psych
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:59 PM on 9/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
chapter 1
chapter 1
2
New cards
who is the father of psychology?
wilhelm wundt
3
New cards
major researchers that shaped the field
william james, sigmund freud, ivan pavlov, john b watson, and bf skinner
4
New cards
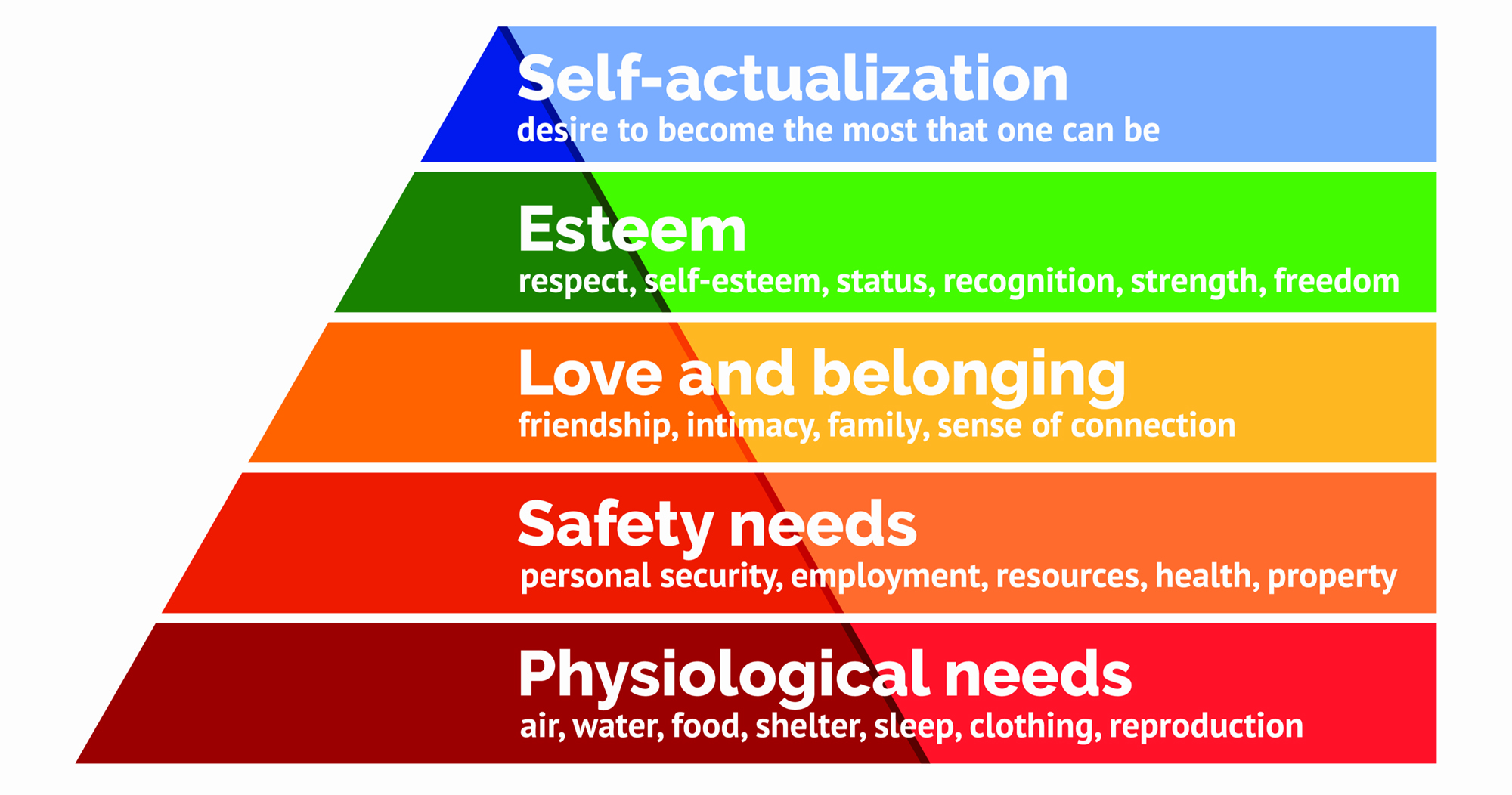
maslows hierarchy of needs
bottom to top
5
New cards
freuds actual contributions
taught psychologists how important it is to employ the use of the scientific method and to use more testable hypotheses
6
New cards
area of psychology 1
cognitive psych - give
attention to problem solving, language, and memory
attention to problem solving, language, and memory
7
New cards
area of psychology 2
developmental psych - studies development across a lifespan; physical aging, cognitive skills, moral reasoning, social behavior
8
New cards
area of psychology 3
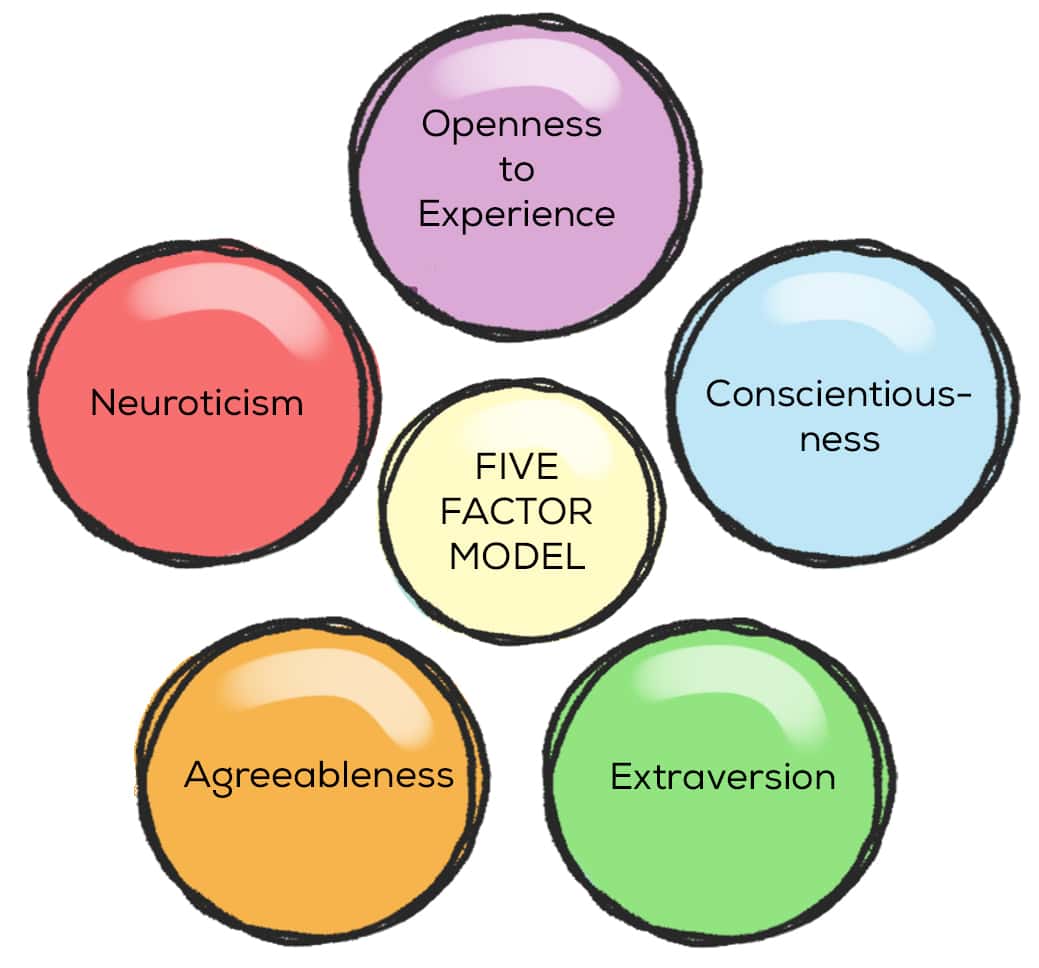
personality psych - focuses on patterns of thoughts and behaviors that make people unique; personality traits are quantitatively measured. EX. myers-briggs type indicator; big five-factor model (aka OCEAN)
9
New cards
area of psychology 4
social psych - focuses on how we interact with and relate to others; EX. milgram experiments
10
New cards
area of psychology 5
school psych - concerned with the science and practice of psychology with children, youth, families; learners of all ages; and the schooling process
11
New cards
area of psychology 6
industrial & organizational psych - applies psychological theories, principles, and research findings in business settings
12
New cards
area of psychology 7
health psych - focuses on how health is affected by biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors
13
New cards
area of psychology 8
sports and exercise psych - psychological aspects of sports performance, including motivation and performance anxiety, and the effects of sport on mental and emotional wellbeing
14
New cards
area of psychology 9
clinical and counseling psych - clinical; focuses on diagnosing and treating psychological disorders and other problematic patterns of behavior; counseling; focuses on emotional, social, vocational, and health related outcomes in
individuals who are considered psychologically healthy
individuals who are considered psychologically healthy
15
New cards
constructs
construct is a variable that is not directly observable; EX. weather, job satisfaction
16
New cards
chapter 2
chapter 2
17
New cards
quantitative
means you can quantify or put a “value” on the information; gather data in the form of numbers; EX. surveys
18
New cards
qualitative
is descriptive—you’re describing a situation with words, not numbers gather data in the form of information; EX. interviews
19
New cards
theory
well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed
phenomena
phenomena
20
New cards
hypothesis
testable prediction about how the world will behave if our idea is correct,
and it is often worded as an if-then statement.
and it is often worded as an if-then statement.
21
New cards
naturalistic observation
observing behavior in its natural setting while blending in to the setting
22
New cards
archival research
relies on looking at past records or data sets to look for interesting patterns or relationships
23
New cards
longitudinal research
data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time
24
New cards
correlation
a statistical relationship between two or more variables
25
New cards
positive correlation
variables move in the same direction; for example, time spent studying and grades; when time spent studying increases, grades also increase
26
New cards
negative correlation
variables move in opposite directions; for example, time spent watching stranger things and grades in an art class; when time spent watching stranger things increases, art class grades decrease
27
New cards
correlation does not equal causation
correlation does not equal causation
28
New cards
conditions to determine causation
1. temporal precedence- one variable happens before another (cause precedes effect)
2. establish a relationship- the two (or more) variables are related (usually correlation) (cause is related to effect)
3. rule out alternatives- you can conclude that there aren’t any other reasons it may seem like the variables are related
4. why- you can logically explain why one variable causes another
2. establish a relationship- the two (or more) variables are related (usually correlation) (cause is related to effect)
3. rule out alternatives- you can conclude that there aren’t any other reasons it may seem like the variables are related
4. why- you can logically explain why one variable causes another
29
New cards
experimental group
the group that receives the treatment
30
New cards
control group
the group that doesn’t receive the treatment (but doesn’t
know)
know)
31
New cards
single blind study
participants don’t know if they’re in the control group or the experimental groups but the researchers know
32
New cards
double blind study
neither the participants nor the researchers know who is in the control group or the experimental group
33
New cards
reliablity
refers to the ability to do the same study more than once and arrive at the same (or incredibly similar) findings
34
New cards
validity
the accuracy of a given result in measuring what it is designed to measure
35
New cards
ethics
most important things: don’t make up data; don’t fake results; don’t lie, just don’t; every study that’s published in a peer-reviewed journal has to be
approved by an Institutional Review Board (IRB) pretty much every college has its own IRB; some IRBs have a reputation for being quite strict but that’s a good thing
approved by an Institutional Review Board (IRB) pretty much every college has its own IRB; some IRBs have a reputation for being quite strict but that’s a good thing
36
New cards
chapter 3
chapter 3
37
New cards
peripheral nervous system
made up of thick bundles of axons, called nerves, carrying messages back and forth between the CNS and the muscles, organs, and senses in the periphery of the body (i.e., everything outside the CNS) the PNS has two major subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system
38
New cards
central nervous system
the portion of the vertebrate nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord
39
New cards
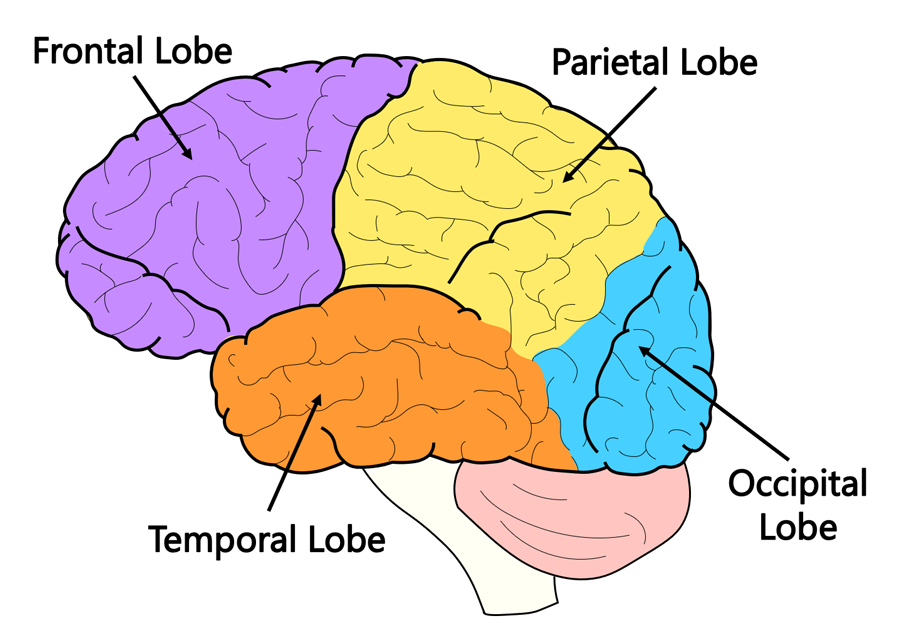
lobes of the brain
40
New cards
endocrine system
consists of a series of glands that produce chemical substances known as hormones
41
New cards
chapter 4
chapter 4
42
New cards
internal stimuli
pain, hunger, thirst, sleepiness, and being aware of our thoughts and emotions
43
New cards
external stimuli
includes seeing the light from the sun, feeling the warmth of a room, and hearing the voice of a friend
44
New cards
melatonin
the hormone that makes us (as humans) feel sleepy
45
New cards
sleep debt
people with less sleep than they’re supposed to get will accrue sleep
debt; result of insufficient sleep on a chronic basis
debt; result of insufficient sleep on a chronic basis
46
New cards
REM
rapid eye movement - darting movements of the eyes under closed eyelids
47
New cards
stages of sleep
1. phase between wakefulness and sleep: when we drift off to sleep
2. the body goes into deep relaxation
3. deep sleep
4. deep sleep
5. REM sleep
2. the body goes into deep relaxation
3. deep sleep
4. deep sleep
5. REM sleep
48
New cards
lucid dreams
dreams in which certain aspects of wakefulness are maintained during a dream state
49
New cards
sleep disorders
insomnia - a consistent difficulty in falling or staying asleep
narcolepsy - sleep disorder in which the sufferer cannot resist falling
to sleep at inappropriate times
narcolepsy - sleep disorder in which the sufferer cannot resist falling
to sleep at inappropriate times
50
New cards
substance use disorders
often uses more of the substance than they originally intended to and they continue to use that substance despite experiencing significant adverse
consequences, evident by aspects of physical and psychological dependence
consequences, evident by aspects of physical and psychological dependence
51
New cards
chapter 5
chapter 5
52
New cards
senses we experience
hearing, seeing, smelling, tasting, and touch/feeling, balance, pain, temperature
53
New cards
subliminal messages
are messages we receive but aren’t consciously aware that they’re being delivered
54
New cards
just noticeable difference threshold (JND)
difference in stimuli required to detect a difference between
the stimuli
the stimuli
55
New cards
pain perception
inflammatory pain - signal that some type of tissue damage has occurred
neuropathic pain - pain from damage to neurons of either the peripheral or central nervous system
congenital insensitivity to pain - a rare genetic disorder where a person is born without the ability to feel pain
neuropathic pain - pain from damage to neurons of either the peripheral or central nervous system
congenital insensitivity to pain - a rare genetic disorder where a person is born without the ability to feel pain
56
New cards
gestalt principles
field of psychology based on the idea that the whole is different from the sum of its parts
57
New cards
similarity
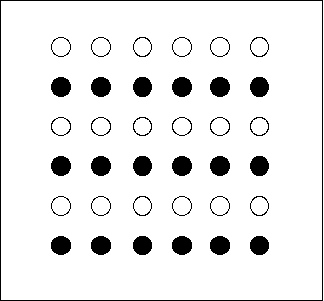
58
New cards
proximity
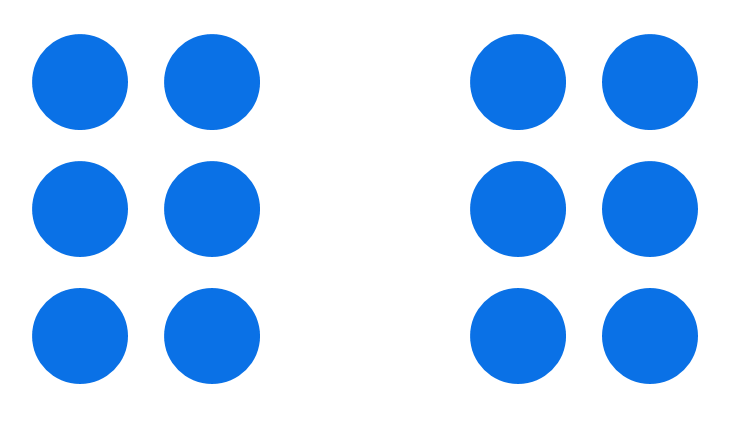
59
New cards
continuity
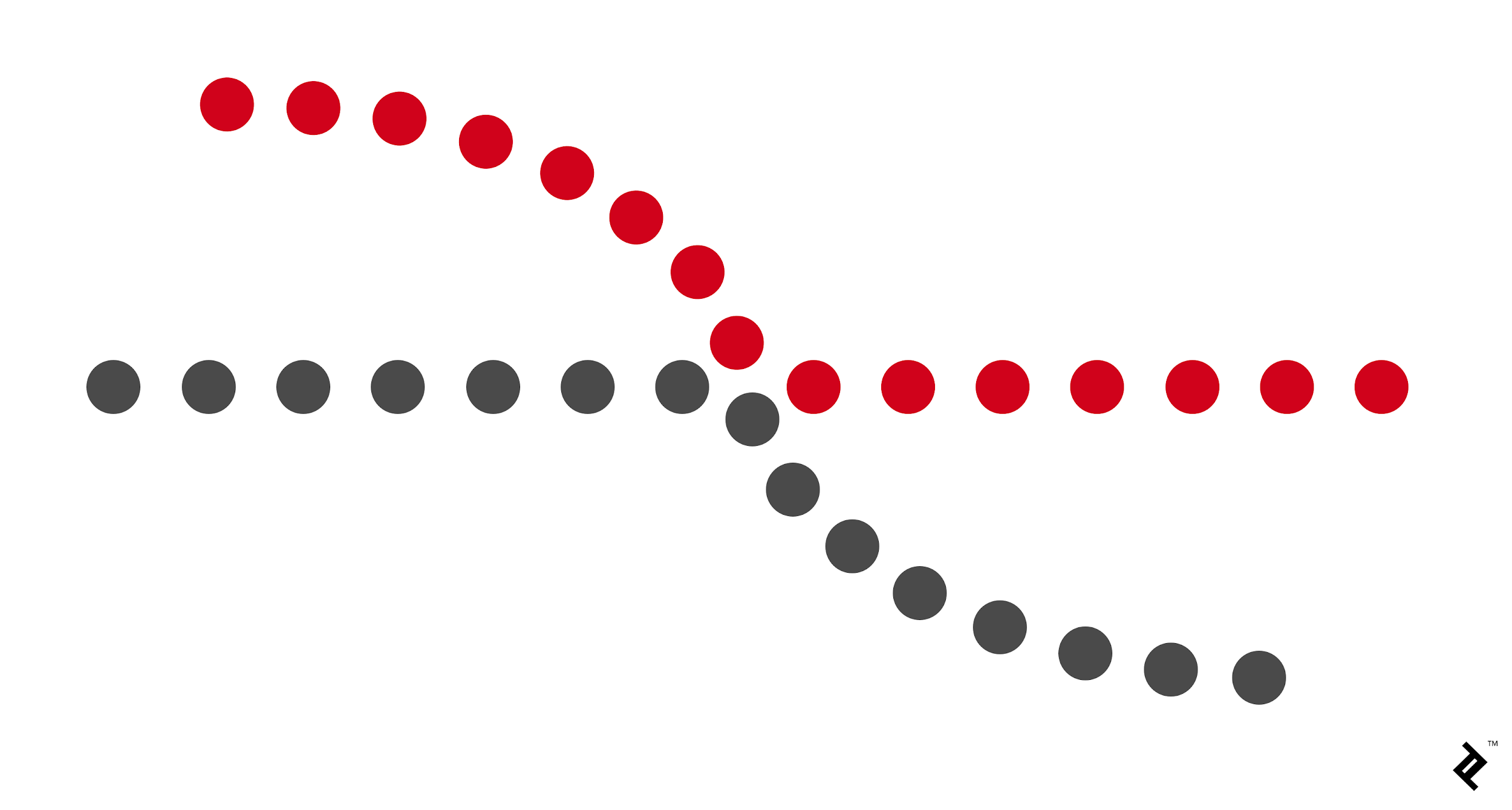

60
New cards
closure