Barrons AP Psychology Flashcards
1/564
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
565 Terms
Introspection
- 1st wave of psychology
- practice of accurately recording cognitive reactions to simple stimuli
- asking people to look inside and assess the patterns of their cognition
- do not currently influence modern psychology

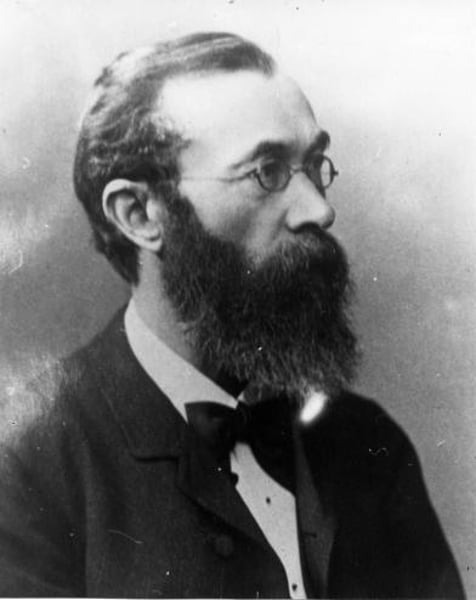
Wilhelm Wundt
- set up the first psychology lab in Germany
- trained his subjects in introspection
- father of structuralism

structuralism
the idea that the mind operates by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations
- old school of psychology that focused on the structure of the mind using introspection
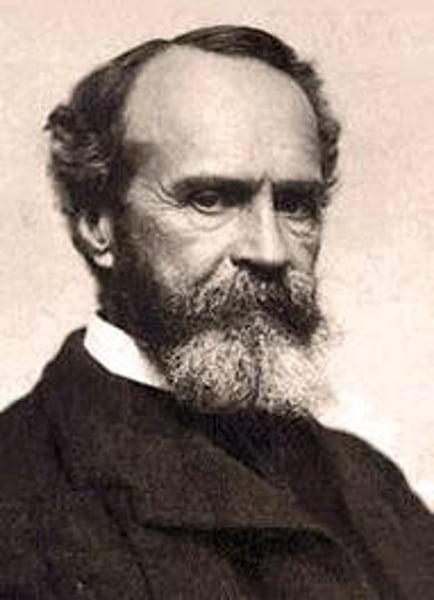
William James
- published Principles of Psychology (the first psych textbook)
- father of functionalism

functionalism
- old school of psychology that studied how the brain's structures identified function in our lives
Gestalt psychology
- second wave of psychology
- "the whole experience is often greater than the sum of its parts"
- old school of psychology that examined a person's total experience of thought and behavior
Psychoanalytic theory
- third wave of psychology
- old school headed by Sigmund Freud
- examined repressed memories and unconscious drives through dream analysis, word association, and projective tests
- criticized for being unscientific and unverifiable

unconscious mind
a part of our mind over which we do not have conscious control that determines (partly) how we think and behave
- discovered by Sigmund Freud

repression
the pushing down into the unconscious events and feelings that cause so much anxiety and tensions that our conscious mind cannot deal with them
behaviorism
- fourth wave of psychology
- dominant school of thought from the 1920s to 1960s
- John Watson, Ivan Pavlov, B.F. Skinner
- understood psychology as a science that must limit itself to observable phenomena (not unobservable concepts)
- looked at only stimuli, responses, and reinforcement
reinforcement
environmental stimuli that either encourage or discourage certain responses
stimuli
environmental events that trigger a response
response
physical reactions to stimuli
multiple perspectives
- fifth and final wave of psychological thought
- many psychologists describe themselves as eclectic because they pull from __________________
eclectic
- drawing from multiple perspectives
- characteristic of the fifth and final wave of psychology (contemporary perspectives)
- claims that no one perspective has all the answers to the variety of human thought and behavior
humanist perspective
- perspective of psychology
- partially in reaction to the reduction of human goodness and cognition by behaviorism
- Abraham Maslow, Carl Rogers
- stressed individual choice and free will --. we choose most of our behaviors and these choices are guided by physiological, emotional, or spiritual needs
- theories are not easily tested with scientific theory
psychoanalytic perspective
- perspective of psychology
- emphasizes that the unconscious mind controls much of our thought and action
biopsychology (neurological) perspective
- perspective of psychology
- explains human thought and behavior strictly by biological processes
- human cognition and reactions are caused by the effects of our genes, hormones, and neurotransmitters
evolutionary (Darwinian) perspective
- perspective of psychology
- explains human thoughts and actions in terms of Darwin's natural selection
- psychological traits are advantageous for survival and are passed down through generations
cognitive perspective
- perspective of psychology
- examine human thought and behavior in terms of how we interpret, process, and remember environmental events

Social-cultural (sociocultural) perspective
- perspective of psychology
- looks at how our thoughts and behaviors vary from people living in other cultures
- emphasizes on the influence culture has on thoughts and behavior -> importance of cultural norms
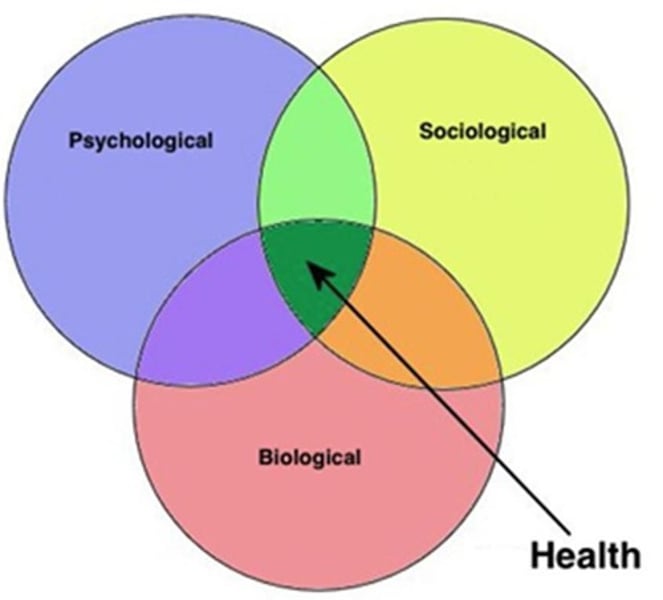
Biopsychosocial perspective
- perspective of psychology
- modern idea that acknowledges human thinking and behavior results from biological, psychological, and social factors
hindsight bias
the tendency to think (after hearing some information) to think that you knew it all along
- it is easy to explain why an event happened after the fact
applied research
research with clear, practical applications
basic research
research that explores questions of interest without immediate real-world applications
hypothesis
a TESTABLE statement that expresses a relationship between two variables
independent variable
the variable of an experiment being manipulated
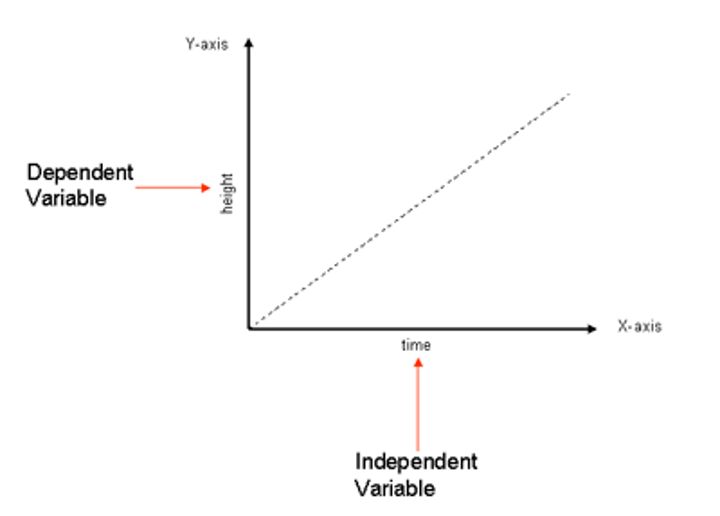
dependent variable
- the variable that changes based on the independent variable
- the variable being tested and measured
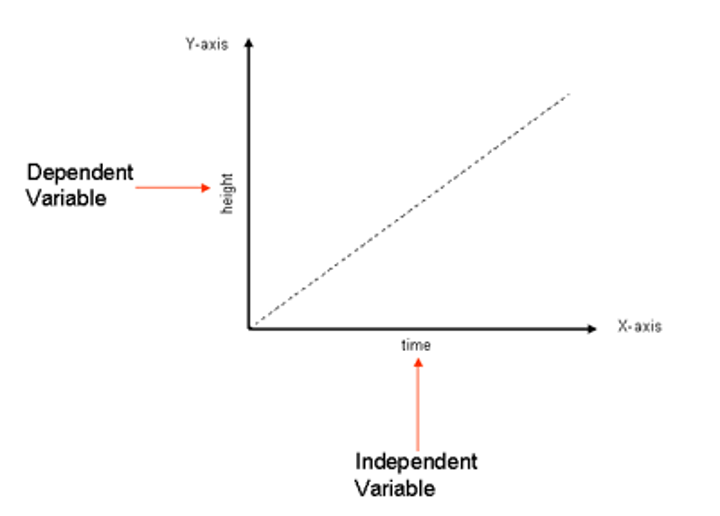
theory
a ______________ aims to explain a phenomenon with a set of testable hypotheses with the hope of collecting supporting data
operational definition
- an explanation of how a variable will be defined and measured
- makes an experiment able to be replicated
validity
an experiment has ________ when it measures what the researcher set out to measure; it is accurate
reliability
an experiment has __________ when it can be replicated; it is consistent
- if another researcher can conduct the same experiment and get similar results
sampling
the process by which participants of an experiment are selected
sample
the group of participants of an experiment
population
the __________ includes anyone or anything that could possibly be selected to be in the sample
representative sample
when a sample group is representative of the population --> if it has been randomly selected
random sampling
the process of selecting a sample from a population that ensures every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected
- makes it more likely the sample will be representative and findings can be generalized

stratified sampling
- additional action taken to increase the likelihood that a sample is representative
- process that allows researcher to ensure that the sample represents the population on some criteria
experiment
research method that is carefully controlled so it can show a causal relationship
laboratory experiment
experiments conducted in a lab (highly controlled environment, less realistic)

field experiment(s)
experiments conducted out in the real world; less controlled, more realistic

confounding variable
and difference between the experimental and control conditions (except for the independent variable) that might affect the dependent variable
- reduced through random assignment
random assignment
means that each participant has an equal chance of being placed into the control and experimental groups
- controls for participant-relevant confounding variables
controls
efforts to limit situation-relevant and participant-relevant confounding variables
- placebo, single- and double-blind procedures, counterbalancing, control groups
group-matching
used to ensure that the experimental and control groups are equivalent on some criterion
experimenter bias
- a kind of situation-relevant confounding variable
- the unconscious tendency for researchers to treat members of the experimental and control groups differently to increase the chance of confirming their hypothesis
- different than fraud: purposing falsifying data
double-blind procedure
- eliminates chance of experimenter bias
- when neither the participants or the researchers are able to affect the outcome of the research
single-blind procedure
when only the participants do not know to which group they have been assigned
- minimizes the effect of demand characteristics (cues about the purpose of the study)
response (participant) bias
the tendency for subjects of an experiment to behave in certain ways
social desirability
a type of response bias in which subjects tend to give answers that reflect well on themselves
Hawthorne effect
the alteration of behavior by the subjects of a study due to their awareness of being observed
- proves the need for a control group to compare experimental data
Placebo method
method of control in which the control group is given an inert and identical substance
- allows the separation of psychological and physiological effects of a drug/process
correlation
expresses a relationship between two variables without ascribing cause
- can be positive (predicting presence) and negative (predicting absence)
survey method
- involves asking people to fill out surveys
- looks for correlation, cannot prove causation (no independent, dependent variables)
naturalistic observation
research method in which researchers observe their participants in their natural habitats without interacting with them at all; sacrifices control for realistic and rich description of participant behavior

case study
research method used to get a full, detailed picture of one participant; findings cannot be generalized to a larger population
descriptive statistics
statistics that simply describe a set of data
- examples: frequency distribution, histograms
measures of central tendency
- attempt to mark the center of a distribution
- mean, median, mode
outlier
values of data that can distort the mean and skew distributions
- when a set of data contains an outlier, medians are better measures of central tendency
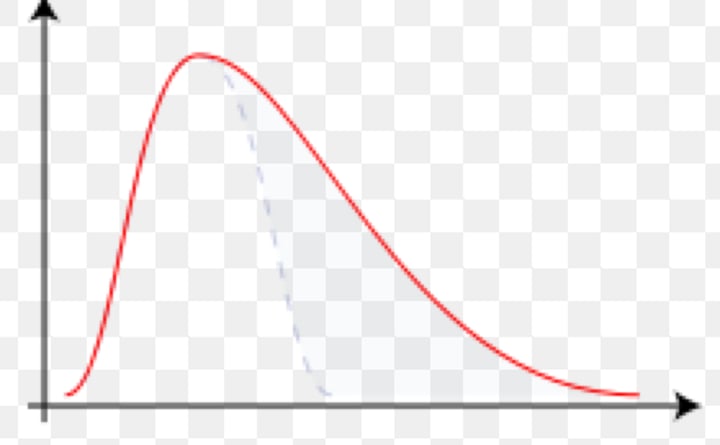
positively skewed
when a set of scores contains more low scores than high scores and the and the mean is higher than the median
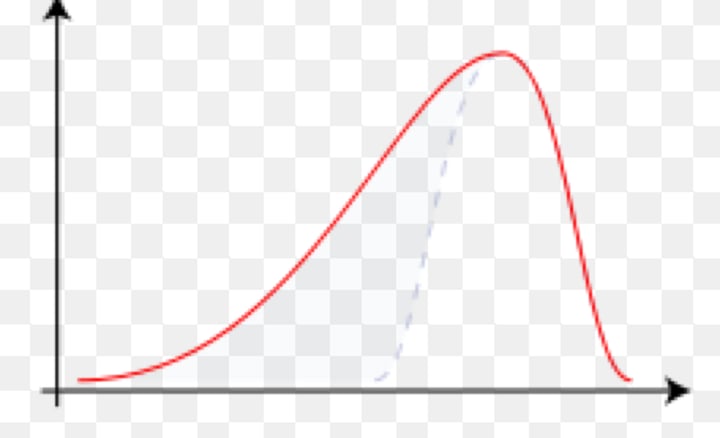
negatively skewed
when a set of scores contains more high scores than low scores and the mean is lower than the median
measures of variation
- statistical measures that depict the diversity of a distribution
- range, variance, standard deviation
z score
measure of the distance of a score from the mean in units of standard deviations
normal curve
- 68% within 1 std. dev
- 95% within 2 std. dev
- 99% within 3 std. dev
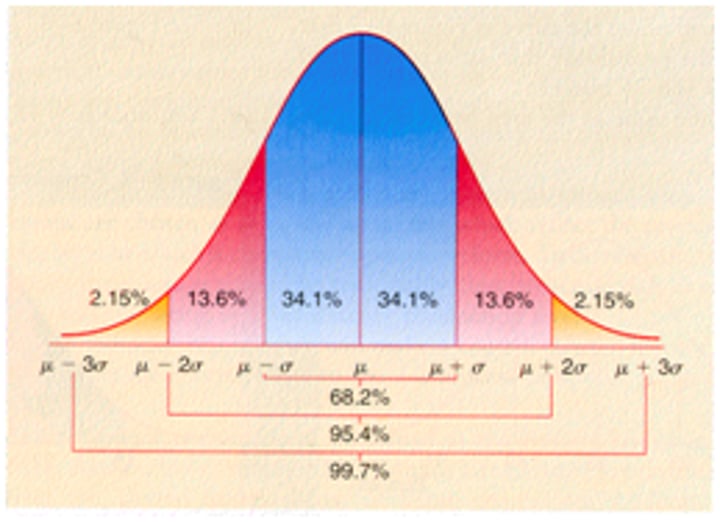
correlation coefficient
- computation showing the strength of a correlation
- range from -1 to 1
inferential statistics
as opposed to descriptive statistics; used to determine if findings can be applied to the larger population
sampling error
the extent to which the sample differs from the population
p value
value that gives the probability that the difference between the groups is due to chance
- never equal to 0
- more correlation and larger sample = low p value
statistical significance
p value of less than 0.05 --> a 5% chance that that the results occurred by chance
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- the board to which any type of academic research must first propose the study
- reviews research proposals for ethical violations and/or errors in procedure
standards of a human experiment
- no coercion
- informed consent
- anonymity or confidentiality
- risk evaluated and communicated
- debriefing
neuroanatomy
the study of the parts and functions of the neurons
neuron
individual nerve cell; entirely make up the nervous system
dendrites
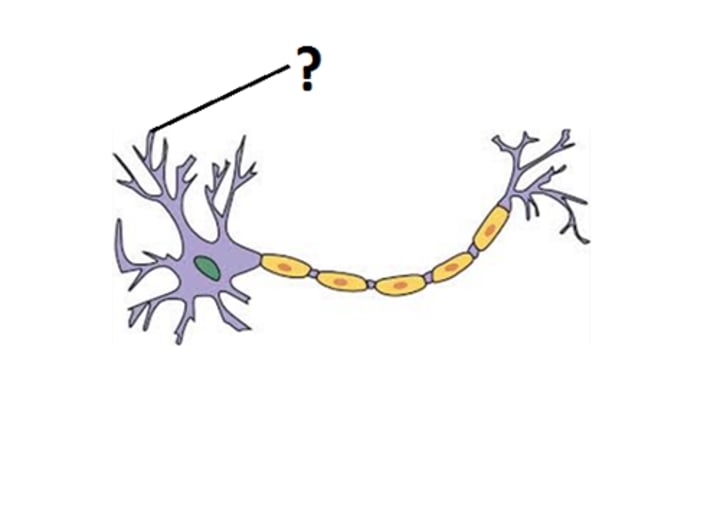
rootlike parts of the cell that stretch out from the cell body; grow to make synaptic connections with other neurons
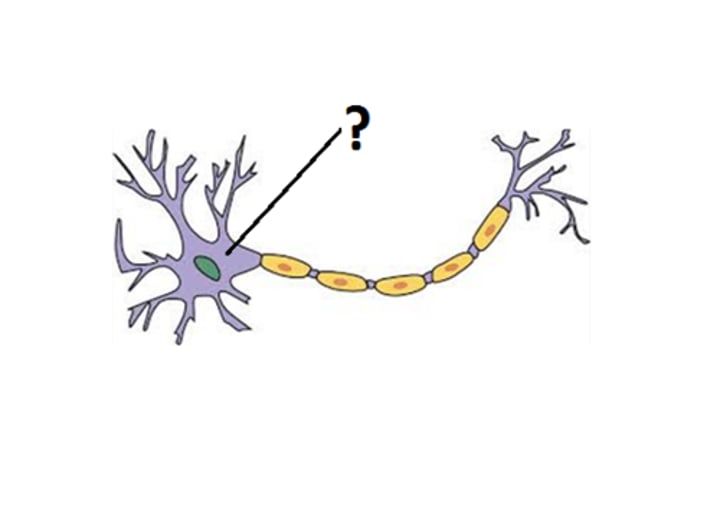
cell body (soma)
part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and other parts necessary to cell function
axon
part of a neuron; wirelike structure ending in the terminal buttons that extends from the soma
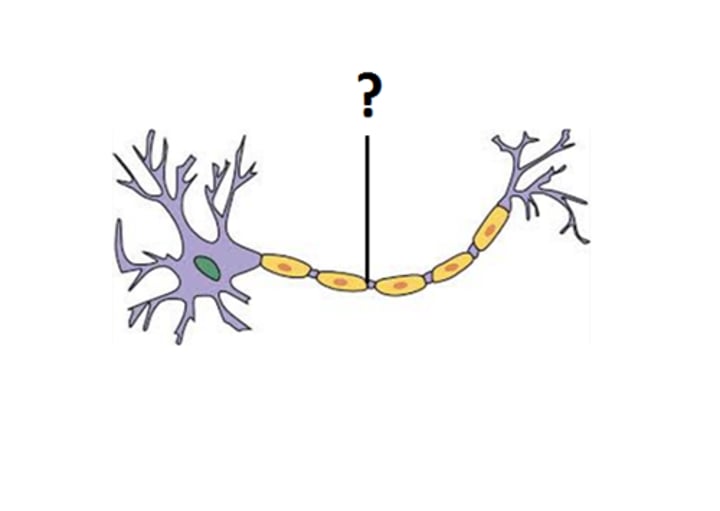
myelin sheath
part of a neuron; a fatty covering around the axon of some neurons that speeds neural impulses like insulation on electrical wire
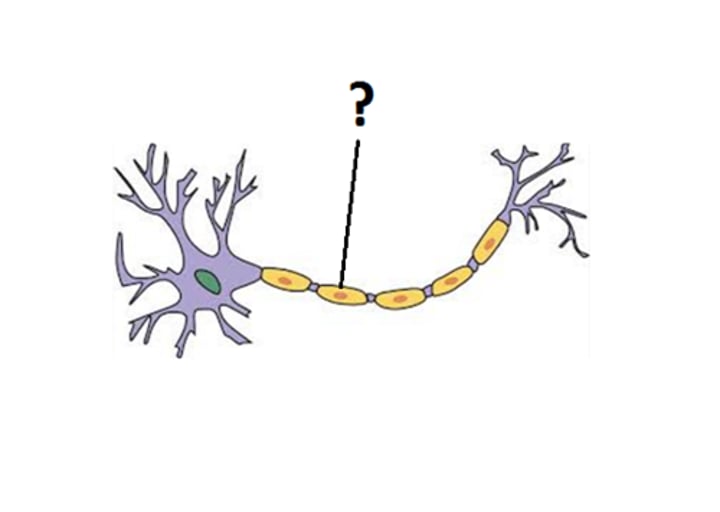
terminal buttons (axon terminal)
part of a neuron; the branched end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters and connects through the synapse to the dendrites of the next neuron
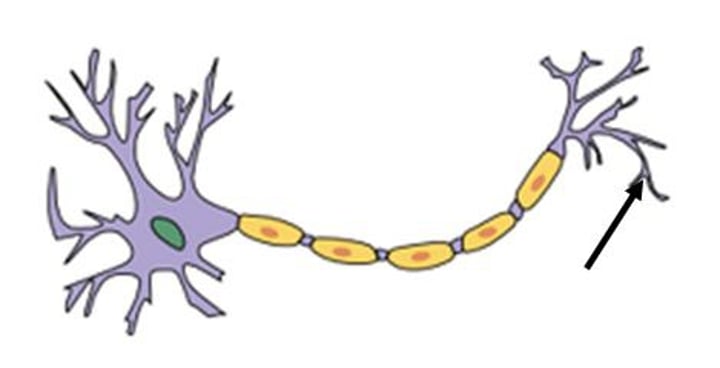
neurotransmitters
chemicals contained in the terminal buttons of a neuron that enable neurons to communicate; fit into receptor sites on the dendrites of the next neuron like a key in a lock
synapse
part of a neuron; the space between the terminal buttons of one neuro and the dendrites of the next neuron; where neurotransmitters move from cell to cell
receptor sites
places on the dendrites of a receiving neuron that take in the neurotransmitters of the sending neuron
threshold
the amount of stimulation it takes the action potential to be triggered in a neuron
action potential
- when an electric signal is fired down the neuron
- when the electrical charge is sent down the neuron, causing the membrane to become permeable and allow positive ions to flood in, triggering the next node to trigger and so on
all-or-none principle
the principle that a neuron either fires completely or does not fire at all, similar to a bullet in a gun
- the neuron will fire with the same "strength" every time regardless of how strong the stimuli is
- neurons can only have one action potential at a time
excitatory neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters that excite the next cell into firing - build up to cross the threshold and trigger action potential
inhibitory neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters that inhibit the next cell from firing - stop action potential from moving to the next neuron cell
acetylcholine
- neurotransmitter
- controls motor movement
- lack of _________ is associated with Alzheimer's
dopamine
- neurotransmitter
- controls motor movement and alertness
- lack of dopamine is associated with Parkinson's disease
- too much dopamine is associated with schizophrenia
endorphins
- neurotransmitter
- function as pain control
- involved in addition to drugs and alcohol
serotonin
- neurotransmitter
- controls mood
- lack of serotonin is associated with clinical depression
GABA
- neurotransmitter
- important inhibitory transmitter
- too little can cause seizures and insomnia
glutamate
- neurotransmitter
- important excitatory transmitter; involved in memory and learning
- too much causes migraines, seizures
norepinephrine
- neurotransmitter
- deals with alertness and arousal
- too little can cause depression
afferent (sensory) neurons
the neurons that take sensory information to the brain
interneurons
the neurons that take the messages from the brain or spinal cord and send them elsewhere to the brain or to different neurons
efferent (motor) neurons
neurons that take information from the brain to the rest of the body
central nervous system (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
spinal cord
body structure of the CNS made up of all the nerves housed within the bones of the skull and vertebrae that transmits information from the rest of the body to the brain
- highway to the brain, allows reflex reactions to occur without conscious processing
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
consists of all of the nerves in your body besides those of the brain and spinal cord
- divided into two categories: autonomic and somatic
somatic nervous system
the part of the PNS that controls voluntary muscle movements --> the motor cortex of the brain sends impulses to muscles allowing us to move