Job Control Language (JCL)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
JCL
Is used to submit jobs to the system. Job is one unit of work. JCL consists of statements and their parameters. There are three types of statements: JOB (specifies the information of the job such as jobname, programmer name and programmerid), EXEC (specifies the program/procedure to use), DD (specifies the files to use in the job) and 2 types of parameters: positional (should be coded in specified order and position eg: accounting info should be coded after job keyword if not JCL error will come), keyword (can appear in any order)
JCL is useful to run the Batch processes.
JCL syntax
the record length should be 80 to write a JCL code: lrecl : 80, should be in upper case (caps on),
first 2 characters on every line is an identifier //,
name of the job: 8 characters it should be same as the name of the pds member,
operand: JOB/EXEC/DD
Accounting info:
other parameters like programmer name
//NAMEFIELD OPERAND PARAMETERS
comment: //* writing comment in the same line /*comment
end jcl : /*
Job Statement
Also known as job card.
line identifier //
name of the job: sortjob - 8characters max, can be alphanumeric, first character should never be a number
JOB operand
accounting info: refers to the person or group to which the CPU time is owned. System specific. not mandatory. used to uniquely identify a user can be emp id or name of dept. multiple (1234, ‘HR’). To skip this parameter we can give ,
programmer name: not mandatory
keyword parameter - can come in any order:
Class= can be A to Z or 0 to 9. every class defines a certain function. jobs similar in some aspect are grouped together in one class For eg: class P is for print. class=Z, class=1
priority= PRTY: 0 to 15. 15 is the highest and 1 is the least.
notify= which person to notify when job completes? - our ID. can also give &sysuid (person who submits the job will get notified)
message class: MSGCLASS= a to z or 0 to 9. specifies the o/p destination for the job messages. P - print the output. A- could mean fax the job output, D - could mean email the output
message level: MSGLEVEL=(Statement, Msg) Specifies the type of messages to be written to the o/p. message level can be 0,1,2, message can be 0, 1
Statement- 0, job statements only
1, JCL along with symbolic parameters expanded
2, JCL only
MSG- 0, messages written only on abnormal termination
1, messages written irrespective or normal/abnormal termination
Type run: TYPRUN: scan(only scan the JCL for syntax errors and don’t run) or hold(hold the job don’t execute it can be executed if required )
Time: max time the job can execute TIME=(50,00) 50 minutes
region: specifies the amount of address space that will be accolated to the job execution. nK(kilobyte) or nM(megabyte) region=5K
When a parameter is omitted it takes up the default system value which was defined by the system administrator.
exec statement
Used to invoke the pgm/proc that we want to execute
Tells system what pgm/proc to execute.
One JCl can have multiple EXEC statements
syntax: //stepname EXEC parameters
stepname - 1 to 8 characters, coded from column 3. First character must be alphabetic or nation character ($ , # , @)
positional parameters used:
PGM - it refers to the program name to be executed in the job step
PROC - it refers tot he procedure name to be executed in the job step
a procedure refers to a set of JCL statements that are stored in a library and retrieved by its name.
a procedure may contain one or more EXEC statements.
Keyword parameters:
PARM: used to pass values to the pgm being executed
ACCT: specifies the accounting info of the job step. ACCT=(userid)
TIME: MAximum time allocated for the step execution. TIME=(mm,ss) of TIME=ss
region: Specifies the amount of address space to be allocated for the job execution. REGION = nK | nM
When parameters are omitted default is used
DD statements
DD - Dataset definition
Define all the datasets to be used in the JCL.
Syntax: //DDname DD parameter
DDname must be 1-8 characters long, coded from column 3, first char must be alphabetic or national char(@,#,$)
Positional Parameters:
‘*’ : * begins an in-stream data set
Dummy: used for testing pf a JCL. Tells the system to not use any i/p/o/p for this DD statement
Data: In-stream dataset containing statements, which begin with //
Keyword parameters:
DSN: Dataset Name (DSN) is used to give the name of the Dataset. DSN= PHYSICAL Dataset name
DISP: Disposition describes the status of the dataset, what to do with the dataset on normal end of the job and what to do with the dataset on the abnormal end of the job.
DISP=(status, normal end disposition, abnormal end - disposition)
status: NEW- dataset will be created by the DD statement
OLD- dataset already exists, existing data will be overwritten and the job step will have exclusive access until completion of job set
SHR - dataset already exists and will be read, multiple jobs can access it at the same time
MOD - dataset already exists, if not then new dataset will be created. Data will be added at the bottom of the existing data.
normal end - CATLG, UNCATLG, DELETE, KEEP, PASS
abnormal end - CATLG, UNCATLG, DELETE, KEEP
CATLG- dataset is retained with an entry in the system catalog
UNCATLG- dataset is retained but the system catalog entry is removed.
KEEP- Dataset is retained without changing any of the catalog entries
DELETE- dataset is deleted from user and system catalog.
PASS- used for normal end only. this is used when the dataset is to be passed and processed by the next job step in a JCL
Default value: DISP=(NEW,DELETE,DELETE)
DCB: Data control Block (DCB) specifies the values for creating a new dataset
It contains various parameters:
LRECL: record length of the dataset
RECFM: record format of the dataset such as FB, U,VB
BLKSIZE: Blocksize of the dataset
DSORG: Dataset organization (PS(for PS), PO (for pds))
Space: Specifies the space required for the dataset.
SPACE=(spaceunits, (primary, secondary, directory-blocks),RLSE)
UNIT: specifies what type of storage to use for the dataset
UNIT=DASD | SYSDA
DASD will store the dataset in Direct access storage device which is like a tape storage
SYSDA will store it in next available disk storage type
VOL: specifies the volume number on the device where the dataset needs to be stored. VOL=SER=(v1,v2). vi,v2 are volume serial numbers
SYSOUT: specifies the o/p destination based on the class. SYSOUT = class, where class is A then o/p is printer. * then o/p goes to the same destination as that of the MSGCLASS.
JOB processing
JCL Submission → Job entry subsystem (JES) → JCL interpretation in JES ( JCL is converted into text that JES understands and stored in dataset called as spool) → JES decides the priority based on class and prty. If no JCL errors then job is queued → Job execution and log creation in spool.
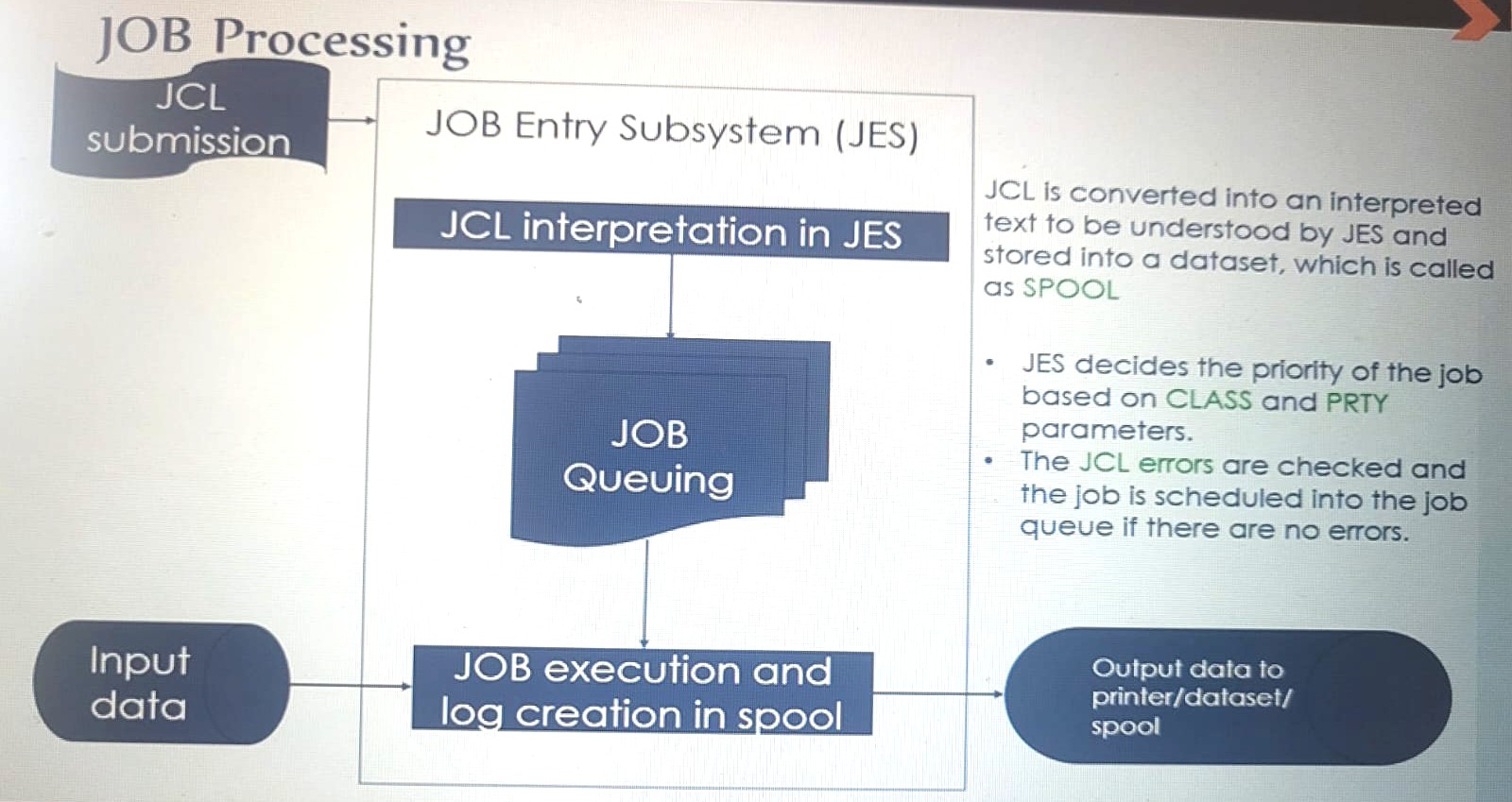
JES
Job Entry Subsytem is used to:
1) submit jobs to the system
2) schedule the processing of the job
3) Control the output of the jobs
SPOOL
Simultaneous Peripheral Operations Online is a dataset which stores the:
Interpreted text for the JCL execution
messages related to job execution, such as job log
output data from the job execution such as errors
system display search facility (SDSF) is used to view spool.
Return codes
When a job executes a return code is set based on the status of execution. Cav vary from 0 to 4095.
0 - Successful execution
4 - Successful execution with warnings
8 - Errors
12 - Severe Error
16 - Major Error
MAXCC is the maximum of the return code from all of the job steps.
SDSF
System Display and Search Facility is used to review the job output. Its primary purpose is to display printed output in the spool area.
SDSF can be used to:
View and search the system log
hold, release, cancel and purge jobs
monitor jobs while they are processed
display job output
control the order in which jobs are processed
SDSF can be used to save the data to a dataset for backup.
SDSF commands
TSO SDSF to go to spool or use 13.14.
ST to see all jobs
? - List the datasets
s jobname - search jobname
Owner userid - show jobs owned by userid
owner * - show all the jobs
f jobname - find and locate to jobname
pre jobname - prefix of jobname eg - pre sor* - will list all the jobs starting with sor
P - purge the dataset - that job log in spool will be deleted
C - cancel the job
xdc - store the output to a dataset
JESMSGLG - message log, execution time, when was it submitted, user who submitted it, class executed- basic info on the job
JESJCL - will have the whole JCL
JESYSMSG - system message - has all details step by step
SYSOUT will have info on each step separately. SYSOUT step01, SYSOUT step02 etc.
Instream Procedure
Procedure (its like function, way to reduce the lines of code by writing the redundant code in procedure) which is defined in the same JCL.
SYntax:
//procname PROC
//steps
// PEND
calling:
//step2 exec procname
Symbolic Parameters
Used to pass values to the procedure. Always starts with an &. We can give any name except reserved keywords.
//procname PROC
//steps EXEC PGM=IEFBR14
// DD1 DD DSN=&DNAME,
// DISP and other parameters
// PEND
calling:
//step2 exec procname,DNAME=TRAIN04.TEST1
//step3 exec procname,DNAME=TRAIN04.TEST2
can be used to pass value for part of the name too- like just one qualifier:
//DD1 DD DSN=TRAIN04.&MNAME..PS1
calling:
//step2 exec procname,MNAME=TEST1
starts with & and ends with . or we can also use space: TRAIN04.&MNAME..PS1
if its the last qualifier then no need for . TRAIN04.&MNAME
Cataloged Procedures
Cataloged procedure will be in another location and we can call it in JCL
The location has to be mentioned in the jcl. JCLLIB is the kwyword. that proclib is the stepname can be anything
//PROCLIB JCLLIB ORDER=TRAIN.TEST.JCLLIB
//STEP1 EXEC CREPSPR,DNAME=TRAIN04.TEST.PS1
Nested Procedure
Calling another procedure within a procedure. We can have upto 15 levels of nesting:
eg:
//CREPSPR PROC
//STEP1 EXEC PGM=IEFBR14
//DD…
//STEP2 EXEC ANOPRC,FNAME=TAY /* let this is another proc
// PEND
JOBLIB - JOB LIBRARY
Its for load module, its executable. Default location of load modules is SYS1.LINKLIB. When we don’t specify the load lib, JCL will first check the default location, if not found it will give abend S806.
to solve it we have to specify the load module. JOBLIB is used and it is given after the JOB CARD and is applicable to whole JCL
//JOBLIB dd dsn=TRAIN04.TEST.LOAD,DISP=SHR
So now it will search the PGM in the specified location and if its not found then it will search in default.
multiple dataset loc can be given:
//JOBLIB dd dsn=TRAIN04.TEST.LOAD,DISP=SHR
// dd dsn=TRAIN04.TEST.LOAD1,DISP=SHR
// dd dsn=TRAIN04.TEST.LOAD2,DISP=SHR
STEPLIB
Its for load module, its executable. STEPLIB is given after the step. It will find the location of the program specifeid in the steplib. If JCl have both JOBLIB and STEPLIB then steplib will be used and joblib will be ignored. It is applicable to that step only
//STEP1 EXEC PGM=PGMA
//STEPLIB DD DSN=TRAIN.CRS.LOAD,DISP=SHR
// dd dsn=TRAIN04.CRS.LOAD1,DISP=SHR
JCLLIB
Its for JCL code. Used to tell the location of JCL code
//stepname JCLLIB ORDER=TRAIN04.TEST.JCLLIB
we can give more than 1 loc:
//proclib JCLLIB ORDER=(TRAIN04.TEST.JCLLIB,TRAIN04.TEST2.JCLLIB)
COND parameter
It is used to decide whether to execute a step or not.
Cond= (returncode, operator, stepname)
eg: COND=(0,EQ,STEP01) - if the cond is true then step is bypassed and if it is false then it executed.
COND=(8,LE)
operators: GT, LT, EQ, NE, GE (greater than or equal), LE (Less than or equal).
COND can be given in a JOB statement or an EXEC statement. COND code does not work on the first step in a JCL.
COND can be given in the job statement if that cond has to be applied to every steps. //NATARKIJ JOB 1,NOTIFY=&SYSUID,COND=(0,EQ) - it will be applied all the steps except the first step.
Never execute a step/ to skip a step - COND
COND=(0,LE) - this step will always be true thats why the step will not execute
to always execute a step - COND
COND=(4095,LT) - this step will always be false thats why the step will execute
COND=ONLY
the step will only execute if any of the previous steps has abended.
COND=EVEN
execute even if abend occurs.
IF..ELSE in JCL
//check1 if rc = 0 then
//step2 exec pgm=sort
// endif
if else:
//check1 if rc = 0 then
//step2 exec pgm=sort
//else1 else
//step3 exec pgm=sort
// endif
for abend
//check1 if abend then
if else will work on first step of JCL and COND parameter doesn’t.
GDG
Generation Data Group is a group of files related to each other and having a common name.
eg: a bank can have datasets containing the names of its new customers in JAN,FEB and so on. There will be twelve datasets per year for the bank. These datasets will be grouped together to form a GDG instead of twelve different datasets
BANK.CUST.MON.G0001V00
BANK.CUST.MON.G0002V00
G001 stands for generation number
V00 stands for version number - version for the same version
GDG base→ to create a GDG, a dataset called GDG base is first created. All the generations are then modeled from this base.
BANK.CUST.MON → GDG base
Max np. GDG generations - 255
to access the latest generation - BANK.CUST.MON(0)
second most recent - BANK.CUST.MON(-1) and the rest so on
IDCAMS is used to define/alter/delete a GDG.
Parameters:
Limit - max number of generations that a GDG can hold.
EMPTY - uncatlogs all generation once limit is reached.
NOEMPTY - uncatolgs only the oldest generations once limit is reached
SCRATCH - deletes the generation when uncataloged
NOSCRATCH - does not delete the generation when uncatologed.
Create a GDG
//STEP01 EXEC PGM=IDCAMS
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//SYSIN DD *
DEFINE GDG(NAME(TRAIN04.TEST.GDGGEN) -
LIMIT(12) -
NOEMPTY -
SCRATCH
to create generations:
//STEP01 EXEC PGM=IEFBR14
//DD1 DD DSN=TRAIN04.TEST.GDGGEN(+1),
// DISP=(NEW,CATLG,DELETE),
// SPACE=(TRK,(100,100),RLSE),
// DCB=(LRECL=80,RECFM=FB,BLKSIZE=800,DSORG=PS)
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
to delete:
//DD1 DD DSN=TRAIN04.TEST.GDGGEN(0),
// DISP=(OLD,DELETE,DELETE) referencing the gdg:
to reference a GDG gen in the same JCL it is created then we have to give TRAIN04.TEST.GDGGEN(+1), disp=shr
latest version not created in the same JCL- TRAIN04.TEST.GDGGEN(0), disp=shr
second most- TRAIN04.TEST.GDGGEN(-1), disp=shr and so on
Delete GDG
//STEP01 EXEC PGM=IDCAMS
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//SYSIN DD *
DELETE GDG(NAME(TRAIN04.TEST.GDGGEN) GDG FORCE
/*
we can also give PURGE in place of FORCE. PURGE will delete even if the retention period of the GDG is not expired. Force will delete will only delete if retention period has expired.
REXX
/* REXX */
Say ‘HELLO WORLD’
say ‘Enter you name: ‘
PULL name
a = 0
DO until a = 5
say ‘this is’ A ‘times printing’
a = a+1
end
execute - 1) give → ex in front of dataset
2) go to 6 in ispf → ex ‘rexx.code(hello)’
3) tso ex ‘rexx.code(hello)’
4) go to ready prompt and give → ex ‘rexx.code(hello)’
VSAM
Virtual Storage Access Method. VSAM is a data access method in Mainframe.
Access method: it defines the technique that is used to store and retrieve data
An access method has:
1) its own structure to organize data - in VSAM→ Data and index component. Data is organized in control intervals
2) System-provided programs (or macros) to define datasets - IDCAMS
3) utility program to process datasets - IDCAMS
IDCAMS is used to define VSAM datasets
VSAM can’t be viewed using ISPF
VSAM are also called clusters.
Control intervals- VSAM stores and retrieves data from disk as control intervals. In every read one CI is read from the disk and put into the memory
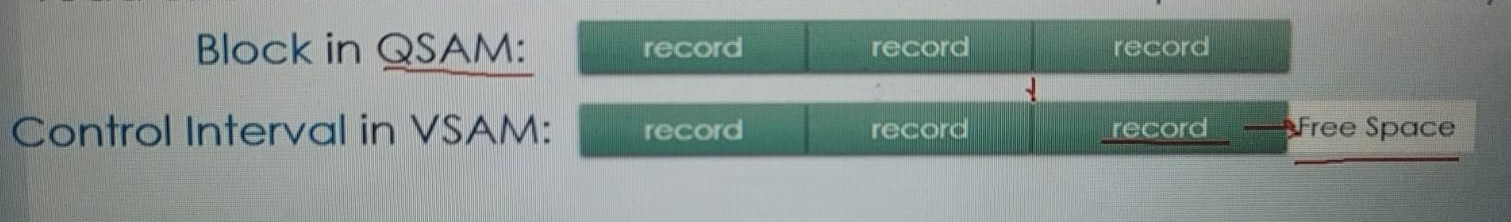
CI has record record record record free space RDF RDF CIDF
Records, free space (free space is the % of free space reserved in a CI and CA), CI fields: RDF(Record Definition Field) is 3 bytes long, it describes the length of records and CIDF (Control Interval Definition Field) is 4 bytes long, it contains the info about the CI
Default size of CI is 4096 bytes. Max of 32kb.
Control Area(CA): two or more CY are grouped together to form a CA.
VSAM size is always a multiple of CA:
eg: if CA = 8192 KB then VSAM = n*8192 kb
index consists of sequence set and index set. every control area has a seq set associated with it. every record in seq set points to one CI. Index set points to seq sets. seq set useful for sequential processing. Every record of seq set stores the last address of the CI. every record in index set will point to last address of seq set. Index set is used for direct access and seq set is used for sequential access
Free space= %CI to be free, %CA to be free → eg: freespace =(20,25) means 20% of every CI and 25 % of the whole CA will be free. Its useful to insert data in VSAM. It is provided during the creation of the VSAM
VSAM splits: when a record is being inserted into a VSAM which has no more space in the CI, then a Ci split occurs. done the area where record has to be inserted. It creates free space.

QSAM
Access method on Mainframe. PS files are created and stored using QSAM.
QSAM stores data as blocks. A block is a collection of records. In every read whole block is copied into the memory.
This equivalent to Control Interval in VSAM. Records are stored and retrieved from the disk as Control Interval (CI). In every read one CI is read from the disk and put into memory.
Types of VSAM
KSDS - every record is retrieved and inserted using a key value. Thus it has 2 components: Data and Index.
Data has actual Data inside whereas the index points to the location of the data.
RRDS - the record can be accessed using record number
ESDS - the records are retrieved in the sequence they were added. just like PS
LDS - the data is stored in byte-streams. Like notepad
KSDS
Key-Sequenced Data set- records are stored in ascending seq by key. Always sorted by the key. keys are unique. No duplicate records are possible in KSDS.
Parameters to create KSDS:
i) Name
2) keys: its syntax is keys(length offset) for eg: if key is 23413 - length = 5 and offset is 0 i.e. the index position which we want to be key. so keys will be keys(5 0)
suppose we want 34 in 23413 be the key then keys will be keys(2,1). max length of key 255.
3) RECSZ: length of most of the records. record size→ RECSZ(average maximum)
if a record has fields emp no, emp name and address and approx. length of each field is 5 + 30 +53 then avg is 90 and max maybe 200.
4) FREESPACE (%CI %CA)
5) INDEXED: it tells the system that the VSAM is KSDS. It is NUMBERED for RSDS, NONINDEXED for ESDS and LINEAR for LDS
6) CISZ (Control Interval Size): Default is 4096 Bytes. Can be a maximum of 32K
7) SPACE: The amount of total space allocated to VSAM. Syntax: Unit(primary secondary) eg: Tracks(30 50)
8) VOLUME: The volume serial where VSAM will reside is given here.
create KSDS JCL
//STEP01 EXEC PGM=IDCAMS
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//SYSIN DD *
DEFINE CLUSTER( -
NAME(TRAIN04.TEST.KSDS) -
INDEXED -
KEYS(5 0) -
RECSZ(90 200) -
FREESPACE(10 20) -
TRACKS(50 30) -
CISZ(8192) -
volume(ZASYS1))
/*
ESDS
Entry-sequenced Data set, records are stored in the order they are added