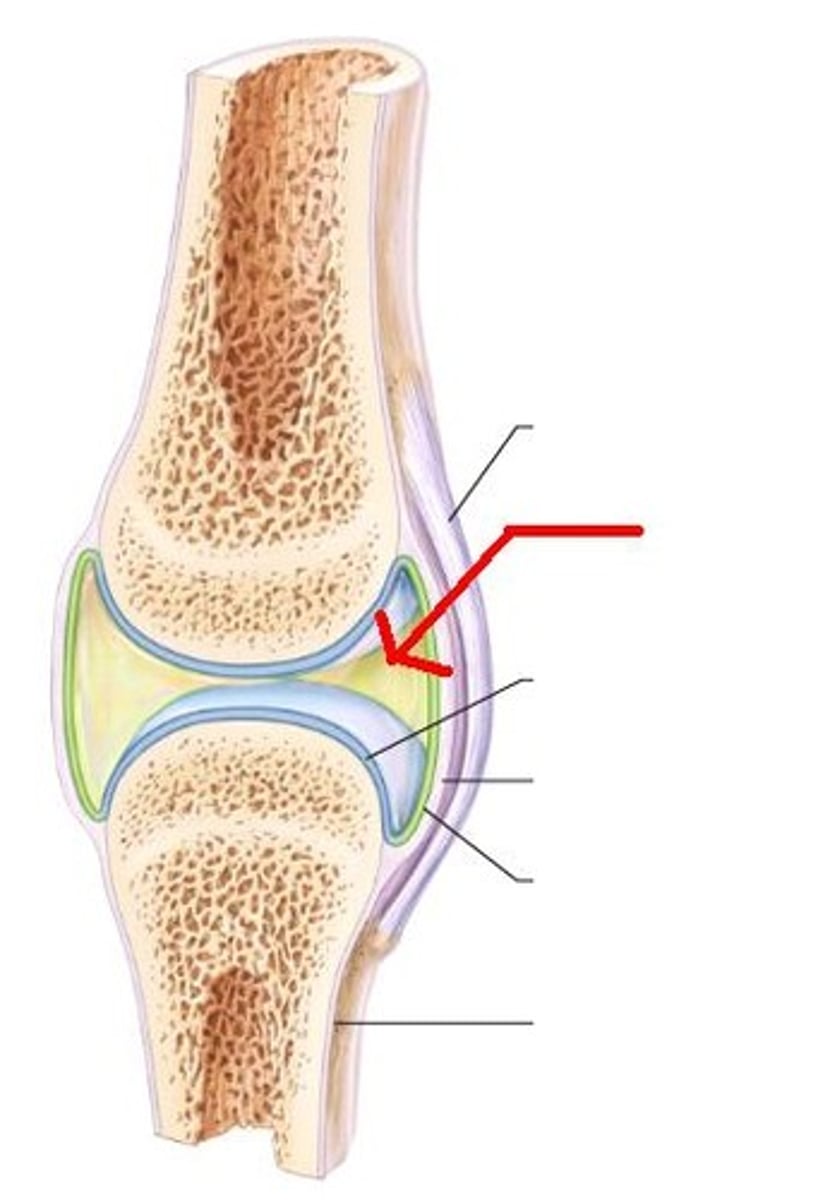
Synovial membrane
membrane lining the capsule of a joint
What are the functions of the integument system?
protecting the body from:
- fluid loss
- injury
- infection
- temperature regulation
- collecting information from the outside
Skin: Epidermis
Outer layer of skin that consists of dead cells that stop water loss and protect the body against invasion by microorganisms.
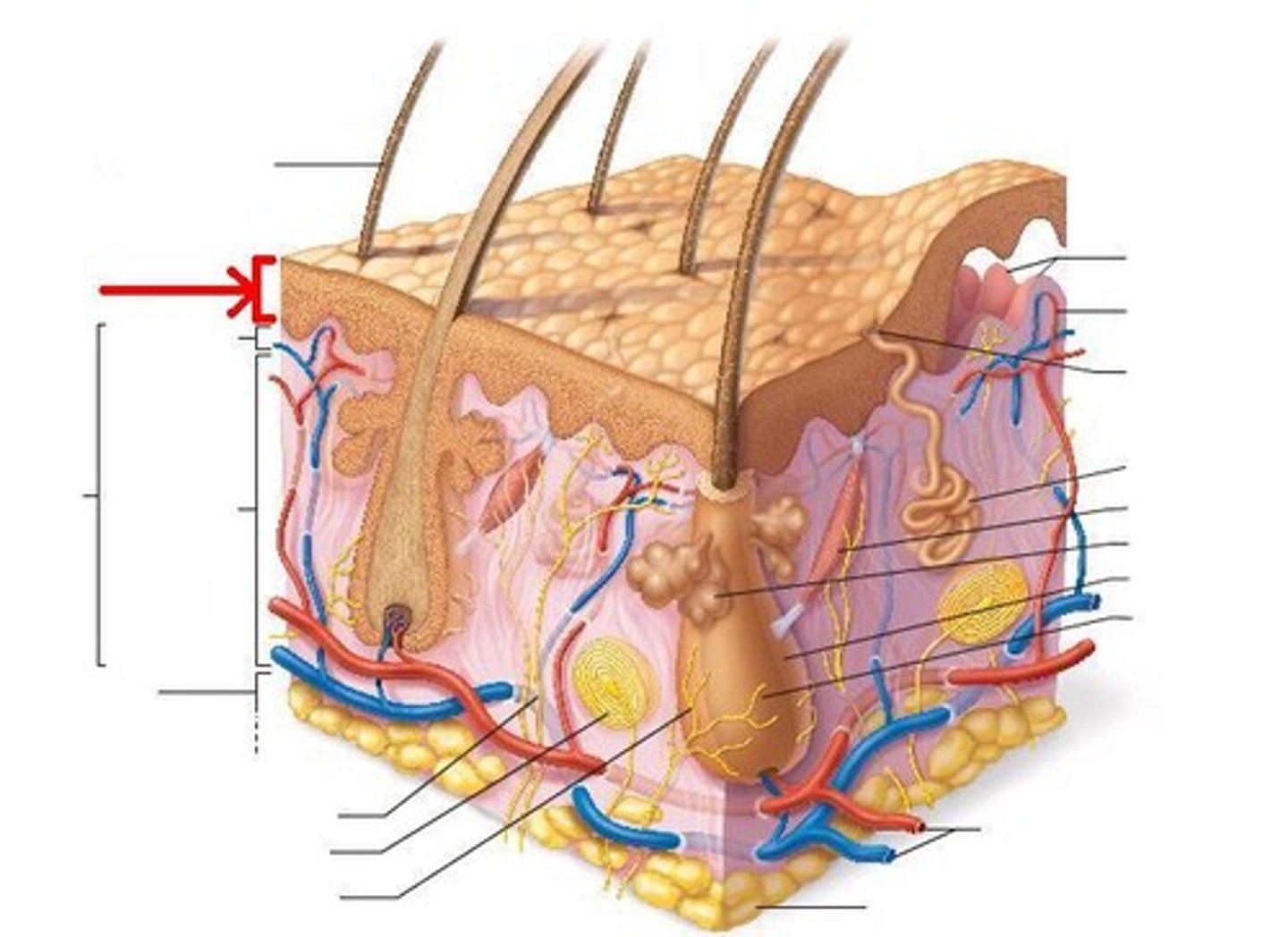
Skin: Dermis
Middle layer of skin containing sensory receptors, sweat glands, hair follicles and small blood vessels.
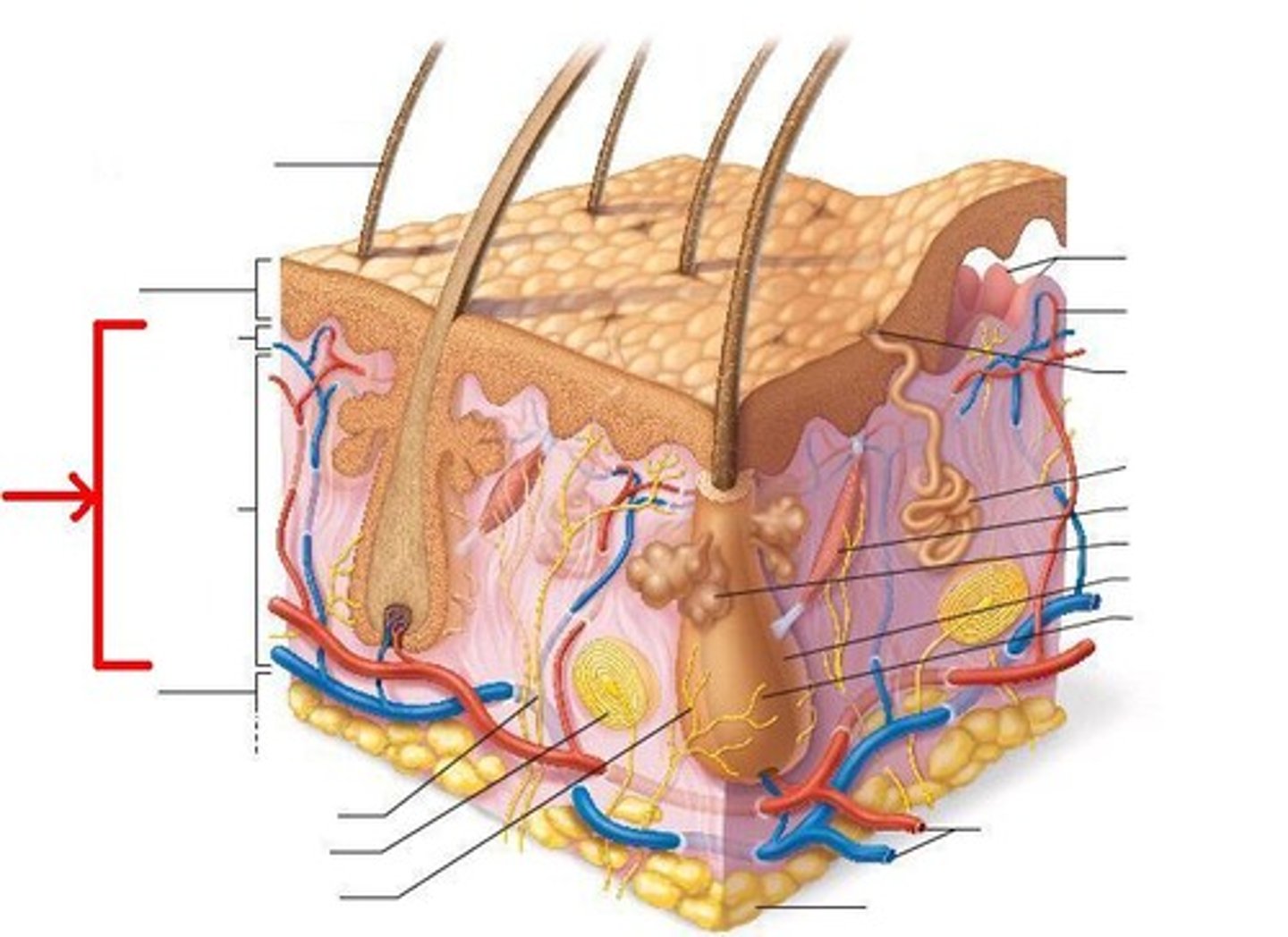
Skin: Hair
Flexible epithelial structures composed of keratinized cells; produced by the hair follicle.
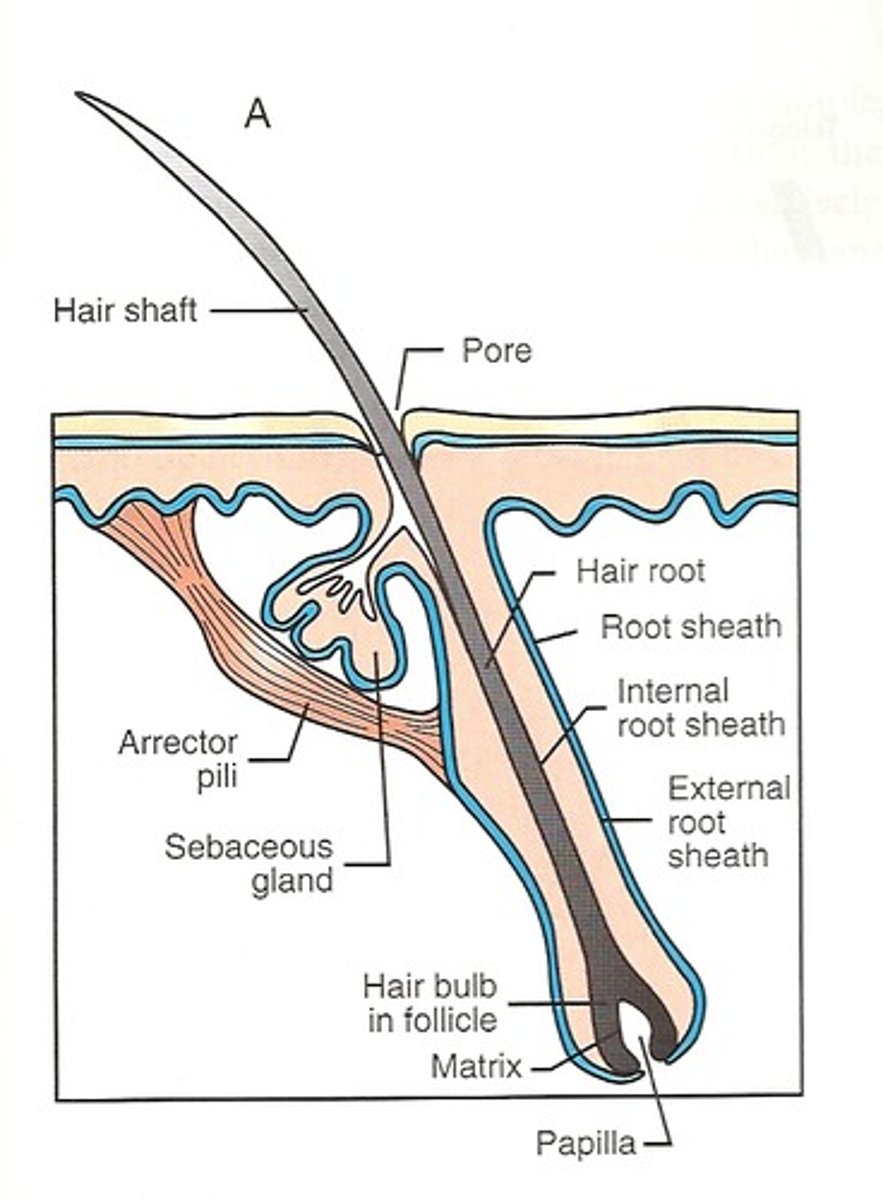
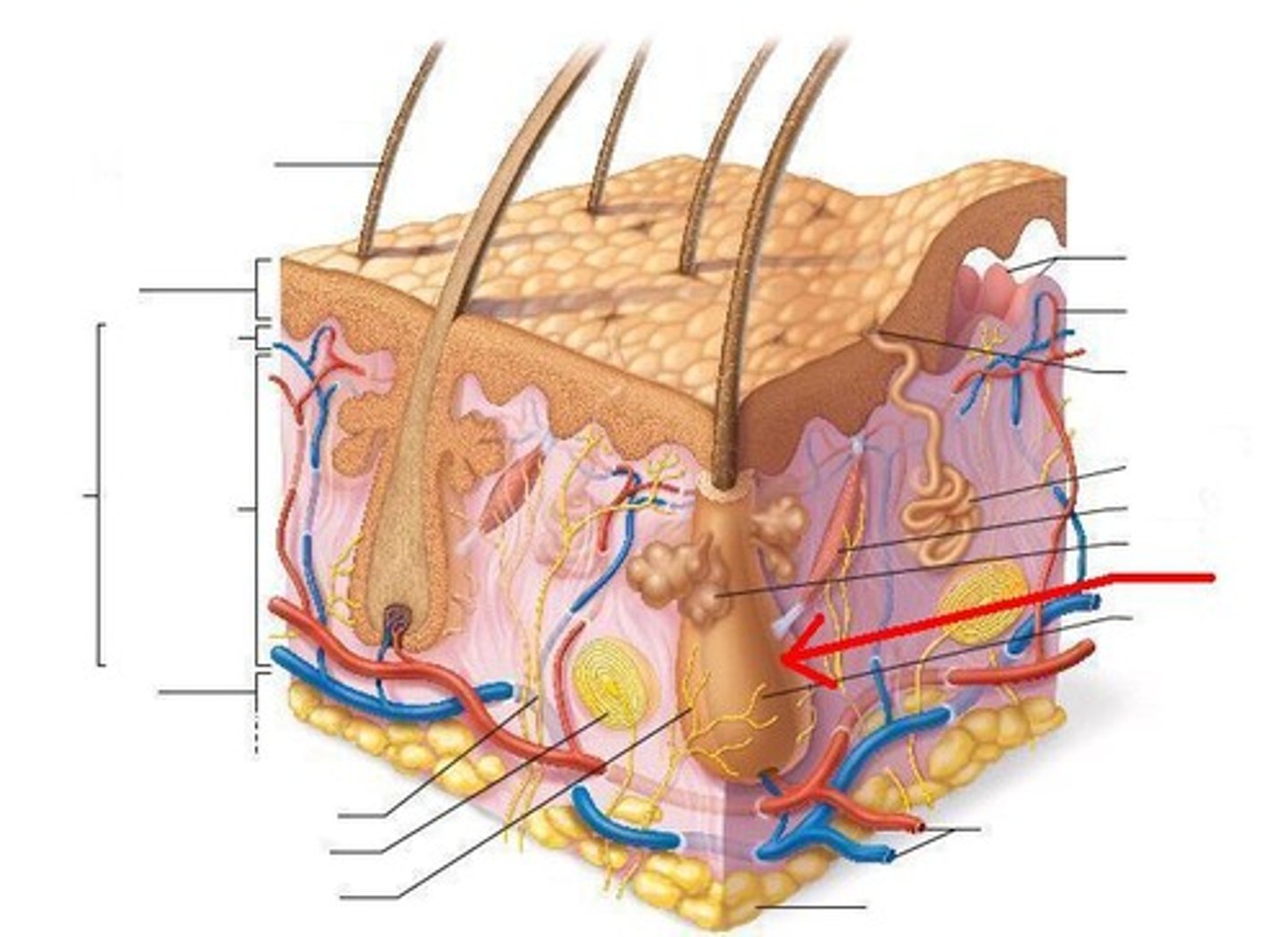
Skin: Hair follicle
Structure of both inner and outer root sheaths that produces hair.
Skin: Sebaceous gland
Glands that excrete sebum into hair follicles
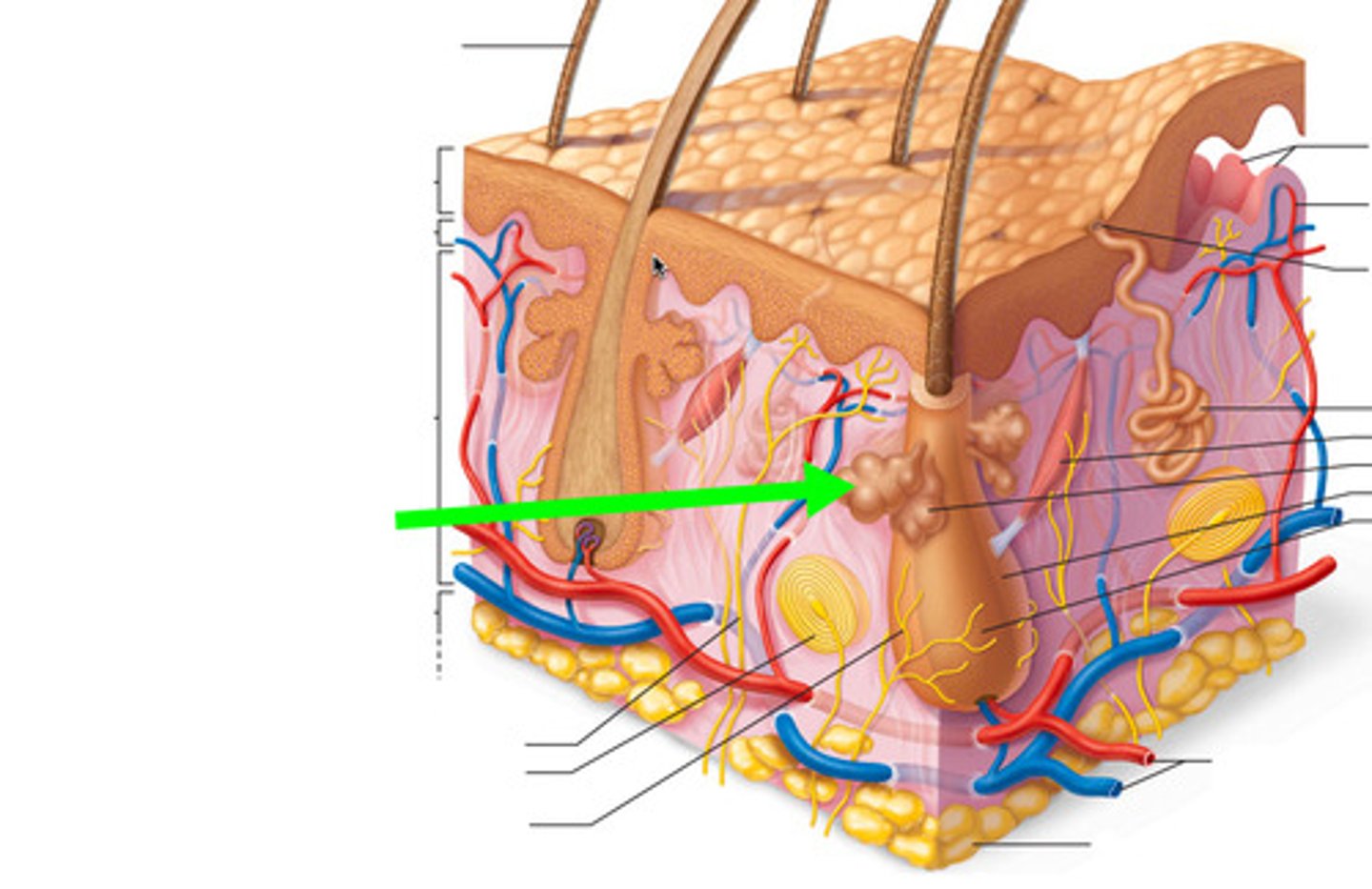
Skin: Sweat gland
The glands that secrete sweat, located in the dermal layer of the skin.
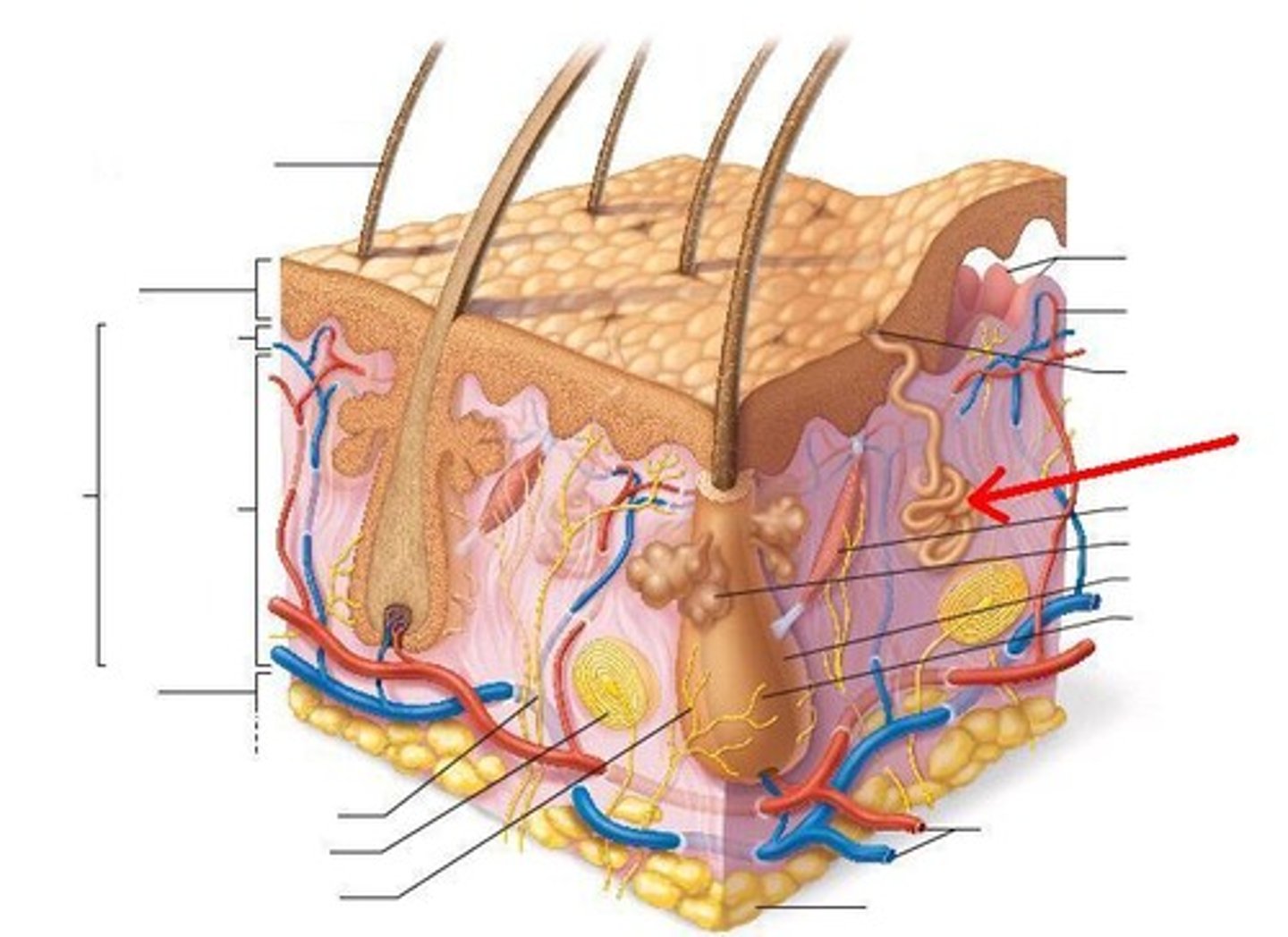
5 layers of epidermis (deep to superficial)
1. stratum basale
2. stratum spinosum
3. stratum granulosum
4. stratum lucidum
5. stratum corneum
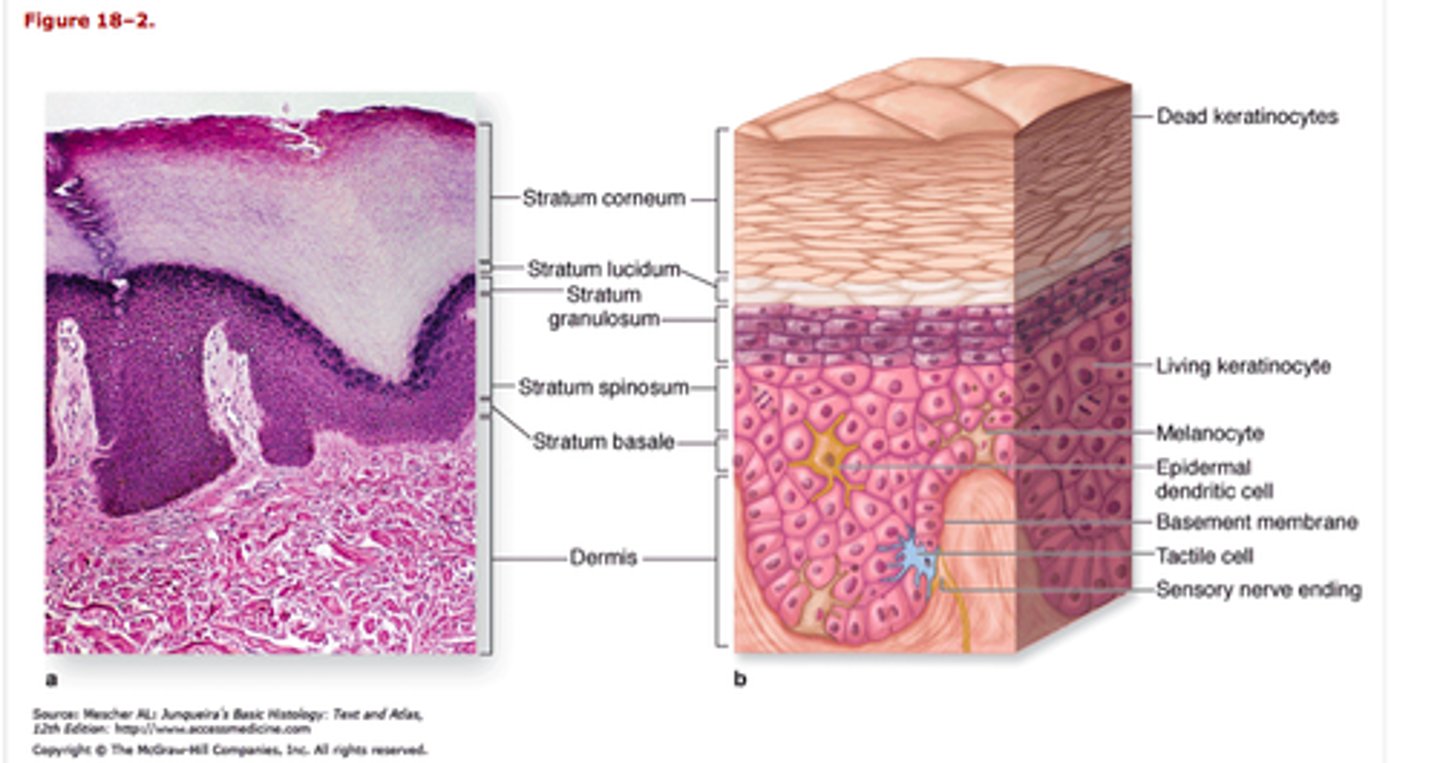
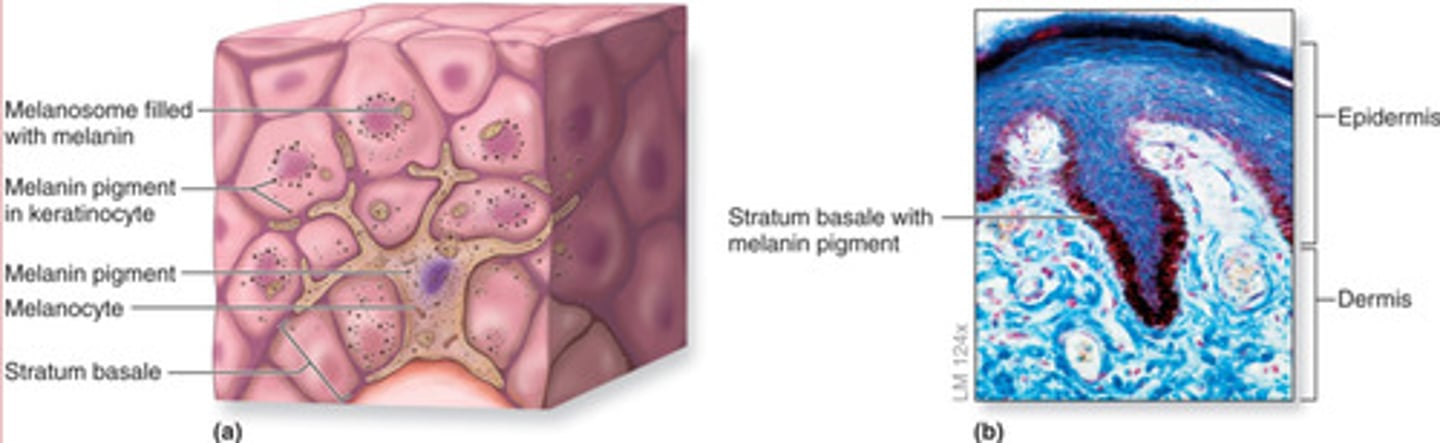
What cells are responsible for skin color?
melanocytes
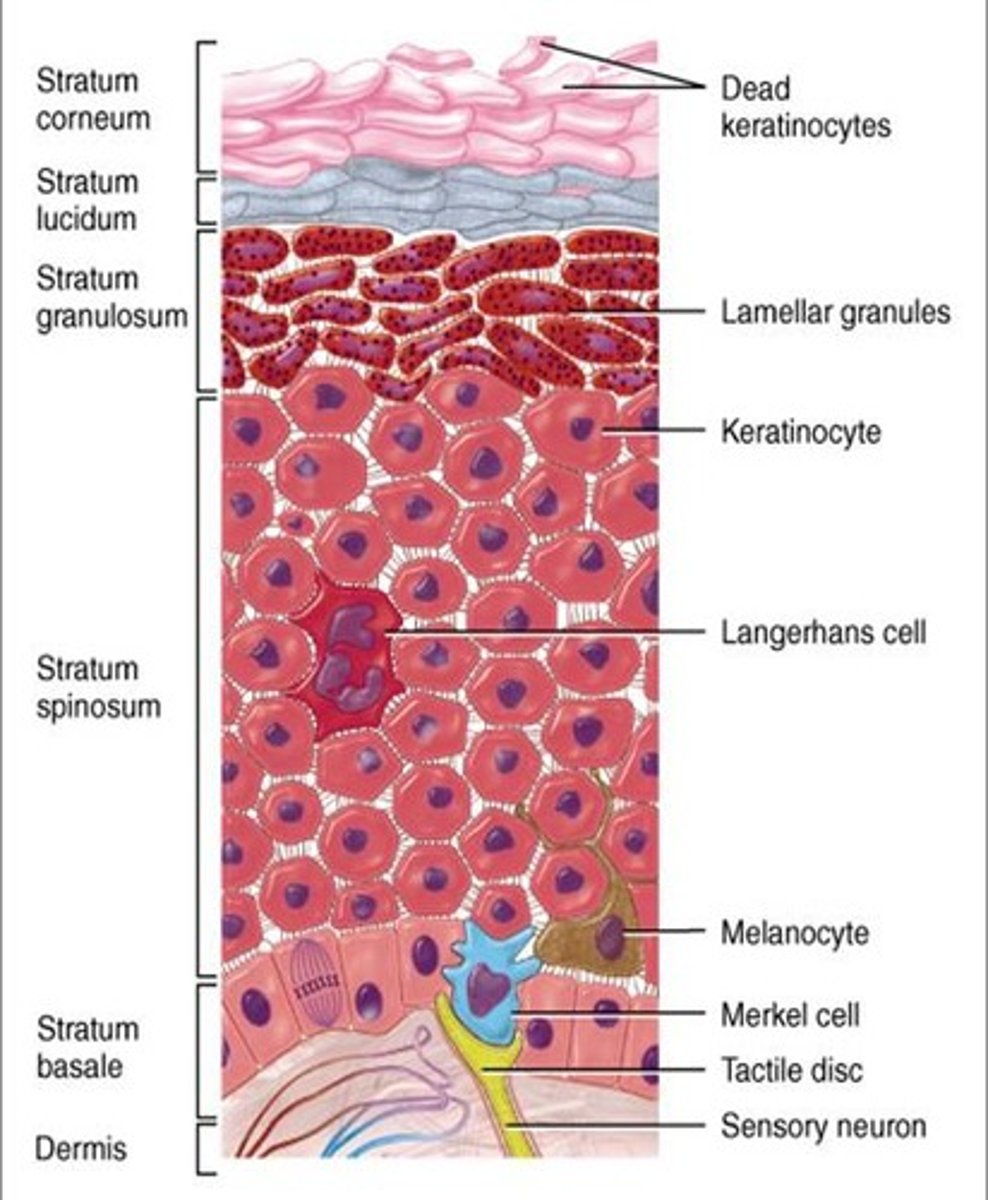
Melanin production
Stimulated by exposure to sunlight and protect cells below by absorbing and blocking UV radiation
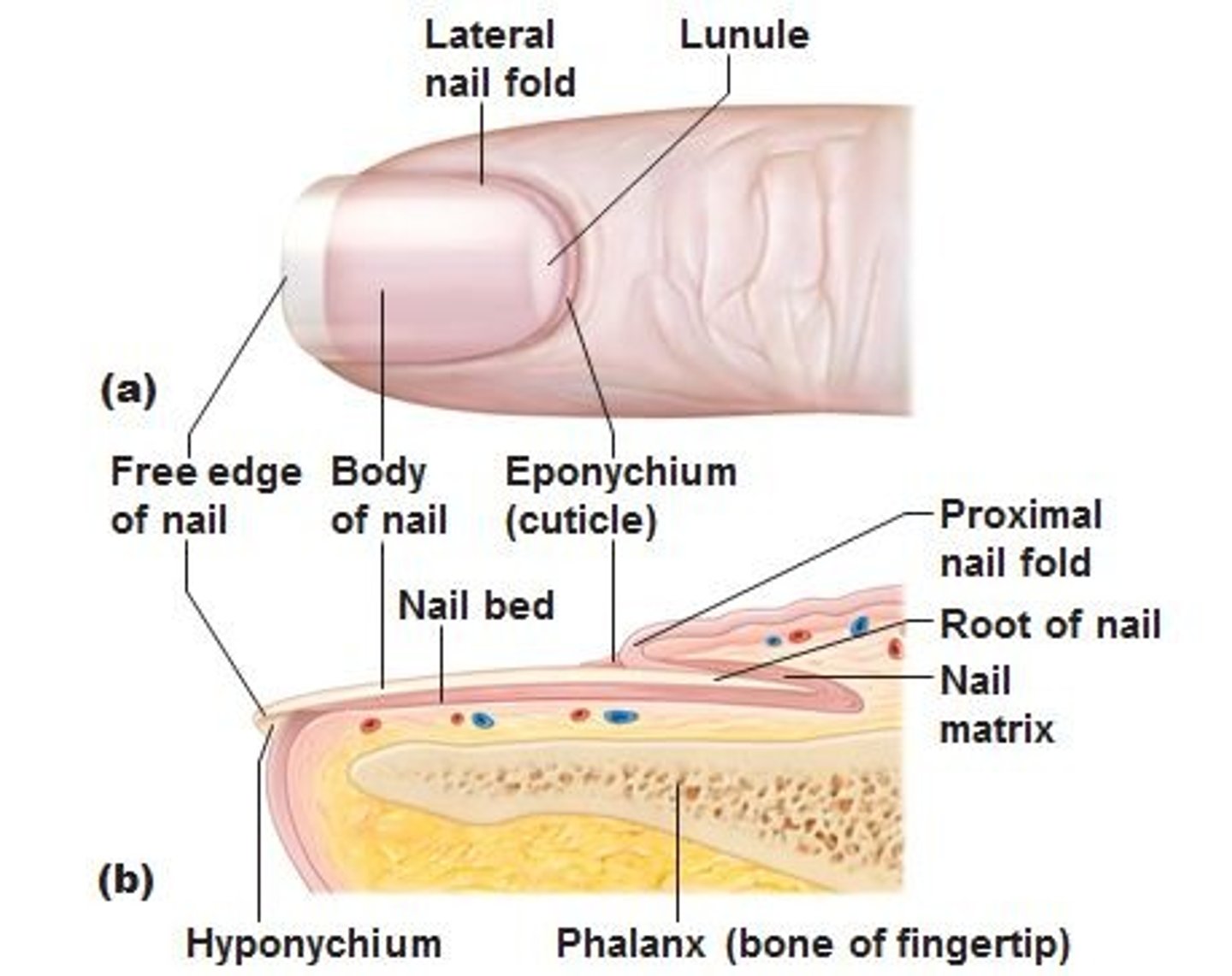
Nails are composed of
hard, keratinized epidermal cells located over the dorsal surfaces of the ends of fingers and toes
arrector pili muscle
The small, involuntary muscle in the base of the hair follicle; causes hair to "stand up" when the muscle contracts.
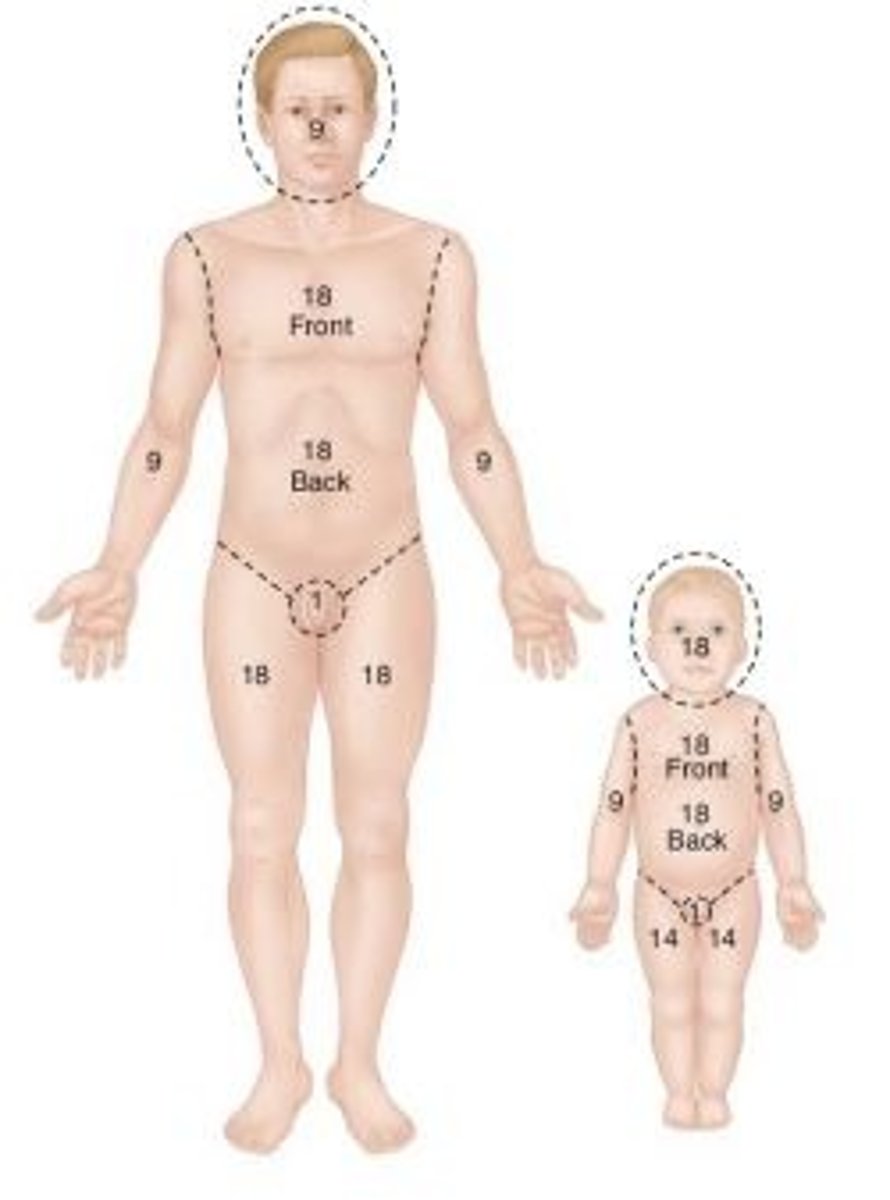
Rule of Nines
a method used in calculating body surface area affected by burns
First-degree burn
Superficial burns through only the epidermis.
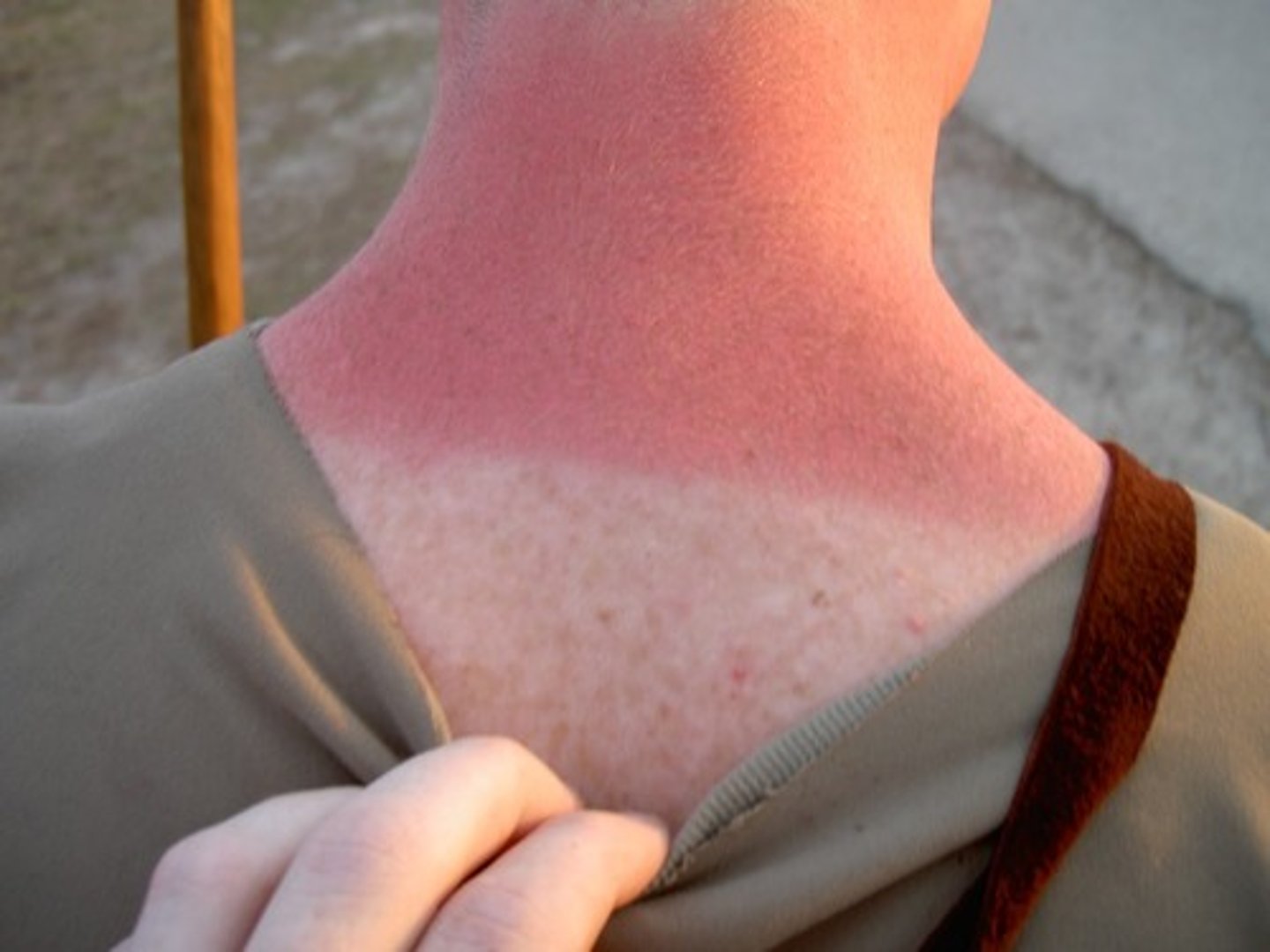
Second-degree burn
A burn marked by pain, blistering, and superficial destruction of dermis with edema and hyperemia of the tissues beneath the burn.
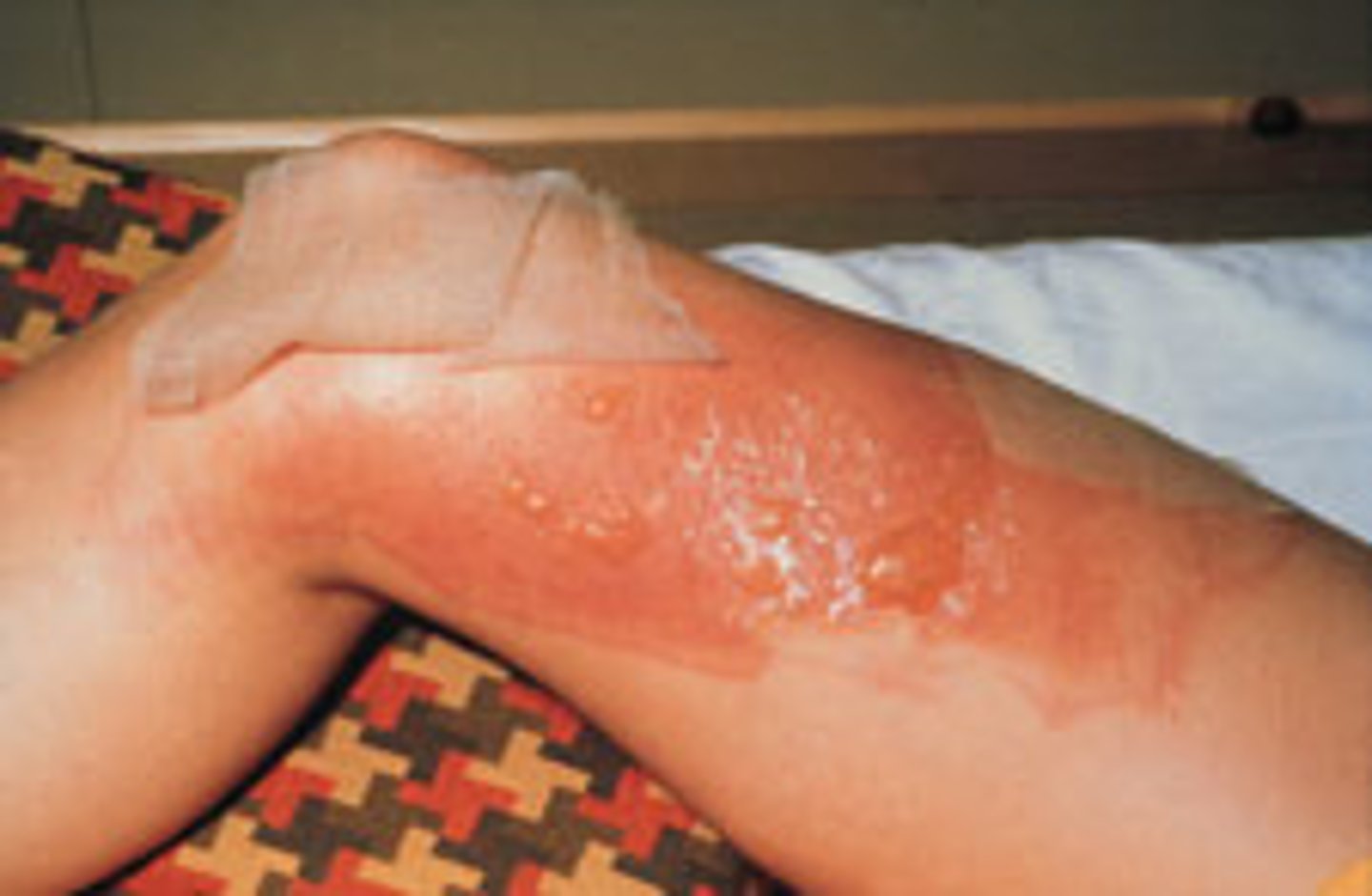
Third-degree burn
a burn involving all layers of the skin; characterized by the destruction of the epidermis and dermis, with damage or destruction of subcutaneous tissue
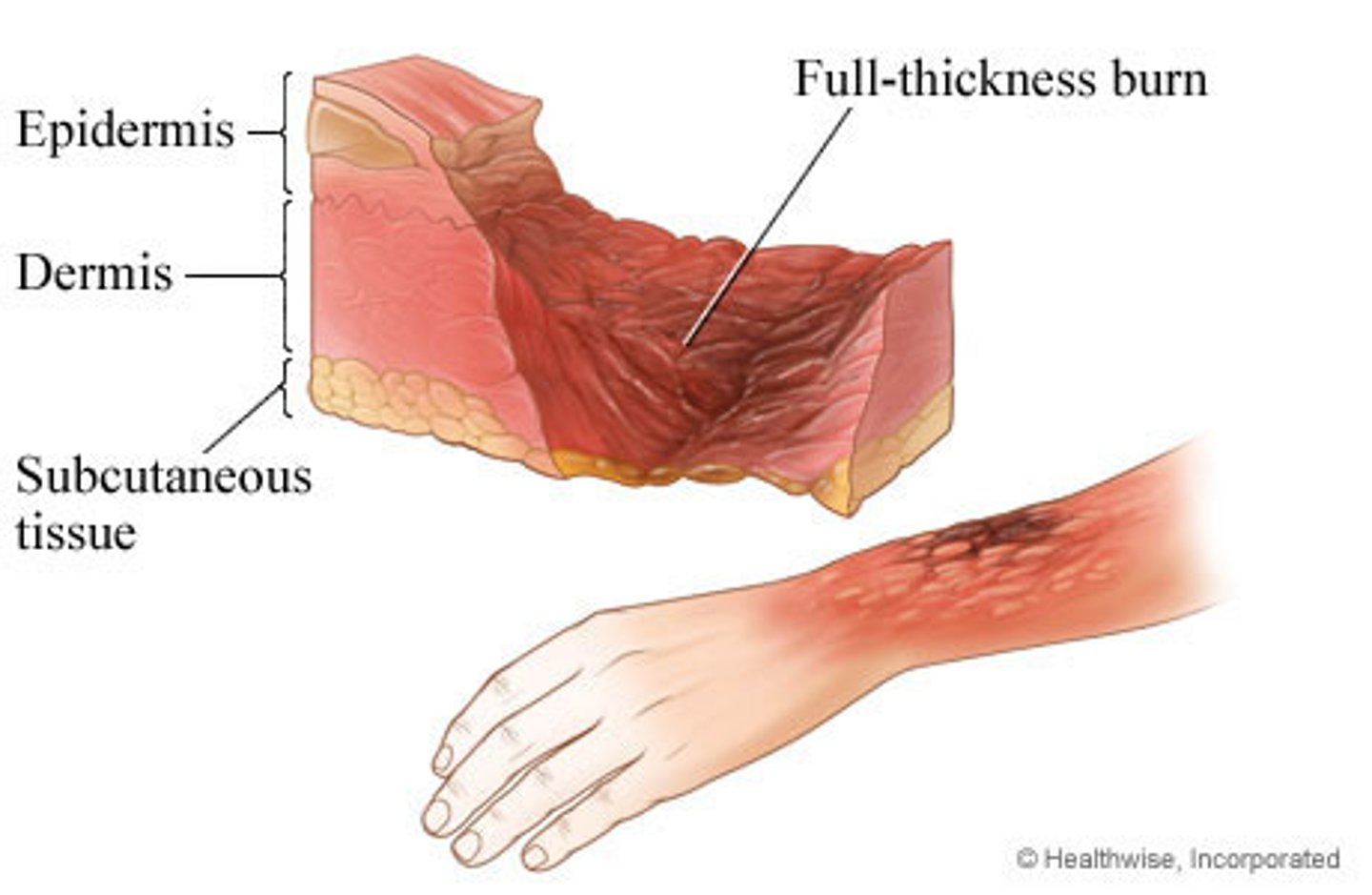
Fourth-degree burns
involves not only all layers of skin, but also underlying fat, muscles, bone, or internal organs.
Skin cancer
abnormal growth of skin cells
Basal cell carcinoma
Most common and least severe type of skin cancer; often characterized by light or pearly nodules.
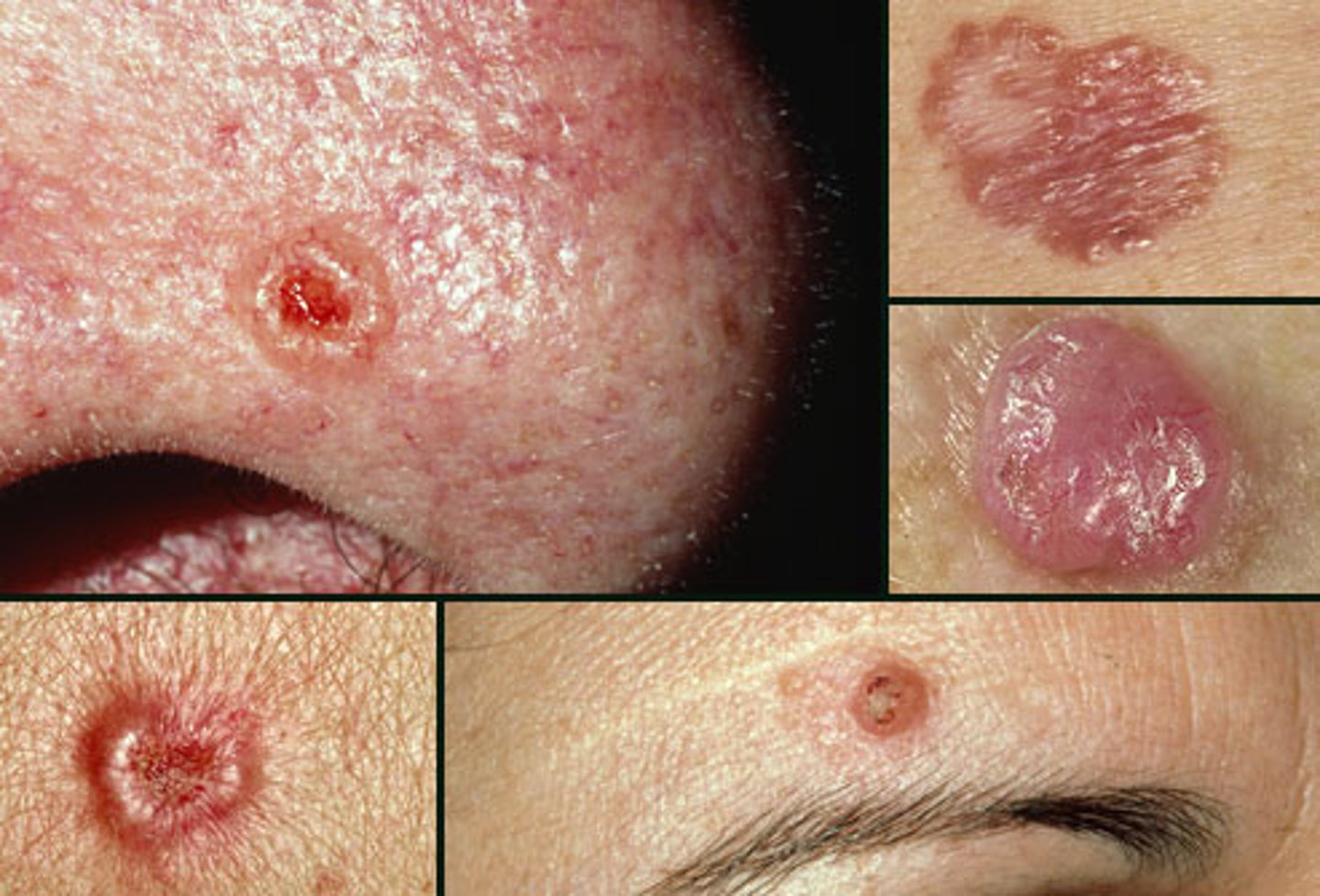
Malignant melanoma
Most serious form of skin cancer; often characterized by black or dark brown patches on the skin that may appear uneven in texture, jagged, or raised.
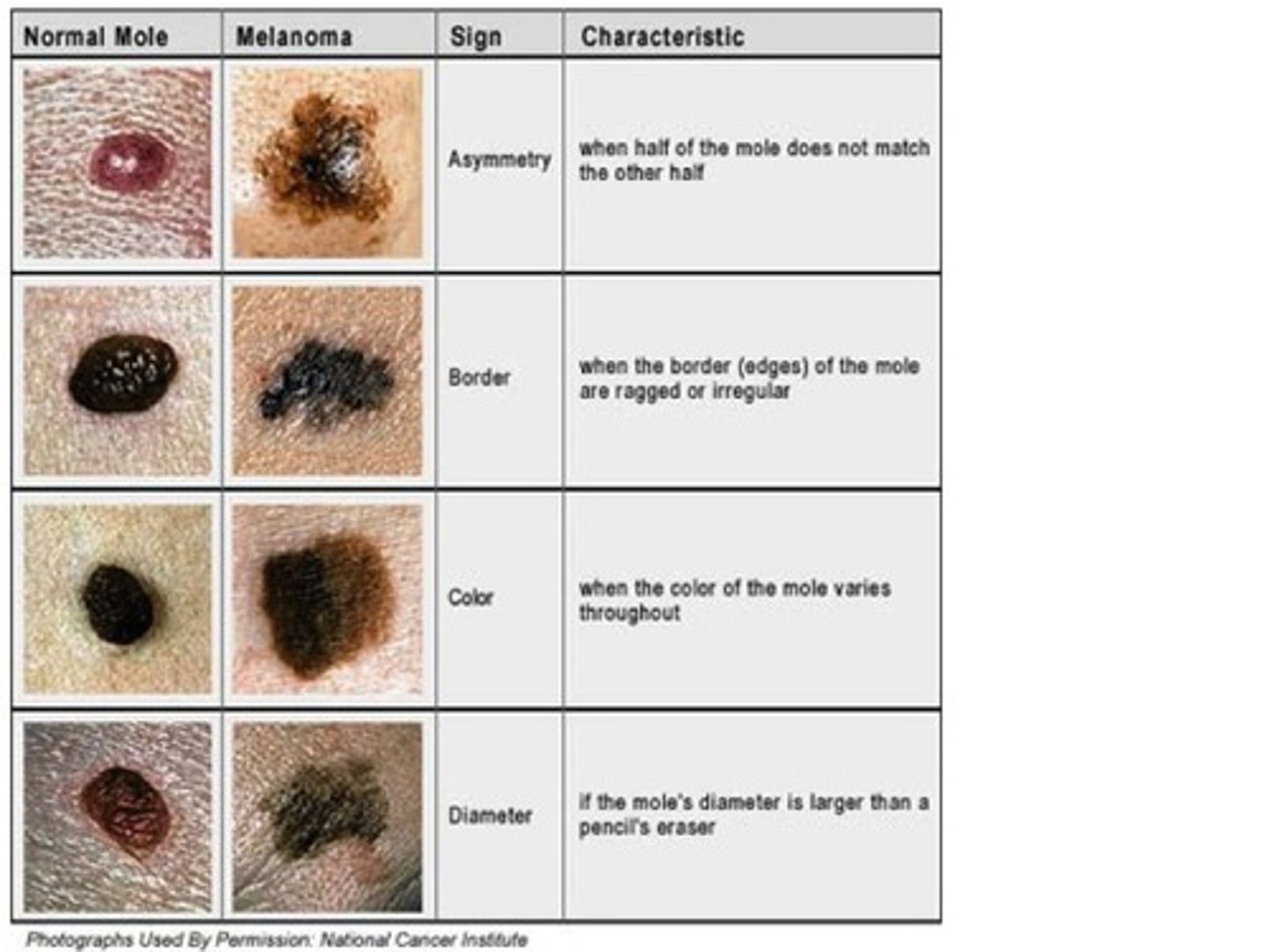
ABCDE rule
asymmetry, border, color, diameter, evolving

Function of the lymphatic vessels
Collect excess tissue fluid and blood proteins
Return tissue fluid and blood proteins to bloodstream
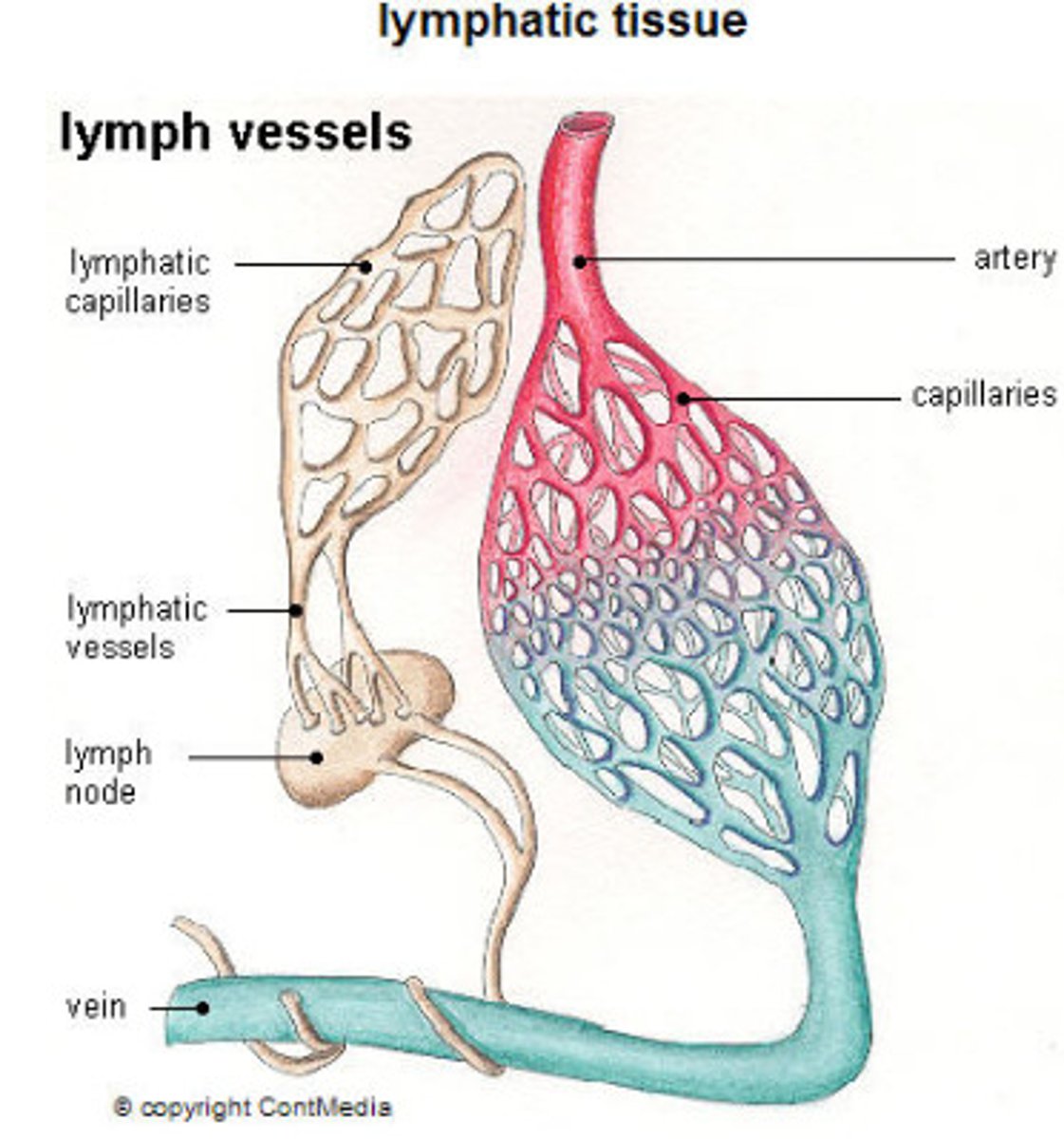
2 structures of the lymphatic system
1. lymphatic vessels and 2. lymphoid tissues
Function of lymph
protects the body from disease
Lymph node
a small knob of tissue in the lymphatic system that filters lymph, trapping bacteria and other microorganisms that cause disease
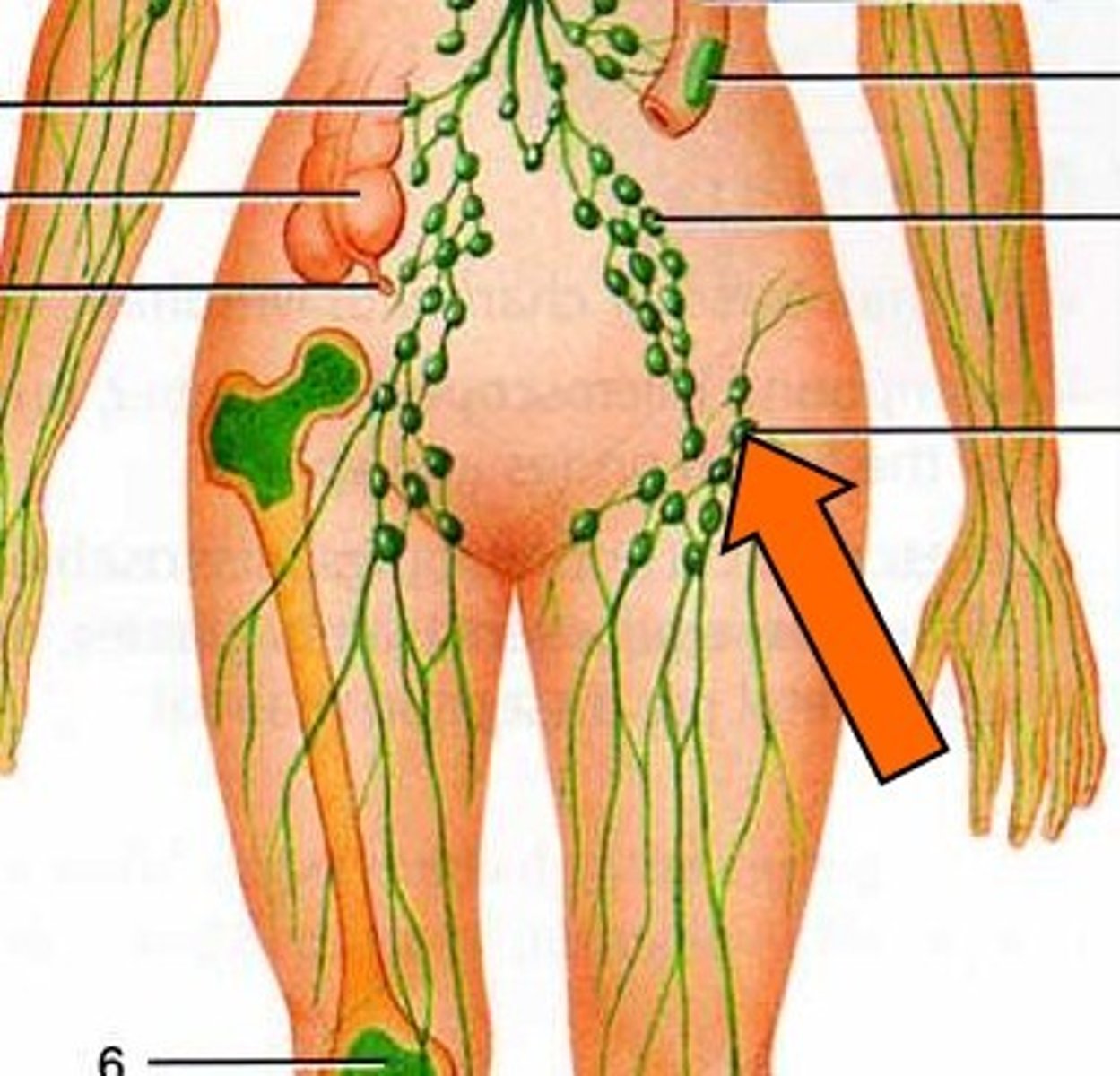
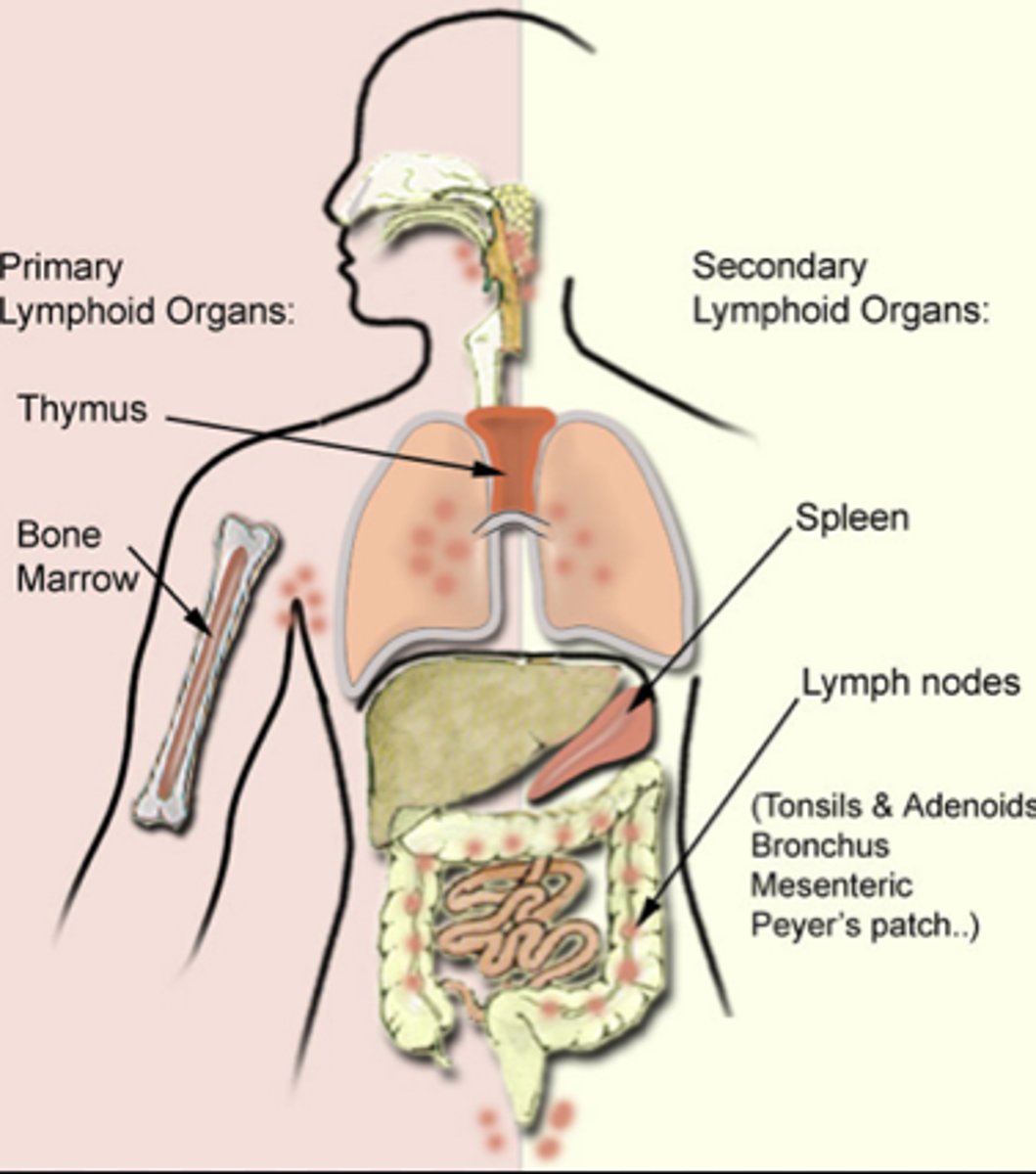
Lymphoid organs
-Consist of lymph nodes, spleen, appendix, adenoids, thymus, tonsils, and small patches of tissue in the small intestines.
Lymph Nodes: Located at intervals through the lymph vessel system. Contains lymphocytes and plasma cells.
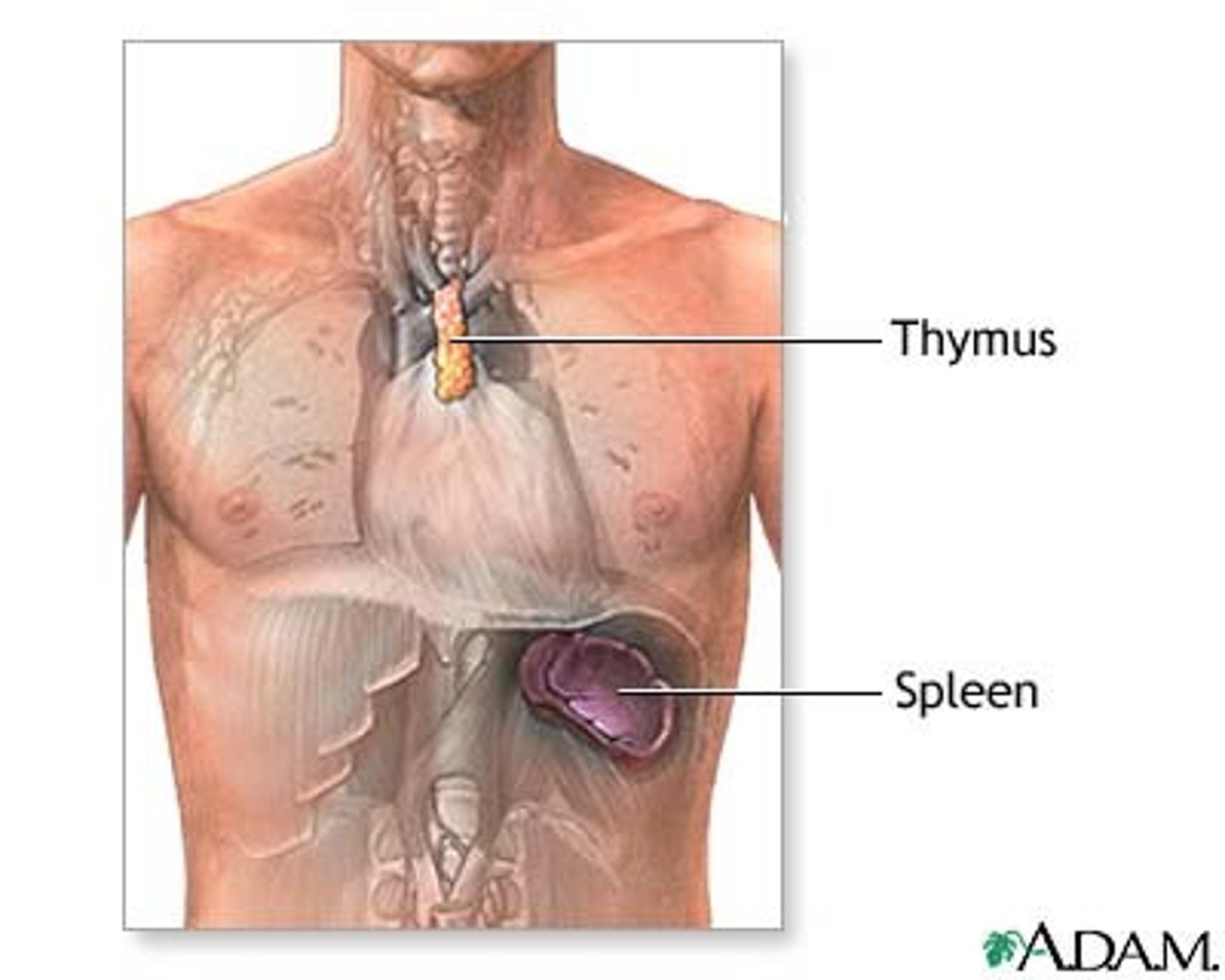
Spleen: Filters blood, stores of RBC and macrophages.
Thymus: Secrets hormones. Major site of lymphocyte production.
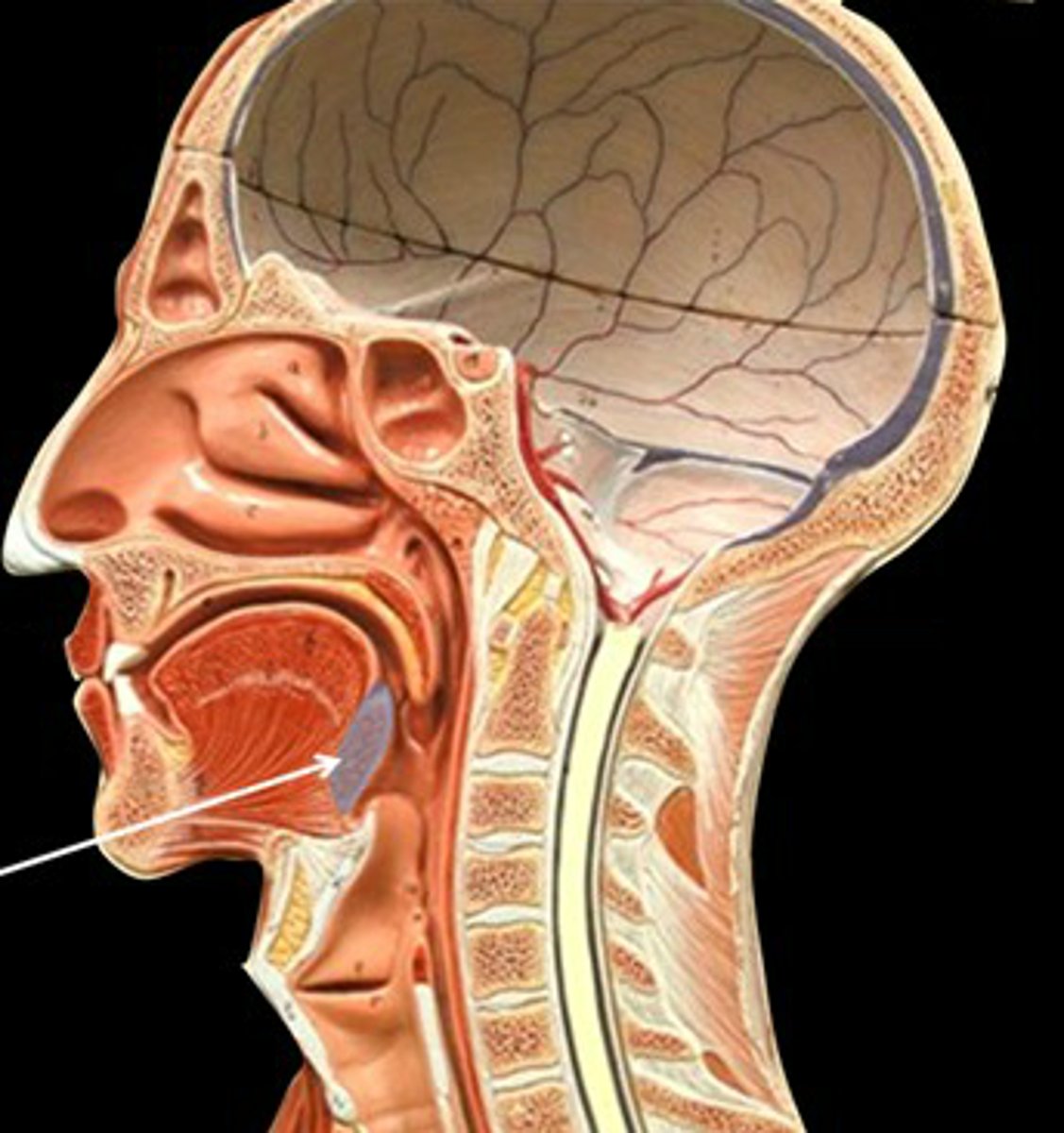
Function of tonsils
Help defend the body against infection by trapping pathogens that enter the throat.
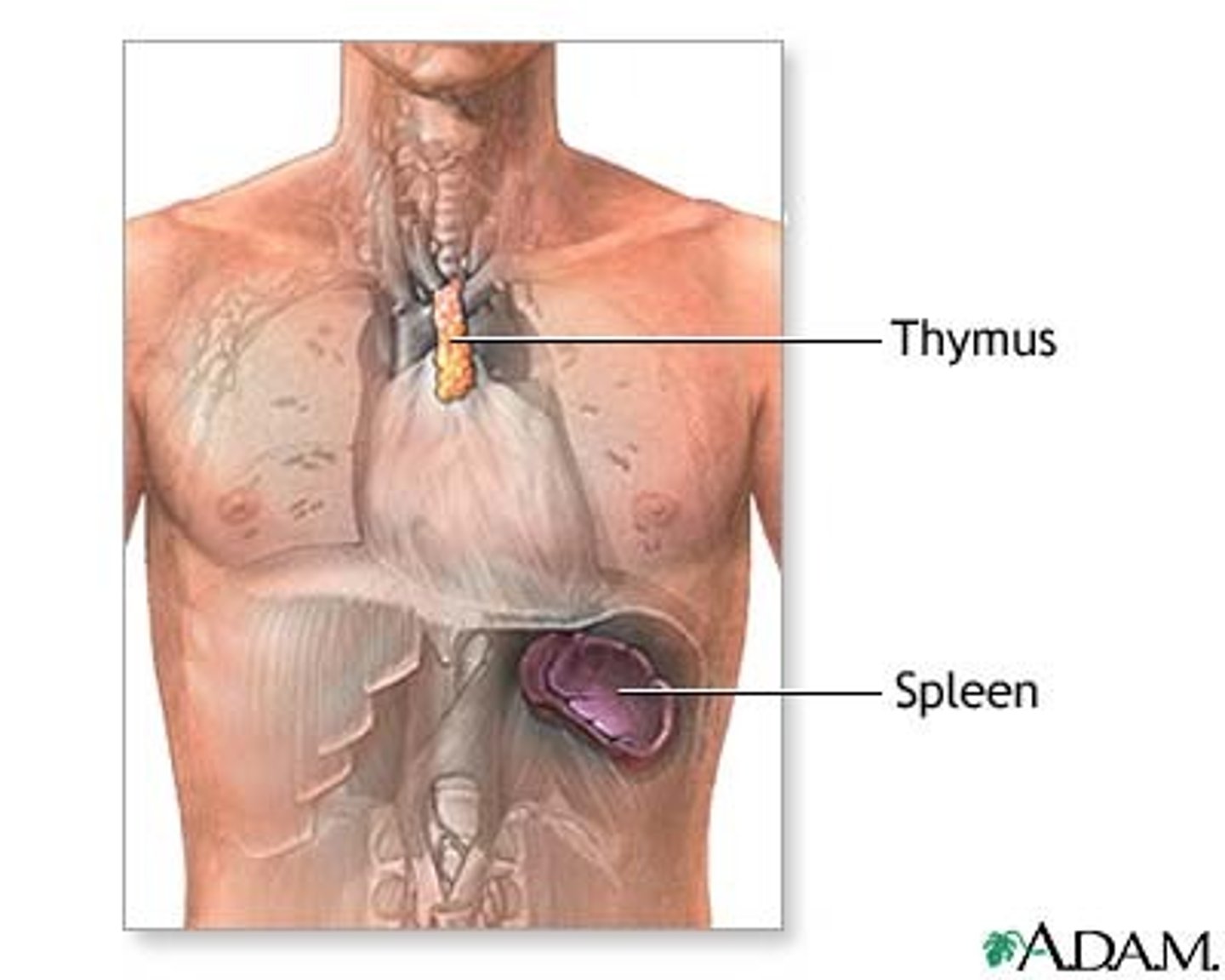
Function of thymus
site of T cell maturation
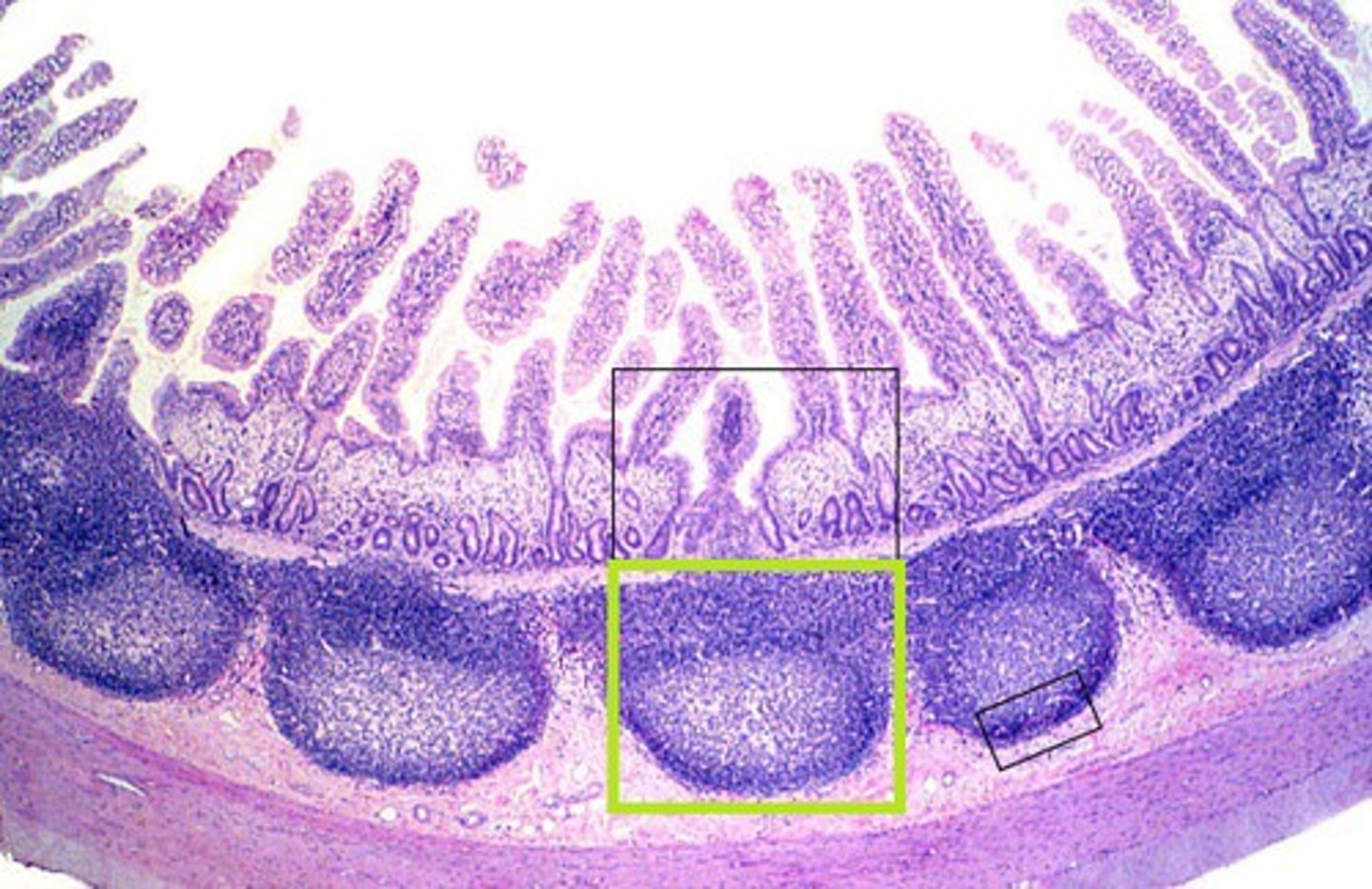
Function of Peyer's Patches
Capture and destroy bacteria in the intestine
Function of the spleen
- forms monocytes & lymphocytes
- stores RBC & releases into circulation if needed
- filters old RBC's from blood
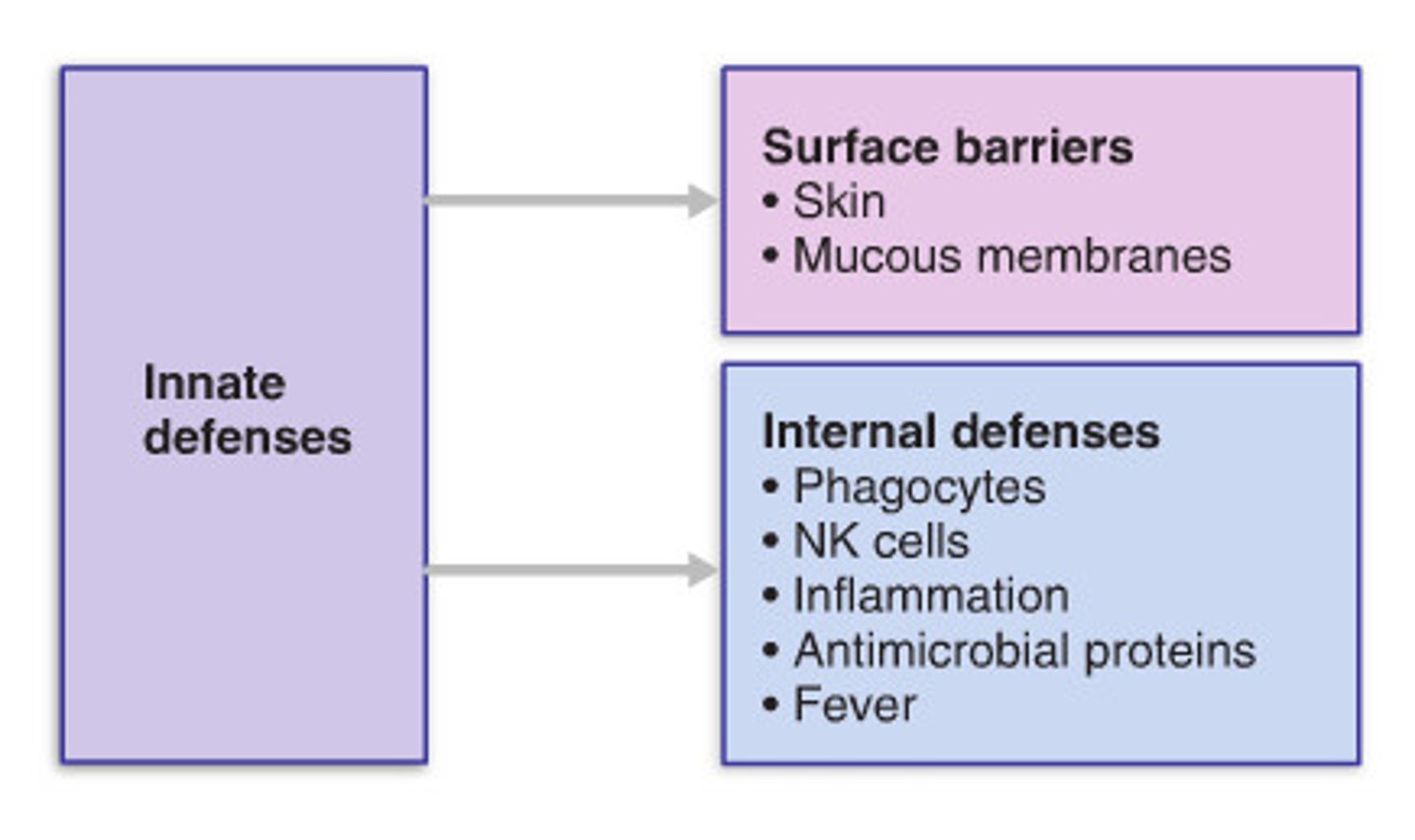
1st line of defense in the immune system
Physical barriers
- skin
- tears
- mucus
- saliva
- stomach acids
2nd line of defense in the immune system
Inflammation (immunity) - functions immediately as an effective barrier to microbes
Role of natural killer cells
- not phagocytes
- kill abnormal cells by secreting cytotoxic perforins and granzymes
- produce cytokines to trigger other immune cells
Describe the inflammatory response
Cells at the wound release histamines which dilate blood vessels. This brings more blood (with phagocytes) to the wound
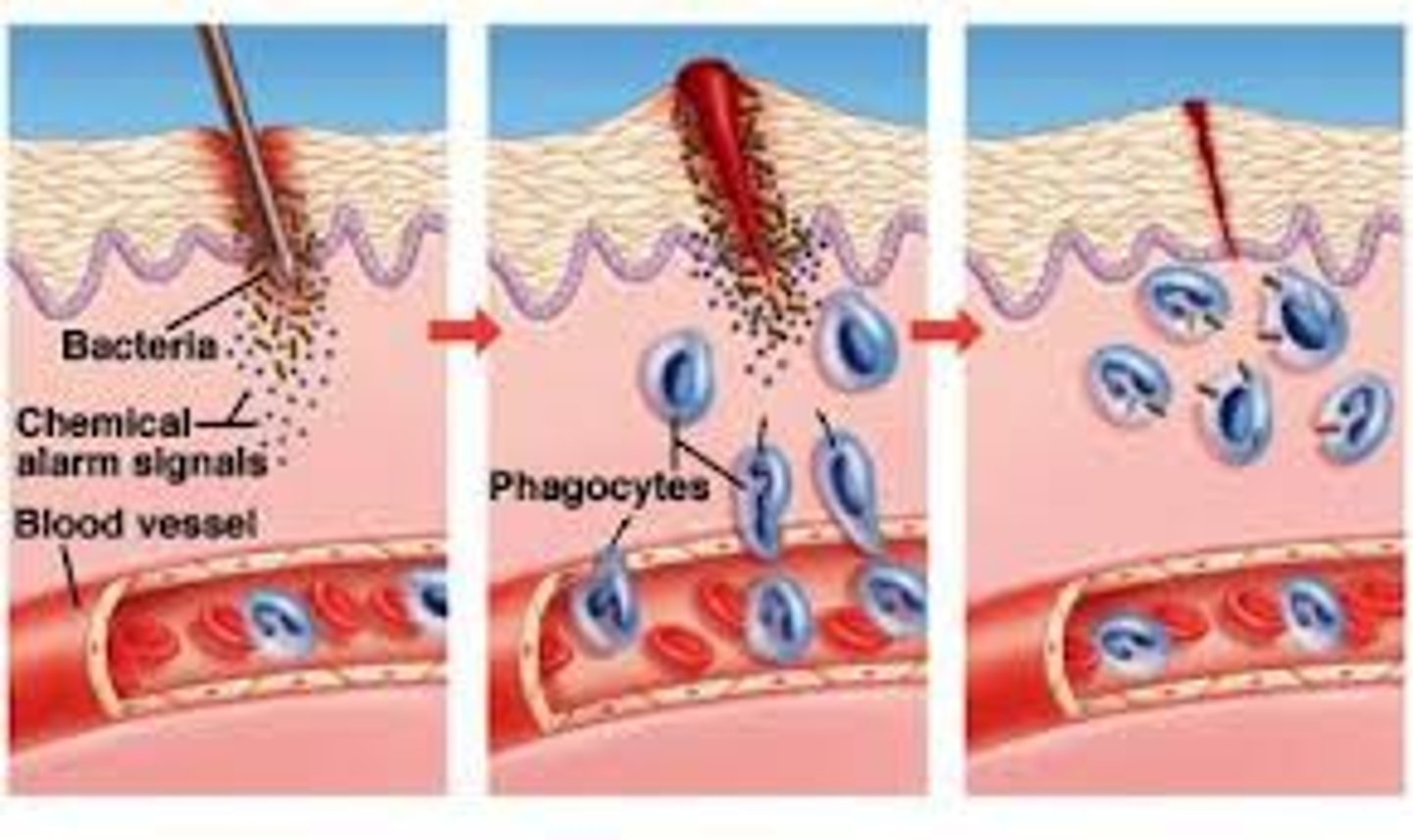
Phagocyte function
type of white blood cell the engulfs dead cells

innate body defenses
nonspecific, general barriers; from skin to phagocytes to fever to inflammation
Role of a fever
Fever is a defense mechanism that can destroy many types of microbes.
Fever also helps fight viral infections by increasing interferon production.
While high fevers can be dangerous, some doctors recommend letting low fevers run their course without taking aspirin or ibuprofen.
Immune response
the body's specific recognition, response, and memory to a pathogen attack
Antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
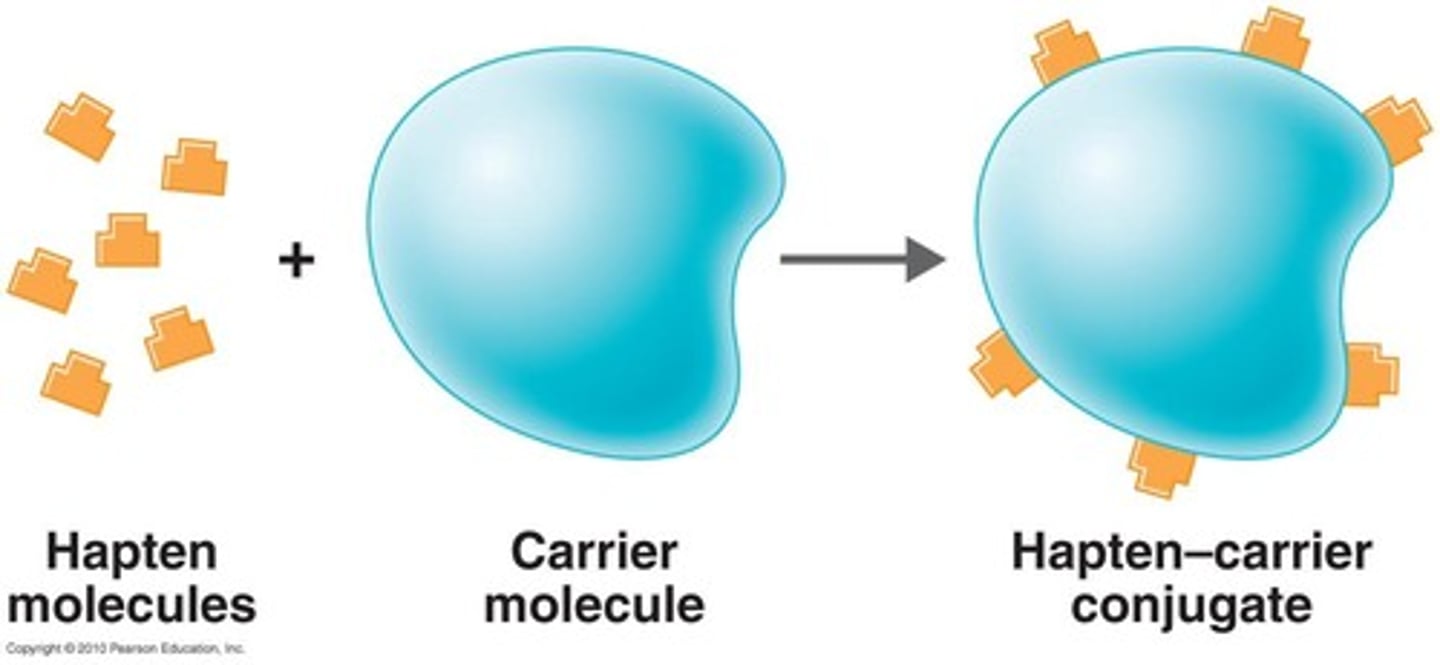
Hapten
small molecule that has to bind to a larger molecule to form an antigen
B cell
A lymphocyte that produces proteins that help destroy pathogens.
T cell
a lymphocyte that identifies pathogens and distinguishes one pathogen from another
Humoral immunity
B cells produce antibodies after exposure to specific antigens; type of adaptive immunity
Role of plasma cells
specific immunity produced by B cells that produce antibodies that circulate in body fluids
Monoclonal antibodies
a collection of identical antibodies that interact with a single antigen site
Antibodies
Specialized proteins that aid in destroying infectious agents
5 antibody classes
IgM, IgA, IgD, IgG, IgE
4 major types of transplants
Autografts, isografts, allografts, xenografts
Autografts
tissue transplanted from one site to another on the same person
Isografts
tissue grafts from an identical person (identical twin)
Allografts
grafts transplanted from individuals that are not genetically identical but belong to the same species
Xenografts
tissue taken from a different animal species
Allergies
Inappropriate or excessive immune responses to antigens
Autoimmune diseases
Diseases caused when the immune system loses tolerance for self and turns against certain molecules in the body.
Immunodeficiencies
failure of the immune system to protect the body adequately from infection, due to the absence or insufficiency of some component process or substance.