Psych Actions of Drugs- Ch.1
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
How many nerve cells (neurons/gray matter) in the brain?
86 billion
How many glial cells (support cells/white matter) in the brain?
85 billion
How many synapses in the brain?
100 trillion
Only place in brain where nerve cells can regenerate
hippocampus
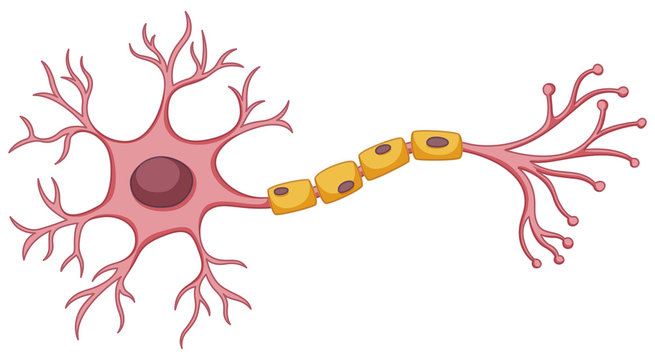
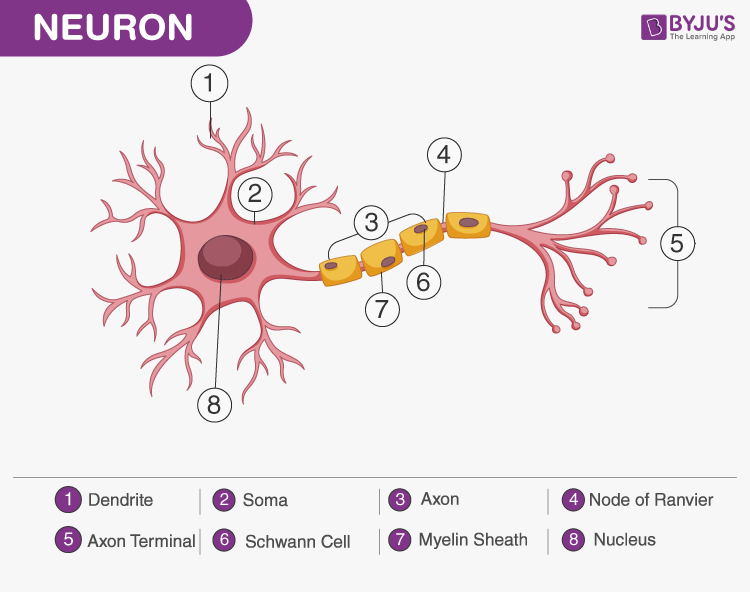
label 8 things
label 8 things
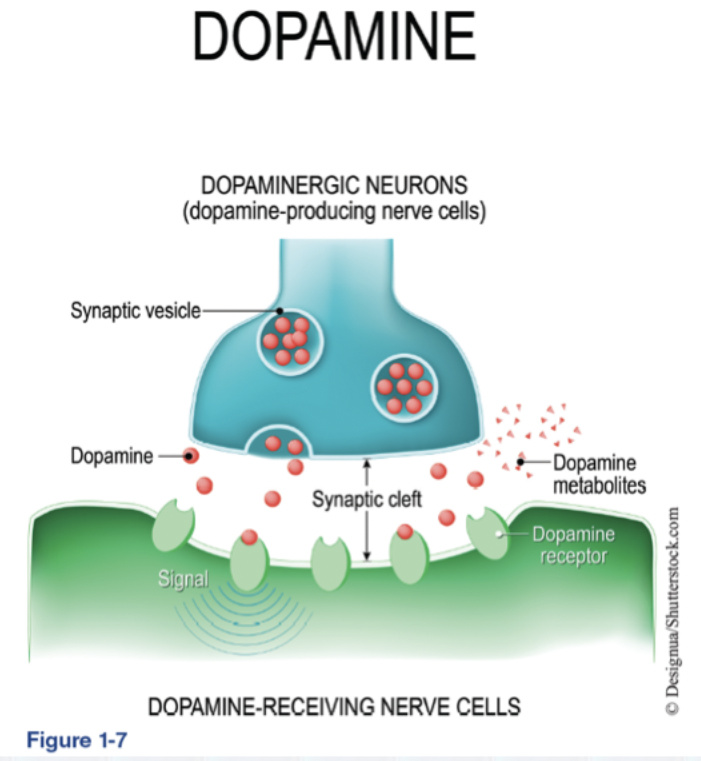
Myelin
fatty deposits that provide support and efficiency for neurons
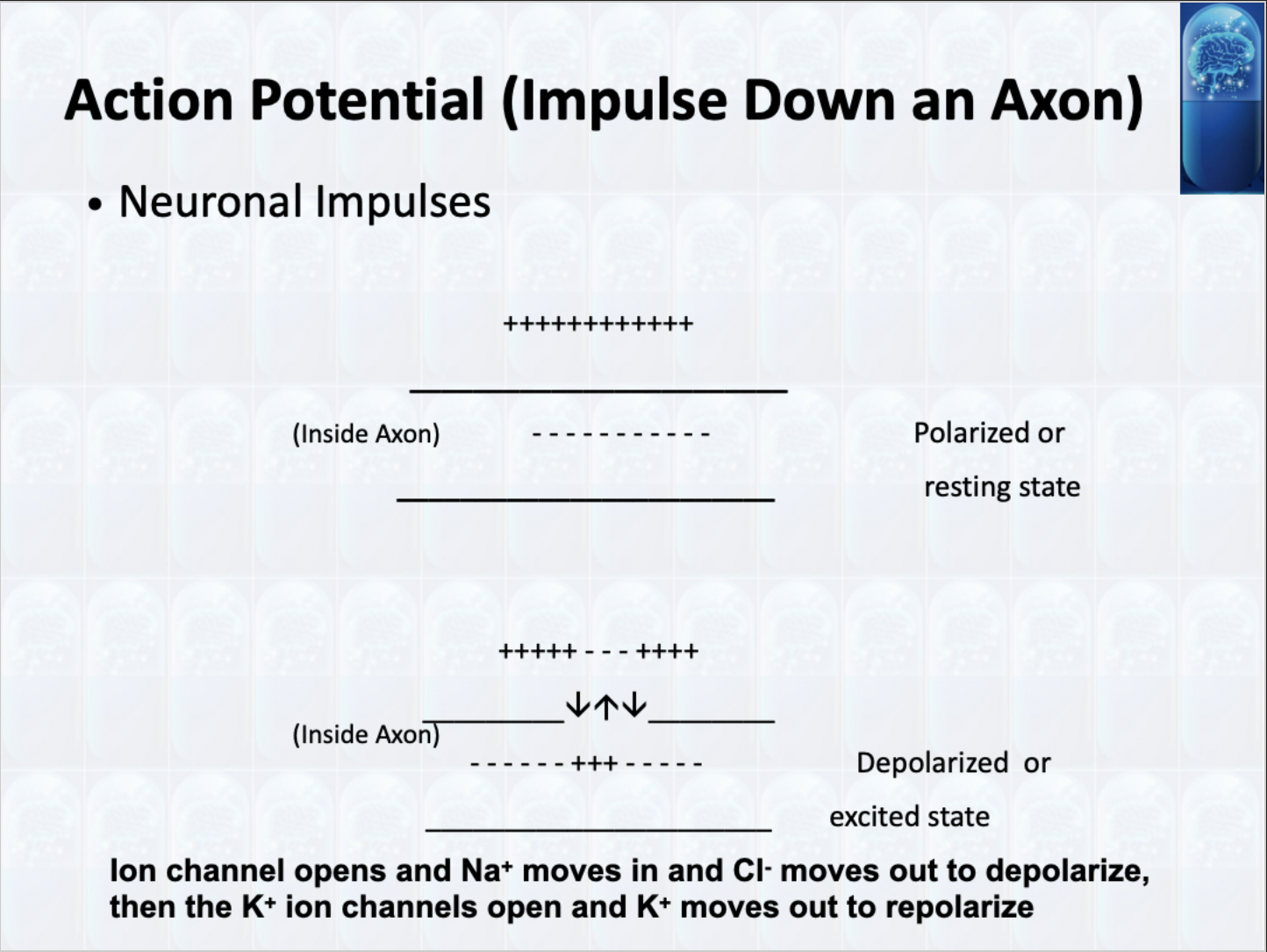
Action Potential
Function of glial cells
surround/insulates neurons, prevents NT from spreading to other synapses, absorb NT and recycle, can release NT (GLUTAMATE)
Dale’s Principle
Neurons release only one type of NT (false)
Oligodendrocytes
Creates myelin sheath around neuron cell axons in the CNS. Makes up most of white matter in the brain
Astrocytes
Anchors neurons to blood supply. Provides scaffolding to hold synapses together in CNS. Remove excess ions and recycle NT
Microglia
Macrophage cells that scavenge for waste- main CNS immune function
3 types of chemical synapses that increase/decrease NT release:
axodendritic (targets dendrites), axosomatic (targets soma), axoaxonic (targets axons)
2 types of receptors and where they’re typical
Inhibitory (presynaptic) & Excitatory (Postsynaptic)
2 types of Receptor mechanisms
Ionic (“ligand-gated”) & Metabolic (“G-Protein”)
2 Types of changes in receptors
Up (increase # of receptors) & Down (decrease # of receptors) regulation
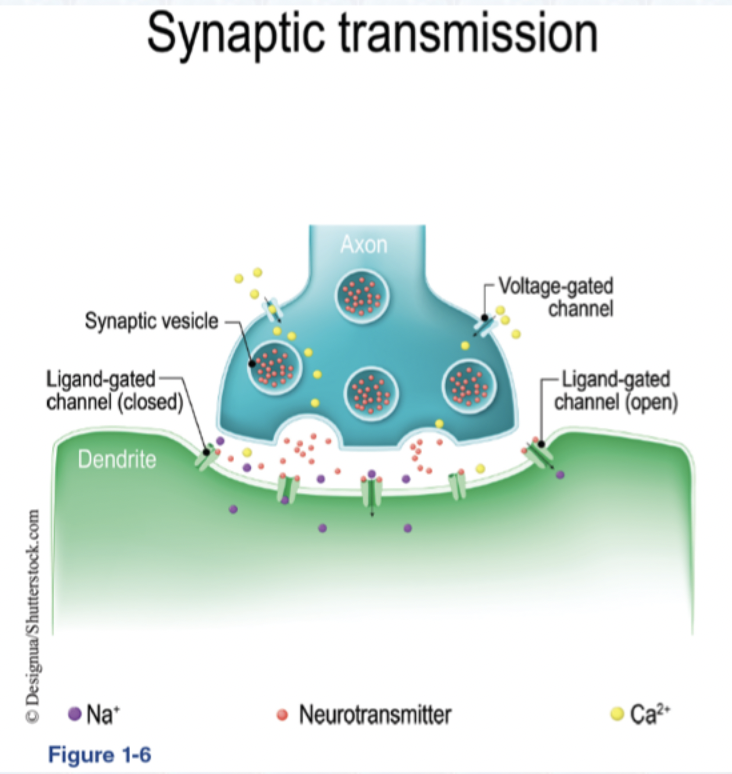
Which Receptor Mechanism is this?
Ionic
Which Receptor Mechanism is this?
Metabolic (G-Protein)
Autoreceptor Activity
On presynaptic neuron detect amount of NT in cleft; regulate REUPTAKE. If not enough, release more NT. If too much, release less NT.
Reuptake Transporters
Reuptake Channels. Removal of NT from synapse. Metabolized for resynthesis or Metabolized and eliminated (Ex. SERT, DAT, NET)
NT Metabolism
Breakdown or waste removal by enzymes like Monoamine oxidase (MOA-A/B), Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT), and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Excitatory Receptor
Agonist (increase action) & antagonist (decrease action)
Inhibitory Receptor
Agonist (decrease action) & Antagonist (increases action)
Primary excitatory NT?
Glutamate
Primary inhibitory NT?
GABA
Monoamine
One amino group
Catecholamine
Monoamine that also has catechol group and arise from tyrosine (epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine)
Norepinephrine (NE)
Arousal, reward, Vasoconstriction/Vasodilation, Blood pressure, SNS
Dopamine (DA)
Motor function, reward, cognition/learning, impulse control, endocrine function, addiction
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5HT)- SEROTONIN
Mood, Anxiety, Aggression, Satiety and food motility, Sleep, Pain reduction, Sexual functioning
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A NT that deals with Cognition/Learning, Memory, Arousal, Muscle activation, PNS
Allosteric binding
Binding on a receptor near the NT’s binding site but not at the actual NT binding site
Glutamate
Receptors 9NMDA & AMPA) are ligand-gated
GABA
Neurotransmitter that plays role in calming and relaxing body. GABA(A) receptor is ionic, GABA(B) receptor is g-protein. Drugs like benzos and alcohol act allosterically on GABA receptors
Norepinephrine (NE)
A neurotransmitter and hormone that plays a vital role in the body's response to stress and other situations. Binds to adrenergic receptors: Alpha (a1 and a2) and Beta (b1, b2, and b3)
Andrenergic Alpha-1
most important NE receptor for reward in nucleus accumbens
Vasoconstriction, increased blood pressure, mydriasis (dilate pupils), bladder sphincter closyre
Andrenergic alpha 2
inhibits NE release and may be important in decreasing anxiety
Inhibit NE, ACh, and insulin release
Beta 1
Andrenergic receptor that affects tachycardia, increased lipolysis, increased heart contractions, increase4 release of renin
b2
Andrenergic receptor involved in vasodilation, bronchodilation, increasead glucose utilization, relaxed uterine smooth muscle. Binds to NE & E
Dopamine
d1, d2, d3, d4
d1
Most numerous DA receptor in the brain. Most numerous in caudate, putamen, substantia nigra, amygdala, frontal cortex.
Locomotion, reward/reinforcement/addiction, learning/memory, impulse control, affect, attention
d2
highest concentration in caudate, putamen, nucleus accumbens, substantia nigra, and ventral tegmental area.
Locomotion, reward/reinforcemnt, addiction, learning/memory, impulse control, affect, attention, psychosis
d3
Mainly in nucleus accumbens and limbic system
Locomotion, reward/reinforcemnt, addiction, cognition
d4
Least numerous DA receptor in brain. Moderately in hippocampus, substantia nigra, nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and frontal cortex
Locomotion, cognition
d5
Less numerous than d1 located mainly in prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex, substantia nigra, hypothalamus, hippocampus
Locomotion, cognition
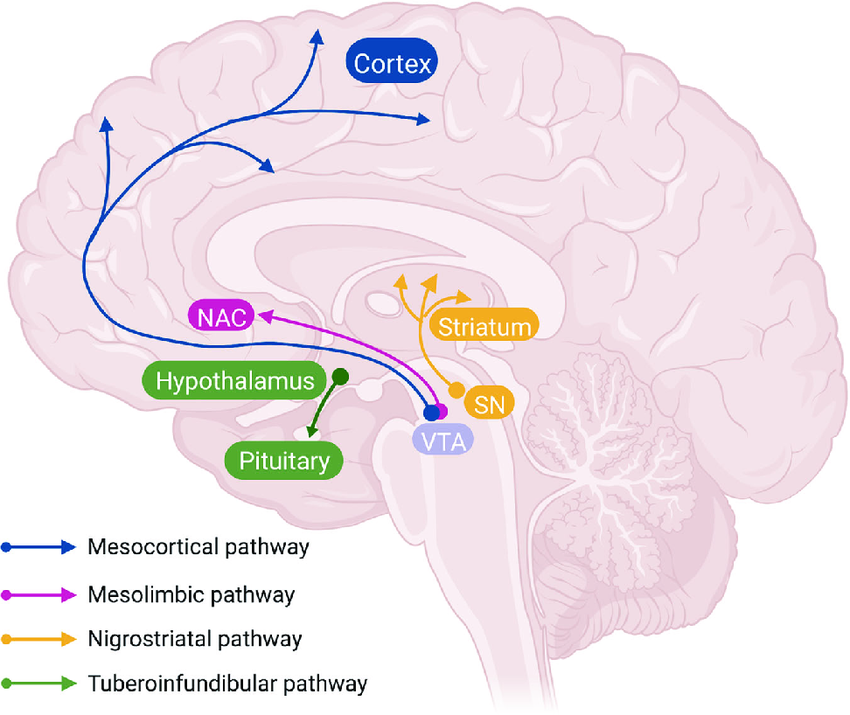
4 Main DA Pathways
Mesolimbic, Mesocortical, Nigrostriatal, Tuberoinfundibular
Mesolimbic
Hyperactivity leads to Hallucinations, Delusions, Euphoria
Primarily lined with d2 receptors
Positive Dopamine Theory of Schizophrenia
Tegmentum to nucleus accumbens, part of ventral striatum
Mesocortical
Hyperactivity leads to Cognitive and affective NEGATIVE symptoms of schizophrenia
d1 & d2 receptors
Tegmentum to dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and ventromedial prefrontal cortex
Nigrostriatal
Extrapyrimidal Motor System
Substantia nigra to striatum
Controls involuntary movements
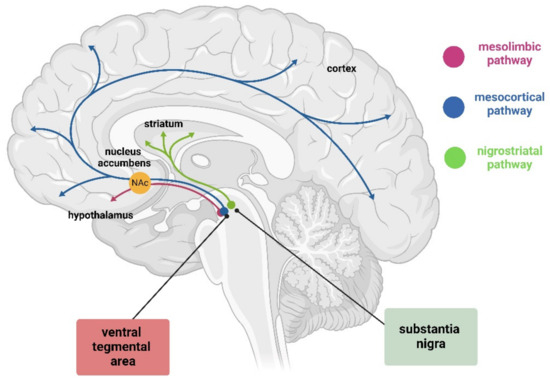
Tuberoinfundibular
Prolactin secretion (lactation and mammary gland growth)
Hypothalamus to pituitary
5-HT1a
Found in: CNS & blood vessels
Function: Addiction, Aggression, Anxiety, Sexual Functioning, Mood, Nausea, Pupil Dilation, Sleep, Detection of pain
Inhibitory nature
5-HT2a
Found in: CNS, blood vessels, smooth muscle, peripheral nervous system, GI tract
Function: Addiction, Anxiety, Appetite, Cognition, Learning, Memory, Sleep, Vasoconstriction, Sexual behavior
Acetylcholine (Ach) 2 types of receptors
Nicotinic
Muscarinic
Nicotinic Receptors
N1 or Nm- found in neuromuscular junctions
N2 or Nn- found in CNS, ANS, Adrenal Medulla
Prefrontal Cortex
allows functional planning, daily coordination, functionality
Frontal Lobe
Reasoning, planning, problem solving, regualting emotions, regulating sexual urges, impulse control, speech (movement), motor movement
Parietal Lobe
Sensation (regulating senses), perception of stimuli (pressure, pain, touch), movement (orientation), visual recognition
Temporal Lobe
Perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, interpretation of smells and sounds, formation of memory, speech (understanding)
Occipital Lobe
Visual Processing, movement recognition, color recognition
Executive Functions
Controlled in the prefrontal cortex (anterior portion of frontal love) = reasoning, planning, problem solving, impulse control
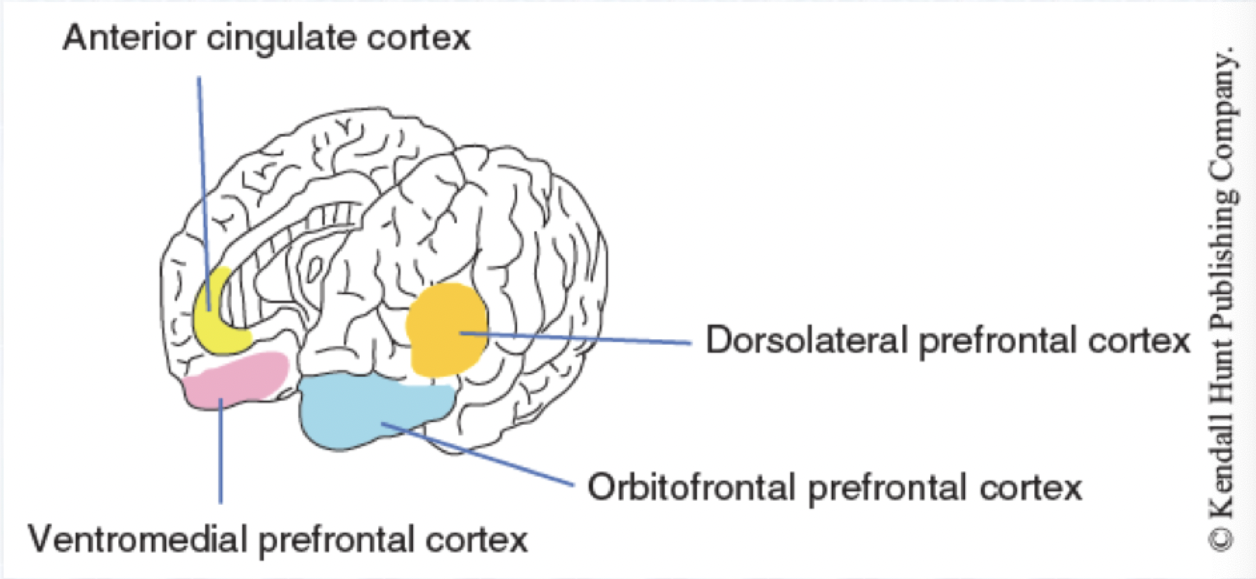
Go Systems
Structure: Anterior Cingulate Cortex (gyrus)
Function: Maintain attention on desired activities, planning, self-initiation, goal-directed
Structure: Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex
Function: Working memory, planning, strategy
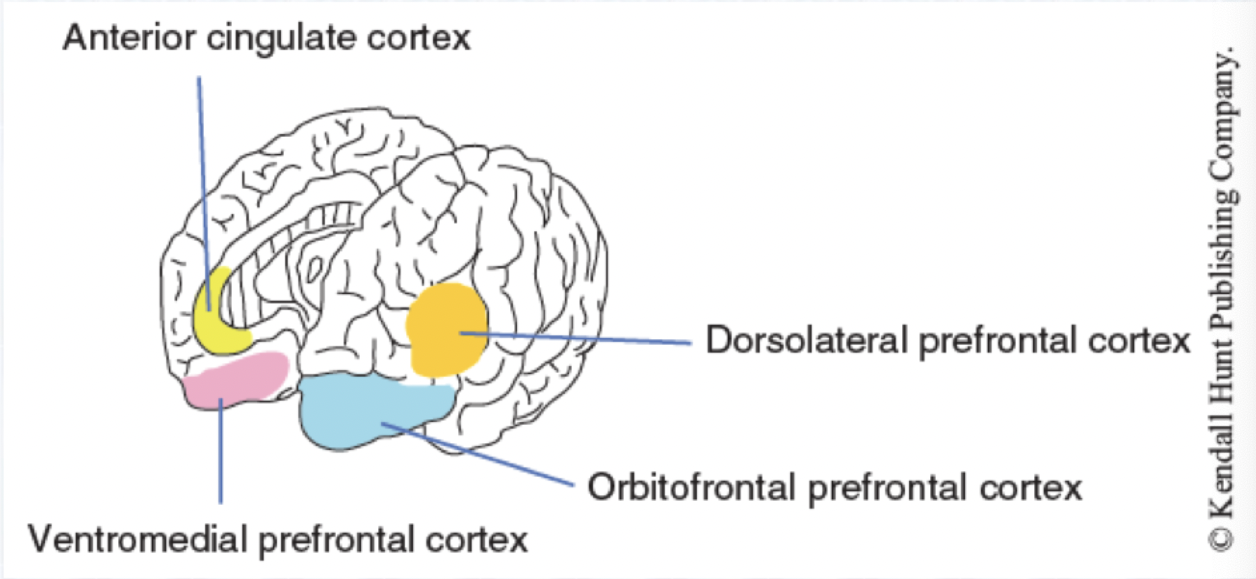
Stop Systems
Structure: Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex
Function: Response inhibition, sustained attention, memory retrieval, shifting
Structure: Orbitofrontal Prefrontal Cortex
Function: Assigning value of stimulus, integrating reward and punishment
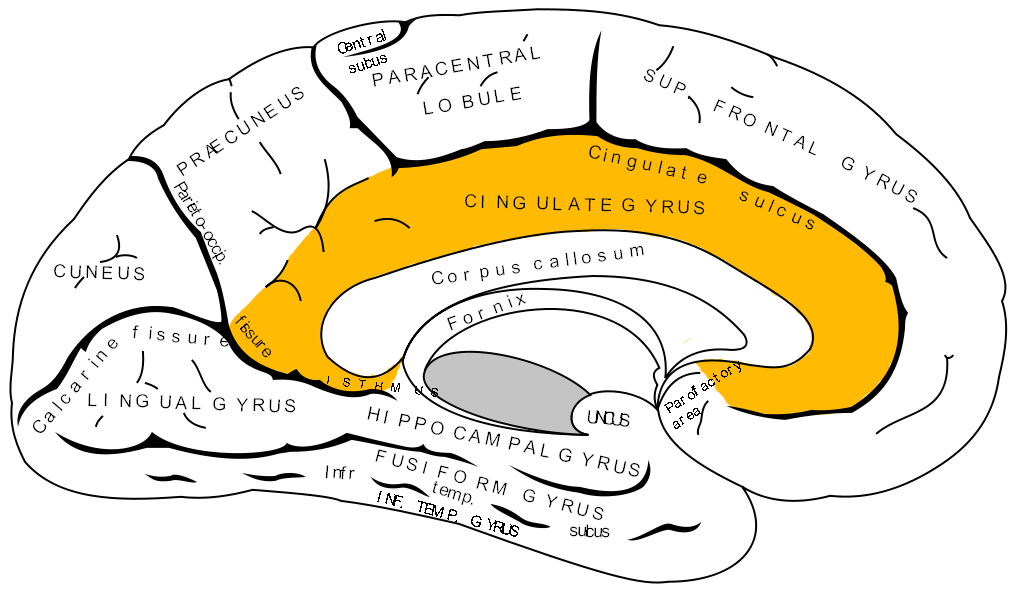
Limbic System
emotion system
Cingulate Cortex (gyrus)
Connect limbic system and prefrontal cortex; affect regulation
OCD & anxiety
Septum Pellucidum and Nuclei
Part of pleasure center (w/ nucleus accumbens, medial hypothalamus, subthalamic nuclei)
Schizophrenia, impulse control disorders, addiction
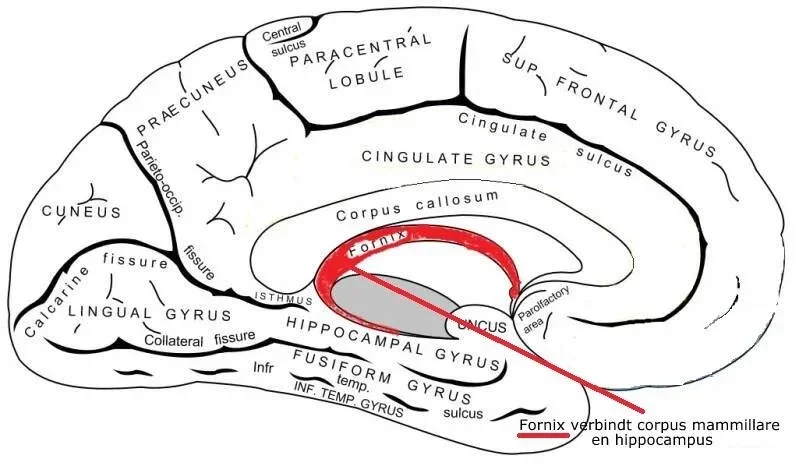
Fornix
Carries signals from hippocampus to septal nuclei and mammillary bodies
memory and emotion
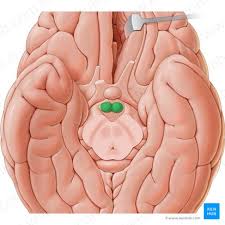
Mammilary Bodies
Relays from the amygdala and hippocampus
recognition & smell memory
Hippocampus
Transfer short-term memory into long-term memory, new learning, spatial recognition, impulse and emotion control
Alzheimer’s, other dementias, memory deficits, depression
Amygdala
Elicits and control aggression, threat appraisal
Impulse control disorders, conduct disorders, depression, anxiety, personality disorders (antisocial, borderline)
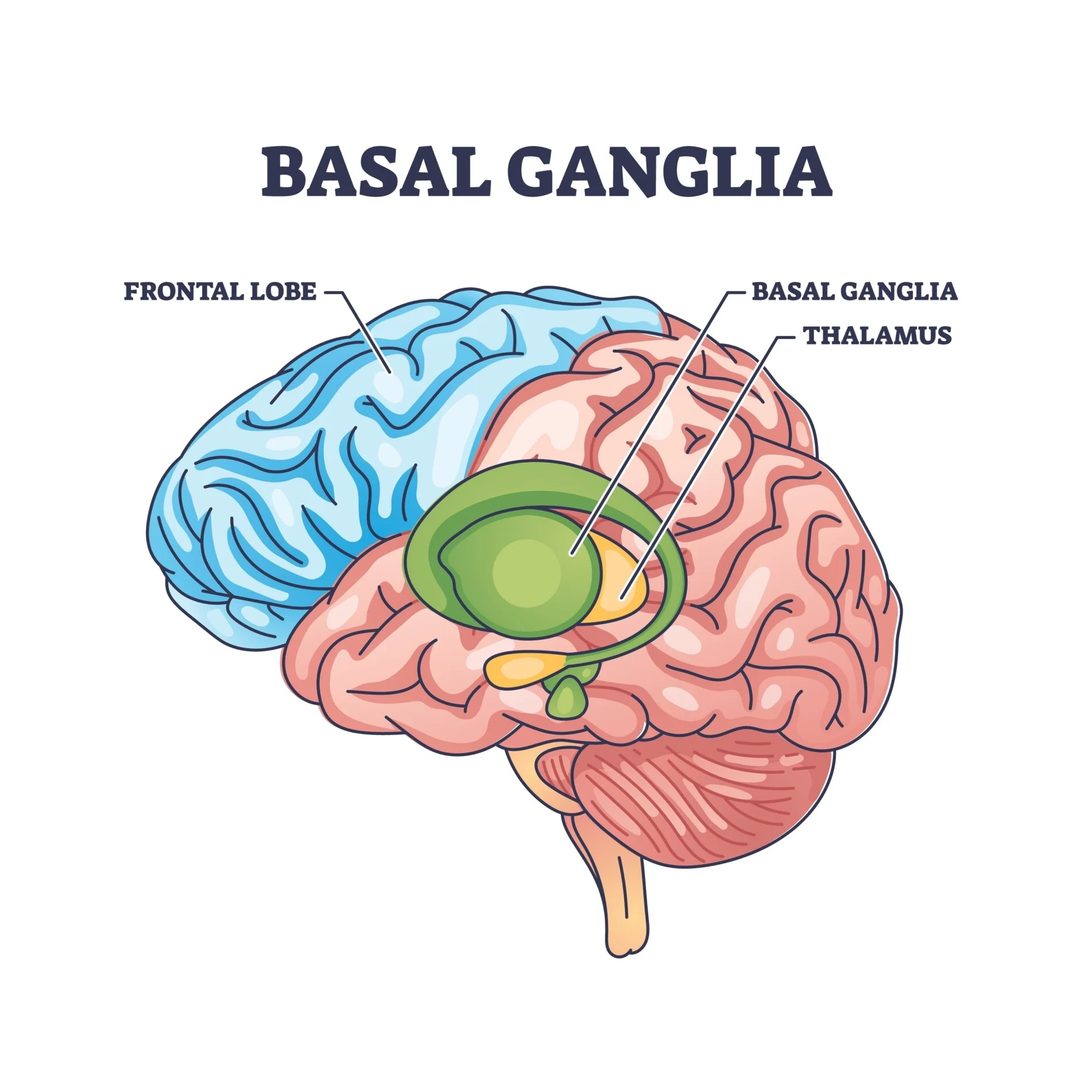
Basal Ganglia
Striatum, Nucleus Accumbens, Globus Pallidus, Substantia Nigra
a cluster of nuclei found deep to the neocortex of the brain. It has a multitude of functions associated with reward and cognition but is primarily involved in motor control.
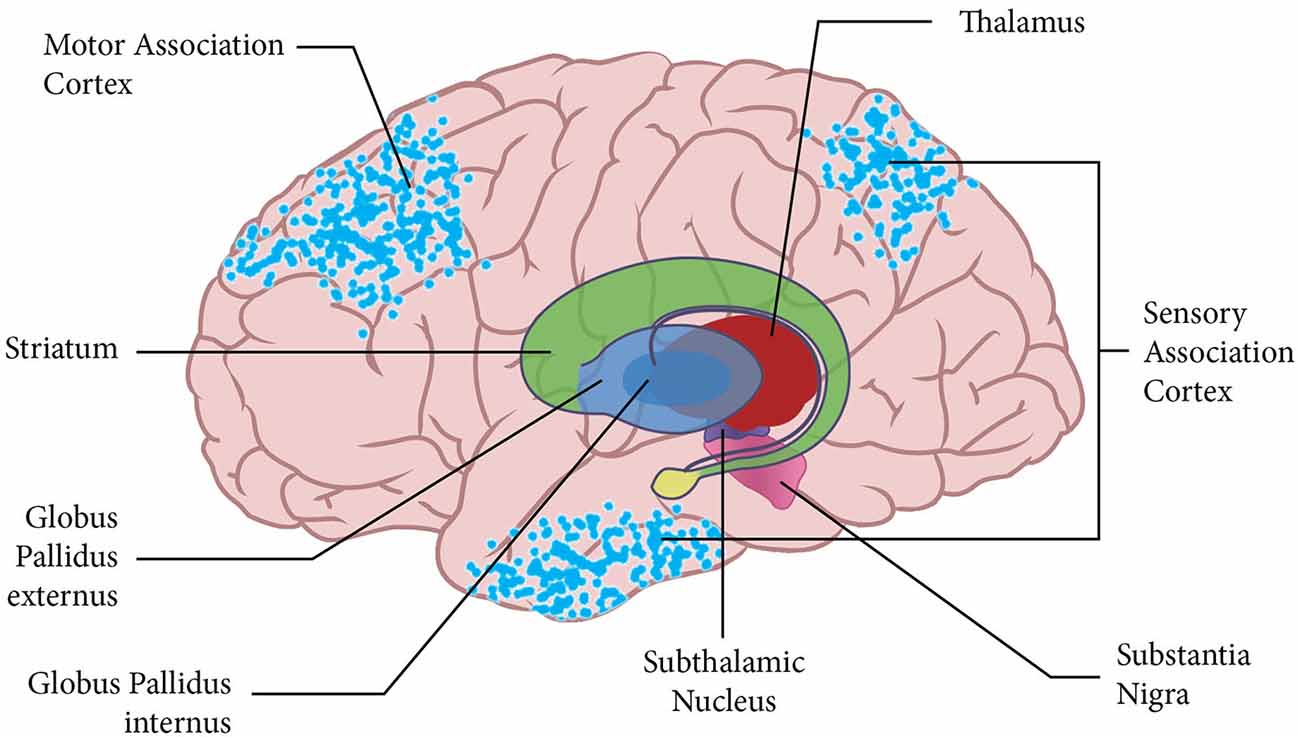
Striatum
Planning and modulation of movement. NMDA (glutamate) receptors modulating dopamine activity
Parkinsons, Huntingtons, Other Choreas, Tourettes, OCD, Schizophrenia, ADHD
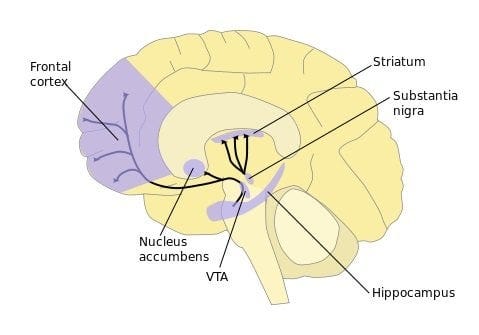
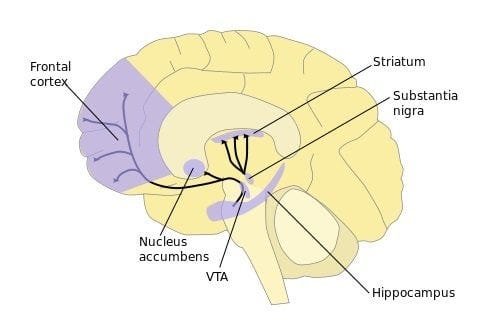
Nucleus Accumbens
Dopamine innervation for reward, pleasure, addiction, aggression, fear, impulsivity
Substance abuse, addictive disorders, OCD, anxiety, mood disorders, ADHD
Globus Pallidus
Relay from Striatum to thalamus. Inhibits excitatory input from cerebellum, NMDA (glutatmate) receptors modulating dopamine activity
Tremors, jerks, spasmodic movement, schizophrenia, ADHD
Substantia Nigra
Reward, addiction, motor planning, learning
Parkinsons, addiction, schizophrenia
Autonomic Nervous System
Automatic functions such as heart rate, breathing, sweating, digestion, excretion. Two complementary systems make up the ANS
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Energy Conservation
Sympathetic Nervous System
Fight or flight
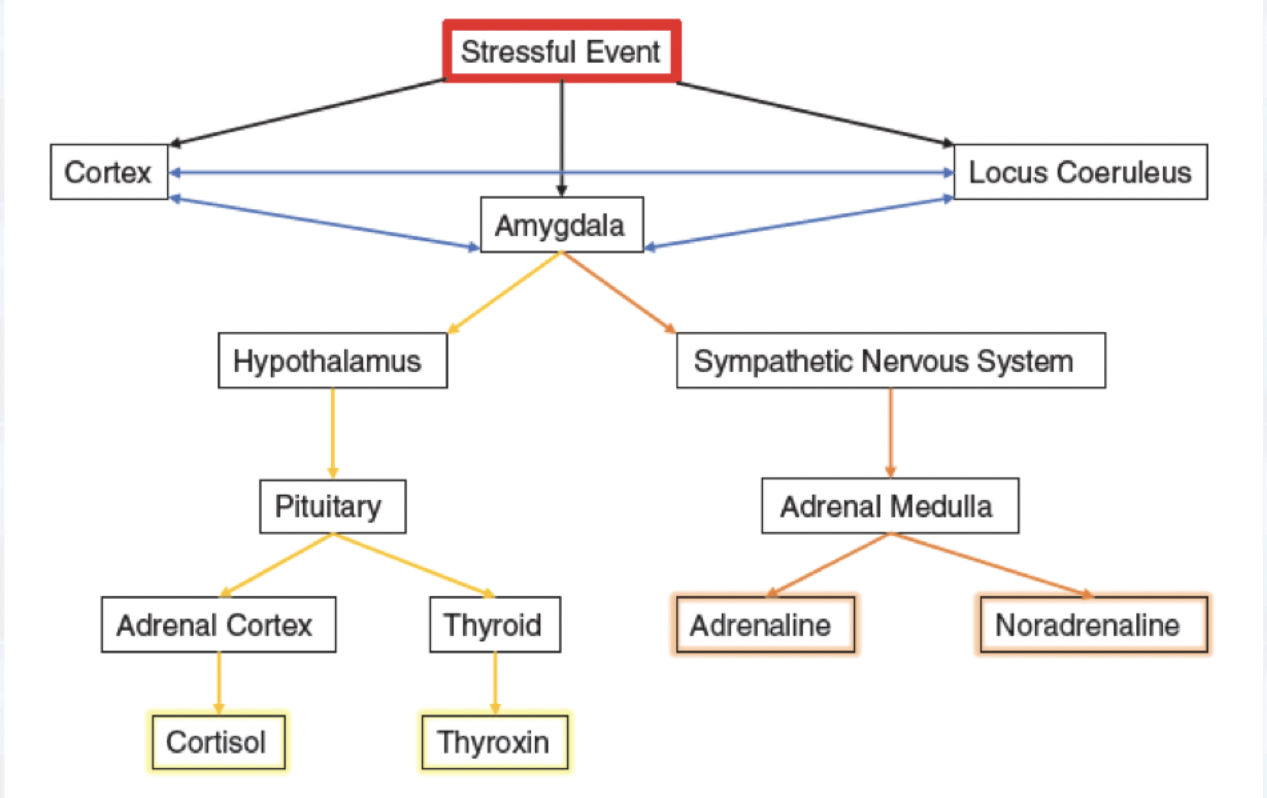
Neural Response to trauma and stress
HPA Axis and SNS
Pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drug
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Elimination
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption
Drug associated factors:
Molecular weight (size to pass the blood brain barrier)
Degree of ionization
Lipophilic/Lipophobic
Formulation
Patient Associated Factors:
Route of admission
Presence of food in stomach
Stomach acidity and gastric mobility
Bioavailability
Amount of active drug in system
Pharmacokinetics: Distribution
Membrane Permeability
Membrane Barriers- all drugs passing blood brain barrier must be lipophilic
Reservoir storage- Lipophilic drugs stored in body fat
Protein Binding- usually bind to albumin, but also to red blood cells and a acid glycoprotein
Pharmacokinetics: Metabolism
(Biotransformation)
Most psychotropics are metabolized hepatically (liver), not lithium
Phase 1 Reaction- degradation by cytochrome P450 enzymes
Phase 2 Reaction- Conjugation
Enzyme Inhibition
Increases drug levels
Enzyme Induction
Decreases drug levels
Cytochrome P450 (+ inducers)
Enzymes which reduce drugs to a more water soluble (polar) form
Smoking
Alcohol
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Phenobarbital
Chlorpromazine
Pharmacokinetics: Elimination
Primarily via kidneys
Half Life (T1/2)
Distribution and/or elimination half life
Steady State
Amount administered is = to the amount eliminated. It takes 4-5 T1/2 to reach steady state
Loading Dose
Initial high does to rapidly achieve therapeutic concentrations
Onset
First clinical effects
Duration
Length of time drug works
Titration
Balancing drug dose against symptoms
Pharmacodynamics: What the drug does to the body
Alter rate of synthesis: more/less NT
Alter storage rate: more/less NT (leaky vesicles)
Alter release: more/less release of NT
Alter reuptake: more/less (Ex. SSRI’s block reuptake = more NT in synapse)
Alter deactivation by enzymes: reduce action of enzymes that break down NT so there is more NT in synapse
Block or mimic receptor site attachment: block and prevent attachment to receptors, mimic NT at the receptor site, may be allosteric regulation
Up and Down Regulation
Drug causes body to change # of receptor sites
Up: increase # of receptors, most commonly due to decreased stimulation (E.g. receptors are blocked) or decreases in NT
Down: decrease # of receptors, most commonly due to increased stimulation due to increased NT
Effects of drugs on receptors:
Agonists
Partial agonists
antagonist
partial inverse agonist
inverse agonist
Mimics NT by stimulating postsynaptic receptors
Partially mimics NT
Blocks receptor site
Partially causes opposite reaction of NT
Causes opposite reaction of NT
Efficacy
Degree to which drug works as intended
Potency
Amount of drug necessary to produce 50% of maximal response
ED 50
Effective dose 50; dose that produces desired effect in 50% of subjects
LD 50
lethal dose 50; dose that is lethal to 50% of subjects (animal studies)