Pulmonary
1/396
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
397 Terms
acute bronchitis
infection of the lower respiratory tract associated with inflammation and/or bronchospasm
what are 90% of acute bronchitis cases caused by?
viral infection
what are the signs and symptoms of acute bronchitis?
cough, wheezing, SOB, chest tightness
what test can you order when you are trying to differentiate between acute bronchitis and pneumonia?
chest XR
treatment for acute bronchitis?
supportive
if wheezing: bronchodilator (SABA: albuterol)
cough medicine
steroids (prednisone) - inhaled, systemic
what are some possible complications of acute bronchitis?
post-bronchitic cough, pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, pneumothorax
how can you educate patients on prevention from acute bronchitis?
follow contagious precautions, wash hands, don’t share food
bronchiolitis
respiratory illness w/ inflamed bronchioles, mucus production, and possible airway obstruction
in what population is bronchiolitis most prevalent in?
peak in 2-6 months old; common in 2 year olds
what are the signs and symptoms of bronchiolitis?
- URI symptoms (fever, congestion/drainage)
- cough
- noisy/raspy breathing
- signs: SOB, wheezing, nasal flaring, retraction, irritability, hypoxia (severe case), apnea
what tests should be done when bronchiolitis is suspected?
pulse oximetry and CXR to rule out pneumonia
treatment for bronchiolitis?
supportive (fluids, Tylenol, Motrin)
O2 if hypoxic
how can you educate patients on prevention from bronchiolitis?
prophylactic palivizumab (for high-risk infants)
What is the etiology for Bronchiolitis?
RSV
metapneumovirus
parainfuenza
influenza
What are complications to Bronhiolitis?
hypoxia
apnea
resp failure
treatment aimed at helping the patient feel better, minimize complications, and support optimal recovery
supportive care
what supportive care can be given to help treat a fever?
Tylenol, Motrin, fluids
what supportive care can be given to help treat bodyaches?
Tylenol or Motrin
what supportive care can be given to help treat wheezing?
SABA (short acting beta agonist)
not for RSV
what supportive care can be given to help treat hypoxia?
O2
what supportive care can be given to help treat dehydration?
fluids
highly contagious viral infection transmitted by respiratory route
influenza
what are the pathogens that cause influenza?
orthomyxovirus (type A, B, C) through respiratory droplet
why do we have an annual epidemic with influenza?
due to antigen drift
what are the symptoms of influenza?
fever, chills, coryza, myalgias, congestion, non-productive cough, GI sxs
What are some differentials for influenza?
URI
pnemonia
covid
viral syndrome
pertusis
legionnaires dz
treatment for influenza?
when should you consider antiviral?
what antiviral can be given?
supportive
all acutely ill patients, especially high risk patients (very young/old, pregnant, comorbidities)
oral oseltamivir (Tamiflu) 75 mg BID x 5 days
Which tests can be given for Influenza?
rapid flu test
What are complications to influenza?
OM
sinusitis
pneumonia
pneumonitis
sepsis
death
If fever persists longer than 4 days with patients with the flu and they have a productive cough, and WBC >10,000, what can be suspected?
secondary bacterial infection
What are the methods for influenza prevention?
vaccination first
Chemoprophylaxis is an option for the unvaccinated, those within 2 weeks of vaccination, or immune compromised
high risk pts get oseltamivir 75 mg QD x 7 days from last exposure
in long term care: oseltamivir 75 mg QD x 2 wks
When do we start to admit patients with influenza?
pneumonia + flu
hypoxia
altered mental status
consider admission if pregnant
severe acute respiratory syndrome spread via respiratory droplets
COVID-19
What is the etiology of Covid-19?
Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
what are the symptoms of COVID-19?
cough, fever/chills, myalgias, dyspnea, fatigue, sore throat, loss of taste/smell, congestion, runny nose, diarrhea, n/v
what are the 3 tests that can be done for COVID-19?
1. molecular (PCR)
2. rapid antigen (do they have COVID?)
3. antibodies (have they had COVID in the past?)
What are some differentials for COVID?
URI
HA
pharyngitis
flu
viral syndrome
pneumonia
Gastroenteritis
treatment for COVID-19?
outpatient?
inpatient?
supportive
outpt (for mild-moderate at risk for severe): supportive, Paxlovid PO x 5 days (start within 5 days of onset) or Remdesivir IV (start within 7 days of onset)
inpt: Remdesivier (if not on O2)
add Dexamethasone (if on O2),
Dexamethasone + Baricitinib or Tocilizumab (if on high-flow or non-invasive ventilation)
anticoagulation
who should get admitted if they have COVID?
- respiratory complications
- hypoxia (<88% pulse ox)
- advanced age
- immunosuppression
- chronic disease
- thrombotic event
- multisystem involvement
What are complications to COVID?
pneumonitis
pneumonia
ARDS
resp failture
pleural effusion
myocardiitis
DVT
Pulmonary embolism
AKI
GI sx
long covid - fatigue, muscle weakness
infection of one or both of the lungs
pneumonia
who is at the greatest risk of developing pneumonia?
<2 yrs, > 65 yrs, smokers, chronically ill
what prevention can be given for penumonia?
pneumococcal vaccine, influenza vaccine, COVID-19 vaccine, adequate HIV tx
who should the pneumococcal vaccine be given to?
adults 65 and older or high risk populations aged 19-64
any pneumonia that results from contagious infection outside of a hospital or clinic or within 48 hrs of admission
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
what are the risk factors for CAP?
- older age
- tobacco use
- excessive alcohol use
- comorbid conditions
what testing is required for CAP diagnosis?
what additional testing should be ordered if there are inpatient?
CXR or CT
sputum, blood cultures x2, CBC, CMP, influenza, COVID-19
what treatment should be given for CAP for a patient that is healthy and being treated outpatient?
Amoxicillin 1 g TID
OR
Doxycycline 100 mg BID
OR
macrolide (azithromycin or clarithromycin)
what treatment should be given for CAP for a patient that has comorbidities and being treated outpatient?
macrolide (azithro or clarithro) OR doxycycline AND beta-lactam (amoxicillin-clavunate or cephalosporin)
OR
fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)
what treatment should be given for CAP for a patient that is being treated inpatient (no ICU)?
fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)
OR
macrolide (azithro or clarithro) AND beta-lactam (amox-clavunate, ceftriaxone)
pneumonia that develops more than 48 hours after a hospital admission
Nosocomial pneumonia
nosocomial pneumonia occurring >48 hours after being admitted in the hospital
HAP (hospital acquired pneumonia)
pneumonia in patient on mechanical ventilator support for >48hrs
VAP (ventilator associated pneumonia)
what are the signs & symptoms of pneumonia?
productive cough, fever, SOB, increased HR + RR, hypoxia, crackles, egophony, dullness
treatment for nosocomial pneumonia?
1. empiric abx
2. narrow abx regimen (once culture results available)
+ supportive
group of lung diseases affecting the interstitium (tissue and space around the alveoli of the lungs), causing scarring
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
how would subacute interstitial lung disease present?
progressive dyspnea for weeks/months
cough
fatigue
decreased diffusion capacity
restriction
the space between the airspaces and vascular structures is usually ______, but ILD makes this space _______
thinner; thicker
what is FEV1?
forced expiratory volume in 1 second
what is FVC?
forced vital capacity
how would a restrictive lung condition look for FEV1?
normal
how would a obstructive lung condition look for FEV1?
decreased
how would a restrictive lung condition look for FVC?
decreased
how would a obstructive lung condition look for FVC?
normal or decreased
how would a restrictive lung condition be for FEV1/FVC ratio?
normal to increased
if the FEV1/FVC ratio is above the lower limit of normal, it is indicative of what type of lung disease?
normal or restrictive
if the FEV1/FVC ratio is below the lower limit of normal, it is indicative of what type of lung disease?
obstructive
what are some late disease signs/symptoms of interstitial lung disease?
tachypnea, decreased lung volumes, digital clubbing, right sided heart failure
what would you see on a CXR/CT chest in a person with interstitial lung disease?
ground glass appearance, nodular, cystic, honeycomb, fibrotic changes
what diagnostics can be used for interstitial lung disease?
PFTs, serologies, lavage, biopsy
progressive, extensive remodeling and scarring of the lungs due to an unknown cause
Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias (idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis)
what are the classic findings of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia on CXR/CT?
ground glass, honeycombing, fibrotic changes, traction bronchiectasis (usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP))
what are the symptoms of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia?
gradual onset of dyspnea, cough, fatigue
diffuse crackles
how are ILD exacerbations often treated?
- high flow oxygen (if presenting with acute respiratory failure)
- rule out infectious etiology
- broad spectrum abx and corticosteroids (high dose)
treatment for idiopathic interstitial pneumonia?
limited therapeutic options
lung transplant only cure
anti-fibrotics: nintedanib or pirfenidone (may slow progression)
chronic multisystem inflammatory non-caseating granulomatous disease
sarcoidosis
what are the signs & symptoms of sarcoidosis?
50% asymptomatic
fever, malaise, dry cough, dyspnea, erythema nodosum, lymphadenopathy
what would you expect to see on the following labs in a person with suspected sarcoidosis?
ACE
calcium
ESR
increased in all
what imaging would you order for sarcoidosis and what would you expect to see on them?
CXR: b/l hilar adenopathy and fibrotic changes
CT: parenchymal abnormalities (that aren't seen on xray)
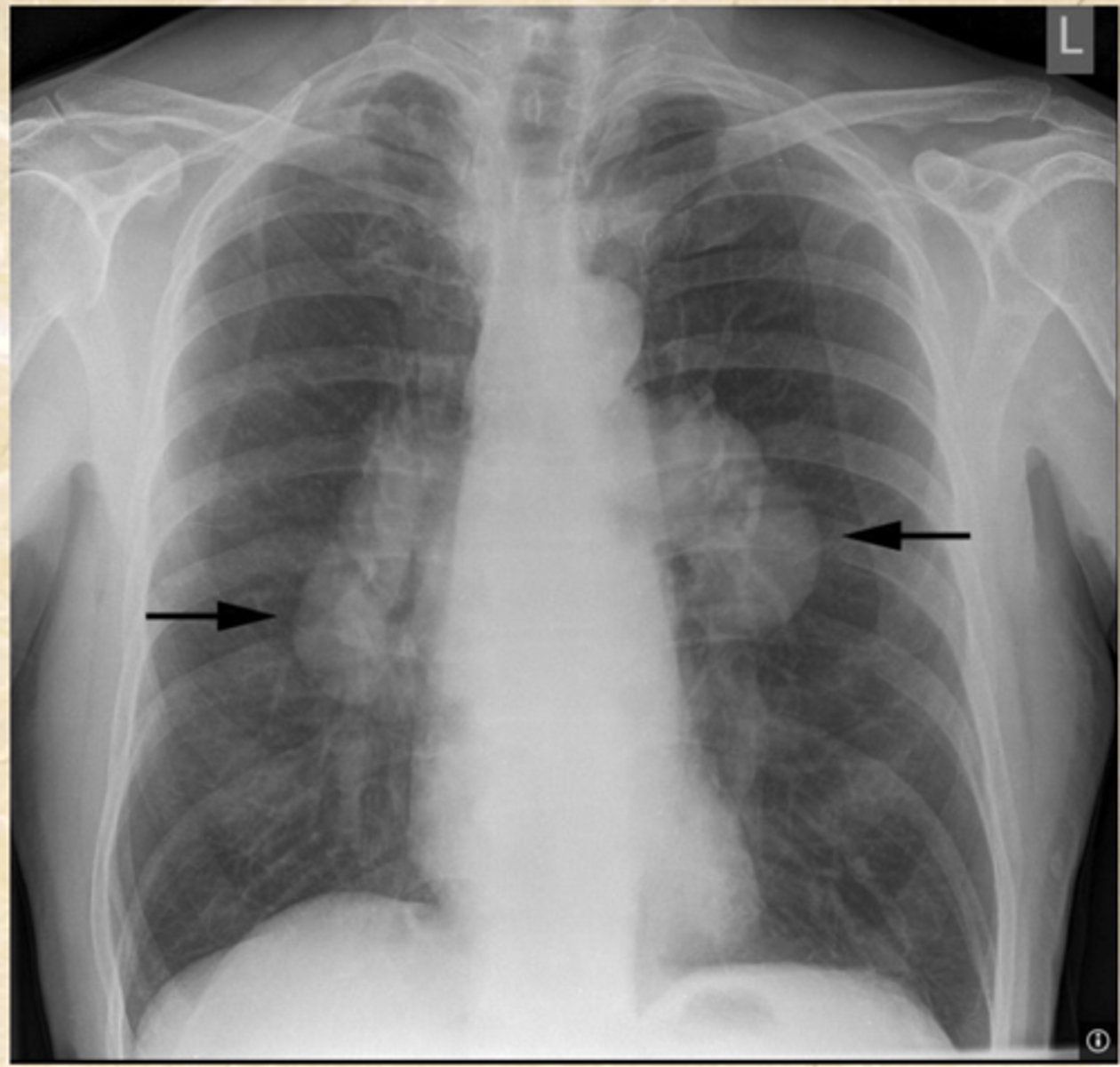
what is shown here?
Hilar adenopathy
what are the ways in which you can make a sarcoidosis diagnosis?
biopsy (would see noncaseating granulomas)
patients with sarcoidosis should also have a complete ______ exam
eye
treatment for sarcoidosis?
oral corticosteroids (prednisone)
immunosuppressants if steroids failed (methotrexate, azathioprine, infliximab)
referral
what monitoring should be done for patients with sarcoidosis?
ACE levels, yearly exams, PFTs, eye exams, CXR, EKG
what can cause lung inflammation that is indistinguishable from other ILDs?
clinical manifestations of these?
connective tissue disease (CTD)
dyspnea, cough, fever, weight loss, general malaise
a group of lung disorders where ILD is caused by a medication
drug induced ILD
what are the more common drugs that can cause drug induced ILD?
amiodorone and macrobid
damage to the lungs in which particles from a fire coat the alveoli and prevent the normal exchange of gases
smoke inhalation
treatment for smoke inhalation?
- 100% O2
- bronchodilators
- suctioning of secretions
- PEEP
- burn treatment
- hydroxycobalamin
what are the essentials for diagnosing e-cigarette/vaping associated lung injury?
1. Hx of vaping w/n 3 months
2. chest image findings
3. r/o infectious cause
what are the signs & symptoms of e-cigarette/vaping associated lung injury?
SOB, chest pain
GI sxs
tachycardia & tachypnea
hypoxia
treatment for e-cigarette/vaping associated lung injury?
supportive
corticosteroids
what would be seen on CXR in e-cigarette/vaping associated lung injury?
b/l pulmonary opacities
abnormal condition caused by dust in the lungs, with chronic inflammation, infection, and bronchitis
pneumoconiosis
lung disease from inhalation and deposition of coal dust particles
coal workers pneumoconiosis
what are the signs & symptoms of coal workers pneumoconiosis?
usually asymptomatic
dyspnea, cough, rales
Rheumatoid Arthritis /w Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis
Caplan syndrome
what would be seen on imaging with coal workers pneumoconiosis?
biopsy?
nodules in upper lung and fibrosis
dust laden macrophages
disease due to silica or glass dust in the lungs; occurs in mining occupations
silicosis
what are the signs & symptoms of silicosis?
often asymptomatic
dyspnea, cough, crackles