by 124L - animal dev. & muscle physiology
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms

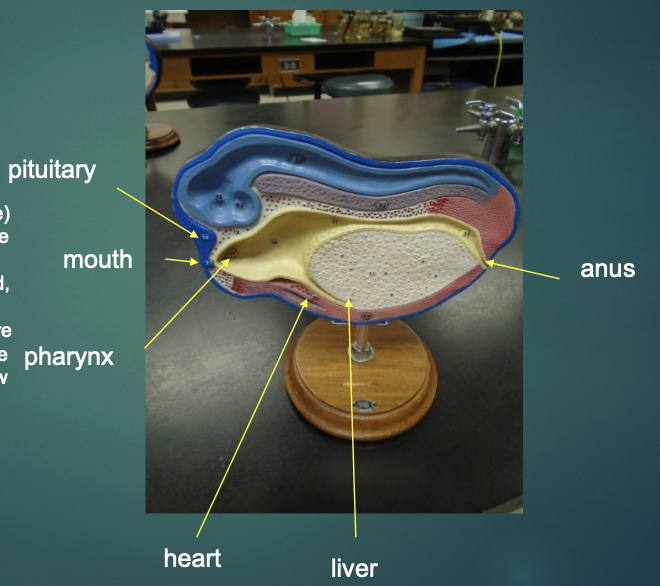
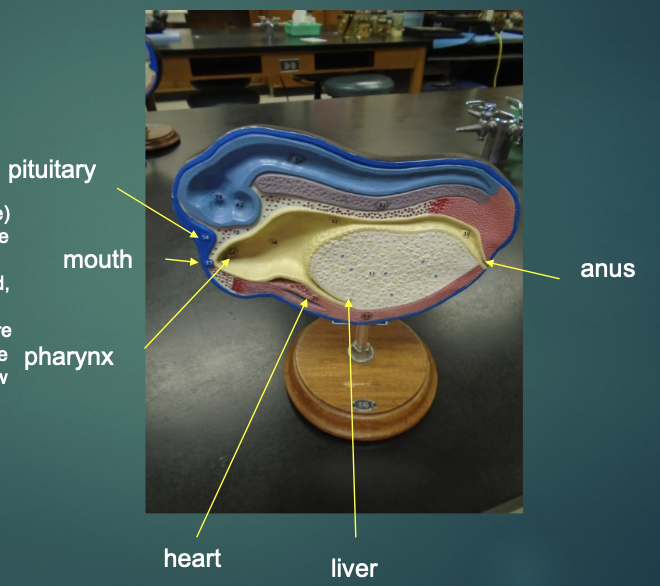
What structures are the arrows pointing to?
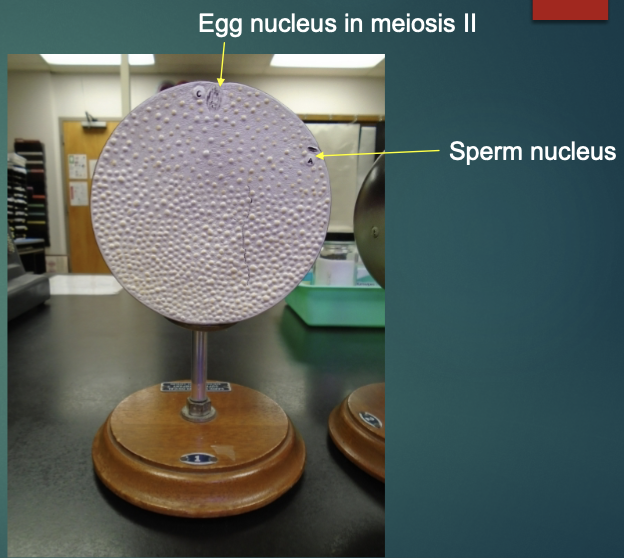
explain the state of an unfertilized egg in terms of the fertilization stage (according to this model)
the egg nucleus is yet to finish meiosis
no fertilization —> egg is flushed out with monthly cycle
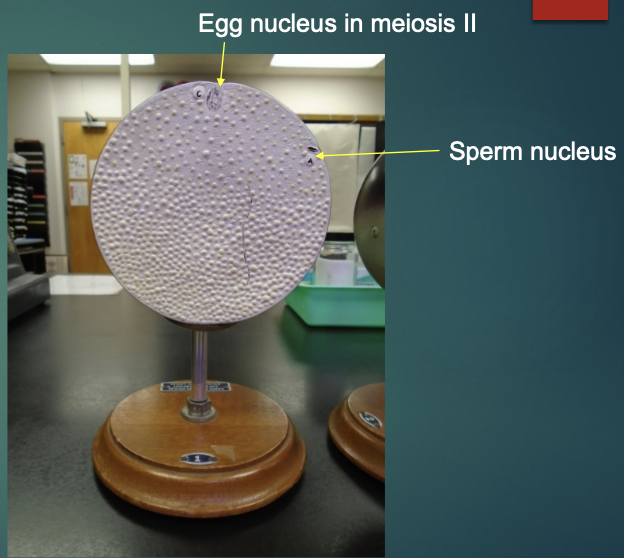
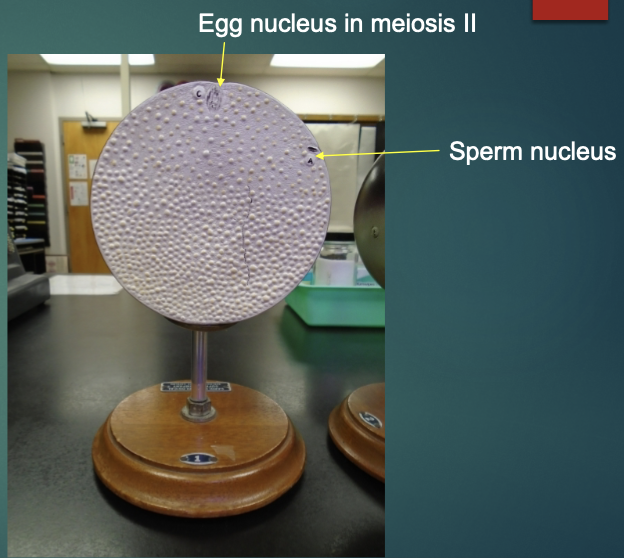
explain the state of a fertilized egg in terms of the fertilization stage (according to this model)
finishes meiosis II, the egg is at metaphase II
polar body (unstable cell) is kicked off
egg nucleus fuses with sperm nucleus

explain the state of an embryo in terms of the first cleavage process (according to this model). be able to identify the dark hemisphere, the animal pole, the light pole (vegetal pole) on this model
divides single diploid cell into lots of smaller cells
no change in size
the first cleavage is polar/vertical

explain the state of an embryo in terms of the second cleavage process (according to this model).
second division/cleavage is along the polar/vertical axis
at the end of this process, there are 4 cells in the embryo
what is each cell that is produced from cleavage called?
blastomere

explain the state of the embryo in terms of the third cleavage process (according to this model).
third cleavage is along the horizontal/equatorial axis
this yields an embryo of 8 cells/blastomeres

explain the state of the embryo in terms of the fourth cleavage process (according to this model).
embryo has 16 cells total
cleavage will continue until a solid ball of cells (morula) is produced

explain the state of the new morula in terms of the blastulation process (according to this model).
characterized by a fluid-filled space forming (blastocoel)

what structure is the arrow pointing to in this model?
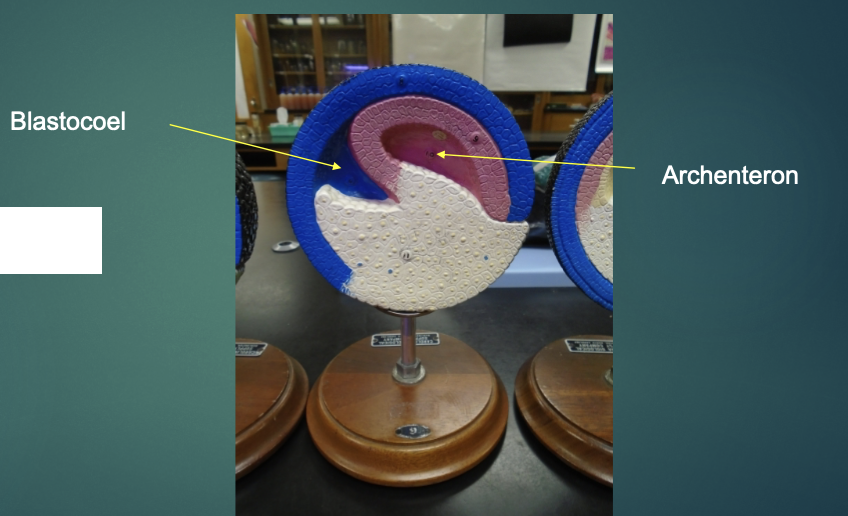
blastocoel
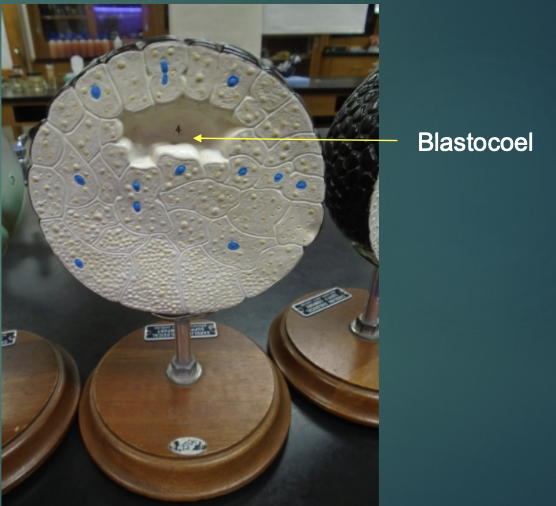


what is occurring in this model?
the process of forming a blastocoel still continues

what structure is the arrow pointing to?
dorsal lip of blastopore
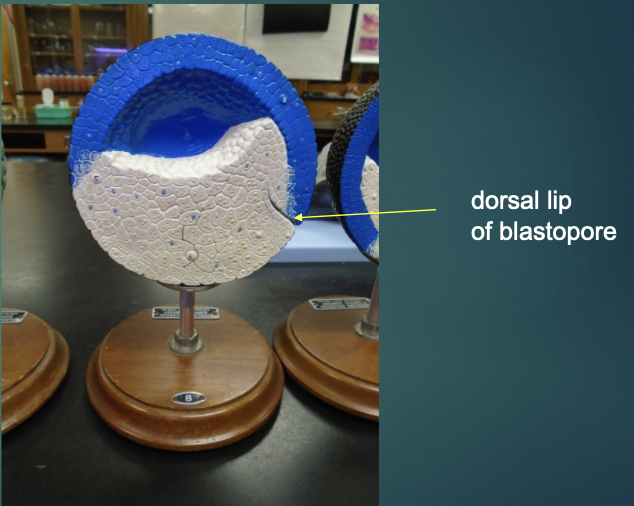
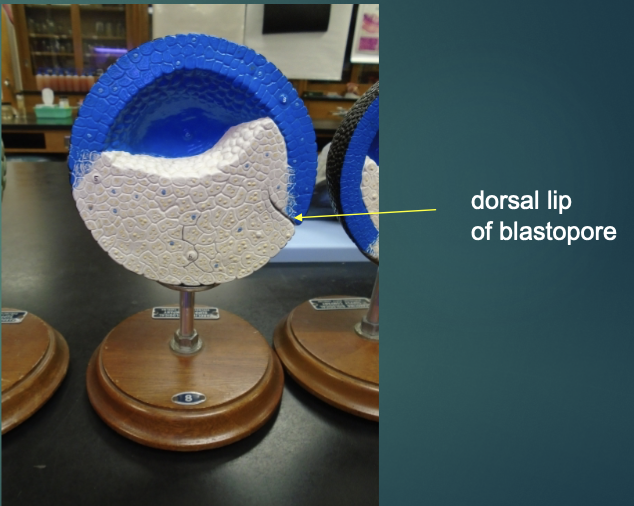


explain the state of the embryo in terms of the blastula process (according to this model).
embryo is now called the blastula
the ectoderm is now formed as the upper layer that’s shaded blue
what is the importance of the blastopore?
this is where cells invaginate inward during the process of gastrulation (where three primary germ layers are laid down)
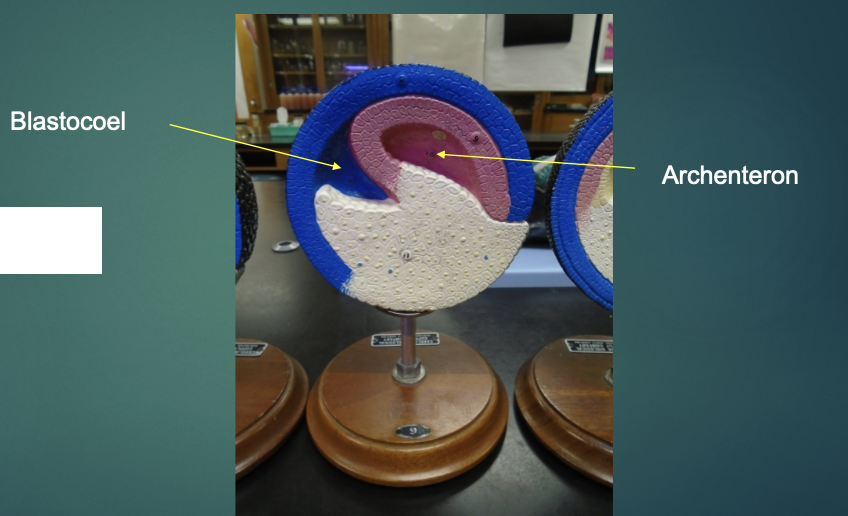
explain the state of the blastula in terms of the gastrulation process (according to this model).
cells are now migrating inward
the blastocoel is being obliterated, a new cavity (archenteron) is developing in its place
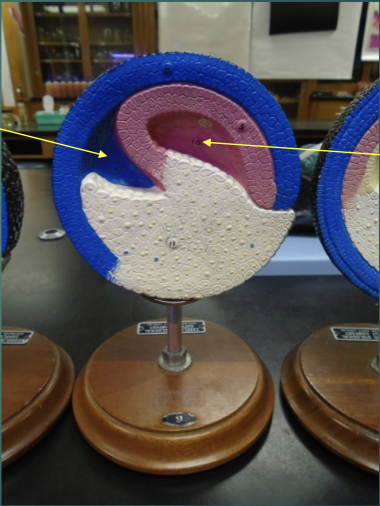
what structures are the arrows pointing to?
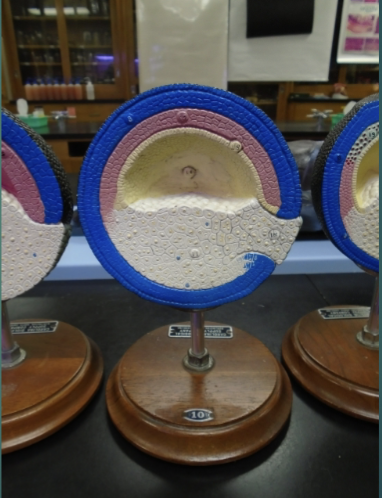
explain the state of the blastula in terms of the last stage of the gastrulation process (according to this model).
all three germ layers are formed
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm are present (blue, pink, yellow)
this is the first time the cells become differentiated

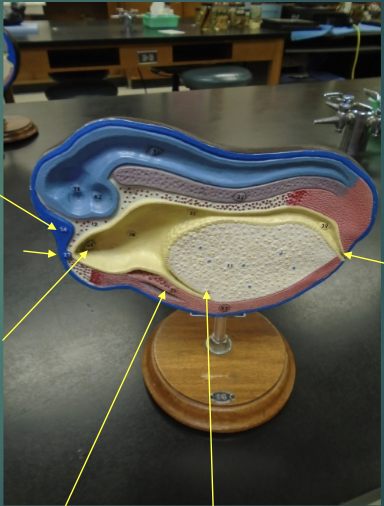
what structures are the arrows pointing to?


explain the state of the blastula in terms of the neurulation/organogensis process (according to this model)
formation of the nervous system (neurulation) and organs (organogensis)
first 2 organs to form: neural tube from ectoderm & notochord from mesoderm

explain the state of the blastula in terms of the neurulation/organogensis process (according to this model)
neural tube continues to form at the top of the model
archenteron begins to take a dif. shape on as it forms the gut
the vegetal pole cell area reduces in size as it’s used up to fuel the active cell division above it

explain the state of the blastula in terms of the neurulation/organogensis process (according to this model)
top of the model is where the ectodermal cells have sunk in and formed a ditch
ditch covered over itself and begun to sink downward into the embryo
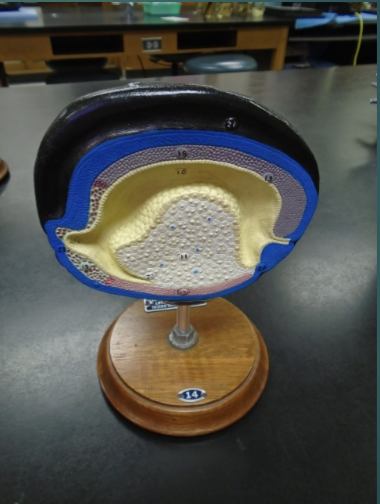
explain the state of the blastula in terms of the neurulation/organogensis process (according to this model)
the ectodermal ditch continues to sink into the embryo
archenteron region’s ends have migrated to each end of the embryo
when it reaches the left end of the model that’s where the mouth will be
right side of the embryo: blastopore opening —> anus
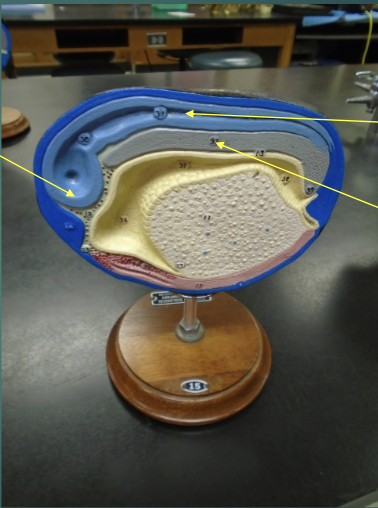
what structures are the arrows pointing to?
explain the state of the blastula in terms of the neurulation/organogensis process (according to this model)
the sunk end ectodermal cells are now lighter blue —> neural tube
blue - from ectoderm, light blue - ectoderm is specialized
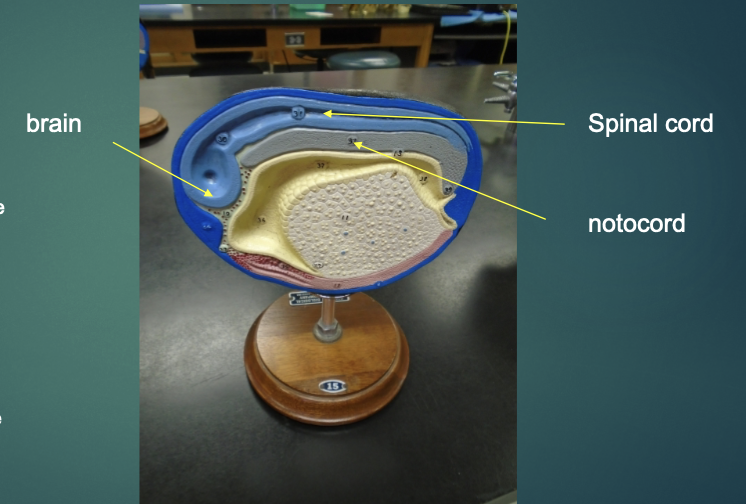
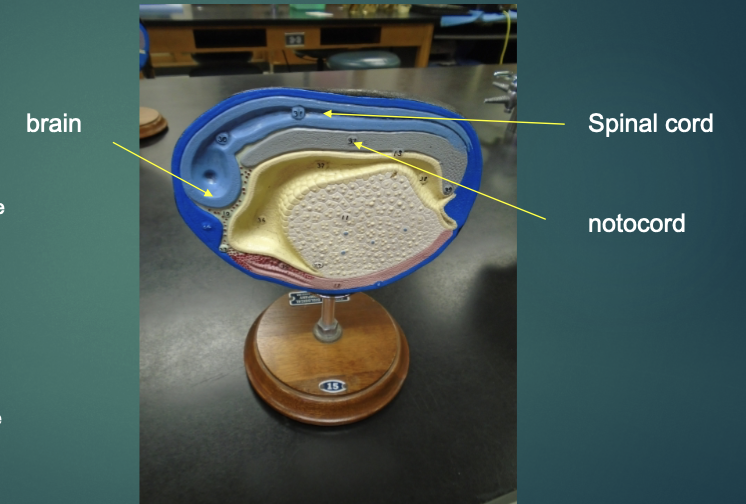
the left end of the model becomes the brain
tapering area that leads from this will become the spinal cord
what structures are these arrows pointing to?
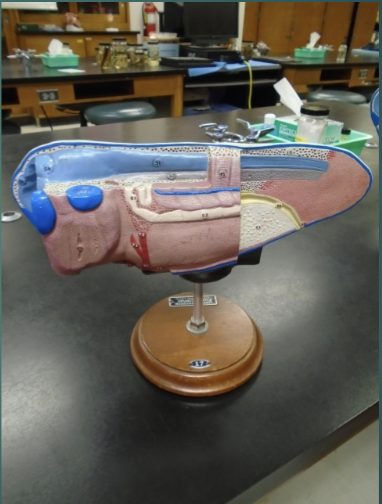
explain the state of the blastula in terms of the neurulation/organogensis process (according to this model)
neural tube (light blue) continues on its development to produce the brain and spinal cord
the notochord (grayish-purple) provides a “support beam” for cell attachment and also gives cues to where cells need to migrate in order to produce required structures
endoderm now stretches from mouth to anus ends of embryo
explain the state of the blastula in terms of the neurulation/organogensis process (according to this model)
one celled zygote transformed into a shape that looks closer like the frog’s tadpole stage
blood vessels are now visible
reddish regions are beginning to produce muscle
define differentiation
the process by which unspecialized cells become specialized cells that are ordered in the tissues and organs of the animal
define morphogenesis
the development of the animal’s shape, or body form, and organization.
what does embryonic development begin with?
fertilization
define fertilization
the union of two haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote (a fertilized egg)
what are the two functions of fertilization?
to combine 2 haploid sets of chromosomes, contained in the gametes of 2 different individuals, into a single diploid set (1n + 1n = 2n)
to activate the egg
a. binding of the sperm with the egg causes a chain of metabolic reactions within the egg that triggers the onset of development
explain how the meiosis stages change for an egg in a female depending on the timeline of her life
at birth, born w all eggs they will ever have (prophase I)
each menstrual cycle, eggs progress to metaphase II and stop
if unfertilized: it will be lost w menstrual flow
what follows fertilization?
cleavage
define cleavage & summarize the process.
a rapid succession of cell divisions that produce a solid ball of cells from the zygote
the embryo doesn’t grow in size during this time
cytoplasm of one large cell is partitioned off into many smaller cells (blastomeres)
list the different axes that correspond with the different cleavages
first and second - vertical/polar
third - horizontal/equatorial
what is produced as cell division continues?
morula (solid ball of cells)
what forms in the center of the morula?
a fluid-filled cavity called a blastocoel
what stage does the developing embryo enter after the blastocoel is formed?
blastula stage (hollow ball of cells)
what follows cleavage?
gastrulation
summarize the gastrulation process.
cells from the outer surface of the embryo begin to migrate inward toward the center
specifically move through the blastopore (mouth in protosomes, anus in deuterostomes)
blastocoel is obliterated and the new archenteron cavity is formed, which becomes the digestive tract when fully developed.
3 primary germ layers develop
developing embryo from blastula —> gastrula
what are the 3 germ layers?
ectoderm (outer layer)
mesoderm (middle layer)
endoderm (inner layer)
what structures does the ectoderm produce?
nervous system
epidermis & associated glands of the skin (sweat and sebaceous)
inner ear
lens of the eyes
adrenal medulla
what structures does the mesoderm produce?
notochord
lining of the coelom (body cavity)
muscles
skeleton
gonads
kidneys
most of circulatory system
lymphatic system
dermis of skin
adrenal cortex
what structures does the endoderm produce?
lining of the digestive tract
organs that originate as out-pockets of the archenteron (ex: liver, pancreas, gall bladder)
thyroid
parathyroid
lungs
thymus
urinary bladder
what comes after gastrulation?
neurulation
summarize the process of neurulation.
outer, ectodermal cells flatten out and sink downward to form a groove called the neural groove
edges of either side of the groove eventually become elevated —> neural folds
folds come toward each other, eventually touching, then fusing to form a hollow neural tube
what comes after neurulation?
organogenesis (the formation of organs)
summarize the process of organogensis.
first organs take shape: neural tube (from dorsal ectoderm) and notochord (from dorsal mesoderm)
neural tube —> brain and spinal cord
notochord —> intervertebral discs between the vertebrae
blocks of mesoderm begin to condense, forming blocks of somites —> vertebrae of backbone
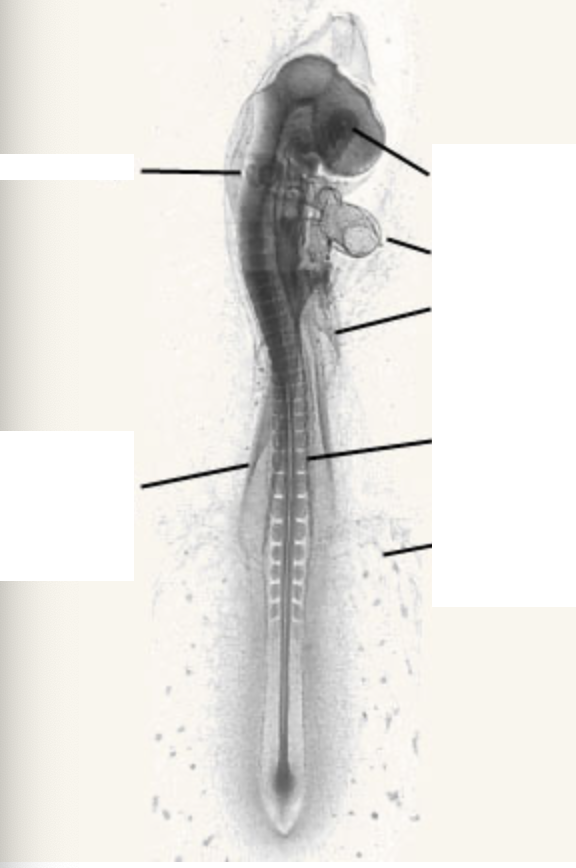
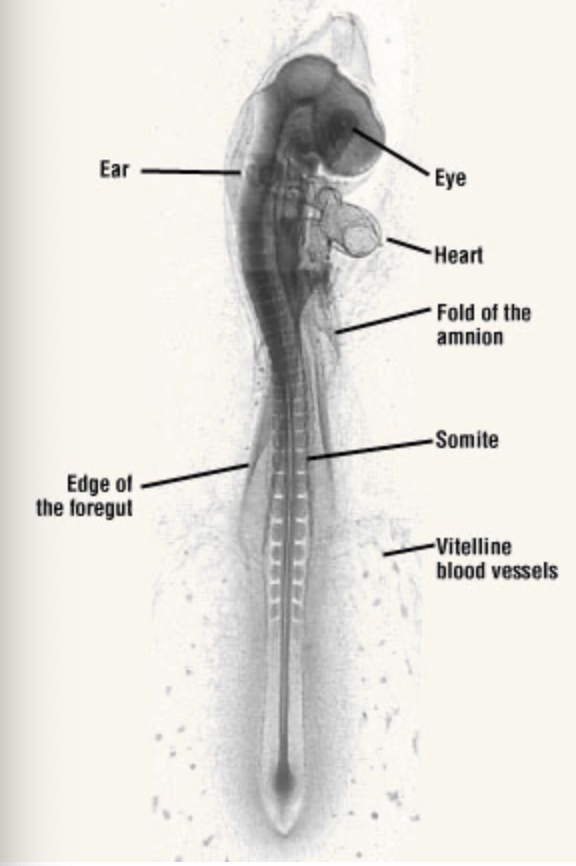
label this picture with the corresponding structures.
what is the function of the following extra-embryonic membrane of the amniotic egg: chorion
Develop the villi and the placenta that will provide a pathway for exchange from the mother to the fetus, making it a pivotal part of the development
what is the function of the following extra-embryonic membrane of the amniotic egg: amnion
A transparent sac filled with colorless fluid that serves as a protective cushion during embryonic development
what is the function of the following extra-embryonic membrane of the amniotic egg: yolk sac
Serves as an absorptive epithelium for nutrient uptake and secretion as well as the origin of the first blood cells
what is the function of the following extra-embryonic membrane of the amniotic egg: allantois
Serves as a temporary respiratory organ while its cavity stores fetal excretions
how is a frog egg particularly different?
they’re polar in the sense that there are 2 distinct hemispheres:
one hemisphere actively divides to form the animal (animal pole)
second hemisphere doesn’t divide but rather provides the energy for the actively dividing cells in the animal pole (vegetal pole)
acts as the yolk
summarize the process of fertilization and cleavage
two haploid gametes form a diploid zygote
cleavage follows right afterwards, rapidly dividing cells to produce solid balls of cells from the zygote
a morula is produced from here —> blastocoel —> blastula
what are the three basic muscle types?
cardiac, smooth, skeletal
skeletal muscle is usually attached to what?
bone
what do skeletal muscles move?
skeleton
the ____ nervous system controls skeletal muscles
somatic
are skeletal muscles voluntarily or involuntarily controlled?
voluntarily
where do you usually find smooth muscle?
hollow organs & tubes
stomach
intestines
bladder
blood vessels
smooth muscle is controlled by the _____ nervous system
autonomic
smooth muscle control is largely what?
hormones
where is cardiac muscle found?
heart muscle
what two factors does it respond to?
ANS and hormones
skeletal muscle contains many muscle cells called ______ which are bound by what?
muscle fibers; connective tissue
a single muscle cell contains many _____ which extend the length of the cell
myofibrils
muscle cells contract along their _______
length
striations are seen in which two types of muscle?
cardiac and skeletal
myofibrils contract _______ which in turn, contract __________
myofibrils; muscle fibers
myofibrils exhibit alternate dark and light bands along their what? this results in a similar banding pattern seen in the muscle cell itself.
length
skeletal muscle is often called what?
striated muscle
which 2 of the 3 muscle types are striated?
cardiac and skeletal
in a myofibril, the dark bands are called ________
a bands
in a myofibril, the light bands are called _____
i bands
in the middle of the I bands are other bands called _________
z bands
the a bands have light areas bisected by bands called ______
m lines
the functional unit of the myofibril is called a(n) _______
sacromere
a sacromere extends from what to what?
z line to another z line
contraction of myofibrils is caused by the contraction of each _______
sacromere
a sacromere is comprised of two proteins called what?
actin and myosin
a thin filament consists mostly of 2 molecules of ________
actin
a thick filament is comprised of hundreds of ________ molecules
myosin
thin filaments are connected at one end to the ______, a structure that runs across the myofibril
z line
the thick filaments are connected to the _____, a structure that runs across the myofibril
m line
the dark areas of the a band correspond to regions where what two structures overlap?
thick and thin filaments
the light area in the middle of the a band (called the _______) consists of thick filaments only
h zone
the width of the a band corresponds to what?
length of thick filaments
the _______ correspond to regions consisting of thin filaments only.
i band
both types of filaments are anchored, thin to _____ and thick to ______
z line; m line
the z and m lines run through the myofibrils and thus align what?
sacromeres
the width of the ___ band remain constant throughout contraction
A
contraction does narrow the ___ bands and the ___ zone as the ___ lines come closer together. also, the dark areas of the ____ band become wider
contraction does narrow the I bands and the H zone as the Z lines come closer together. also, the dark areas of the A band become wider
the width of the A band equals the length of the _____ filaments
thick
since the width of the A band remains constant, the ____ filaments do not shorten during contraction
thick
do the thin filaments shorten during contraction?
no
sacromeres contracts the muscle cell which leads to the contraction of what?
myofibrils and then the muscle itself
muscle cells contract because the ____ are connected to the cell membranes
z lines
a myosin molecule consists of 6 polypeptide chains. how many are light? how many are heavy?
2 heavy
4 light