BI122 periard Exam #1
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
What are the 3 components of the cardiovascular system?
Blood
Heart
Blood Vessels
What are the 5 functions of blood?
1: Transportation (of:)
-Oxygen
-Carbon Dioxide
-Nutrients
-Waste products
-Hormones - from endocrine glands
2: Regulation: (of pH and electrolytes in the ECF)
3: Restrict Fluid Loss: (if vessel is damaged clotting occurs to stop fluid loss)
4: Defense: (against pathogens and toxins.)
5: Stabilization: (of body temp)
How does blood help stabilize body temperature?
Increase in body temperature = vessels transport blood to the skin & heat is lost.
Decrease in body temperature = vessels transport blood to vital organs & heat is conserved.
What are the formed elements of blood?
erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
What is hematocrit?
% of formed elements out of the total blood volume.
Why do males have a larger blood volume than females?
Due to average body sizes, males typically have more muscle mass and require more blood flow.
What are the 2 main components of plasma?
Plasma is composed of 92% WATER and 8% PLASMA SOLUTES; forms about 55% of whole blood.
Examples of plasma solutes
Plasma proteins (Albumins, Globulins, Fibrinogen, Enzymes and Hormones)
-Nutrients/wastes
-Respiratory Gases
-Electrolytes
Which plasma protein is more abundant? And which plasma protein is a major contributor to osmotic pressure?
Albumins; a major contributor to osmotic pressure
- to maintain water balance between tissues and blood-
What is hematopoiesis? (hemopoiesis)
A process that produces formed elements.
*before birth - occurs in yolk sac, spleen, and liver
*after birth - occurs in red bone marrow.
What are hemocytoblasts and what is their function?
They are multi-potent stem cells, found in red bone marrow, producing all formed elements after stimulated by hormones
percentage of erythrocytes in blood
~45%
percentage of leukocytes in blood
1%
Percentage of platelets in the Blood
1%
Function of RBCs (erythrocytes)
Transports respiratory gases.
Characteristics of erythrocytes
Anucleate
Bioconcave shaped
Mostly hemoglobin
What actually binds to oxygen?
Heme binds to O2
Why is carbon monoxide dangerous?
It binds with hemoglobin, reducing the blood's oxygen carry-capacity
What is erythropoiesis? And how are they controlled?
RBC formation; Regulation of Erythropoiesis = hormonally controlled. -Affected by low or high O2 levels in blood
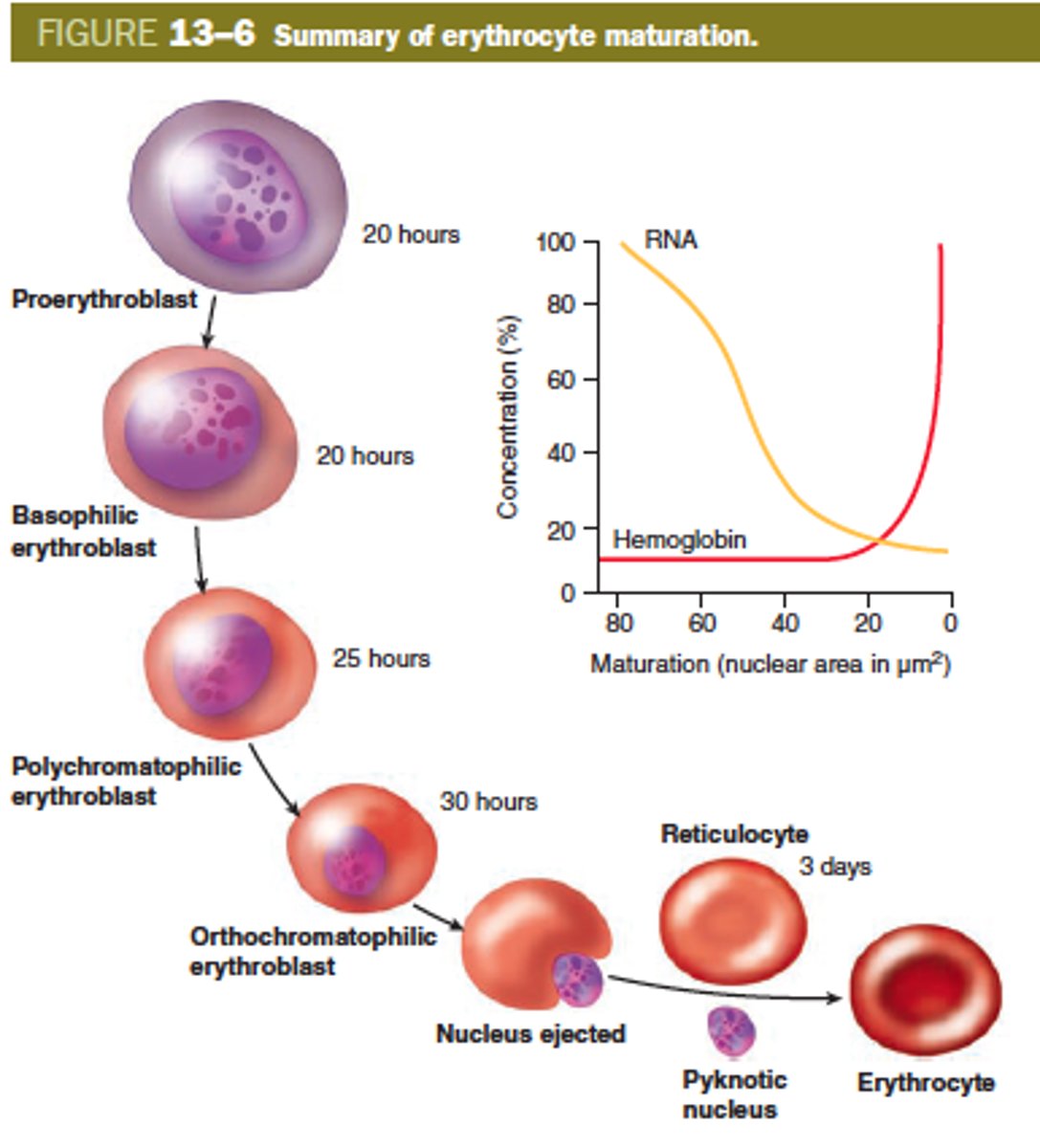
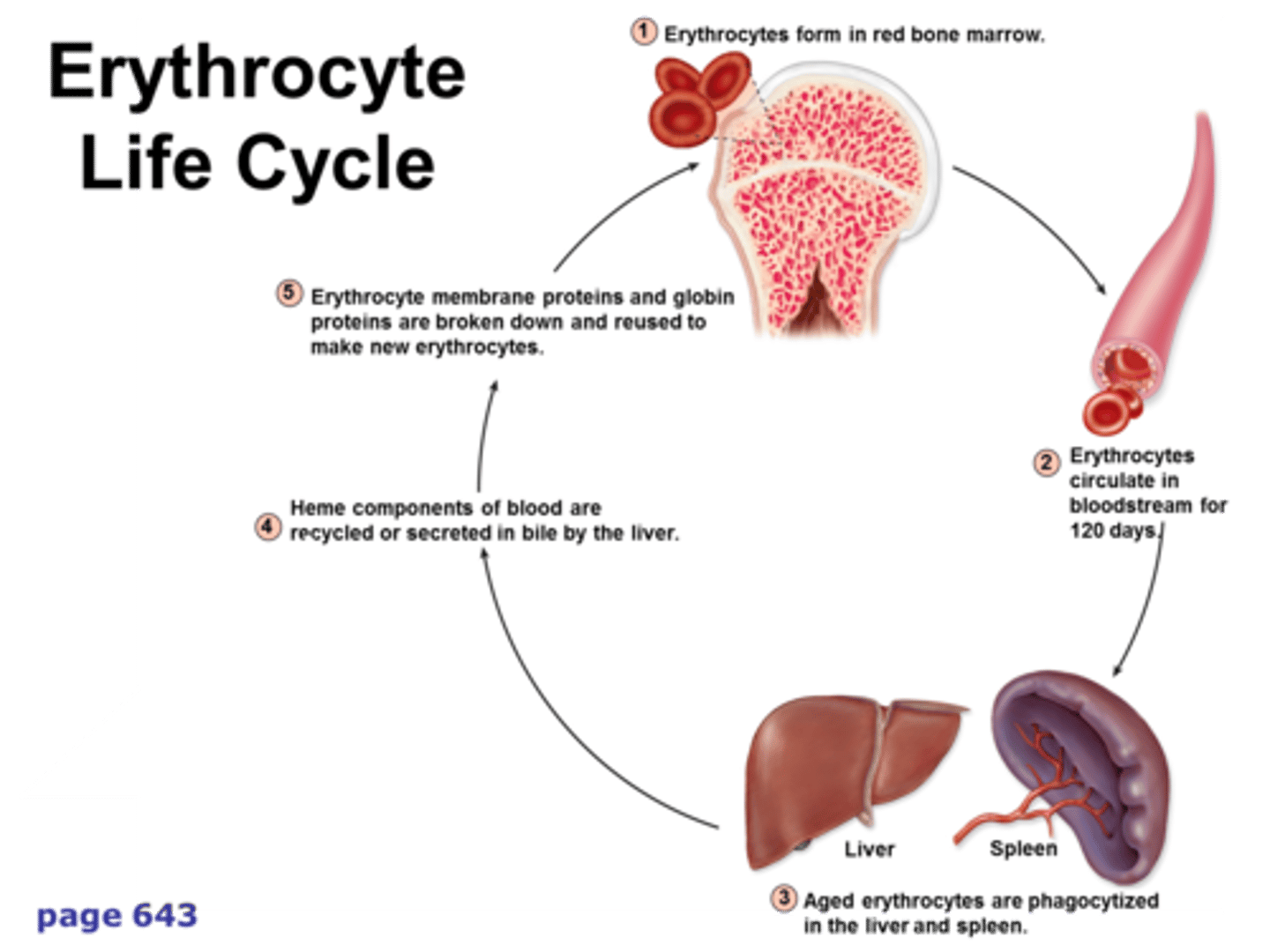
life of an erythrocyte
Nutrients are absorbed in small intestine
Blood transports nutrients to red bone marrow
RBM erythrocytes arise from hemocytoblasts.
Erythrocytes life span = 120 days
Macrophage destroys old erythrocytes
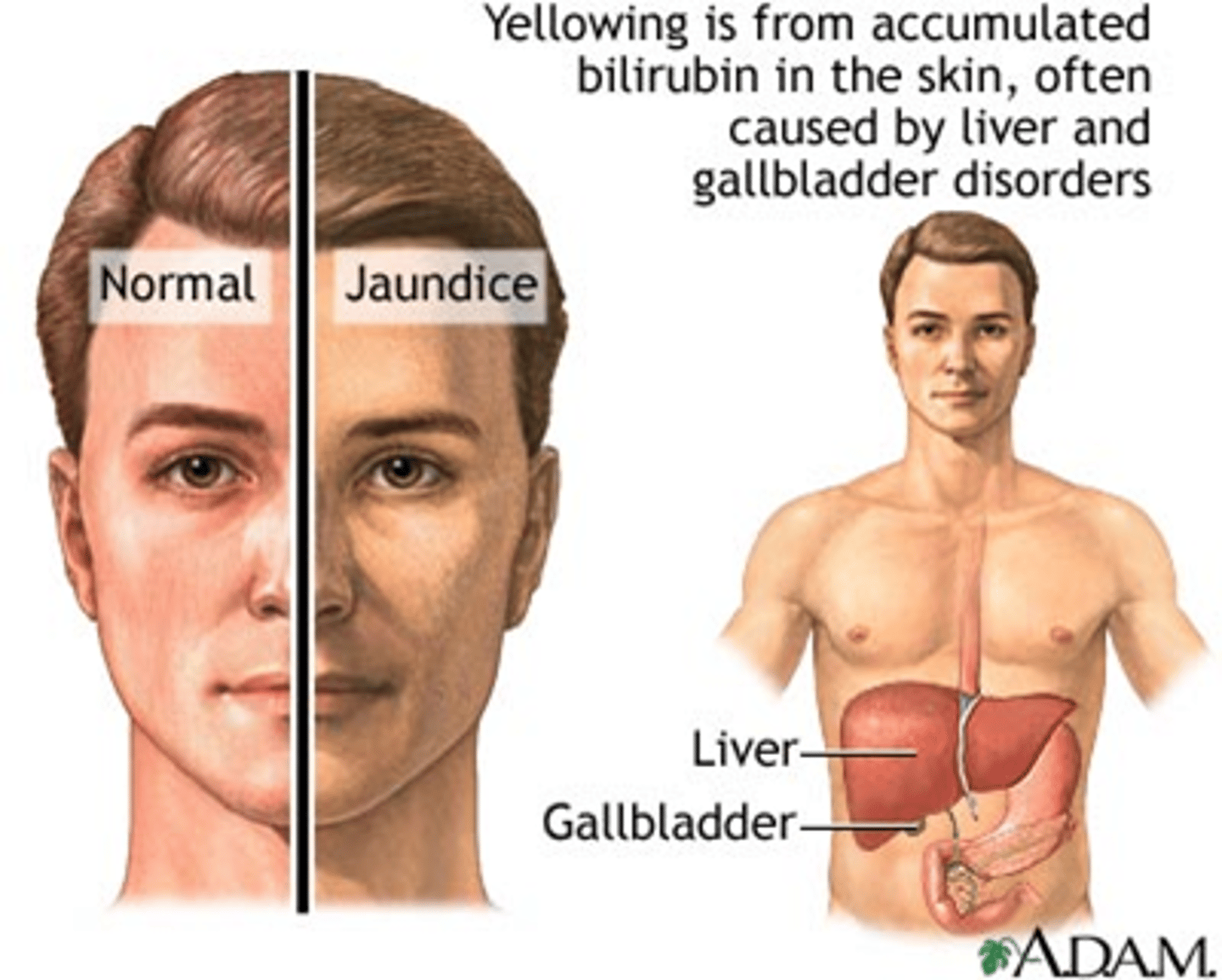
What is jaundice and what causes it?
Yellowish discoloration of skin and eyes due to increased circulation of bilirubin in peripheral tissues
-> Due to liver not processing bilirubin or bile ducts blocked
Erythropoietin, Is it positive or negative feedback?
EPO is a hormone that stimulates RBC production; released by kidneys. -Negative feedback
What is blood doping?
the injection of oxygenated blood into an athlete before an event in an attempt to enhance athletic performance.
How does blood doping relate to erythropoiesis
basically adding more blood to body after it made new ones = bad
What is anemia?
Abnormally low oxygen-carrying capacity of blood.
iron deficiency anemia
anemia resulting when there is not enough iron to build hemoglobin for red blood cells; most common type!
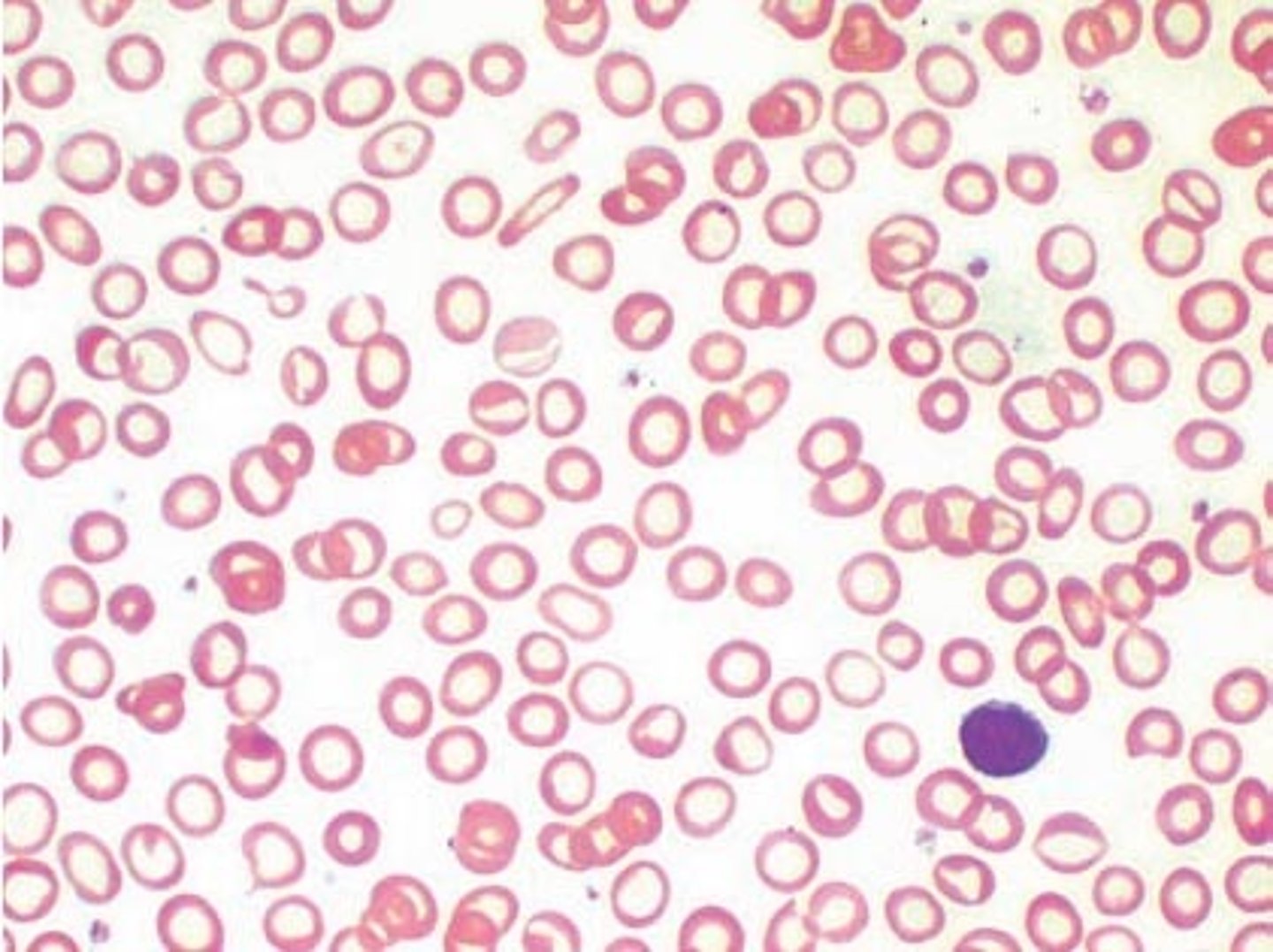
pernicious anemia
Vitamin B12 deficiency = prevents stem cell division in red bone marrow
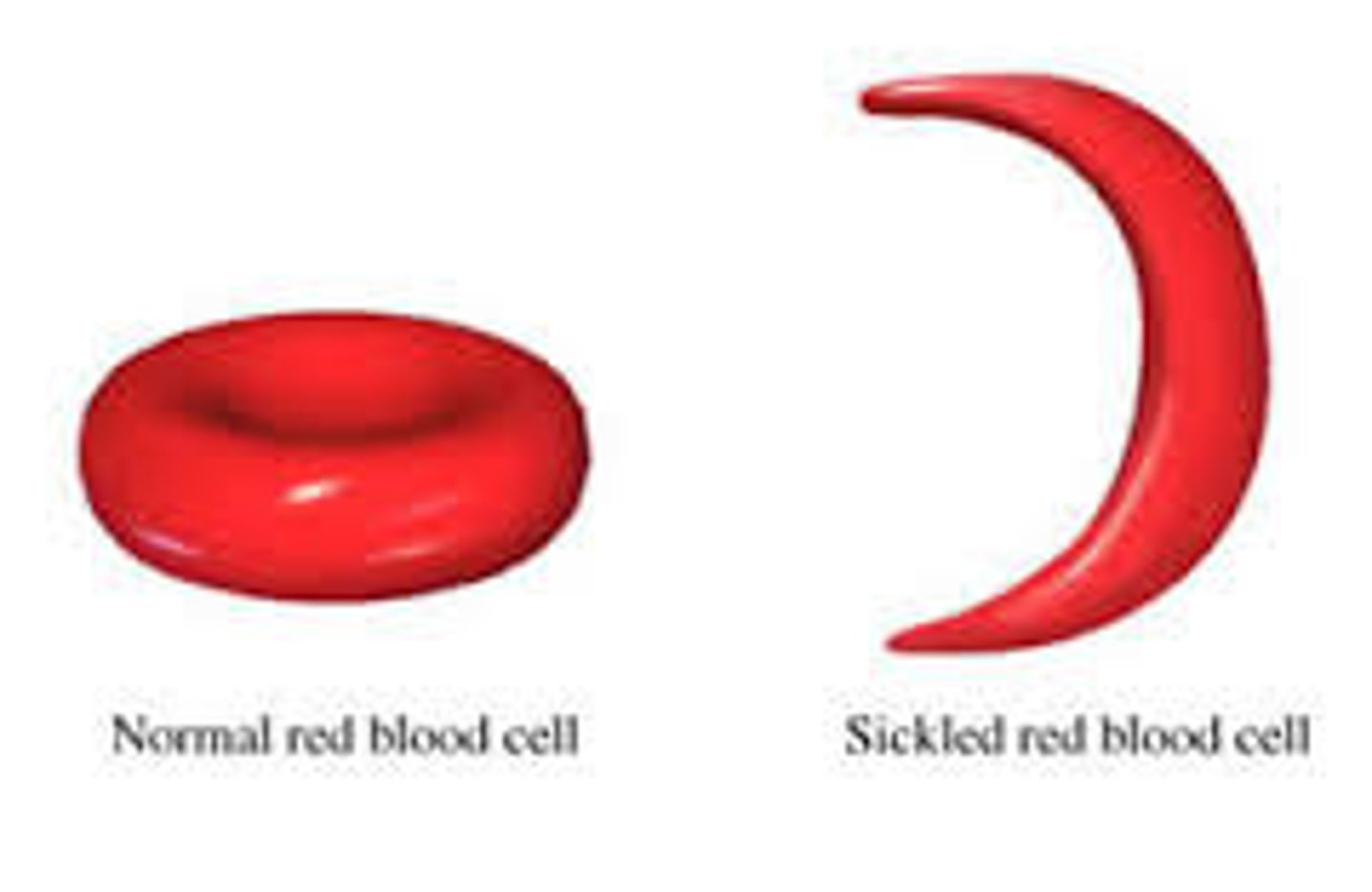
sickle cell anemia
results from abnormally shaped hemoglobin -usually genetic
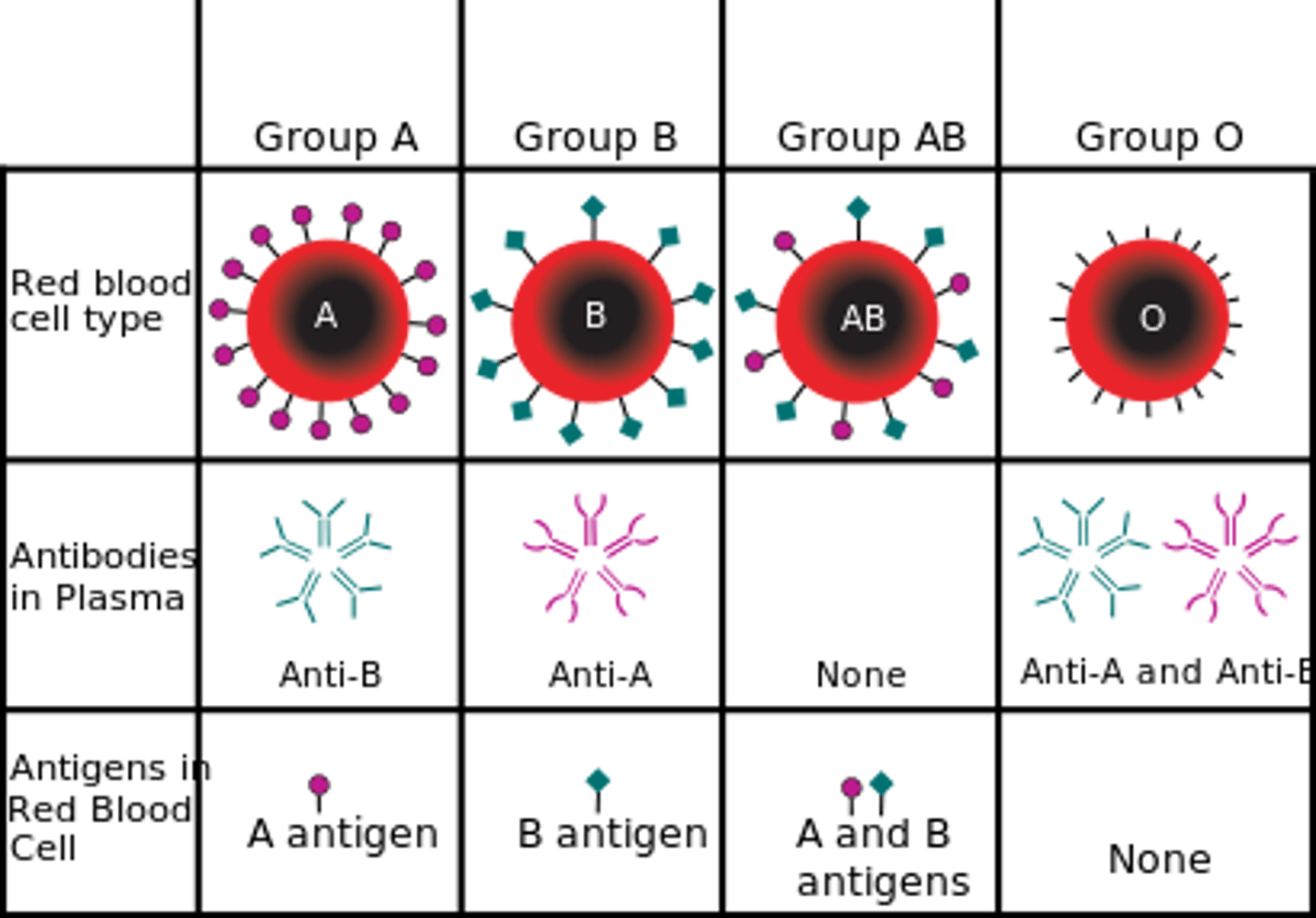
What determines a blood type?
antigens on surface of RBC
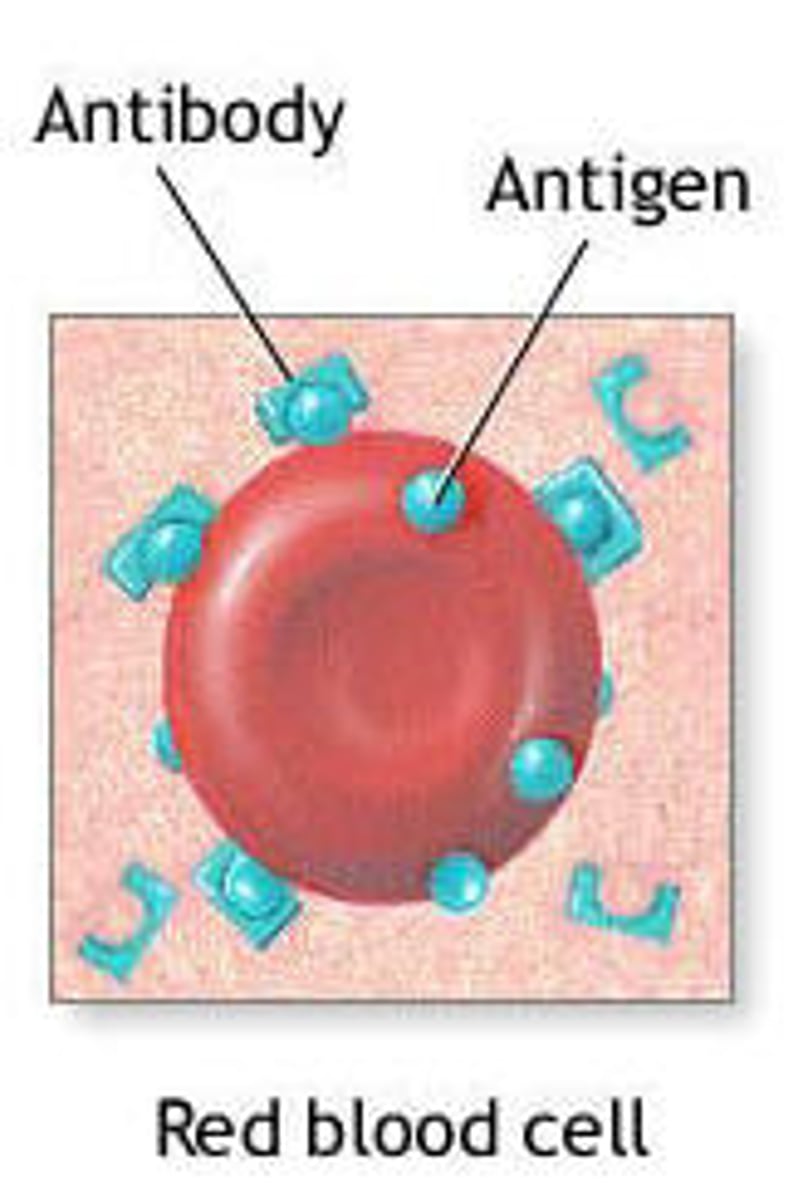
What is an antigen?
Substance on a RBC that triggers a protective defense mechanism called an immune response
Agglutination
Process of clumping RBC that occurs when antigens on RBCs of one blood type are exposed to the corresponding antibodies (agglutinins) of another blood type
ABO blood group system
What blood type is the universal donor?
O
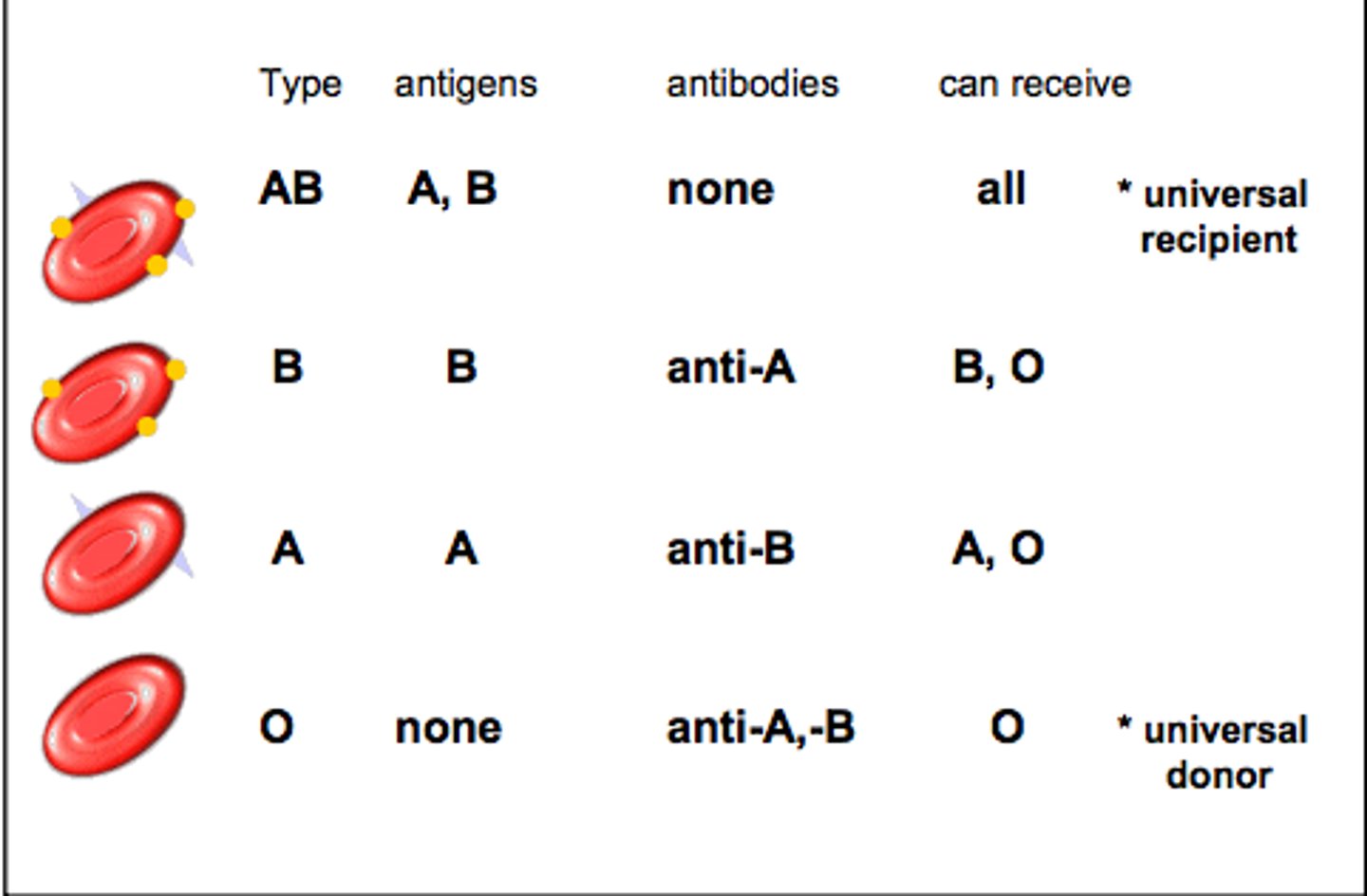
What blood type is the universal recipient?
AB
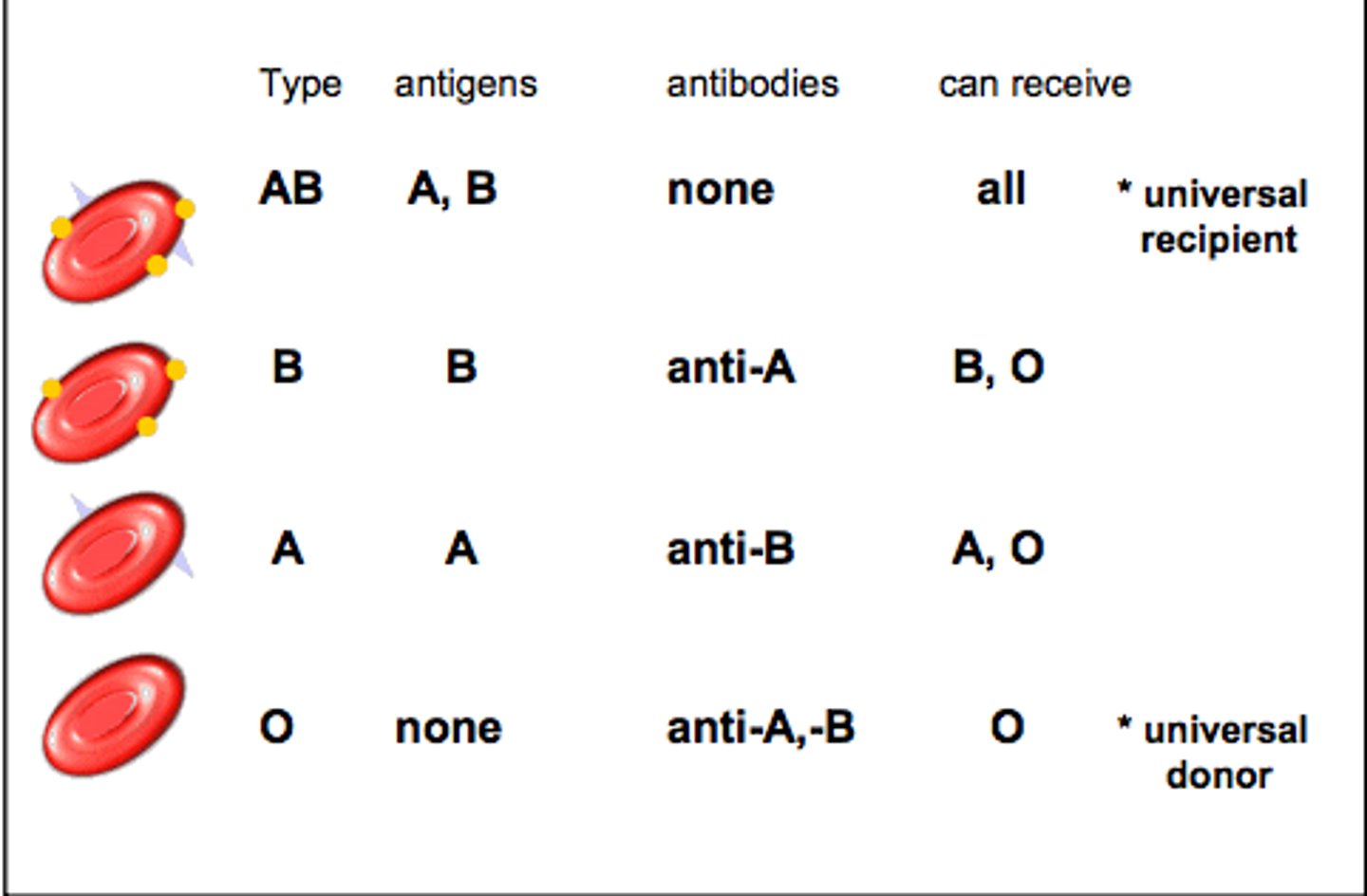
What antibodies do people not make until after exposure to a certain RBC antigen?
anti-Rh
hemolytic disease of the newborn
anti-Rh antibodies of a sensitized Rh- mother, cross the placenta and destroy the RBC'S of a Rh+ baby, leading to fetal anemia.
RhoGAM
drug prevents a mother's blood from becoming sensitized to foreign antibodies from her fetus

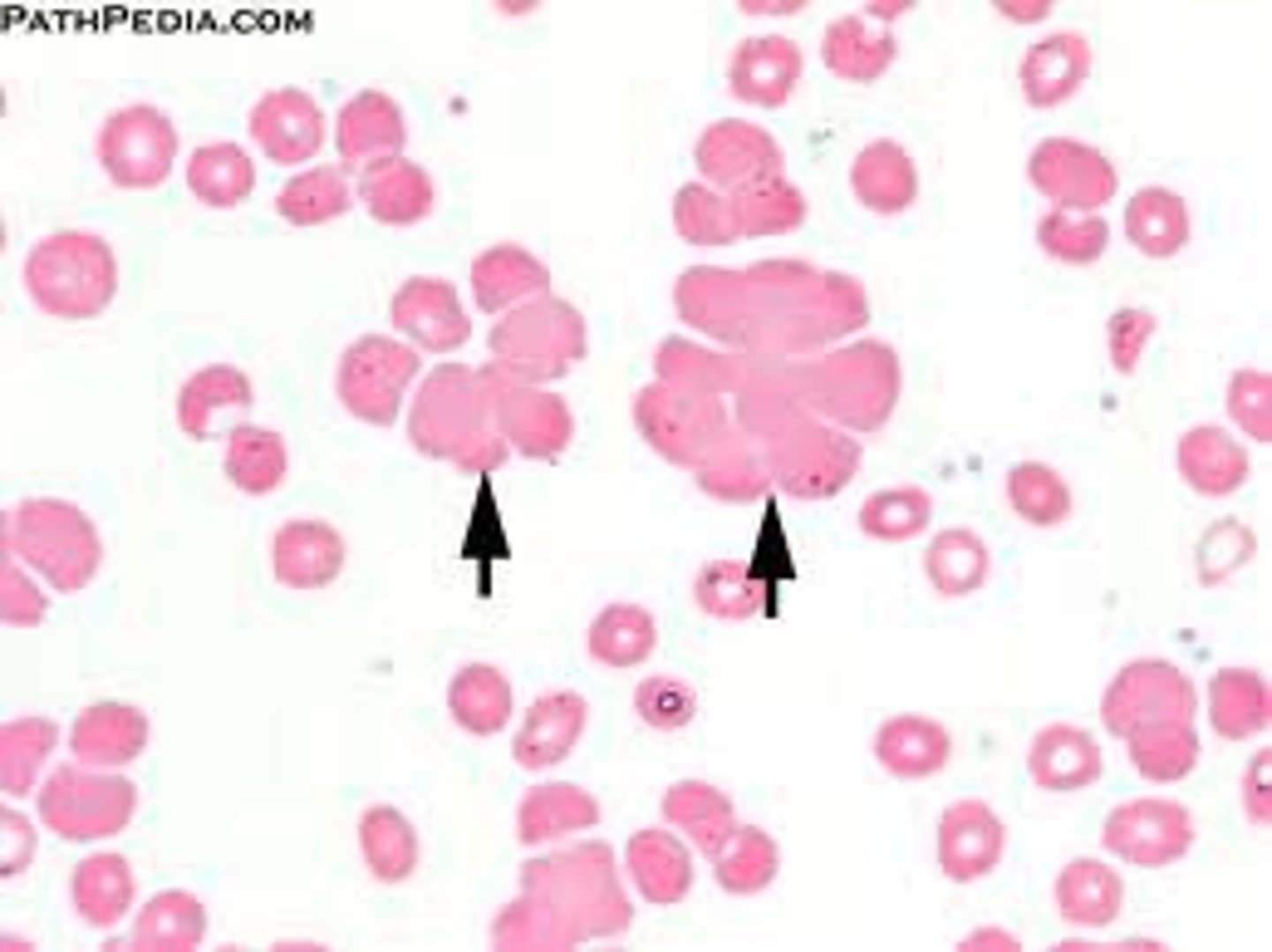
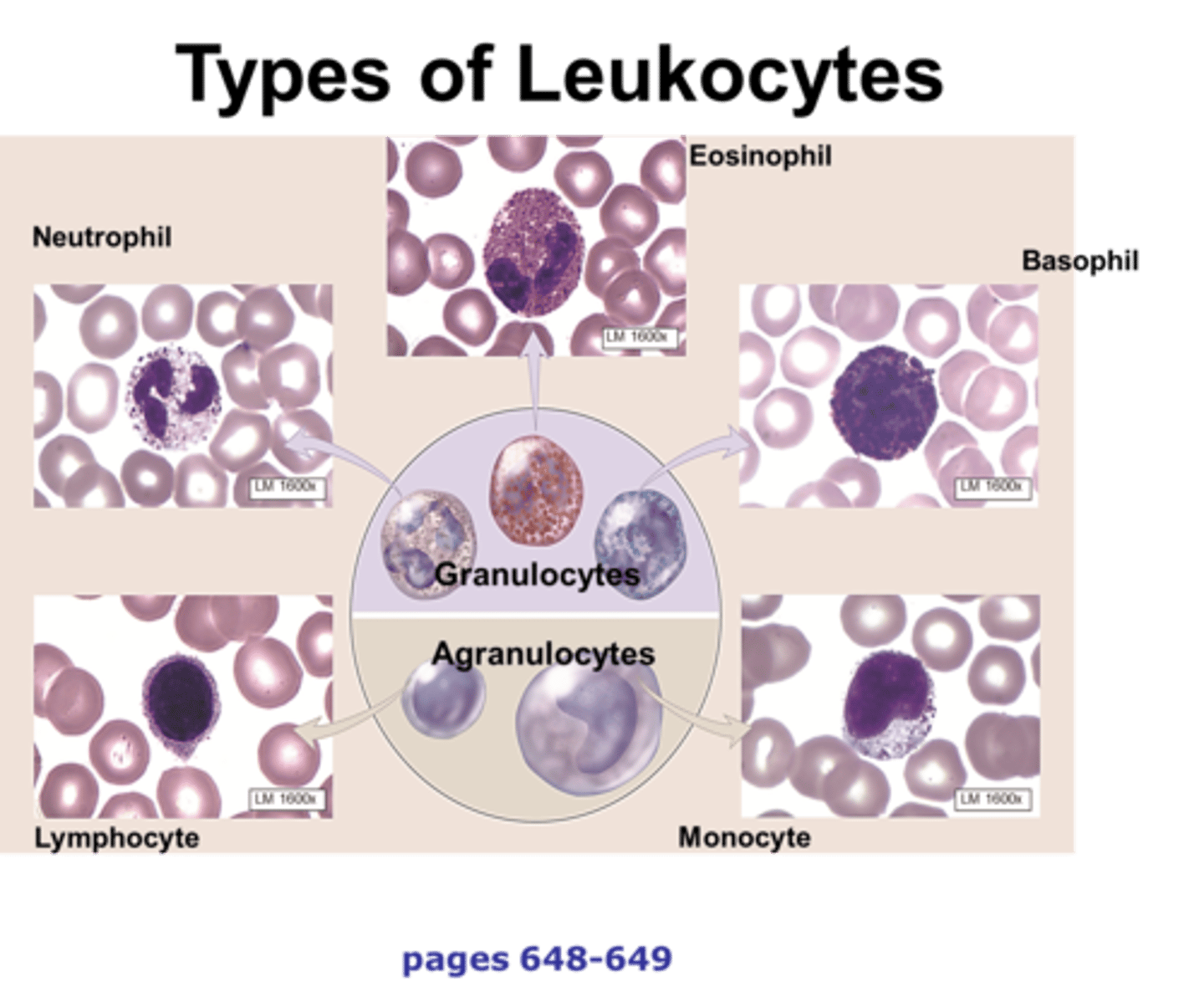
Leukocytes
have nuclei, no hemoglobin, make up little % of blood, spend its time outside bloodstream
Ameboid
WBC movement like an amoeba
diapedesis (emigration)
they can change shape to squeeze into and out blood through the endothelium (blood vessel lining cells)
positive chemotaxis
movement toward a chemical stimulus leading them to damaged tissue and invading pathogens.
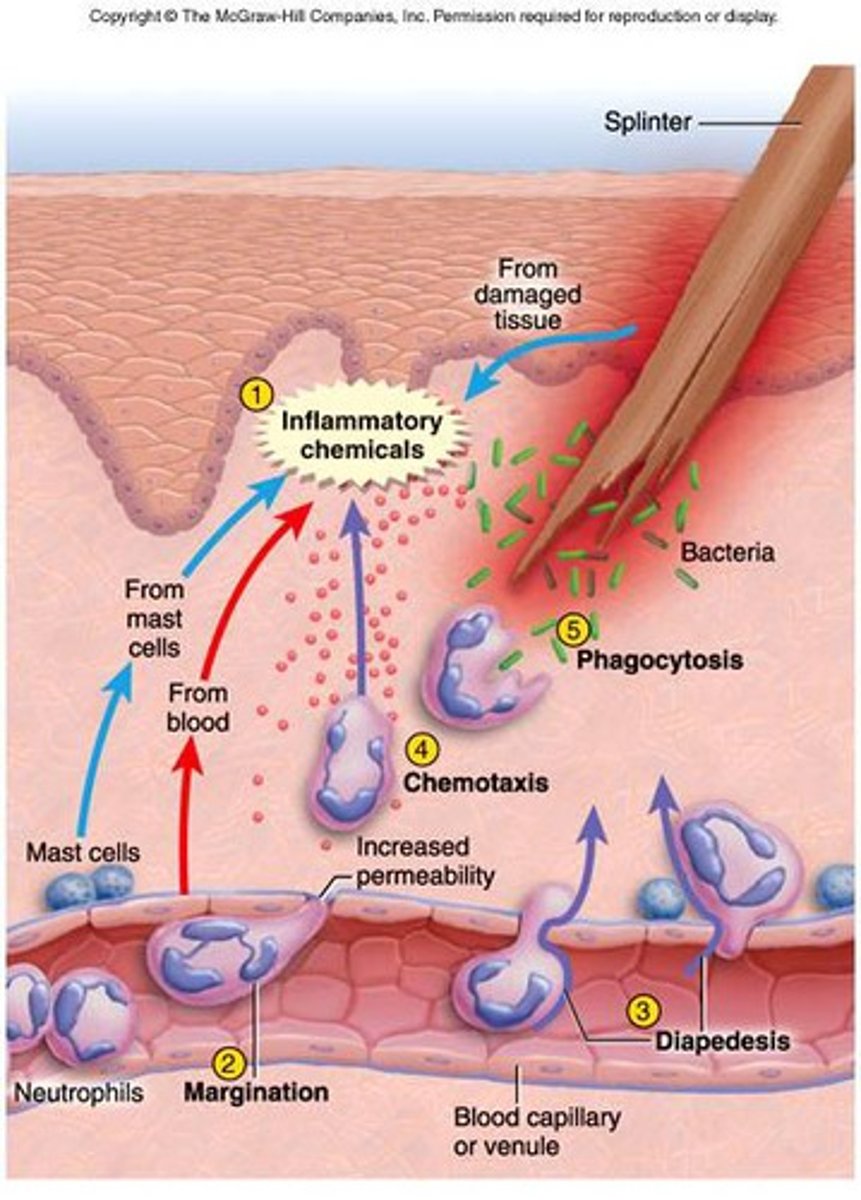
Phagocytosis
they can engulf and digest pathogens (Neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes can phagocytize)

Granulocytes
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils (names refer to granules' certain stains)
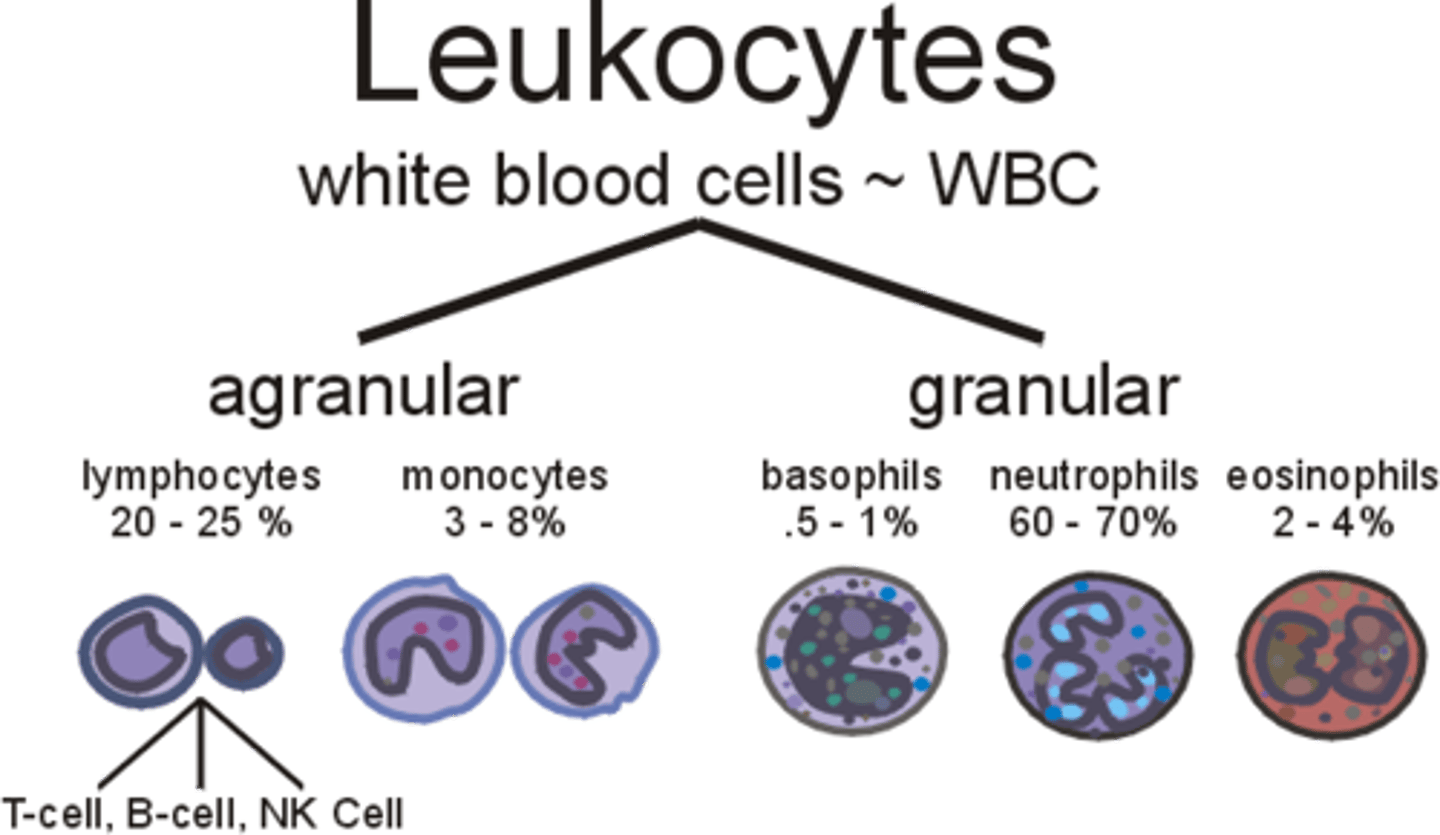
Agranulocytes
lymphocytes, monocytes. (small specific granules in cytosol not visible under microscope - a = without)
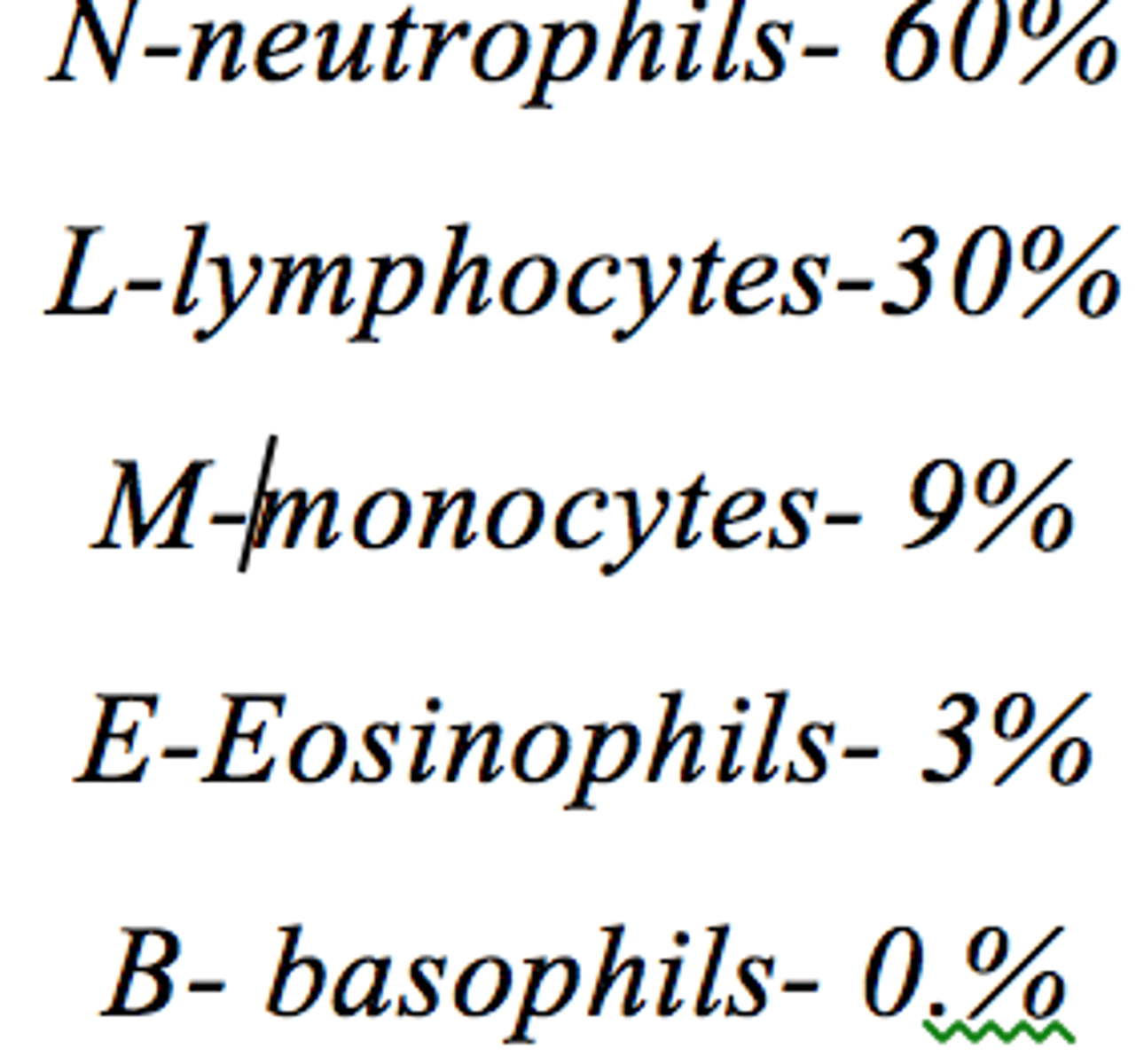
Never Let My Engine Blow
60, 30, 8, 2, 0
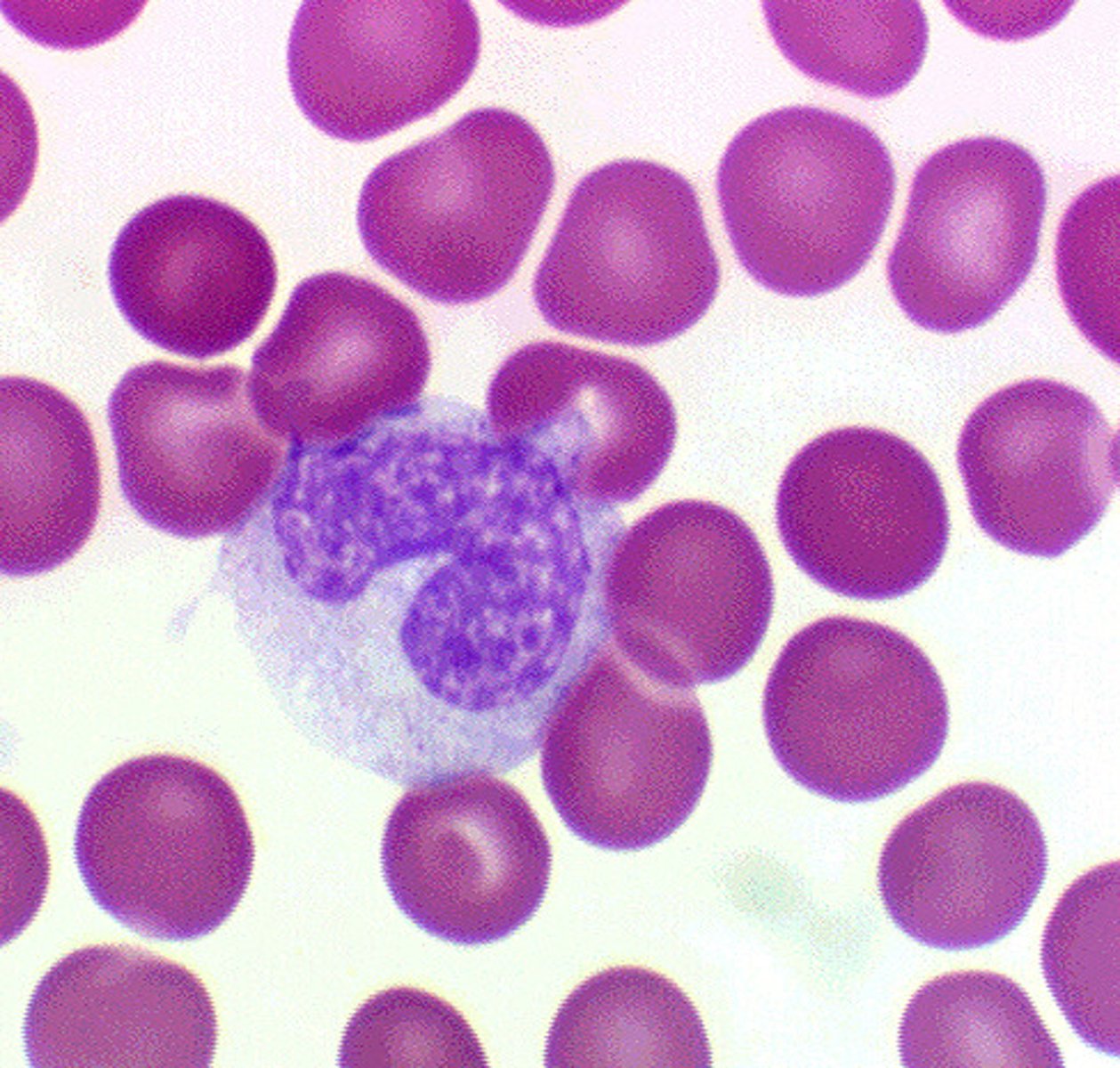
Neutrophils
A type of white blood cell that engulfs bacteria and is most abundant.
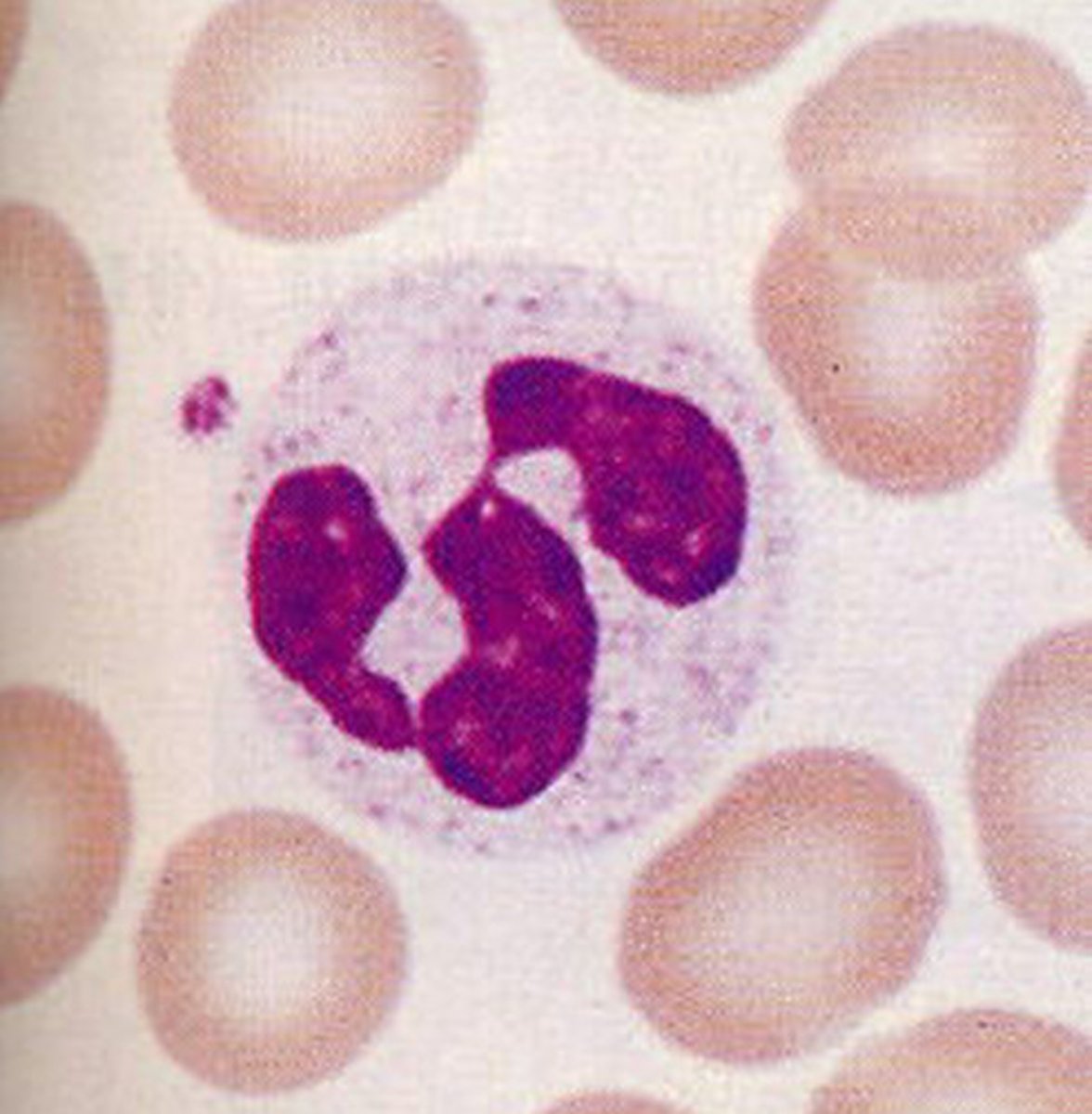
Eosinophils
Engulf antibody-labeled material
Increase during allergic reactions and parasitic worm infections
Release chemical mediators to destroy parasitic worms
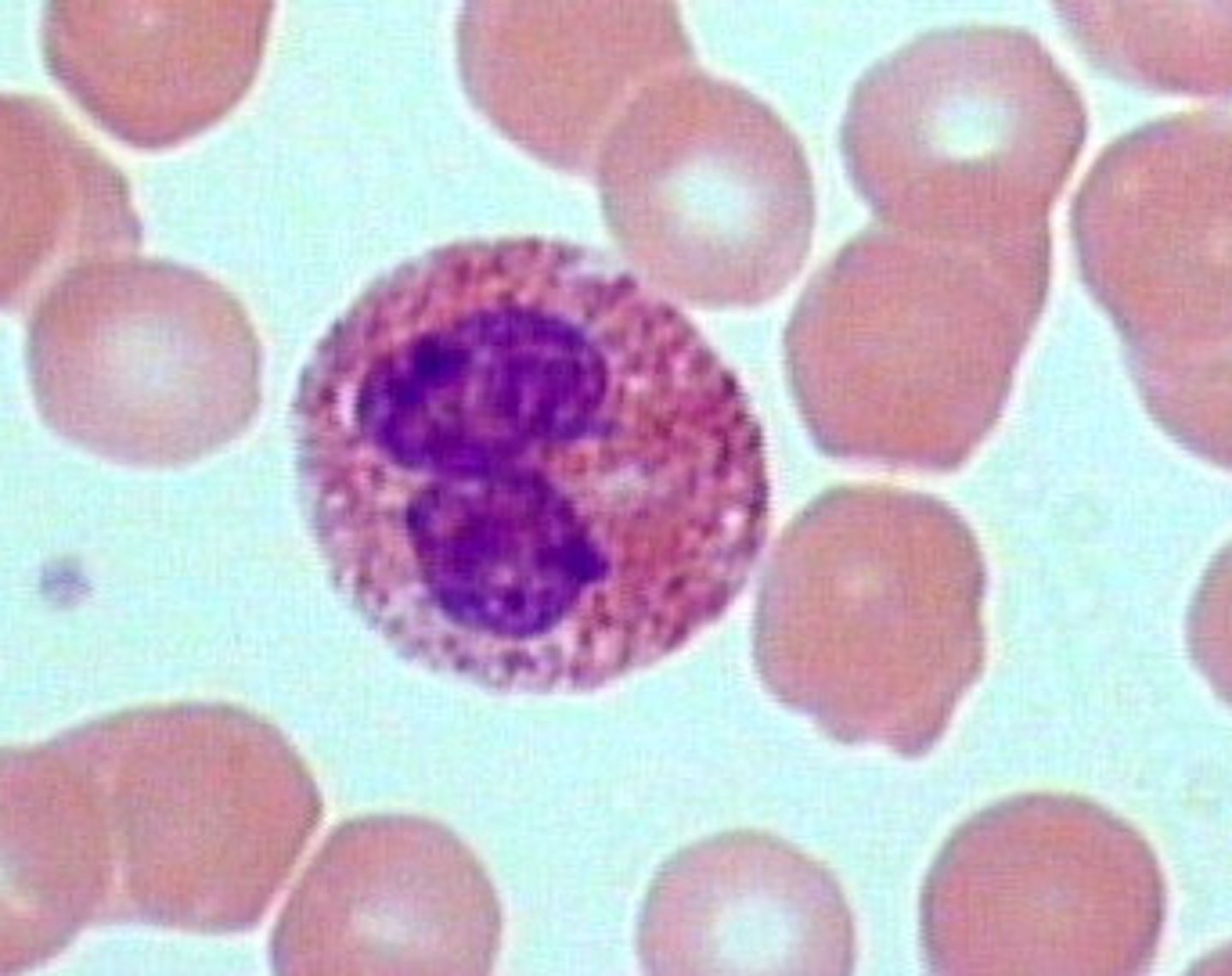
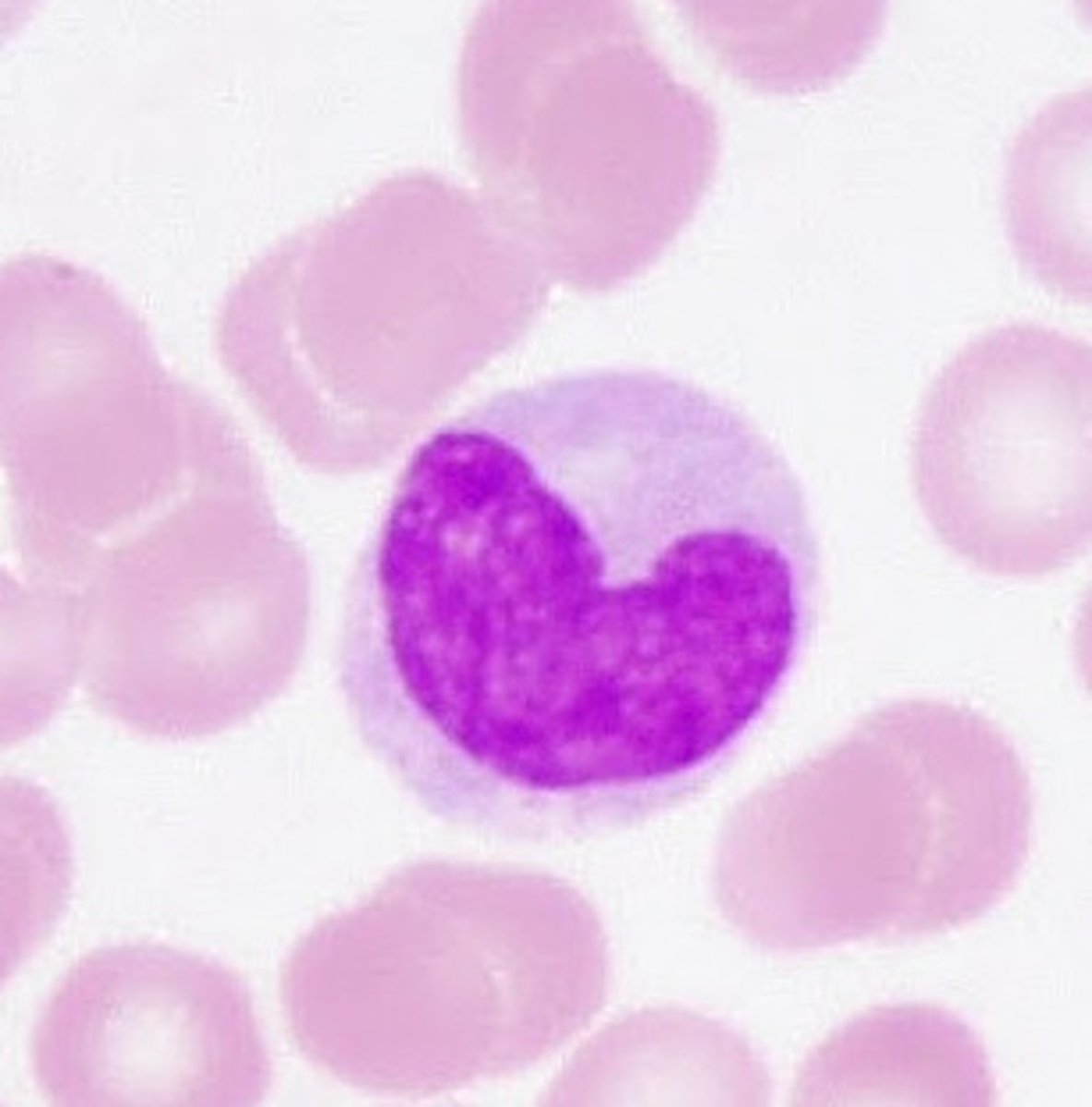
Basophils
A circulating leukocyte that produces histamine when entering damaged tissue because it promotes inflammation...(also least abundant)
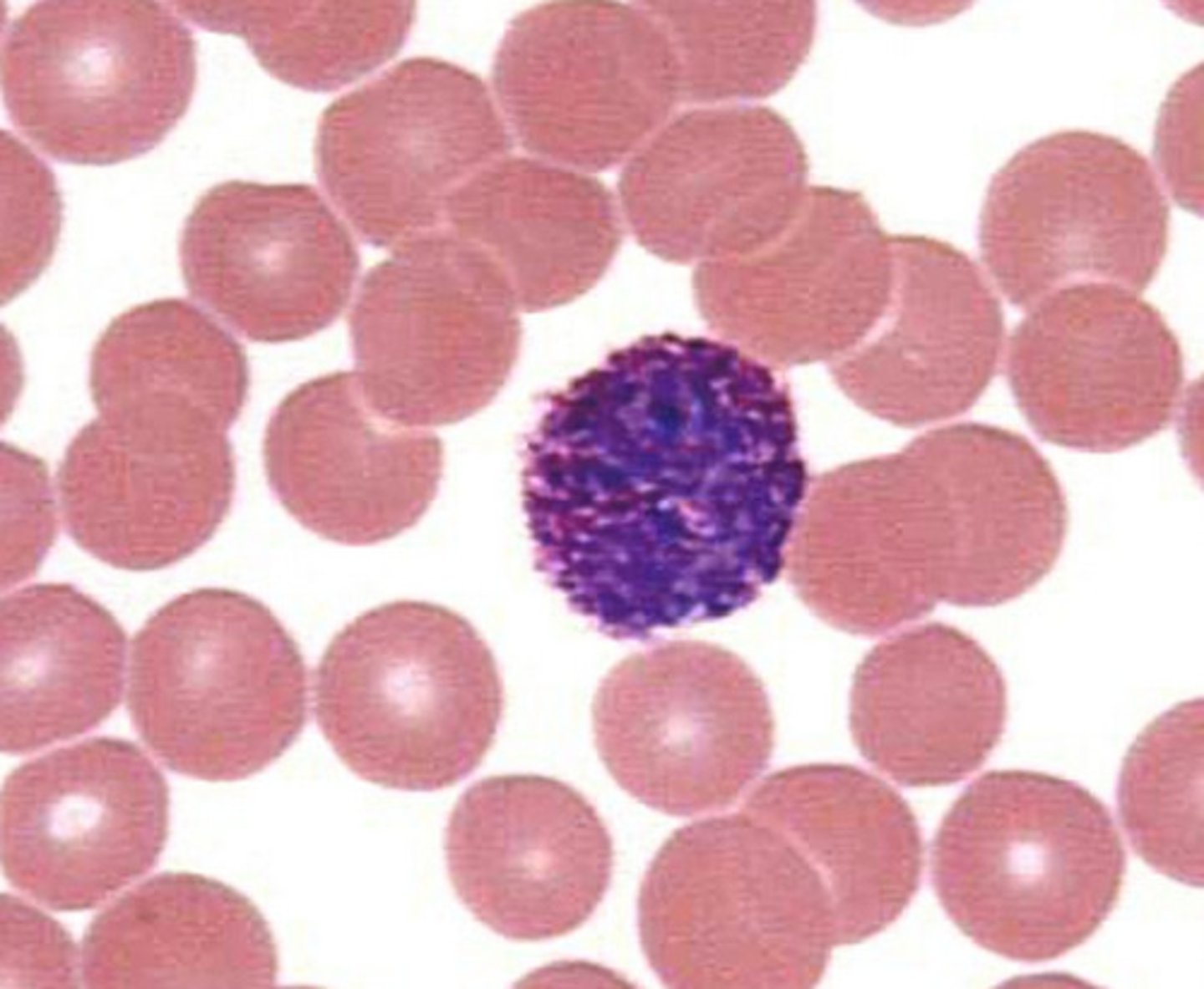
Lymphocytes
A type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off infections...T and B cells....
Have a dark stained nucleus
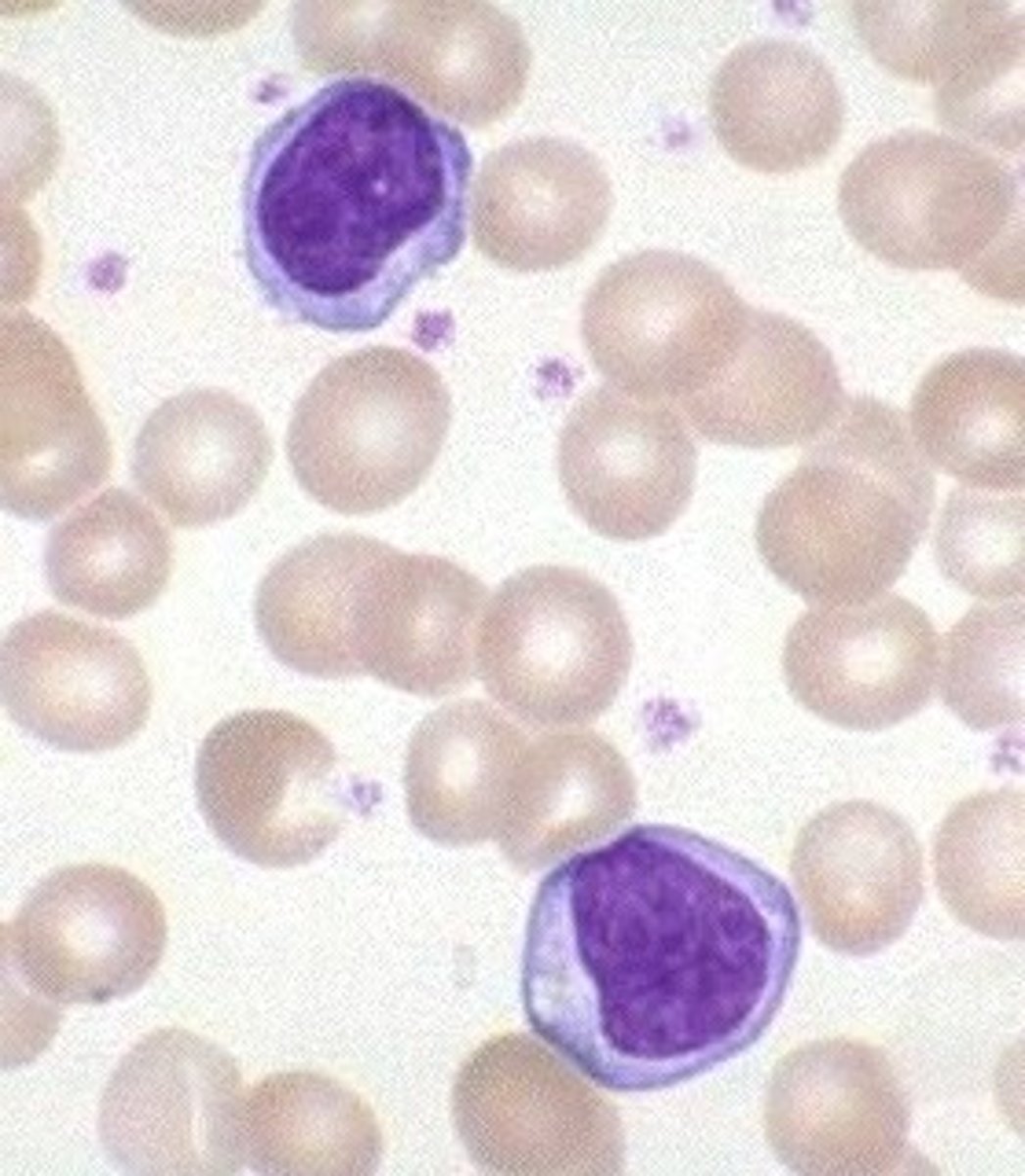
Monocytes
Leave circulation, enter tissue, and differentiate into Macrophages. Kidney shaped nucleus and phagocytize pathogens
Macrophages
leukocyte that destroys damaged or worn RBCs; activates lymphocytes to mount an immune response; actively phagocytic
What is leukemia?
Group of cancers that usually begin in red bone marrow and result in abnormal white blood cells.
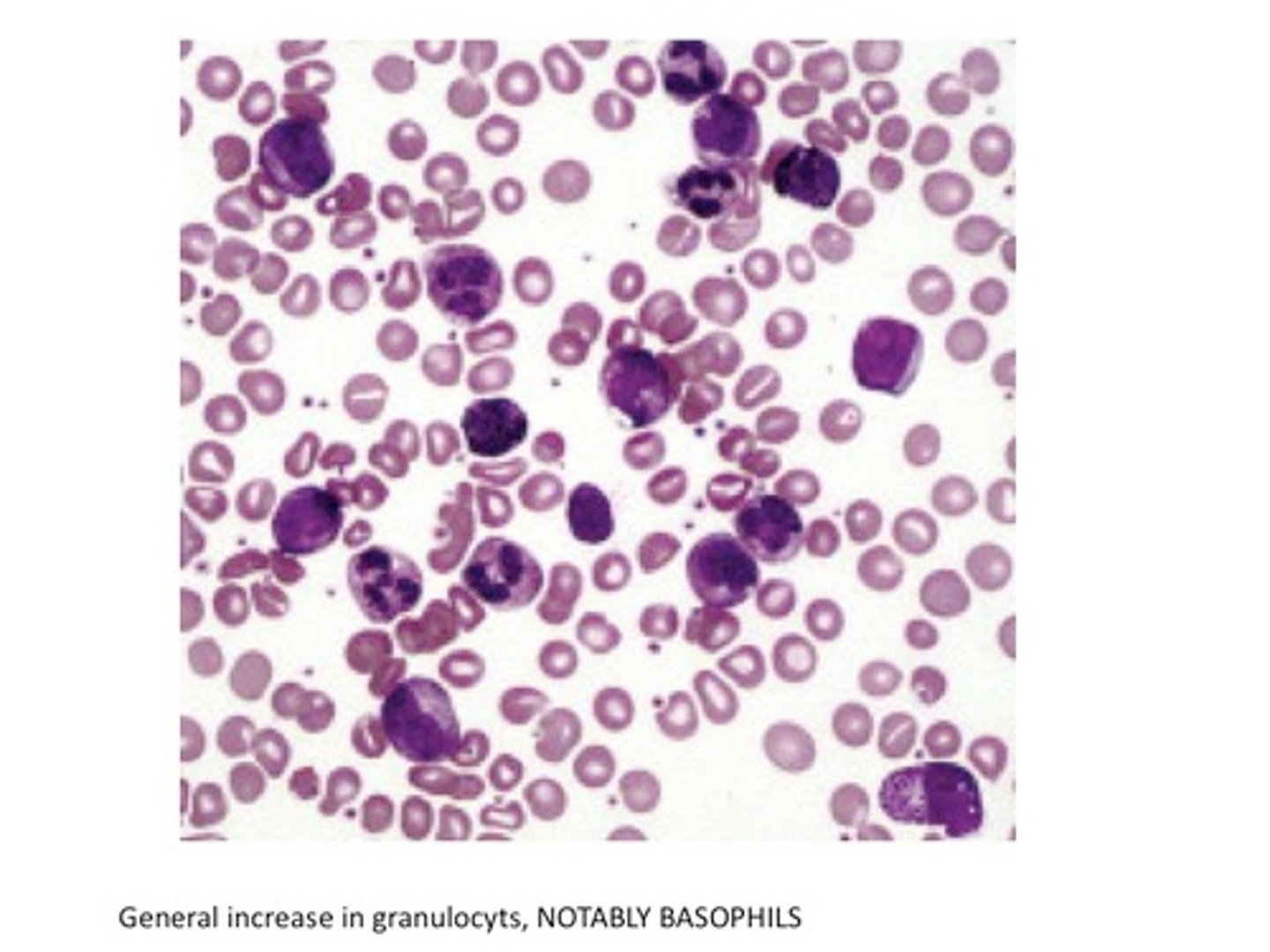
Leukocytosis
Abnormal increase/elevation of WBC (due to infection or stress)
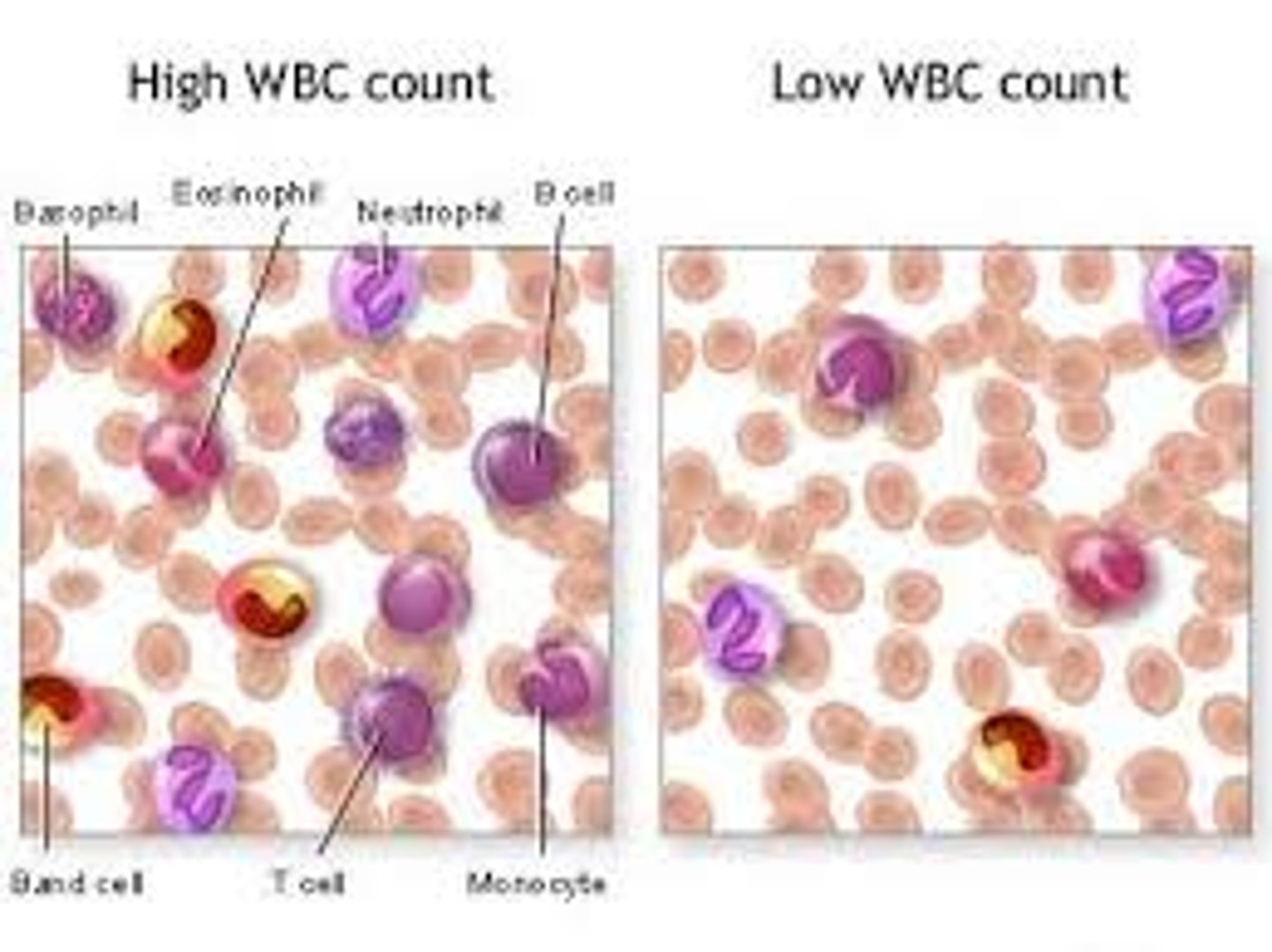
Leukopenia
Abnormally LOW white blood cell count
What are platelets?
Small fragments of cells that help blood clot
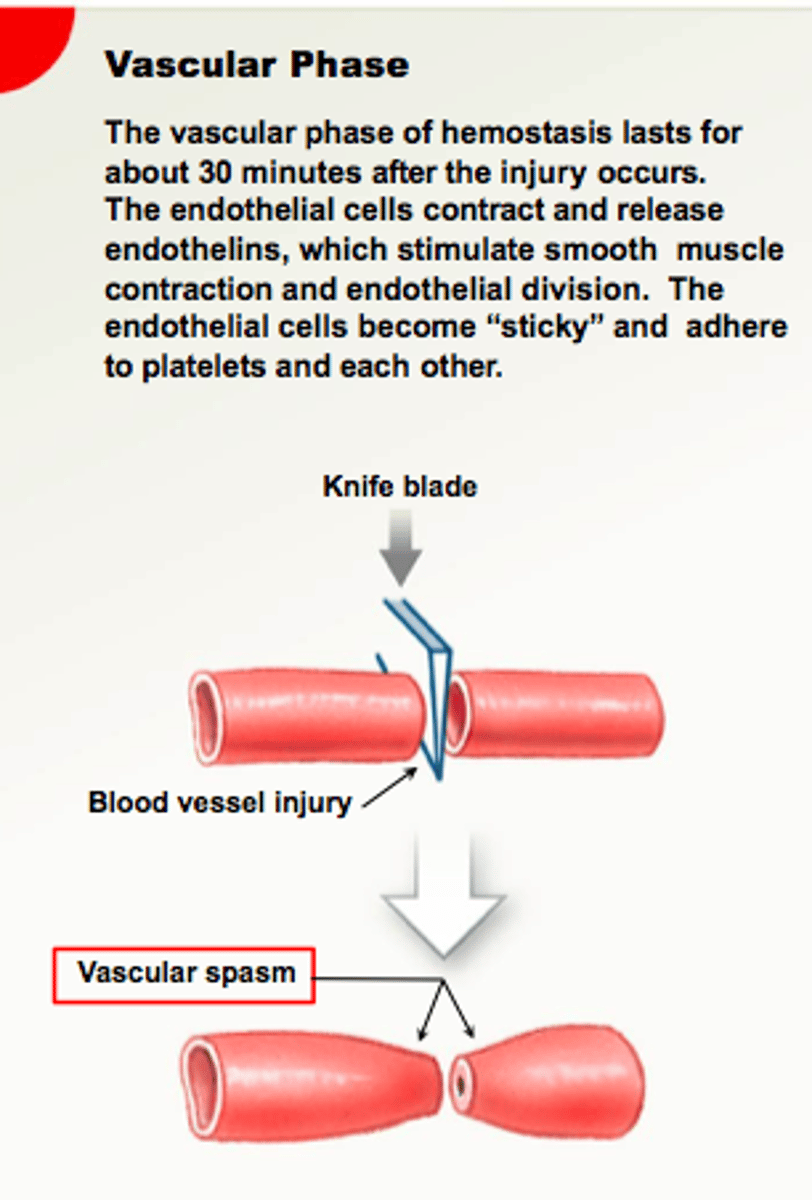
Phases of Hemostasis (stopping of a bleed)
1. Vascular phase
2. Platelet phase
3. Coagulation phase
vascular phase
endothelium releases chemicals that attract platelets to the site and stimulate cell growth and repair;
Promote vasoconstriction ("squeeze")
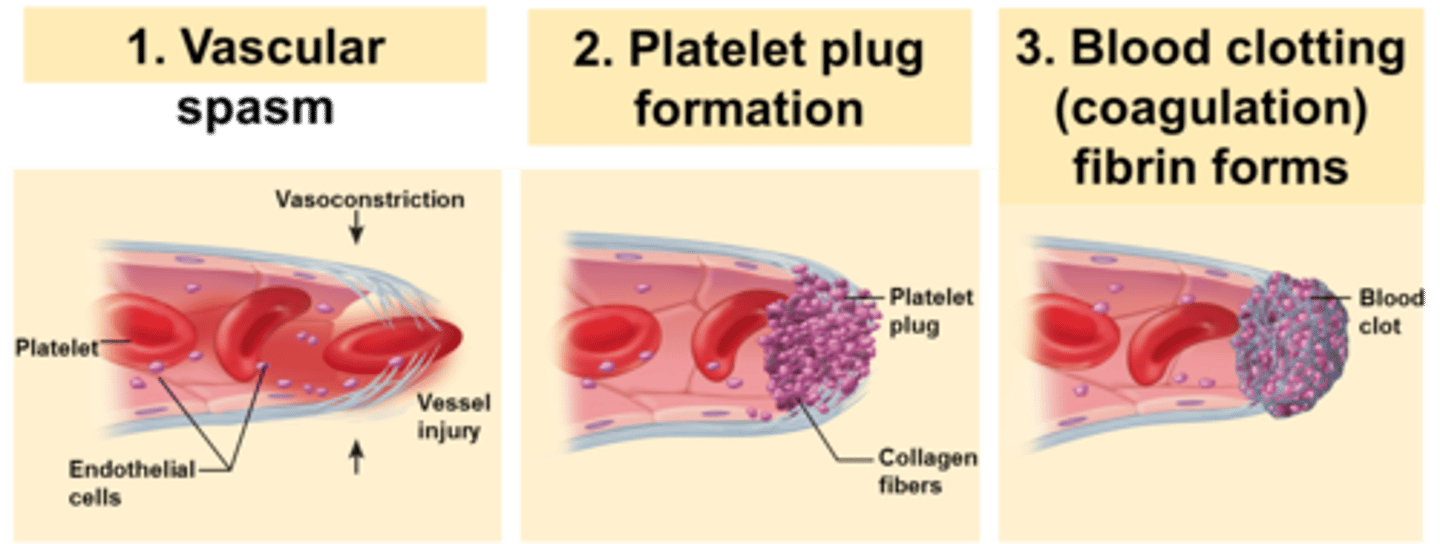
vasoconstriction
the constriction of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure.
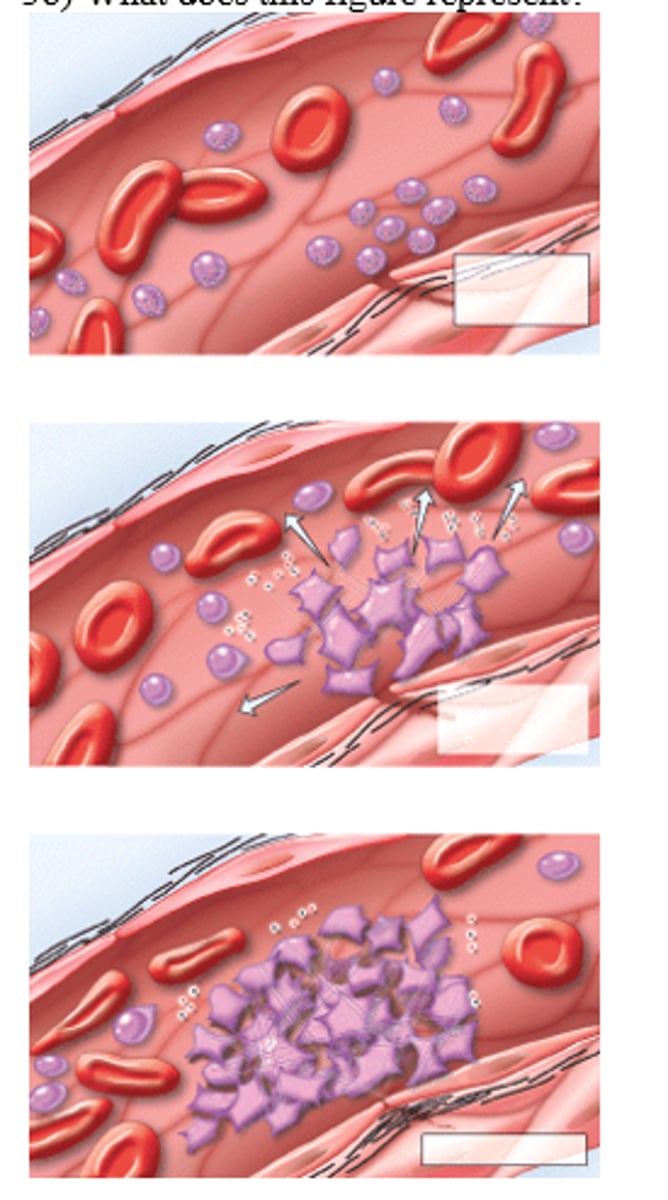
Platelet phase
1: Platelets flowing by stick to damaged area = Adhesion
2: Platelets stick together forming a temporary PLUG = Aggregation
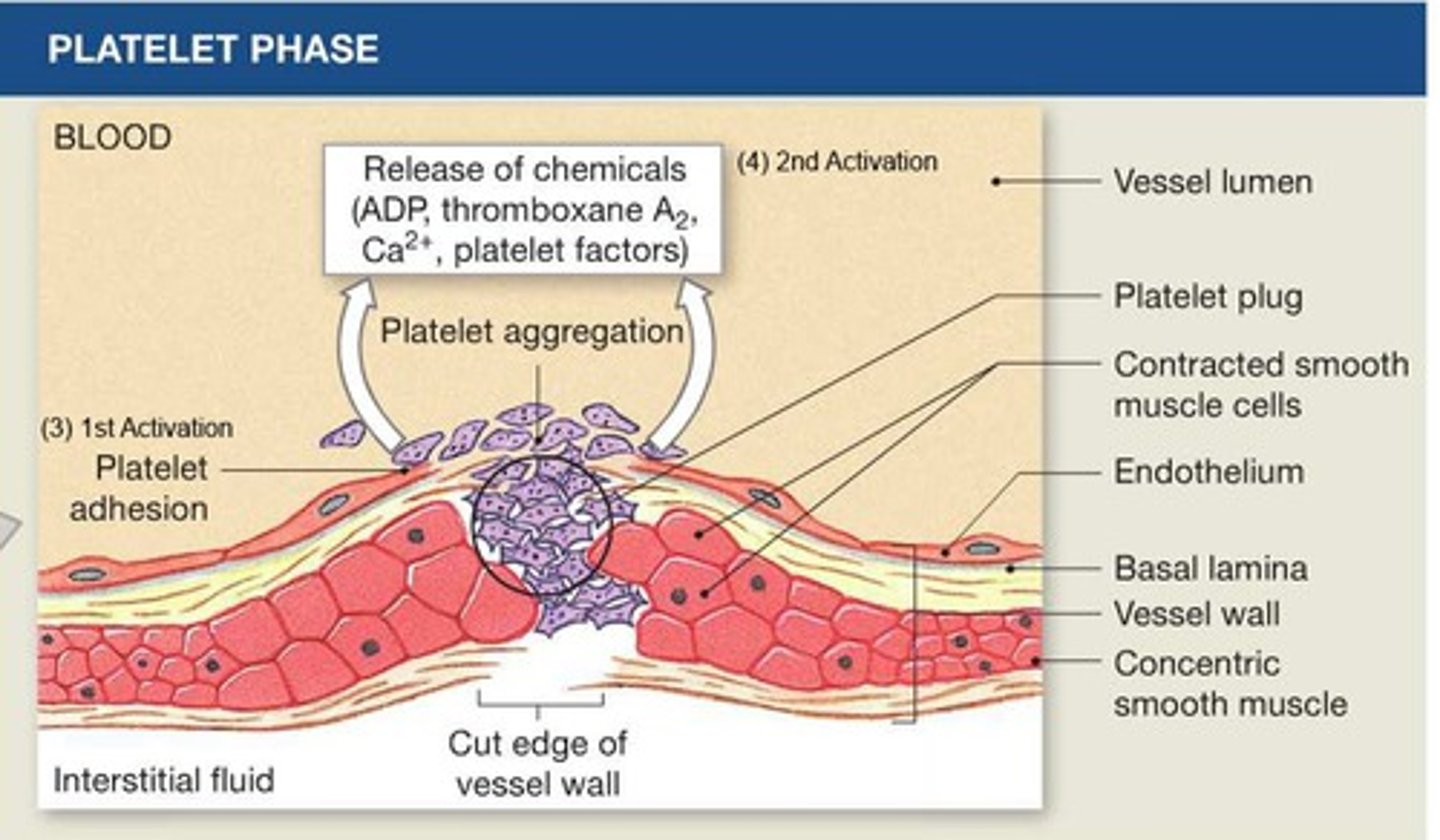
Coagulation phase of hemostasis
blood clotting; conversion of circulating fibrinogen into fibrin... --- forms the true clot!
Fibrinogen
plasma protein that is converted to fibrin in the clotting process
hydrostatic pressure
moves solutes and water out of capillaries and into interstitial fluid; occurs at arteriole end of a capillary
osmotic pressure
solutes (albumin) creates a pressure that draws water back into capillaries; occurs at venule end of a capillary
semilunar valves open
As ventricles contract and intraventricular pressure rises, blood is pushed up against semilunar valves, forcing them open.
What is clot retraction?
which is a process that pulls the cut edges of the vessel together -part of coagulation phase (retract vessels together)
What is fibrinolysis? How is TPA involved?
the enzymatic breakdown of the fibrin in blood clots; TPA is a drug that immediately dissolves clots "clot buster" helping restore blood flow to brain.
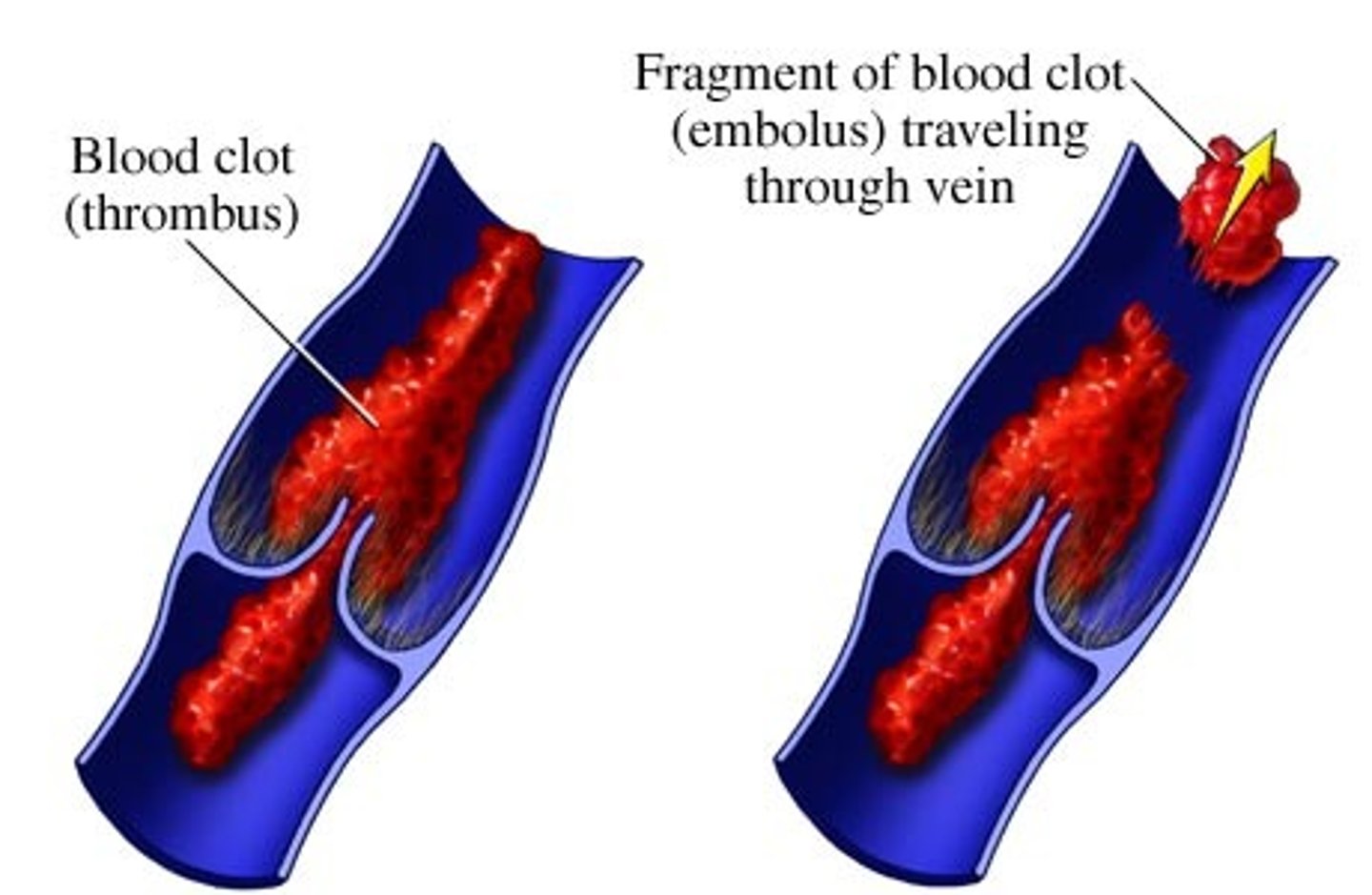
What is an embolus?
Blood clot freely floating in bloodstream - which can cause strokes.
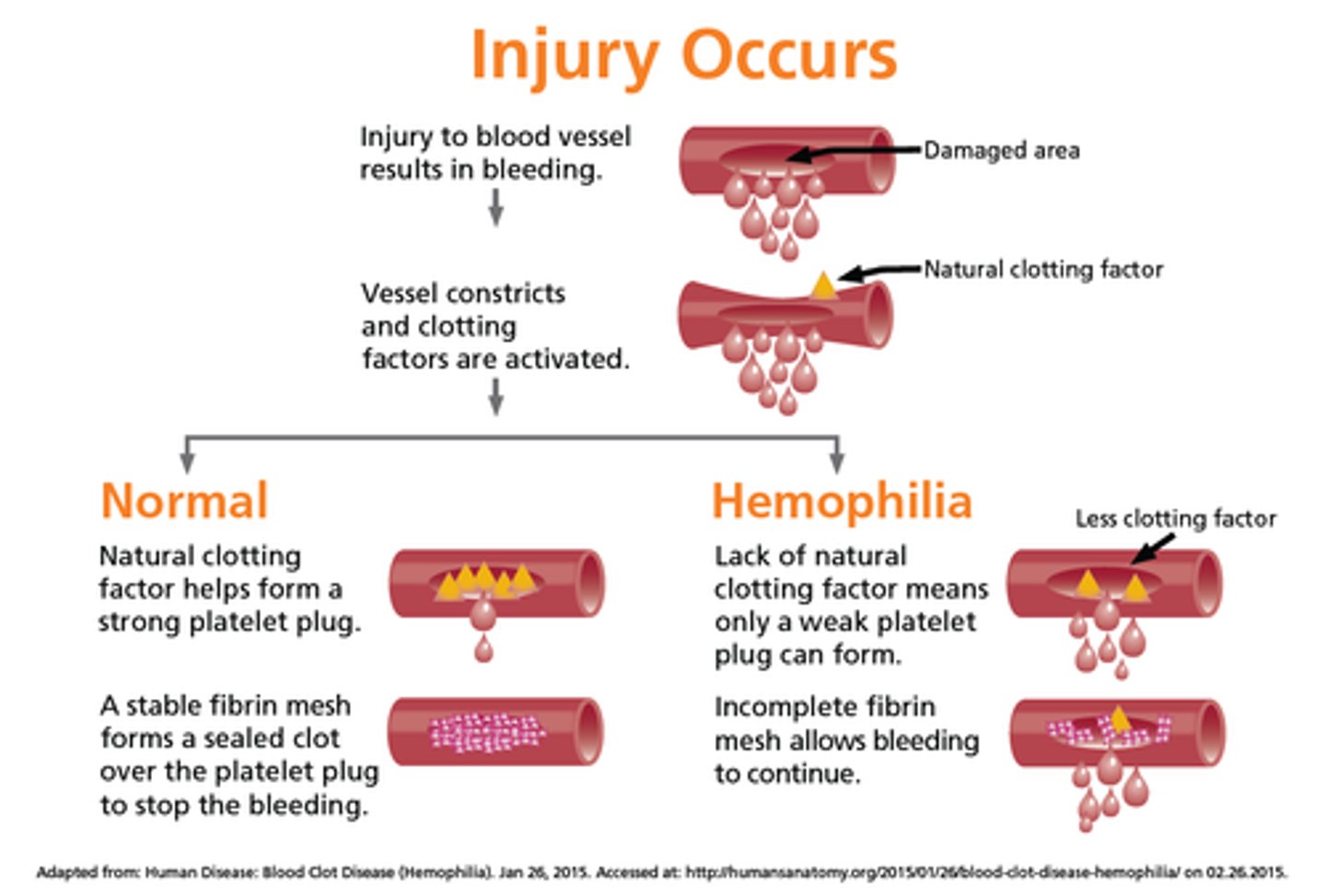
What is hemophilia? What causes it?
inherited bleeding disorders caused by lack of clotting factors; bleeding severely...-affects males more often
pulmonary circuit
pumps blood to and from lungs (right side pumps into it)
systemic circuit
pumps blood to and from body (left pumps into it)
What is the covering of the heart called?
pericardium
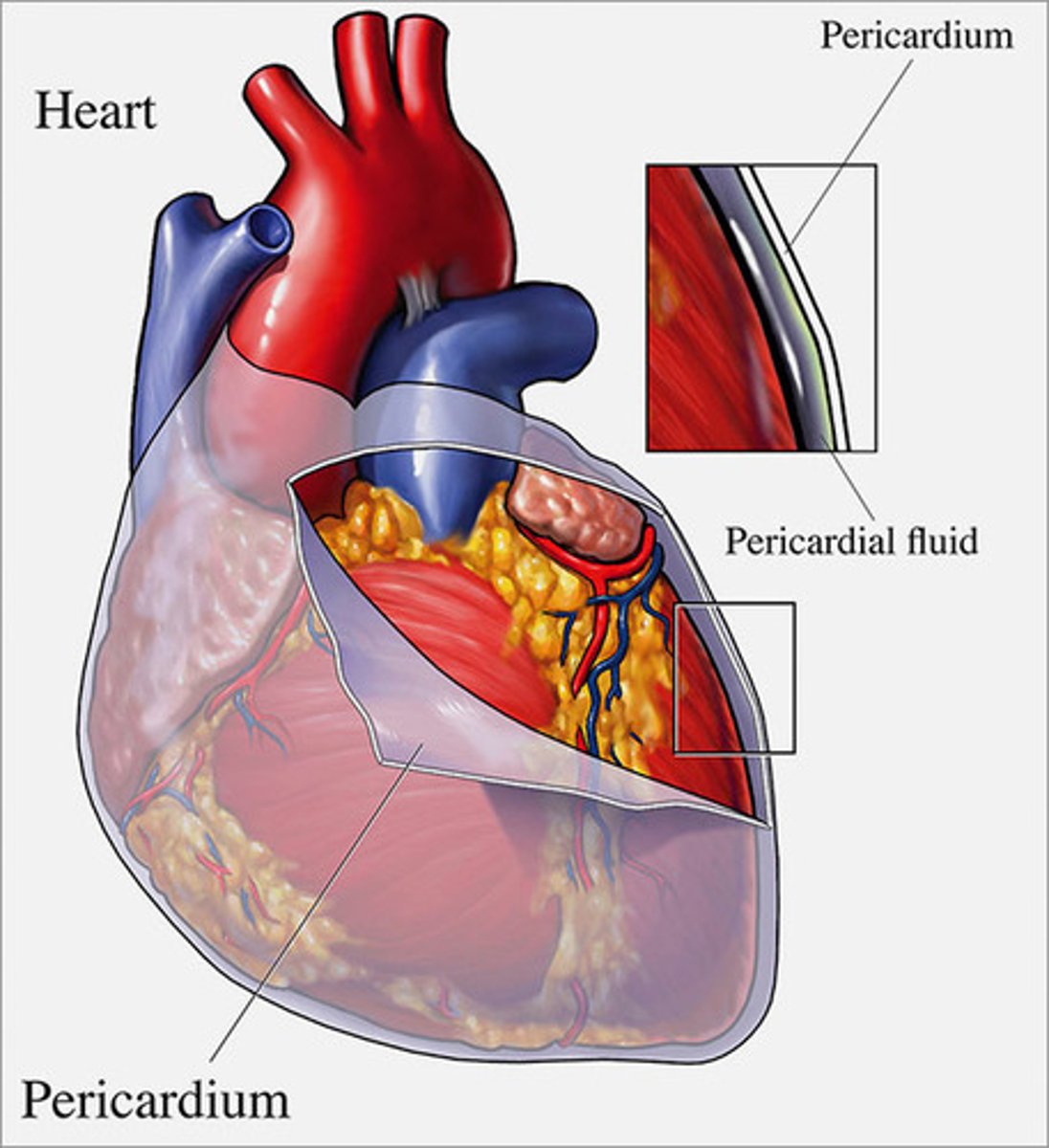
Functions of the pericardium
-Protects and anchors the heart
-Allows for the heart to work in a relatively friction-free environment
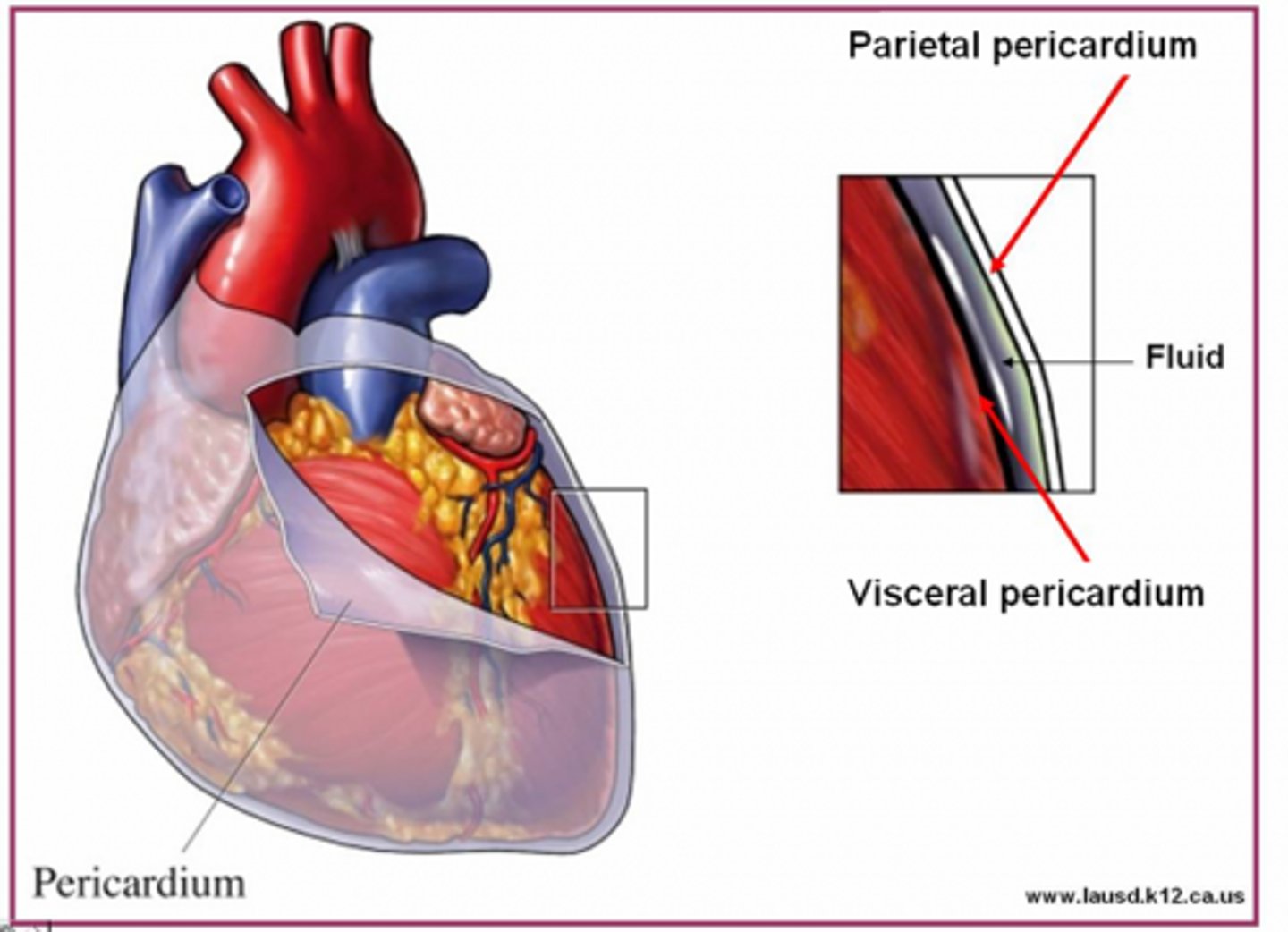
inflammation of the pericardium
Pericarditis
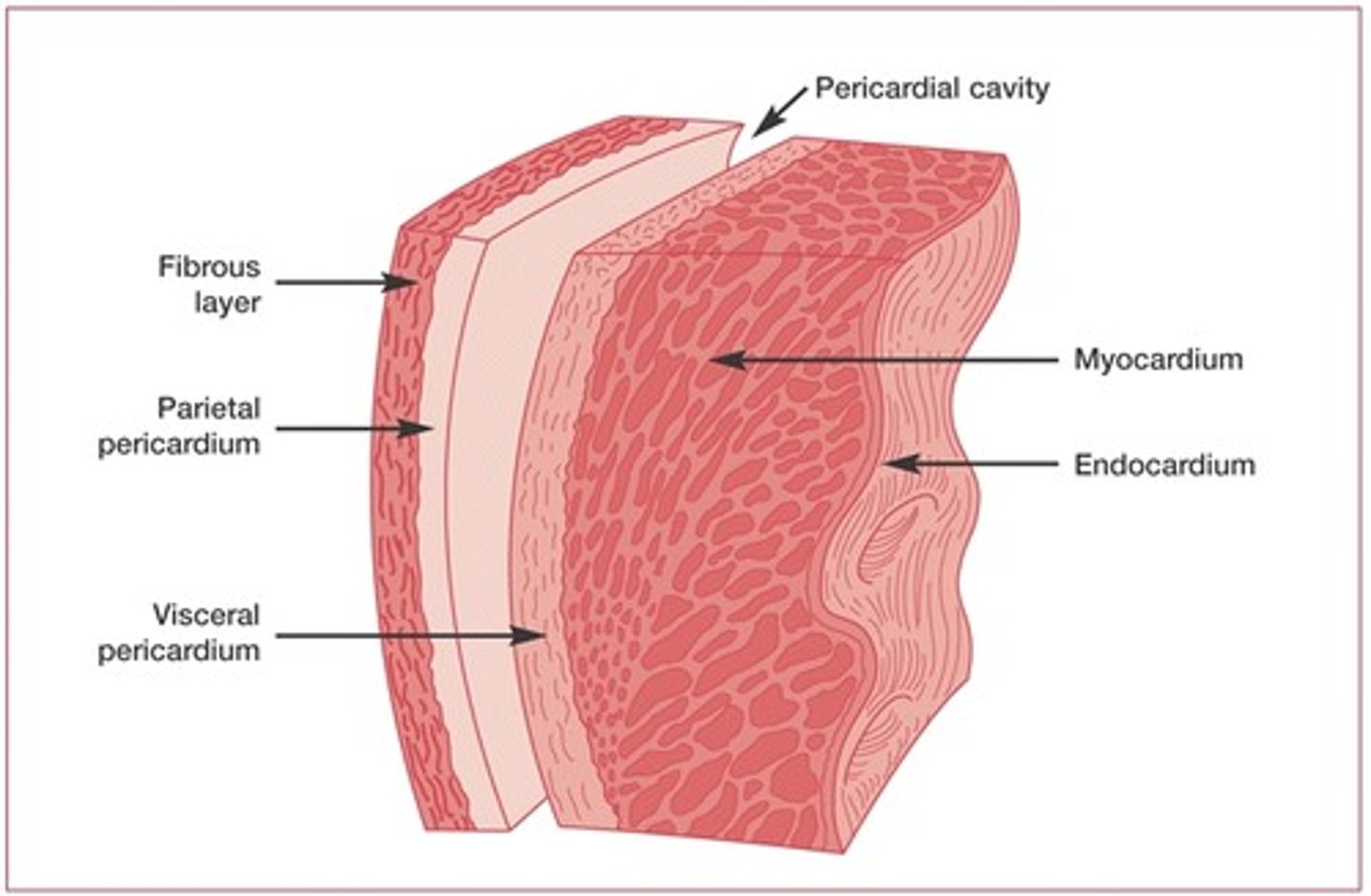
3 layers of the heart wall
1. Epicardium
2. Myocardium
3. Endocardium
Do veins convey blood toward or away from the heart?
To the heart
Do arteries convey blood toward or away from the heart?
Away from the heart
What is the largest artery in the body?
aorta
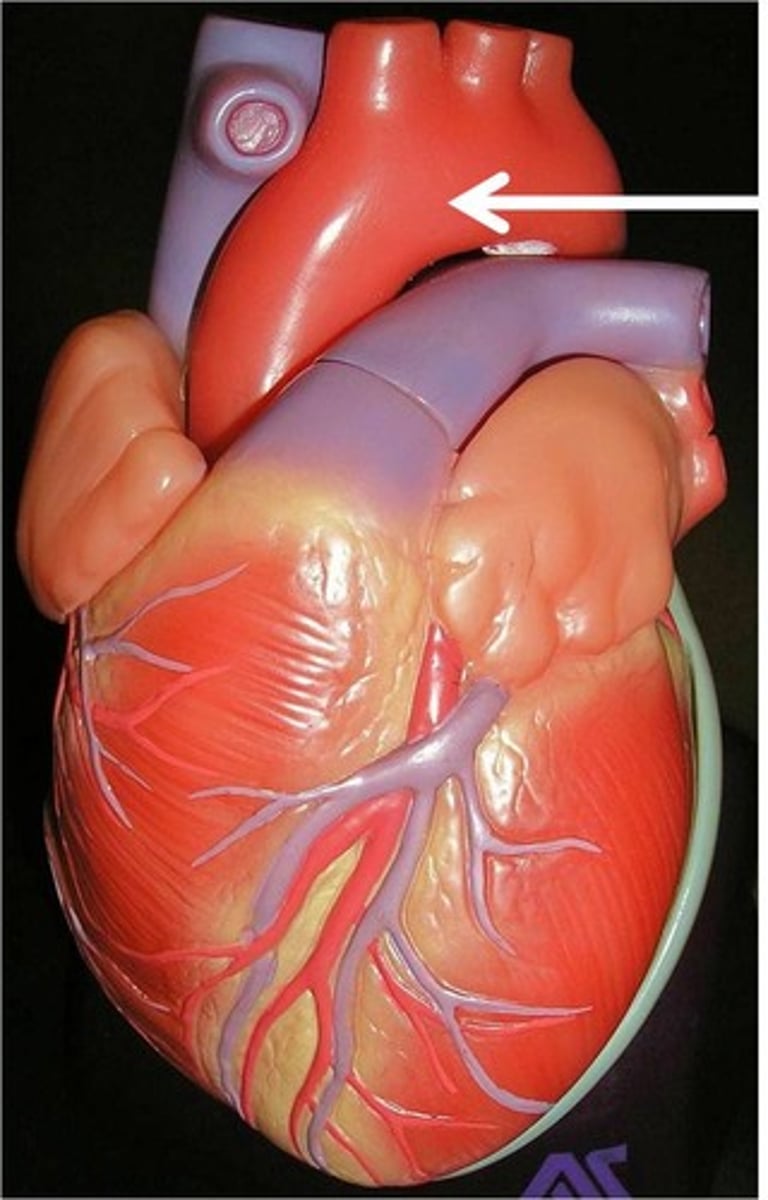
Epicardium
portion that covers the friction free environment
What chambers is the coronary sulcus between?
between atria (upper chambers) and ventricles (lower chambers)
What chambers are the interventricular sulci between?
between left and right ventricles
interatrial septum
separates the two atria
interventricular septum
separates the right and left ventricles
What is the function of heart valves?
ensure one way flow of blood
Why is the myocardium surrounding the left ventricle is so much thicker than the right ventricle?
Left side needs to pump to all body tissues vs right side only pumping to lungs (closer to heart) There needs more force to pump to other body tissues.
Blood flow of the heart
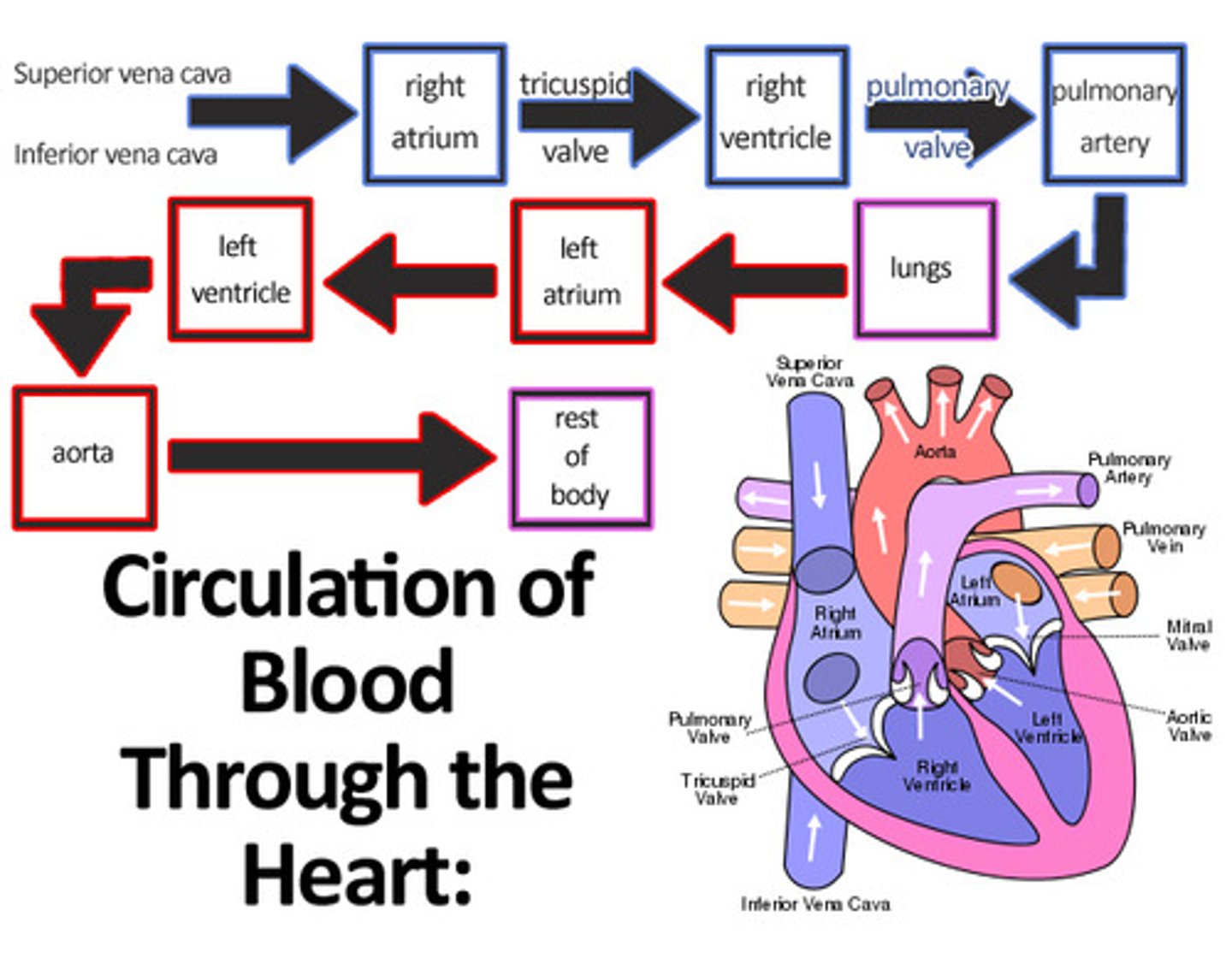
Why does the blood have coronary circulation?
Myocardium needs its own blood supply
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
Areas of partial or complete blockage of coronary circulation, usually due to plaque
What structure of the heart does the coronary circulation dump into?
Right atrium
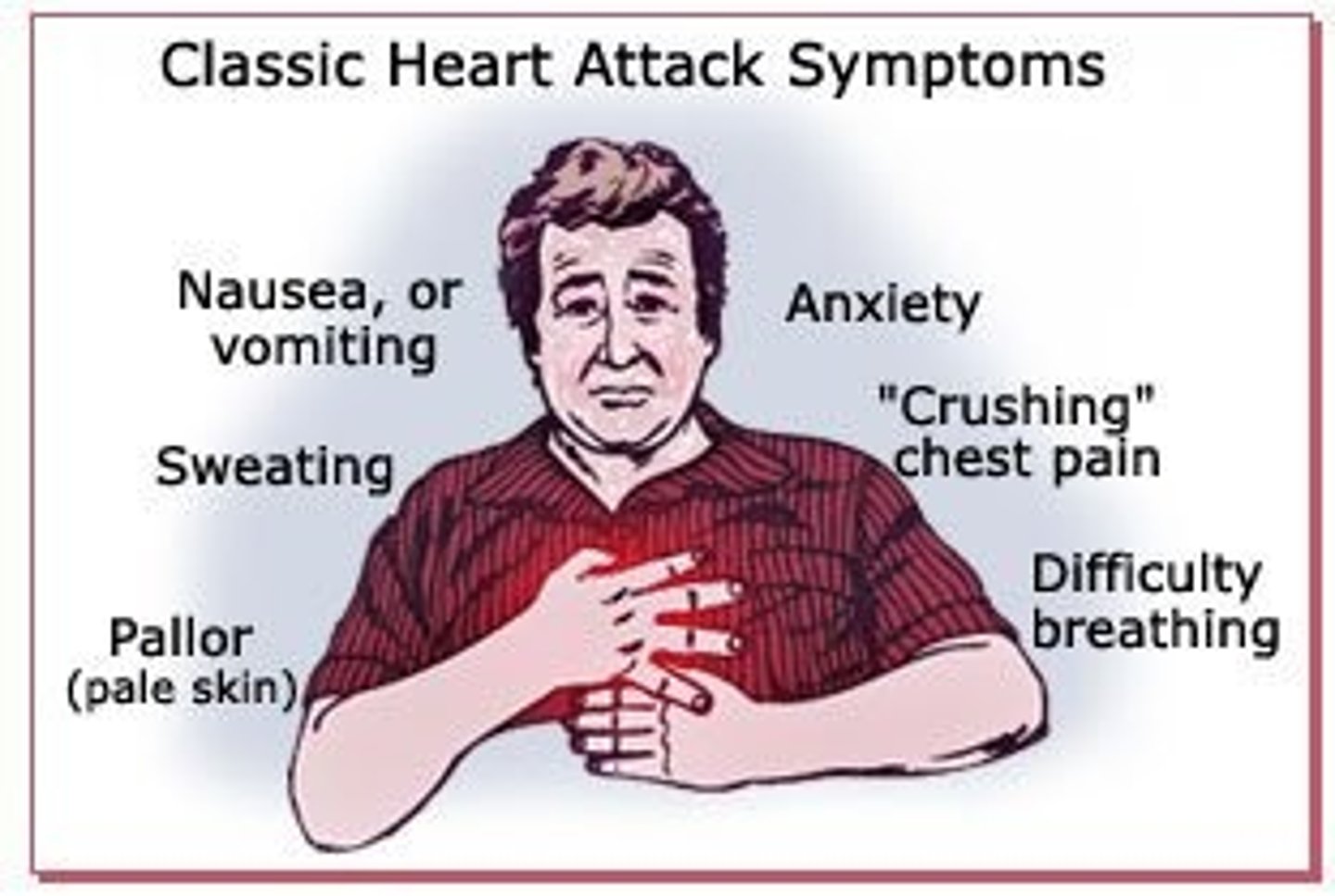
myocardial infarction
Heart attack occurs due to lack of oxygen to heart tissue (myocardium)
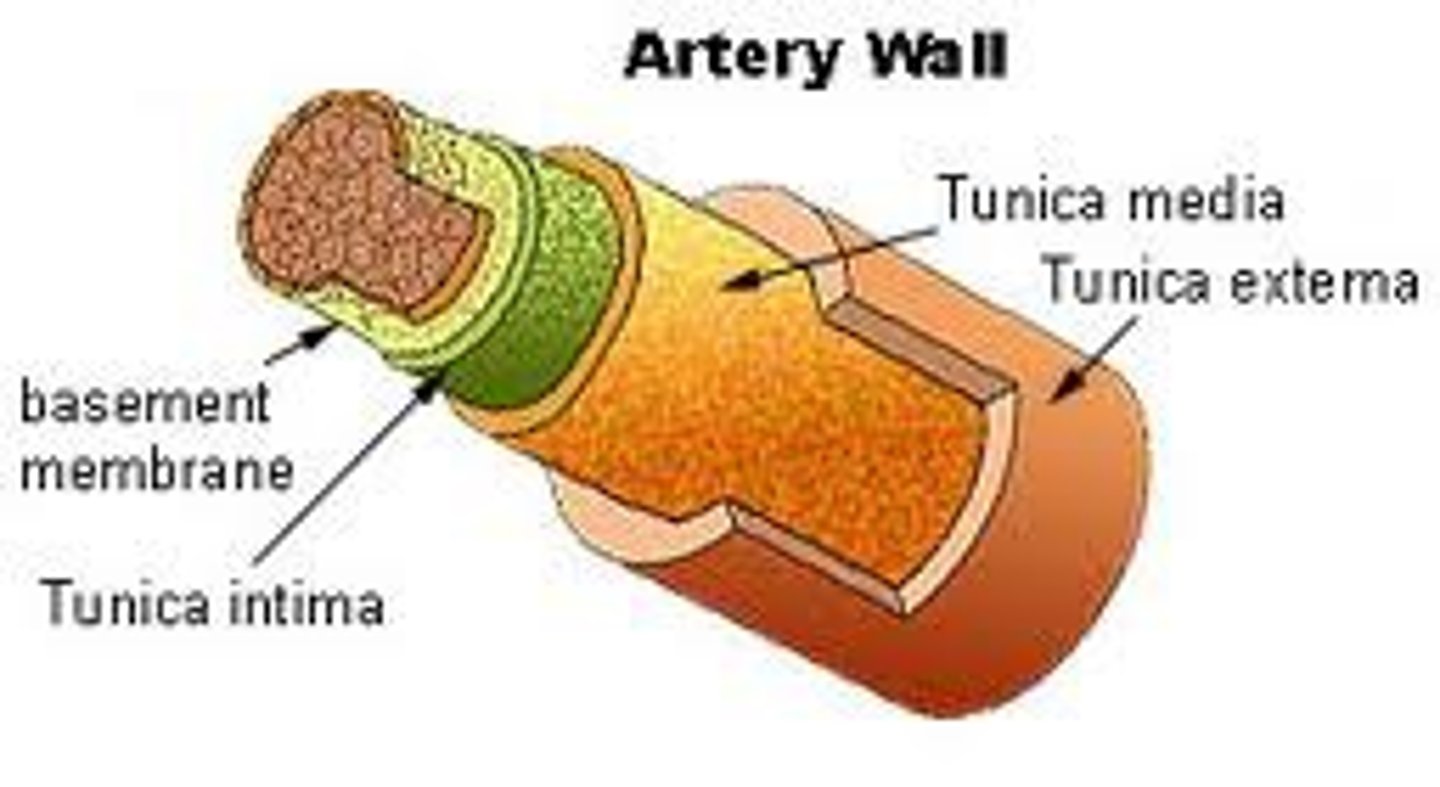
What is a lumen of a blood vessel?
blood-containing space surrounded by tunics (layers)
Tunics of Blood Vessel Walls
tunica intima,
tunica media,
tunica externa
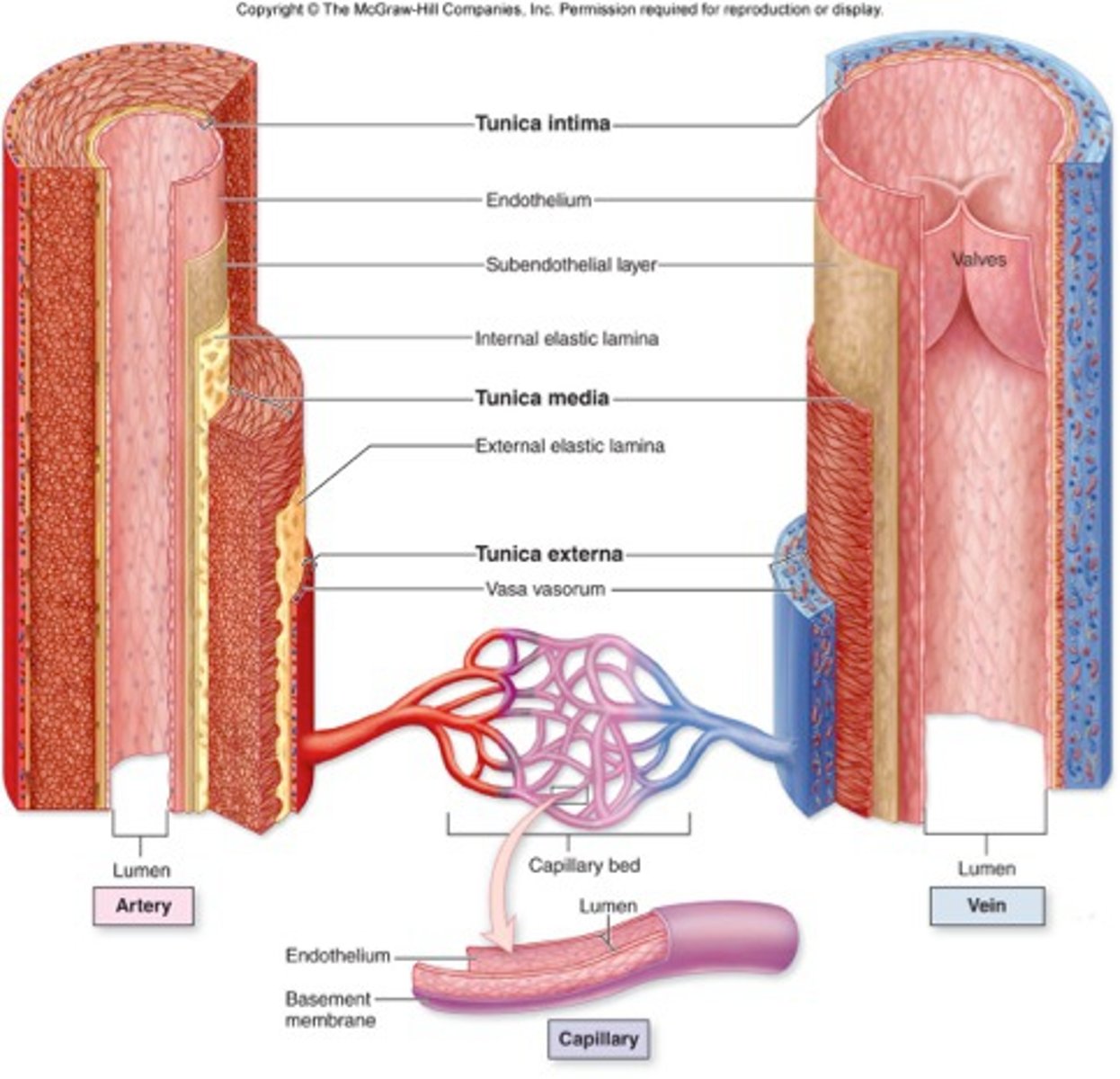
Tunica intima function
forms smooth frictionless layer to allow efficient blood flow
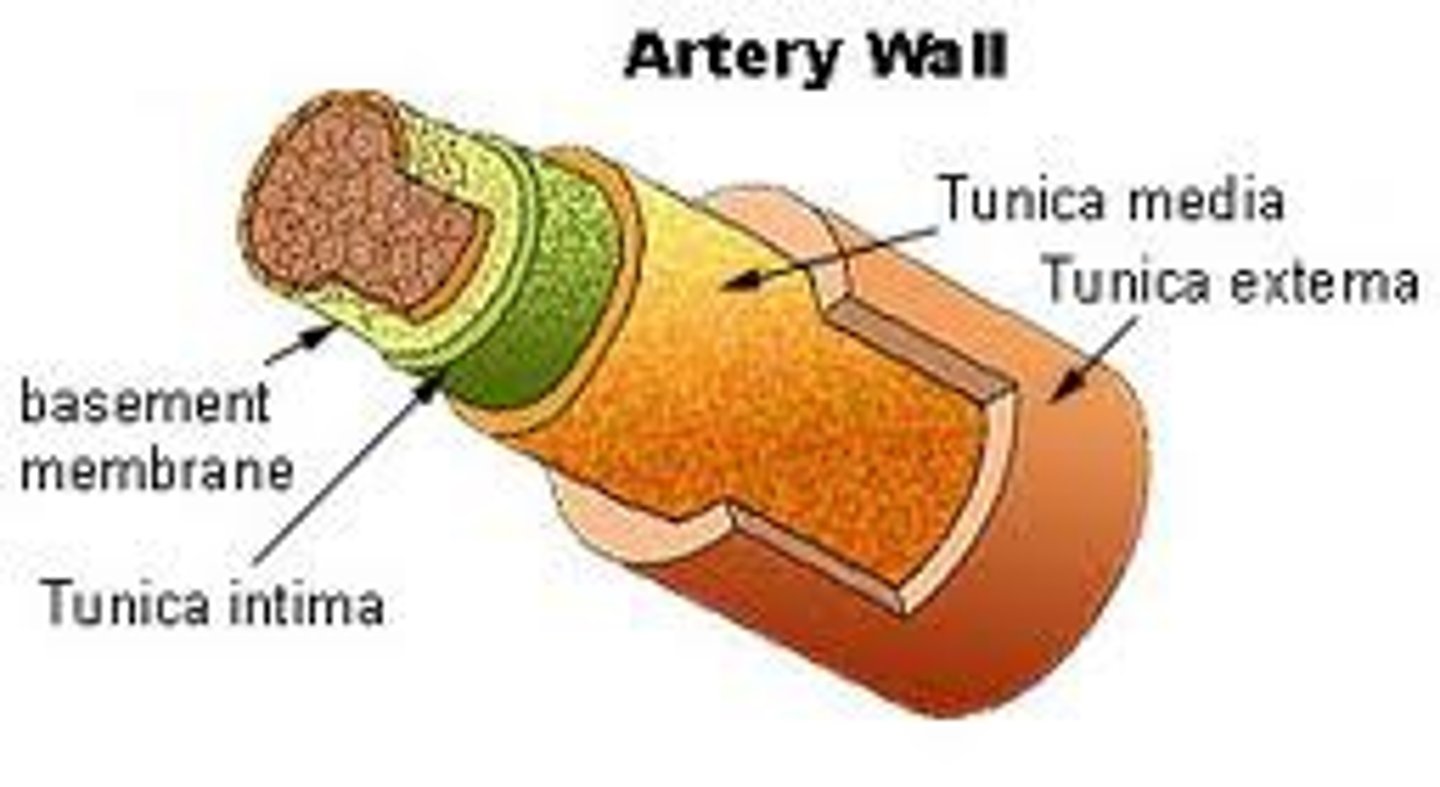
Tunica externa function
protects and reinforces the vessel, and anchors it to surrounding structures.
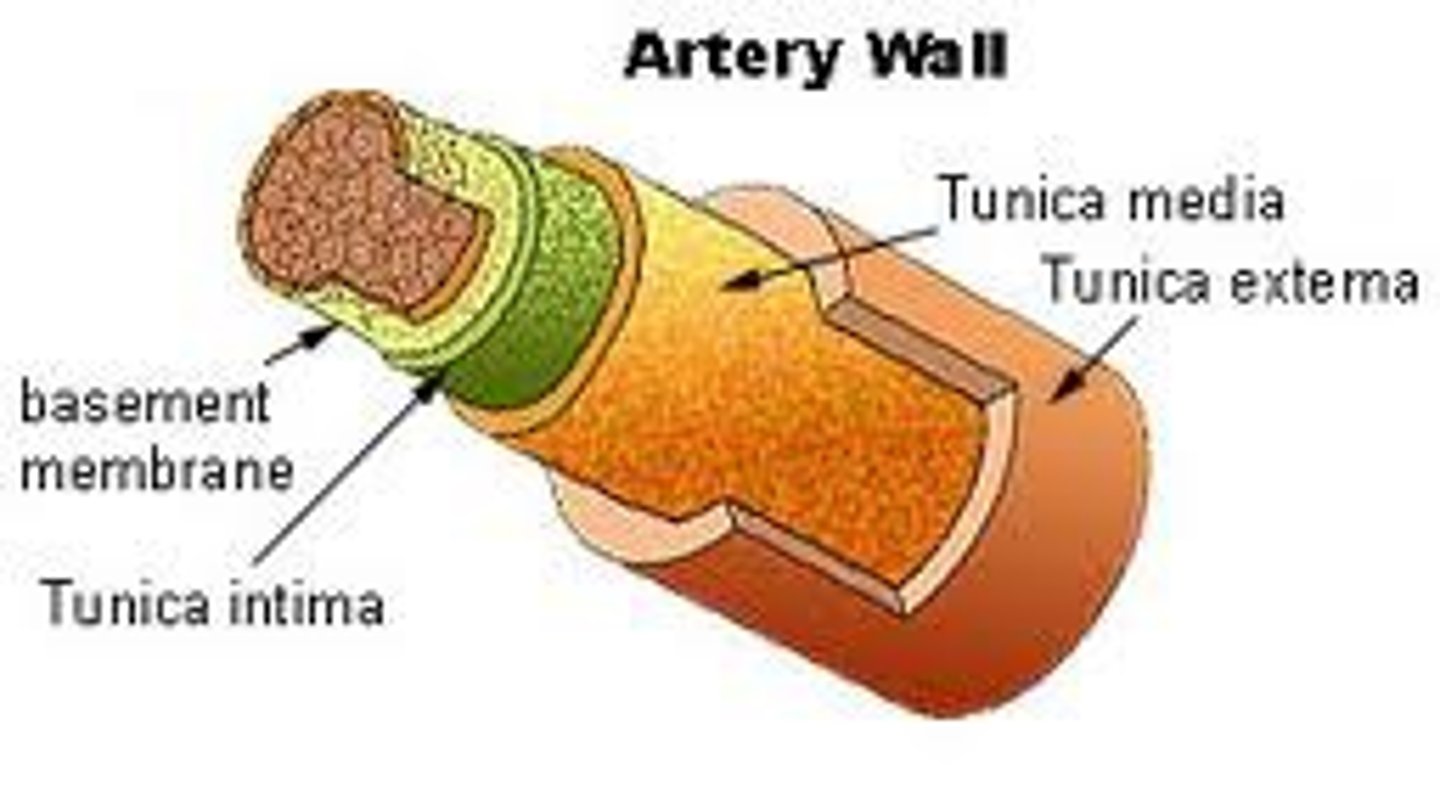
Tunica media function
Controls dilation and constriction of vessels
What portion of the nervous system controls vasoconstriction/vasodilation?
sympathetic system
What is the function of all the elastic fibers in elastic arteries?
can withstand large blood pressure fluctuations - can expand & recoil.
What is the function of the smooth muscle in the tunica media?
for vasoconstriction and vasodilation
What is the function of capillaries?
site of exchange between blood and tissues
what structure regulates how much blood enters them
precapillary sphincter
What is an edema?
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in interstitial spaces of tissues.