Geology 1121 Ch.14
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What does a stream flow reflect?
plate tectonics and climate systems
What is a stream?
any body of water that flows over land in a channel
What is a river?
major branch of a stream
What is a tributary?
side channels of a stream
What are headwaters?
beginning of a stream
What is the mouth of a stream?
the end of the stream
What is discharge?
amount of water passing through a given point in a measured period of time
What is the formula for discharge?
Q=AV
What is Q in the discharge formula?
stream discharge
What is A in the discharge formula?
area of channel (L x W)
What is V in the discharge formula?
flow velocity
What is the largest river system in the world?
Amazon river (175,000 m³/sec)
What is laminar flow?
smooth water movement
What part of a channel does water move the fastest?
the center
What is turbulent flow?
rough water movement
What type of water flow is most common?
turbulent
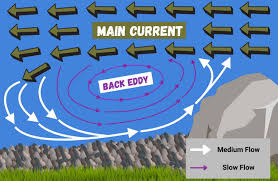
What is an eddy?
isolated ring chape current of water
What is a whirlpool?
rapidly rotating mass of water
What is an abrasion (type of erosion)?
sand and pebbles carried by a stream erode rock along the stream channel
What is an headward erosion(type of erosion)?
upstream erosion
What are potholes (type of erosion)?
deep holes in the rock created by pebbles and cobbles that get caught in an eddy
What is scouring (type of erosion)?
removal of loose fragments from channel by rapidly moving water
What is undercutting (type of erosion)?
force of falling water splashing on nearby rocks wearing them away leaving a ledge that collapses (waterfalls)
What is suspended load(sediment transport)?
sediment grains that swirl in water w/o settling (normally sand and silt)
What is bed load(sediment transport)?
all materials carried by stream along stream bed (typically sand, pebbles, cobble)
What is dissolved load(sediment transport)?
all ions in solution from soluble minerals (gives water its taste)
What is saltation?
grains “jump” from bottom of channel into water column after hitting a rock or similar at bottom of stream
What is runoff?
all water flowing on earths surface
What is a drainage divide?
ridge that separates streams; rainfall runs down either side of the divide
What is a drainage basin?
area that funnels water into a stream
What is a permanent stream?
stream that flows all year (fed by precipitation and groundwater
What is an ephemeral stream?
stream that flows during heavy rains
Where is the groundwater table in an ephemeral stream?
below the channel
When do lakes form?
when stream flow is obstructed
What is a delta?
place of sediment deposition at mouth of river
How do you grow a delta?
add more sediment
What is a flood?
when water spills out of its channel onto the flood plain
Is flooding healthy?
flooding is indicative of a healthy river (natural occurence)
What are the characteristics of a floodplain?
composed of fine grained sediments
agricultural resource (nutrient rich)
bordered by natural levees
How do natural levees form?
water spills over existing levees and fills the floodplain leaving behind sediment at the rivers edge
What do natural levees do?
confines water to stream channel and protects against future floods
What is a flash flood?
floodwaters rise so fast that it may be impossible to escape water
What is a meandering stream?
single channel with winding and twisting snake like bends
What is a meander bend?
bend or curve in the stream
How do meandering streams/bends occur?
a stream erodes outer banks of bends and deposits sediment against the inner bank
What is a point bar?
inside bank of a stream, slower current
What is a cut bank?
outside bank of stream (erodes away)
What is an oxbow lake?
u-shaped lake formed from abandoned meander loop
What is a braided stream?
stream with many dividing and interlocking channels separated by small islands (high sediment load with high water velocity)