Descriptive Terminology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Radiolucent
Black or dark areas on radiograph, such as tissues that are soft or thin. They permit the passage of the beam with little to no resistance. Examples, caries, air space, soft tissues, dental pulp, and PDL space
Radiopaque
White or light areas on radiograph; tissues are thick or dense and absorb or resist the passage of the beam. Like gold, amalgam, enamel bone, dentin and lamina dura
What is descriptive terminology?
Terms used to describe the appearance, location, and size of a lesion verbally when communicating and when documenting in the client record/chart.
What are some normal radiolucent anatomical landmarks or conditions?
Mandibular foramen, mandibular canal, mental foramen, lingual foramen, submandibular fossa, bone marrow spaces (trabceulations), sutures, maxillary sinus, incisive foramen, developing tooth cysts.
What are the terms used to describe radiolucent lesions?
Appearance, location, size
What are terms to describe location?
Interradicular, edentulous, pericoronal, periapical,
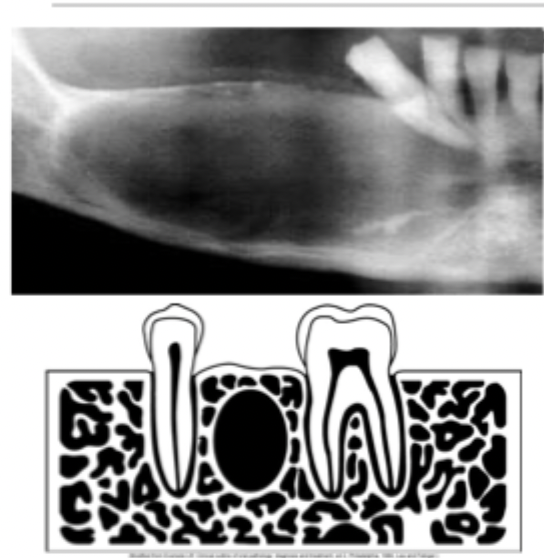
What is interradicular?
Area between the roots of adjacent teeth like lateral periodontal cyst.
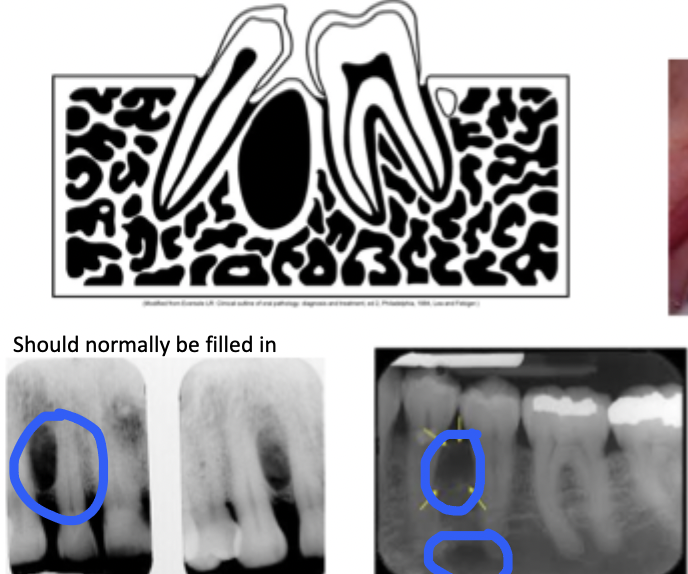
What is edentulous zone?
An area without teeth
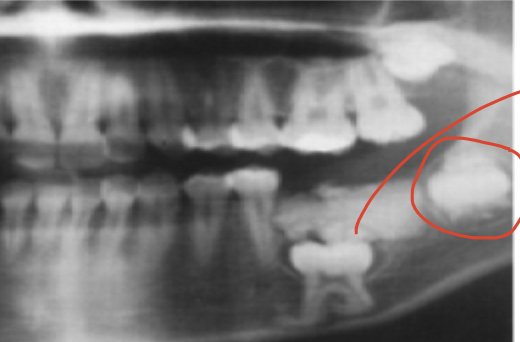
What is periocoronal location?
area around the crown of an impacted tooth (common- mand 8’s)
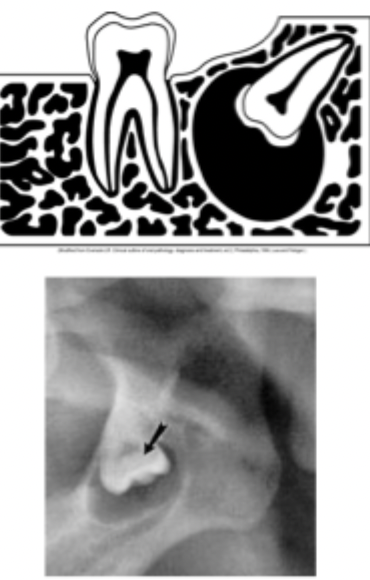
What is periapical location?
a lesion located around the apex of a tooth. Like a periapical cyst secondary to pulpal necrosis.
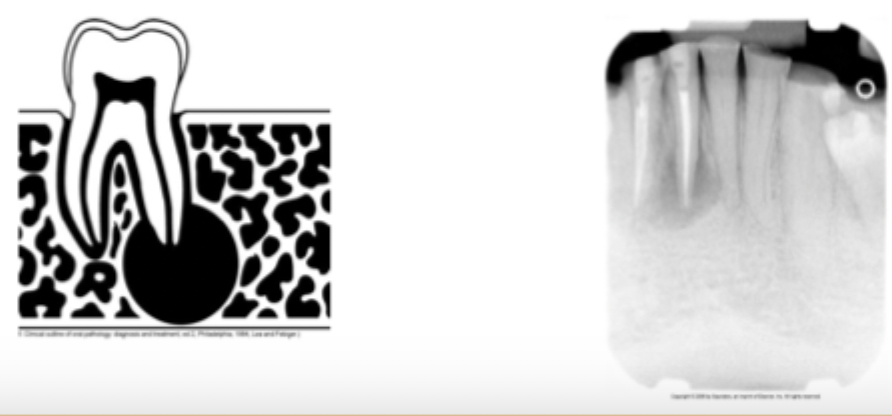

What does unilocular mean?
one compartment, small, non expansive can be corticated, or non-corticated
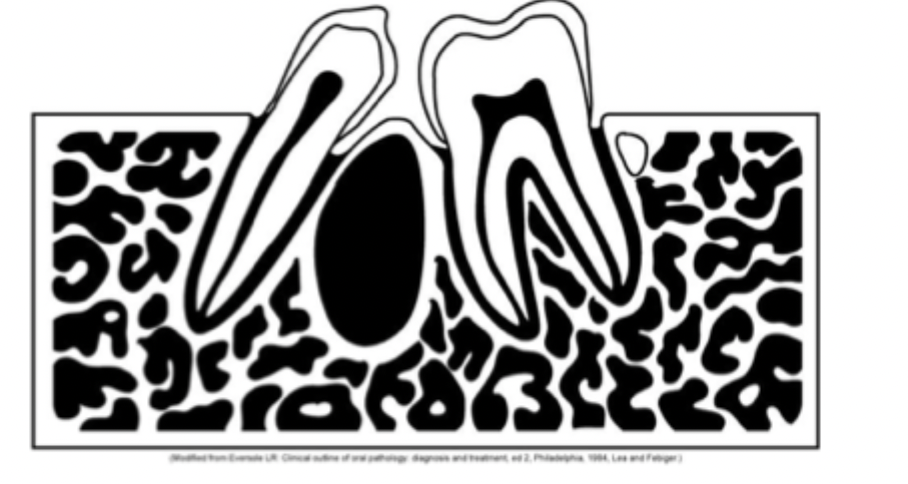
What would this be?
Unilocular corticated radiolucent lesion in intra-radicular location
Unilocular lesion with corticated borders
The lesion exhibits a thin well-demarcated radiopaque rim of bone at the periphery. Usually indicative of a benign slow growing process.
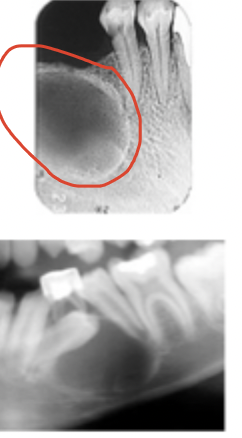
Unilocular lesions with non-corticated borders
The lesion does not exhibit a thin radiopaque rim of bone at the periphery. The periphery appears fuzzy or poorly defined. May represent a benign or malignant process.
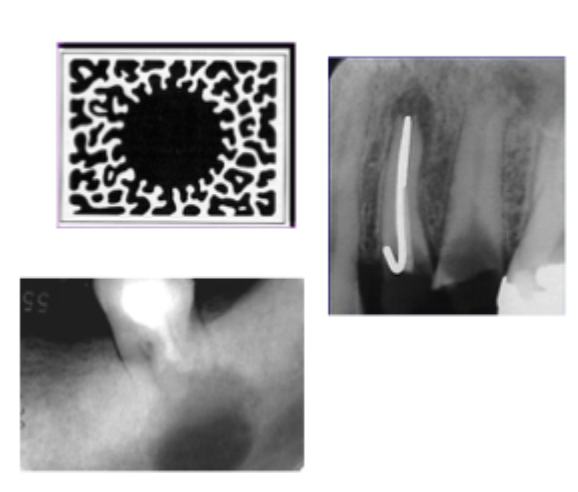
Multilocular radiolucent lesions
A lesion that exhibits multiple radiolucent compartments, frequently expansible. Typically benign lesions with aggressive growth potential.
What are some example of multilocular radiolucent lesions?
Odontogenic keratocyst, ameloblastoma, central giant cell granuloma
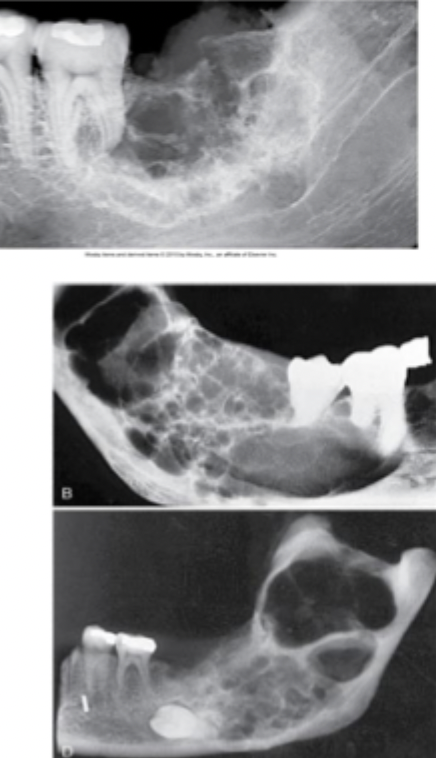
Ameloblastoma
An example of multilocular lesion, can be malignant or benign. Often discovered during routine dental exam. May cause bony expansion.
What is an example of a pericoronal radiolucent lesion?
Dentigerous cyst, you can see a lesion near the crown of the tooth but it has to be an impacted tooth to see a pericoronal lesion.
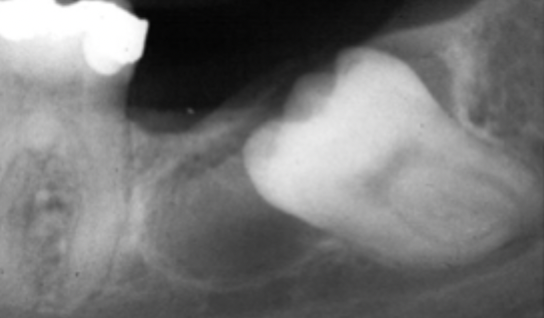
Is alveolar bone loss radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiolucent
What unit do we measure the size of lesions?
millimeters to centimeters
What are terms used to describe the appearance of radiopaque lesions?
focal opacity, target lesion, multifocal confluent, irregular, ground glass, or mixed lucent opaque
Focal Opacity
A well-defined, localized radiopaque lesion on a radiograph. Example: condensing osteitis
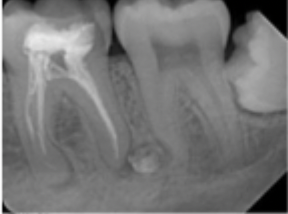
Is condensing osteitis radiolucent or radiopaque?
Radiopaque
What is an example of focal opacity?
condensing osteitis
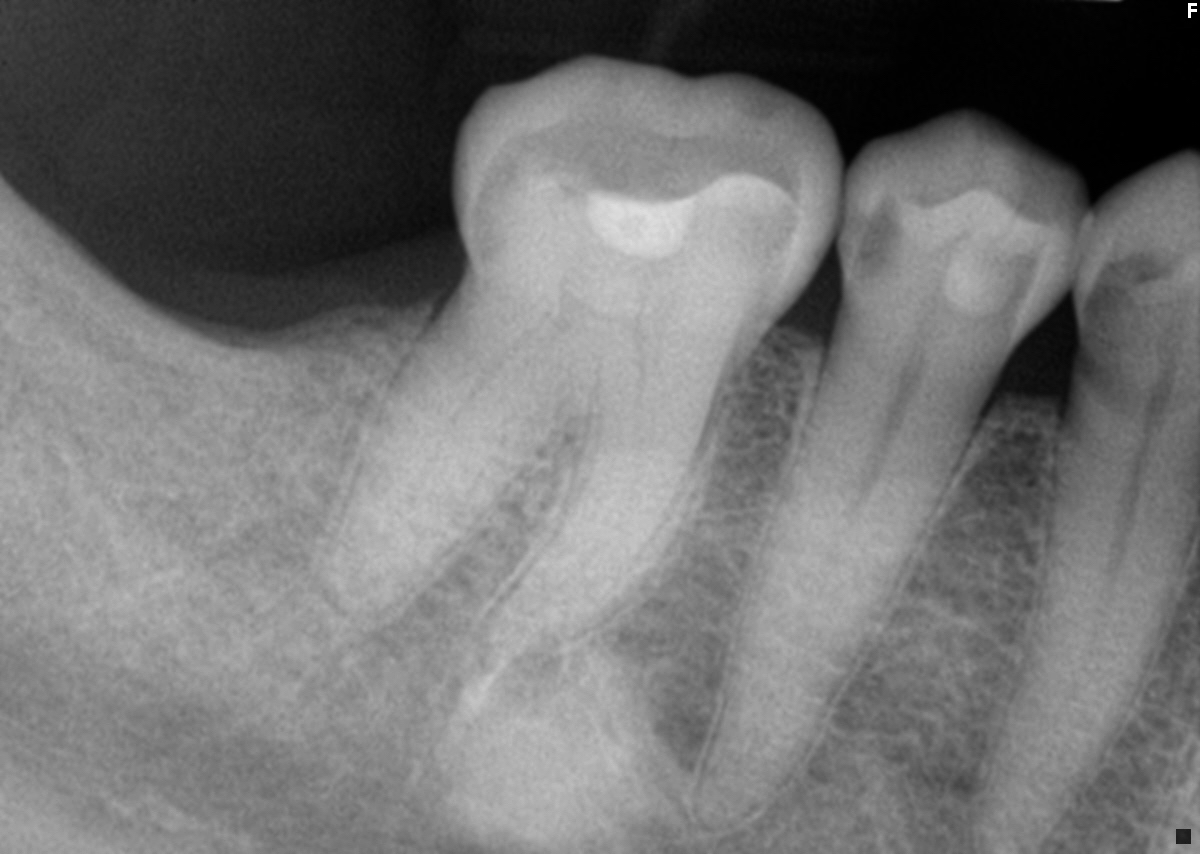
What is this lesion?
condensing osteitis
What is a target lesion?
A well-defined, localized radiopaque area surrounded by a uniform radiolucent halo.
What is an example of a target lesion?
Benign cementoblastoma
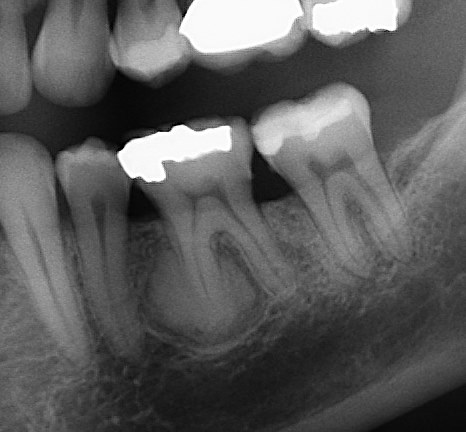
What is this lesion?
target lesion, a benign cementoblastoma
What is multifocal confluent?
A type of radiopaque appearance where there are multiple radiopacities that appear to overlap or flow together.

What is an example of multifocal confluent?
Osteitis deformans
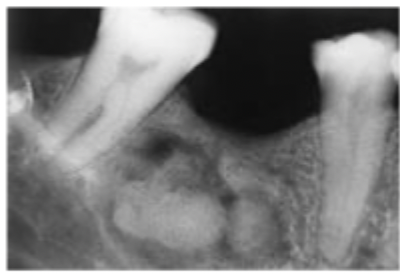
What is this lesion?
An example of multifocal confluent called osteitis deformans.
What is mixed lucent opaque?
A type of lesion appearance where it exhibits both a radiopaque and a radiolucent component. Often represent calcifying tumours.

What is an example of mixed lucent opaque?
Compound odontoma
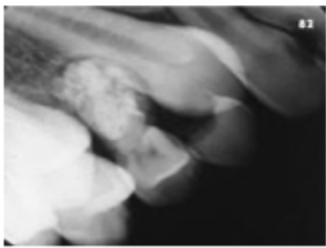
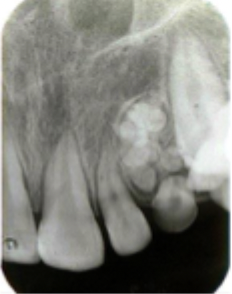
What is this lesion?
A mixed lucent opaque lesion called compound odontoma
What is irregular ill-defined?
A radiopacity that may exhibit an irregular, poorly defined pattern. May represent a malignant condition.

What is an example of irregular ill-defined?
Osteosarcoma
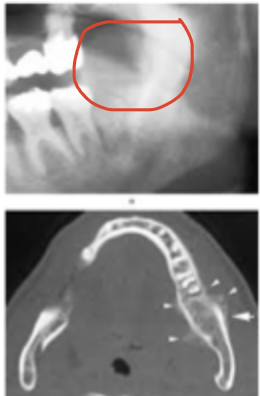
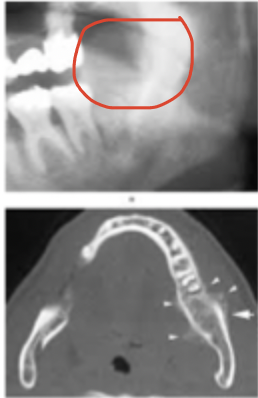
What is this lesion?
irregular ill defined osteosarcoma
What is ground glass appearance?
A granular or pebbled radiopacity that resembles pulverized glass. Often said to resemble the appearance of texture of an orange peel.

What is an example of ground glass?
Fibrous dysplasia
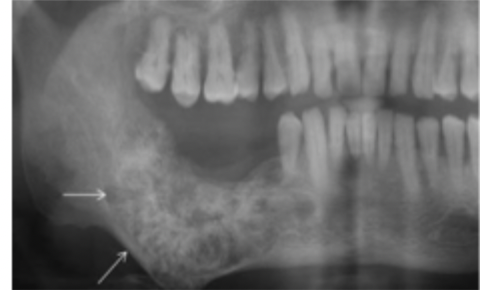
What is this lesion?
Ground glass, fibrous dysplasia
Soft tissue opacity
Appears as a well-defined, radiopaque area located in the soft tissue.

What is an example of a soft tissue opacity?
Calcified lymph node or sialolith
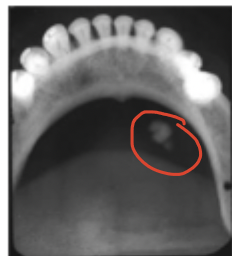
What is this an example of?
Soft tissue opacity, sialolith
What is a radiopaque periapical lesion?
Periapical refers to a radiopaque lesion loacted around the apex of the tooth
What is an example of a periapical radiopaque lesion?
Benign cementoblastoma
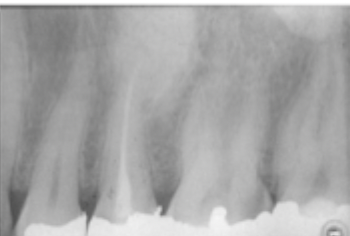
Interradicular location for radiopaque
A radiopaque lesion located between the roots of adjacent teeth
What is an example of a radiopaque interradicular lesion?
sclerotic bone
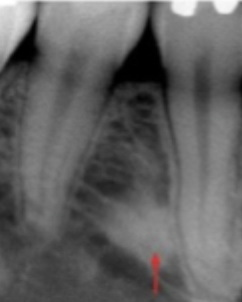
What is this lesion?
sclerotic bone
What is an example of a radiopaque lesion in the edentulous zone?
Complex odontoma
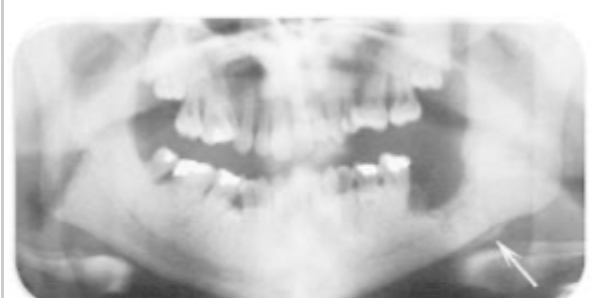
What is an example of a radiopaque and radiolucent lesion in a pericoronal location?
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor