Biology Ch. 32 - Integumentary System
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
epidermis
The outer superficial layer of skin, which contains keratin and melanin.
inner epidermal layer
The layer of the skin that continually divides by mitosis to replace cells that are lost from the skin's surface.
muscles
contract causing hair and skin to stand up and form a goose bump.
Vitamin D
made when skin is exposed to ultraviolet light, and is important in bone formation.
first degree burn
damage to skin is characterized by redness, mild discomfort, and the death of only epidermal cells.
compact bone
The part of the bone labeled A
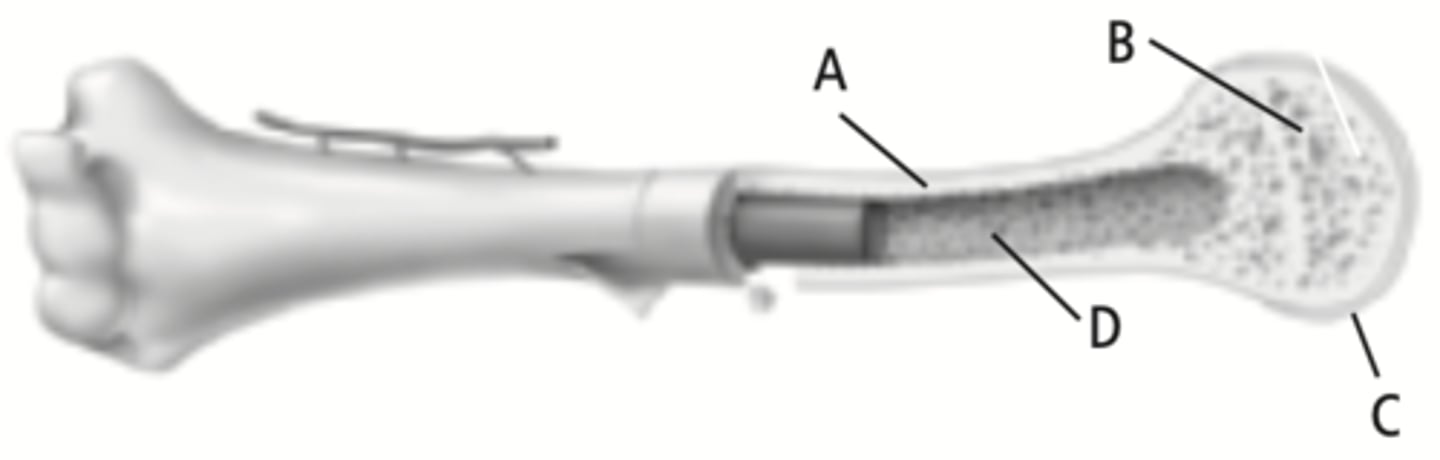
spongy bone
The part of the bone labeled B
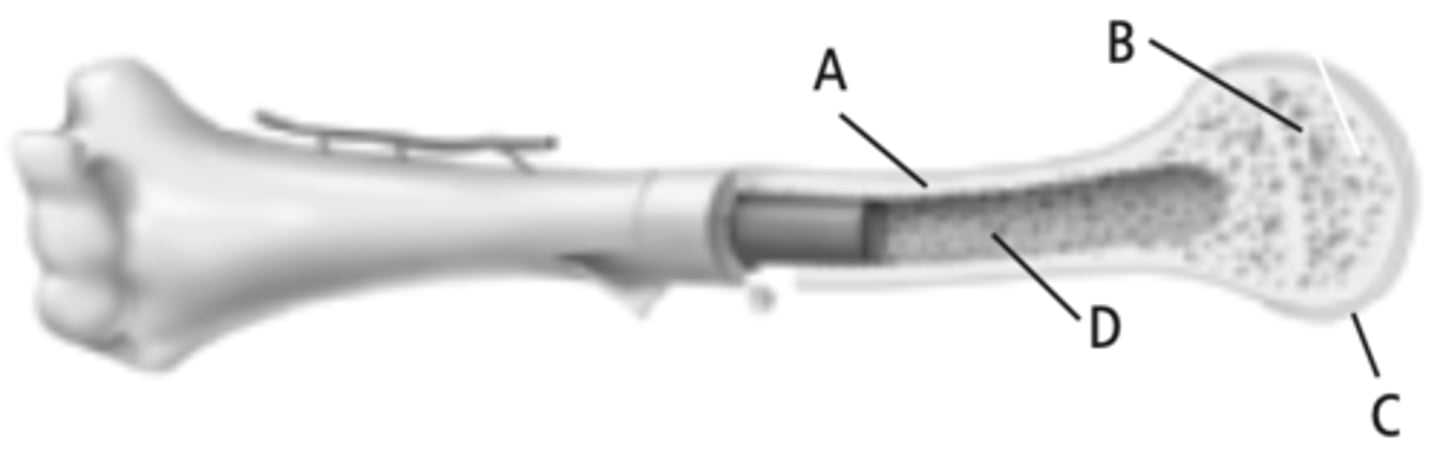
cartilage
The part of the bone labeled C
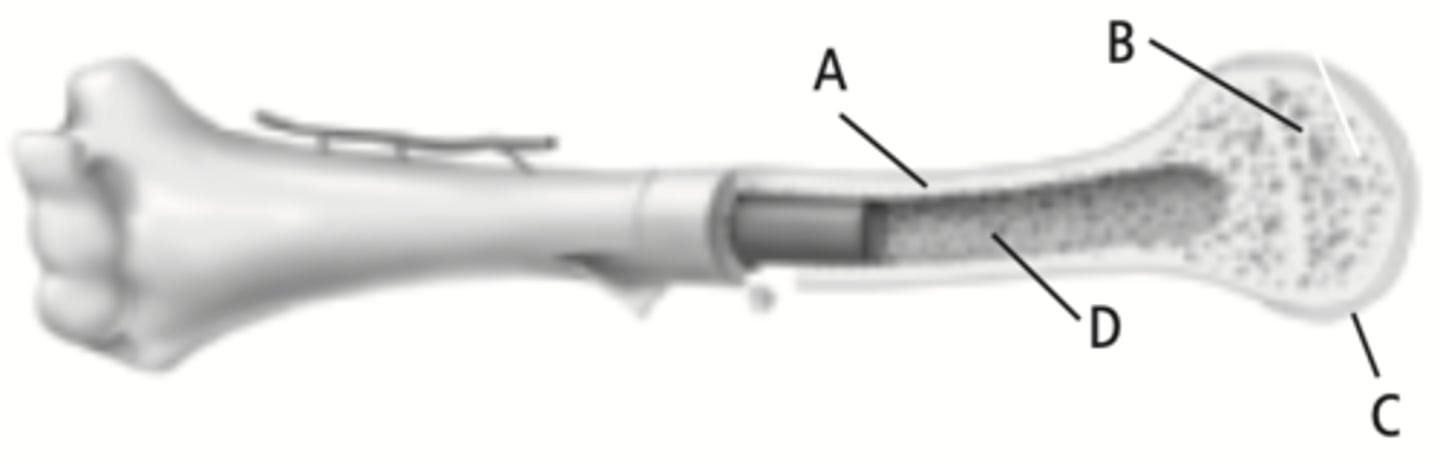
marrow cavity
The part of the bone labeled D

red bone marrow
produces red and white blood cells and platelets.
hinge joint
An elbow is an example of this type of joint
ball-and-socket joint
A shoulder is an example of this type of joint
sprain
caused when a ligament is damaged due to twisting or overstretching.
muscles under conscious control
skeletal muscle
muscles under unconscious control
smooth muscle and cardiac muscle
skeletal muscles
are arranged in opposing, or antagonistic pairs. When one contracts, the other relaxes.
weight lifters have
more fast-twitch muscles
long distance runners have
more slow-twitch muscles
oxygen
limits ATP available for muscle contraction during strenuous activity.
sarcomere
The part of the muscle that contracts.
melanin
A pigment that absorbs sunlight to protect the cells.
types of skin tissues
Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, Muscle tissue, Nerve tissue.
cardiac muscle
Muscles arranged in a network with efficient and rhythmic contractions.
actin and myosin
Protein filaments that make up myofibrils.
appendicular skeleton
includes bones of the shoulders, arms, hands, hips, legs, and feet.
sebaceous gland
produces oil
Osteoblasts
the cells responsible for the growth and repair of bones.
sequence for vitamin production in skin
exposure to sun--vitamin D production--absorption of calcium
axial skeleton
includes the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum.
sliding filament theory
Nerve signals cause actin filaments to move while myosin remains still.